
InCC: Hiding Information by Mimicking Traffic In Network Flows
Luis Campo Giralte, Cristina Conde, Isaac Martin de Diego and Enrique Cabello
Universidad Rey Juan Carlos, Madrid, Spain
Keywords:
Storage Covert Channel, Network Flow, P2P Applications.
Abstract:
This article proposes and implements a light-weight covert channel called InCC, which is designed to produce
a undetectable communication channel between systems. This channel, fully transparent to any network anal-
ysis, is able to send messages on the same production network without compromising its existence. By using
techniques like encryption, address spoofing, signatures and traffic analysis, the channel is able to hide the
flows on the network without compromising the source and destination.
1 INTRODUCTION
Traditionally, network covert channels were classi-
fied into storage and timing channels despite the fact
that there is no fundamental distinction between them
(5200.28-STD, 1985). The storage channels involve
the direct/indirect writing of object values by the
sender and the direct/indirect reading of the object
values by the receiver. On the other hand, timing
channels involve the sender signaling information by
modulating the use of resources over time so that
the receiver can observe and decode the information
properly.
One of the main drawbacks of existing network
covert channels is that they only send small amounts
of information, since otherwise the connection could
be detected. When using timing channels, the amount
of packets needed to send information is quite high.
Notice that timing channels use variable time in order
to encode the binary information. On the other hand,
network storage channels are capable of sending more
information in comparison with timing channels, but
by using DPI (Deep packet inspection) technique ren-
ders most of them detectable.
In this article we propose a storage network
covert channel called InCC (Invisible Covert Chan-
nel) which is capable of hiding the communication
between two peers without compromising their exis-
tence. One of the main differences of the proposed
system as compared with the existing ones is that
InCC learns from the network and generates traffic
that mimics the existing one on the network. This
feature makes InCC a perfect network covert channel,
capable of going undetected by any DPI technique.
The proposed system has been tested using some
open-source traffic engines and to test the effective-
ness of the covert channel, we have implemented a
prototype on Python that enables secure communica-
tion between transparent network systems. The main
idea of the proposal is to camouflage the flows on the
network traffic in order to remain unnoticed for any
type of network analysis. So even if the flows are
detected by a network analysis, the traffic generated
by the channel cannot be identified. InCC learns the
traffic most commonly used by the network, being ca-
pable of hiding the new flows generated in this traffic
in order to communicate systems.
The organization of this paper is as follows. The
related work is discussed in Section 2. The discussion
of the methods proposed, together with the descrip-
tion, is presented in Section 3. The implementation
details are presented in Section 4. The experiments
carried out can be found in Section 5 and, finally, a
conclusion is reached in Section 6.
2 RELATED WORK
The most common techniques for hiding information
on network flows are network covert channels (Lla-
mas et al., 2005; Zander et al., 2007b; Sellke et al.,
2009; Nussbaum et al., 2009; Rios et al., 2012),
which focus on hiding data in various network proto-
cols like IPv4, TCP, DNS, HTTPS, etc. Applications
like Skype use covert channels (Freire et al., 2009) on
HTTP traffic in order to hide their communications,
and many others use these techniques in order to com-
ply with ISP network restrictions. The most relevant
5
Campo Giralte L., Conde C., Martin De Diego I. and Cabello E..
InCC: Hiding Information by Mimicking Traffic In Network Flows.
DOI: 10.5220/0004436600050014
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT-2013), pages 5-14
ISBN: 978-989-8565-73-0
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

works are shown next, with the most interesting tech-
niques by the different authors classified in Table 1.
(Dittmann et al., 2005) examine the existing VoIP
applications with respect to their extensibility to
steganographic algorithms. They have also paid at-
tention to the part of steganalysis in PCM audio data
that allows us to detect hidden communications while
running VoIP communication with the usage of the
PCM codec. They show the results for their PCM ste-
ganalyzer framework that is able to detect this kind of
hidden communication by using a set of 13 first and
second order statistics.
(Liu et al., 2009) use covert timing channels by
encoding the modulated message in the inter-packet
delay of the underlying overt communication chan-
nel such that the statistical properties of regular traf-
fic can be closely approximated. The system was de-
signed for UDP traffic by hiding the covert traffic on
networks with on-line gaming traffic.
Most timing channels are based on the use of a
time variable in order to encode the information. This
increases the number of packets sent on the network
-an evidence of the channel’s existence, which is the
largest disadvantage of timing channels (Zhang et al.,
2011). In addition, jitter and delays are of no avail on
these channels.
Storage channels are becoming of increasing in-
terest for the research community. This is due to the
arrival of new techniques that allow the hiding of in-
formation, such as stenography. The most interesting
research will now be evaluated and later classified.
(Zander et al., 2007a) compare the different en-
coding techniques and also propose two new im-
proved encoding schemes based on the IP TTL
field. They group the existing techniques for encod-
ing covert information into the TTL field into three
classes: (a) Direct encoding encodes covert bits di-
rectly into bits of the TTL field, (b) Mapped encoding
encodes covert bits by mapping bit values to specific
TTL values and (c) Differential encoding encodes
covert bits as change between subsequent TTL val-
ues. The weakness of this model is the high amount
of packets that have to be sent to the destination, since
the limitation of the TTL field is 8 bits.
(Nussbaum et al., 2009) propose a system called
TUNS which is an IP over DNS tunnel. Their system
only uses the CNAME record of the DNS header. It
encodes the IP packets using a Base32 encoding with-
out splitting the IP packets into several smaller DNS
packets. The main problem of this model resides in
the fact that, by using a good DNS analyzer most of
the bogus packets could be detected due to modify the
use of the DNS CNAME record.
(Luo et al., 2009) propose a system called
CLACK, which encodes covert messages into the
TCP acknowledgements (ACKs). Their system is
based on a persistent flow of TCP data. They find
two objectives: to provide a reliable covert channel,
similar to the reliable data service provided by TCP,
and increase the cost of detecting the covert channels.
Their weakest point is that they assume that all trans-
missions are perfect, i.e. lossless, packet order pre-
served and no duplicate packets, and this is not very
common on the Internet network.
(Wendzel and Zander, 2012) shows a method for
detect switching covert channels (PSSCCs). PPC-
SSs transfer hidden information by sending networks
packets with different selected network protocols
such as HTTP, POP3, etc. Protocols are therefore
linked to secret values, e.g., a HTTP packet could rep-
resent the value ’1’ and a SMTP packet could repre-
sent the value ’0’. The weakness of this model relay
on the high amount of packets that the sender needs
to sent in order to encode the information.
(Mazurczyk and Szczypiorski, 2009) present
steganographic methods that utilize mechanisms for
handling over-sized IP packets: IP fragmentation,
PMTUD (Path MTU Discovery) and PLPMTUD
(Packetization Layer Path MTU Discovery). They
modify the offset value of the fragmented packets to
add the information payload and also modify certain
IP flags. However, the detection of these methods are
trivial due to the short number of IP fragmented pack-
ets on the networks.
(Lucena et al., 2004) describe an approach to
application-layer protocol steganography, showing
how they can embed messages into commonly used
TCP/IP protocols such as SSH and HTTP. They also
introduce the notion of semantics preservation, which
ensures that messages still conform to the host proto-
col, even after embedding. Strong semantics preser-
vation ensures that the meaning of the message is
unchanged, while weak semantics preservation only
guarantees the less stringent condition that the mes-
sage be semantically valid. Their main shortcoming
is that their model only works in specific protocols
such as HTTP.
(Fu et al., 2002) present a flow-based architecture
for network traffic camouflaging. They hide both the
message traffic pattern and the fact that camouflaging
itself is taking place, while at the same time guaran-
teeing the QoS requirement of the message flow. The
idea is to embed the packets of the message flow into
the packets of another flow, denoted as carrier flow,
which in turn may be generated by a well-known net-
work service. The system’s main drawback is that it
replaces the carrier payload, making changes in the
payload vulnerable to detection simply by checking
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
6

the same packet in different paths.
(Burnett et al., 2010) present a system called
Collage, which allows users to exchange messages
through hidden channels in sites that host user-
generated content, such as photo-sharing sites. To
send a message, the user embeds it into covert traf-
fic and posts the content onto some site, where re-
ceivers retrieve the content using a sequence of tasks.
Their evaluation shows that performance overhead is
acceptable when sending small messages such as web
articles, emails and so on. The system’s weakest point
is that the communication cannot be interactive due to
its architecture.
(Rios et al., 2012) examine the Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for search new forms
of covert communications. They shows that is pos-
sible to create covert channels on specific fields (xid,
Sname, File and Option) of the DHCP messages. The
problem of the solution proposed lies in the DHCP
scope and also the fields are easily detectable using a
dedicated analyzer.
Below, Table 1 offers a classification of the re-
viewed papers under the following labels: Cryptog-
raphy, if the system uses some type of cryptography
functions for hiding the information; Modify L7, if
the system modifies application layers such as HTTP,
DNS, etc.; Modify IP, if the technique involves the
modification of some IP fields for hiding informa-
tion; Modify TCP/UDP, if it includes the modification
of TCP/UDP fields for enclosing the covert message;
Timing, if it uses timing techniques to hide messages
on the flow; and finally, Network, if the system reacts
in a different way to network traffic.
Notice that most covert channel classifications are
based on storage or timing channels, as shown in Ta-
ble 1. Most of the studies are actually related to stor-
age channels, since the amount of information in stor-
age channels is larger than in timing channels. One of
the weaknesses of timing channels is that they need
a high amount of packets to send information to the
destination. According to the Table, InCC could be
classified as a storage channel, dynamically adapted
to network traffic.
3 INVISIBLE COVERT CHANNEL
The purpose of this section is to introduce the chan-
nel, first by describing the system (detailed further be-
low in subsection 3.1), then by reviewing the different
parts and techniques involved (subsections 3.2, 3.3,
3.4 and 3.5).
InCC offers a solution for communicating two
systems by using storage covert channels. This
is achieved by combining several hiding techniques
which allow the systems to share information without
compromising source and destination.
3.1 System Description
InCC supports the following specifications in order
to avoid being detected: a) The channel uses a port-
walking technique (inspired by the port-knocking
(Miklosovic, 2011; Degraaf et al., 2005; Tariq et al.,
2008) technique), which consists in emulating P2P
traffic management of ports in order to disturb any
traffic analysis. P2P applications generate a huge
amount of disturbing traffic to random ports previ-
ously negotiated by the applications. b) Encryption
of the main payload packet by using RC4 (Rcf4557,
2006), with the introduction of some variations such
as key rotation. RC4 is chosen due to the simplicity
of the code and the negligible CPU overload. c) The
channel uses IP spoofed addresses for both source and
destination. Consequently, only source and destina-
tion will know the spoofed IP addresses. And finally,
d) it uses signatures from other systems, such as Snort
(Snort, 2013) or OpenDPI (OpenDPI, 2013). The
channel is capable of inserting the signatures on the
generated flows in order to camouflage the flows with
those existing on the network.
Figure 1 illustrates how the channel operates. No-
tice that the sender and the receiver may belong to
either the same or to different networks, being A and
B users who are sharing files via P2P, as detailed in
Figure 7. Both sender and receiver are authenticated
by RSA (Rfc2246, 1999) or port-knocking (Mikloso-
vic, 2011; Degraaf et al., 2005; Tariq et al., 2008)
mechanisms at the initialization state. In our design,
InCC uses standard RSA authentication, but notice
that the authentication phase is out of scope of the
paper. As seen in Figure 1, once the authentication
state has passed the sender and the receiver could re-
ceive messages on ports X and Y. Elements A and B
are P2P users sharing a file. The different states in the
channel may be summarized as:
1. The source detects a P2P session between A and
B, the detection being made by signatures.
2. The sender sends out a message to the receiver
including the following information: a P2P iden-
tifier which identifies the signature detected at the
P2P session; A’s IP address (src
ip) and source
port (src
port); B’s IP address (dst ip) and desti-
nation port (dst port); and optionally, an acknowl-
edgement flag. All the messages have been previ-
ously encrypted by RC4.
3. Once the message has been decoded and the fields
InCC:HidingInformationbyMimickingTrafficInNetworkFlows
7
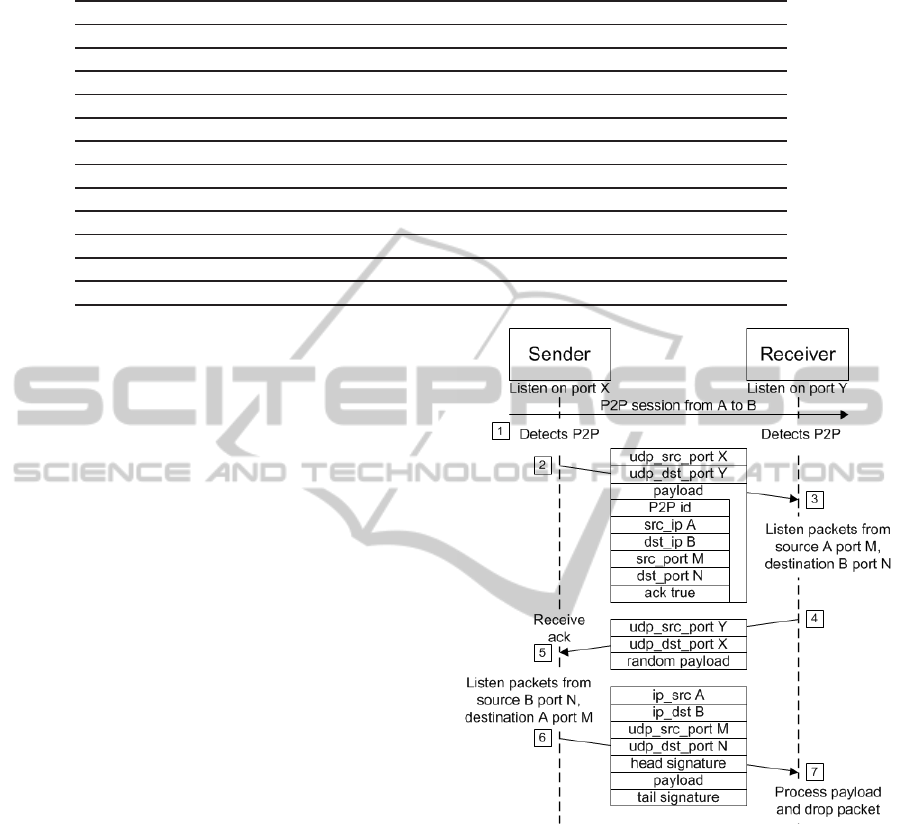
Table 1: Network covert channels techniques.
Author Cryptography Modify L7 Modify IP Modify TCP/UDP Timing Network
(Zander et al., 2007a) * *
(Luo et al., 2009) * *
(Wendzel and Zander, 2012) * *
(Lucena et al., 2004) * *
(Burnett et al., 2010) * *
(Fu et al., 2002) * * *
(Rios et al., 2012) *
(Dittmann et al., 2005) * *
(Mazurczyk and Szczypiorski, 2009) *
(Nussbaum et al., 2009) * *
(Liu et al., 2009) *
InCC * * * *
processed by the receiver, the receiver’s behavior
changes.
4. The receiver sends out an acknowledgement mes-
sage to the sender because the ACK flag had been
previously activated. The payload of the message
is made up of random bytes whose only purpose
is to disturb the flow’s analysis.
5. The sender gets the acknowledgement and under-
stands that new messages should use A and B’s IP
addresses and ports, as well as the signature de-
tected in the previous message.
6. The sender sends out a datagram with the P2P sig-
nature detected and all the payload encrypted by
RC4. Notice that the IP addresses and the ports
used are A and B’s.
7. The receiver intercepts the message, decodes it
and processes its fields, then sends it one layer
up enclosing an incident report. Note that the re-
ceiver drops the packet in order to avoid ICMP
unreachable port packets that could be suspicious.
After describing the channel, we proceed to the
different techniques involved in the system. This has
the following options: ’Port walking’, so the flow can
change from different ports; ’Payload noise’, which
adds trash noise to the payload; ’IP randomness’,
which enables the use of spoofed addresses in order
to communicate source with destination; and finally,
’Signature poisoning’, which inserts known traffic
signatures into the generated payload. These options
will be discussed next.
3.2 Port Walking
Port knocking (Miklosovic, 2011; Degraaf et al.,
2005; Tariq et al., 2008) is a technique whereby au-
thentication information is transmitted across closed
network ports. A machine using port knocking closes
Figure 1: InCC description.
all network ports to all hosts but logs incoming pack-
ets. A program watches the firewall logs for certain
sequences of packets, which encode authentication in-
formation and make a request for opening or closing
ports. Based on this information, the port knocking
system can choose to open network ports to the origi-
nating host. In essence, port knocking enables or dis-
ables services which are invisible most of the time,
and which appear on the network by a combination of
special IP packets. So secure systems could enable or
disable their reporting mechanism by using this type
of technique.
By using the same principle as port knocking, we
have created port walking (refer to Figure 2). This is a
technique which consists in generating several flows
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
8

Figure 2: InCC port walking.
between the source and the destination machines,
much in the same way as P2P applications. P2P ap-
plications generate a lot of flows in order to send and
receive information over the distributed network. By
using this idea, the InCC behaves like P2P applica-
tions, which use random ports in order to avoid fil-
tering and shaping. Thus, for every object sent to the
destination a new port parameter is added to the pay-
load. If the object size is too large, then InCC splits
it into several packets (only when this option is en-
abled at the initialization state or when AB identifies
P2P traffic). This feature is recommended when Bit-
Torrent (BitTorrent, 2013), Gnutella, Skype, or simi-
lar applications which use random ports for signaling,
file-transfer, etc. are detected.
As shown in Figure 2, to synchronize the destina-
tion and the source ports of both sender and receiver,
InCC sends out the following ports (src
port for the
sender and dst
port for the receiver), either randomly
or by using the distribution ports previously detected
in a P2P session.
The tcpdump output below shows a port Walk-
ing technique without acknowledgement, where
192.168.1.1 represents the sender, 192.168.1.2 the re-
ceiver, and 2000 the initialization port.
IP 192.168.1.1.
47578
> 192.168.1.2.
2000
: len 123
IP 192.168.1.1.
35690
> 192.168.1.2.
7030
: len 157
By contrast, a tcpdump output of a port Walking tech-
nique with acknowledgement is shown next. Notice
that the acknowledgement uses the same port. Ports
2000 and 7949 in the output are used to verify the ac-
knowledgement.
IP 192.168.1.1.
47578
> 192.168.1.2.
2000
: len 123
IP 192.168.1.2.
2000
> 192.168.1.1.
33225
: len 53
IP 192.168.1.1.
36347
> 192.168.1.2.
7949
: len 163
IP 192.168.1.2.
7949
> 192.168.1.1.
36347
: len 23
It is possible to use full random ports to make the flow
analysis more difficult, allowing the receiver to send
Table 2: BitTorrent port usage.
Application Flows Ports
BitComet 10890 8617
BitLord 890 587
Vuze 1704 1528
Azuerus 2512 2257
uTorrent 1865 1668
BitTorrent 1819 1112
the acknowledgements from different ports as shown
in the output below.
IP 192.168.1.1.
47578
> 192.168.1.2.
2000
: len 123
IP 192.168.1.2.
1280
> 192.168.1.1.
33225
: len 53
IP 192.168.1.1.
36347
> 192.168.1.2.
7949
: len 163
IP 192.168.1.2.
98634
> 192.168.1.1.
36347
: len 23
In order to check the viability of this technique, we
evaluate the most use BitTorrent clients for study how
many ports this type of applications uses. As shown
on table 2, during 4 minutes we capture traffic and
study how many ports and flows this applications
uses. Taking into account this information we can ar-
gue that on average this applications uses 2628 dif-
ferent ports on a single session. So by having this
technique implemented on our proposal we will dis-
turb network analysis due to the difficulty of analyze
these flows.
3.3 Payload Noise
The algorithm RC4 has vulnerability problems
(Klein, 2008; Mantin, 2005; Paul and Preneel, 2004),
with frequency analysis-based attacks. However, by
using techniques such as key rotation these vulnera-
bilities could be partially solved. The behavior of the
mentioned techniques can be observed in Figures 3,
4 and 5. These figures represent the dispersion of the
packet payload frequency generated by InCC without
any signature. The byte is represented on the x-axis,
whereas on the y-axis we find the number of occur-
rences of the x byte. As shown in Figure 3, when
we encrypt 10.000 objects by using the same key, the
byte frequency distribution of RC4 is poor and a fre-
quency attack could be launched. However, when the
channel uses a random key, as shown in Figure 4, the
resiliency is better than in the previous case.
Notice that the dispersion of the frequency data
in Figures 4 and 5 are similar, whereas in terms of
compression they are different due to the trash noise
added to the payload.
We propose to add noise to the payloads, what we
call ’payload noise’. This consists in adding the key
value pair of random bytes to some parts of the object,
in our case a dictionary, as shown in Figure 6. By us-
ing this technique we get the same frequencydistribu-
tion (see Figure 5) as the one in Figure 4, which uses
InCC:HidingInformationbyMimickingTrafficInNetworkFlows
9
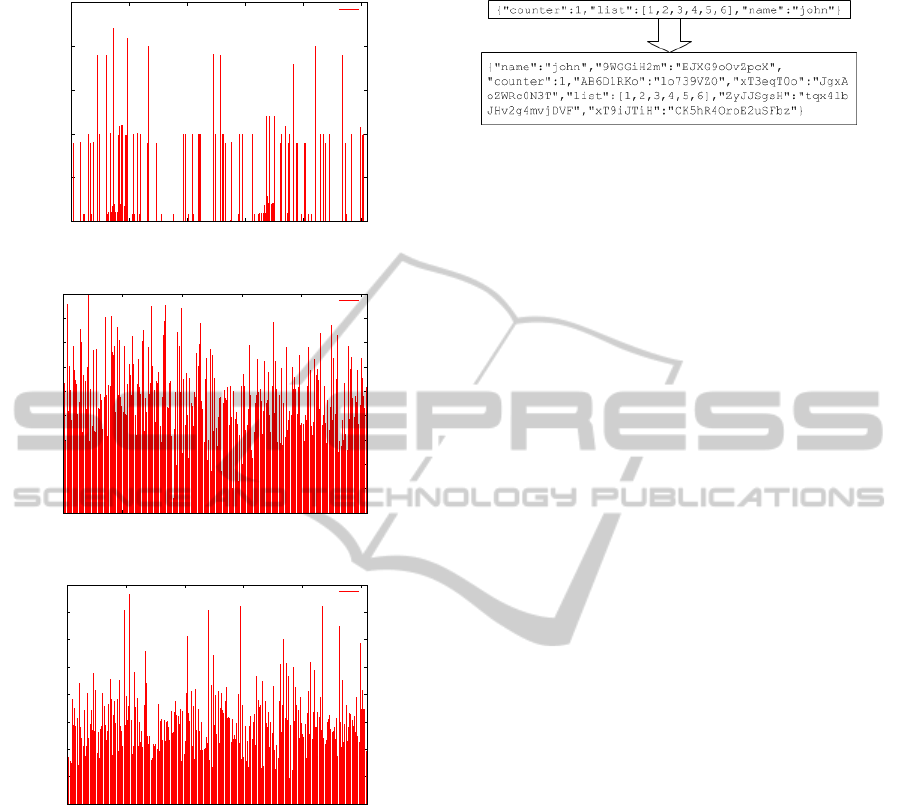
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
25000
0 50 100 150 200 250
Count
Byte
Frequencies
Figure 3: 10.000 objects with RC4.
260
280
300
320
340
360
380
400
420
440
0 50 100 150 200 250
Count
Byte
Frequencies
Figure 4: 10.000 objects with RC4 and random key.
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
0 50 100 150 200 250
Count
Byte
Frequencies
Figure 5: 10.000 objects with RC4 and noise payload.
random key. On the other hand, this technique fixes
the payload to a specific size in order to generate pay-
load sizes which already exist on the network. For ex-
ample, if the AB process detects BitTorrent with size
packets of 300 bytes, then the packet generated with
this technique will generate packets of 300 bytes in
order to camouflage them with the current bit-torrrent
traffic detected by the AB process.
The process of adding noise to the payload is
achieved by using dictionaries and JSON (JavaScript
Object Notation), as shown in Figure 6. The addi-
tion of random key value pairs in this figure gives us
a fuzzy frequency value and increases the object size.
However, this technique only gives us extra bytes to
cope with specific payload sizes, and does not give us
an encryption method like RC4.
Figure 6: Noise payload serialization.
3.4 IP Randomness
One of the interesting things about InCC is that the IP
addresses of the generated datagrams do not belong to
any of the systems trying to communicate with each
other (see figure 7). This is achieved by learning the
most used IP addresses on the network, or by config-
uring the IP address with spoofed addresses from the
source and destination networks.
This technique consists of the following points:
• When Sender and Receiver are in the process of
learning from the networks, all the IP addresses
identified by the signatures are stored on a tem-
porary memory (called temporary IP address).
These IP addresses are temporary because they
depend on the flow duration and on the type of
user. For example, if a user spends 20 minutes
downloading a large file from a torrent client, the
temporary IP of this user will have a duration of
20 minutes due to the flows generated by the tor-
rent application.
• If node Sender wants to send messages to node
Receiver the channel has two options: first, using
the temporary addresses, or second, using random
addresses. Random addresses are IP addresses
generated by changing the last digit of the source
network’s IP address.
Thus, if an advance administrator manages a transit
network, our flows will be completely hidden to any
analysis the attacker could conduct because the IP ad-
dresses are spoofed or even used by other systems
such as web-servers, email-servers, etc.
The use of temporary IP addresses by the chan-
nel has the advantage of learning from active IP
addresses, for instance the address of a P2P user
from another network. For our purposes, we use C
class addressing, so for a 192.168.0.0 network the
random address would range from 192.168.0.1 to
192.168.0.254.
In Figure 7, the Sender node represent the system
which wants to share information, the R routers are
transient routers, and A and B are two users sharing
a file with a P2P application. When the Sender and
Receiver detects P2P activity they stores the source
and destination addresses (A,B), as seen in point t1
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
10
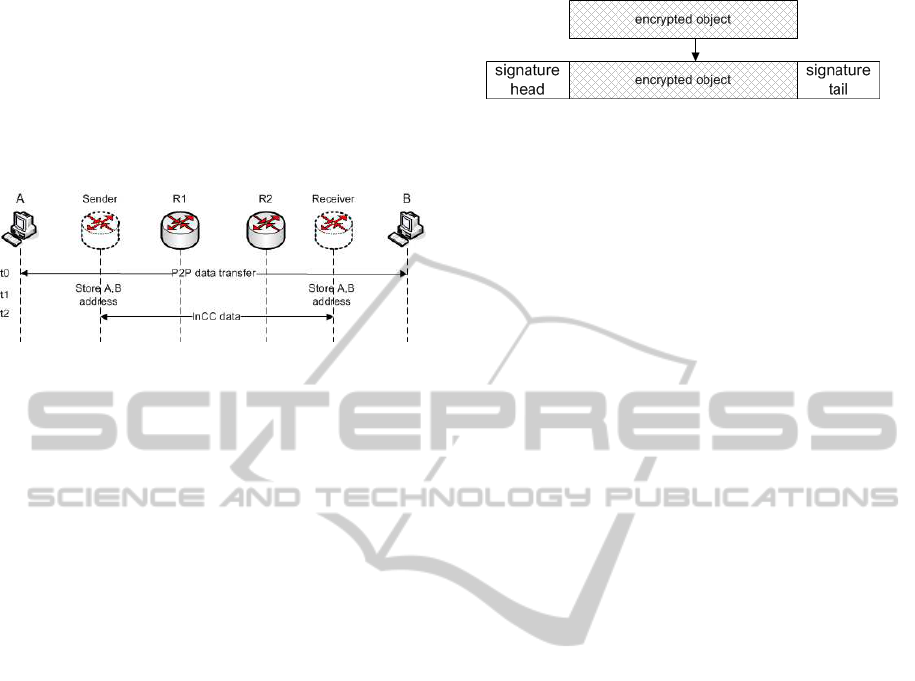
of the figure. Then, when the Sender needs to trans-
fer information to the Receiver, it sends IP traffic with
B’s destination address and A’s source address, as ob-
served in point t2. Notice that the Receiver will never
forward the traffic to B, since this flow is generated in
a non-natural way and will always be destroyed after
being processed by destination (see point 7 in subsec-
tion 3.1).
Figure 7: IP usage mechanism.
One of the strengths of the temporary addresses is
that the datagrams generated by InCC can be camou-
flaged with the source traffic detected by A and B.
This gives more robustness to the channel with re-
spect to the random addresses, which do not depend
on the network IP addresses. On the contrary, random
addresses using spoofed addresses could be more sus-
picious because the IP addresses generated would be
unique in the network and an advance attacker could
notice the lack of response of the IP address, for ex-
ample by using port scanning techniques. One of the
main drawbacks of this technique is that Sender and
Receiver should be on the same network path than A
and B, in order to spoof properly the IP addresses.
However, this could be solved having installing Bit-
Torrent clients on the network path.
3.5 Signature Poisoning
NIDS and tools like tcpdump (Tcpdump, 2013) can
be used by network administrators in order to inspect
the traffic. Normaly commercial systems and open
source solutions use network signatures in order to
identify the network flows. So by using signatures
from different tools (Hippie, 2013; OpenDPI, 2013;
Snort, 2013), the channel hides the flows with the
network’s current traffic. The channel is only imple-
mented on UDP for the proof of concept, so our flows
are capable of hiding with DNS, BitTorrent, Gnutella
or any other application that uses UDP and may have
a signature for identifying the flow.
Figure 8 shows how the signatures provided by
third parties are added to the encrypted payload. No-
tice that some signatures have head and tail, depend-
ing on the signatures provided.
The following tcpdump output shows an InCC
message. This packet contains the initial payload
Figure 8: Signature Poisoning.
bytes 0x474e and 0x4403, which correspond to a sig-
nature for the Gnutella protocol. The rest of the
packet is encrypted by RC4.
IP 192.168.1.1.55728 > 192.168.1.2.4399: UDP
0x0000: 4500 00ce 2e5b 4000 4011 8870 c0a8 0101
0x0010: c0a8 0102 d9b0 112f 00ba 2044
474e 4403
0x0020: 578e df02 9088 bd1b e3db d268 5bf4 4ffc
0x0030: d626 4e10 9440 c93e c1a1 6249 ce2d 92df
4 PROTOTYPE
IMPLEMENTATION
The channel consists of a light-weight multi-platform
library with two differentiated processes, called Ap-
plication behavior (AB) and Obfuscator (OB). As
shown in Figure 9, process AB is in charge of ana-
lyzing the network traffic by using signatures. These
signatures are provided by external subsystems like
Snort, or even OpenDPI, and loaded on a database.
AB identifies some of the flows with the traffic sig-
natures provided, learning from the identified flows
the packet size distribution. AB then informs OB that
the protocol identified at the previous stage is the best
suited for usage, and, by implementing the techniques
described in the previous subsections, OB sends the
message from the external subsystem to the destina-
tion.
Figure 10 shows the OB process flow with InCC.
This process generates the final payload of the packet
using the different options attached to the payload.
These options are: First, noise is added to the pay-
load (described in section 3.3); second, a random port
is added in order to change ports for the next packets
(explained in section 3.2); third, a new key is added to
give more robustness to the RC4 algorithm if needed
(described in section 3.3); four, a behavior identifier
is forwarded to the destination; five, a full encryption
of the current payload takes place; and finally, a sig-
nature of the traffic identified is added to the network
(for further details see section 3.5).
Taking into account these options, the flows gen-
erated will be camouflaged on the network. This al-
lows the external systems to share information with-
out compromising their existence on the network. Our
method does not modify the packets, as happens with
Xinwen et al. (Fu et al., 2002), and does not de-
pend on specific protocols as Lucena et al. explain
InCC:HidingInformationbyMimickingTrafficInNetworkFlows
11
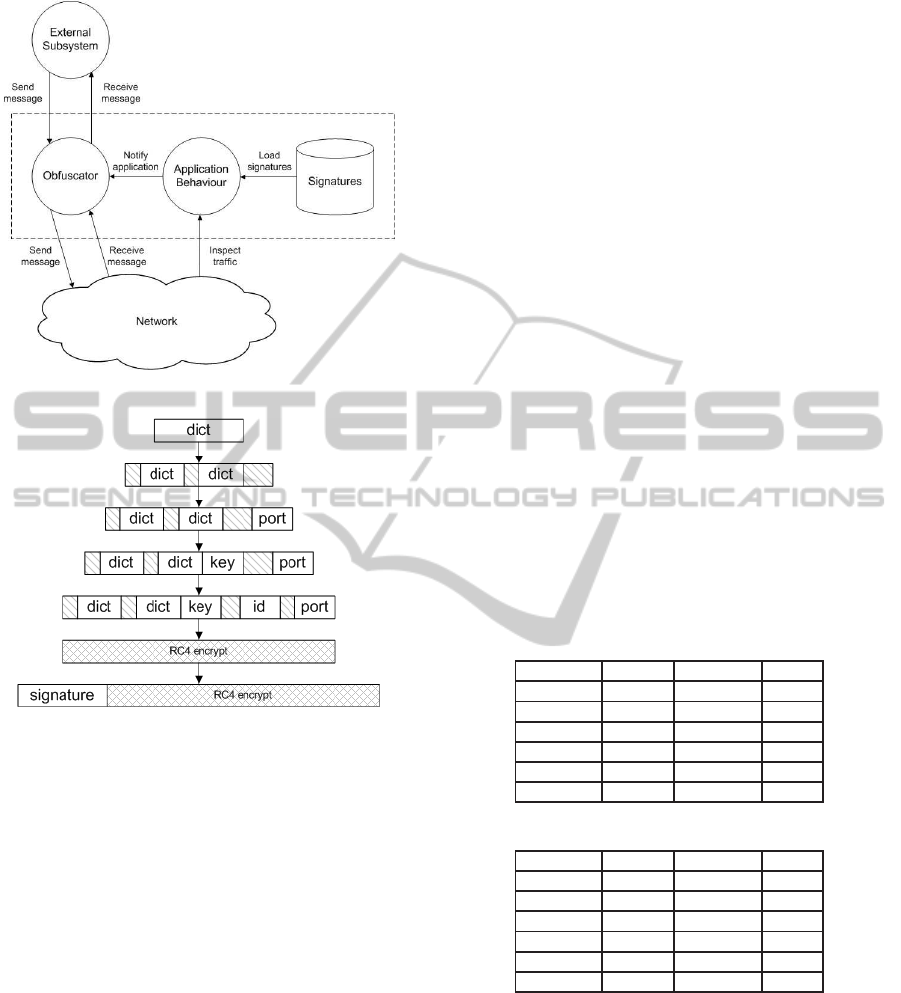
Figure 9: InCC Process.
Figure 10: InCC Obfuscator Process Flow.
in their model (Lucena et al., 2004). On the contrary,
our channel depends on traffic signatures, where the
amount of available signatures from different open-
source projects (Snort, 2013; OpenDPI, 2013; Hippie,
2013) is high.
5 EXPERIMENTS
The tests were carried out by two PC Linux with ker-
nels 2.6.38, one of them having a CPU Intel core duo
3.16GHz, and the other with a CPU Intel core duo
2GHz. First we generated Gnutella traffic with an
application on one of the PCs. We chose the signa-
tures from Gnutella because generating real traffic is
achievedjust by downloading theapplication and cap-
turing the traffic on a pcap file. Secondly, we gener-
ated one flow between the two PCs (with the char-
acteristics described in previous sections) by using
InCC and by setting up the behaviorto Gnutella. Then
the traffic generated was captured on a pcap file.
All capabilities were implemented in our configu-
ration, developing a complete test of all the modules
presented. This is because the costs of having a real
environment are much higher due to the expenditure
in routers, web-servers, links, etc. But as shown in
Figure 7, which is just a small part of the previous
figure, we can emulate this environment with only a
single network LAN and two PCs as a proof of con-
cept.
Thirdly, we merge the traffic generated by
Gnutella with the one generated by the channel. By
using tools like Snort (Snort, 2013) and OpenDPI
(OpenDPI, 2013), we analyze network traffic and we
inject the merged traces, resulting in the fake flows
being completely hidden from the rest of the traffic.
Also, the flows will be identified with the provided
signature as shown in the following tables.
Tables 3 and 4 represent the detection rates ob-
tained by OpenDPI in order to check InCC’s viability.
Table 2 shows OpenDPI detecting a Gnutella session,
including byte distribution, and number of flows and
packets. On the other hand, Table 3 shows how the
new flow generated by InCC is detected by OpenDPI
as Gnutella. Notice that the flow generated by InCC
contains 51 packets, 13.827 bytes and a packet av-
erage size of 271 bytes, an amount which is large
enough for reporting network incidents.
Table 3: Gnutella traffic.
Protocol Packets Bytes Flows
Unknown 61215 19031577 17
Dns 10 960 3
Http 115 44107 11
Netbios 53 7679 3
Gnutella 102656 30658221 270
Icmp 563 52454 21
Table 4: Gnutella traffic and InCC.
Protocol Packets Bytes Flows
Unknown 61215 19031577 17
Dns 10 960 3
Http 115 44107 11
Netbios 53 7679 3
Gnutella 102707 30672048 271
Icmp 563 52454 21
To test the performance of the channel, partic-
ularly the library’s CPU overload (see Figure 11),
10.000 objects were generated using the different op-
tions described in subsections 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, and 3.5.
The results shed light on the consumption, negligible
for all the options supported by InCC.
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
12
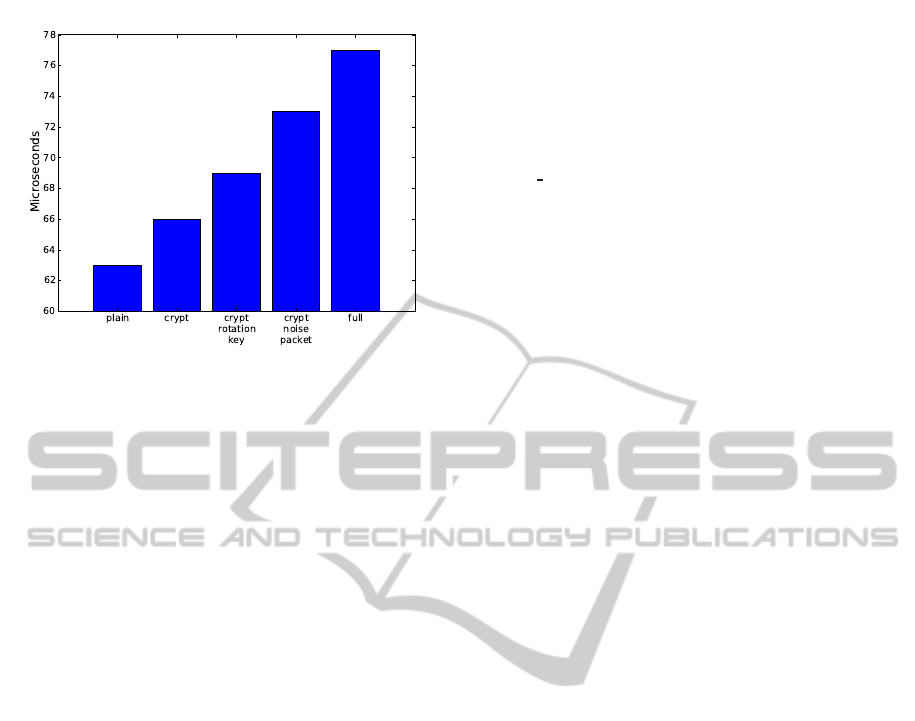
Figure 11: InCC option costs.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This article presents a light-weight library for covert
channels, capable of communicating with other sys-
tems from different networks. By using the options
described in the previous sections the channel is ca-
pable of sending information to other systems without
compromising their existence. The channel is modu-
lar and any of the options can be configured indepen-
dently. The source code is under the terms of the GPL
and is available on https://github.com/camp0/incc.
We propose a new technique which evades detec-
tion by camouflaging the flows with the existing ones
on the network. InCC was designed for UDP traffic in
order to check the viability of its implementation and
test its functionality. However, it would be possible to
extend it to TCP flows in order to camouflage the gen-
erated flows with the ones detected on the network.
Many P2P applications send packet garbage in or-
der to disrupt the traffic analysis of the ISP networks.
One possible extension to InCC is the production of
fake datagrams to disturb all sorts of analysis during
the transmission of InCC flows. When there is not
enough traffic for InCC to identify, the administrators
could install P2P applications in order to help camou-
flage the InCC flows, thus making the channel more
resilient and robust.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially funded by Vulcano
project (ref 442808215-8215-4-9) funded by Spanish
ministry of Science and Innovation.
REFERENCES
5200.28-STD, D. (1985). Trusted Computer System Evalu-
ation Criteria. Dod Computer Security Center.
BitTorrent (2013). The bittorrent protocol specifi-
cation, version 11031. http://bittorrent.org/beps/
bep
0003.html.
Burnett, S., Feamster, N., and Vempala, S. (2010). Chip-
ping away at censorship firewalls with user-generated
content. In Proceedings of the 19th USENIX confer-
ence on Security, USENIX Security’10, pages 29–29,
Berkeley, CA, USA. USENIX Association.
Degraaf, R., Aycock, J., and Jacobson, M. (2005). Improved
port knocking with strong authentication. In In Proc.
21st Annual Computer Security Applications Confer-
ence (ACSAC 2005, pages 409–418. Springer.
Dittmann, J., Hesse, D., and Hillert, R. (2005). Steganog-
raphy and steganalysis in voice-over ip scenarios: op-
erational aspects and first experiences with a new ste-
ganalysis tool set. In Delp, E. J. and Wong, P. W.,
editors, Security, Steganography, and Watermarking
of Multimedia Contents, volume 5681 of Proceedings
of SPIE, pages 607–618. SPIE.
Freire, E. P., Ziviani, A., and Salles, R. M. (2009). On met-
rics to distinguish skype flows from http traffic. J.
Network Syst. Manage., 17(1-2):53–72.
Fu, X., Guan, Y., Graham, B., Bettati, R., and Zhao, W.
(2002). Using parasite flows to camouflage flow traf-
fic. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE Workshop on
Information Assurance.
Hippie (2013). Hi-performance protocol identification en-
gine. http://sourceforge.net/projects/hippie/.
Klein, A. (2008). Attacks on the rc4 stream cipher. Des.
Codes Cryptography, 48(3):269–286.
Liu, Y., Ghosal, D., Armknecht, F., Sadeghi, A.-R., Schulz,
S., and Katzenbeisser, S. (2009). Hide and seek in
time - robust covert timing channels. In Backes,
M. and Ning, P., editors, ESORICS, volume 5789 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 120–135.
Springer.
Llamas, D., Miller, A., and Allison, C. (2005). An eval-
uation framework for the analysis of covert channels
in the tcp/ip protocol suite. In ECIW, pages 205–214.
Academic Conferences Limited, Reading, UK.
Lucena, N. B., Pease, J., Yadollahpour, P., and Chapin, S. J.
(2004). Syntax and semantics-preserving application-
layer protocol steganography. In Proceedings of the
6th Information Hiding Workshop, pages 164–169.
Luo, X., Chan, E. W. W., and Chang, R. K. C. (2009).
Clack: A network covert channel based on partial ac-
knowledgment encoding. In ICC, pages 1–5. IEEE.
Mantin, I. (2005). Predicting and distinguishing attacks on
rc4 keystream generator. In EUROCRYPT,pages 491–
506.
Mazurczyk, W. and Szczypiorski, K. (2009). Steganog-
raphy in handling oversized ip packets. CoRR,
abs/0907.0313.
Miklosovic, S. (2011). Pa018 - term project - port knocking
enhancements. http://www.portknocking.org/view/
resources.
InCC:HidingInformationbyMimickingTrafficInNetworkFlows
13

Nussbaum, L., Neyron, P., and Richard, O. (2009). On ro-
bust covert channels inside dns. In Gritzalis, D. and
Lopez, J., editors, SEC, volume 297 of IFIP, pages
51–62. Springer.
OpenDPI (2013). Opendpi. http://www.opendpi.org/
opendpi.org/index.html.
Paul, S. and Preneel, B. (2004). A new weakness in the rc4
keystream generator and an approach to improve the
security of the cipher. pages 245–259.
Rcf4557 (2006). The rc4-hmac kerberos en-
cryption types used by microsoft windows.
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4757.txt.
Rfc2246 (1999). The tls protocol. http://www.ietf.org/rfc/
rfc2246.txt.
Rios, R., Onieva, J. A., and Lopez, J. (2012). Hide
dhcp:
Covert communications through network configura-
tion messages. In Gritzalis, D., Furnell, S., and Theo-
haridou, M., editors, Proceedings of the 27th IFIP
TC 11 International Information Security and Privacy
Conference (SEC 2012), volume 376 of IFIP AICT,
pages 162–173, Heraklion, Crete, Greece. Springer
Boston, Springer Boston.
Sellke, S. H., Wang, C.-C., Bagchi, S., and Shroff, N. B.
(2009). Tcp/ip timing channels: Theory to implemen-
tation. In INFOCOM, pages 2204–2212. IEEE.
Snort (2013). Snort. http://www.snort.org/.
Tariq, M., Baig, M. S., and Saeed, M. T. (2008). Associ-
ating the authentication and connection-establishment
phases in passive authorization techniques.
Tcpdump (2013). Tcpdump. http://www.tcpdump.org/.
Wendzel, S. and Zander, S. (2012). Detecting protocol
switching covert channels. 37th Annual IEEE Con-
ference on Local Computer Networks, 0:280–283.
Zander, S., Armitage, G. J., and Branch, P. (2007a). An
empirical evaluation of ip time to live covert channels.
In ICON, pages 42–47. IEEE.
Zander, S., Armitage, G. J., and Branch, P. (2007b). A sur-
vey of covert channels and countermeasures in com-
puter network protocols. IEEE Communications Sur-
veys and Tutorials, 9(1-4):44–57.
Zhang, D., Askarov, A., and Myers, A. C. (2011). Predictive
mitigation of timing channels in interactive systems.
In Proceedings of the 18th ACM conference on Com-
puter and communications security, CCS ’11, pages
563–574, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
14
