
A Personalised Approach in Informal and Inquiry-based Learning
Alexander Mikroyannidis
Knowledge Media Institute, The Open University, Milton Keynes MK7 6AA, U.K.
Keywords: Personalised Learning, Self-regulated Learning, Personal Learning Environment, Informal Learning,
Inquiry-based Learning.
Abstract: Personalised learning has emerged as a novel approach to learning, putting learners in the spotlight and
providing them with the tools for building their own learning environments according to their learning needs
and aspirations. Personalised learning is closely connected to self-regulated learning, which enables learners
to take complete control over their learning. This paper presents the strategies involved with the application
of personalised learning in two different case studies. These case studies originate from two European
research projects and concern informal and inquiry-based learning respectively.
1 INTRODUCTION
Personal Learning Environments (PLEs) are
gradually gaining ground over traditional Learning
Management Systems (LMS) by facilitating the lone
or collaborative study of user-chosen blends of
content and courses from heterogeneous sources,
including Open Educational Resources (OER).
The implementation of PLEs for supporting
different types of learners involves a number of
challenges. This paper presents two distinct case
studies where personalised learning has either been
applied or is currently being applied. The first case
study has to do with informal learning in the context
of the European project ROLE. The second case
study builds on the lessons learned from the first
case study and is concerned with inquiry-based
learning in the context of the new European project
weSPOT.
The remainder of this paper is organised as
follows: Section 2 describes the background and
introduces the main concepts related to personalised
and self-regulated learning. Section 3 presents the
informal learning case study of the ROLE project
and discusses the methodology adopted for
personalised learning in this case. Section 4
introduces the inquiry-based learning case study of
the weSPOT project and describes the strategy for
deploying personalised learning in this context.
Finally, the paper is concluded in section 5 and the
next steps of this work are outlined.
2 BACKGROUND
The Learning Management System (LMS) has
dominated Technology-Enhanced Learning (TEL)
for several years. It has been widely used by
academic institutions for delivering their distance
learning programmes, as well as for supporting their
students outside the classroom. The LMS has been a
powerful tool in the hands of educators, enabling
them to complement face-to-face teaching in the
classroom with remote work by individual students,
as well as groups of them. Popular examples of such
systems used by the academic and the business
world include Blackboard (www.blackboard.com),
Moodle (http://moodle.org), and Sakai
(http://sakaiproject.org) (Bri et al., 2009;
Wainwright et al., 2007; Abel, 2006; Watson et al.,
2007).
However, the advent of Web 2.0 has altered the
landscape in TEL. Learners nowadays have access
to a variety of learning tools and services on the
web. These tools and services are usually provided
by different vendors and in many cases are open and
free. Repositories like Wikipedia
(www.wikipedia.org), YouTube
(www.youtube.com), SlideShare
(www.slideshare.net) and iTunes U
(www.apple.com/education/itunes-u) offer access to
a wide range of learning materials for free.
Augmenting and configuring the diverse and
distributed Web 2.0 tools and services in order to
address the needs and preferences of individual
183
Mikroyannidis A..
A Personalised Approach in Informal and Inquiry-based Learning .
DOI: 10.5220/0004414201830187
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2013), pages 183-187
ISBN: 978-989-8565-53-2
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

learners is a significant challenge for modern online
learning environments.
As opposed to formal learning, which is mostly
instructor-led, informal learning is driven by self-
study and the initiative of individuals, as well as
communities of learners with common goals. The
transition from the traditional approach of LMS to
Web 2.0-based learning solutions bears significant
benefits for informal learners. It puts emphasis to
their needs and preferences, providing them with a
wider choice of learning resources to choose from.
In addition, the success of initiatives such as the
Khan Academy (www.khanacademy.org) has
proven the importance of Web 2.0-enabled
crowdsourcing in informal learning.
The Personal Learning Environment (PLE) is a
facility for an individual to access, aggregate,
manipulate and share digital artefacts of their
ongoing learning experiences. The PLE follows a
learner-centric approach, allowing the use of
lightweight services and tools that belong to and are
controlled by individual learners. Rather than
integrating different services into a centralised
system, the PLE provides learners with a variety of
services and hands over control to them to select and
use these services the way they deem fit (Chatti et
al., 2007; Fiedler and Väljataga, 2010; Wilson,
2008).
The emergence of the PLE has greatly facilitated
the use and sharing of open and reusable learning
resources online. Learners can access, download,
remix, and republish a wide variety of learning
materials through open services provided on the
cloud. Open Educational Resources (OER) can be
described as “teaching, learning and research
resources that reside in the public domain or have
been released under an intellectual property license
that permits their free use or repurposing by others
depending on which Creative Commons license is
used” (Atkins et al., 2007).
Self-regulated learning (SRL) comprises an
essential aspect of the PLE, as it enables learners to
become “metacognitively, motivationally, and
behaviourally active participants in their own
learning process” (Zimmerman, 1989). Although the
psycho-pedagogical theories around SRL predate
very much the advent of the PLE, SRL is a core
characteristic of the latter. SRL is enabled within the
PLE through the assembly of independent resources
in a way that fulfils a specific learning goal. By
following this paradigm, the PLE allows learners to
regulate their own learning, thus greatly enhancing
their learning
3 AN INFORMAL LEARNING
CASE STUDY
The European project ROLE (Responsive Open
Learning Environments; www.role-project.eu) is
aiming at empowering learners for lifelong and
personalised learning within a responsive open
learning environment. In order to study and evaluate
the applications of PLEs in a variety of learning
contexts, the ROLE project has setup a number of
test-beds. The Open University (OU), UK comprises
one of the ROLE test-beds, concerning the learners’
potential transition from formal to informal learning.
This transition is being implemented within this test-
bed as a transition from the traditional LMS towards
the PLE paradigm (Mikroyannidis, 2011;
Mikroyannidis and Connolly, 2012a; Mikroyannidis
and Connolly, 2012b).
The test-bed in question is the OER repository
OpenLearn offered by the OU. OpenLearn
(http://openlearn.open.ac.uk) currently offers more
than 6,000 hours of study materials in a variety of
formats. These include materials repurposed as OER
from original OU courses i.e. formal delivery as well
as bespoke OER created by both OpenLearn
academics and non-OU educators, i.e. enabling
informal delivery.
OpenLearn users are primarily informal learners,
who want to find and study OER either individually
or in collaboration with others. These learners can be
in formal education e.g. taking an accredited
University course elsewhere and simply looking for
additional materials to add value to their primary
course or they maybe, what is often described as,
“leisure” learners i.e. those who simply want to learn
for themselves with no expectation of formal
accreditation.
OpenLearn currently uses Moodle as a LMS
platform. Therefore, in order to add value to those
potential learning experiences, this test-bed has
endeavoured to raise awareness of PLEs and SRL
with the community of informal learners that are
actively using OpenLearn for their learning. This has
been done primarily through the production of
bespoke OER as OpenLearn courses that raise
awareness about ROLE and its approach in
personalised and self-regulated learning (see
http://tinyurl.com/role-course and
http://tinyurl.com/role-srl-course for more details).
Figure 1 shows a sample learning activity from these
courses. The learning activity in question introduces
learners to the use of a widget for finding learning
resources.
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
184

This transition attempts to transform and improve
the OpenLearn user’s experience by enabling
individuals to build and personalise their learning
environment, thus gaining more control over their
learning process through the use and manipulation of
OER study materials. The aforementioned bespoke
OER that have been developed by the ROLE project
also provide guidance on how someone can use a
PLE in order to better organise their learning and
improve their SRL skills.
In addition, the adoption of certain ROLE
widgets inside study units of the OpenLearn
platform is offering further value to informal
learners by supporting a stronger framework to
foster learning communities. This presents an
opportunity to individual informal learners to be part
of a shared learning experience instead of a lone
study.
Figure 1: A learning activity featuring a ROLE widget
inside an OpenLearn course.
4 AN INQUIRY-BASED
LEARNING CASE STUDY
weSPOT (Working Environment with Social,
Personal and Open Technologies for Inquiry Based
Learning; http://wespot-project.eu) is a new
European project, aiming at propagating scientific
inquiry as the approach for science learning and
teaching in combination with today's curricula and
teaching practices. weSPOT aspires to lower the
threshold for linking everyday life with science
teaching in schools by technology. weSPOT
supports the meaningful contextualization of
scientific concepts by relating them to personal
curiosity, experiences and reasoning.
weSPOT addresses several challenges in the area
of science learning and technology support for
building personal conceptual knowledge. The
project focuses on inquiry-based learning with a
theoretically sound and technology supported
personal inquiry approach. In inquiry based-
learning, learners take the role of an explorer and
scientist and are motivated by their personal
curiosity, guided by self-reflection, and develop
knowledge personal and collaborative sense-making
and reasoning.
As we have learned from the ROLE project,
what is often missing from the PLE, is not the
abundance of tools and services, but the means for
binding them together in a meaningful way.
weSPOT will address this issue by providing ways
for the integration of data originating from different
inquiry tools and services. Most importantly though,
weSPOT will enable the cognitive integration of
inquiry tools by connecting them with the students’
profiles, as well as their social and curricular
context. Individual and collaborative student actions
taking place within different inquiry tools will
update the learning history and learning goals of the
student, thus providing them with a cohesive
environment for monitoring and self-regulating their
learning process and progress.
The Web 2.0 paradigm offers new opportunities
for social learning by facilitating interactions with
other learners and building a sense of connection
that can foster trust and affirmation (Weller, 2009).
Social learning, according to Hagel, et al. (Hagel et
al., 2010), is dictated by recent shifts in education,
which have altered the ways we catalyze learning
and innovation. Key ingredients in this evolving
landscape are the quality of interpersonal
relationships, discourse, personal motivation, as well
as tacit over explicit knowledge. Social media offer
a variety of collaborative resources and facilities,
which can complement and enrich the individual’s
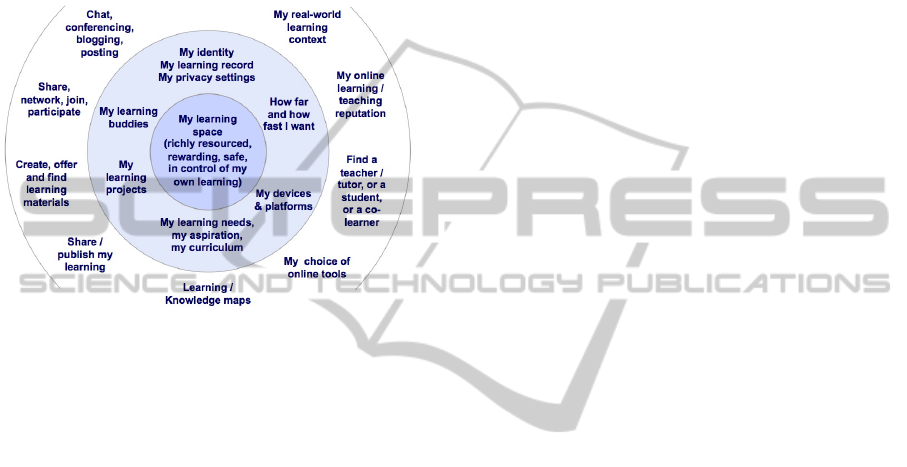
personal learning space, as shown in Figure 2.
weSPOT will provide students with the ability to
build their own inquiry-based learning environment,
enriched with social and collaborative features. This
will allow them to filter inquiry resources and tools
according to their own needs and preferences.
Students will be able to self-regulate their inquiry-
based learning process by planning, organising and
executing it in collaboration with their peers.
Students will also be able interact with their peers in
APersonalisedApproachinInformalandInquiry-basedLearning
185
order to reflect on their inquiry process, receive and
provide feedback, mentor each other, thus forming
meaningful social connections that will help and
motivate them in their learning. From a learner’s
perspective, this approach will offer them access to
personalized bundles of inquiry resources
augmented with social media, which they will be
able to manage and control from within their
personal learning space.
Figure 2: Personal learning space, resources, and social
interactions (Shum and Ferguson, 2010).
5 CONCLUSIONS
Personalised and self-regulated learning is offering
new capabilities to learners, by allowing them to
build and use learning environments that meet their
particular learning needs, thus taking control over
their learning journey. This paper presented the
premises of applying personalised learning in two
distinct case studies, concerning informal and
inquiry-based learning respectively.
The lessons learned from the informal learning
case study of the ROLE project have provided us
with an insight into some of the challenges
associated with the deployment of PLEs for
supporting informal learners in the context of using
and manipulating OER. Building on these lessons,
we plan to proceed with the deployment of PLEs in
the inquiry-based learning context of the weSPOT
project, in order to further explore the challenges
and opportunities of personalised and self-regulated
learning. The overall lessons learned from
investigating these two different case studies and
learning contexts will enable us to formulate a set of
best practices regarding the successful
implementation and deployment of PLEs for
supporting SRL both in informal and formal
education settings.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research leading to these results has received
funding from the European Community’s Seventh
Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under
grant agreement N° 318499 - weSPOT project. The
research work described in this paper has also been
partially funded through the ROLE Integrated
Project, part of the Seventh Framework Programme
for Research and Technological Development (FP7)
of the European Union in Information and
Communication Technologies.
REFERENCES
Abel, R. J. (2006) Best Practices in Open Source in Higher
Education Study: The State of Open Source Software.
The Alliance for Higher Education Competitiveness,
Inc., Lake Mary, FL, USA. http://www.a-
hec.org/media/files/A-HEC open source hed
030106.pdf.
Atkins, D. E., Brown, J. S. & Hammond, A. L. (2007) A
Review of the Open Educational Resources (OER)
Movement: Achievements, Challenges, and New
Opportunities. The William and Flora Hewlett
Foundation, http://www.oerderves.org/wp-content/
uploads/2007/03/a-review-of-the-open-educational-
resources-oer-movement_final.pdf.
Bri, D., Garcia, M., Coll, H. & Lloret, J. (2009) A Study
of Virtual Learning Environments. WSEAS
TRANSACTIONS on ADVANCES in ENGINEERING
EDUCATION, 1(6), 33-43.
Chatti, M. A., Jarke, M. & Frosch-Wilke, D. (2007) The
future of e-learning: a shift to knowledge networking
and social software. International Journal of
Knowledge and Learning, 3(4/5), 404-420.
Fiedler, S. & Väljataga, T. (2010) Personal learning
environments: concept or technology? PLE
Conference. Barcelona, Spain http://
pleconference.citilab.eu/wp-content/uploads/2010/07/
ple2010_submission_45.pdf.
Hagel, J., Seely Brown, J. & Davison, L. (2010) The
Power of Pull: How Small Moves, Smartly Made, Can
Set Big Things in Motion. New York: Basic Books.
Mikroyannidis, A. (2011) Supporting Self-Regulated
Learning within a Personal Learning Environment:
The OpenLearn case study. In Kravcik, M., Law, E. &
Nussbaumer, A. (Eds.) International Workshop on
Self-Regulated Learning in Responsive Open Learning
Environments (SRL-ROLE 2011), 11th IEEE
International Conference on Advanced Learning
CSEDU2013-5thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
186

Technologies (ICALT 2011). Athens, Georgia, USA,
IEEE Computer Society Publications.
Mikroyannidis, A. & Connolly, T. (2012a) Introducing
Personal Learning Environments to Informal Learners:
Lessons Learned from the OpenLearn Case Study.
PLE Conference. Aveiro, Portugal
http://oro.open.ac.uk/34501/.
Mikroyannidis, A. & Connolly, T. (2012b) Responsive
Open Learning Environments at the Open University.
World Conference on E-Learning in Corporate,
Government, Healthcare & Higher Education (E-
Learn). Montreal, Canada http://
academicexperts.org/conf/elearn/2012/papers/37248/,
Association for the Advancement of Computing in
Education (AACE).
Shum, S. B. & Ferguson, R. (2010) Towards a social
learning space for open educational resources. 7th
Annual Open Education Conference (OpenED2010).
Barcelona, Spain.
Wainwright, K., Osterman, M., Finnerman, C. & Hill, B.
(2007) Traversing the LMS terrain. Proceedings of the
35th annual ACM SIGUCCS fall conference. Orlando,
Florida, USA, ACM, 355-359.
Watson, W. R., Lee, S. & Reigeluth, C. M. (2007)
Learning Managemnt Systems: An Overview and
Roadmap of the Systematic Application of Computers
in Education. Advances in Computer-Supported
Learning. IGI Global.
Weller, M. (2009) Using learning environments as a
metaphor for educational change. On the Horizon,
17(3), 181–189.
Wilson, S. (2008) Patterns of personal learning
environments. Interactive Learning Environments,
16(1), 17-34.
Zimmerman, B. J. (1989) A Social Cognitive View of
Self-Regulated Academic Learning. Journal of
Educational Psychology, 81(3), 329- 339.
APersonalisedApproachinInformalandInquiry-basedLearning
187
