
Framework for Enabling Scalable Learning Game AI
Gabriel Iuhasz
1
, Victor Ion Munteanu
1,2
and Viorel Negru
1,2
1
Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics, West University of Timis¸oara, bvd. V.P
ˆ
arvan 4, Timis¸oara, Romania
2
Institute e-Austria Timis¸oara, bvd. V.P
ˆ
arvan 4, Timis¸oara, Romania
Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence, AI Framework, Game AI.
Abstract:
The video game industry is a multibillion-dollar industry in which, due to general short deadlines, game visu-
als as well as gameplay elements are worked in parallel up until the very last minute. This means that even if
the AI system has been designed in parallel with the other game elements, once a change has been made in the
late stages of the game development, the AI may prove to be inadequate to the given job.
Our article covers some of the existing frameworks for game AI and proposes a multi-agent system which
serves as a framework for scalable learning game AI through integration of existing machine learning tech-
niques.
1 INTRODUCTION
Modern video games have become ever more com-
plex over the last decade. This complexity is observ-
able not only in the visual aspect of the games but also
in the general gameplay.
Most of them share characteristics with real life
scenarios such as military command, air traffic con-
trol (Lewis et al., 2011), racing etc. Games can be
thought of as stochastic environments in which un-
foreseen event are part of the gameplay mechanic.
Games are meant to be fun but they also possess
some interesting problems to the academic Artificial
Intelligence (AI) community. Sadly most develop-
ment done in games up to 2000-2002 was in the field
of visuals, letting the AI to be underdeveloped. This
is a direct result of the fact that in order to create a vi-
able AI system the game itself has to be in a complete
or nearly complete state. However this is rarely the
case as hard deadlines and last minute changes to the
gameplay hinder game AI development.
In his work (Buro, 2003), M. Buro has highlighted
the fundamental AI research problems posed by video
games. An AI system has to handle: resource man-
agement, decision making under uncertainty, spa-
tial and temporal reasoning, collaboration, opponent
modeling and learning, adversarial real-time plan-
ning.
Generally speaking, modern video games, espe-
cially real time strategy (RTS), games pose a signifi-
cantly harder challenge to AI research than more tra-
ditional games such as chess or backgammon (Aha
et al., 2005). This is largely because of the meta-game
present in most modern video games.
Meta-gaming is defined as any strategy, action or
method used in game which transcends the rule set
of the game and / or its environmental limitations. In
RTS games for example meta-gaming includes strat-
egy prediction, ad-hoc strategy creation and any rel-
evant information which can be deduced using envi-
ronmental data but is not immediately apparent.
Furthermore, one of the most important charac-
teristic the modern video games have is that they are
inherently multi-agent systems (MAS), meaning that
there exists a group of agents that cooperate or are in
conflict interacting with each other.
1.1 Game Domain
Games can be categorized based on many character-
istics like:
• Available information – based on the type of
information provided, human or computer con-
trolled players can deal with complete / incom-
plete information regarding the state space of the
game, in the case of incomplete information mak-
ing it necessary to deal with reasoning under un-
certainty.
• Interaction – players can have limited / unlimited
opportunity to interact with the environment this
means that sequential / concurrent moves are al-
lowed.
189
Iuhasz G., Ion Munteanu V. and Negru V..
Framework for Enabling Scalable Learning Game AI.
DOI: 10.5220/0004449301890196
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE-2013), pages 189-196
ISBN: 978-989-8565-62-4
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

• Equality – refers to asymmetry. In most games
each player starts with no material advantage over
the other. For example in chess each player has
the same number and type of pieces at the start of
the game, however this is not the case in modern
video games.
1.1.1 Strategy
Strategy games refer to simulations in which the
player controls a certain number of units and must
defeat it’s opponents. Furthermore, in some games
it can also construct buildings and units by following
specific tech trees. They can be divided into RTS and
turn based strategy games (TBS).
From the AI point of view, strategy games fall
into the categories highlighted by M. Buro in (Buro,
2003). Furthermore, 3 levels of reasoning that a game
playing AI has to accomplish in order to provide an
adequate opposition to a player have been identified:
• NPC Micromanagement – entails low level unit
actions such as selecting the target to attack, unit
movement etc. All of these actions and the de-
cision making regarding these actions has to be
done as fast as possible. The usual unit of mea-
surement is actions per minute (APM).
• Tactical thinking – how to best utilize a squad
of units, analyzes the terrain in order to deter-
mine if it is an advantageous position. This seems
as a straight forward problem but we must con-
sider that it requires coordination between multi-
ple units of different types.
• Strategic Level – deals with the selection or con-
struction of the overall strategy.
In terms of Russell and Norvig’s task environment
properties (Russell and Norvig, 2003), strategy games
are partially observable, deterministic, sequential, dy-
namic, continuous, and a multi-agent environment.
One major difference between RTS and TBS
games is given by the state-space complexity which
can be computed as follows in the case of RTS games:
O((t ×x × y)
n
) (1)
Where n denotes the number of units at play, t de-
notes the number of unit types in a game while x and
y denotes the size of the environment.
In the case of a RTS game such as StarCraft de-
veloped by Blizzard Entertainment when applying
Equation (1) the state-space can be approximated to
10
11500
. This number also includes illegal positions.
When compared with the state space of chess, which
is estimated at 10
43
, it gives us a small glimpse into
the complexity of the problem space (Shannon, 1988).
Another important difference is that of decision
complexity which was first proposed by Aha (Aha
et al., 2005). Which is:
O((w · a · p) + (t · d · s) + (b · (r + c))) (2)
Where w is the number of workers, a types of
worker unit assignments, p is the average number of
workplaces, t is the number of troops, d the number of
movement directions, s the number of troop stances, b
the number of buildings, r average number of research
options, c average number of unit types at buildings.
In the case of StarCraft, by applying Equation (2),
it can be approximated to 1 million possible actions
in contrast to 30 in the case of chess.
1.1.2 First-Person Shooters
First-Person Shooters (FPS) are weapon-based com-
bat simulations in which the protagonist (the player’s
avatar) has to defeat a number of Non-Player Charac-
ters (NPC) to complete a certain goal. Although this
seems as pretty basic gameplay mechanic, it poses
some important problems to be solved.
There are many types of FPS games, however in
most the AI is focused on micromanagement. For ex-
ample, in squad based FPS there are two levels: mi-
cromanagement and tactical reasoning. The AI needs
to organize the opposing forces in such a way to pro-
vide a suitable level of resistance by utilizing coor-
dination between the units and by using the environ-
ment to its advantage.
1.1.3 Racing
Racing games refer to the category of games which
imply driving a car through a course and if usually
focuses on achieving best times and first place (as in
real life racing).
Unlike the other game genres, a car racing game
only needs the micromanagement level as it only
deals with individual units (cars) and needs to reason
about their actions in order to win a race.
1.2 General Framework Considerations
There are a number of agent based architectures for
AI in games. The key point that needs to be taken
into consideration in the design phase is the “goal” of
these systems.
Another major consideration is the type of adap-
tation mechanism (learning) that a system implement,
which can be offline and online learning.
During offline learning the system evaluates its
performance after a game session thus being able to
learn from previous mistakes. The main disadvantage
ENASE2013-8thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
190

of this type of learning is that it doesn’t provide imme-
diate results and requires some form of bootstrapping
in order to be effective. This bootstrapping can be in
the form of game replays which the system analyzes
or by direct user intervention.
The second type of learning is done online that is
during gameplay. While this provides a potential so-
lution to the main drawback of offline learning algo-
rithms it introduces another problem, namely incon-
sistency.
During gameplay machine learning algorithms are
susceptible to learn undesired behaviors. In the case
of the offline approach this, although undesired, is
consistent throughout a game instance as opposed to
online learning where behavior can alternate between
undesired and desired several times during the same
game instance. For instance if a unit has learned that
it is strong against a particular type of unit in an online
learning system it may unlearn this fact and produce
unwanted behavior.
In order to alleviate the shortcomings of tradi-
tional symbolic, offline and learning based game AI
frameworks a hybrid approach is needed. A tradi-
tional symbolic agent can be loosely or tightly cou-
pled with a ML technique to more efficiently and
dynamically solve a given problem better than stan-
dalone agent setup could.
This approach can also benefit in terms of devel-
opment costs because even if during the latter stages
of development gameplay changes are implemented a
ML algorithm can be more easily adapted than a sym-
bolic approach. With little to no human intervention
thus reducing production time and cost.
1.3 Existing Frameworks
There are a number of notable frameworks dealing
with game AI that are presented in the following sub-
sections.
1.3.1 Cognitive Architecture
The cognitive architecture is designed for develop-
ing mechanisms that highlight human cognition and
provides mechanisms that are required for integrat-
ing heterogeneous competencies and are able to rea-
son about multiple goals (Langley and Choi, 2006). It
also focuses on performing evaluation at the system
level (Lehman et al., 1996).
One example of such a system is the ICARUS
cognitive architecture which has been applied to real-
time domains like urban simulation and FPS (Choi,
2011). It uses means-ends analysis when confronted
with new problems at the same time it lack some fun-
damental structures for standard game AI problems
such as micromanagement actions.
SOAR is another cognitive architecture that of-
fers multitasking as well as planning capabilities. It
also performs state abstractions and a learning mech-
anism called chunking that is a caching mechanism
and is used to intermix learning and problems solving
(Lehman et al., 1996).
1.3.2 Goal-Driven Autonomy Models
Goal-driven autonomy (GDA) models provide a
framework for creating agents capable of respond-
ing to unanticipated failures during plan execution in
complex, dynamic environments (Aha et al., 2005).
It uses a conceptual model which specifies sub-
tasks that enable an agent to detect, and reason about
to unanticipated events. This framework contains sev-
eral components and establishes interfaces between
them but it leaves the implementation details unre-
stricted.
The GDA model has been used for RTS games
(Mu
˜
noz-Avila et al., 2010), naval strategic simulation
(Molineaux et al., 2010) and FPS (Mu
˜
noz Avila et al.,
2010). Within these frameworks some machine learn-
ing techniques have been used such as reinforcement
learning (Jaidee et al., 2011).
1.3.3 Reactive Planning
Reactive planning has been used to create au-
tonomous software agents (Loyall, 1997). In this type
of systems, no action is planned in advance as each
action is selected at every instant. This enables them
to handle events that are part of the meta-game such
as strategies.
Systems that use reactive planning are particularly
adept at handling real-time environments or more
specifically tasks that require real-time actions.
The main strength of reactive planning is the abil-
ity to enact incomplete plans while pursuing goal-
directed task thus being able to adapt to changes in
the environment (Pryor and Collins, 1996; Josyula,
2005).
1.3.4 Case-based Reasoning
Case-based reasoning is a methodology that enables
the creation of systems that learn from experience
(Ontan et al., 2008).
It has been applied to solve some particular prob-
lems in RTS games such as strategic and tactical se-
lection (Fagan and Cunningham, 2003) as well as mi-
cromanagement (Szczepanski and Aamodt, 2009).
FrameworkforEnablingScalableLearningGameAI
191

2 FRAMEWORK
2.1 Requirements
We have identified several shortcomings present in
existing systems along with others we consider to be
important for game AI.
The majority of the systems or frameworks are not
scalable as they are geared towards one particular ap-
proach to the given problem and are largely created to
showcase it.
Most of them normally use methods such as Finite
State Machines (FSM), expert systems, decision trees
etc. Although these methods can be quite successfully
deployed in games they are almost always hard-coded
thus lacking adaptability and become predictable in a
very short amount of time.
One solution is to employ machine learning
(ML) techniques such as Artificial Neural Networks
(ANN), genetic algorithms (GA), Bayes Networks
etc. These techniques give some significant benefits
such as adaptability but also have some drawbacks.
One of the major drawbacks is that these meth-
ods are resource intensive both in memory and CPU
time. This is a problem because on average AI system
get 15 to 20% of the overall CPU time during game-
play. Most of the computing resources are used by
the game engine to render and create the game envi-
ronment (Millington and Funge, 2009).
Another important consideration when designing
an agent framework for game AI is the impact of la-
tency on the performance and playability of the game.
Some work has been done to identify the level of lag
that is acceptable in the case of modern video games
(Claypool and Claypool, 2006).
The most sensitive game genre is that of driving
games while the least sensitive is games that follow
the omnipresent model in which RTS games are situ-
ated. In short RTS games have a low sensitivity to lag
and have a threshold of up to 1000 milliseconds. This
makes them in some ways ideal in full or in part for
cloud integration.
Also the fact that they poses the most variety when
it comes to AI problems makes them a prime can-
didate for academic testing of novel problems solv-
ing techniques as well as many other fields of re-
search such as optimization problems, co-evolution
and many more (Lucas et al., 2012).
2.2 Architecture
We propose a multi-agent architecture for an adap-
tive game AI framework. As we stated in the pre-
vious sections, games are inherently multi-agent ori-
ented complex systems thus our architecture follows
this paradigm, as can be seen in Figure 1.
Our framework focuses on the above stated prob-
lems and enables the testing of several ML techniques
by using a modular design (through agents) that en-
ables the encapsulation of different ML techniques
within it, thus enabling it to be extremely flexible.
Because some ML techniques are scalable our
framework can manage agents of high cardinality thus
enabling on the fly scaling of agents.
In order to ensure the quality of service and sta-
bility of our framework we implement some con-
trol mechanisms that monitor the frameworks perfor-
mance and performs optimization actions.
We have identified 7 types of agents necessary
in a scalable AI framework. By scalable we mean
that some agents have a cardinality larger than one in
some situations. Some agents have a modular design
which enables new methods and/or interfaces to be
integrated this aiding adaptability.
It should be noted that the ML method imple-
mented in the modules are largely governed by the
type of problem to be solved. Some techniques such
as Bayesian models can be used in opponent mod-
eling and plan recognition (Synnaeve and Bessi
`
ere,
2011; Synnaeve and Bessi
`
ere, 2012) while ANN and
genetic algorithms can be used in micromanagement
task and tactical analysis (Shantia et al., 2011).
The agents are as follows:
API Agent – handles the connection to the game in-
stance via the API module. As the framework is
intended for a plethora of game genres each game
has an API that enables communication with the
game client. As there is no universal API for
games we adopted a modular design that enables
us to create an agent stub and add individual API
modules as needed.
Negotiation Agent – handles cooperation tasks as
in many games coordination and cooperation be-
tween factions is possible.
Database Agent – handles all database queries from
the framework. This agent knows where each
database is and how to communicate with it. Be-
cause in our framework we have different types
of data and data access needs different database
types may be necessary in a single instance of our
framework. This type of agent also has a mod-
ule that will implement the specific communica-
tion interface for each database.
Reactive Agent – this type of agents are wrapped
around reactive modules. Their primary role is
to receive and process input and the return the re-
sults. Because of their role, they mostly run in
ENASE2013-8thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
192
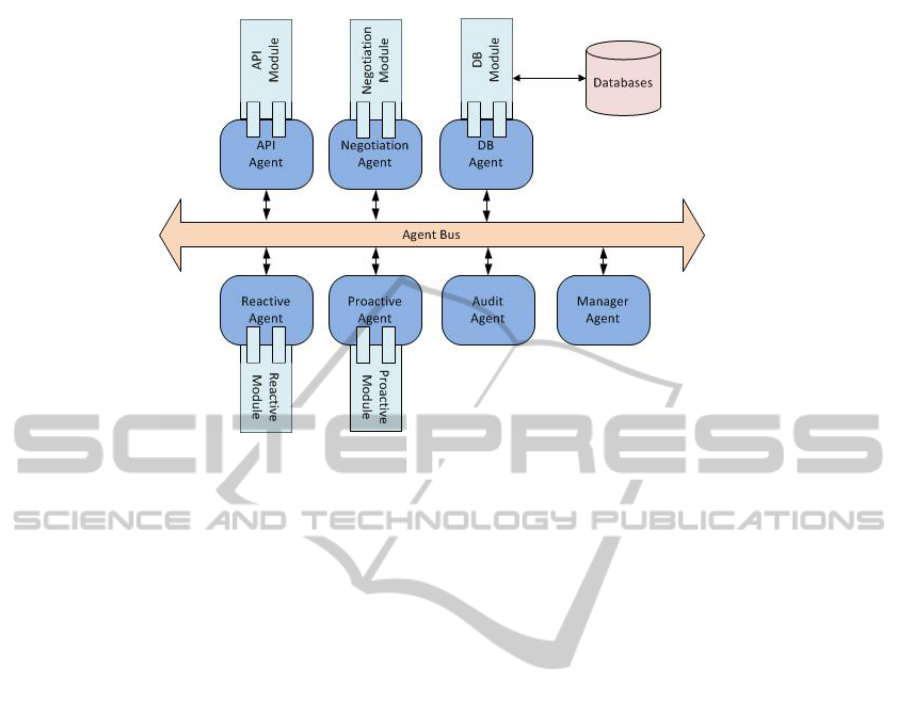
Figure 1: General Framework.
a “stateless” manner thus easily being considered
as highly scalable. In a game AI they are usually
used for quick decisions like avoiding a rocket,
analyzing what a unit sees etc.
Proactive Agent – this type of agents are wrapped
around proactive modules. They feature long run-
ning agents which are seldom required to scale.
In a game AI they are usually used for planning,
setting objectives etc.
Audit Agent – handles the monitoring of the frame-
work. It uses rules to identify any anomalies
that happen in the system and notifies the Man-
ager Agent if one should occur. For example if
one agent in our framework is overtaxed the audit
agent detects this sends a notifying the Manager
Agent of the situation.
Manager Agent – is in charge of the system. It man-
ages all the agents in the system, scaling them ac-
cording to specific policies.
Levels of Abstraction
A tasks inherent in games can be divided into 3 lev-
els of abstraction. The first level deals with high
level thinking and dynamic knowledge acquisition
and posses the highest degree of abstraction. In
essence this level makes strategic decisions about
long-term goals. These decisions can involve logis-
tic management tasks, build-order creation and recon-
naissance. The most suitable agent type present in this
level are proactive agents.
The second level of abstraction handles unit group
movement and coordination. In some games certain
additional tasks are necessary such as terrain analy-
sis and/or opponent modeling. At this level, depend-
ing on the task, reactive and proactive agents are nec-
essary. For example an agent that controls a squad
of agent needs to know the best deployment for its
squad. In order to do this it needs the terrain analyzed
so it calls a terrain analysis agent to tell it which po-
sition will give it the best advantage possible. In this
example the agent that controls the squad is a proac-
tive agent while the terrain analysis agent is a reactive
agent.
The third and last level of abstraction is by far the
most common in games. It handles individual unit ac-
tions and mostly made up of reactive agents. These
agent have a simple task namely to maximize each
units utility during gameplay. Each agents utility de-
pends on the genre of game as in a racing game the
utility can be measured in lap times while in a RTS
game it can be measured as the overall toughness and
danger (effectiveness) of a unit in battle.
One of the most important characteristics of the
video game domain is the large number of entities
(agents) and the heterogeneity of their needs. Any
holistic AI framework is in fact a distributed decision
making system. Furthermore as some levels of de-
cision making is present in almost all game genres
from the semantic point of view, a common language
is needed. In order to accomplish this our framework
needs at the very least a glossary of terms in order to
facilitate communication between agents and other AI
frameworks.
A generalized game ontology can serve as the
knowledge base of the framework and represents not
only a simple taxonomy but also some more complex
FrameworkforEnablingScalableLearningGameAI
193

relationship that can be used to solve some in game
problems such as the intransitive superiority problem
present in most tactical or team based games. Such
and ontology can also be used to standardize the game
AI frameworks.
An important consideration is the nature of the
coupling between the ML modules and the agent
shell. Based on (Zhang and Zhang, 2004) we can
see that system encapsulation is an important prob-
lem that need to be addressed in our framework. In
our case the most relevant types are tightly-coupled
and loosely-coupled systems.
In loosely-coupled systems both elements need to
be able to solve sub-problems with their unique com-
putational properties. They lack access to each oth-
ers internal mechanisms thus having to pass relevant
information through data files. In contrast tightly-
coupled systems pass information via memory resi-
dent data structures.
It is easy to deduce that the former type of sys-
tem is easier to develop, verify and validate than the
latter but it also suffers because of the communi-
cation overhead between its components and redun-
dancy of effort. The type of coupling used is dictated
by the game genre and ML techniques used (Zhang
and Zhang, 2004).
It is important to note that there exist several mod-
els of coupling but we consider that they are ill fit-
ted to our frameworks requirement. The transforma-
tion model is unusable in the case of some ML tech-
niques as a symbolic model is translated into a ML
one. This however is extremely hard to accomplish
in the case of ANNs. Furthermore a fully-integrated
model is extremely appealing at first because of the
benefits present by sharing data structures and knowl-
edge representation.
However in a scalable AI framework for games
full integration must be done from the design phase
and has to take into account a vast array of ML tech-
niques that can be used. This fact hinders framework
flexibility.
3 CASE STUDY
In order to show that our framework is capable of be-
ing instantiated for a large variety of games we choose
a RTS such as Starcraft developed by Blizzard Enter-
tainment which was split into 3 tiers of reasoning as
seen in Figure 2.
At tier 0 we have 2 reactive agents:
• Unit agents – handle low level micro actions of
each individual unit in the game environment.
• Spawn agents – initialize each unit agent as
needed and attached to it is a learning module
which implements a ML algorithm. As we see
in (Gabriel et al., 2012) a neuroevolutionary tech-
nique can be used to accomplish online meta-
game learning.
Tier 1 is comprised of two types of agents. In con-
trast to T0 which had reactive agent here we have one
reactive and one proactive agent:
• Terrain analysis agent – is, by its nature, a reac-
tive agent and whose job is to identify meaning-
ful environmental features such as choke points.
These identified features can then be used to cre-
ate a tactical or even strategic advantage. It should
be noted that because of the nature of the problem
this agent is highly scalable as the environment
can be split up into smaller sections for which an
instance of the agent is assigned. This is similar
to rendering in computer graphics.
• Tactical agent – is a proactive agent whose main
functionality is that of coordination of a large
number of units as well as tactical appraisal of
game states based on the terrain analysis informa-
tion it receives. Attached to it is also a learning
module which can implement any number of ML
methods.
The last tier is where high level reasoning takes place
and has only proactive agents:
• Strategic agent – handles task generation based on
a policy (goal oriented strategic planning).
• Economic agent – handles resource gathering op-
erations while the Recon agent handles reconnais-
sance of the environment.
Because of the complex nature of the tasks this
tier has to accomplish online learning is vital thus at-
tached to the strategic agent there is also a learning
module.
As we mentioned in the previous paragraphs some
agent types have learning modules attached to them.
These modules are meant to enhance the flexibility of
our framework as they allow different types of learn-
ing mechanisms to be implemented without having to
resort to drastic redesign each time a new methods is
considered or benchmarked. These methods can in-
clude Bayes Nets for tactical planning, ANN and GA
for micromanagement and Goal-Driven Behavior for
strategic planning to name but a few.
The remainder of the system is comprised mainly
of utility agents detailed in the previous section.
One important remark is that the API agent also
performs some environmental data preprocessing be-
fore sending the information to requesting agents.
ENASE2013-8thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
194
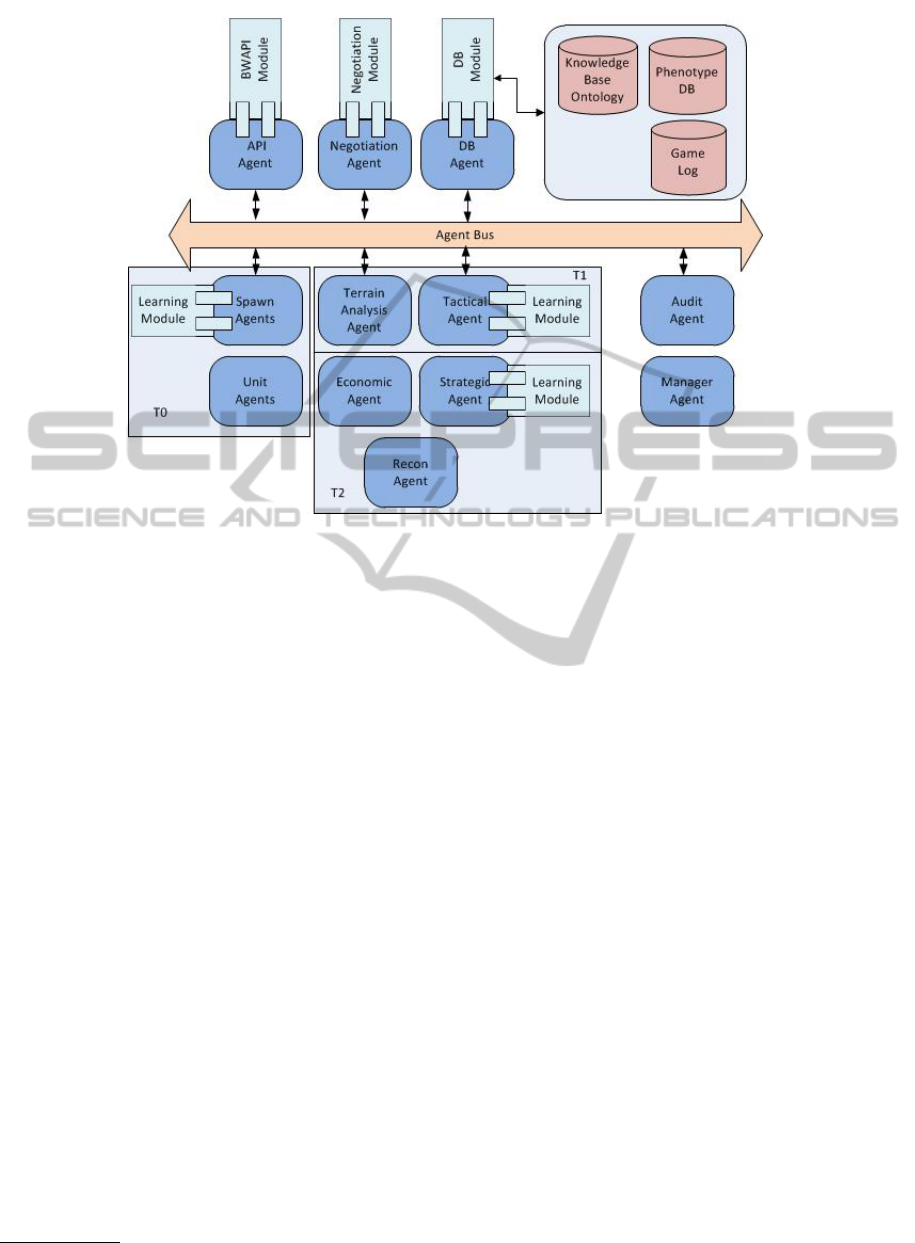
Figure 2: RTS game based on framework.
The interface with the game instance is done with the
help of an API like the BWAPI
1
in the case of Star-
craft.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we presented a scalable AI framework
for modern video games. It features a modular de-
sign that enables it to incorporate different ML. Each
module implements a ML technique that is then be
attached to an agent shell, enabling tightly or loosely
coupled architectures.
An important feature of our framework is the fact
that it has been designed to be highly scalable. The
audit and manager agents are able to monitor and
scale, if necessary, particular agent types in order to
optimize the performance of the game AI. This fea-
ture is very important because some ML techniques
such as the Monte Carlo Method can be computation-
ally expensive. It also facilitates the deployment of
some algorithms which are considered in AI research
as being too expensive in order to be used effectively
in real time games and applications.
We have shown that our framework can be eas-
ily mapped on a RTS game that has the three levels
of abstraction present in the majority if not all video
games. A general ontology is needed that can serve
1
http://code.google.com/p/bwapi/
as a knowledge-base and also help standardize video
game AI frameworks. It should be easily expanded in
order to fit each game genres idiosyncrasies.
A novel addition to our framework is the addition
of a dedicated agent that handles negotiation task with
other frameworks and can directly influence overall
system goals. This feature is not present in other AI
frameworks and presents a novel avenue of research.
It is also important to note that our framework is a
perfect candidate for deployment on a cloud comput-
ing infrastructure as each instance of an agent can in
theory be deployed on a separate computing platform.
Further research will address some open problems
such as the need for a game ontology and address the
issue of scaling in cloud environments.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially supported by the Romanian
national grant PN-II-ID-PCE-2011-3-0260 (AMI-
CAS), FP7-REGPOT-CT-2011-284595 (HOST) and
by the strategic grant POSDRU/CPP107/DMI1.5/S/
78421, Project ID 78421 (2010), co-financed by the
European Social Fund Investing in People, within the
Sectoral Operational Programme Human Resources
Development 2007–2013. The views expressed in
this paper do not necessarily reflect those of the cor-
responding projects’ consortium members.
FrameworkforEnablingScalableLearningGameAI
195

REFERENCES
Aha, D. W., Molineaux, M., and Ponsen, M. (2005). Learn-
ing to win: case-based plan selection in a real-time
strategy game. In Proceedings of the 6th international
conference on Case-Based Reasoning Research and
Development, ICCBR’05, pages 5–20, Berlin, Heidel-
berg. Springer-Verlag.
Buro, M. (2003). Real-time strategy gaines: a new ai re-
search challenge. In Proceedings of the 18th inter-
national joint conference on Artificial intelligence, IJ-
CAI’03, pages 1534–1535, San Francisco, CA, USA.
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.
Choi, D. (2011). Reactive goal management in a cognitive
architecture. Cogn. Syst. Res., 12(3-4):293–308.
Claypool, M. and Claypool, K. (2006). Latency and player
actions in online games. Commun. ACM, 49(11):40–
45.
Fagan, M. and Cunningham, P. (2003). Case-based plan
recognition in computer games. In Proceedings of the
Fifth ICCBR, pages 161–170. Springer.
Gabriel, I., Negru, V., and Zaharie, D. (2012). Neuroevo-
lution based multi-agent system for micromanage-
ment in real-time strategy games. In Proceedings of
the Fifth Balkan Conference in Informatics, BCI ’12,
pages 32–39, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Jaidee, U., Mu
˜
noz Avila, H., and Aha, D. W. (2011). Inte-
grated learning for goal-driven autonomy. In Proceed-
ings of the Twenty-Second international joint confer-
ence on Artificial Intelligence - Volume Volume Three,
IJCAI’11, pages 2450–2455. AAAI Press.
Josyula, D. P. (2005). A unified theory of acting and agency
for a universal interfacing agent. PhD thesis, College
Park, MD, USA. AAI3202442.
Langley, P. and Choi, D. (2006). A unified cognitive archi-
tecture for physical agents. In proceedings of the 21st
national conference on Artificial intelligence - Volume
2, AAAI’06, pages 1469–1474. AAAI Press.
Lehman, J. F., Laird, J., and Rosenbloom, P. (1996). A
gentle introduction to soar, an architecture for human
cognition. In In S. Sternberg & D. Scarborough (Eds),
Invitation to Cognitive Science. MIT Press.
Lewis, J. M., Trinh, P., and Kirsh, D. (2011). A corpus anal-
ysis of strategy video game play in starcraft: Brood
war. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Conference of
the Cognitive Science Society.
Loyall, A. B. (1997). Believable agents: building interac-
tive personalities. PhD thesis, Pittsburgh, PA, USA.
AAI9813841.
Lucas, S. M., Rohlfshagen, P., and Perez, D. (2012). To-
wards more intelligent adaptive video game agents: a
computational intelligence perspective. In Proceed-
ings of the 9th conference on Computing Frontiers, CF
’12, pages 293–298, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Millington, I. and Funge, J. (2009). Artificial Intelligence
for Games, Second Edition. Morgan Kaufmann Pub-
lishers Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA, 2nd edition.
Molineaux, M., Klenk, M., and Aha, D. W. (2010). Goal-
driven autonomy in a navy strategy simulation. In in
Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth AAAI Conference
on Artificial Intelligence. AAAI Press.
Mu
˜
noz Avila, H., Jaidee, U., Aha, D. W., and Carter, E.
(2010). Goal-driven autonomy with case-based rea-
soning. In Proceedings of the 18th international con-
ference on Case-Based Reasoning Research and De-
velopment, ICCBR’10, pages 228–241, Berlin, Hei-
delberg. Springer-Verlag.
Mu
˜
noz-Avila, H., Aha, D. W., Jaidee, U., Klenk, M., and
Molineaux, M. (2010). Proceedings of the twenty-
third international florida artificial intelligence re-
search society conference, may 19-21, 2010, daytona
beach, florida. In Guesgen, H. W. and Murray, R. C.,
editors, FLAIRS Conference. AAAI Press.
Ontan, S., Mishra, K., Sugandh, N., and Ram, A. (2008).
Learning from demonstration and case-based plan-
ning for real-time strategy games. In Prasad, B., edi-
tor, Soft Computing Applications in Industry, volume
226 of Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing, pages
293–310. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Pryor, L. and Collins, G. (1996). Planning for contingen-
cies: a decision-based approach. volume 4, pages
287–339, USA. AI Access Foundation.
Russell, S. J. and Norvig, P. (2003). Artificial Intelligence:
A Modern Approach. Pearson Education, 2 edition.
Shannon, C. E. (1988). Computer chess compendium.
chapter Programming a computer for playing chess,
pages 2–13. Springer-Verlag New York, Inc., New
York, NY, USA.
Shantia, A., Begue, E., and Wiering, M. (2011). Connec-
tionist reinforcement learning for intelligent unit mi-
cro management in starcraft. In IJCNN, pages 1794–
1801.
Synnaeve, G. and Bessi
`
ere, P. (2011). A bayesian model for
plan recognition in rts games applied to starcraft. In
AIIDE.
Synnaeve, G. and Bessi
`
ere, P. (2012). Special tactics: A
bayesian approach to tactical decision-making. In
CIG, pages 409–416.
Szczepanski, T. and Aamodt, A. (2009). Case-based reason-
ing for improved micromanagement in real-time strat-
egy games. Proceedings of the Workshop on Case-
Based Reasoning for Computer Games, 8th Interna-
tional Conference on Case-Based Reasoning, ICCBR
2009, pages 139–148.
Zhang, Z. and Zhang, C. (2004). Agent-Based Hybrid Intel-
ligent Systems. SpringerVerlag.
ENASE2013-8thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
196
