
Dynamic Characteristics Control of 2-DOF Manipulator with
Artificial Muscles and Differential Gear using Disturbance Observer
T. Watanabe, D. Kamo, D. Tanaka, T. Nakamura and H. Osumi
Department of Precision Mechanics, Chuo University, 1-13-27 Kasuga, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 112-8551, Japan
Keywords: Artificial Muscle, Differential Gear, Disturbance Observer, Nominal Model.
Abstract: Recently, the demand for robots that operate in the fields of nursing and human life have increased due to
the aging population and falling birthrates. Since these robots are intended to operate near humans, it is
necessary they should have increased safety measures. Moreover, since it is desired that these robots use
actuators that are light and soft, in several cases artificial muscles have been used as actuators. However, the
Mckibben-type artificial muscles that are most commonly used have several drawbacks. Therefore, we
developed a straight-fiber-type artificial muscle that was utilized to construct a two degree-of-freedom (2-
DOF) manipulator. Because the manipulator is equipped with a differential gear mechanism, it is capable of
performing 2-DOF bending and torsion motions using only one mechanism. However, the rotation speed of
gears respectively differs in this mechanism, so the interference occurs in unintended directions because the
speed of contraction and extension of the artificial muscle respectively differs. To address this problem, we
introduce the disturbance observer (DOB) in the control system. Finally, we show that using our proposed
DOB control method results in less interference in the 2-DOF manipulator than when using the proportional
integral (PI) control method.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the number of older people requiring
nursing has increased. However, the number of
young people working in nursing homes has
decreased. Therefore, the demand for robots that can
provide medical treatment and assistance in nursing
homes has increased. However, in order to decrease
the effect of collisions, these robots should have
safety and flexibility compared to currently used
robots.
To satisfy these requirements, several robots use
pneumatic artificial muscles as actuators. The most
commonly used pneumatic artificial muscles are the
Mckibben-type (Klute et al., 1999); (Tondu and
Zagal, 2006); (Bong-Soo et al., 2009). However,
Mckibben-type muscles have problems in regards to
low durability and lack of output. Pleated pneumatic
artificial muscles (Daerden et al., 2001) is that the
radial expantion is large, and are not flexible we
require, because they are not made from rubber.
Therefore, in this study, we adopt the straight-fiber-
type pneumatic artificial muscles that we developed
in prior work (Nakamura et al., 2003). It has been
experimentally and theoretically shown that these
type of artificial muscles have a greater contraction
ratio and more power than conventional McKibben-
type muscles (Chou and
Hannaford, 1994);
(Nakamura, 2006). Moreover, because the straight-
fiber-type muscles be made of rubber, they are
extremely high durability, lightweight and flexible.
They can be used to construct manipulators that
have greater drivable range and torque. In addition,
to compensate for the nonlinear properties of the
artificial muscle, we applied a mechanical
equilibrium model as a feedforward controller
(Nakamura and Shinohara, 2007); (Nakamura and
Maeda, 2008).
Using a straight-fiber-type pneumatic artificial
muscle, we developed a six degrees of freedom (6-
DOF) manipulator (Maeda et al., 2009). In order to
achieve a more precice movement similar to humans,
we want to extend the manipulator to have 7-DOF.
In addition to an extra degree of freedom, we also
want this manipulator to be flexible and light.
Consequently, the mechanism of this manipulator
needs to be compact. Thus, we developed a 2-DOF
artificial muscle manipulator with a differential gear
mechanism (Kamo et al., 2011). Consequently, the
bending and rotation motion, as well as their
122
Watanabe T., Kamo D., Tanaka D., Nakamura T. and Osumi H..
Dynamic Characteristics Control of 2-DOF Manipulator with Artificial Muscles and Differential Gear using Disturbance Observer.
DOI: 10.5220/0004426801220129
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2013), pages 122-129
ISBN: 978-989-8565-71-6
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
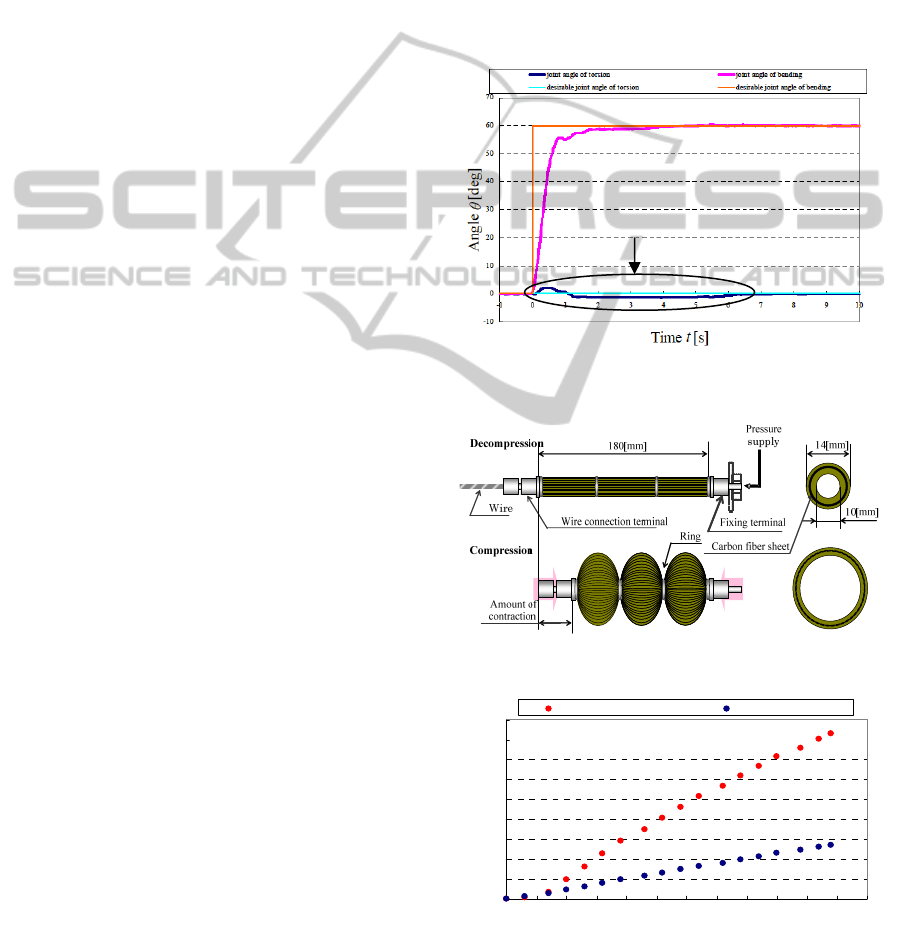
stiffness can be controlled by a single mechanism.
This differential gear mechanism drives by
contracting antagonistic artificial muscles.
However, the speeds of contraction and
expansion of the artificial muscles differ. Therefore,
since the rotational speeds of the right and left gears
in this mechanism are different, interference in
unintended directions occurs, as shown in Figure 1.
To address this problem, we introduce in the
control system the disturbance observer (DOB). The
DOB provides robustness by estimating the
disturbance and using feedback to cancel it (Wakui
et al., 2012). For example, the DOB is used to
control the joints of humanoid robots and enables
them to walk stably even if the model mismatch and
vibrations presense (Xing et al., 2010). Furthermore,
the DOB has been used for backlash compensation
of a DC motor (Jung et al., 2004). Moreover, the
DOB can be used to force the output response to
follow a nominal model. The angle response of the
right (left) gear can be corresponded with that of left
(right) gear, and consequently decrease interferences
in unintended directions.
The remainder of this paper is organized as
follows: In Section 2, we describe the shape of the
muscle and its characteristics. In Section 3, we
provide an introduction to DOB theory. In Section 4,
we describe the mechanism of the 2-DOF artificial
muscle manipulator with differential gears and its
control system. In Section 5, we conduct
experiments to compare the PI and DOB conrtollers
and validate the effectivness of the DOB control
method. Section 6 provides a summary and
concluding remarks.
2 STRAIGHT-FIBER-TYPE
PNEUMATIC ARTIFICIAL
MUSCLE
2.1 Straight-fiber-type Pneumatic
Artificial Muscle
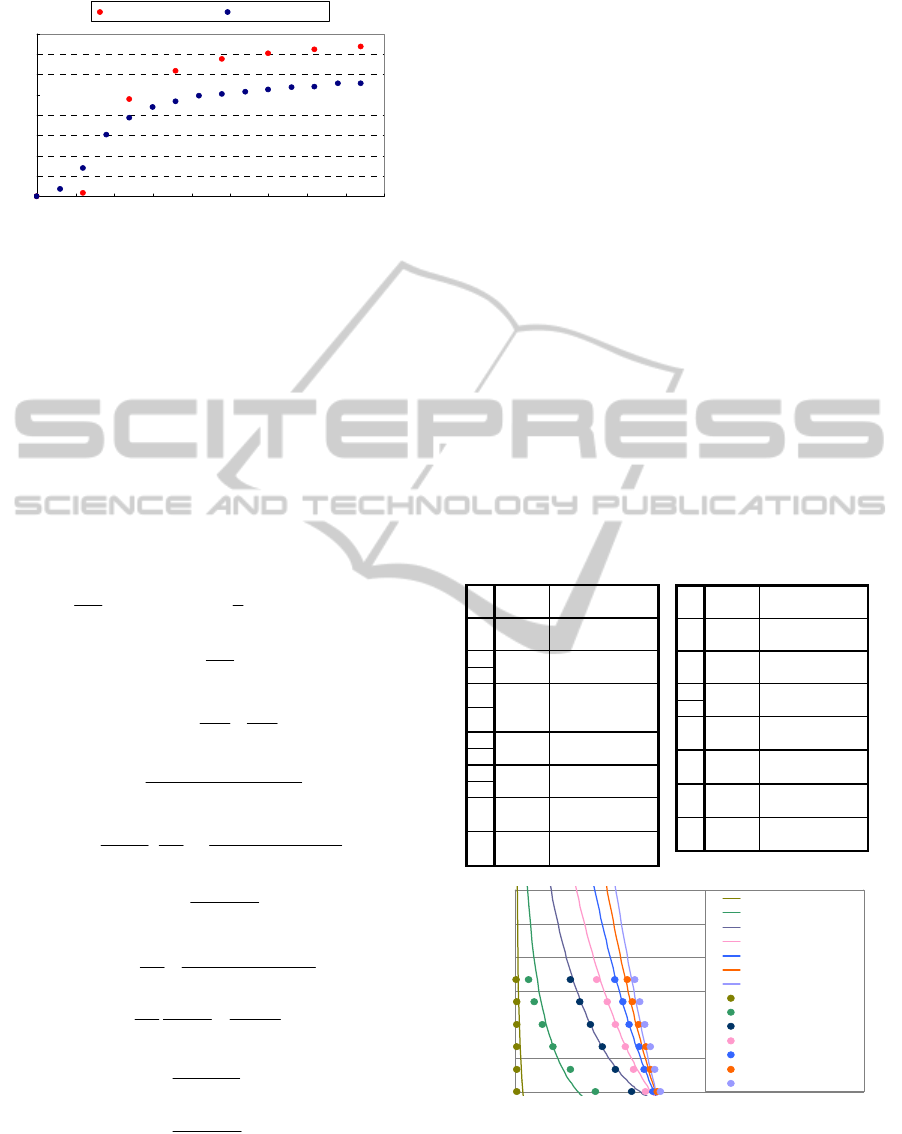
Figure 2 shows a schematic of the straight-fiber-type
artificial muscle. The tube shown is made of natural
latex rubber and a carbon fiber sheet that is inserted
along the direction of the long-axis. The two ends of
the tube are fixed by terminals. Therefore, the
artificial muscle expands in the radial direction and
contracts in the axial direction when air pressure
applies.
In Figures 3 and 4, we compare the pressure
characteristics of the Mckibben-type and straight-
fiber-type artificial muscles as a function of the
contraction force and rate of contraction,
respectively. We observe that the inner diameter and
the length of both types of artificial muscles are the
same size as shown in Figure 3. However, the
straight-fiber-type artificial muscle produces a larger
contraction force and rate of contraction than the
McKibben-type artificial muscle. This difference
occurs because the former muscle restricts
expansion only in the axial direction, whereas the
reticular fiber structure of the latter restricts
expansion in both the axial and radial directions.
Figure 1: Experimental results from controlling the joint
angle during a bending motion.
Figure 2: Straight-fiber-type pneumatic artificial muscle.
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6
Pressure[MPa]
Contraction force[N]
strai
g
ht-fiber-t
yp
e McKibben-t
yp
e
Figure 3: Relationship between pressure and contraction
force.
Response with interference
DynamicCharacteristicsControlof2-DOFManipulatorwithArtificialMusclesandDifferentialGearusingDisturbance
Observer
123
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45
Pressure[MPa]
Rate of contraction[%]
straight-fiber-type McKibben-type
Figure 4: Relationship between pressure and rate of
contraction.
2.2 Mechanical Equilibrium Model
The straight-fiber-type artificial muscle we
developed has highly nonlinear characteristics.
Moreover, because the gains of the input and output
angles are unequal and the position control tends to
be unstable. Therefore, we use the mechanical
equilibrium model to linearize it (Nakamura, 2007;
Nakamura and Maeda, 2008). The equations of the
model are expressed as
1 1101 2202 1202 1201
(,, ) ()() ()()
djd
PKGG GG
21 01 32 02 21 01 22 02
2
1
22 02 31 01 21 01 32 02
2
() () () ()]
/()() ()()
jd
a
a
a
K
GG GG
Kr
K
GG GG
K
(1)
1
21
22
(,, )
jd
a
djd
aa
K
K
P
KP
KK
(2)
idiidii
diii
dii
lxxl
xl
x
0
2
2
0
5.0
5.1
0
0
')'(
'2
)'(
(3)
2
0
000
2
0
0
0
01
cossin4
)(
i
iii
i
i
i
iai
ii
d
l
d
tK
G
(4)
ii
i
ii
nbd
M
G
0
0
02
tan
)(
(5)
i
i
i
i
i
i
i
i
ii
i
i
ii
nb
dM
d
l
d
l
G
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
000
0
0
03
tan
sin
4
cossin
2)(
(6)
3
'
1
1
d
d
rr
x
(7)
3
'
2
2
d
d
rr
x
(8)
In Table 1, we present the parameters of these
equations. The subscript number is used to
discriminate between artificial muscles 1 and 2.
When the same equation is used for both muscles,
we use subscript i. Here,
and
d
represent the
pulley angle and desirable value, respectively. P
1
and P
2
, computed from Equations (1) and (2),
respectively, are the pressure values required to
realize
d
. Therefore,
and
d
have a linear
relationship. And then, torque is fed back to those
equations. In this study, we use equilibrium model
linearization (EML) to perform compensation.
Therefore, we can express EML in the control
system as a linear transfer function.
Moreover, we can control the joint stiffness K
j
by
inputting a desirable value K
jd
. If the stiffness
characteristic constants K
a1
and K
a2
are equal, the
joint stiffness K
j
is proportional to the initial
pressure P
0
. Thus, we can select the joint stiffness
we desire.
Figure 5 shows a comparison between theoretical
and experimental results of the relationship between
force applied and contraction observed. This result
shows that the experimental results are in agreement
with the theory. Hence, the mechanical equilibrium
model provides the sufficient accuracy required to
perform position and stiffness control.
Table 1: Parameter of EML.
d
[rad] Desirable angle
[Nm] Load torque
P
1
P
2
[Pa] Pressure
01
02
[rad]
The central angle of
the arc shape of the
muscle
x
d1
x
d2
[m]
Desirable
contraction
1
2
[rad] Angle of slack wire
b
i
[mm] Width of glass fiber
i
Approximation
constant number
r [mm] Radius of the pulley
n
Number of the glass
fiber
K
j
[Nm/rad] Joint Stiffness
K
a1
K
a2
Fixed stiffness
number
l
0i
[m]
Length between cap
and ring
d
0i
[m]
Diameter of
artificial muscle
t
i
[m]
Thickness of
artificial muscle
Fiber constant
number
d
[rad] Desirable angle
[Nm] Load torque
P
1
P
2
[Pa] Pressure
01
02
[rad]
The central angle of
the arc shape of the
muscle
x
d1
x
d2
[m]
Desirable
contraction
1
2
[rad] Angle of slack wire
b
i
[mm] Width of glass fiber
i
Approximation
constant number
r [mm] Radius of the pulley
n
Number of the glass
fiber
K
j
[Nm/rad] Joint Stiffness
K
a1
K
a2
Fixed stiffness
number
l
0i
[m]
Length between cap
and ring
d
0i
[m]
Diameter of
artificial muscle
t
i
[m]
Thickness of
artificial muscle
Fiber constant
number
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
0.0 20.0 40.0 60.0 80.0 100.0 120.0 140.0 160.0
Amount of contraction [mm]
Contraction force [N]
0.06MPa_Theoretical
0.12MPa_Theoretical
0.18MPa_Theoretical
0.24MPa_Theoretical
0.30MPa_Theoretical
0.36MPa_Theoretical
0.42MPa_Theoretical
0.06MPa_experimental
0.12MPa_experimental
0.18MPa_experimental
0.24MPa_experimental
0.30MPa_experimental
0.36MPa_experimental
0.42MPa_experimental
Figure 5: Comparison between theoretical and
experimental results of the relationship between force
applied and contraction observed.
ICINCO2013-10thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
124
3 DISTURBANCE OBSERVER
THEORY
To date, we have used a PI controller to control the
position of the 2-DOF manipulator. However,
because the PI controller cannot compensate for the
dynamic characteristics of the system, we apply the
DOB here.
3.1 Disturbance Observer Theory
Figure 6 shows a block diagram of the DOB (Wakui
et al., 2012). The DOB is composed of the plant, the
inverse of the plant, and a filter. The nominal model
represents the transfer function of the ideal response,
which is arbitrarily selected. The DOB operates as
follows. First, it uses the difference between the
ideal input and actual response to estimate the
disturbance. Second, the estimated disturbance
passes through the filter and is used as feedback.
Therefore, because the disturbance is canceled, the
output becomes equal to the input. If the transfer
function of the filter is F(s) = 1, the relation between
the input and output is expressed by Equation (9).
)()()( srsPsy
n
(9)
While a mismatch between the output of the plant
and the desirable value (output of the nominal
model) is detected, feedback is performed and the
output value changes according to Equation (9).
Therefore, we can control the interference in
unintended directions because the angle response of
the right and left gears corresponds with the nominal
model.
r
P(s)
+
-
y
Filter&Inverse
Plant
Pn(s)
Nominal model
+
-
F(s)/Pn(s)
)(sP
)(sPn
)(sF
))()(( sPnsP
:Nominal model
:Filter
:Plant
r
P(s)
+
-
y
Filter&Inverse
Plant
Pn(s)
Nominal model
+
-
F(s)/Pn(s)
)(sP
)(sPn
)(sF
))()(( sPnsP
:Nominal model
:Filter
:Plant
)(sP
)(sPn
)(sF
))()(( sPnsP
:Nominal model
:Filter
:Plant
Figure 6: Block diagram of DOB.
3.2 Filter Design Theory
The transfer function of filter F(s) is expressed by
Equation (10).
n
Ts
sF
)1(
1
)(
(10)
Here, T is an arbitrary parameter representing the
time constant of the filter. For the system to be
stable, the degree of the filter n must be greater than
or equal to that the degree of P
n
(s).
4 2-DOF MANIPULATOR
WITH DIFFERENTIAL GEAR
MECHANISM
4.1 2-DOF Manipulator with
Differential Gear Mechanism
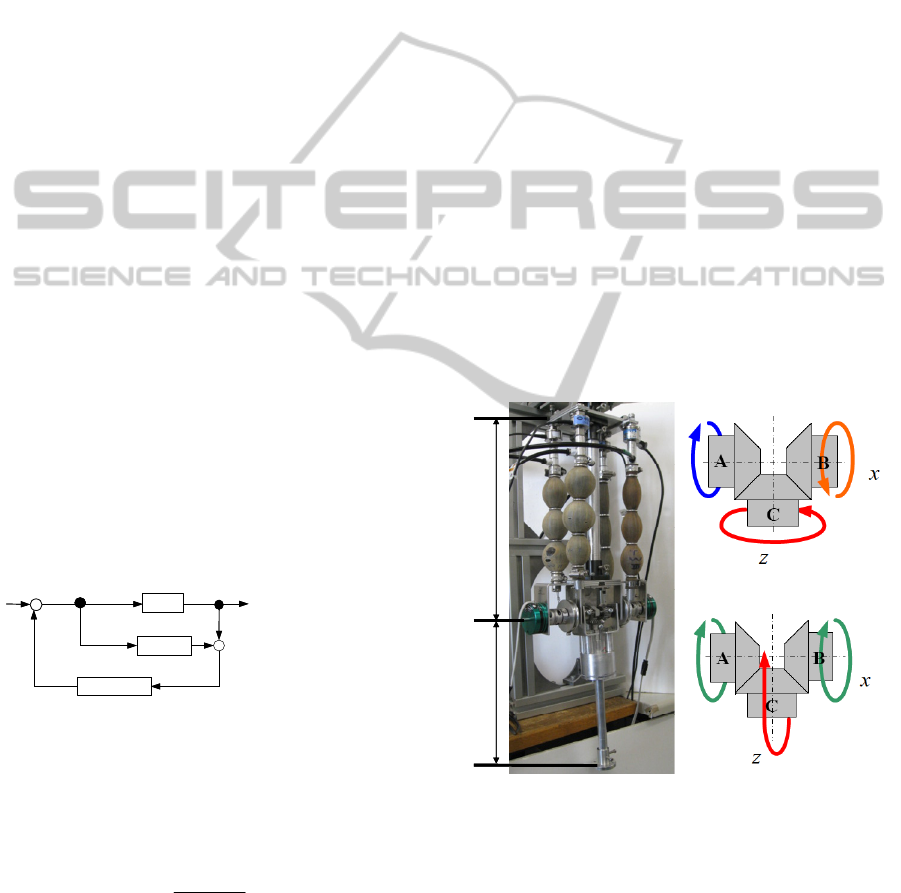
In Figure 7, we present the 2-DOF manipulator with
a differential gear mechanism used in this study. The
upper arm, the lower arm and the weight of the
manipulator are 310 mm, 260 mm and around 2.5 kg
respectively. And then, the manipulator is mainly
composed of two pairs of antagonistic artificial
muscles and a differential gear. The antagonistic
artificial muscles are connected by a wire through a
pulley.
In Figure 7 (b) and (c), we illustrate the motions
the manipulator can perform. When bevel gears A
and B rotate in opposite directions, bevel gear C is
fixed around the x-axis and rotates around the z-axis.
In this study, this motion of the manipulator is
termed as torsion motion. When bevel gears A and B
rotate in the same direction, bevel gear C is fixed
around the z-axis and rotates around the x-axis with
bevel gears A and B. In this study, this motion of the
manipulator is termed as bending motion.
Upper arm
310 [mm]
Lower arm
260 [mm]
Upper arm
310 [mm]
Lower arm
260 [mm]
Figure 7: 2-DOF manipulator with differential gear
mechanism.
4.2 Experimental System
Figure 8 shows a schematic of the experimental
system used for the 2-DOF artificial muscle
manipulator. The artificial muscles are connected to
an air compressor via proportional solenoid valves.
(a) 2-DOF manipulator.
(b) Torsion motion.
(c) Bending motion.
DynamicCharacteristicsControlof2-DOFManipulatorwithArtificialMusclesandDifferentialGearusingDisturbance
Observer
125
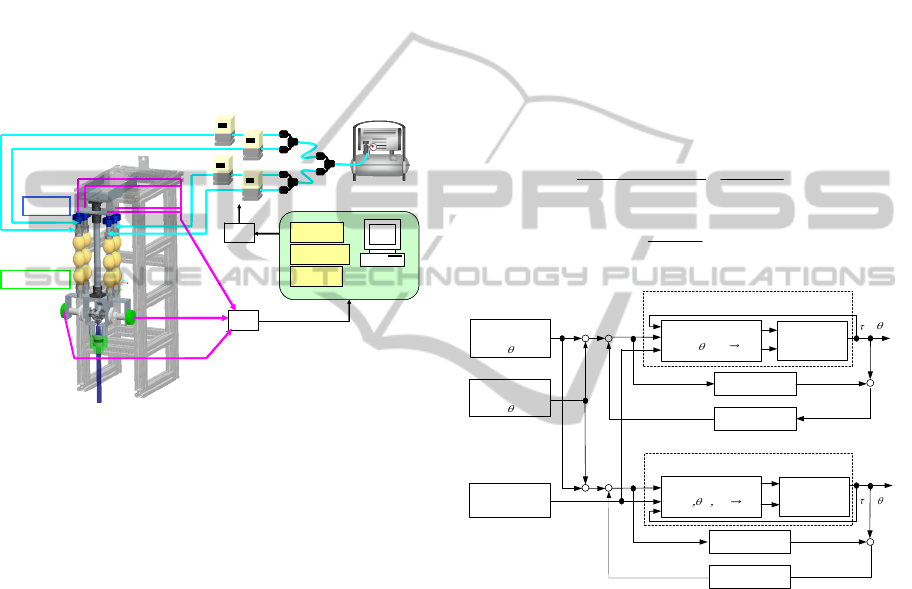
Thus, we use the proportional solenoid valves to
control the air pressure provided by the air
compressor. The air pressure applied to each
artificial muscle is controlled by a PC that is
connected to the proportional solenoid valves. At
equilibrium, a pressure of P
0
is applied to both
muscles. When we apply a pressure of +
P to one
artificial muscle and at the same time a pressure of
−
P to the other, the pulleys begin to rotate because
the contractile forces of the two artificial muscles
differ. Moreover, the rotation of the pulley causes
the differential gear to begin rotating, which in turn
drives the 2-DOF artificial muscle manipulator.
D/A
A/D
Air compressor
Proportional
solenoid valve
Potentiometer
Loadcell
Simulink
MATLAB
dSPACE
PC
D/A
A/D
Air compressor
Proportional
solenoid valve
Potentiometer
Loadcell
Simulink
MATLAB
dSPACE
PC
Simulink
MATLAB
dSPACE
PC
Figure 8: Schematic of the experimental system.
4.3 Control System
We designed a control system for the manipulator
using Simulink. The control inputs were applied
using dSPACE. Figure 9 shows the block diagram of
the manipulator control system. We introduced the
DOB in the control system to control the output
angles of pulleys A and B. The controller considers
all responses as disturbances, except those of the
nominal model. We use the desirable bending angle
dA
, desired torsion angle
dB
, output angles
A
and
B
detected by the potentiometer, desirable joint
stiffness k
jd
, and load torque
in the EML to
compute the air pressure that should be applied to
each artificial muscle.
We execute the torque feedback by using the
load cell connected each artificial muscles. Because
the force acting on each artificial muscle was
measured by the load cell, we can calculate the load
torque in one antagonistic artificial muscle by taking
the force gap.
We showed the nominal model by dead time and
the first-order system. We selected the nominal
model by performing experiments using the PI
controller and examining the response of the
manipulator. From the experimental results, we
concluded that the dead time was 0.02 s, and the
time constant of the first-order system was 0.35.
Next we analyzed the vibration and trajectory
tracking performance of the system and set the time
constant of filter to T = 0.5. Because the nominal
model is expressed by a first-order system, we set
the order of the filter to n = 1. In addition, because
we want to compare the PI control with the DOB
control, we set the desirable joint stiffness to a fixed
value, k
jd
= 0.08. The transfer functions of the
nominal model P
n
(s) and filter F(s), are expressed by
Equations (11) and (12), respectively. The transfer
function of the dead time is expressed using the Pade
approximation.
135.0
1
30000300
30000300
)(
2
2
s
ss
ss
sP
n
(11)
15.0
1
)(
s
sF
(12)
Desirable Torsion
Joint Angle
EML of Pulley B
K
P
EML of Pulley A
K ,
, P
Nominal model
Pn(s)
+
-
+
+
+
-
Desirable Bending
Joint Angle
Artificial
Muscle
Manipulator
dm
dA
dB
-
+
A
B
jdA
jdB
dn
Desirable Joint
Stiffness
K
jd
A
B
Artificial
Muscle
Manipulator
Filter & Inverse
F(s)/Pn(s)
+
-
Nominal model
Pn(s)
Filter & Inverse
F(s)/Pn(s)
+
-
dA
dB
Plant P(s)
Plant P(s)
Figure 9: Block diagram of the manipulator control system.
5 JOINT ANGLE
CONTROL EXPERIMENT
AND EXAMINATION
First, we applied a 50 deg step signal as input for
bending and torsion, while the manipulator had no
load. Then, we repeated the same experiment with a
manipulator load of 0.5 N.
5.1 Examination of Joint Angle Control
Experiment
Here, we present the experimental results obtained
and discuss our findings. We omit responses
ICINCO2013-10thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
126
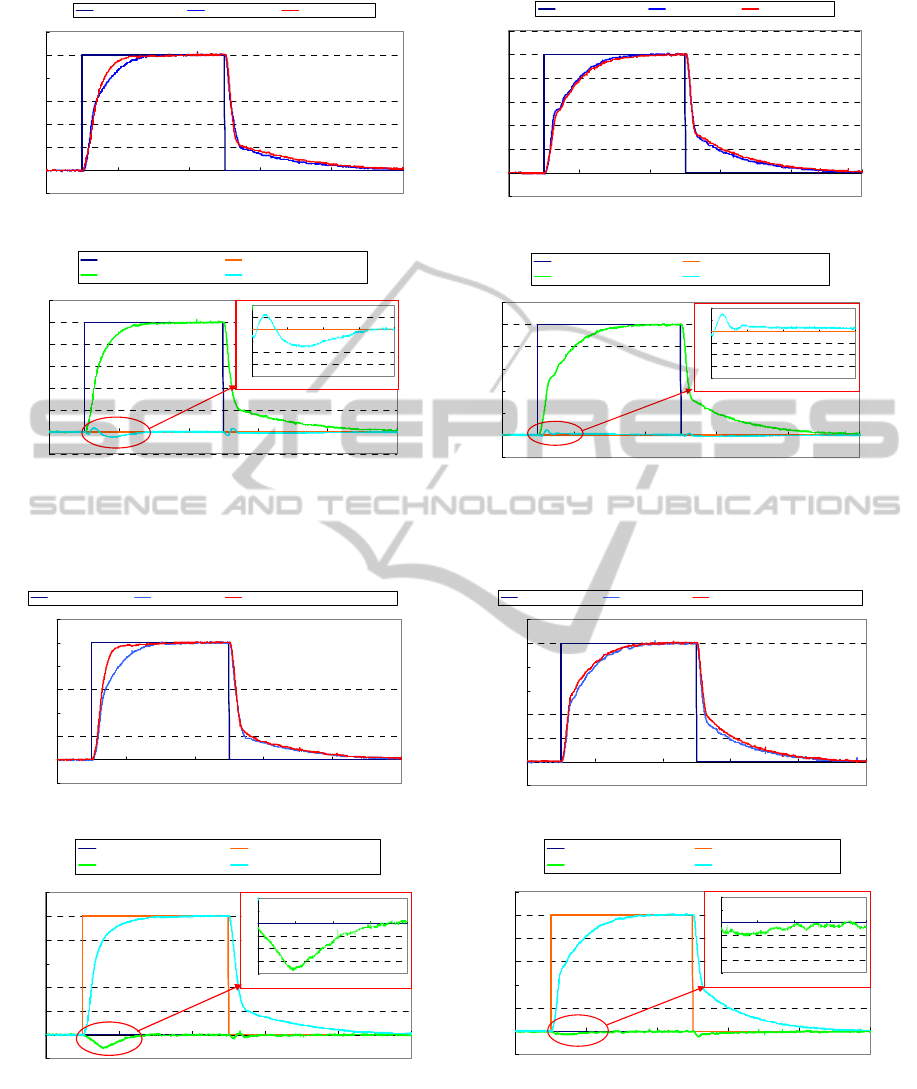
obtained for a load of 0.5 N, because they are
approximately equal to the ones obtained for no load.
In Figures 10-13, we present experimental results
obtained when a 50 deg step signal was applied as
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0246810
Time [s]
Angle [deg]
Input torsion 50[deg] PulleyA response PulleyB response (reversing response)
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0246810
Time [s]
Angle [deg]
Input bending 0[deg] Input torsion 50[deg]
Experimental bending response Experimental torsion response
-6
-4.5
-3
-1.5
0
1.5
3
1.1 1. 6 2.1 2. 6 3.1
Time [s]
Angle [deg ]
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0246810
Time [s]
Angle [deg]
Input bending 0[deg] Input torsion 50[deg]
Experimental bending response Experimental torsion response
-6
-4.5
-3
-1.5
0
1.5
3
1.1 1. 6 2.1 2. 6 3.1
Time [s]
Angle [deg ]
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0246810
Time [s]
Angle [deg]
Input torsion 50[deg] PulleyA response PulleyB response (reversing response)
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0246810
Time [s]
Angle [deg]
Input bending 0[deg] Input torsion 50[deg]
Experimental bending response Experimental torsion response
-6
-4.5
-3
-1.5
0
1.5
3
1.1 1.6 2.1 2.6 3.1
Time [s]
Angle [deg ]
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0246810
Time [s]
Angle [deg]
Input bending 0[deg] Input torsion 50[deg]
Experimental bending response Experimental torsion response
-6
-4.5
-3
-1.5
0
1.5
3
1.1 1.6 2.1 2.6 3.1
Time [s]
Angle [deg ]
(a) Responses of pulleys.
(a) Responses of pulleys.
(b) Responses of joint angles.
(b) Responses of joint angles.
Figure 13: Experimental results of torsion motion while
applying DOB control.
Figure 12: Experimental results of torsion motion while
applying PI control.
Joint angle error
Joint angle error
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0246810
Time [s]
Angle [deg]
Input bending 50[deg] Pulle yA response P ulleyB response
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0246810
Time [s]
Angle [deg]
Input bending 50[deg] Input torsion 0[deg]
Experimental bending response Experimental torsion response
-6
-4.5
-3
-1.5
0
1.5
3
1.1 1.6 2. 1 2.6 3.1
Time [s]
Angle [deg]
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0246810
Time [s]
Angle [deg]
Input bending 50[deg] Input torsion 0[deg]
Experimental bending response Experimental torsion response
-6
-4.5
-3
-1.5
0
1.5
3
1.1 1.6 2. 1 2.6 3.1
Time [s]
Angle [deg]
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0246810
Time [s]
Angle [deg]
Input be nding 50[deg] PulleyA response PulleyB response
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0246810
Time [s]
Ang
l
e [
d
eg]
Input bending 50[deg] Input torsion 0[deg]
Experimental bending response Experimental torsion response
-6
-4.5
-3
-1.5
0
1.5
3
1.1 1.6 2.1 2.6 3. 1
Time [s]
Angle [de g]
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0246810
Time [s]
Ang
l
e [
d
eg]
Input bending 50[deg] Input torsion 0[deg]
Experimental bending response Experimental torsion response
-6
-4.5
-3
-1.5
0
1.5
3
1.1 1.6 2.1 2.6 3. 1
Time [s]
Angle [de g]
a) Responses of pulleys.
(b) Responses of joint angles.
Figure 10: Experimental results of bending motion while
applying PI control.
Figure 11: Experimental results of bending motion while
applying DOB control.
(a) Responses of pulleys.
(b) Responses of joint angles.
Joint angle error
Joint angle error
DynamicCharacteristicsControlof2-DOFManipulatorwithArtificialMusclesandDifferentialGearusingDisturbance
Observer
127
input for bending and torsion, while the manipulator
had no load. Figure 10 shows experimental results
for an input signal of bending of 50 deg, while
applying PI control. Figure 10 (a) shows the angular
responses of pulleys A and B, and Figure 10 (b)
shows the response of the joint angle.
Next, we discuss differences between the PI and
DOB control methods. In Figure 10 (b), we observe
that the joint angle error occurs in the direction of
torsion. This result is caused by the errors in the
angular responses of pulleys A and B, as shown in
Figure 10 (a).
In Figure 11, we present experimental results for
an input signal of bending of 50 deg, while applying
DOB control. In Figure 11 (b), we observe that the
joint angle error in the direction of torsion has been
reduced. This result occurs because the angular
response of pulley A is approximately equal to that
of pulley B, as shown in Figure 11 (a). Figures 12
and 13 present experimental results for an input
signal of torsion of 50 deg, while applying PI and
DOB control, respectively. The response of pulley B
present by reversing the real response of it to
compare the response, though the real response of
pulley B is opposite to that of pulley A in torsion
motion. Similar to the experimental results of
bending motion, we observe that the joint angle error
caused by torsion motion was also reduced with
DOB control.
5.2 Examination and Comparison
using the Area of the Joint
Angle Error
Next, we evaluate the interference in unintended
directions as the area of the joint angle error in the
cases of no load and a load of 0.5 N.
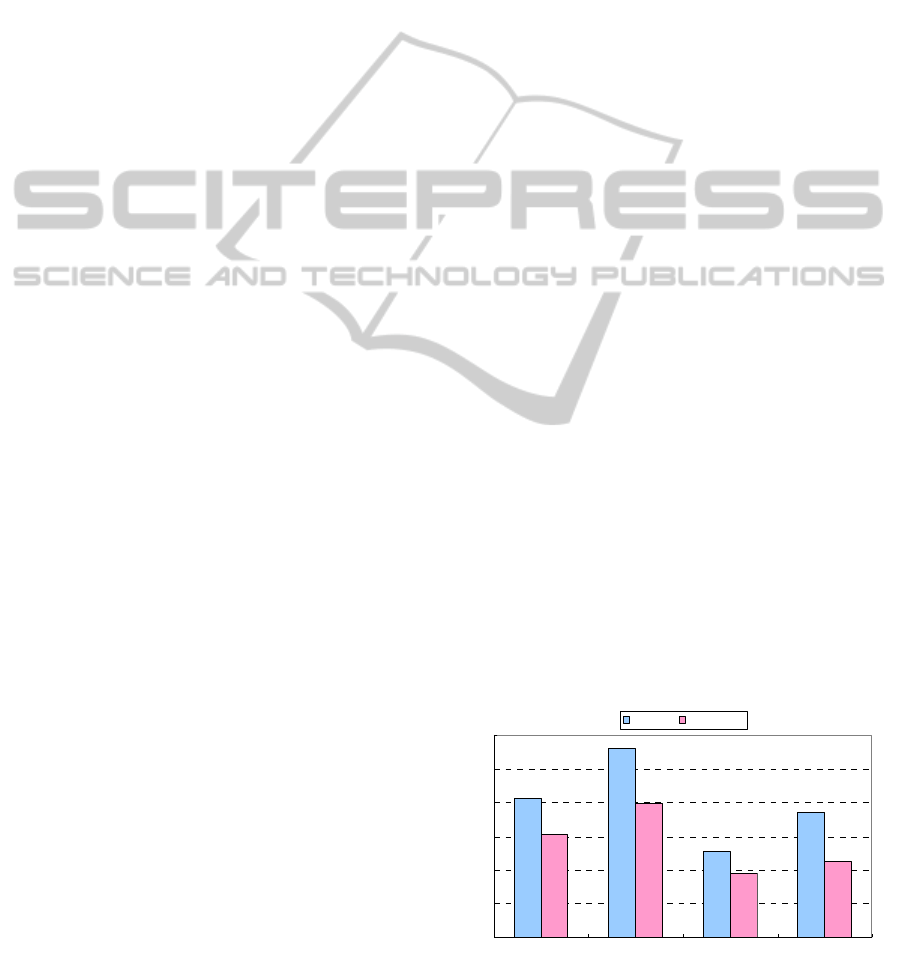
In Figure 14, we present the evaluation results
obtained for the area of the joint angle error. The
area expresses by integrating the joint angle error
per unit of time. The vertical axis shows amount of
the joint angle error and the unit is assumed to be
dimensionless. In Figure 14, it shows by hyphen.
First, we discuss differences between the PI and
DOB control methods. From Figure 14, we observe
that the area of the joint angle error when applying
DOB control is smaller than when applying PI
control. Specifically, the area of the error was
reduced by approximately 40% in the case of an
input signal of torsion of 50 deg and a load of 0.5 N.
This result occurs because the angular response of
pulley A is approximately equal to that of pulley B.
Therefore, we conclude that DOB control
successfully compensates for interferences in
unintended directions.
Second, we discuss differences between the areas
of error caused during bending and torsion motions.
In our results, we observe that regardless of the load
and control method used, the area of error of torsion
is larger than that of bending. We explain this result
by Figure 15. Figure 15 present the force caused in
bevel gear C. Because the interference occurs in
bending direction when applying torsion motion in
Figure 12 and 13, the component of the gravity
direction is assumed to act, as shown Figure 15 (b).
And then, F
A
and F
B
represent the rotational force of
bevel gears A and B, respectively. The interference
in unintended direction occurs because the balance
of the force in interference direction caused bevel
gear C collapses. That is, the interference occurs
because the force generated on bevel gears A side
and B side differs respectively. In Figure 15, in
bending motion, the gravity load f
g
acts in the same
direction for F
A
and F
B
, respectively. At this time,
the interference is not easily generated because the
resultant force on bevel gears A side and B side is
the same, respectively. However, f
g
acts in opposite
direction for F
A
, whereas f
g
acts in the same
direction for F
B
in torsion motion. Therefore,
because the resultant force on bevel gears A side and
B side differs, respectively, the interference in
torsion motion is easily generated than in bending
motion. Thus, we conclude that this is the reason
why the area of error in torsion is larger than that in
bending.
Third, we examine the area of error of bending in
the cases of no load and for a load of 0.5 N. From
the results obtained, we see that the area of error of
bending for a load of 0.5 N is smaller than that with
no load. We believe that the manipulator could not
rotate easily because the load restricted the motion
of the torsion. For the same reason, the area of error
of torsion in the case of a load of 0.5 N was smaller
than that in the case for no load.
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
F=0[N],
bending50[deg]
F=0[N],
torsion50[deg]
F=5[N],
bending50[deg]
F=5[N],
torsion50[deg]
Amount of joint angle error [-
]
PI control DOB control
Figure 14: Area of error in the direction of interference.
ICINCO2013-10thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
128

F
A
F
B
A
BB
A
C
C
F
A
F
B
Gravity load : f
g
f
g
f
g
f
g
f
g
C
C
A side
B side
B side
A side
F
A
F
B
A
BB
A
C
C
F
A
F
B
Gravity load : f
g
f
g
f
g
f
g
f
g
C
C
A side
B side
B side
A side
(a) Bending motion. (b) Torsion motion.
Figure 15: The force caused in bevel gear C.
On the basis of these results, we conclude that
regardless of the presence of load, the DOB control
is more effective than PI control in reducing the
interference in unintended directions.
6 CONCLUSIONS
We adopted the DOB in the control system of a 2-
DOF manipulator with straight-fiber-type artificial
muscles and a differential gear mechanism.
Experimental results show that regardless of the
presence of load, the DOB control method performs
better that the PI control in reducing the interference
in unintended directions. Hence, we prove the
effectiveness of our proposed DOB control method.
In the future, we apply the DOB control to a
manipulator with multiple degrees of freedom and
show that the interference is reduced even if the
weight of the manipulator gains by increasing the
degree of freedom.
REFERENCES
Bong-Soo, K., Kothera, C. S., Woods, B. K. S., Wereley,
N. M. (2009). Dynamic modeling of Mckibben
pneumatic artificial muscles for antagonistic actuation.
in Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on
Robotics and Automation, 12-17 May., pp.182-187.
Chou C. P. and Hannaford, B. (1994). Static and Dynamic
Characteristics of McKibben Pneumatic Artificial
Muscles. in Proceedings of IEEE International
Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Diego,
California, USA, 8-13 May, pp. 281-286.
Daerden, F., Lefeber, D., Verrelst, B. and Van Ham, R.
(2001). Pleated Pneumatic Artificial Muscles:
Compliant Robotic Actuators. in Proceedings of
IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent
Robots and Systems, Hawaii, USA, pp.1958-1963.
Jung, B. -J., Kong, J.–S., Lee, B.–H., Ahn, S.–M., Kim,
J.–G. (2004). Backlash compensation for a humanoid
robot using disturbance observer. in Proceedings of
30th Annual Conference of IEEE on Industrial
Electronics Society, Busan, South Korea, 2-6 Nov.,
vol.3, pp. 2142- 2147.
Kamo, D., Maehara, M., Tanaka, D. and Nakamura, T.
(2011). Development of a manipulator with straight-
fiber-type artificial muscle and differential gear
mechanism. in Proceedings of 37th Annual
Conference of IEEE on Industrial Electronics Society,
Melbourne, Australia, 7-10 Nov., pp.98-103.
Klute, G. K., Czernieki, J. M. and Hannaford, B. (1999).
McKibben Artificial Muscles: Pneumatic Actuators
with Biomechanical Intelligence. in Proceedings of the
IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced
Intelligent Mechatronics, Atlanta, USA, pp. 221-226.
Nakamura, T. (2006). Experimental Comparisons between
McKibben type Artificial Muscles and Straight Fibers
Type Artificial Muscles. SPIE International
Conference on Smart Structures, Devices and Systems
III, San Diego, California, USA
Nakamura, T. and Maeda, H. (2008). Position and
Compliance Control of an Artificial Muscle
Manipulator using a Mechanical Equilibrium Model.
in Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on
Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, California, USA,
10-13 Nov., pp. 3431-3436.
Nakamura, T., Saga, N. and Yaegashi, K. (2003).
Development of Pneumatic Artificial Muscle based on
Biomechanical Characteristics. in Proceedings of
IEEE International Conference on Industrial
Technology, Maribor, Slovenia, pp. 729-734.
Nakamura, T. and Shinohara, H. (2007). Position and
Force Control Based on Mathematical Models of
Pneumatic Artificial Muscles Reinforced by Straight
Glass Fibers. in Proceedings of IEEE International
Conference on Robotics and Automation, Roma, Italy,
10-14 April, pp. 4361-4366.
Maeda, H., Nagai, H., Nakamura, T. (2009). Development
of a 6-DOF manipulator actuated with a straight-fiber-
type artificial muscle. in Proceedings of IEEE/RSJ
International Conference on Intelligent Robots, St.
Louis, USA, 10-15 Oct., pp.607-612.
Tondu, B., Zagal, S. D. (2006). McKibben artificial
muscle can be in accordance with the Hill skeletal
muscle model. in Proceedings of IEEE/RAS-EMBS
International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and
Biomechatronics, 20-22 Feb., pp.714-720.
Wakui, S., Hashimoto, S., Takanashi, H., Nakamura, K.
(2012). Fundamentals of Control Engineering
Available to Industry, CORONA. Tokyo Japan, 1
st
edition.
Xing, D., Su, J., Liu, Y. and Zhong, J. (2011). Robust
approach for humanoid joint control based on a
disturbance observer. Journal of Control Theory &
Applications, IET, 22 Sep., vol.5, no.14, pp.1630-1636.
DynamicCharacteristicsControlof2-DOFManipulatorwithArtificialMusclesandDifferentialGearusingDisturbance
Observer
129
