
An Approach for Modeling Real-time Requirements with SysML
and MARTE Stereotypes
Fab´ıola Gonc¸alves C. Ribeiro and Michel S. Soares
Faculty of Computing, Federal University of Uberlˆandia, Uberlˆandia, Brazil
Keywords:
Real-time Systems, Requirements Engineering, Modeling Software, MARTE, SysML.
Abstract:
The specification, analysis and design of real-time systems (RTS) are activities that are highly dependent
on an effective understanding of the application domain and on the thorough representation of their basic
requirements. The use of model-based approaches for the development of RTS systems tends to contribute
to minimizing the complexity of the system development. UML has been used intensely in recent years
for modeling requirements of real-time software. However, UML alone does not completely represent the
important features associated with these systems. UML is a language that has several extension capabilities
enabling the creation of specific profiles. This article will explore the use of UML profiles SysML and MARTE
for the modeling of RTS software requirements, with its main area of application being the control of urban
traffic. The main objective is to demonstrate the application of SysML with MARTE stereotypes, which
enables the modeling and tracing of individual software requirements.
1 INTRODUCTION
Requirements engineering is the process by which
the requirements for systems and software products
are gathered, analyzed, documented and managed
throughout the development life-cycle. UML (OMG,
2011c) has traditionally been used to document user
requirements through Use Case diagrams (Xu et al.,
2011), with the purpose of creating graphical specifi-
cation to scenarios of software execution. This means
that requirements are organized into stories of using
the system that acts as a friendly point between users,
technical and business stakeholders (Helming et al.,
2010) (Heisel and Cote, 2011).
There are some issues involved with using Use
Case diagrams for modeling real-time requirements.
The main purpose of a Use Case diagram in the con-
text of requirements is to describe scenarios of re-
quirements, not individual requirements. In addi-
tion, Use Cases are specific to describing functional
scenarios, without concerns about representing non-
functional properties. Use Cases are extremely infor-
mal, and can be easily misused when too many de-
tails are modeled. According to (Bianco et al., 2002),
temporal constraints and concurrent activities are not
well-expressed in UML. As discussed in (Silvestre
and Soares, ), UML presents difficulty in expressing
non-functional properties of the system, very impor-
tant requirements for real-time applications.
Proposals to address the problems of UML in
relation to modeling real-time software were cre-
ated. These include the profiles SPT (OMG, 2005),
MARTE (OMG, 2011a) and SysML (OMG, 2010).
These profiles extend UML and add elements that
model time requirements, system requirements and
non-functional properties. The SPT profile (SPT
stands for “Schedulability, Performance and Time”)
provides a mechanism for the annotation of a set of
pre-defined stereotypes and tagged values (Xu et al.,
2003). SPT offers support for some of the an-
notations of non-functional properties (NFPs), such
as support for symbolic variables and expressions
through its specialized language Tag Value (TVL).
SPT provides time related concepts such as the no-
tions of instant and duration, concepts for modeling of
events and time related stimulus (Bennett and Field,
2004). However, its approach was not formally de-
fined enough to allow new definitions of NFPs by the
user or for different specialized fields.
MARTE and SysML profiles have been studied
and applied in practice in past years in domains such
as product lines (Belategi et al., 2010), concurrent
systems (Shousha et al., 2012), and in other industrial
environments (Iqbal et al., 2011) (Iqbal et al., 2012).
However, few approaches were proposed with a fo-
cus on applying MARTE and SysML together to de-
70
C. Ribeiro F. and S. Soares M..
An Approach for Modeling Real-time Requirements with SysML and MARTE Stereotypes.
DOI: 10.5220/0004449800700081
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2013), pages 70-81
ISBN: 978-989-8565-60-0
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

sign real-time systems. One of these approaches was
published in (Quadri et al., 2012b), in which a sys-
tems modeling language is defined based on subsets
of MARTE and SysML, allowing iterative refinement
from high-level specifications all the way down to fi-
nal implementation. Another approach was proposed
in (Quadri et al., 2012a), but its focus was not based
on requirements design. In addition, only functional
requirements are described with the SysML Require-
ments diagram.
In this article the strategy is to combine the
MARTE and the SysML profiles with the purpose
of improving the specification of requirements for
real-time systems. The main focus is to show how
these profiles can be combined in order to demon-
strate its applicability for the modeling of time, per-
formance, system configuration, and of course, the
functional and non-functional requirements of real-
time systems. The created model is applied to model-
ing requirements of a Road Traffic Control System.
2 BACKGROUND ON MARTE
AND SysML
Among the proposed UML profiles, two are used in
this article. SysML, because of its Requirements di-
agram, and MARTE, with the many stereotypes used
to specify non-functional properties. The profiles are
briefly introduced in this section.
2.1 MARTE
The architecture of the MARTE profile consists of
three main packages named MARTE Foundations,
which aims at defining fundamental concepts for em-
bedded real time systems and brings concepts that
serve as a general basis for the description of most
of the elements linked to the remainder of the speci-
fication, the MARTE Design Model, which provides
the necessary support to conduct a detailed specifica-
tion of a project for real time embedded systems and
the MARTE Analysis Model, which provides con-
cepts for verification and validationof models (Kumar
and Jasperneite, 2010) (OMG, 2011b). (Silvestre and
Soares, ). In addition to these packages, the MARTE
profile proposes numerous other sub-packages. The
MARTE Foundations relates to the scope of this
work (more specifically the first three sub-packages)
and, for this reason, these are briefly described as fol-
lows.
• Core Elements. This sub-package has the basic
elements for behavioral modeling and the seman-
tic representation of its running time. The objec-
tive of this model is to provide a high-level view
of the semantics of execution time for modeling
elements.
• Non-functional Properties Modeling - NFPs
This sub-package offers paths to specify non-
functional properties of real-time systems, such
as memory usage and power consumption. It also
explains how the NFPs can be connected to ele-
ments of the model.
• Time Modeling - Time. This package allows the
modeling of time and related structures over time.
Concepts related to physical time, logical time,
and representation of instants representing time
bases, and occurrences of events over time, are
clearly defined in this sub-package.
• Generic Resource Modeling - GRM. This sub-
package provides all the necessary stereotypes
and tagged values to represent features such as
means of communication, computing resources
and storage resources. It also includes resources
that are needed to deal with the modeling of ex-
ecution platforms with different levels of abstrac-
tion and modeling. The GRM package along with
the package Time can be used to specify time con-
straints and, when used with the package NFP, can
be used for specifying the quality of services.
• Allocation Modeling - Alloc. The MARTE pro-
file allows designers to model the applications and
execution platforms. An application element in
MARTE can be a service, computation or a func-
tion of the operating system. An execution plat-
form is a collection of connected resources repre-
senting the hardware architecture.
2.2 SysML
The SysML profile (OMG, 2010) allows the modeling
of various types of applications in engineering sys-
tems, enabling the specification, analysis, design, ver-
ification and validation of complex systems (OMG,
2010). The introduction of the SysML Requirements
diagram provided support for modeling individual re-
quirements and their relationships. The basic graph-
ical node to design requirements diagrams is shown
in Figure 1. The SysML Requirements diagram al-
lows the requirements relationships to be represented
in various manners. These relationships are briefly
described as follows.
The Derive Requirement Relationship is repre-
sented by the stereotype << deriveReqt >>. It de-
scribes a requirement that was derived from another
requirement. This relationship explicitly shows when
AnApproachforModelingReal-timeRequirementswithSysMLandMARTEStereotypes
71

<<stereotype>>
Requirement
text: "Capturing information of the approaches"
id: "TMFR5.1"
Figure 1: Basic node for SysML requirements diagrams.
a requirement can result in other requirements. The
hierarchyRequirementRelationship describes a re-
quirement that is contained within another require-
ment, which means that the relationship allows re-
lating requirements in different hierarchical levels.
For instance, high-level business requirements may
be gradually broken down into more detailed soft-
ware requirements, forming a hierarchy. This rela-
tionship is represented by a circle with a plus sign in-
side (
L
). Each design element of the model has the
purpose directly or indirectly to satisfy a requirement
of the system. The Satisfy Relationship describes
which design element performs/satisfies a particular
requirement. The Copy Relationship describes a re-
quirement that is a copy of another requirementt. This
relationship is applicable when there is a need in the
modeling of requirements for reusing a particular re-
quirement in another context. The Copy Relationship
is denoted as a dotted arrow pointing from the copy to
the original and the stereotype << copy >>.
The Verify Relationship connects a test case with
the requirement that is verified by this test case. A test
model usually defines a large number of test cases that
test whether requirements are (or are not) properly
implemented in the system. This relationship is de-
noted with a dashed arrow, pointing from the test case
in the direction of a requirement, with the stereotype
<< verify >>. The Refine Relationship specifies
that one model element describes the properties of a
requirement in more detail. For example, a functional
requirement can be refined by one or more use cases.
The Trace Relationship is a relationship between a
requirement and an arbitrary model element. It de-
scribes a general relationship for reasons of traceabil-
ity only. The trace relationship is very general and its
semantics are therefore poor.
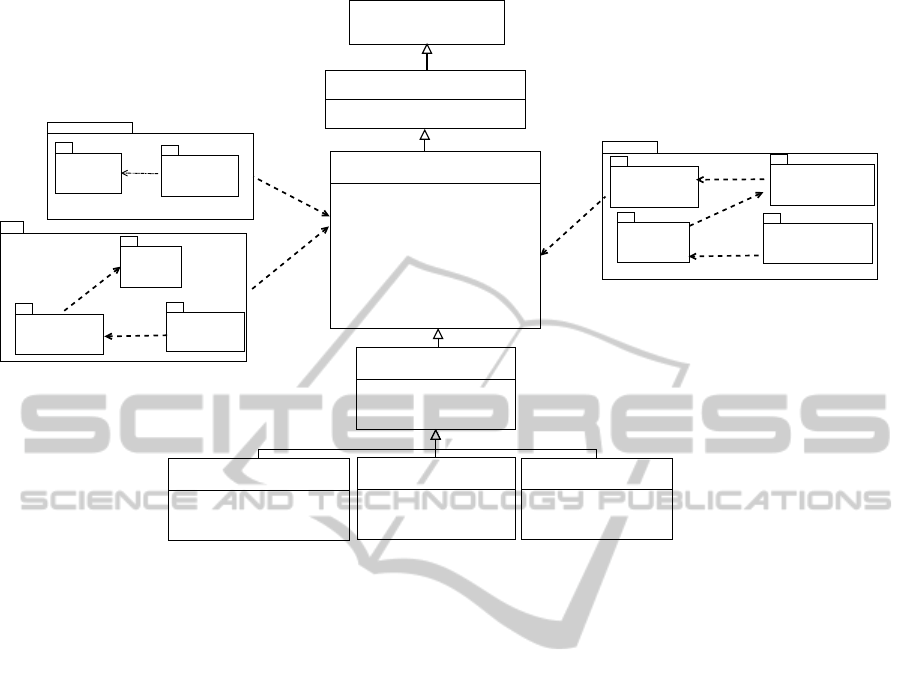
3 PROPOSED METAMODEL
FOR SysML AND MARTE
Based on the concepts presented in the previous sec-
tions that provided the basics of SysML Requirements
diagram and the broad power of expressiveness with
the elements of MARTE, we have created a meta-
model that extends SysML and MARTE and adds
elements from the domain. The metamodel is de-
picted in Figure 2. The SysML Requirements dia-
gram has been extended to allow a new representa-
tion for software requirements. The created attributes
for the extended requirements take into account many
of the specifications contained in the IEEE 830-1998
standard for describing software requirements (IEEE,
1998).
An extended requirement (represented by the
stereotype << ExtRequirement >>) is proposed
in this article, including additional attributes.
In addition, derived from this extended require-
ment, an extended requirement for non-functional
requirements is proposed (represented by <<
ExtRequirementNRF >>) with additional attributes.
Three types of non-functional requirements were pro-
posed in the meta-model, as seen in Figure 2. The
attributes of Requirements are ID, title and text. The
title is unique and briefly indicates the requirement
context. The text attribute is a short explanation of
the requirement.
The new defined attributes for ExtRequirement
are: priority, type, classification, abstractLevel, con-
straint, scenario, creationDate, modificationDate, and
versionNumber. The priority attribute defines the rel-
evance of a requirement in relation to the other, i.e.,
indicating the order in which the requirements should
be addressed. Values are of type String, including for
instance, priority of type “must”, “should”, “could”,
and “won’t”. The type attribute indicates special fea-
tures of a requirement, as for instance, if it sets a sys-
tem’s behavior, if it represents some special state, if
it relates to events, or if it represents timed elements
(clocks). It is important to note that for modeling
with the SysML Requirements diagram with MARTE
stereotypes’, it is indispensable to import packages
from MARTE Foundations that relate to the behav-
ior of an element of the domain (CoreElements pack-
age), with non-functional properties (NFPs) and with
the timing and structure of access time of modeling
elements (package Time). The new classification
attribute describes whether the requirement is func-
tional, non-functionalor if it is specific to the domain.
The level attribute indicates the classification level of
the requirement in the hierarchy. The constraint at-
tribute enables showing requirements that have some
type of restriction. This attribute is of type Boolean.
If it is set to true, the identifier (ID) and the detailed
description of this restriction are contained in a table
of restrictions. Scenario is an attribute of type String
which basically identifies the scenario to which the re-
quirement is related. The attributes creationDate and
modificationDate attributes are of type string and are
related to the creation date of the requirement and the
date on which it was modified. The attribute version-
Number is useful to keeping track of multiple ver-
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
72
MARTE:: Time
MARTE::CoreElements
NFPs
<<MetaClass>>
UML4SysML::Class
BasicTimeModels
MultipleTimeModels
TimeAccesses
TimeRelatedEntities
<<merge>>
<<import>>
<<import>>
<<import>>
Foundations
Causality
<<import>>
NFP_Nature
NFP_Declaration
NFP_Annotation
<<import>>
<<import>>
<<import>>
<<stereotype>>
ExtRequirement
priority: String
type: String
classification: String
abstractLevel: String
constraint: boolean
scenario: string
creationDate: Date
modificationDate: Date
versionNumber: int
<<stereotype>>
Timing
typeTime: String
minResponseTime: float
maxResponseTime: float
<<stereotype>>
ExtRequirementNFR
externalFac: String
cost: String
levelQoS: String
<<stereotype>>
Performance
respTime: float
capacityOp: int
recoveryTime: float
<<stereotype>>
Safety
integrity: String
acessLevel: String
limitedC: boolean
<<stereotype>>
Requirement
text: String
id: String
Figure 2: Metamodel for SysML and MARTE.
sions of the requirement. The last three requirements
are very important for defining an extension of control
to check the integrity of a requirement from changes
performed throughout the specification.
The stereotype ExtRequirementNFR is used to de-
scribe non-functional requirements of software. The
proposed attributes are externalFac, cost, and lev-
elQoS. ExternalFac determines whether a require-
ment is dependent on an external factor in order to be
developed. It is an attribute of type string and gives a
brief description of the dependency factor. The cost
attribute allows for the establishment of criteria of
costs to satisfy a requirement that influences directly
in those decisions concerning the viability of its de-
velopment. Possible values to be assigned include
High, Medium, or Low. The levelQos demonstrates
the level of quality required for the requirement.
The timing type of non-functional requirement re-
lates to the description of time of a software. Its at-
tributes are typeTime, which can assume the values
physical time or logical time, minResponseTime and
maxResponseTime, which are used to describe tim-
ing constraints of a requirement.
The performance type has three attributes. Re-
spTime indicates the maximum response time asso-
ciated with a requirement. Its value allows for the
establishment of which level of performance is to be
associated or is to be guaranteed by the requirement.
The capacityOp attribute indicates the possible num-
ber of simultaneous operations that are allowed in a
given time period (e.g., number of reports generated
for storage, operations per second, and so on). The
attribute recoveryTime describes the maximum time
required for recovery from a failure.
The safety type of non-functional requirement has
attributes integrity (level of integrity that must be
guaranteed), acessLevel (establish the level of access
of stakeholders to a function), and limitedC (enables
the demonstration of whether communication should
be limited between this requirement and other func-
tions/modules of the system.
3.1 MARTE Stereotypes
In most cases, the concepts defined in the domain,
both for the sub-package of MARTE CoreElements,
the sub-package Non-Functional Properties and, the
sub-package Time presented in the last section are
represented in MARTE through a stereotype that ex-
tends a UML modeling element. Thus, the UML ex-
tensions required for supporting the concepts defined
in MARTE and the stereotypes are described in this
section.
The set of extensions used to support Core Ele-
ments (Table 1), NFPs (Table 2) and Time (Table 3)
for UML modeling is organized and addressed ac-
AnApproachforModelingReal-timeRequirementswithSysMLandMARTEStereotypes
73
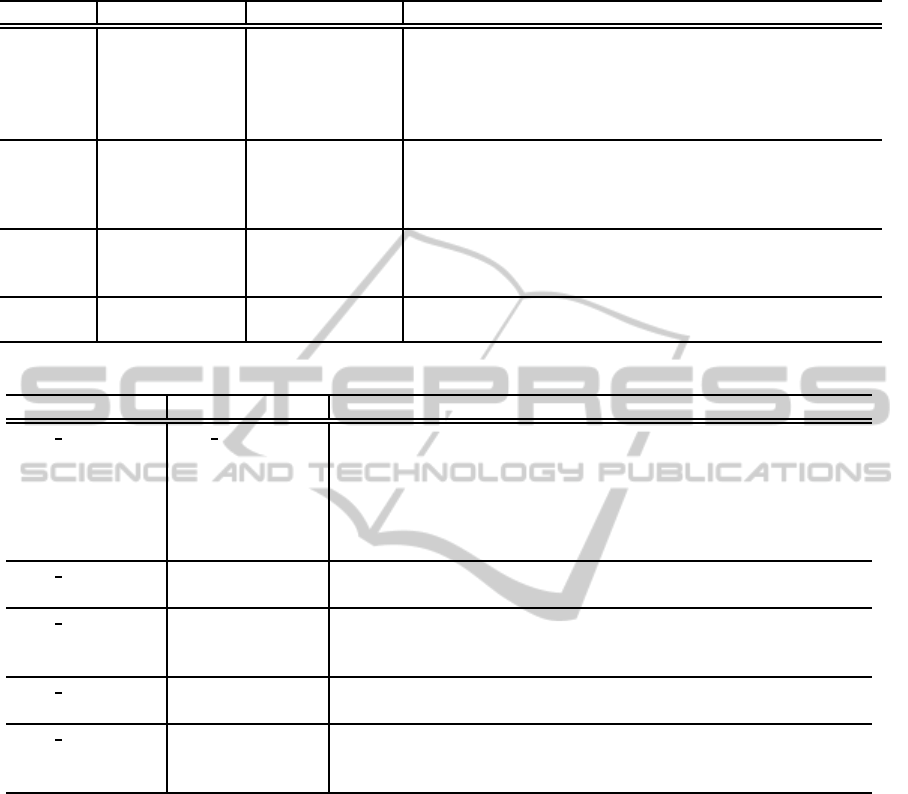
Table 1: Package MARTE Foundations: Stereotypes of CoreElements.
Package Domain Model Stereotype Name Definition
Causality Modal Behavior Configuration Representing the system configuration, can be defined by a
set of elements system assets(for instance, application
components, the components of the platform, hardware
resource), and/or by a set of operating parameters (for
instance, the QoS parameters or functionalparameters).
Causality Modal Behavior Mode Identifies an operating segment within the runtime system
that is characterized for a determined configuration. Work
in a particular way can imply that a set of system entities
are active during that operational fragment.
Causality Modal Behavior ModeBehavior Specifies a set of mutually exclusive modes. Its dynamics
is represented by connection modes by means of Mode
Transsitions.
Causality Modal Behavior ModeTransition Describes the modeled system in switching mode.
ModeTransition may be produced in response to a Trigger.
Table 2: Package MARTE Foundations: Stereotypes of Non-Functional Properties.
Domain Model Stereotype Name Definition
NFP Anotation Nfp Constraint Aims to apply a condition or restriction to the elements modeled.
Specifically, restrictions for NFP support textual expressions to
specify assertions about programming, performance and other
characteristics of embedded systems and their relationship with
others by means of mathematical or logical variables and expres-
sions of time.
NFP Declaration Nfp It is intended to declare, qualify and assign data types extended
to NPFs values.
NFP Declaration NfpType A NfpType is a type whose instances are identified only by
specifications of NFPs values. A NfpType contains specific
attributes to support the modeling of types of NFPs tuples.
NFP Nature Dimension Establishing a relationship between a quantity and a set of base
quantities in a given system quantity.
NFP Nature Unit It is a qualifier of values measured in terms of which magnitudes
of other quantities (which has the same physical dimension) may
be declared.
cording to the application context of domain concepts.
In section 4, only the elements relating to the specifi-
cation requirements for real-time systems are used.
4 CASE STUDY IN TRAFFIC
SYSTEMS CONTROL
4.1 Background on Road Traffic
Control Systems
With the growth in traffic volume, drivers are faced
with many decisions that need to be made in order
to safely proceed on to their designated right of way.
The primary form of control and release of right of
way is through traffic signals. Current control equip-
ment can provide a wide variety of resource capabili-
ties usually organized in fixed time, actuated time and
adaptative time.
In the Fixed-Time Signals the values of the cycle
time, duration and sequence of phases have fixed cal-
culated values based on historical intersection flow.
Any change in programming should be modified me-
chanically in the controller. According to (Roger
et al., 2003), traffic signals that use fixed time are
more affordable to purchase, install and maintain than
actuated time. A deficiency associated with this type
of control is that it is not possible to adjust the fluctu-
ation of traffic throughout the day.
Actuated Traffic Signals vary at the green phase
based on demand from the intersection as measured
in detectors installed in an approach. Actuated traffic
signals are composed of four components: the sen-
sors, the control unit, the traffic lights and the con-
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
74

Table 3: Package MARTE Foundations: Stereotypes of Time.
Domain Model Stereotype Name Definition
TimedRelatedEntities TimedElement Abstract stereotype to be used for associating/
referencing one(s) Clock(s) to one model element.
TimeAccess Clock Introduces a general concept of clock. Represents
an instance of clockType which provides access to
time.
- ClockType A classifier for Clock and is related with time.
Defines attributes to specify the nature of time
(discrete/dense) or system of time(physical/logical).
TimeAccess TimedValueSpecification Specification of a set of instances of the
TimeValue. The property interpretation can force
the interpretation of this value as a duration
or specification of instants. Like a TimedElement
one TimedValueSpecification makes
references to Clock.
TimedRelatedEntities TimedConstraint Represents constraints imposed at any value instant
or in duration value associated with the model
elements linked to clocks.
TimedRelatedEntities ClockConstraint The objective is to impose dependencies between
Clocks or among types of Clocks. Like a
TimedElement one ClockConstraint makes references
to Clock.
TimedRelatedEntities:: TimedEvent Represents events whose occurrences are explicitly
TimedEventsModels
related to Clocks. The attribute repetition refers to
a repetition factor, i.e., the number of occurrences
successive from TimedElement.
TimedRelatedEntities:: TimedProcessing Represents activities where there is knowledge of
TimedProcessingModels
the start time and end or with a known duration
whose instants are explicitly linked to clock.
TimedRelatedEntities:: TimedInstantObservation Denotes an instant in time associated with the occur-
TimedObservation
rence of an event and observed for a given clock.
TimedRelatedEntities:: TimedDurationObservation Denotes some time interval associated with the
TimedObservation
execution, request or occurrence events observed
in one or two clocks. For being specialization of
TimedElement the TimedDurationObservation
makes references to Clock.
- TimedDomain These refer to model elements that can refer to
clocks to express that their behavior depends on
time.
necting cables. These detectors vary in technology,
but the most common are the inductive loop detectors
where a wire loop is installed in the street and is car-
ried with a mild electric current that creates an electric
field.
For an actuated control, there are three parameters
of time: the minimum time for the green phase, the
extension of green phase, and the maximum time for
the green phase. Independent of demand, the green
phase is defined for the minimum time. Depending on
the flow of vehicles, and if the maximum duration of
the green phase is not achieved, then the green phase
time can be extended.
Figure 3: Road Intersections.
This paper focuses on the requirements needed to
provide control capability for actuated intersections
with interconnection of traffic signals, i.e., the oper-
ation of traffic signals in a network. Figure 3 de-
picts a graphical representation for a road with n-
intersections. The set of requirements for the design
AnApproachforModelingReal-timeRequirementswithSysMLandMARTEStereotypes
75

of a coordinated traffic control system is presented in
section 4.2.
4.2 Systems Requirements
In this section, a subset of a list of requirements for
a Road Traffic Management System (RTMS) is pre-
sented, using natural language to be further modeled
and analyzed. The list of requirements presented in
Table 4 is a subset from a document which contains
137 atomic requirements for a RTMS. This subset
of requirements focuses on demonstrating the capa-
bilities of an actuated controller and, also, the func-
tional and non-functional requirements involved with
the synchronization of actuated controllers in a road
network.
4.3 Proposed scenarios
The SysML Use Case diagram is derived without
modifications from UML. Figure 4 presents major
functions for the proposed system and allows for the
representation of external entities exercising influence
in a scenario (which describes a set of requirements).
It is possible to represent the interconnection of a
use case with SysML by using the relationship refine
(Figure 5). Figure 5 shows an example in which a
use case proposed in Figure 5 is refined by a set of
requirements described in the SysML Requirements
diagram. Table 1 demonstrates a proposal for the trac-
ing of all the scenarios described in Figure 4.
The classification proposed in Table 5 improves
the representativeness of the SysML refine relation-
ship. Thus, relationships between requirements are
documentedfrom the early definition of requirements.
The proposed framework/metamodel (whose applica-
tion is shown in 7) covers completely several inherent
features important for real-time systems.
4.4 Modeling Requirements for a Road
Traffic Control System
Figure 7 demonstrates how to apply the SysML Re-
quirements diagram with MARTE stereotypes for
modeling non-functional properties, runtime seman-
tics that are suitable for real-time and embedded sys-
tems, more specifically to the proposed requirements
for a Traffic Control system as specified in Table 4.
In Figure 7, the main requirements and the respective
modeling using the SysML Requirements diagram
extended with MARTE stereotypes are presented.
The requirement TM1 has as type the stereo-
type Mode (of Causality::ModalBehavior). It demon-
strates the necessary logic to represent and control an
operating segment as, for instance, a traffic control
system for all active entities/elements of the opera-
tional fragment. This requirement has a SysML re-
lationship << hierarchy >> with the basic require-
ments for a traffic control system, including require-
ments TM3, TM4, TM5 TM7, TM8, TM9, TM11,
TM15 and TM17. It is worth noting that the mod-
ePreemp requirement (TM7) has a constraint rep-
resented by the << nf p
Constraint >> stereotype
(from NFPs::Nfp Constraint) which applies a tempo-
ral restriction to “ensure the performance” of a crit-
ical requirement. For instance, the priority passage
of emergency vehicles is indicated by the attribute
kind = offered, which demonstrates the value space to
support/restrict this requirement (this modeling could
also be achieved by using VSL annotations from these
restrictions in the model). The requirement TM7 is of
type TimedEvent (of TimedRelatedEntities:: TimedE-
ventsModels) since it relates to an event whose start
and end are not defined as a priori. However, the de-
cision to attend this occurrence is directly linked to a
Clock.
It is worth noting that the requirement TM1
is related to the requirement Chronometric us-
ing the stereotype << TimedElement >> (of
Time::TimedRelatedEntities) which is a spe-
cialization of ClockType, both belonging to
the package Time::TimeAcess. The stereotype
<< TimedElement >> is important in this context,
as it should be used whenever it is necessary to
associate a (few) Clock(s) to a model element (in this
case the TM1 requirement). The TM1 requirement
should be elaborated within time constraints to
ensure several important non-functional requirements
for traffic control systems. Thus, it is necessary to
create a << clock >> Chronometric >> stereotype
enabling the TM1 the access to time structure. The
attributes of this clock are nature, an enumeration
of TimeNatureKind of TimeTypesLibrary library,
which serves to specify the discrete or dense nature
of a time value (in this case the time is discrete),
unitType, a TimeUnitKing dimension imported from
modelLibrary::MARTE
Library::MeasuremenUnits,
which defines the supported unit type (in this case the
unit is ms), and the resolution which expresses the
clock granularity (in this case by default it was set to
1.0).
The control logic of the controller is of type actu-
ated time. The TM5 requirementrelates hierarchically
to TM1. It defines the configuration of the control
system. This is represented through the stereotype
<< Configuration >> ( of CoreElements:: Causal-
ity::ModalBehavior). This stereotype shows the sys-
tem configuration that can be defined by a set of ac-
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
76

Table 4: Requirements for a Road Traffic Control System.
ID Requirement Name
TM1 The system must control the standard of vehicular traffic at the intersection.
TM2
The system must allow synchronization of traffic signals.
TM3
The system should collect all kinds of information of the road approaches in order
to properly evaluate these data.
TM4
The system must allow management of traffic history.
TM5
The system must actuate in response to intersection traffic flow.
TM6
The system must coordinate green time of intersections in a synchronous way.
TM7
The system must have the emergency preemption mode, i.e., preferential
movement of emergency vehicles.
TM8
The system must allow control of intersection in response to manual commands.
TM9
The system must allow control of intersection in response to replace remote commands.
TM10
The system must control the semaphore of the intersections.
TM11
The system of the intersection should be able to interact with the software control panel.
TM12
The system must calculate the delay to the controllers of intersections.
TM13
The system must optimize the flow of traffic.
TM14
The system must set the mode/state flag in response to the current processing of intersection control.
TM15
The system must minimize blockages along the highway.
TM16
The system must efficiently changeplans for liberation of platoons.
TM17
The system must check traffic demand with maximum precision.
TM18
The system must allow for incident management.
TM19
The system must configure green phase time for intersections.
TM20
The system must coordinate the green phase time of the intersections
precisely. With minimum time of 50ms and maximum time of 150ms.
Controlling Traffic
Standard
Operator Traffic Control
emergency vehicle
Maintainer
Synchronizing
Semaphores
Collect
Information
Adaptive Control
<<extends>>
Actuated Control
<<extends>>
Perform of Emergency
Preemption
Control Controller
Manage Incidents
Manage History
Sensor
<<include>>
Traffic Signals
Figure 4: Scenarios for Traffic Control System.
Requirement
use case
<<refine>>
Figure 5: Relationship Refine.
AnApproachforModelingReal-timeRequirementswithSysMLandMARTEStereotypes
77

Synchronizing
Semaphores
<<TimedEvent>>
synchronizationState
text: "Synchronization
of semaphores"
id: TM2
priority: must
type: -
classification: Non Function
abstrationLevel: 3
constraint: -
scenario: Sc4
creationDate: 20.12.12
modificationDate: 10.01.13
versionNumber: 2
externalFac: delay time
cost: high
levelQoS: high
responseTime = 50ms
capacityOp: -
recoveryTime = 100ms
<<stereotype>>
greenSych
text: "Coordinating green time"
id: TM6
priority: must
type: -
classification: Non Functional
abstrationLevel: 3
constraint: false
scenario: Sc4
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
externalFac: time coordinate
cost: high
levelQoS: high
integrity: Medium
acessLevel: Medium
limitedC: false
<<Chronometric>>
greenSych
text: "Coordinating green time"
id: TM20
priority: must
type: -
classification: Non Functional
abstrationLevel: 3
constraint: false
scenario: Sc1, Sc4
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
externalFac: time coordinate
cost: high
levelQoS: high
typeTime: physico
minResponseTime: Medium = 50ms
maxResponseTime = 150ms
<<stereotype>>
miniBlockage
text: "Minimization of"
blockages"
id: TM15
priority: must
type: -
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc1, Sc4
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<refine>>
<<refine>>
<<refine>>
<<refine>>
Figure 6: Synchronizing Semaphores and their requirements.
Table 5: Tracing Scenarios.
Scenario Name Scenario ID Actor Related Requirement ID Related
Controlling Standard Sc1 Operator TM1, TM4, TM10, TM11,
TM12, TM13,TM14, TM15,
TM16, TM19, TM20
Adaptive Control
Sc2 Traffic Signals -
Actuated control Sc3 Traffic Signals TM5
Synchronizing semaphores
Sc4 Traffic Signals TM2, TM6, TM15, TM20
Collect Information
Sc5 Operator, Sensor TM3
Control Controller
Sc6 Maintainer, Traffic Signals TM8, TM9, TM11
Manage Incidents
Sc7 Operator TM18
Manage History
Sc8 Operator TM17
Emergency Preemption
Sc9 Emergency Vehicle, Traffic Signals TM7
tive elements from the system. The type attribute
of requirement TM5 is ModeBehavior (of CoreEle-
ments::Causality::ModalBehavior), because the ac-
tuated control mode is unique to the control system,
i.e., it is the only one considered at the intersections
of this case study.
The requirement TM5 derives from TM10,
which is responsible for controlling the control
plans for signaling the intersections. The sig-
naling plan changes depending on the volume
of road traffic. Thus, through an association
with TM14 with << modeTransition >> stereo-
type (of CoreElements::Causality::ModalBehavior),
the signaling plan transitions to a certain state
of the signals (red, green, yellow, green ex-
panded, and so on) specified at TM14. The re-
quirement TM14 is of type TimeProcessing (of
Time::TimedRelatedEntities::TimedProcessing). This
is interesting for clarifying that the change of states
signaled is an activity where there is great impor-
tance in knowing the time of start and finish for each
state, and thus create strategies to ensure/get higher
performance. The timing restriction for this require-
ment precisely demonstrates that the same process-
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
78

<<hierarchy>>
<<deriveReq>>
<<stereotype>>
controlStandard
text: "Control the standard
of vehicular traffic"
id: TM1
priority: must
type: Mode
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc1
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<Configuration>>
actuatedControl
text: "Control actuated
of the intersection"
id: TM5
priority: must
type: ModeBehavior
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc3
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
In this case, the state’s
uniquecontroller will
be actuated.
<<Clock>>
Chronometric
{nature =discrete, unitType=
ms, resolution=1.0}
<<dimension>>
TimeUnitKing
<<unit>>: s
<<unit>>: tick
<<unit>>: ms
<<unit>>: us
unit: min
unit: hr
+unit: day
<<clockType>>
{nature=TimeNatureKind, unitType=TimeUnitKing}
resolution(read only) = 1.0
currentTime(): Real
<<Clock>>
Logical
{nature =discrete, unitType=
ms, resolution=1.0}
imported from modelLibrary::
MARTE_Library::MeasuremenUnits
<<TimedElement>>
<<TimedElement>>
<<enumeration>>
TimeNatureKind
discrete
dense
imported from TimeTypesLibrary
<<TimedEvent>>
synchronizationState
text: "Synchronization
of semaphores"
id: TM2
priority: must
type: -
classification: Non Function
abstrationLevel: 3
constraint: -
scenario: Sc4
creationDate: 20.12.12
modificationDate: 10.01.13
versionNumber: 2
externalFac: delay time
cost: high
levelQoS: high
responseTime = 50ms
capacityOp: -
recoveryTime = 100ms
<<stereotype>>
demandTraffic
text: "Check traffic
demand"
id: TM17
priority: must
type: -
classification: Non Functional
abstrationLevel: 3
constraint: false
scenario: Sc8
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
externalFac: -
cost: high
levelQoS: high
integrity: high
acessLevel: Medium
limitedC: false
<<deriveReq>>
<<deriveReq>>
<<stereotype>>
greenSych
text: "Coordinating green time"
id: TM6
priority: must
type: -
classification: Non Functional
abstrationLevel: 3
constraint: false
scenario: Sc4
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
externalFac: time coordinate
cost: high
levelQoS: high
integrity: Medium
acessLevel: Medium
limitedC: false
<<stereotype>>
planControl
text: "Control plan"
id: TM10
priority: must
type: Mode
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc1
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<modeTransition>>
<<modeTransition>>
finish processing/changes state
<<stereotype>>
stateFlag
text: "Set the mode/state flag"
id: TM14
priority: must
type: TimeProcessing
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc1
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<deriveReq>>
<<deriveReq>>
<<stereotype>>
informationCollect
text: "Collect information
of the approaches"
id: TM3
priority: should
type: -
classification: Non Functional
abstrationLevel: 2
constraint: false
scenario: Sc5
creationDate: 20.12.12
modificationDate: 10.01.13
versionNumber: 2
externalFac: up to 10GB
cost: low
levelQoS: medium
<<stereotype>>
historyTraf
text: "Management of traffic
history"
id: TM4
priority: must
type: -
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc1
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<stereotype>>
modePreemp
text: "Emergency preemption"
id: TM7
priority: must
type: TimedEvent
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc9
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<stereotype>>
optimizeFlow
text: "Optimization
of the flow"
id: TM13
priority: should
type: -
classification: Non Function
abstrationLevel: 3
constraint: -
scenario: Sc1
creationDate: 20.12.12
modificationDate: 10.01.13
versionNumber: 2
externalFac: delay time
cost: high
levelQoS: high
responseTime = 50ms
capacityOp: -
recoveryTime = 100ms
<<stereotype>>
miniBlockage
text: "Minimization of"
blockages"
id: TM15
priority: must
type: -
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc1, Sc4
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<stereotype>>
efficChange
text: "Efficiently change
plans"
id: TM16
priority: must
type: -
classification: Non Function
abstrationLevel: 3
constraint: -
scenario: Sc1
creationDate: 20.12.12
modificationDate: 10.01.13
versionNumber: 2
externalFac: -
cost: high
levelQoS: high
responseTime = 50ms
capacityOp: *
recoveryTime = 50ms
<<stereotype>>
interactPanel
text: "Interact with
the control panel"
id: TM11
priority: must
type: -
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc1, Sc6
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<stereotype>>
remoteComm
text: "Remote commands"
id: TM9
priority: must
type: -
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc6
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<stereotype>>
manualComm
text: "Manual commands"
id: TM8
priority: must
type: -
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc6
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<nfp_Constraint>>
{kind} = offered
{minTime = 50ms and maxTime =150ms}
<<nfp_Constraint>>
{kind} = required
{maxTime =150ms}
<<Chronometric>>
timeGreen
text: "Set time green"
id: TM19
priority: must
type: TimeEvent
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc1
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<Chronometric>>
gapCalc
text: "Calculating the delayed"
id: TM12
priority: must
type: TimeProcessing
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc1
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<Chronometric>>
greenSych
text: "Coordinating green time"
id: TM20
priority: must
type: TimeProcessing
classification: Non Functional
abstrationLevel: 3
constraint: false
scenario: Sc1, Sc4
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
externalFac: time coordinate
cost: high
levelQoS: high
typeTime: physico
minResponseTime: Medium = 50ms
maxResponseTime = 150ms
<<stereotype>>
manageInc
text: "Management Incident"
id: TM18
priority: should
type: -
classification: Functional
abstrationLevel: 1
constraint: false
scenario: Sc7
creationDate: 01.10.12
modificationDate: 02.01.13
versionNumber: 3
<<deriveReq>>
<<deriveReq>>
Figure 7: Final Model.
ing must have a minimum quantitative level (specified
with kind = required) to run with at most 150ms.
Requirements TM19 and TM20 are stereotyped
with << Chronometric >> characterizing them as
requirements that exist in a physical time, and are of
type TimedEvent (of TimedRelatedEntities:: TimedE-
ventsModels), due to the fact that they are linked to
TM14 (by hierarchy relationship of SysML) and rep-
resent specific Events of change of the flag state. Its
type is TimedEvent, whose occurrences are directly
linked to a Clock (in this case Clock Chronometric).
The requirement TM12, of type TimeProcessing (be-
cause its processing time instant refers explicitly to
clocks), refers to a structure of physical time. It is
through this requirement that the delay (delay/offset)
is acknowledged between a controller of an intersec-
tion and the subsequent intersections.
As observed, much of this specification refers to
the time structure access through physical clocks.
MARTE also enables logical time modeling. For
this reason, a structure of time that specializes <<
clockType >> and sets the logical time necessary to
demonstrate that the TM2 requirement relates to syn-
chronizing semaphores is created at an intersection
network. It does not carry a long pre-signed physi-
cal time; it can only be seen as reading and detecting
the flow of the processing approaches, the setting of
the control plan strategy, and so on. Therefore, there
is an explicit physical time and it depends on the pro-
cessing logic of several other elements.
AnApproachforModelingReal-timeRequirementswithSysMLandMARTEStereotypes
79

5 DISCUSSION
There are two works that combine SyML and
MARTE profiles, and which can be compared to this
work. In the works of (Quadri et al., 2012a) and
(Quadri et al., 2012b), the project MADES is pre-
sented. This methodology was developed after cur-
rent practices for developing embedded real-time sys-
tems are applied in the field of aviation industries and
surveillance. A major contribution relates to the pre-
sentation of a complete methodology based on the
combined use of SysML and MARTE for design,
validation, simulation and automatic code generation
while integrating aspects such as component reuse.
The work of (Gomez et al., 2012) proposes a
multi-view approach based on SysML and MARTE
for modeling views of energy consumption and their
relationships with other functional/non-functional
and structural/behavioral elements. In this approach,
each domain can be treated separately in different
views while maintaining strong connections towards
other views. To this end, the MARTE profile is used
to define the model of hardware architecture. In addi-
tion, the MARTE package of Non-Functional Proper-
ties is used for setting properties such as power, volt-
age and frequency. SysML is used to specify, through
the parametric model, the equations that define math-
ematical relationships between non-functional inter-
ests of different views. The approach proposed in
MADES (Quadri et al., 2012a) differs from the pro-
posal of this study, first by contemplating a compre-
hensive methodology for developing embedded sys-
tems and real-time. Second, in this methodology by
joining a consistent set of diagrams MADES (exten-
sion of the diagrams belonging to the profiles related
to the project) for specification of system require-
ments, initial behavior specification, functional speci-
fication, refined functional specification, specification
of hardware / software, detailed specification of hard-
ware / software and specification of allocation.
According to the extensive bibliographic research
conducted until the present moment, there are stud-
ies in scientific literature which focuses on demon-
strating the applicability of UML and SysML with
MARTE stereotypes for documentation, classification
and modeling of software requirements for real-time
systems. Despite the existence of several approaches
for modeling software requirements and for model-
ing specific requirements of real-time, as described in
previous sections, requirements engineering for real-
time systems still lacks representative models that are
expressive, complete and correct. As described by
(Espinoza et al., 2009), despite an increasing number
of profiles being built in many areas for the design
of some types of systems, a single profile may not be
adequate to cover all aspects required as, for example,
the multidisciplinary aspects in the field of real-time
systems.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The main objective of the approach proposed in this
article is to demonstrate the application of SysML Re-
quirements diagram with MARTE stereotypes, which
enables the modeling of individual software require-
ments for real-time systems. The focus is to create
an approach for modeling specific software require-
ments which allow the representation of the neces-
sary features of real-time systems (based on research
demonstrating the specific requirements) and, also,
timing requirements and performance requirements.
As previously reported, the SysML Requirements di-
agram shows explicitly the various types of relation-
ships between different requirements, increasing the
spectrum of understanding and defining the require-
ments of a real-time system. However, the SysML
profile by itself does not guarantee the representation
of temporal, behavioral, and performance require-
ments, nor provides elements for explicit representa-
tion of system configurations. The MARTE profile
provides key resources to specify non-functional re-
quirements for real-time systems, generally time re-
quirements. In this paper, these features were made
explicit by means of classification and use of MARTE
stereotypes. Thus, the combination of these profiles
in the presented approach demonstrated the complete
and expressive nature of the representation of various
requirements. SysML contributes with constructors
to define requirements and their relationships. Be-
sides, MARTE completes the precision of the sce-
nario with well-formed non-functional annotations.
The concepts of SysML and MARTE, articulated in
the SysML Requirements diagram are complemen-
tary covering many of the purposes of specifying re-
quirements for real-time systems.
As each requirement is described separately, the
complexity of changes is minimized, since a change
in any requirement can be made completely and con-
sistently maintaining the structure and style of the
set of requirements. Expressing each requirement
separately is highly desirable. This feature is ad-
dressed in this article by modeling requirements us-
ing the SysML Requirements diagram, and by orga-
nizing the relationships between requirements. The
MARTE profile provides, in the proposed representa-
tion, a clear description of the various relevant aspects
of requirements definition of real-time systems, as for
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
80

instance, temporal aspects and constraints.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank CNPq (www.cnpq.br)
and FAPEMIG (www.fapemig.br - EDITAL
FAPEMIG 01/2011, Grant APQ-01589-11) for
the financial support.
REFERENCES
Belategi, L., Sagardui, G., and Etxeberria, L. (2010). Marte
mechanisms to model variability when analyzing em-
bedded software product lines. In 14th Proceedings
of the International Conference on Software Product
Lines, pages 466 – 470.
Bennett, A. J. and Field, A. J. (2004). Performance Engi-
neering with the UML Profile for Schedulability, Per-
formance and Time: a Case Study. In 12th Annual
International Symposium on the IEEE Computer So-
ciety’s, pages 67–75.
Bianco, V. D., Lavazza, L., and Mauri, M. (2002). A for-
malization of uml statecharts for real-time software
modeling. In Integrate Design and Process Technoly
(IDPT), pages 1 – 8.
Espinoza, H., Cancila, D., Selic, B., and Gerard, S. (2009).
Challenges in combining sysml and marte for model -
based design of embedded systems. In 5th European
Conference (ECMDA-FA), pages 98 – 113.
Gomez, C., DeAntoni, J., and Mallet, F. (2012). Multi-view
power modeling based on uml, marte and sysml. In
EUROMICRO-SEAA, pages 17 – 20.
Heisel, M. and Cote, I. (2011). A UML Profile and Tool
Support for Evolutionary Requirements Engineering.
In 15th Software Maintenance and Reengineering,
pages 161–179.
Helming, J., Schneider, F., Haeger, M., Kaminski, C.,
Bruegge, B., and Berenbach, B. (2010). Towards a
unified requirements modeling language. In 15th In-
ternational Workshop on Requirements Engineering
Visualization (REV), pages 53–57.
IEEE (1998). IEEE Recommended Practice for Software
Requirements Specifications.
Iqbal, M. Z., Arcuri, A., and Briand, L. (2011). Code Gener-
ation from UML/MARTE/OCL Environment Models
to Support Automated System Testing of Real-Time
Embedded Software. Technical Report 2011-04, Ver-
sion 2, Simula Research Laboratory.
Iqbal, M. Z. Z., Ali, S., and Yue, T. ad Briand, L. C. (2012).
Experiences of Applying UML/MARTE on Three In-
dustrial Projects. In 15th Model Driven Engineering
Languages and Systems (MoDELS), pages 642 – 658.
Kumar, B. and Jasperneite, J. (2010). Uml profiles for mod-
eling real-time communication protocols. Journal of
Object Technology, 9:178–198.
OMG (2005). UML Profile for Schedulability, Perfor-
mance, and Time, Version 1.1. Technical report,
OMG.
OMG (2011a). UML Profile for MARTE: Modeling and
Analysis of Real-time Embedded Systems Version,
1.1. Technical report, OMG.
OMG, M. (2011b). Modeling and Analysis of Real-Time
and Embedded Systems (MARTE)- version 1.1. Tech-
nical Report Formal/2011-06-02.
OMG, S. (2010). Systems Modeling Language (SysML)
Specification - version 1.1.
OMG, U. (2011c). Linguagem de Modelagem Unificada -
version 2.3. verso 2.3.
Quadri, I. R., Brosse, E., Gray, I., Matragkas, N. D., In-
drusiak, L. S., Rossi, M., and Bagnato, A. Sadovykh,
A. (2012a). MADES FP7 EU project: Effective high
level SysML/MARTE methodology for real-time and
embedded avionics systems. In 7th Int. Workshop
on Reconfigurable Communication-centric Systems-
on-Chip (ReCoSoC), pages 1 – 8.
Quadri, I. R., Soares, L., Gray, I., Indrusiak, L. S., and
Bagnato, A. Sadovykh, A. (2012b). MADES: A
SysML/MARTE high level methodology for real-time
and embedded systems. In 7th Int. Conf. on High-
Performance and Embedded Architectures and Com-
pilers, pages 1 – 2.
Roger, P. R., Elena, S. P., and William, R. M. (2003). Traffic
Engineering. Prentice Hall, New Jersey, NJ, USA, 3
edition.
Shousha, M., Briand, L. C., and Labiche, Y. (2012). A
uml/marte model analysis method for uncovering sce-
narios leading to starvation and deadlocks in concur-
rent systems. IEEE Transactions on Software Engi-
neering, 38(2):354–374.
Silvestre, E. A. and Soares, M. S. Multiple view archi-
tecture model for distributed real-time systems using
marte.
Xu, J., Li, T., Xie, Z., and Gao, T. (2011). Use cases and
feedback in functional requirements analysis. In Infor-
mation Technology, Computer Engineering and Man-
agement Sciences (ICM), volume 2, pages 54–57.
Xu, J., Woodside, M., and Petriu, D. (2003). Performance
analysis of a software design using the uml profile for
schedulability, performance and time. In Int. Conf. on
Modelling Techniques and Tools for Computer Perfor-
mance Evaluation, pages 291 – 310.
AnApproachforModelingReal-timeRequirementswithSysMLandMARTEStereotypes
81
