
Heterogeneous Models Matching for Consistency Management
Mahmoud El Hamlaoui
1,2
, Sophie Ebersold
1
Bernard Coulette
1
, Adil Anwar
3
and Mahmoud Nassar
2
1
University Toulouse 2-Le Mirail, IRIT Laboratory, MACAO Team, Toulouse , France
2
University of Med V Souissi ENSIAS, SIME Laboratory, IMS Team, Rabat, Morocco
3
University of Med V Agdal, EMI, Siweb Laboratory, Rabat, Morocco
Keywords: DSL, Matching, Consistency, Heterogeneity, Correspondence.
Abstract: The overall goal of our approach is to relate models of a given domain. Those models are manipulated by
different actors, and are thus generally heterogeneous, that is, described with different DSLs (Domain Spe-
cific Languages). Instead of building a single global model, we propose to organize the different source
models as a network of models, which provides a global view of the system through a virtual global model.
The matching of these models is done in a unique correspondence model composed of relationships that are
instantiated from a correspondence meta-model. This meta-model is composed of a generic part – common
to all the domains – and of a specific part which depends on the specific domain modelled. In this paper, we
focus on the elaboration of the correspondence model based on a correspondence meta-model, through a
vertical relationship named “refine”. The approach is illustrated on a representative use case (a Bug Track-
ing System).
1 INTRODUCTION
Today, the development of complex systems is
based on a varied set of languages, tools and envi-
ronments that are generally used separately by mod-
elling experts working on different dimensions of a
project. In addition, developers are often located in
distant geographical areas, as is the case in distribut-
ed collaborative development, which complicates
their cooperation.
Among problems that typically arise in this type
of situation, we can mention the fact that different
terminologies and terms can be used to represent the
same concept or that the same term can be used to
express different concepts. More generally, design-
ers of complex systems are facing hard problems
due to heterogeneity and distribution.
This issue has been initially tackled in various
domains, namely: databases (Castano et al., 2001),
semantic web (Fenza et al., 2008), embedded sys-
tems (Eker et al., 2003)… In the avionics domain for
example, it is common to develop various models
corresponding to different points of view on a given
system: mechanical, thermal, electrical, computing,
etc. Thus, the whole system is represented as a set of
separate, heterogeneous models (i.e. derived from
different meta-models, expressed in different DSL
(Domain Specific Language)) which focus on spe-
cific parts of the system.
MDE (Model Driven Engineering) provides
some means of addressing this problematic by con-
sidering models as first class items. This allows
reasoning about those systems and applying auto-
matic transformations to them.
The first solution that comes to mind is to com-
pose those different source models into a global one,
in order to have one single representation, which is
easier to maintain. Our research team has been
working for years on this composition issue as de-
scribed in (Anwar et al., 2010) (Ober et al., 2008)
but so far, we have restricted our work to UML
source models. Globally, composition approaches
proposed in the literature rely on the elaboration of
one global model and have two major drawbacks
related to source models heterogeneity. The first
disadvantage concerns the structure of the meta-
model associated to the composed model; indeed,
there is no consensus on whether it should be con-
structed from the union of all elements coming from
the source models or from their intersection. The
second disadvantage concerns the semantics used to
represent a model element of a composed model
given that the source models may use different se-
mantics.
181
El Hamlaoui M., Ebersold S., Coulette B., Anwar A. and Nassar M..
Heterogeneous Models Matching for Consistency Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0004448401810188
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE-2013), pages 181-188
ISBN: 978-989-8565-62-4
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Instead of building a single global model, we
propose a new approach consisting in organizing the
different source models as a network of models that
provides a global view of the system. This network
is composed of models connected via relationships
called “correspondences”. Producing such a set of
interrelated models allows then to perform MDE
operations on these models (such as composition,
weaving, changes tracking, maintenance, etc.).
The overall goal of our approach is to link heter-
ogeneous models – of a given domain – that are built
by different actors. Matching of these models is
done through the elaboration of a correspondence
model which contains relationships that are instanti-
ated from a correspondence meta-model. This meta-
model is composed of a generic part – common to
all the domains – and of a specific part which de-
pends on the given application.
In this paper, the focus is on the elaboration of
the correspondence model. The remainder of this
paper is structured as follows. Section 2 introduces
the running example that has been chosen to illus-
trate our approach. Section 3 presents our corre-
spondence meta-model and the matching process.
Section 4 discusses in details how correspondences
at the model level can be established through re-
finement of correspondences at the meta-model
level. Section 5 investigates the related works and,
finally, the paper is concluded in Section 6.
2 RUNNING EXAMPLE
To illustrate our approach, we have chosen an ex-
ample − based on a real project − that performs bug
tracking: BTS (Bug Tracking System). This system
aims to offer to different actors, based on their dif-
ferent status (Team leader, developers, testers,…),
the ability to report dysfunctions, comment them,
track the status of an anomaly, notify collaborators
of problems encountered, suggest solutions or possi-
bilities of circumvention. The choice of this example
seems relevant because it involves different actors,
working with different points of view, from the
analysis of users’ requirements to the implementa-
tion of the proposed solution.
We consider that in the domain of bug manage-
ment, there are three business domains covering
various aspects: user requirements management,
anomalies management and business process model-
ling. Each business domain is described in a dedicat-
ed language and manipulated by actors with specific
roles:
The Analyst: Responsible for modelling custo-
mer needs as requirements (business domain: us-
er requirements management). The produced
model is expressed in SysML;
The Software Architect: Responsible for model-
ling anomalies (business domain: software de-
velopment). He creates his model in Mantis;
Process Engineer: Responsible for bugs tracking
process modelling (business domain: process
modelling). He creates his model in BPMN.
2.1 Requirements Model
To assess the quality and validity of any project, you
must ensure that it meets the user’s requirements
that are described in a textual document. We assume
that these requirements are then represented by a
requirement model (Figure 2) conform to the SysML
meta-model (Figure 1). The system to build must be
able to satisfy the requirements described in this
model. For simplicity’s sake, we limit the descrip-
tion of the BTS to a few requirements. For instance,
the requirement “Declaration of an anomaly” in-
cludes a sub-requirement “Summary of an anoma-
ly”, itself refined by additional constraints to be
respected by the “Reporter” during the declaration of
the anomaly.
Figure 1: Extract of the SysML meta-model.
Figure 2: Snapshot of the BTS requirement model.
2.2 Software Development Model
The software development model chosen in our case
is based on the Mantis meta-model (mantisbt, 2010).
Mantis is an open source solution in the bug ma-
ENASE2013-8thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
182
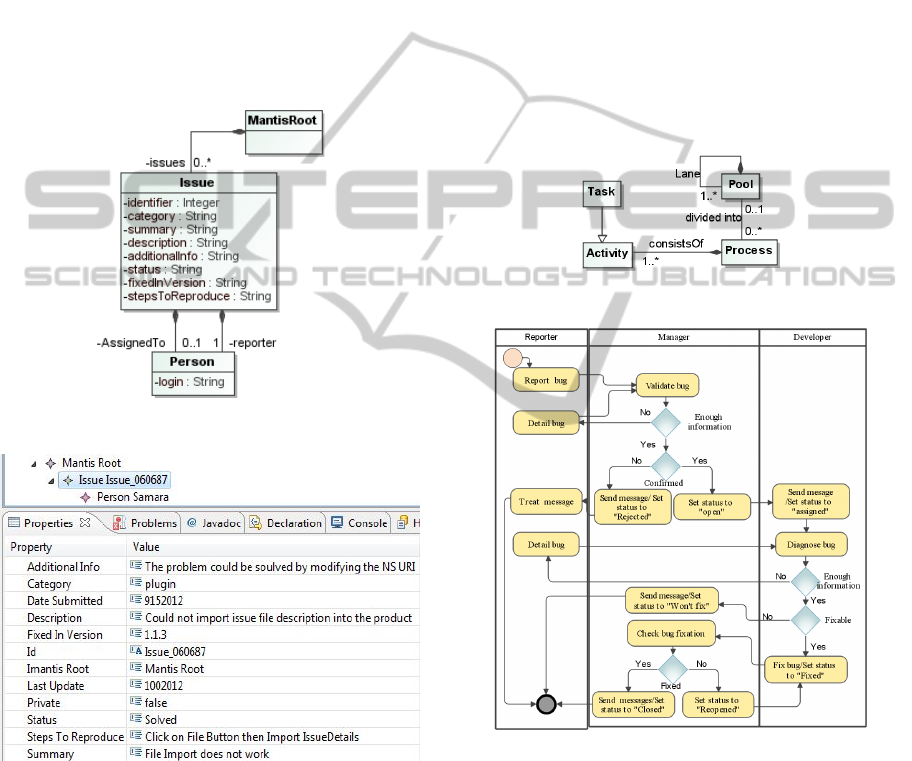
nagement field.
Figure 4 illustrates an example of the mantis
model that conforms to the Mantis meta-model
(Figure 3). The term “Issue” is used to define an
anomaly (bug). An anomaly is characterized by a
unique identifier (“060687” in the example), infor-
mation about the anomaly, namely, a category, a
summary, a description, a status, steps which led to
the anomaly (“stepsToReproduce”) and the two
types of involved people with the “reporter” and
”assignedTo” roles. The first role indicates the per-
son that reports the anomaly, whereas the second
one indicates the person to whom the anomaly is
assigned.
Figure 3: Extract of the Mantis meta-model.
Figure 4: Snapshot of the BTS Mantis model.
2.3 Business Process Model
The treatment of an anomaly can be seen as a busi-
ness process that various collaborators must follow
in order to solve the anomaly. We suppose that the
process engineer used BPMN (BPMN, 2011) for
modelling the business process. A snapshot of the
process expressed in conformity with BPMN meta-
model (Figure 5) is presented in Figure 6. Required
roles in this process model are “manager”, “report-
er” and “developer”. Just after having reported a
bug, the “reporter” must set the status of the anoma-
ly to “new”. An email is automatically sent to the
project manager (PM) who has the “viewer” role as
he is not directly involved in the correction of the
anomaly. Once the PM has validated the issue, he
must assign it to a “developer” and change the status
to “open”. Otherwise, if the anomaly is not validated
by the PM, he must reassign it to the “reporter” to
request additional description. Once the “developer”
has corrected the anomaly, he must inform the PM
and change the status to “Fixed”. The PM, notified
by the change, rechecks the proposed solution and
modifies the anomaly status to “closed”, if it has
been corrected.
Figure 5: Extract of the BPMN meta-model.
Figure 6: Snapshot of the BTS BPMN model.
3 ESTABLISHING
HETEROGENOUS MODEL
CORRESPONDENCES
In this section we present our approach for establish-
ing correspondences between heterogeneous models.
It consists in analysing input models in order to
identify relationships that exist among them and to
HeterogeneousModelsMatchingforConsistencyManagement
183

store them into a model of correspondences. We
discuss below the elaboration of the correspondence
model as well as the proposed matching process.
3.1 Correspondence Meta-Model
To implement our approach we have defined a meta-
model for correspondences called “MMC” (Figure
7). It was designed to meet two main quality criteria:
genericity and extensibility. MMC provides a “ge-
neric” part – common to all domains - that defines a
syntactic description of most common types of cor-
respondences. MMC can be extended depending on
the specificities of the domain under consideration,
in order to support the concepts relating to specific
business areas. It is done through specializations of
the “DomainSpecificCorrespondence” meta-class.
Figure 7: Overview of the MMC correspondence meta-
model (generic part).
MMC includes the following concepts:
LinkModel: Abstract meta-class that represents
all the links established between at least two
models;
CorrespondenceLink: Abstract meta-class that
defines correspondence relationships between el-
ements belonging to different models. Connected
to a meta-class Element by one 1...* relationship,
this meta-class allows, conceptually, defining n-
ary relations connecting more than two items at
once. Defining a correspondence link is done
through specialization of ”CorrespondenceLink”,
by introducing two abstracts meta-classes: “Do-
mainIndpendent-Correspondence” and “Domain-
Specific-Correspondence”;
DomainIndependentCorrespondence: Abstract
meta-class that represents the generic links that
may exist in different domains;
DomainSpecificCorrespondence: Abstract meta-
class representing links between models of the
same domain. New types of correspondences are
specified by specialization of this concept ac-
cording to the studied area;
Similarity: Concrete sub-class of “DomainInde-
pendentCorrespondence” that defines a corre-
spondence relating model elements representing
the same concept without being completely iden-
tical. Such similarity may be syntactic or seman-
tic. In the first case we speak of polysemy while
we use the term of synonymy in the second case.
The latter will not be addressed in this paper;
Equality: Concrete indirect sub-class of “Do-
mainIndependentCorrespondence” that repre-
sents a link relating identical model elements, i.e.
having the same structural and semantic descrip-
tions. For example, for a model element dupli-
cated in several models there will be an equality
among these copies;
Dependency: Concrete sub-class of “Domain-
IndependentCorrespondence” that represents a
relationship between model elements through a
function. For instance: Arithmetic operation on
model elements of type Real: (Total_TTC
=Total_HT*(1+TVA)); Concatenation of model
elements of type String (Full_Name =
First_Name + Last_Name);
Co-Dependency: Concrete indirect sub-class of
“DomainIndependentCorrespondence” that de-
fines a mutual dependency between model ele-
ments, where any change concerning one may af-
fect the others;
Generalization: UML concept in which one ele-
ment of a model B is based on another model el-
ement of a model A, allowing the extension of A
by reusing its elements in B.
Association: UML concept through which two
particular associations are defined namely com-
position and aggregation.
3.2 Matching Process
The proposed matching process aims at describing
the steps required to perform the matching between
heterogeneous source models, in order to obtain a
correspondence model. The produced model is
called M1C (model of correspondence at M1 level)
and contains the correspondences between elements
of models representing the system to develop.
Firstly, the process introduces the various mod-
els, their respective meta-models and the meta-
model of correspondences (MMC) in its initial state.
Subsequently, a verification step of the expressive-
ness of the MMC is triggered in order to inspect and
ensure that the MMC contains enough types of cor-
ENASE2013-8thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
184
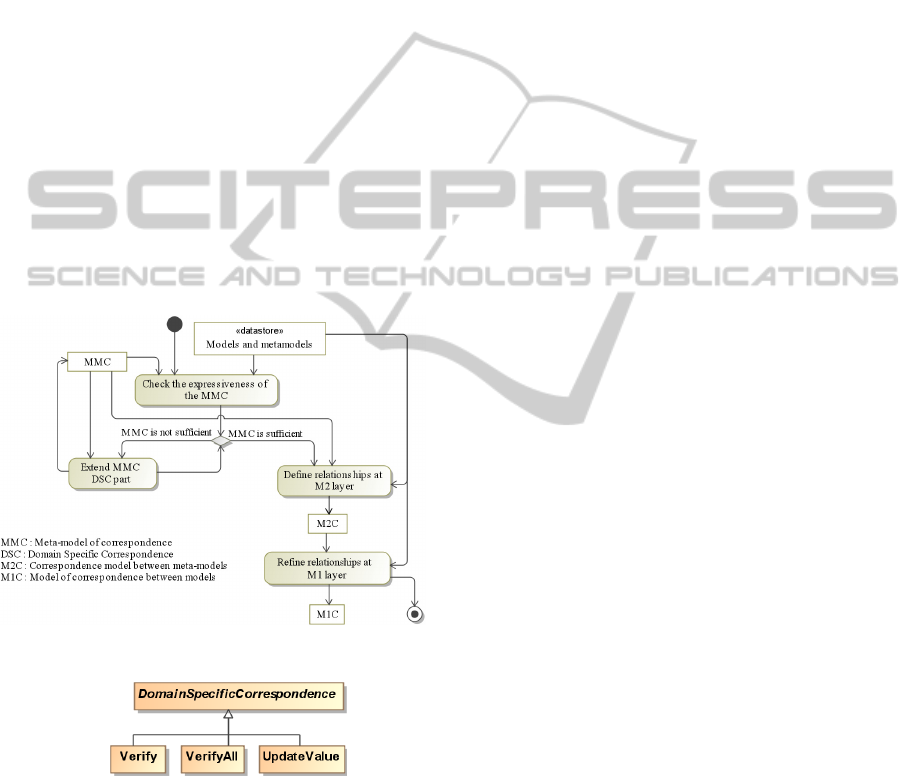
respondences (links) to set up among models, for a
given application domain. If the domain expert (ac-
tor whose responsibility covers the entire application
domain), considers that the proposed links are not
sufficient to express other relationships that might
exist between (meta-)model elements, the “Domain-
SpecificCorrespondence” meta-class
of MMC is
extended. The extension enables the domain expert
to add missing links, so as to enrich the MMC with
concepts specific to a given business domain. Figure
9 shows examples of such concepts that are needed
particularly in the context of BTS. For the “verify”
link for example, as we use a requirement model in
our domain, we must ensure that a given (meta-)
model element verifies the requirement(s) to which
it is linked. Once the MMC contains the necessary
concepts, the matching operation can be launched. It
begins by identifying relations between meta-
elements so as to produce the correspondence model
called M2C. Relationships stored in M2C are thus
refined, through a process that is described further,
to obtain the final model M1C which comprises the
relationships between model elements.
Figure 8: The whole matching process.
Figure 9: Extract of the specific part of the MMC meta-
model for BTS domain.
4 SETTING UP
CORRESPONDENCE LINKS
In this paper, we assume that correspondence rela-
tionships are set manually by the domain expert. He
is supposed to know the types of links that may exist
between the meta-elements, and their meaning. Ne-
vertheless, an assistance tool may be used. Indeed it
is possible to infer some relationships on the basis of
OCL constraints as well as knowledge bases (ontol-
ogies) that can be used as input of the matching
process.
Thereby, as explained in the matching process
presented in section 3.2, we propose to specify rela-
tionships at the abstract level (M2) in order to mini-
mize the modelling effort, and thus to reuse them
through refinement relationships at the concrete
level (M1).
4.1 Reusing High Level Links through
a Refinement Relationship
Refinement is a classical way to reuse. It can be seen
as a crossing from different levels of abstractions
with the purpose of adding details when passing
from a higher level to a more concrete one.
In the context of MDA, that notion may be repre-
sented as a transformation of a PIM (Platform Inde-
pendent Model) that represents a high level of ab-
straction to a PSM (Platform Specific Model) that
represents a lower one. According to (Agner et al., ),
even though refinement is a key concept in MDA, it
is loosely defined, and open to misinterpretation. In
a model refinement operation, most elements from
the abstract model (PIM) are copied into the refined
model (PSM), while other elements must be changed
in order to ensure specific properties.
The “refine” notion has also been defined in
UML (UML, 2007) as a stereotype for “Abstrac-
tion”. Abstraction is a directed relation from a de-
pendent element to an independent one stating that
the dependent element (concrete) depends on the
other one (abstract).
In our approach we distinguish two types of re-
lationships:
Relationships between meta-model elements:
“High Level Relationships” that are called HLR,
Relationships between model elements: LLR (for
“Low Level Relationships”).
A transition from HLR to LLR is similar to a trans-
formation of a PIM into a PSM in the context of the
MDA. This is done by projecting abstract relation-
ships on the concrete level.
Starting by identifying, relationships (called me-
ta-relationships) between meta-elements at the meta-
model level (M2C) allow establishing, in a second
step relationships between elements at the model
level (M1C). The principle consists in defining a
relationship once at the meta-model level and then
HeterogeneousModelsMatchingforConsistencyManagement
185

reuse it each time needed at the model level. In other
words, relationships among meta-model elements
induce relationships between model elements.
4.2 From HLR to LLR Relationships
To illustrate the use of the “refine” relation, we
consider Figure 10, whose objective is twofold: it
describes both HLRs among meta-elements at the
abstract level, and also how elements at concrete
level are related through LLR via refinements of
HLRs.
Figure 10: Examples of HLR & LLR relationships from
BTS modelling.
The upper side of the figure shows a graphical
view of an extract of M2C. This model is organized
as a set of different kinds of HLR relationships es-
tablished in the context of the BTS domain. For
example, the figure illustrates a “verifyAll” link that
relates the meta-element “requirement” on one side
to the meta-element “MantisRoot” on the other side.
Another example is “similarity” link that defines a
ternary relation between the following meta-
elements: “additionalInfo”, “Task” and “Require-
ment”.
HLR relationships are manually created. The
definition of these meta-relationships is done only
once during the modelling cycle but they are ex-
ploited for each relationship among model elements
instantiated from the meta-relationships. In other
words, the M2C model is used as input to establish
relationships at the model level. A meta-relationship
cannot give a full concretization at the model level.
It is necessary, depending on needs, to enrich the
relationships to adapt them at the model level.
The bottom part of Figure 10, shows LLR rela-
tionships belonging to the M1C model, obtained
through HLR refinements.
Figure 11: Process of model matching.
We present above a process (Figure 11) that
shows how such LLRs are built. First, one must
identify elements to relate (a mechanism to notify
the need to create the missing elements should be
provided). After that, creation of relationships is
performed via three steps (Automatic creation of
relationships, Potential adaptation and Verification):
Automatic creation of relationships: It is a fully
automated operation that duplicates all the rela-
tionships and their properties defined at the me-
ta-level and adapt them at the model level. In
other words, there are as many LLRs for a given
HLR than n-tuples of concerned instances. Let us
consider two model elements m1 and m2 such as
m1ϵ Mod1 and m2 ϵ Mod2; a correspondence
connects m1 and m2 if there exists a correspond-
ence at the meta level between mm1 and mm2
where mm1ϵ MM1, mm2 ϵ MM2, m1 is an in-
stance of mm1, m2 is an instance of mm2, and
Mod1 conforms to MM1 and Mod2 conforms to
MM2. Technically, LLRs can be created through
a Higher Order Transformation (HOT) (Tisi
et al., 2010) that is generated automatically. This
HOT transforms M2C that contains HLRs, into
an ATL model. This latter contains rules that can
be executed in order to produce the M1C model.
Potential adaptation: LLRs created during the
first step, may not be totally suitable for the ex-
pert designer. He may have to make choices
about certain actions to be performed (Barbier,
2009); (e.g. to preserve the desirable properties
or to add details or information on links, so as to
precise the semantics). Technically, a second
HOT is created to generate an ATL model that
contains rules for refining LLRs depending on
the domain expert’s needs. To do this, we exploit
the refine mode of ATL language (Agner et al., ).
It consists in transforming a model itself (M2M
transformation) by modifying a small part of
ENASE2013-8thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
186

ATL rules without rewriting the whole ones;
Verification: This last step consists in ensuring
that refinements have been done correctly. It
means that one must verify that each LLR is in
the context of one HLR. For example, one cannot
have a “semantic” link type of a HLR which is
refined, by the expert, with the “composition”
link type, instead of “equality” link.
To sum up, LLRs are created implicitly from in-
stances of related meta-elements but they may also
be explicitly refined by the domain expert depending
on the context.
5 RELATED WORKS
Several research works are related to models match-
ing.
In AMW (Del Fabro et al., 2005), authors de-
scribe a language that allows using M2M transfor-
mations for model comparison. But according to
(Kolovos, 2009), the meta-model of AMW turns to
be unusable to identify correspondences. Developers
must add extensions to the meta-model, so as to
permit the definition of links, even for the obvious
ones (like similarity). To optimize the representation
of a composed model, authors of the same team
propose a model virtualization technique (Clasen
et al., 2011). Such a technique may be useful for im-
plementing our approach, especially models tracing
and impacts calculation in case of source models
evolution.
ECL (Kolovos et al., 2006) is a matching lan-
guage which is difficult to use because it requires
specialized skills and great efforts, since relation-
ships are manually identified and created textually.
Moreover, the result of the matching operation is a
trace of correspondence, which contains the needed
relations after performing a set of rules. To exploit
the precedent trace and so to be able to reuse the
result for MDE purposes (e.g. composition), the
developer must do a serialization step to transform
the traces into a model of correspondences.
The Kompose approach (Drey et al., 2009) ad-
dresses the composition of homogeneous source
models. The process of matching must be parameter-
ized by defining signatures at the meta-model level
in order to define specific matching operators. In this
approach, the heterogeneity of models is not taken
into account yet, and tools are still at a prototype
stage.
In general, studied matching approaches have
shortcomings at two moments of the matching pro-
cess: before and after the creation of the correspond-
ence model. Regarding the first moment, we can
notice the lack of balance between the ability to
express correspondences and their reusability (ex-
isting approaches are based mainly on only one of
both criteria). In addition, these approaches only
operate binary links and therefore cannot establish
complex n-ary links relating a model element to any
set of elements belonging to other models. Con-
cerning the second moment, we can note that studied
approaches produce a correspondence model be-
tween each pair of input models; so for n input mod-
els, [n * (n-1)]/2 correspondence models must be
created, which leads to a large number of separate
models without any connection between them and
which makes their management very difficult and
almost impossible to automate.
6 CONCLUSIONS
AND PERSPECTIVES
Our general research work addresses the mainte-
nance of interrelated heterogeneous models in the
context of complex systems development. Thereby,
we are interested in establishing relations between
heterogeneous models described through different
DSLs corresponding to different business areas of an
application domain. In this paper, we have first pro-
posed a process to establish links between such
heterogeneous source models via a semi-automatic
matching operation based on a correspondence me-
ta-model (MMC) that may be adapted according to
specific business areas. The generic part of MMC
captures relations based on basic semantic links.
MMC can be thus extended through specialization of
the “DomainSpecificCorrespondence” meta-class
according to specific domains. Relationships among
source models are identified first at the meta-model
level and then refined at the model level. The pro-
posed approach has a wider operating range − thanks
to this high-level definition − than transformation
rules which restrict themselves to describing how an
element is obtained by transformation from another
one.
There are several perspectives to our current
work. Firstly, after an abstract syntax describing
different types of relationships among model ele-
ments is defined, we will create a concrete special-
ized notation for these relationships and formalize
their semantics. Secondly, we intend to validate our
approach by developing a matching tool called HMT
HeterogeneousModelsMatchingforConsistencyManagement
187

(Heterogeneous Matching Tool) whose architecture
is already defined. Thirdly, we will exploit the cor-
respondence model to address some maintenance
issue in the case where source models evolve. Our
goal is to provide a semi-automatic collaborative
process allowing to (i) update the M1C model, (ii)
calculate impacts of a change in a given source
model, (iii) propose modifications to maintain the
consistency of the system.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank the PHC Volubilis committee for funding
this project (MA/11/254), and our colleague K.A.
Kedji for his valuable remarks.
REFERENCES
Agner, L., Soares, I., Stadzisz, P., and Simao, J. Model
refinement in the model driven architecture context.
Journal of Computer Science, 8.
Anwar, A., Ebersold, S., Coulette, B., Nassar, M., and
Kriouile, A. (2010). A rule-driven approach for com-
posing viewpoint-oriented models. Journal of Object
Technology, 9(2):89–114.
Barbier, E. (2009). Contrats de transformation pour la
validation de raffinement de modèles. IDM 2009 Actes
des 5emes journées sur l’Ingénierie Dirigée par les
Modèles, page 1.
BPMN, O. (2011). Omg bpmn-v2.0.
http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/2.0/PDF.
Castano, S., De Antonellis, V., and De Capitani di Vimer-
cati, S. (2001). Global viewing of heterogeneous data
sources. IEEE Trans. on Knowl. and Data Eng.,
13(2):277–297.
Clasen, C., Jouault, F., and Cabot, J. (2011). Virtualemf: a
model virtualization tool. In Advances in Conceptual
Modeling. Recent Developments and New Directions,
pages 332–335. Springer.
Del Fabro, M., Bezivin, J., Jouault, F., Breton, E., and
Gueltas, G. (2005). AMW: a generic model weaver.
Proceedings of the 1ère Journée sur l’Ingénierie Diri-
gée par les Modèles (IDM05), 3(4.7):7–11.
Drey, Z., Faucher, C., Fleurey, F., Mahé, V., and Vojtisek,
D. (2009). Kermeta language. Reference Manual.
Eker, J., Janneck, J. W., Lee, E. A., Liu, J., Liu, X.,
Ludvig, J., Neuendorffer, S., Sachs, S., and Xiong, Y.
(2003). Taming heterogeneity-the ptolemy approach.
Proceedings of the IEEE, 91(1):127–144.
Fenza, G., Loia, V., and Senatore, S. (2008). A hybrid
approach to semantic web services matchmaking. In-
ternational Journal of Approximate Reasoning,
48(3):808–828.
Kolovos, D., Paige, R., and Polack, F. (2006). Model
comparison: a foundation for model composition and
model transformation testing. In Proceedings of the
2006 international workshop on Global integrated
model management, pages 13–20. ACM.
Kolovos, D. S. (2009). Establishing correspondences
between models with the epsilon comparison lan-
guage. In Proceedings of the 5th European Conference
on Model Driven Architecture - Foundations and Ap-
plications, ECMDA-FA ’09, pages 146–157, Berlin,
Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
mantisbt (2010). Mantis bug tracker.
http://www.mantisbt.org/index.php.
Ober, I., Coulette, B., and Lakhrissi, Y. (2008). Behavioral
Modelling and Composition of Object Slices Using
Event Observation. In Bruel, J.-M., Czarnecki, K., and
Ober, I., editors, ACM/IEEE International Conference
on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems
(MODELS), Toulouse, 28/09/2008-03/10/2008, num-
ber 5301 in LNCS, pages 219–233,
http://www.springerlink.com. Springer.
Tisi, M., Cabot, J., and Jouault, F. (2010). Improving
higher-order transformations support in atl. Theory
and Practice of Model Transformations, pages 215–
229.
UML, O. (2007). Uml 2.0: Superstructure specification.
http://www.omg.org/spec/UML/2.1.2/Superstructure/P
DF/.
ENASE2013-8thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
188
