
Artefact-oriented Business Process Modelling
An Ontological Dependency Approach
Yu-Chun Pan, Yinshan Tang and Stephen R. Gulliver
Informatics Research Centre, Henley Business School, University of Reading, Reading, RG6 6UD, U.K.
Keywords: Artefact-oriented, Activity Theory, Organisational Semiotics, Ontology, Business Process Modelling.
Abstract: Business process modelling can help an organisation better understand and improve its business processes.
Most business process modelling methods adopt a task- or activity-based approach to identifying business
processes. Within our work, we use activity theory to categorise elements within organisations as being
either human beings, activities or artefacts. Due to the direct relationship between these three elements, an
artefact-oriented approach to organisation analysis emerges. Organisational semiotics highlights the
ontological dependency between affordances within an organisation. We analyse the ontological
dependency between organisational elements, and therefore produce the ontology chart for artefact-oriented
business process modelling in order to clarify the relationship between the elements of an organisation.
Furthermore, we adopt the techniques from semantic analysis and norm analysis, of organisational
semiotics, to develop the artefact-oriented method for business process modelling. The proposed method
provides a novel perspective for identifying and analysing business processes, as well as agents and
artefacts, as the artefact-oriented perspective demonstrates the fundamental flow of an organisation. The
modelling results enable an organisation to understand and model its processes from an artefact perspective,
viewing an organisation as a network of artefacts. The information and practice captured and stored in
artefact can also be shared and reused between organisations that produce similar artefacts.
1 INTRODUCTION
An organisation can be seen as a system that has
inputs, processes, and outputs, and also contains
various parts integrated to accomplish the shared
goal (Senge, 1990). The system view enables
management to view the organisation in flows,
processes and relationships, to achieve optimal
results (Seddon, 2008). The flows, processes and
relationships in a system are usually defined by the
sequence of activities and tasks. Hammer and
Champy (1993) defined a business process as a
collection of activities with a goal that takes one or
more types of input to create a valuable output to the
customer. Eriksson and Penker (2000) argued that a
business process focuses on addressing how work is
performed rather than describing the output of a
process. Business process therefore contains a
sequence of work activities that together contribute
to the customers’ desired outcome.
Business process modelling provides a shared
understanding and analysis of business processes
(Aguilar-Savén, 2004). It captures how the activities
are being performed, the sequence of activities
involved, and the presence of the business process in
a chosen approach. Business process modelling
helps an organisation conceptually structure the
architecture of its business process. The results of
business process modelling can therefore be used for
software development and for business process
restructuring (Phalp and Shepperd, 2000).
There are numerous methods and techniques for
business process modelling, which were all
developed for different purposes and needs (Aguilar-
Savén, 2004). The majority of business process
modelling methods capture the sequence and details
of activities, and then represent an organisation by
visualising or grouping the captured activities via
various techniques. Various attributes are used in
different methods for defining business process,
such as human roles (Holt et al., 1983), data and
information (Gane and Sarson, 1977, Yourdon and
Constantine, 1979), actions (Lakin et al., 1996), data
objects (Douglass, 2000), and duration (Aguilar-
Savén, 2004). Despite the numerous attributes used,
activities are still normally the starting point for
223
Pan Y., Tang Y. and R. Gulliver S..
Artefact-oriented Business Process Modelling - An Ontological Dependency Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0004398502230230
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2013), pages 223-230
ISBN: 978-989-8565-61-7
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

business process modelling. However, by reviewing
and analysing the elements within an organisation,
we identify the three elements as human agents,
artefacts and activities, and the interdependent
relationship between them. Due to the direct link
between these three elements, an instance of any
type of elements can be used as a basis to identify
the relevant instances of the other two elements. In
order to gather artefact-oriented information about
activities and human agents, a business process
modelling method that captures the business flow
from an artefact perspective has been developed.
In order to develop an artefact-oriented method
for business process modelling, we first adopted
activity theory to understand the relationship
between human beings, activities and artefacts.
Organisational semiotics was chosen as the
theoretical basis for the artefact-oriented method
development. The ontology chart for artefact-
oriented business process modelling was then
produced, however we extended the ontology chart
by applying the techniques from semantic analysis
and norm analysis in order to develop the artefact-
oriented business process modelling method, and
allow us to identify the artefact and agent’s activities.
Each step of the above method will be explained and
demonstrated in more details, via use of a supporting
example.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Activity Theory and Organisations
Business process modelling has been an important
topic in the study of business, because it facilitates
organisations to understand and improve their
business processes, therefore working towards better
performance. In order to model a business process, it
is essential to understand the structure, components
and workflows of an organisation. We used activity
theory (AT) (Engestrom et al., 1999) to define the
elements of organisations. AT identifies each goal
driven activity as an analysis unit. An activity model
contains object, subject and artefact. An object is
both something given and something projected or
anticipated. Object is the thing being modified to fit
the purpose. Subject is the human being that is being
motivated by the object to perform tasks to reach a
goal. Artefact refers to the mediating tools that can
either be physical or mental. Additionally, AT states
that activity model is artefact-mediated and object-
oriented, and the context has to be considered while
analysing human activities. The outcome of one
activity model can be the object or artefact of
another activity model. An AT model can therefore
operate independently, or cooperate with other
activity models. An organisation can be seen as a
network of activities. The interaction between the
object and the human subject is through the
mediation of tools. AT has been applied to
understand business process (Larkin, 2003, Rozycki
et al., 2012), and the process deconsolidation is
based on different perspectives of agents. According
to AT, subject modifies objects to generate outcome
(Barthelmess and Anderson, 2002). Activities are
therefore significantly related to human beings,
objects and tools. Both tools and objects are the
artefacts that are being modified or utilised by
human beings when performing activities. The
object of an activity can be reused as a tool by
another activity model. Hence, the tools and objects
can be categorised together by nature, whilst also
being viewed as a set of activities, since any form of
organisation requires the collaboration of human
beings performing sets of activities or tasks. Hence,
we define three major elements in an organisation as
being human, activities and artefacts. These three
elements construct to form an organisation through
intertwined relationships. An organisation can be
seen as a network of artefacts that are linked to
human beings and activities. Hence, artefacts, as
well as activities, can also be seen as the linkages in
a system, as artefacts within a system can normally
be defined at the input and output of the systems and
sub-systems. The sub-systems pass artefacts from
one sub-system to another; with the output of one
sub-system acting as the input of its succeeding sub-
system. By focusing on the input and outputs
between sub-systems, a more artefact-oriented
perspective for examining organisations emerges. As
artefacts are often directly involved with human
activity, the relationship between artefact instances
can further reveal the relationship between artefacts
and human beings; i.e. artefacts can be used as the
base for stakeholder mapping (Pan et al., 2013).
2.2 Organisational Semiotics
Organisational semiotics (OS) is a discipline that
applies semiotics to organisational study. It focuses
on the nature, function and effect of information and
communication within organisations (Liu, 2000).
Semantic Analysis Method (SAM) and Norm
Analysis Method (NAM) of OS are selected for this
research. SAM is a set of methods to elicit and
specify user’s requirements in a formal and precise
format, and the building blocks of SAM include
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
224

affordances, agents and ontological dependency
(Liu, 2000, Bonacin et al., 2004). Gibson (1986)
defined affordances as patterns of behaviours that
are meaningful in the context of society. Affordance
is the perceived and actual properties of the thing,
and the properties determines the possible use of the
thing (Norman, 1988). Stamper (1985) explained
that a physical object can also be defined as an
affordance given the object’s ability to enable
patterns of behaviours. Hence, the entities, objects or
artefacts that can be utilised by human beings in an
organisation are all affordances. Agents are also
affordance, which distinguish themselves from other
affordances by being able to take responsibilities for
their own and others’ actions (Salter and Liu, 2002).
Agents can be individuals, groups or organisations,
as long as the agent takes responsibility for their
actions. Furthermore, affordances defined in a given
context are not isolated from each other. There are
relationships between affordances. The ontological
dependency means that the existence of an
affordance relies on its antecedents. The
relationships between affordances can therefore be
shown in an ontology chart where the nodes
normally represent universal affordances rather than
particular affordance instances.
Based on the results from SAM, NAM further
identifies and analyses rules and patterns of artefact
behaviour. NAM contains four steps, namely
responsibility analysis, proto-norm analysis, trigger
analysis and detailed norm specification (Liu, 2000).
The results of norm analysis can help the
organisation understand and potentially improve its
processes. These steps can be utilised to analyse and
model the activities related to the artefacts within the
organisation, once the ontological dependency
within the organisation has been clarified.
3 METHODS
By reviewing the literature in AT, OS and business
process modelling, we have identified the potential
use of artefacts as an approach to business process
modelling. AT and OS provide the theoretical
foundation for understanding the elements within
organisation and the ontological dependency among
them, which is used to develop the ontology chart
for artefact-oriented business process modelling.
Artefact orientation and ontological dependency
within organisation will be discussed in section 4.
The ontology chart for artefact-oriented business
process modelling demonstrates how agents and
afforded acts can be identified and linked through
artefacts in a defined environment. We also adopted
the concepts and analysis techniques from SAM and
NAM. The semantic analysis techniques helped
identify the affordances in the defined environment
and to examine the relationship between them. Once
the affordances and the relationship amongst them
are clarified, the techniques from NAM were used to
assign responsible agents to the identified afforded
acts and to further analyse the rules for the afforded
acts. The details of each step will be addressed in
section 5, with an example to demonstrate each step
of the artefact-oriented business process modelling.
4 ARTEFACT AND
ONTOLOGICAL DEPENDENCY
Developed from AT, artefacts, human agents and
activities have been identified as the three major
elements within an organisation. Organisations
would not be able to function with the absence of
any of the three elements. Artefacts are being
processed or produced by human agents performing
activities; and therefore they are the three co-
dependent corners of a triangle that explains how
organisation functions.
In order to understand the overall picture of an
organisation, any of the three major elements can be
used as the focal perspective to gather information
of the relevant occurrences of the other two
elements. By using artefact (affordance) as the
analysis unit, we aim to capture the associated
activities (afforded acts) and human subjects
(agents). Hence, our next step is to produce an
ontology chart for artefact-oriented business process
modelling. Each organisation as a system is
composed of many affordances and agents that are
related to, and have an effect on, each other through
their ontological dependency. The artefacts in the
system are the affordances of the system. The
artefacts are the linkage between sub-systems as the
input and output of the sub-systems. The artefacts
within a system can represent the components,
which refer to raw materials, services, or parts that
are required to deliver an output that is desired by
the end customers of a system (Pan et al., 2012).
The stakeholders are those who are involved
with the organisation, either actively or passively
(Vos and Achterkamp, 2006). The role-name
indicates that an agent has a specific role. The
agent’s afforded acts are the activities of the system.
Based on the semiotic analysis of stakeholders and
components, an ontology chart (
Figure 1) is
Artefact-orientedBusinessProcessModelling-AnOntologicalDependencyApproach
225

produced. The business environment is the root to all
affordances, since all of the affordances are
dependent on the business environment. Therefore,
the affordances would not exist if there was no
business environment. All of the items in the
ontology chart are affordances, with the affordances
on the right of the ontologically being dependent on
the affordances to its left; i.e. its ontological
antecedent. The names attached to the lines between
the agents and afforded acts refer to the roles of the
agents. Determiners are a special type of affordances
that represent the measurement standards, which are
marked with a # symbol. The outputs are dependents
on the components, as the components are
assembled to produce the output. The oval shapes
represent the agents and standard affordances
(artefacts). The agents include the organisation and
stakeholders, and the artefacts cover both the output
and components. The rectangular boxes refer to the
afforded acts performed by agents. The ontology
chart reveals the ontological relationship between
the artefacts, human agents, and activities. Hence, an
organisation can be analysed and modelled
accordingly.
5 ARTEFACT-ORIENTED
BUSINESS PROCESS
MODELLING
Based on the concept of artefact orientation and the
ontology chart for artefact-oriented modelling, an
artefact-oriented method for business process
modelling is proposed. The modelling method
contains five steps, which will be explained and
demonstrated with a case study example in the
following sections.
5.1 Unit System Scoping
The scope of any system needs to be defined before
the analysis can be conducted. Scoping the unit
system sets the boundary, which ensures that the
analysis covers all of the essential parts and excludes
the elements beyond the scope.
A university’s programme support team is
selected for the case study. Since the programme
support team supports all of the postgraduate
programmes across the faculty, instead of any
specific school, the faculty is considered as the
business environment. Other schools and
departments are within the faculty; however they are
not the part of the defined organisation for process
modelling, yet might fall into the stakeholder
category as agents that interact with the unit system.
5.2 Artefact Identification
The modelling unit for this method is based on the
artefact instances, and therefore the artefacts need to
be identified first, once the scope has been defined.
Artefacts include the outputs and the components in
the defined organisation. Common data collection
methods, such as observation, interview and
document review (Sapsford and Jupp, 1996), can be
applied to identify the artefacts. The outputs are the
artefacts produced by the defined organisation for its
customers. The artefacts can be either tangible or
intangible, depending upon the nature of the defined
organisation. An output is the final product of the
organisation, and it can be the end result of either
routine manufacturing or an ad hoc project. Once the
outputs are identified, the analyst can further break
down the outputs into components.
The components of an output are the raw
material, parts, information and/or services that are
required to produce the output. Human agents
perform a set of activities to modify and process a
group of components to deliver a specific output.
Identifying the components of each output requires
the analyst to produce a component-based structure
(Pan et al., 2012) for each identified output, which
reveals the relationship between the output,
components, and sub-components.
There can be numerous outputs in a defined
organisation. For each identified output, the output
name, output ID, required components and the
specification have to be decided. The output ID
should be unique and readable by a machine, as this
ID can be used as a tag to identify the information
related to a specific output. The output name is the
term that human agents use to describe the output.
The ‘required components’ column lists all
component IDs for components that are required to
produce the output. The specification column
provides a brief description of the output, which
should include the functions, purposes, uses,
limitations, etc. In addition, more columns can be
added, as deemed necessary. In the context of the
programme support team example, we observed
their processes and conducted semi-structured
interviewed with two team members in order to
identify the organisation outputs, and their related
components, as shown in
Table 1 and Table 2.
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
226
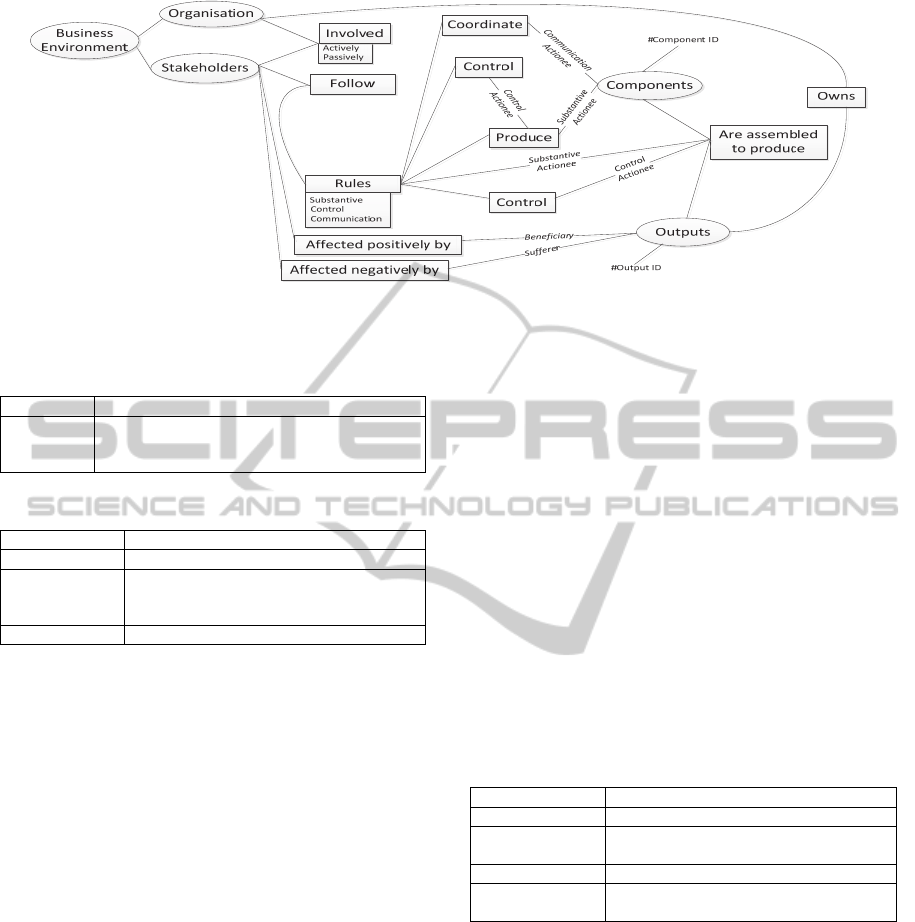
Figure 1: Ontology chart for Artefact-oriented business process modelling.
Table 1: Output list.
System Programme Support Team
Outputs
Programme Summary Report (PGT001)
Student Transcripts (PGT002)
Module Distribution Statistics (PGT003)
Table 2: Output description.
Output ID PGT001
Output Name Programme Summary Report
Required
Components
Student Information (PGT101)
Module Marks (PGT102)
Degree Classification (PGT103)
Specifications To be produced before the exam board
5.3 Activity Analysis
Activities are the afforded acts performed by agents.
The activities enable the artefacts to achieve their
defined purpose. For each output, the related
activities are divided into two categories, namely
assembling activities and post-assembling activities.
Assembling activities are the activities that
transform the components into the output. Not only
does an assembling activity apply to the physical
assembling of parts in a manufacturing domain, but
also apply to the collation of intangible services and
information. The assembling activities include
substantive activities and control activities that
ensure the substantive activities complying with the
rules. Post-assembling activities refer to the
activities that happen between the output and the
agents who are affected by the output.
OS classified activities into substantive activities,
communication activities and control activities (Liu,
2000). Substantive activities refer to the tasks and
activities that fulfil the main purpose of the action.
Communication activities enable the right sub-
components available at the right time at the right
place. Control activities ensure that all coordination
and production activities are conducted according to
the relevant regulations. The rules and regulations
are enforced by the conduction of control activities.
Hence, we identify that there are substantive
activities, communication activities and control
activities for each component.
Hence, there are five groups of activities
associated to identified output and components.
Each artefact should have a table listing all of the
associated activities. Each identified activity is then
assigned an activity ID, activity name, activity type,
and description. In the example of programme
support team, once the tables of activities that are
related to the output and components are produced,
the activity description can be generated for each
activity.
Table 3 is an example of activity
description.
Table 3: Activity description.
Activity ID PGTAC1023
Activity Name Checking the final mark
Associated
Artefact
PGT001, PGT102
Activity Type Control
Activity
Description
Ensuring that the final mark was decided
according to the regulations
5.4 Agent Identification
In the ontology chart for artefact-oriented business
process modelling, agents include the organisation
and the individuals. The organisation owns the
outputs, yet outputs are essentially dependent on
stakeholder components. All of the components are
ontologically dependent on agents who enable
components by performing their afforded acts.
Based on the afforded acts performed by the agents,
the agents can be categorised by their roles. For each
output, there are five types of roles, namely owner,
substantive actionee, control actionee, beneficiary
Artefact-orientedBusinessProcessModelling-AnOntologicalDependencyApproach
227

and sufferer. For each identified component, there
should be substantive actionee, control actionee and
communication actionee. Each agent is linked to a
certain set of activities, and the agent’s role name
should reflect its afforded acts directly.
For the example, one output and one component
have been chosen to identify the related agents.
Once the relevant agents have been identified, an
agent description is then produced for each
identified agent.
Table 4 and Table 5 are the examples
of the agent identification and description.
Table 4: Output-agent identification.
Output ID PGT001
Owner Programme Support Team
Substantive
Actionee
Administrator (PGTAG002)
Senior Administrator (PGTAF003)
Control Actionee Team Manager (PGTAG001)
Beneficiary Exam Board (PGTAG201)
Sufferer N/A
Table 5: Agent description.
Agent ID PGTAG002
Agent Name Administrator
Agent Type Substantive, Communication
Contact Admin@example.ac.uk
Location Room 105, Admin Building
5.5 Rule Specification
The techniques from trigger analysis and detailed
norm specification of NAM (Liu, 2000) are adopted
to conduct rule specification. In order to formalise
the activities, it is essential to identify and specify
the norms that realise the activities. Hence, for each
identified activity, the analyst should specify the
activity type, time, associated artefacts, associated
agents and rule specification. The format of
behavioural norm (Liu and Dix, 1997) is considered
suitable for the rule specification, because most rules
and regulations in the business environment fall into
the category of behavioural norms. The format is
constructed as follows (Liu and Dix, 1997).
Whenever <condition> If <state> Then <agent> Is
<deontic operator> To <action>
This format is selected to present the rule
specification for each identified activity. All rules
within each identified activity need to be scripted
and listed to allow activity analysis.
Table 6 is an
example of activity rule specification.
5.6 Modelling Result
Each step of the artefact-oriented business process
modelling method provides a set of information
respectively. Once all of the steps are completed, the
component-based structures of identified outputs can
be used to reveal the organisation’s fundamental
processes from an artefact perspective. By using the
tables produced in artefact identification, activity
analysis, agent identification and rule specification,
all of the activities and agents within the
organisation can be explicitly linked to the output
and component to which they are related. Hence, the
practices and information can be encapsulated into
the artefact analysis unit. A component might be
associated to more than one output, and accordingly
the practice and knowledge embedded in the
component can be shared between outputs.
Table 6: Activity rule specification.
Activity ID PGTAC1023
Act Type Control
Rule
Specification
Rule 1:
Whenever <the resit box is ticked> If <the
resit mark is greater than 50%> Then
<administrator> Is <obliged> To <record
the final mark at 50%>
Rule 2:
Whenever <the resit box is ticked> If <the
resit mark is less than 50%> and <the resit
mark is greater than the calculated final
mark> Then <administrator> Is <obliged>
To <keep resit mark as the final mark>
6 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
This paper developed the ontology chart for artefact-
oriented business process modelling based on AT
and OS and then further proposed the artefact-
oriented method for business process modelling. An
artefact-oriented approach is different to a functional
flow, as it aims to treat the organisation as a system,
and place focus on the inputs and outputs of an
organisation. As a system, constructed of sub-
systems, an organisation can be modelled by
considering the outputs that it produces. The outputs
themselves can also be broken down and modelled;
with each artefact systematically used as an analysis
unit to extract activity and agent information. Based
on the ontology chart that defines the relationships
between agents, afforded acts and artefacts, we
propose an artefact-oriented method for business
process modelling. The method contains five steps
that identify the artefacts within the defined
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
228

organisation and analyse the agents and activities
around the artefacts. The modelling results show the
organisation’s outputs and their component-based
structures, which view an organisation as a network
of artefacts. For each identified artefact, there will
be relevant agents and activities identified.
The term ‘artefact’ in the proposed artefact-
oriented approach is not to be confused with the
term ‘artifact’ in artifact-centric business process
model (Bhattacharya et al., 2007). In artifact-centric
business process model, artifacts are the moving
business-relevant objects/data that are created,
evolved and normally archived as they pass through
a business (Cohn and Hull, 2009), which contains
both the attributes and states describing the identity
of the artifact and its current stage in its lifecycle
(Bhattacharya et al., 2009). The term ‘artefact’ is our
approach does not refer to the data, but the things
actually being modified or produced.
The artefact-oriented approach focuses on an
organisation’s conceptual structure based on
artefacts. The artefacts are ontologically
interdependent. Unlike activity-focused modelling,
artefact-oriented modelling does not rely on the
sequence of activities, but the ontological
interdependency of artefacts. When the relationship
between artefacts is output-component relationship,
the component will need to be sourced or produced
before the production of the output can take place.
However, the existence of the component does not
necessarily lead to the production of the output, and
the relationship between them is not sequential.
Between the artefacts, as components, required by
the same artefact (output) there is also no sequential
relationship at all. There is no specific order in
which the components need to be sourced for the
production of the output. As long as the required
components are sourced, the production of the
output can be done, and the sequence of components
is irrelevant. Therefore, the artefacts can be viewed
and modified independently without affecting other
artefacts, while they are still ontologically
interdependent, which enables the flexibility of
artefacts as a base for process modelling.
Additionally, because the artefact-oriented
modelling method records the agent and activity
information linked to the artefact, the recorded
relationship between artefacts, agents and activities
can then be used in the event of an emergency, or in
the case of business process redesign, to identify
those agents involved and activities that will be
affected. If a specific agent or activity becomes
unavailable or faulty, the organisation can quickly
identify which outputs and components will be
affected. The component-based structure also gives
the organisation a clear view of which artefacts are
being to produce specific artefacts. The organisation
can use this information to consider which artefacts
can be replaced or reused across the whole
organisation. The activity of similar artefacts can be
reviewed and potentially improved by using
benchmarking criteria. The proposed method is
predominantly designed to capture and analyse the
formal and technical part of the organisation. Some
of the informal norms in the organisation might still
be captured and recorded, but some might not
necessarily be captured; if the informal activities do
not have a direct involvement with an artefact.
However, this issue can be resolved by incorporating
techniques that focus on informal norms.
Moreover, the modelling results can also be used
to design and configure Information System (IS). In
the example of programme support team, the
different IDs can all be used as the primary keys in
the database. The rule specifications can help
programmers or enterprise consultants compute the
business processes. The modelled business processes
than can be coded or implemented within software
systems. By formalising the information around the
artefacts, each artefact can then be considered as a
software component; with each artefact-based
software component truly reflecting its counterpart
in real world; and the practice of information sharing
can be conducted on the basis of artefacts. In
conclusion, the artefact-oriented method for process
modelling provides a novel perspective for
identifying and analysing business processes, as well
as agents and artefacts, as the artefact-oriented
perspective demonstrates the fundamental flow of an
organisation; with the information and practices
embedded in artefact allowing reuse across both the
organisation and/or the industry. Since the artefact
analysis unit consider the drill-down detail of
multiple level sub-components, the basis of
information and practices sharing can be scaled.
This scaling allows organisations to use the same
modelling approaches, irrelevant of the complexity
of the artefact; as additional levels can be added as
required in areas of complexity to allow scope of
modelling to be manageable.
Not only does the artefact-oriented approach lay
the groundwork for business process modelling, but
it paves the foundation for IS design and
configuration. The modelling results provide an
alternative basis for IS design, with the rule
specifications enabling the automation of process in
IS. The software component of information system
can be constructed based on the artefacts, instead of
Artefact-orientedBusinessProcessModelling-AnOntologicalDependencyApproach
229

the conventional functional processes. The
development of artefact-oriented approach to
business process modelling is at an early stage.
Extension of this concept needs to be applied in
more scenarios, where task-centric methods
currently apply, in order to further refine the concept
and develop related methods or techniques.
REFERENCES
Aguilar-Savén, R. S. 2004. Business process modelling:
Review and framework. International Journal of
Production Economics, 90, 129-149.
Barthelmess, P. & Anderson, K. M. 2002. A View of
Software Development Environments Based on
Activity Theory. Computer Supported Cooperative
Work (CSCW), 11, 13-37.
Bhattacharya, K., Gerede, C., Hull, R., Liu, R. & Su, J.
2007. Towards formal analysis of artifact-centric
business process models. Proceedings of the 5th
international conference on Business process
management. Brisbane, Australia: Springer-Verlag.
Bhattacharya, K., Hull, R. & Su, J. 2009. A data-centric
design methodology for business processes. Handbook
of Research on Business Process Modeling, 503-531.
Bonacin, R., Baranauskas, M. C. C. & Liu, K. 2004. From
Ontology Charts to Class Diagrams: Semantic analysis
aiding systems design. Proceedings of the 6th
International Conference on Enterprise Informaiton
Systems. Porto, Portugal.
Cohn, D. & Hull, R. 2009. Business artifacts: A data-
centric approach to modeling business operations and
processes. Bulletin of the IEEE Computer Society
Technical Committee on Data Engineering, 32.
Douglass, B. P. 2000. Real-time UML : developing
efficient objects for embedded systems, Reading, Mass.
; Harlow, Addison-Wesley.
Engestrom, Y., Miettinen, R. & Punamaki-Gitai, R.-L.
1999. Perspectives on activity theory, Cambridge,
Cambridge University Press.
Eriksson, H.-E. & Penker, M. 2000. Business Modeling
With UML: Business Patterns at Work, New York,
Wiley & Sons.
Gane, C. & Sarson, T. 1977. Structured Systems Analysis :
Tools and Techniques, N Y, Improved Systems
Technologies.
Gibson, J. J. 1986. The ecological approach to visual
perception, Erlbaum.
Hammer, M. & Champy, J. 1993. Re-engineering the
Corporation: A Manifesto for Business Revolution,
New York, Harper Business.
Holt, A. W., Ramsey, H. R. & Grimes, J. D. 1983.
Coordination systems technology as a programming
environment. Electrical Communication, 57, 307-314.
Lakin, R., Capon, N. & Botten, N. 1996. BPR enabling
software for the financial services industry.
Management Services, 40, 18-20.
Larkin, P. a. J. 2003. Government Business Process
Analysis with Activity Theory. In: Whymark, G. (ed.)
Transformational Tools for 21st Century Minds:
National Conference 2003. Eveleigh, Australia:
Knowledge Creation Press.
Liu, K. 2000. Semiotics in Information System
Engineering, Cambridge, UK, Cambridge University
Press.
Liu, K. & Dix, A. 1997. Norm Governed Agents In
CSCW. 1 st Int. Conference on Computational
Semiotics. Paris.
Norman, D. A. 1988. The psychology of everyday things,
New York, Basic Books.
Pan, Y.-C., Tang, Y. & Gulliver, S. 2012. A Component-
Based Method for Stakeholder Analysis. In: Liu, K. &
Filipe, J. (eds.) The 4th International Conference on
Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
(KMIS 2012). Barcelona, Spain: SciTePress.
Pan, Y.-C., Tang, Y. & Gulliver, S. 2013. Mutual
Dependency Grid for Stakeholder Mapping: A
Component-Based Approach to Supply Chain
Participant Analysis. In: Liu, K., Li, W. & Gulliver, S.
(eds.) The 14th International Conference on
Informatics and Semiotics in Organisations (ICISO
2013). Stockholm, Sweden: SciTePress.
Phalp, K. & Shepperd, M. 2000. Quantitative analysis of
static models of processes. Journal of Systems and
Software, 52, 105-112.
Rozycki, E., Keller, S. & Cybulski, J. 2012. Business
process affordances through the lens of activity theory
In: Lamp, J. (ed.) The 23rd Australasian Conference
on Information Systems (ACIS 2012). Geelong,
Victoria ACIS.
Salter, A. M. & Liu, K. (eds.) 2002. Using semantic
analysis and norm analysis to model organisations,
London, GB: Springer.
Sapsford, R. J. & Jupp, V. 1996. Data collection and
analysis, London, Sage in association with The Open
University.
Seddon, J. 2008. Systems thinking in the public sector : the
failure of the reform regime - and the manifesto for a
better way, Axminster, Triarchy.
Senge, P. M. 1990. The fifth discipline : the art and
practice of the learning organization, New York,
Doubleday.
Stamper, R. 1985. Knowledge as Action: a logic of social
norms and individual affordances. In: Gilbert, G. &
Heath, C. (eds.) Social Action and Artificial
Intelligence. Aldershot, Hampshire: Gower Press.
Vos, J. F. J. & Achterkamp, M. C. 2006. Stakeholder
identification in innovation projects: Going beyond
classification. European Journal of Innovation
Management, 9, 161-178.
Yourdon, E. & Constantine, L. L. 1979. Structured design:
fundamentals of a discipline of computer program and
systems design, Englewood Cliffs; London, Prentice-
Hall.
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
230
