
A New Metric for Multimedia Retrieval in Structured Documents
Sana Fakhfakh, Mohamed Tmar and Walid Mahdi
Laboratory MIRACL, Institute of Computer Science and Multimedia of Sfax, Sfax University, Sfax, Tunisia
Keywords:
Mutlimedia Retrieval, Geometric Distance, Structure, Image.
Abstract:
Most documents available in Textual Database or in Internet are strongly structured. This is the case for
example for scientific papers or written documents using markup languages (HTML, XML). This information
provided by the structure can be exploited by systems of information retrieval to define the granularity of
elements to return in response to a request made by a user or to improve the relevance of these results. In
this article, We are interested in recovering multimedia elements. Like this, we propose a new metric for
multimedia retrieval in XML documents which is based on computing a geometric distance between XML
nodes while taking into account kinship ties and proximities between them. This measure will introduce a new
source of evidence for multimedia retrieval in structural documents which aims at finding relevant multimedia
element that focus on the user information need. Experiments have been undertaken to show the effectiveness
of our method.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today, digital documents have become more and
more complex by integrating heterogeneous textual,
structural, and multimedia metadata. The generic
markup language XML (eXtensible Markup Lan-
guage) has gradually established itself as a support
tool not only for data exchange but also for storage.
Managing XML documents requires the development
of new methods to efficiently analyse such complex
information and so to facilitate personalized access to
XML corpuses (Bray et al., 2003).
In this context, XML retrieval is a straightforward
frameworkthat requires such methods. XML retrieval
consists of retrieving potentially relevant document
fragments for a given information need. These frag-
ments include multiple information types such as tex-
tual or multimedia elements in a structured way.
In this article, we focus on the presentation of a
new metric which is essentially based on structure of
XML document that specifies the relevance of a me-
dia element without recourse to its physical content
(audio, video, and image). Indeed, the structure of
XML document is used to identify and describe the
various components of textual and non-textual. In ad-
dition, the structure describes nature of elements and
relations between them. Therefore, the distance be-
tween a pair of nodes in XML document plays an
important role for determining the relevant elements.
In this context, we took advantage of this hypothesis
to compute a new metric based on the geometric dis-
tance between nodes.
This article is organized as follows: in the second
section, we present an overview of existing work in
the field of multimedia retrieval in XML document. In
the third section, we describe our approach of calcu-
lating distances between nodes in an XML document
that focuses on defining a set of proximity relations
with the geometric distances to best meet user needs
(specificity and completeness). In the fourth section,
we exploit the results of the application of our method
on INEX 2007. The fifth section, we conclude this pa-
per and we discuss our future work.
2 STATE OF THE ART
The advent of structured documents has caused new
problems in information retrieval world, and more
specifically in multimedia elements retrieval. These
problems are strongly related to nature of these doc-
uments that provide the structure as a new source
of evidence. Thus, nowadays, XML documents in-
clude multimedia elements of different types (audio,
video and image)implicitly embedded in the textual
elements. These multimedia elements (such as phys-
ical objects) do not contain enough information to be
able to answer a given query. Therefore, the com-
240
Fakhfakh S., Tmar M. and Mahdi W..
A New Metric for Multimedia Retrieval in Structured Documents.
DOI: 10.5220/0004443302400247
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2013), pages 240-247
ISBN: 978-989-8565-60-0
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

pute of relevance score of multimedia element must
be based on the information made textual and struc-
tural of other nodes XML neighboring (Hliaoutakis
et al., 2006).
Several works with deal XML document as a flat
source of information and ignore the structure of
XML documents. In this context, (Schlieder and Hol-
ger, 2002) say: ”Ignore the document structure is to
ignore its semantics”. Indeed, XML document is used
to describe a set of data by a structure that provides a
semantic lexicon. Thus, it facilitates the presentation
of information in terms of interpretation and exploita-
tion. Replying to this need, new works appear in the
field of multimedia retrieval that takes into account
the structure as source of relevant information.
Existing work in structured retrieval of multime-
dia elements is decomposed in two classes. The
first class includes some works which proceed to
adopt some traditional technical of retrieval informa-
tion as language model. In this context, the team
CWI/UTwente performs a step of filtering results to
keep the fragments containing at least one multime-
dia element (Westerveld et al., 2007)(Tsikrika et al.,
2008).
The second class includes the specific work to be
structured multimedia retrieval. This class uses the
structure as a source of evidence in the process of se-
lection of multimedia elements. As first step, (Kong
and Lalmas, 2005) proposed a method which com-
bines structure of XML document (XPath) with the
use of links (XLink). This method is to divide XML
document into regions. Each region represents an area
of ancestors of the multimedia element. Its score is
calculated in function of the scores of each region.
This method exploits vertical structure only. In a sec-
ond time, (Torjmen et al., 2010) have used the ad-
dition of horizontal structure to the notion of hier-
archy. (Torjmen et al., 2010) use a method called
”CBA” (Children, Brothers, Ancestors), which takes
into consideration the information carried by the chil-
dren , brothers and fathers nodes for calculate the rel-
evance of multimedia elements. The authors propose
an alternative method ”OntologyLike” which is based
on the identification of XML document to ontology.
To calculate the similarity between nodes the authors
use similarity measures (Rada et al., 1989)(Hirst and
St-Onge, 1997)(Wuand Palmer, 1994) that are mainly
based on the number of edges to calculate the distance
between nodes.
There are other approaches to multimedia retrieval
based on exploiting the links in XML document
(Awadi and Torjmen, 2010). This work was improved
by proposing a hybrid approach that combines struc-
ture with using of links that are considered as seman-
tic links (Aouadi et al., 2012). This method above to
divide the document into regions according the hier-
archical structure and the location of image in docu-
ment. This factor plays a role in the weighting of links
for compute the score of image.
In this paper, we propose a new metric for mul-
timedia retrieval in XML documents which involves
the use of geometric distances to calculate the rele-
vance of each node from the multimedia node. This
method consists of placing the nodes of XML doc-
ument in Euclidean space and define each node by
a vector of coordinates to calculate then the distance
between each pair of nodes. This distance will play
a beneficial role to calculate the score of multimedia
element.
3 PROPOSED APPROACH
The structure of XML document, which is composed
by a root, a set of nodes with elements and attributes,
influences the relevance of an XML fragment. The
notion of structure is also to identify and describe the
various components of textual and non-textual, which
is structured document. Relevant elements retrieval
can then be based on these elements rather than the
element itself. In this direction, we focused on prox-
imity, kinship and nesting relations by defining a set
of geometric distances to best represent multimedia
elements according to their vicinity. Determining the
degree of contribution of each text node in the calcula-
tion of relevance of the multimedia element is mainly
carried of depending in distance between the node it-
self and the multimedia element.
In this paper, we present a new source of evidence
”geometric” dedicated to multimedia retrieval which
is based on intuition that each textual node contains
information that describes semantically a multimedia
element. And the participation of each text node in the
score of a multimedia element varies with its position
in there XML document.
For compute the geometric distance, we initially
place the nodes of each XML document in a Eu-
clidean space for calculate the coordinates of each
node by the algorithm 1 defined below. Then, we
compute the score of a multimedia element depend-
ing on the distance between each textual node.
For presentation of structural information, we an-
alyzed the structure of XML documents and its repre-
sentation in the tree form and we choose a new geo-
metric metric for the representation elements of XML
document. Each node must be presented in a Eu-
clidean space and distance will be calculated between
the multimedia element and textual node.
ANewMetricforMultimediaRetrievalinStructuredDocuments
241
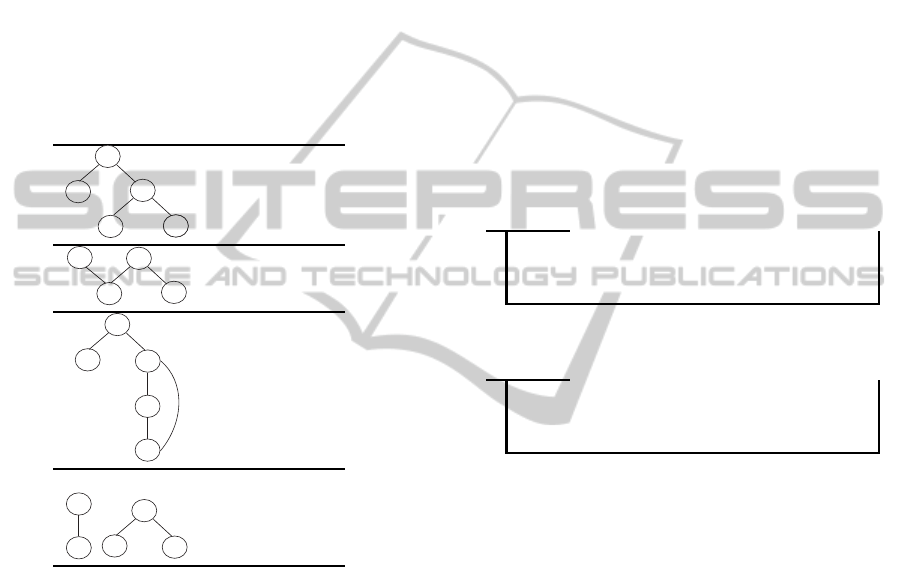
3.1 The properties of an XML Tree
An XML tree is described by a set of relationships
between nodes. Formally an XML tree is a pair A =
(E, R) where E is a set of XML elements and R ⊂ E
2
,
((p, q) ∈ R if p is the parent of q)is a set of relations
satisfying:
∃!r ∈ E, ∀q ∈ E − {r}, (r, q) ∈ R (1)
With r is the root of the tree.
∀p ∈ E − {r}, ∃!q ∈ E, (p, q) ∈ R (2)
Each node has a parent except the root r.
Table 1: Checking properties of an XML tree.
A
B
C
D
E
XML tree
A
B
D
C
Non-XML tree
A
B
C
D
E
Non-XML tree
A
B
D
C
E
Non-XML tree
In Table 1, we present some trees (we see that A
is the root element in the four examples). The first is
an XML tree, but others are not because they do not
satisfy the properties specified by equations 1 and 2.
∀n ∈ N
∗
, we define the function A
n
according
to the hierarchy operated and descendants of the
element explored by:
∀q ∈ E,
A
n
(q) =
{q} if n = 0
A
n−1
(p) if ∃ p ∈ E, (p, q) ∈ R and n > 0
∅ else
The depth of the tree A = (E, R) is defined by:
depth(E, R) = argmax
q∈E,n∈N,A
n
(q)6=∅
n (3)
3.2 Exploitation Relationships of
Proximity and Kinship
The XML tree representation allowed us to unveil
certain relationships of neighboring, brotherhood and
offspring. Indeed, the distance d which separate two
or more brothers with their common ancestors itera-
tively is the same. And brothers of the same hierarchi-
cal level are equidistant. These distances are defined
according to the relationship of contiguity and seman-
tic similarity between nodes. These distances are not
quantized but will be extracted in function of the po-
sition of each textual node in XML tree.
All these properties result in: For all q
i
=
(x
i1
, x
i2
···x
im
) and q
j
= (x
j1
, x
j2
···x
jm
) where Q is
a set of vectors in R
m
.
• In the same hierarchy, if there are more than two
brothers then these adjacent nodes are equidistant:
property 1
∀q
i
, q
j
, q
k
∈ Q, if A
1
(q
i
) = A
1
(q
j
) = A
1
(q
k
)
d(q
i
, q
j
) = d(q
i
, q
k
)
• The distance between any node and its descen-
dants is the same:
property 2
∀q
i
, q
j
, q ∈ Q, n ∈ N, A
n
(q
i
) = A
n
(q
j
) = q
d(q
i
, q) = d(q
j
, q)
Example:
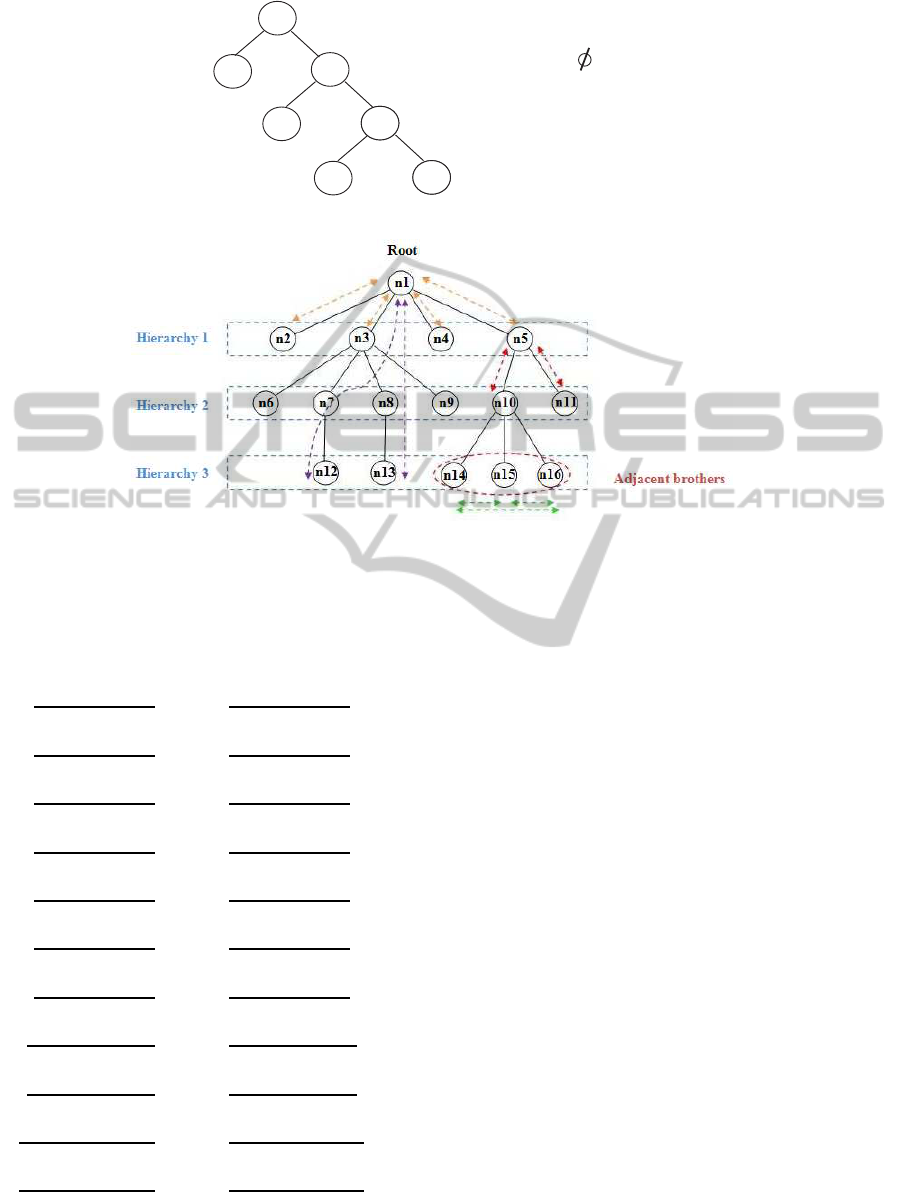
Figure 2 shows the representation of the different
relationships that exist in XML tree. From these rela-
tionships, we can generate system of equations taking
into account for kinship relationships nodes based on
hierarchy and adjacency. These relationships are de-
cried by equalities in this order (these equations are
only examples):
d(n
1
, n
2
) = d(n
1
, n
3
)
d(n
1
, n
2
) = d(n
1
, n
4
)
d(n
1
, n
2
) = d(n
1
, n
5
)
d(n
2
, n
3
) = d(n
2
, n
4
)
d(n
2
, n
3
) = d(n
3
, n
5
)
d(n
2
, n
3
) = d(n
2
, n
5
)
d(n
2
, n
3
) = d(n
4
, n
5
)
d(n
1
, n
14
) = d(n
1
, n
15
)
d(n
1
, n
14
) = d(n
1
, n
16
)
d(n
14
, n
15
) = d(n
14
, n
16
)
d(n
14
, n
15
) = d(n
15
, n
16
)
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
242
A
B
A
C
D
AE
F
AG
A3 ( G ) = A2 ( E ) = A1 ( C ) = A0 ( A ) = { A }
A5 ( E ) = A4 ( C ) = A3 ( A ) =
A2 ( G ) = A1 ( E ) = A0 ( C ) = { C }
Figure 1: Example of the application of the A
n
on an XML tree.
Figure 2: Schematization relations of proximity and kinship between nodes.
We proceeded to make distributions necessary to
group unknown in one side and numbers on the other
side so we try to associate each XML node coordinate
vector and we replaced the distance d a dissimilarity
distance. We obtain a system of equations:
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
1
− n
2
)
2
−
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
1
− n
3
)
2
= 0
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
1
− n
2
)
2
−
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
1
− n
4
)
2
= 0
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
1
− n
2
)
2
−
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
1
− n
5
)
2
= 0
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
2
− n
3
)
2
−
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
2
− n
4
)
2
= 0
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
2
− n
3
)
2
−
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
3
− n
5
)
2
= 0
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
2
− n
3
)
2
−
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
2
− n
5
)
2
= 0
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
2
− n
3
)
2
−
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
4
− n
5
)
2
= 0
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
1
− n
14
)
2
−
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
1
− n
15
)
2
= 0
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
1
− n
14
)
2
−
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
1
− n
16
)
2
= 0
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
14
− n
15
)
2
−
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
14
− n
16
)
2
= 0
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
14
− n
15
)
2
−
p
∑
m
i=1
(n
15
− n
16
)
2
= 0
With m is the dimension of the Euclidean space.
3.3 Properties of Geometric Distances
between XML Elements
Once we havedefined these relations, we obtain a sys-
tem of nonlinear equations. Initially, the objective is
to identify the number of equations is equal to N
1
+N
2
where N
1
(respectively N
2
) is the number of equations
generated by the property 1 (respectively property 2):
N
1
=
∑
p∈Q
|{q∈Q,(p,q)∈R}|≥3
C
|{q∈Q,(p,q)∈R}|
2
− 1 (4)
N
2
=
∑
p∈Q
∑
n∈N
∗
∑
q∈Q, A
n−1
(q)={p}
|{s∈Q,(q,s)∈R}|≥2
(|{s ∈ Q, (q, s) ∈ R}|− 1)
(5)
The resulting system is nonlinear, its resolution
requires the use of an approximate resolution multi-
dimensional method where we used iterative solution
method (see Algorithm 1). The process begins by
assigning to each XML node a random vector coor-
dinates. Trying to improve the coordinate values of
each node according to an error value (the sum of the
squared deviations). At each iteration, the coordinates
are improved together with the minimization of this
error. The algorithm stops when the error reaches its
minimum value (no improvement is possible). Let Q
the set of vectors obtained at a given iteration during
the course of the algorithm, the error is defined by:
ANewMetricforMultimediaRetrievalinStructuredDocuments
243

error(Q) =
∑
q
i
,q
j
,q
k
∈Q,
A
1
(q
i
)=A
1
(q
j
)=A
1
(q
k
)
(d(q
i
, q
j
) − d(q
i
, q
k
))
2
+
∑
q
i
,q
j
,q∈Q,n∈N,
A
n
(q
i
)=A
n
(q
j
)=q
(d(q
i
, q)− d(q
j
, q))
2
Algorithm 1: Resolution algorithm approximate nonlin-
ear system of equations.
Require: (Q = (q
1
, q
2
...q
|Q|
), R) :an XML tree as
q
i
=(q
i1
,q
i2
...q
im
) ∀i ∈ [1, |Q|]
m:dimension
for (i, j) ∈ [1, |Q|]
2
do
q
ij
← random value
end for
Q
1
← (q
1
, q
2
...q
|Q|
)
repeat
P ← Q
1
for (i, j) ∈ [1, |Q|]
2
do
Q
2
← (q
1
, q
2
...q
i−1
, q
i
+ d
j
(1), q
i+1
···q
|Q|
)
Q
3
← (q
1
, q
2
...q
i−1
, q
i
+ d
j
(ε), q
i+1
···q
|Q|
)
Q
4
← (q
1
, q
2
...q
i−1
, q
i
+ d
j
(1− ε), q
i+1
···q
|Q|
)
t ← 0
while error(Q
1
) > error(Q
2
) > error(Q
3
) >
error(Q
4
) do
Q
4
= (q
1
, q
2
...q
i−1
, q
i
+2
t
d
j
(1), q
i+1
···q
|Q|
)
t=t+1
end while
t ← 0
while error(Q
1
) < error(Q
2
) < error(Q
3
) <
error(Q
4
) do
Q
1
= (q
1
, q
2
...q
i−1
, q
i
−2
t
d
j
(1), q
i+1
···q
|Q|
)
t=t+1
end while
while |error(Q
1
) − error(Q
2
)| > ε do
Q
5
←
Q
1
+ Q
2
2
let Q
5
= (p
1
, p
2
...p
|Q|
)
if error(p
1
, p
2
...p
i−1
, p
i
−
d
j
(ε), p
i+1
··· p
|Q|
) >
error(p
1
, p
2
...p
i−1
, p
i
+ d
j
(ε), p
i+1
··· p
|Q|
)
then
Q
1
← Q
5
else
Q
2
← Q
5
end if
end while
end for
until P = Q
1
With ∀v ∈ R, D
j
(v) = (d
1
, d
2
···d
m
) is as:
d
k
= {
0 if k 6= j
v otherwise
3.4 Presentation of the Multimedia
Element
A multimedia element (eg image) does not contain
textual content. His score is based on textual nodes
in its neighborhood (Figure 3). The transition from
the XML tree structure representation of elements in
Euclidean space, where we exploit the dissimilarity
distances separating a multimedia node and other tex-
tual nodes, is performed by extracting the equations
satisfying the properties defined in the section 3.2 and
the application of the algorithm 1 defined in section
3.3(Figure 3 and Figure 4).
A
B
C
D
F
E
H
G
L
K
M
N
J
I
O
P
Q R
S
T
Figure 3: Representation of multimedia element H based on
structural information.
Figure 4: Representation of multimedia element H based on
geometric information.
To calculate the distance between a node n and
multimedia element H, it suffices to calculate the Eu-
clidean distance between their respective feature vec-
tors q
n
and q
H
:
dist(n, H) =
s
m
∑
i=1
(q
n
− q
H
)
2
(6)
With m is the dimension of the Euclidean space. q
n
is defined by: q
n
=(xn
i1
, xn
i2
... xn
im
) with xn are the
coordinates comprising the vector characteristics of
node n. And q
H
is defined by: q
H
=(xH
i1
, xH
i2
...
xH
im
with xH represent the coordinates compose the
vector characteristics of a node H.
For the exploitation of textual information, we
have passed by the steps of removing stopwords
and the radicalization through the Porter algorithm
(Porter, 1980). We calculated the score for each tex-
tual node depending on the frequency of each term
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
244

compose (t f) and the number of elements in the cor-
pus according to the number of elements containing
the term (id f).
A textual node is presented by: n = (n
1
, n
2
···n
|v|
)
where n
i
is the weight of the term t
i
, v is the set of
indexing terms and defined by:
n
i
= t f(t
i
, n) × id f(t
i
) (7)
With
id f(t
i
) = log(
N
N
i
) (8)
Where N is the total number of XML elements in
the corpus, N
i
is the number of elements that contain
the term t
i
and t f(t
i
, n) is the frequency of the term t
i
in n node.
The score of textual node depends on the weight
of each index term. A query is made by the list:
v = (v
1
, v
2
···v
|v|
) where v
i
= {0, 1} according mem-
bership t
i
at the query.
The score of textual node n for the query q is de-
fined by:
rsv(q, n) = q × n
T
=
|V|
∑
i=1
q
i
× n
i
(9)
Where µ is the set of textual elements. The score of
multimedia node H is defined by:
rsv(q, H) =
∑
n∈µ
rsv(q, n)
dist(n, H)
(10)
With dist(n, H) is the distance between the feature
vectors corresponding to the nodes n and H.
This equation leads to assign the importance of co-
operation of all nodes in computing the score of mul-
timedia element that shows its beneficial impact in the
step of retrieving and interrogation.
4 EVALUATION AND RESULTS
For the evaluation we developed a system for index-
ing and retrieving multimedia MXS − index (MIR-
ACL Structural XML Indexing) essentially based on
exploitation of a new measure founded on the geo-
metric structure an XML document as a source of ev-
idence.
MXS− index methodology as schematized in Fig-
ure 5 consists of four main steps: term extraction,
structural metric, node weighing and multimedia el-
ement weighing. The first step is to extract terms
from each node. This step represent a textual index-
ing who use a few NPL (natural processing language)
tools such as: Pruning stop words, radicalization us-
ing the PORTER algorithm ···
The second step consists to extracting the geomet-
ric property from the representation of the structure of
the XML document as tree . The node coordinates are
generated by approximative resolution method.
The third step is a significant and fundamentalstep
in information retrieval process and it is traditionally
determined through term frequency (tf) and inverse
document frequency (IDF). In structured retrieval in-
formation, The score of node is computed as sum of
weight each term in textual element.
The last step consist to compute the rsv of multi-
media element in function of set of the textual nodes
in proximity.
Collection used is extracted from the company
INEX (Initiative for the Evaluation of XML Re-
trieval). INEX 2007 is composed of XML documents
extracted from ”Wikipedia”. This collection consists
of 659,388 heterogeneous documents. The Ad-hoc
XML collection is composed of Wikipedia XML doc-
uments containing multimedia fragments affiliates in
a textual context. (Fuhr et al., 2007) described this
collection and give these statistics described in Table
2.
Table 2: Collection XML Ad Hoc.
Total number of XML documents 659,388
Total number of images 246,730
Average depth of the document structure 6.72
Average number of XML nodes per document 161.35
In this paper, we investigate the use of two types
of queries:
• Queries made by keywords and only ask in return
only images. This task is called ”Content-only” :
CO.
• Queries composed by keywords and structural in-
formation and ask in return fragments multimedia.
This task is called ”Content and structure” : CAS.
Table 3: Results of the impact of geometric metric on the
INEX 2007 based in the MAP(Mean Average Precision).
Content-only Content and structure
MAP 0.2814 0.3102
The evaluation results show that this method pro-
vides a MAP which is equal to 0.2814. This value
increases to 0.3102 by adding another factor in the
evaluation of our method. This factor is the addition
of structural information in the query where perfor-
mance improvement. We also found that the metric
ANewMetricforMultimediaRetrievalinStructuredDocuments
245
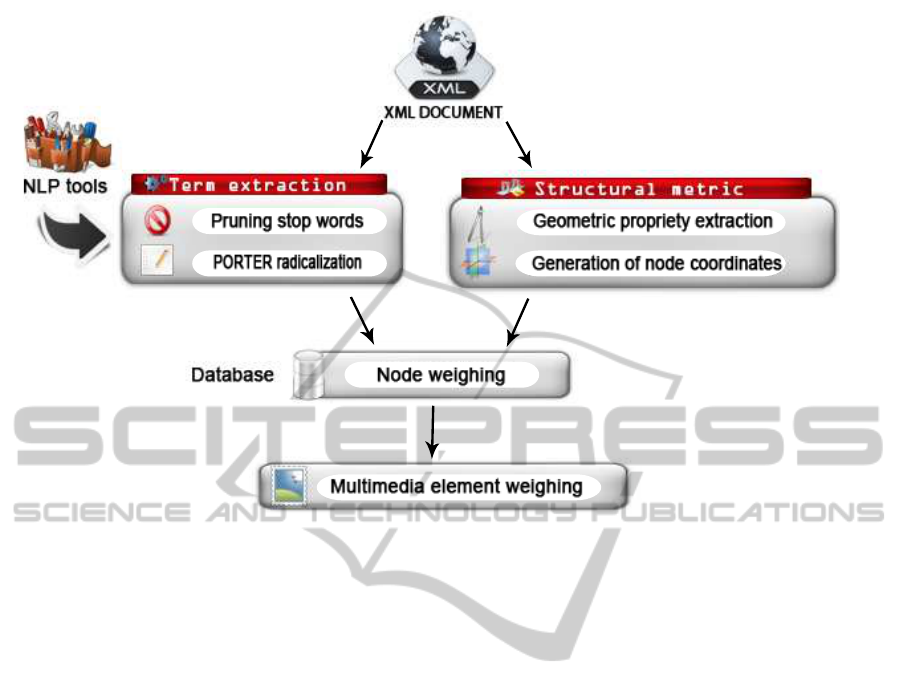
Figure 5: Architecture of our indexing approach MXS− index.
geometry is a relevant factor in retrieving multime-
dia. This factor is used to classify the nodes in order
of relevance to the distance that separates them from
the multimedia(Table 3).
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we are interested in multimedia retrieval
in structured documents (without specific multime-
dia). For this, we proposed a method that supports
the impact of different nodes in an XML document
element defining a new multimedia distance between
nodes. Each node is described by a vector which is
used in definition of a Euclidean space. The score of
a multimedia element is calculated according to the
distance between each node. All these factors should
improve the level of satisfaction in the interrogation
phase. This method combines the textual context im-
plicitly and structural elements an XML document
presented as a to tree.
The use of another source of evidence seems ben-
eficial. Indeed, from the contents of a multimedia el-
ement, we can extract a set of descriptors that pro-
vide visual or other specific information about the
item itself according to its kind (audio, video or im-
age). We have experimentally validated our proposal
on the collection used in the retrieval of structured
documents provided by the company INEX 2007.
REFERENCES
Aouadi, H., Khemakhem, M. T., and Jemaa, M. B. (2012).
Combination of document structure and links for
multimedia object retrieval. J. Information Science,
38(5):442–458.
Awadi, H. and Torjmen, M. (2010). Exploitation des
liens pour la recherche d’images dans des documents
xml. In Proceedings of the 7th French Informa-
tion Retrieval Conference CORIA 2010 - COnf´erence
en Recherche d’Infomations et Applications, Sousse,
Tunisia.
Bray, T., Paoli, J., Sperberg-Mcqueen, C. M., Eve, and
Yergeau, F. (2003). Extensible Markup Language
(XML) 1.0. W3C Recommendation. W3C, fourth edi-
tion.
Fuhr, N., Kamps, J., Lalmas, M., Malik, S., and Trotman,
A. (2007). Overview of the inex 2007 ad hoc track. In
INEX, pages 1–23.
Hirst, G. and St-Onge, D. (1997). Lexical chains as repre-
sentations of context for the detection and correction
of malapropisms.
Hliaoutakis, A., Varelas, G., Voutsakis, E., Petrakis, E.
G. M., and Milios, E. (2006). Information retrieval
by semantic similarity. In Intern. Journal on Semantic
Web and Information Systems (IJSWIS).Special Issue
of Multimedia Semantics, pages 55–73.
Kong, Z. and Lalmas, M. (2005). Xml multimedia retrieval.
In SPIRE, pages 218–223.
Porter, M. (1980). An algorithm for suffix stripping. Pro-
gram, 14(3):130–137.
Rada, R., Mili, H., Bicknell, E., and Blettner, M. (1989).
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
246

Development and application of a metric on semantic
nets. 19:17–30.
Schlieder, T. and Holger, M. (2002). Querying and ranking
xml documents. Journal of the American Society for
Information Science and Technology, 53:489–503.
Torjmen, M., Pinel-Sauvagnat, K., and Boughanem, M.
(2010). Using textual and structural context for
searching multimedia elements. IJBIDM, 5(4):323–
352.
Tsikrika, T., Serdyukov, P., Rode, H., Westerveld, T., Aly,
R., Hiemstra, D., and de, A. P. V. (2008). Structured
document retrieval, multimedia retrieval, and entity
ranking using pf/tijah. In 6th Initiative on the Eval-
uation of XML Retrieval, INEX 2007, volume 4862 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 306–320,
London. Springer Verlag.
Westerveld, T., Rode, H., van, R. O., Hiemstra, D.,
Ramirez, G., Mihajlovic, V., and de, A. V. (2007).
Evaluating structured information retrieval and multi-
media retrieval using pf/tijah. In Fuhr, N., Lalmas, M.,
and Trotman, A., editors, Comparative Evaluation of
XML Information Retrieval Systems, volume 4518 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 104–114,
Berlin, Germany. Springer Verlag.
Wu, Z. and Palmer, M. (1994). Verbs semantics and lexical
selection. In Proceedings of the 32nd annual meeting
on Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL
’94, pages 133–138, Stroudsburg, PA, USA. Associ-
ation for Computational Linguistics.
ANewMetricforMultimediaRetrievalinStructuredDocuments
247
