
Enterprise Architecture Models
Description of Integrated Components for Validation - A Case Study of Student
Internship Programme
Joe Essien and Samia Oussena
School of Computing and Technology, University of West London, St Mary’s Road, Ealing, London, U.K.
Keywords: Enterprise Architecture, Business Processes, Motivation, Validation, Modeling.
Abstract: Enterprise Architecture (EA) has been defined as the organization of a system embodied in its components,
relationships to each other, environment, the principle guiding its design and evolution (IEEE, 2000). Thus
an important characteristic of EA is to provide a holistic view of the enterprise visualizing the relevant as-
pects of the business for specific stakeholders. However, one of the many concerns of this interest has been
how to deal with the complex challenges of implementing the models with the ability to validate its inte-
grated components to ensure conformity with individual stakeholder’s motivation. To achieve this, method-
ologies that describe components in relation to their behavioral attributes, impact on other elements in the
domain and their dependencies have been postulated. Albeit, studies show that these taxonomies do not ad-
equately address this requirement (Lankhorst, 2013). This article analyzes the EA concepts of ArchiMate,
focusing on the business and application layers with the objective to extend motivation with tests specifica-
tions using the model-driven approach thus offer descriptive semantics for validation. The paper contributes
to a better understanding on how EA models can be validated thus improve alignment with the business vi-
sion and strategy. Student Internship Program case study is used to exemplify this hypothesis.
1 INTRODUCTION
Enterprise Architecture has been defined as consist-
ing of coherent principles, methods, and models
used in the design and realisation of organisational
structure, business processes, information systems
and infrastructure (Fischer et al., 2010). Good enter-
prise architecture provides the insight needed to
balance requirements and facilitates that translation
from corporate strategy to daily operations (Lank-
horst, 2013). Through the alignment of business
functions and IT systems, a form of harmonization
between the current state of a business (as-is) and a
desired state of a business (to-be) is achieved (Ven-
katraman et al., 2010). Venkatraman in their later
review identified eight other perspectives in which
EA alignment can be achieved. In addition to these
eight perspectives, four other fusion perspectives are
described, formed from the combination of two of
the individual perspectives (Coleman and Papp,
2006). In all these efforts and many others with re-
spect to definitions of EA, perspective, harmoniza-
tion and alignments, the issues of validation are
completely ignored or at best remain rudimentary.
The positions do not consider the behavioral attrib-
utes of the model’s components as a process that
should undergo test itself. In many organizations,
EA patterns exist that encapsulate business concerns
such as maintenance, upgrades, procurement, inte-
gration, acquisition and mergers, compliance in a
regulatory environment and strategic planning (Wes-
ton et al., 2004), but literal analysis of these patterns
shows many disparate architectures, understood by
each stakeholder from different perspectives. The
connections and dependencies that exist among
these different views can be extremely complex in
some cases (McGovern, 2004). To tackle these phe-
nomena as a prerequisite to determining attributes
behavior, some authors have proposed a distinction
between aspects of EA visualization. One option is
taking the business strategy of an enterprise as the
starting point, and then deriving its IT infrastructure
either via an IT strategy or through the organization-
al infrastructure (Venkatraman, 2010), also referred
to as (top-down) strategy to execution. Another way
conversely, is focusing on IT as an enabler and start-
ing from the IT strategy to derive the organizational
302
Essien J. and Oussena S..
Enterprise Architecture Models - Description of Integrated Components for Validation - A Case Study of Student Internship Programme.
DOI: 10.5220/0004443103020309
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2013), pages 302-309
ISBN: 978-989-8565-61-7
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

infrastructure via a business strategy or based on the
IT infrastructure, referred to as (bottom-up) execu-
tion to strategy. Though these distinctions appear
rational as a means to an end, most large enterprise
elect that business vision and strategy drives EA and
not the reverse. For this reason, this study is con-
strued on the first option and develops conceptual
frameworks that use common business logic and
models to define annotations of EA components to
facilitate validation. The document describes the
process of designing test specifications for an enter-
prise architecture model, uses the Student Internship
program (SIP) as a case study to show a pragmatic
application of the concept and how the specification
can be extended to the model itself. EA is decom-
posed to extract data specifications for building the
validation scenario, spanning the business and appli-
cation abstractions and aggregates requirements into
autonomous business behavior from the perspective
of stakeholders and goals.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
The multi-dimensional interests and unstructured
principles that tagged EA from inception led to use
of heterogeneous set of approaches and modelling
languages (Sessions, 2007). Most EA practitioners
recognize four facets of EA and agree that it com-
prises of the business, application, information, and
technology perspectives (Salmans, 2010). With the
augmentation and advancement on these various
perspectives, methods, approaches and principles
over a period of four decades, one of the biggest
issues facing enterprise architects today is that none
of these single practices is capable of satisfying all
necessary aspects of the enterprise identified collec-
tively (Noran 2003). Attempts to mix and match
rather, has resulted in EAs with inconsistent seman-
tics and weak ontology. Therefore issues regarding
systematic validation techniques become inconse-
quential as architects do not need to stringently scru-
tinize models to see the huge gaps in the composi-
tion of structural layers, artifacts types and depend-
encies. The implication of this is that, with the intro-
duction of advance modelling techniques to auto-
mate EA practices, need to test and validate those
models suddenly emerge as major challenge. Early
frameworks such as the popular ZF, GEAF, FEAF,
TOGAF, SEAM, and OMG did not create extenda-
ble models that support validation (Fischer, 2010);
(Salmans, 2010); (Urbaczewski, 2006). Consequent-
ly, attempts to introduce them at a later stage
through improved versions and sometimes outright
extension such as TOGAF with ArchiMate leave
inconsistencies, omissions and gaps between the
various layers of abstraction. Despite this, it is
agreed that no Enterprise Architecture framework
can completely view the enterprise in its entirety as
comprising of business objectives, business process-
es, roles, organizational structures, organizational
behaviors, information, software applications, com-
puter systems and the relationships between these
various entities (Chen, 2008). Though efforts still
continue to be made towards standardization
(TOGAF, 2012); (OMG, 2012), many frameworks
are specific in scope and purpose and apply to spe-
cific domains, generally weighted towards planning
and business process analysis without commensurate
emphasis on validation and change management.
3 VIEWS AND VISUALIZATION
To achieve quality in enterprise architecture, there is
need to bring together information from unrelated
domains and adopt an approach that is understood
by every stakeholder (Weston, 2004). A Stakeholder
can be an individual, team or external entity that has
interests relative to the system. It is argued that since
stakeholders are influenced by their particular con-
cerns (TOGAF, 2012); stakeholders require specific
views of architecture that focus on their concerns
exclusively. In this context, a view is specified by
means of a viewpoint and describes how particular
concerns of the stakeholders are constructed in rela-
tion with other elements in the EA. It has been con-
tested that stakeholders alone would not provide
substance to a view. Clark et al suggested that mod-
els need to be goal focused and elements of EA
should be goal-driven motivated by constraints and
drivers (Clark, 2011). But goals without substantia-
tion can be abstruse. Several authors in their publica-
tions have defined goals in EA as Business-IT
alignment, Governance, Standardization, Cost reduc-
tion, Consolidation, Agility, Risk management,
Regulatory compliance, business continuity
(McGovern, 2004); (Salmans, 2010); (Sessions,
2007). Goals in this study are intrinsic, can be de-
composed and refer to added value and objectives of
the stakeholder. We adopt an analogous approach
that the stakeholder’s concerns are assessed to derive
goals and that requirements can satisfy goals.
Goals are used with viewpoints to specify busi-
ness behavior and to derive the artifact for extrapola-
tion required for the design of the validation scena-
rio.
EnterpriseArchitectureModels-DescriptionofIntegratedComponentsforValidation-ACaseStudyofStudentInternship
Programme
303

Figure 1: Relationship of stakeholder and goal.
4 MODELLING LANGUAGES
AND VALIDATION
Modelling Language ML is a high level abstraction
language, aimed at representing structures, charac-
teristics and properties at early stage of design
(Chen, 2008). Over the decade, there has been pro-
liferation of ML as means of presenting visual imag-
es of design concepts. The Unified Modeling Lan-
guage (UML), one of such adopted by Object Man-
agement Group (OMG) is a standardized, general-
purpose modeling language in the field of software
engineering and includes a set of graphic notation
techniques to create visual models of object-oriented
software-intensive systems (OMG, 2013). Though it
combines techniques from data modeling (entity
relationship diagrams), business modeling (work
flows) and object modeling, it lacks the versatility
that can visualize the entire enterprise as defined by
IEEE, Lankhorst, DODAF. UML is focused on defi-
nition of system structure and behavior and has no
built-in testing constructs (Baker et al, 2004). The
UML Test profile currently proposed is at a much
lower level of abstract based on Testing and Test
Control Notation Version 3 (TTCN3) and JUNIT
than required in business behavior validation at EA
higher abstraction.
The Zachman framework (ZF) as an EA ap-
proach is a normalized six by six classification
schema for organizing descriptive representations of
an enterprise (Bahill, 2006). The rows represent
distinct stakeholder perspectives of an enterprise,
while the columns describe different areas of interest
within those perspectives. The Zachman framework
is simply a framework rather than a process, a meth-
od, a notation or a tool. Consequently the framework
is rigid as rows and columns cannot be added or
omitted to allow validation or testing. The Zachman
framework is useful more in an enterprise as a gen-
eral assessment tool for organizing a complete and
holistic set of existing architecture descriptions and
artifact sets; and to identify gaps in information and
focus development efforts to fill the gaps. In ZF,
there is no correct modelling tool for any particular
cell. Any modelling tool may be used to depict the
structural components of the cell e.g., UML dia-
grams, analytic equations, functional flow block
diagrams, block diagrams of linear systems theory,
transfer functions, state-space models, differential
equations, object-oriented models, etc (Bahill,
2006). Each entity in the cell may use any represen-
tation for functions, processes, events, objects, data
and interfaces. This makes it very difficult for com-
ponents within ZF cells to share homogeneous anno-
tations, semantics and relationship thus application
of a standardized validation method on its frame-
work is impracticable.
The Extended Enterprise modelling Language
(EEML) was developed as a comprehensive and
generic framework for evaluating models, called
SEQUAL (Krogstie, 2008). SEmiotic QUALity
(SEQUAL) framework is systems modelling top-
down reference model for evaluating the quality of
models. It distinguishes between goals and means by
separating the expected result from procedures
needed to achievement it, through a process based
on linguistic and semiotic on real world view with
participation of the stakeholders. The core of the
framework include the discussion on syntax, seman-
tics, and pragmatics parallel to the use of terms in
the semiotic (Krogstie, 2008).
Though EEML SEQUAL has few desirables, the
associated limitations are enormous as it is com-
pletely domain specific. The representation of busi-
ness rules is dependent on prevalent use and imple-
mentation. Maintenance and knowledge enhance-
ment is key requirement to its usability. EEML is
under further developed in the EU projects Unified
Enterprise ML (UEML) to validate and disseminate
a set of core language for its support as a basis for
interoperability within a smart organization (OMG,
2013).
Another popular means of validating the EA is
the use of maturity matrix commonly referred to as
Dynamic Architecture Maturity Matrix (DYA
AMM). DYA AMM is used as an instrument to
assess the level of Enterprise Architecture Maturity
(EAM) in organizations and often has many (up to
20) key areas that represent a different dimension
within EAM. The DYA AMM assessment method
makes it possible to assess organizations on an over-
all maturity level as well as a specific level. The
information for assessments is gathered through a
survey questions that relate to one of the identified
key areas (Coleman, 2006). However, this method
which is purely qualitative has limitations as lack of
a comprehensive approach to data gathering can
affect judgement. The researcher's presence during
data gathering, which is often unavoidable, can af-
fect the subjects' responses. Issues of ethics, ano-
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
304

nymity and confidentiality can present problems
when presenting findings. Among other concerns,
the questionnaires are sometimes not well under-
stood by the respondents and the CIO bias undoubt-
edly may influence the outcome.
The Open Group Architecture Framework
(TOGAF) is one of the most popular frameworks in
EA. To provide a uniform representation for dia-
grams that describe enterprise architectures, the
ArchiMate EAML is developed to support TOGAF
ADM and to offer an integrated architectural ap-
proach that describes and visualizes the different
architecture domains, their underlying relations and
dependencies. However, assessment methodology is
not integrated with ArchiMate Core or its extension.
Maturity assessment discussed earlier is also de-
ployed in TOGAF ArchiMate to identify the level of
compliance between business vision and business
capabilities. Our rationale for adopting TOGAF and
ArchiMate is on this basis to fill the gap; coupled
with the fact that ArchiMate actually sets the plat-
form for achieving this by offering formal descrip-
tions of components that support reasoning about the
structural and behavioral properties of the organiza-
tion. It provides graphical language for the represen-
tation of EA models and enables the introduction of
annotations and semantics for validation.
5 MOTIVATION DRIVEN
VALIDATION APPROACH
The Motivation Driven Validation Approach
(MDVA) validates scenarios of an instance model
from a logical model incrementally, across the dif-
ferent views and layers of EA by testing component
attributes against goals in the motivation Extension.
This method though deploys the same principles of
Behavior Driven Development (BDD), differs as it
focuses on behavioral specification of the EA arti-
facts rather than objectives. Three steps are iterated;
Specification of model validation rules;
Validation of the rule on the model instance;
Validation of result with motivational goal;
Validation of artifact is based on the desired behav-
ior with attributes set for the related motivational
goal. The MDVA uses structure and behavioral pat-
terns to ensure traceability thus ensuring that the
right design decisions are taken at the modeling
stages. Not only does the MDVA improve the quali-
ty and design of the framework, it also simplifies the
modeling process. The validation scenarios for
MDVA describe the behavior and attributes of the
component to be validated in order to realize set
motivation goal. MDVA ensures better conformance
to user goals and provides the means for model
traceability required for artifact validation. As ac-
cepted by many authors, motivational conceptions
can be used to model the basis that inspires the de-
sign or change of enterprise architecture (Ur-
baczewski, 2006).
6 MDVA METHODOLOGY
The MDVA consist of both the behavioral and the
structural attributes of the EA components. Physical
models of business behavior are created as deriva-
tive instances with different stakeholder perspectives
for validation. Unlike BDD, test basis created are
not based on the business behavior itself but on the
attributes of the artifacts that constitute the model
instance at a high level of abstraction.
6.1 MDVA Design
The MDVA is conceptualized from the ArchiMate
Motivation Extension by deploying motivational
element across the business and application layers.
The methodology iterates correlations of motiva-
tional elements over the taxonomy to establish ex-
tent and coverage of the business behavior defined.
Through the process, gaps and overlapping function-
alities are identified allowing the model to be vali-
dated.
Figure 2: Abstract Syntax of the MDVA schema.
Figure 2 shows the MDVA concept proposed in
this paper. By iterative refinement of business be-
havior on the Business Layer, components are ex-
trapolated into views to aggregate viewpoints for a
EnterpriseArchitectureModels-DescriptionofIntegratedComponentsforValidation-ACaseStudyofStudentInternship
Programme
305

particular test requirement. Constraints are then
applied on the components to derive test attributes
for the logical model. These components form the
test basis for the logical model design. The diagram
depicts realization of physical model instances from
the conceptual and logical models. These are valida-
tion from different views with test scenarios speci-
fied from constraints. Goals are part of the motiva-
tion extension of ArchiMate and ensure alignment
and integration with the core EA. Through an itera-
tive process, these models are revalidated through
each test attribute of the artifact, generating tracea-
bility from specific view for each stakeholder.
6.2 The Case Study
The case study, grounded on student internship pro-
gramme (SIP) at an academic institution is used to
illustrate the MDVA. A system is required with the
aim to implement a program that offer student
placement. The objective is to automate the process
of matching students with employers and intern-
ships, allowing students to manage their CV, search
for internship listings, request and apply for intern-
ship and store their feedback once the internship has
taken place. The system allows employers to man-
age internship listings, track progress on internship
listing and provide feedback on student internships
once they have taken place. Administrators create
users, search and match student CV with opportuni-
ties, forward student CV to employers, track student
visits and generate reports on system usage.
For this paper, a motivational model is required
that can validate models created for student’s view-
point.
7 ArchiMate MODELING
The ArchiMate language provides a means to handle
modeling complexities of modern information-
intensive enterprises. For our modelling concepts
ArchiMate enterprise modeling language is used
with the objective to extend the motivation attributes
with tests specifications using the Model Driven
Approach. Figure 3 shows the complete goals and
aggregation refined for all the viewpoints in the SIP
based on the requirements specified in the case
study. Here the views of Student, Employer and
Career Office are integrated to establish congruency
and to ensure that there are no gaps. The student
needs to be able to search for internship program and
provide feedback; the employer needs to be able to
provide the available internship opportunities as well
as feedback; Career Office automates the match
process as well as generates reports. The overall goal
of the enterprise is to be able to guarantee that “Stu-
dent Start Internship”. Constraints are modeled into
the design and Goals are realized through Require-
ments.
Figure 3: Use Case Goals aggregation.
In the following subsections, the preliminary
process for implementation of the MDVA is carried
out. Models from the motivational Requirements
establish constraints and associations with Business
Role, Business Function, Business Process and
Business objects at the Business Layer. For the pur-
pose of this paper, only the student’s abstraction will
be used with associated Goals.
7.1 Constraints
Though some of the constraints can also apply to the
career office as the career office match students with
placement opportunities also, we focus on student’s
view and present constraint associated with students
only to create our validation scenario. Figure 4 illus-
trates the modelling of constraints that affect the
goal “Start Internship” for students.
The Goal “Start Internship” is realized though
five Requirements which also present the validation
conditions. These are Relevance to study (CM1),
Uploaded CV (CM2), Internship Opportunity is
available (CM3), student is currently in a year of
study permitted for the internship (CM4) and pre-
requisite approvals obtained (CM5) Figure 4. These
conditions form the basis for criteria and scenario
descriptions and the tests procedure needed to vali-
date the model.
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
306

Figure 4: Realization of Constraints within Goals.
7.2 Business Role
Business role is used in a structural organizational
sense to relate with Business processes or Business
functions. Business Role is modeled in the Business
Layer though it can be extended with components
from both the Application and Technology layers
and are assigned primarily to one or more business
processes or business functions. The model created
in Figure 5 for the case study illustrates the assign-
ment of Business Function to a Business Role.
While the Business Function assesses Business Ob-
jects, it triggers Events which initiates relevant
Business Processes. Application Service is invoked
through assess relationship in collaboration with
Application Components and Data Objects.
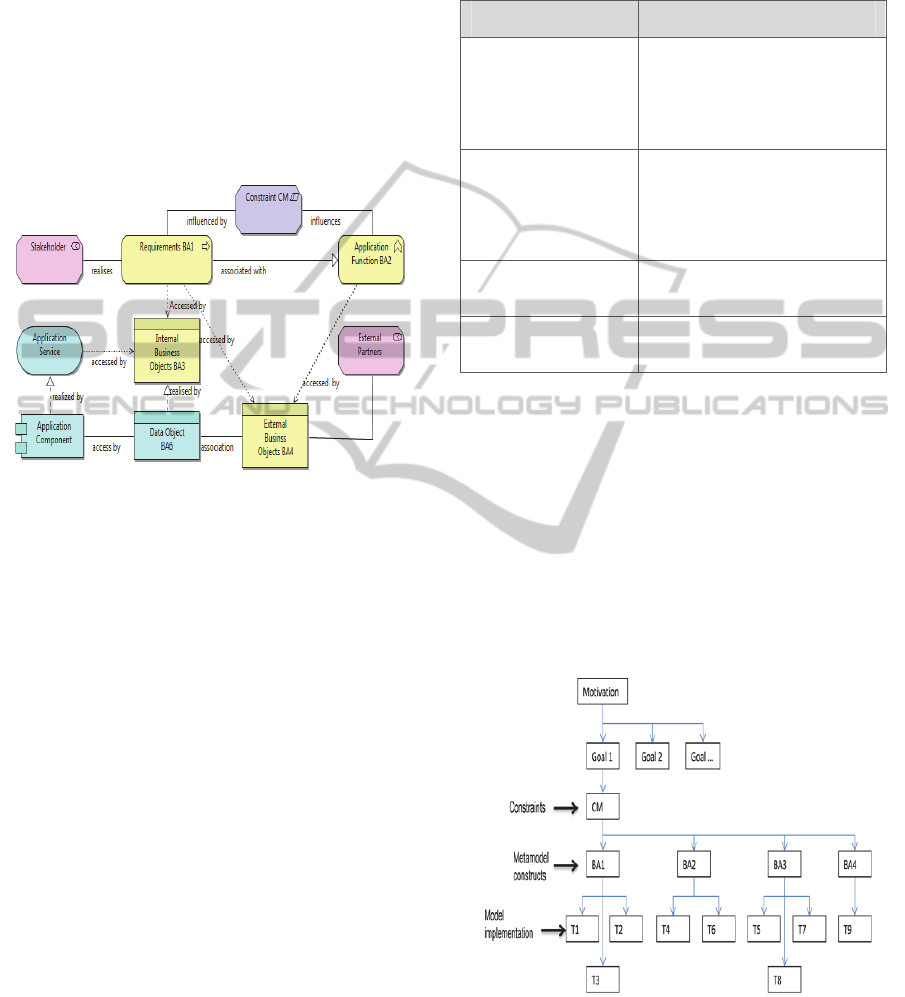
Figure 5: Assignment of Relationships across the Business
Application Layers.
With reference to our case study, the architecture
model can be interpreted from the perspective of the
student as follows; the student as the stakeholder is
assigned the Business Role “Personal Information
Provider” in order to meet the requirement CV up-
load CM2 and realize the Goal “Start Internship
Programme” see Figure 4. The Business Function
“Update Details” is executed using predefined Busi-
ness Object “Data Templates”. On completion of the
task, a Business Event “Update Records” is trig-
gered which initiates Business Processes through the
Application Service to update the Data Objects.
7.3 Business Object
Business objects are manipulated by behavior in this
study. The behaviors under consideration are Busi-
ness Processes, Business Function and Business
Objects. Here Business Process triggers Business
Function while Business Object grants access only
to associated artifacts.
Figure 6: Validation of Business Objects with Business
Processes from Student’s Perspective.
The model in Figure 6 shows an identification of
Business Objects associated with the case study
from the student’s perspective. There is a process
chain for PIT5 exams in T7 to Search for Internship
only after validation through test conditions defined
in the Business Objects T8 and T5. The “Search for
Internship” (T3) triggers “Apply for Internship” (T4)
but both objects collaboratively access “Internship
Listing” T6.
7.4 Business Process
Business Process describes a flow of activities in the
model represented in Figure 5 and 6. The Business
Processes T1, T2 and T3 trigger the Business Func-
tion element T4 (Figure 6) represented as Business
Process in Figure 5 and provides access to the Ap-
plication service. Figure 6 shows aggregation and
composite relationship attributes of the passive
Business Function access relationship with Business
Process. In the case study, the Business Process
represents a workflow consisting of smaller process-
es leading to a Business Function “Apply for Intern-
ship”.
EnterpriseArchitectureModels-DescriptionofIntegratedComponentsforValidation-ACaseStudyofStudentInternship
Programme
307
8 MDVA IMPLEMENTATION
APPROACH
Harnessing the techniques described in previous
sections, MDVA is grounded on the establishment
of concrete test basis, defined at business level sce-
narios and annotated with constraints from the moti-
vation concepts to support comparison between
obtained and expected results. Figure 7 shows the
transformation of Figure 5 relative to Figure 6 to
include constraints defined in Figure 4.
Figure 7: Model transformation of business objective
integrated with motivational constraints.
In implementation of MDVA, we adopt the first
step which is the creation of the conceptual model
from the Goals requirements as a perspective to be
validated, Fig 2 and Fig 7. Then, the next step trans-
forms the conceptual model into a logical model
based on constraint integrated into the taxonomy,
specifying artefacts of the model that are to be test-
ed. During this transformation, the test basis is gen-
erated explicitly including relations mappings with a
traceability of model defined. The third step defines
test scenarios with constraints and creates test condi-
tions for validation of the EA artifacts. This is
shown in Table 1 where in the model in Figure 4,
constraints associated with the Goal “Start Intern-
ship” are extrapolated and cross-referenced with the
business object model in Figure 6 and the architec-
ture model in Figure 7. The constraints CM1, CM2,
CM3, CM4 and CM5 are validated through CM
constraints paths in the model transformation de-
fined in Figure 7 and associated with corresponding
objects in the actual implementation model. The
constraints are applied on the defined artifacts to
identify the existence of the object as well as vali-
date stated conditions. Some of the test conditions
defined in the goal motivation construct are exempli-
fied on the table using business readable domain
specific mnemonics.
Table 1: Application of constraints to model artifacts.
A
rtifact map/
Constraints Description
Low level Definition of Test conditions
for Artifacts Validation
CM1:on
BA1<T1>,BA3<T8 >
Relevance to Study
If Object.T1 = pass PIT5
then result =True
else object.T1 =false endif
if Object.T8->notEmpty()
then result = true
else result =false endif
CM2:on
BA1<T2>,BA3<T5>
CV Uploaded
If Object.T5 ->notEmpty()
then result = true
else result =false endif
if uploadcv().T2=true
then object.T2 ->not empty
result =true endif
CM4: on BA3<T8>
Year of Study
1<year of study<3
CM5: on BA1<T3>
Requisite approvals
CM1+CM2+CM4 = True
At a higher level of abstraction, this can also be
expressed using a BDD notation such as Gherkins
for each of the constraints; For Example,
CM1:BA1<T1>, BA3<T8 >
is validated as;
Given that artifact T1 exist in BA1
And artifact T8 exist in BA3
When Constraint CM1 is parsed in T1
and T8
Then the result shall be True
A simple traceability model to demonstrate this no-
tation usability is shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8: Traceability model for artefact validation.
The MDVA technique addresses the traceability
problem by creating relationships between trans-
formed models and artefacts as part of the conver-
sion process, externalizing the relationships among
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
308

the test-artefact models to allow for comparison with
expected outcome.
9 CONCLUSIONS
MDVA presented in this paper is an approach that
decomposes business processes and develops con-
structs for the models to allow validation. Modelling
motivational goals involve the conceptualization of
different aspects of the enterprise from different
viewpoints and levels of abstraction during the life
cycle of the architecture. This article includes such
conceptualizations derived through modelling and
descriptions of models of the business behavior;
specifying concepts of intentions in terms of goals,
constraints and requirements. The models offer de-
scription of integrated components and illustrate the
relationships between the various artifacts that con-
stitute the taxonomy, relating business vision, mis-
sion and strategy with information systems through
modeling extensions of ArchiMate.
Enterprise Architecture and its management have
continued to be a topic of ongoing and increasing
interest to practitioners. Standardization of concepts
(considering disparities in ZF), methodology (as
consolidated by TOGAF) would facilitate stabiliza-
tion and leverage with new innovations to extend
EA with validation models, notations and semantics.
New technological trends such as cloud computing
and big data pose challenge to EA integration. Crea-
tion of more EA management roles within enterprise
needs to be embraced to allow evolution and provide
more information for further research.
REFERENCES
Baker, P., Dai, Z. R., Grabowski, J., Haugen, O., Lucio,
S., Samuelsson, E., Williams, C. E., 2004. The UML
2.0 testing profile. In Proceedings of the 8th Confer-
ence on Quality Engineering in Software Technology,
Nuremberg (Germany) (pp. 181-189).
Bahill, A. T., Botta, R., & Daniels, J., 2006. The Zachman
framework populated with baseball models. Journal of
EA, 2(4), 50-68.
Chen, D., Doumeingts, G., Vernadat, F., 2008. Architec-
tures for enterprise integration and interoperability:
Past, present and future. Computer and Industrial En-
gineering, 59:647659.
Clark, T., Barn, B. S., Oussena, S., 2011. Leap: a precise
lightweight framework for enterprise architecture. In
Proceedings of the 4th India Software Engineering
Conference (pp. 85-94). ACM.
Coleman, P., Papp, R., 2006. Strategic Alignment: Analy
sis of Perspectives. Proceedings of the 2006 Southern
Association for Information Systems Conference.
Davenport, T., 1993. Process Innovation: Reengineering
work through IT. HBS School Press, Boston.
Fischer, C., winter, R, Aier, S., 2010. What Is an Enter-
prise Architecture Principle? Towards a Consolidated
Definition, Computer and Information Science 2010,
SCI 317, pp. 193–205. springerlink.com Springer-
Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
IEEE Computer Society. IEEE Recommended Practice for
Architectural Description of Software Intensive Sys-
tems. IEEE Standard 1471-2000.
Johannesson, P., Soderstrom, E., 2008. Information Sys-
tems Engineering: From Data Analysis to Process
Networks. Hershey, PA: IGI Publishing. p.58-61.
Krogstie, J., 2008. Using EEML for Combined Goal and
Process Oriented Modeling: A Case Study. Proceed-
ings of EMMSAD 2008.
Lankhorst, M., 2013. Enterprise Architecture at Work:
Modelling, Communication and Analysis. Springer,
Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
McGovern, J., 2004. A practical guide to enterprise archi-
tecture. Prentice Hall Professional.
Noran, O., 2003. An Analysis of the Zachman Framework
for Enterprise Architecture from the GERAM perspec-
tive, Annual Reviews in Control, 27, 163-183
OMG, http://www.omg.org/. Assessed 2013.
Polgreen, J., 2012. Using TOGAF to Develop and Imple-
ment Enterprise Architecture in Government - U.S.
Federal Agencies as Example.
Quartel, D., Engelsman, W., Jonkers, H. 2009. A Goal-
Oriented Requirements Modelling Language for En-
terprise Architecture. Proceedings of the 13th IEEE
International Enterprise Distributed Object Compu-
ting Conference, EDOC 2009, New Zealand.
Salmans, B., Kappelman, L. A.,2010. The State of EA:
Progress, Not Perfection. The SIM guide to enterprise
architecture, 165-187.
Sessions, R., 2007. A Comparison of the Top Four Enter-
prise-Architecture Methodologies, ObjectWatch, Inc.
TOGAF, The Open Group. ArchiMate Version 2.
http://www.opengroup.org/archimate, Oct, 2012.
Urbaczewski, L., & Mrdalj, S. 2006. A comparison of
enterprise architecture frameworks. Issues in Infor-
mation Systems, 7(2), 18-23.
Venkatraman, N., Henderson, J., 2010. Strategic Align-
ment: Leveraging IT for Transforming Organisations,
IBM Systems Journal, Vol 32 No 1.
Weston, J., Defee, J., 2004. Performance Based Enterprise
Architecture Planning – A white Paper, 2004,
http://www.caci.com/.
EnterpriseArchitectureModels-DescriptionofIntegratedComponentsforValidation-ACaseStudyofStudentInternship
Programme
309
