
Flexinterface: A Framework to Provide Flexible Mobile Phone User
Interfaces
Addressing the Elderly Diversity
Vinícius P. Gonçalves
1
, Sibelius Seraphini
1
, Vânia P. A. Neris
2
and Jó Ueyama
1
1
Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of São Paulo, 13566-590, São Carlos-SP, Brazil
2
Department of Computing, Federal University of São Carlos, 13565-905, São Carlos-SP, Brazil
Keywords: Tailorable Interfaces, Flexibility, Cell Phone, Elderly, Middleware, Framework.
Abstract: This paper outlines our work to provide flexible smartphone interfaces targeting the elderly. Our research
employs the Lancaster OpenCom middleware approach running on Android mobile phones. In this paper we
present FlexInterface, an approach for a reconfigurable interface for elderly people and show how our
model can help elderly people while interacting with mobile phones. We claim that flexible interfaces
supports interaction in a more universal manner and in this paper we consider the elderly population. We
carried out an assessment with the elderly to verify the feasibility of the proposal. The results suggest that
there was a reduction in interaction time with the use of flexible interfaces and an increase in user
satisfaction.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to the United Nations, there are currently
893 million people over the age of 60 in the world
(United Nations, 2010). This number will nearly
triple to 2.4 billion by the middle of this century.
"All countries - rich or poor, industrialized or
developing - are seeing their populations age in one
degree or another ", states the document (United
Nations, 2010), adding that the elderly population
growth will be faster than in other sectors of the
population at least by the year 2050.
According to Nielsen (Nielsen, 2011), many
elderly people in industrialized countries are active.
Although they are usually retired, they lead a
dynamic life and often have great interest in modern
technologies, as for instance smartphones. This
study also shows that 18% of the elderly use
smartphones, and that there was a 6% increase in the
purchase of these devices between 2010 and 2011.
However, many of today’s design solutions for
mobile phones target younger audiences, not
including the elderly population (Czaja and Lee,
2007); (Gonçalves et al., 2011); (Wood et al., 2005),
which has specific characteristics. Studies show a
negative association between age and interaction
skills (Hellman, 2007) and a significant reduction in
the number of people over 45 that benefits from
today’s Information and Communication
Technologies (Minister of Industry, 2005).
Thus, it is necessary to provide interfaces that
meet the highest possible number of elderly users,
regardless of their sensory, physical, cognitive and
emotional abilities. One way is to propose user
interfaces that allow changes in their behavior
during the interaction, giving each user the
possibility to adapt the interface according to their
preferences, needs and intended use (Neris and
Baranauskas, 2012); (Gonçalves et al., 2010). In this
context, flexibility refers to changes regarding the
presentation of the interface elements, namely
changes in color, size and window position, as well
as changes in the order of the interaction actions.
It should be highlighted that although there are
some studies in the literature regarding the flexible
design applications on mobile phones for the elderly
(Gonçalves et al., 2011); (Olwal et al., 2011);
(Gonçalves et al., 2012), little is found on the
implementation of these proposals. Therefore, this
paper presents the FlexInterface, a framework that
supports the development of tailored interface
design can determine user profile based on the
behavior pattern. Enabling to adapt the application
to the user needs during interaction.
143
P. Gonçalves V., Seraphini S., P. A. Neris V. and Ueyama J..
Flexinterface: A Framework to Provide Flexible Mobile Phone User Interfaces - Addressing the Elderly Diversity.
DOI: 10.5220/0004451401430150
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2013), pages 143-150
ISBN: 978-989-8565-61-7
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

In order to verify the feasibility of this proposal
given the various requirements of the elderly
population (Gonçalves et al., 2011), an assessment
was conducted with elderly people aged between 60
and 84. The sample group included persons with
little education and higher education and different
backgrounds regarding the use of technology.
This paper is organized as follows: Section 2
presents the OpenCom, an adaptive middleware
which was used as the basis for developing
FlexInterface; Section 3 presents the FlexInterface
approach and evaluates the overload incurred by
FlexInterface on a smartphone; Section 4 describes
the design of flexible interfaces on mobile phones
intended for the elderly and a case study of
FlexInterface with older people and compares the
results of a flexible approach with a non-flexible
one. Section 5 presents the benefits of our approach
and Section 6 presents the conclusion and suggests
future works.
2 OpenCom MIDDLEWARE
APPROACH
FOR CONSTRUCTING
FLEXIBLE INTERFACES
OpenCom (Ueyama et al., 2009) offers advantages
over other middleware because it focuses on creating
flexible systems in environments with scarce
resources (e.g., low memory). It can also be used in
heterogeneous environments, as will be discussed in
more detail below. Other middleware, such as the
Common Object Request Broker Architecture
(CORBA), are not suitable to be used on mobile
devices due to their robustness (Siegel, 1998).
Moreover, CORBA is a software layer that requires
memory resources that the platform of a cell phone
does not have.
Another known approach is ReMMoC (Grace et
al., 2003), which is a reflective middleware platform
that dynamically adapts to support SLP (Veizades et
al., 1997), and allows search and interaction with
web services in a mobile environment. Thus, a
mobile application can interact with a web service
that makes use of the UPnP protocol (Microsoft
Corporation, 2000), without considering how the
implementation should be done.
Thus, as the scope of this research addresses
middleware solutions for adaptive interfaces on
mobile devices, a Middleware approach supported
on OpenCom was defined, because this software
layer supports dynamic adaptation, since the
application components can be reconfigured in
running time. Therefore, depending on the needs of
the system, the middleware adapts to the dynamic
characteristics of the execution environment
(Ueyama et al., 2009).
2.1 OpenCom Overview
OpenCom, besides being open source, has a flexible
and extensible architecture, independent of
language. It is based on a microkernel, where the
features are incremented upon request (Ueyama et
al., 2009).
OpenCom is a reflective and generic middleware
that was developed at the University of Lancaster
(Coulson et al., 2008), and it takes into account
some characteristics, as outlined below:
Domain Independence: a general-purpose
systems technology should provide only general and
fundamental functions, which are independent of the
needs of any particular domain. Thus, it is important
that OpenCom builds generic software belonging to
various domains such as: operating systems,
middleware and embedded systems.
Device Independence: OpenCom is generic
enough and allows creating software for a wide
variety of platforms, such as PCs, set-top boxes and
mobile devices with scarce resources – such as
wireless sensor networks and mobile phones. This is
achieved due to the use of microkernel and the
possibility to add components with particular
functions for each device.
Low Overhead: Due to the limited resources of
some devices (for example: cell phones), it is
necessary that the Kernel of OpenCom not only uses
very little memory but also the minimum amount of
other resources, such as CPU.
The components that provide the functions are
responsible for performing the functions for which
the application was developed. In a calculator, for
example, the addition operation is a component,
while the subtraction operation is another
component. One component is not needed for the
other to function, which allows the component that
is not in use to be eradicated from the memory.
The components interact with other components
in the capsule exclusively through interaction points,
known as: “interfaces” and “receptacles” (Ueyama
et al., 2009). Interfaces are service units provided by
the components (Coulson et al., 2008). The
components can support any number of interfaces.
According to Coulson (Coulson et al., 2008), the
receptacles are “required interfaces” that make
explicit the dependencies of one component to other
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
144

components. The components can support any
number of receptacles. Therefore, they are
fundamental to support of other implemented
modules and the construction of component-based
software approach.
An OpenCom based application works on any
device or operating system, provided it has the
kernel of OpenCom ported to this device. Moreover,
to ensure adaptability, the systems require the
characteristics of each user, which can be acquired
in various ways, from the registration data to the
user navigation observed on the network system.
For this research the development of systems that
adapt to various needs is highlighted; meeting the
requests of different users, different devices and
changes in environmental conditions. Given the
aforementioned considerations, this study did not
consider in its implementation only average needs,
but primarily the differences, as described in the
next section.
3 IMPLEMENTATIONS ISSUES
Using the set of rules that were defined in Section 3,
for the design of flexible interfaces for elderly users,
we developed a functional prototype which provides
the interfaces that can adapt to the older public
during run-time. The FlexInterface is a framework
that assists in implementing flexible interfaces and
was developed by means of Adaptive Middleware
OpenCom. With the aid of this resource, it is
possible to have mobile phone interfaces that adapt
to different older- user profiles.
3.1 The FlexInterface Approach
This research adopts a generic approach to build
adaptive applications in mobile devices. Thus,
(Ueyama et al., 2009) it shows that run-time
reconfiguration is a key feature to handle the
heterogeneous hardware that is inherent in mobile
devices.
Thus, by defining the design of flexible
interfaces so that they meet the many interaction
requirements of the elderly with mobile phones
(Gonçalves et al., 2011), it was possible to develop a
software layer called FlexInterface based on the
OpenCom component model (Ueyama et al., 2009).
FlexInterface is generic and has a flexible and
extensible architecture that is not dependent on
language. It is based on a microkernel, where the
functions are incremented upon request. In this
context, there is FlexComp, which is a generic and
reflective component of FlexInterface that has two
receptacles called FlowScreen and ProfileChecker,
as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: ElderlyFlex Component and its receptacles.
The FlowScreen component is responsible for
storing the sequence of actions/screens that a given
older user profile possesses, so that it can carry out a
task in the device. Thus, with the FlowScreen it is
possible, for example, to determine a sequence of
specific screens, for older adults with a low level of
education, to record a contact in the cell phone’s
agenda (Example: flow of actions / screens: Record
Name > Record Phone > Save Contact).
Additionally, the ProfileChecker component
receives the user’s interaction data and on the basis
of this information, is able to set the most
appropriate type of profile, and then determine
whether it is necessary to reconfigure the
FlexInterface components.
3.2 FlexInterface for Older Users
FlexInterface is a framework supported by the
development of adaptive interface designs that
allows the application to adapt to the needs of the
user during his interaction with it.
With regard to the many requirements which
emerged in the case study with the elderly and which
led to a set of rules being defined for behavior-
based adjustable interfaces (Gonçalves et al., 2011),
two different profiles of elderly people were
selected: seniors with up to fourth grade schooling
(low education) and those with education beyond the
fourth grade (high education).
Given the range of requirements, we used
FlexInterface to provide adaptability to the
interfaces. This meant that, as well as a change of
actions/screen flow and of the interface elements,
changes in the structure and size of the keyboard
were also necessary. In view of this, the ElderlyFlex
has been created, which is an extension of the
FlexComp of the FlexInterface. This extension
includes a new receptacle that is able to load the
Flexinterface:AFrameworktoProvideFlexibleMobilePhoneUserInterfaces-AddressingtheElderlyDiversity
145

keyboard component and is suitable for the profile
determined by the ProfileChecker, as shown in
Figure 3.
Thus, the keyboard is represented by three
components to meet the requirements of elderly
users: a) the default, b) for the elderly with low
education and c) for the elderly with high education
(DefaultKeyboard, LowEducationKeyboard and
HighEducationKeyboard, respectively). Depending
on how the user interacts with the application, the
ProfilerChecker sets the most suitable profile at
runtime and enables the ElderlyFlex to connect to
the keyboard component that is most suited to the
profile, as shown in Figure 2.
(a) (b)
Figure 2: (a) Default Keyboard; (b) Adapted keyboard.
To determine which keyboard is best suited for each
user profile Elderly collected the data from user
input. For each keystroke, the following was
collected:
Given character
Elapsed time (ms) from previous tap
Error (when the user deletes a character)
With regard to the FlexInterface architecture, the
components were developed that require the screen
flow called FlowScreen. For this particular scenario,
it was possible to explore the reconfiguration of the
actions/screen flow. In this case, the ProfileChecker
defines the interaction profile and analyzes the use
of a new layout with a different action flow that can
be used for the interface at the appropriate time.
Thus, owing to the change in the user´s standard
interaction, in the scenario in which the default
screens/actions flow component (DefaultFlow) is
loaded the ProfilerChecker can,for example, set the
low education as the most appropriate default for
this older user. As a result, the default flow
component will be disconnected and destroyed,
freeing up the memory; following this, the
screens/actions flow component for lower education
(LowEducationFlow) will be created and connected
to ElderlyFlex, making the application suitable for
the new interaction default.
It should be noted that when the screens/actions
flow reconfiguration is added, the screens of each
flow establish the interface layout formatting, the
position of the keys, the colors and the voice access,
by strictly adhering to the rules defined by
(Gonçalves et al., 2011) and using the PLuRaL
framework.
Figure 3: Our FlexInterface Components along with implemented Plugable Extensions.
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
146

4 FLEXIBLE USER INTERFACE
DESIGN FOR THE ELDERLY
PEOPLE
The first results of this research report the outcomes
of a case study with older users, in order to support
the formalization of a flexible interface design for
mobile phones to meet the interaction requirements
of the elderly public (Gonçalves et al., 2011);
(Gonçalves et al., 2011). The case study analyzed
the application of a PLuRaL (Neris and
Baranauskas, 2010) framework for the design of
flexible interfaces and older users interacting with
cell phones were observed.
This framework is organized in three pillars. The
first one is to clarify the differences among the
potential users, devices and environments in which
the system can be used. Therefore, this step is to
clarify the problem and identify possible solutions.
The second pillar is the formalization of functional
requirements, which is constructed upon a consistent
view of the domain and that includes rules that
oversee the users’ behavior. Finally, the third pillar
addresses an approach that defines the design of
flexible interfaces through the formalization of
standards for the tailored behavior of the system
(Neris and Baranauskas, 2012).
Considering an approach that emphasizes the
Universal Design (Connell et al., 1997), it is
important to design systems that allow access to
knowledge and information, without physical and
social segregation and also that makes sense to the
largest possible number of users according to their
different sensory, physical, cognitive and emotional
abilities. Thus, it is necessary to approach the elderly
users and understand their peculiarities and
interaction requirements in order to generate tailored
interfaces that meet the preferences and needs of this
target audience.
Therefore, unlike conventional applications, the
development of a tailor-made system requires
designers to consider in their interfaces the different
potential uses, including the progress of users and
their experience with technology.
In order to meet the many interaction
requirements of the elderly public in a flexible
approach that is aligned with the Universal Design
principles (Connell et al., 1997), this paper adopted
the PLuRaL as a reference to guide the design
process and OpenCom to support the
implementation of these flexible interfaces.
However, perceiving that the literature emphasizes
the interaction problems faced by elderly users and
brings little on the various requirements of this
population of users, a practical observation activity
was performed, to learn more about the interaction
diversity of elderly users (Gonçalves et al., 2011).
The observation of the elderly corroborated with
the characterization of the public in question, which
guided and enriched the formal interaction
requirements with mobile phones in six different
aspects, starting with those regarding the physical
aspect of the device, up to the impact of this
interaction with the real world and the adjustable
behavior of a cellular system to meet the interaction
requirements of the elderly (Gonçalves et al., 2011).
In order to verify the FlexInterface proposal, a
practical new observation activity was performed
with a group of eight elderly people aged 60 and 84,
schooling ranging from no education up to higher
education (doctorate) and different experiences with
the use of technology. Accordingly, the next
subsections describe the planning and execution and
formalizes some results derived from the
observation.
4.1 Planning
Hypothesis: based on the different interaction
requirements of the elderly with cell phones, we
believe it makes sense to develop computing
solutions that address the existence of specific
situations, taking into consideration the standards
defined by (Gonçalves et al., 2011) for the tailored
behavior of the interfaces.
Purpose of the Case Study: observe and analyze
elderly user interaction with smart phone flexible
interfaces (smartphones) and verify if there is an
interaction improvement, using as a parameter the
practice carried out by (Gonçalves et al., 2011).
Methodology Applied: in order to analyze the
elderly user interaction using mobile phone flexible
interfaces, a senior user group was invited to
participate in a practice using cell phones. The
purpose of the activity was for the users to save a
contact in the cell’s phonebook and then place a call.
With the data obtained in the observation, it was
possible to see whether FlexInterface had facilitated
the interaction.
Support Material: To conduct the case study, a Term
of Consent, a Profile Survey Questionnaire and a
Participant Observation Form were prepared. The
Term of Consent elucidated the participants
regarding the research objective, the voluntary
participation and its scientific nature. The Profile
Questionnaire Survey had social and cultural
questions that allowed profiling these elderly users.
Flexinterface:AFrameworktoProvideFlexibleMobilePhoneUserInterfaces-AddressingtheElderlyDiversity
147

The Participant Observation Form was designed to
help observe the user during his interaction with the
cell phone. In addition, besides making use of the
observation form, the participants were also being
filmed, so that all the details of the study could be
analyzed.
Devices used: The elderly people were organized
into pairs and during each individual’s interaction
the pair received a Samsung Galaxy 5 with Android
cell phone (smartphone) with OS version 2.2. The
cell phone had the battery charged and with prepaid
credits to make calls.
4.2 Execution
The observation practice of the elderly interacting
with the cell phones took place in a Reference
Center for Social Assistance (CRAS). These users
are part of a group that performs physical activities
intended for seniors, such as dance and theater. In
parallel to these activities, eight people were invited
to participate in some interaction tasks with the cell
phones, as described below.
First, the users were profiled. Furthermore, users
who did not have schooling, or never used cell
phones, or just used them to answer calls could be
identified. However, users with higher or secondary
education besides making calls, also send messages,
take pictures, edit contacts and play on their phones.
It should also be noted that there was a user who had
Alzheimer’s, which according to the teacher of the
group, was in an advanced stage.
For this application scenario a concept test that
allowed adapting the interface to two user profiles
was considered, defined by (Gonçalves et al., 2011):
the elderly with low education (studied up to fourth
grade), and educated elderly (studied beyond the
fourth grade). It was correlated that the low
education profile was characterized by having poor
mobile phone experience.
The participants worked in pairs and each
individual had a cell phone. The users profiles are as
described in Table 1. During the test, the pair sat
side by side during the cell phone interaction. Also,
these users were shown a paper that had the name
and phone number of a person they had to save in
the cell’s phonebook and then call the number in
question.
While the users performed the task with the cell
phone, the researchers conducting the case study
filled out an observation form with questions such
as: Needed help to start the task? The screen size is
adequate for the items?
The elderly were also told that, if necessary, they
could help or ask for help from their partner. The
number that was dialed was a landline number,
which went to the answering machine, which
repeated a message of thanks for their participation.
To define the pairs, an analysis of the profiles
was performed that took into account age and
education.
Table 1: Users profiles.
Pair Users Age
Education
level
Cell phone
usage
1 1, 2 81, 84
Less than 4
year
Never
2 3, 4 66, 60
Less than 4
year
Rarely
3 5, 6 60, 62
More than
12 years
Daily
4 7, 8 65, 69
Less than 4
year
Rarely
Therefore, people with similar ages and education
levels were grouped together. After completing the
task, the authors performed a discussion session with
the pair, raising issues related to flexibility, the
requirements met and the difficulties encountered
during the cell phone interaction.
4.3 Observation Results
In this research approach it is important to
emphasize that the evaluation was done at two
different times and with users of similar profiles.
Thus, the first evaluation focused on supporting the
requirements gathered for the different elderly
public and enable to evaluate the interaction time
and user satisfaction in the commercial solution
available in the cell phone used, that is with no
flexibility. This first assessment is described in a
previous work (Gonçalves et al., 2011). The second
assessment verified the quality of flexible solutions
for the elderly public, reported in this paper.
Taking into account the two practices conducted
with elderly users interacting with smartphones,
comparisons between the solutions presented could
be established: interaction with flexibility and with
no flexibility.
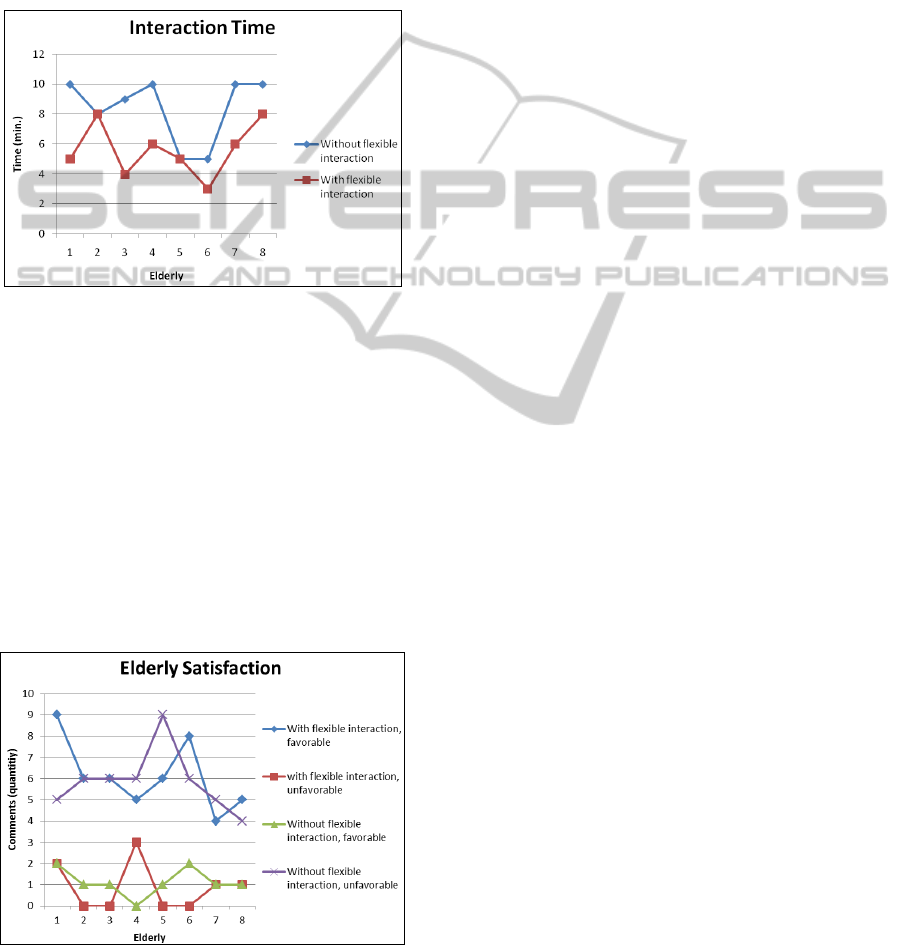
Therefore, from the observation, it was found
that there is a reduction in the time to complete a
task, in the flexible interfaces, when compared to the
interaction time of the non-flexible proposal, as seen
in Figure 4.
In line with the aforementioned, it was perceived
that some of the Pair2 and Pair4 users declared: “I
rather hear the voice than having to type.”; “I loved
talking to the cell phone. It talked to me!” and
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
148
“Telling the phone what it has to do is much easier.
Is this phone for sale?”
Other users, those with low education,
mentioned that the polychromatic interfaces
facilitated their interaction with the device: “You
can see that button well. I loved the color green!”
Unlike what a user that has a doctorate declared:
“Having the color gray does not affect the task.”
This fact corroborates the survey conducted by
(Gonçalves et al., 2011).
Figure 4: Interaction time.
Moreover, it is noteworthy for this survey the
user satisfaction regarding the solutions presented in
the assessment. Thus, it was possible to verify the
satisfaction of these users, represented in the graph
in Figure, through a survey that took into account
favorable and unfavorable comments concerning the
proposals. Therefore, comments like: “The cell
phone vibrated right after I typed in the name. That
was good!”, highlighted by a user of Pair1,
considered as a favorable comment. However, for
comments like the one by a member of the Pair2: “I
click on the ‘A’ and an ‘S’ appears; the key is too
small”, was considered as a negative comment.
Figure 5: Graph showing elderly satisfaction.
Regarding the sequence of actions of a task, it
was observed that those with low education had a
greater ease in performing the task and some of
them, as for example, in the Pair4 pointed out: “I
found the screens to save the name so easy and
beautiful. My son’s cell phone isn’t like that!”
With the experiments with the elderly it was
possible to infer that the use of FlexInterface in
implementing the standards defined by (Gonçalves
et al., 2011) largely met the needs and preferences of
older users in the use of mobile phones.
5 BENEFITS OF OUR
APPROACH
We present the potential benefits of adopting a
generic approach to adaptive interfaces in the field
of smartphones.
Adaptability and Extensibility. The use of adaptive
interfaces allows to modify the interface according to
the individual needs of each user. The generic approach
of FlexInterface allows new user profiles to be added to
an application without the need to change the other
components.
Transfer of Skills. The use of different technologies to
build applications for each device does not enable the
transfer of skills through different tools. Set of skills
and areas of expertise are rarely transferable when
dealing with different technologies. The generic
approach promotes the transfer of skills, given that
developers use only a single tool for developing
applications based on a variety of technologies.
Code reuse/modularity. A generic approach promotes to
reuse a code, hence developers can then reuse
components. For example, in our approach the profile
verification component for the Elderly
(ElderlyProfileChecker) can be reused in other
interfaces that will be used by the elderly.
Universal Design. Our approach respects the different
interaction needs and includes them in the design
proposals. The FlexInterface framework considers a
Universal Design approach (Connell et al., 1992),
designed so that access to knowledge and information is
made without physical and social segregation, and
which makes sense to the largest possible number of
users according to their different sensory, physical,
cognitive and emotional skills.
6 CONCLUSIONS
AND FURTHER WORK
This paper presented FlexInterface, a research that
exploits the use of a middleware approach for
constructing flexible interfaces. Thanks to the
minimal kernel, FlexInterface is deployable on a
Flexinterface:AFrameworktoProvideFlexibleMobilePhoneUserInterfaces-AddressingtheElderlyDiversity
149

wide range of environments, including those with
scarce resources (e.g. smartphones). We argue on
our previous paper in (Gonçalves et al., 2011) that
mobile phone interfaces are particularly designed for
young people. This is a critical issue as the
population of elderly people is increasingly higher,
nowadays. We have shown the suitability of
constructing a flexible interface using the runtime
reconfigurable middleware approach that we
borrowed from OpenCom. This ensures that both the
young and the elderly people can make use of a
single adaptive interface implementation on a
smartphone. We have prototyped FlexInterface and
carried out experiments with the elderly people on a
Galaxy Samsung smartphone running Android.
In future work, we will better describe user
behavior collecting a greater amount of user
interaction data (touch screen clicks, keys, duration,
etc.). This interaction detail will also allow an
element of the screen to be reconfigured
independently of the others. For example, if a user
takes too long to click the Save key having already
entered all the contact data, the interface resets the
color of the key changes so that the user perceives
what action he should do to finish the task.
Accordingly, the detailed behavior together with
the reconfiguration of interface elements allows
these interfaces to adapt to a wider range of features
and skills of elderly users or not.
REFERENCES
Connell, B. R., Jones, M. Mace, R., et al.. About UD:
Universal Design Principles. Version 2.0. Raleigh:
The Center for Universal Design.
http://www.design.ncsu. edu/cud/about_ud/udprin
ciples.htm.1997.
Coulson G., Blair, G., Grace, P., et al.. A Generic
Component Model for Building Systems Software.
ACM Transaction on Computer Systems. 2008.
Czaja, S. J., Lee, C. C. The impact of aging on access to
technology. Universal Access in the Information
Society. 2007.
Gonçalves, V. P., Leite, B. C. S., Carvalho, J. R., et al..
Inspeção de Usabilidade: Um Processo Informatizado
para Melhor Satisfazer os Objetivos do Usuário. In
Anais da II Escola Regional de Informática, Manaus.
2010.
Gonçalves, V. P., Neris, V. P. A., Morandini, M., et al..
Uma Revisão Sistemática sobre Métodos de Avaliação
de Usabilidade Aplicados em Software de Telefones
Celulares. In Anais do X Simpósio Brasileiro de
Fatores Humanos em Sistemas Computacionais e V
Congresso Latino-americano de Interação Humano-
Computador, Porto de Galinhas. 2011.
Gonçalves, V. P., Neris, V. P. A., Ueyama J. Interação de
Idosos com Celulares: Flexibilidade para Atender a
Diversidade. In Anais do X Simpósio Brasileiro de
Fatores Humanos em Sistemas Computacionais e V
Congresso Latino-americano de Interação Humano-
Computador, Porto de Galinhas. 2011.
Gonçalves, V. P., Neris, V. P. A., Ueyama, J., et al.. An
Analytic Approach to Evaluate Flexible Mobile Phone
User Interfaces for the Elderly. In Proceedings of 14th
International Conference on Enterprise Information
Systems, Wrolaw - Poland. 2012.
Grace, P., Blair, G.S. and Samuel, S. ReMMoC: A
reflective middleware to support mobile client
interoperability. In Proceedings of the Symposium on
Distributed Objects and Applications (DOA 2003,
Catania, Sicily, Italy). 2003.
Hellman, R. Universal Design and Mobile Devices.
Proceedings of the 4th international conference on
Universal access in human computer interaction:
coping with diversity. Beijing. 2007.
Microsoft Corporation, “Universal Plug and Play Device
Architecture”, Version 1.0, http://www. upnp.org/
download/UPnPDA10_200006 13.htm, June 2000.
MT - Minister of Industry. Learning a Living - First
Results of the Adult Literacy and Life Skills Survey.
OECD, Paris. http://www.nald.ca/fulltext/learnliv/
learnliv.pdf. 2005.
Neris, V.P.A.; Baranauskas, M.C.C. Making interactive
systems more flexible: an approach based on users'
participation and norms. In Simpósio de Fatores
Humanos em Sistemas Computacionais (IHC 2010):
Belo Horizonte. 2010.
Neris, V.P.A.; Baranauskas, M.C.C. Designing tailorable
software systems with the users participation, 09/2012,
Journal of the Brazilian Computer Society, Vol. 18,
pp. 213-227, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil. 2012.
Nielsen. J. Generation App: 62% of Mobile Users 25-34
own Smartphones. http://blog.nielsen.com/
nielsenwire/online_mobile/generation-app-62-of-
mobile-users-25-34-own-smartphones. 2011.
Olwal, A., Lachanas, D., Zacharouli, E. OldGen: Mobile
Phone Personalization for Older Adults. In:
Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems
(CHI 2011), Vancouver. 2011.
Siegel, J. OMG overview: CORBA and the OMA in
enterprise computing, ACM. v41. n10. 1998.
Ueyama, J., Pinto, V.P.V., Madeira, E.R.M., et al..
Exploiting a Generic Approach for Constructing
Mobile Device Applications. In: The Fourth
International Conference on COMmunication System
softWAre and middlewaRE, Dublin. ACM. 2009.
Veizades, J., Guttman, E., Perkins, C., Kaplan, S. “Service
Location Protocol”, Internet RFC 2165, 1997.
UN - United Nations. ‘Major’ rise in world’s elderly
population: DESA report. http://www.un.org/en/
development/desa/news/population/major-rise-in.html.
2010.
Wood, E., Willoughby, T., Rushing, A., Bechtel, L.,
Gilbert, J. Use of computer input devices by older
adults. The Journal of Applied Gerontology. 2005.
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
150
