
Comparative Analysis of State-of-the-Art Spatial Data Warehouse
Meta-models
Catching the Expressive Power of SDW Schemas!
Alfredo Cuzzocrea
1
and Robson do N. Fidalgo
2
1
ICAR-CNR and University of Calabria, Arcavacata di Rende, Italy
2
Center for Informatics, Federal University of Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil
Keywords: Spatial Data Warehouse and Metamodel.
Abstract: In this paper we provide a comparative analysis of the Spatial Data Warehouse Metamodel (SDWM)
proposal against three state-of-the-art Spatial Data Warehouses (SDW) meta-model proposals. Results of
this analysis allow us to conclude that the SDWM proposal exposes a higher expressive power of the
comparison approaches, and, in addition to this, it allows us to obtain more concise and compact SDW
schemas when compared with the schemas provided by the comparison approaches.
1 INTRODUCTION
Spatial Data Warehouse Metamodel (SDWM) (Del
Aguila et al., 2011; Cuzzocrea & Fidalgo, 2012a;
Cuzzocrea & Fidalgo, 2012b) has been provided
recently with the goal of effectively supporting the
modeling of Spatial Data Warehouses (SDW)
(Bédard et al., 2001; Zghal et al., 2003) by adding
several contributions. Among these, relevant ones
concern with separating the SDW conceptual
modeling from the OLAP data cube (Gray et al.,
1997) conceptual modeling, supporting SDW
complex constructs modeling, and, finally,
stereotyping attributes and measures as spatial
objects directly.
Another nice contribution due to this line of
research is represented by the proposal of a software
environment, called SDWCASE, which allows us to
model a SDW according to the SDW’s design and
modeling principles, in a user-friendly manner.
As a further research effort along the so-depicted
line of research, in this paper we provide a
comparative analysis of the SDWM proposal against
three state-of-the-art SDW meta-model proposals
(Fidalgo et al., 2004; Malinowski & Zimányi, 2007;
Glorio & Trujillo, 2008).
Results of this analysis allow us to conclude that
the SDWM proposal exposes a higher expressive
power of the comparison approaches, and, in
addition to this, it allows us to obtain more concise
and compact SDW schemas when compared with
the schemas provided by the comparison
approaches.
The remaining part of this paper is organized as
follows. In Section 2, we provide an overview of the
SDWM proposal. In Section 3, we introduce a
running example focusing on a SDW of homicide
cases for the secretary of the Public Safety Office of
Pernambuco/Brazil. Next Sections 4-6 are devoted
to the comparative analysis of SDW with the
comparison approaches: (Fidalgo et al., 2004)
(Section 4), (Malinowski & Zimányi, 2007) (Section
5), and (Glorio & Trujillo, 2008) (Section 6). In
Section 7, we provide the results of the comparative
analysis that is the main contribution of our research.
Finally, in Section 8, we provide conclusions and
future work of our research.
2 SDWM IN A NUTSHELL
SDWM (Del Aguila et al., 2011; Cuzzocrea &
Fidalgo, 2012a; Cuzzocrea & Fidalgo, 2012b) is a
meta-model that embeds the following significant
features: (i) disassociating DW dimensional
modeling from OLAP data cube modeling; (ii)
representing the spatiality of a SDW by directly
stereotyping attributes/measures as spatial types,
rather than stereotyping dimension/fact tables as
spatial or hybrid objects; (iii) capturing whether the
302
Cuzzocrea A. and do N. Fidalgo R..
Comparative Analysis of State-of-the-Art Spatial Data Warehouse Meta-models - Catching the Expressive Power of SDW Schemas!.
DOI: 10.5220/0004455903020309
In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2013), pages 302-309
ISBN: 978-989-8565-60-0
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

geometry of a spatial attribute/measure can be
normalized and/or shared; (iv) supporting the
following DW modeling techniques: degenerated
dimensions, many-to-many relationships (bridge
tables), role-playing dimensions, which are
typically-hard modeling cases (Bédard et al., 2001;
Zghal et al., 2003); (v) providing a set of stereotypes
with pictograms that aim at being concise and user-
friendly; (vi) being used as a basic meta-model for
the CASE tool SDWCASE that supports the
modeling of logical SDW schemas, as well as, given
an input SDW schema, checking whether the
schema is syntactically valid.
In Figure 1, the UML class diagram of SDWM is
shown. Here, three relevant enumerations are
introduced: Cardinality, DataType and
GeometricType. Cardinality is used to define whether
a relationship is of kind many-to-one, one-to-many or
many-to-many. In turn, DataType and GeometricType
represent the primitive or spatial data types supported
by SDWM, respectively. Moreover, SDWM exposes
five main meta-classes: Schema, Table,
Relationship, DimensionColumn and FactColumn.
Schema is the root meta-class that corresponds to the
drawing area for a SDW schema. For this reason,
Schema is a composition of zero or more Table and
zero or more Relationship. Finally,
DimensionColumn and FactColumn are just a set of
different types of column.
Figure 1: SDWM UML class diagram.
Besides the previous constructors, SDWM is also
characterized by the following eight specialized
meta-classes (see Figure 1): Fact, Dimension,
Bridge, SpatialMeasure, DegenerateDimension,
ConventionalMeasure, SpatialAttribute and
ConventionalAttribute. These meta-classes address
the main concepts supported by the SDWM
modeling approach. On the basis of this approach, a
Table is specialized in Fact, Dimension or Bridge,
which capture the concepts of (SDW) fact table,
dimension table and a bridge table, respectively. A
FactColumn is specialized in SpatialMeasure,
DegenerateDimension and ConventionalMeasure,
which correspond to a spatial feature type, a
descriptive attribute and a measurable attribute,
respectively. A DimensionColumn is specialized in
SpatialAttribute and ConventionalAttribute, which
represent a spatial feature type and a descriptive
attribute, respectively. Furthermore, a Fact is a
composition of zero or more FactColumn and zero
or more ConventionalAttribute. In turn, a Dimension
and a Bridge are a composition of zero or more
DimensionColumn.
In order to capture tables that are source and
target in a relationship, SDWM introduces two
different associations, named as Source and Target,
respectively. Furthermore, since a dimension can
play different roles (role-playing dimensions),
SDWM introduces the attribute Role to support this
specialized modeling case. Other important SDWM
attributes are: Name, isNormalized, isShared,
hasDescription, Type and Size. Name is used to label
a meta-class. IsNormalized is used to define whether
the position (geometry) of a spatial measure/attribute
has to be normalized in a different table from its
location (description). IsShared is used to define
whether the position of a spatial attribute/measure
has to be shared among several spatial
attributes/measures (to this end, it is necessary to
define the same name and the same geometric type).
HasDescription is used to define whether the
location of a spatial measure has to be stored
(contrary to a SpatialAttribute, which must have a
position and a location, the location of a
SpatialMeasure is optional). Type is used to
associate a type (from the collection of allowed
SDWM types). Finally, Size is used to define the
length of a conventional attribute, a degenerated
dimension or a conventional measure.
SDWM makes use of stereotypes with
pictograms in order to increase its expressive power
and visualization capabilities, namely: Fact Table
, Dimension Table , Bridge Table ,
Conventional Attribute , Conventional Measure
, Degenerated Dimension , Spatial Attribute
, Spatial Measure , Relation , Integer ,
String , Date , Real , Point , Line ,
Polygon , Multipoint , Multiline ,
Multipolygon , Collection . The combined
action of these stereotypes allows us to design “rich”
SDW schemas.
ComparativeAnalysisofState-of-the-ArtSpatialDataWarehouseMeta-models-CatchingtheExpressivePowerofSDW
Schemas
303
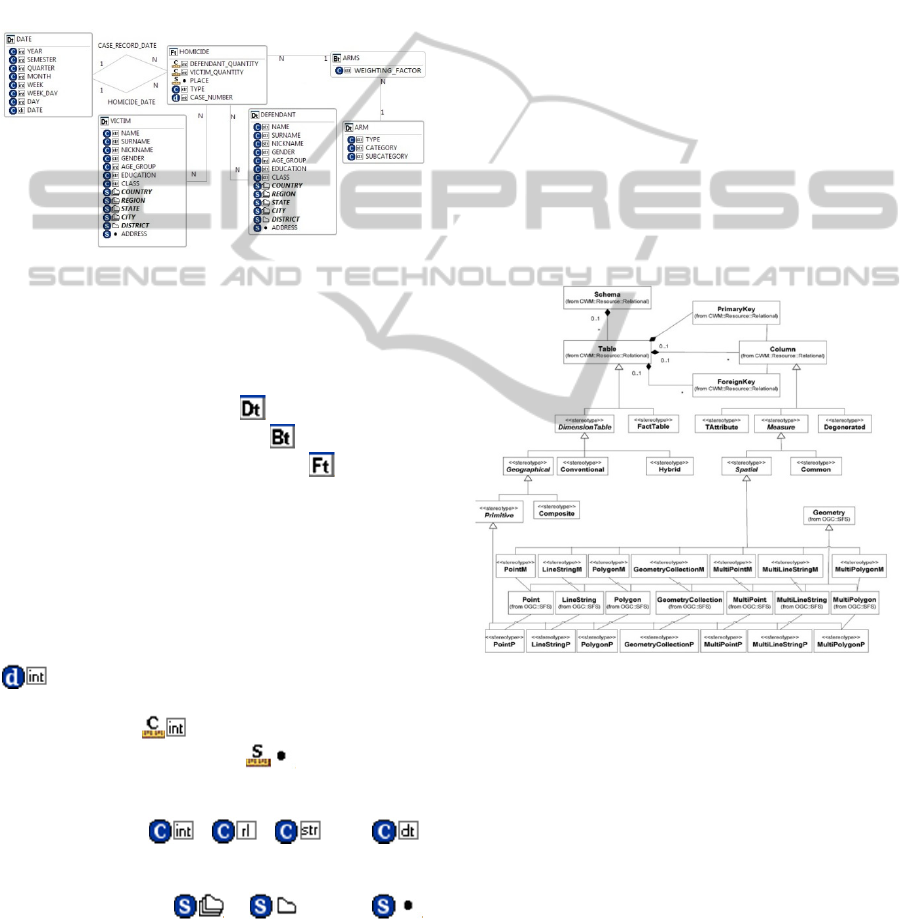
3 RUNNING EXAMPLE: THE
HOMICIDE SDW
In order to assess the effectiveness of the proposed
SDWM approach, we developed a complete case
study focused on a SDW of homicide cases for the
secretary of the Public Safety Office of
Pernambuco/Brazil. This originated quite a complex
schema. A fragment of this schema designed by
means of SDWCASE is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Fragment of the homicide SDW according to
SDWM.
As shown in Figure 2, the homicide SDW is
characterized by the following DW objects. Four
dimension tables: Date, Victim, Defendant and Arm,
which are stereotyped with . One bridge table:
Arms, which is stereotyped with . One fact table:
Homicide, which is stereotyped with . Two role-
playing dimensions: Case_Record_Date and
Homicide_Date. Two many-to-many relationships:
one between Homicide and Victim and another
between Homicide and Defendant. Four one-to-
many relationships: two between Homicide and
Date, one between Homicide and Arms, and one
between Arms and Arm. One degenerated
dimension: Case_Number, which is stereotyped with
. Two conventional measures:
Defendant_Quantity and Victim_Quantity, which are
stereotyped with . One spatial measure: Place,
which is stereotyped with . Twenty-seven
conventional attributes, such as Year,
Weighting_Factor, Name and Date, which are
stereotyped with , , and ,
respectively. Twelve spatial attributes, such as
Country, District and Address, which are
stereotyped with , and ,
respectively.
It is worth to noticing that, in the schema of
Figure 2, spatial attributes Country, Region, State
and City are defined as normalized (depicted with
bold font) and shared (depicted as Italic font).
According to the SDWM modeling approach, this
means that these spatial attributes have their
geometries stored in a table different of the table
containing their descriptions, and their geometries
can be reused between the dimensions Victim and
Defendant. This solution aims at reducing the
overall spatial data volume of the homicide SDW.
4 COMPARISON WITH
(FIDALGO ET AL., 2004)
(Fidalgo et al., 2004; Times et al., 2009; da Silva et
al., 2010) introduce a framework, a meta-model and
a CASE tool for modeling SDW. The proposed
meta-model is depicted in Figure 3 (da Silva et al.,
2010) while the logical model of a SDW focusing on
meteorology data (which makes use of their
proposed CASE tool) is showed in Figure 4 (Times
et al., 2009).
Figure 3: SDW meta-model proposed by (Fidalgo et al.,
2004).
As shown in Figure 3, the meta-model proposed
by (Fidalgo et al., 2004; Times et al., 2009; da Silva
et al., 2010) introduces classical constructs useful to
model a SDW, i.e.: attributes, measures, degenerated
dimensions, primary keys, foreign keys, common
measures, spatial measures, geographical
dimensions, conventional dimensions, hybrid
dimensions and fact tables. However, this models is
not totally complete as some important constructs
are still missing. Particularly, these constructs are:
many-to-many relationships (bridge tables), role-
playing dimensions and spatial attributes. These
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
304

constructs, indeed, are very useful to model real-life
SDW, like the case of our running example focusing
on the homicide SDW (see Figure 2). As a
consequence, we can infer that the meta-model by
(Fidalgo et al., 2004; Times et al., 2009; da Silva et
al., 2010) does not provide a full-support for modern
SDW.
Figure 4: Meteorology SDW according to (Fidalgo et al.,
2004).
As mentioned above, Figure 4 show the logical
model of the meteorology SDW designed by means
of the CASE tool by (Fidalgo et al., 2004; Times et
al., 2009; da Silva et al., 2010), which, obviously,
adheres to their proposed meta-model. Here, one fact
table is defined, i.e. Meteorology, and nine
dimensional tables, i.e. Hydrographic Basin, Basin
Location, Time, Data Collection Platform (DCP),
DCP Location, State, Meso Region, Micro Region,
City. As shown in Figure 4, fact table Meteorology
has only conventional measures (i.e., precipitation
and wind_speed) and dimension tables have both
conventional (i.e., nm_basin in Hydrographic Basin
and year in Time) and spatial (i.e., state in State and
dcp_location in DCP Location) attributes.
Moreover, the use of dimensions stereotyped with
spatial pictograms (i.e., Meso Region and Micro
Region) does not provide a concise/short notation,
as, for each spatial concept, one dimension is
introduced. It is worth to notice that this approach
pollutes the SDW schema as it results in an
excessive and redundant number of spatial concepts
immersed in the schema.
Figure 5 shows the meteorology SDW of Figure
4 modeled by means of SDWCASE according to
SDWM. This originates a SDW schema that is
equivalent to the schema of Figure 4. As an
Figure 5: Meteorology SDW according to SDWM.
alternative to the modeling due to (Fidalgo et al.,
2004; Times et al., 2009; da Silva et al., 2010) (see
Figure 4), in the SDWM modeling (see Figure 5) we
introduce city, micro_region, meso_region and state
as spatial attributes directly and their geometries are
normalized and shared between the dimensions
Hydrographic Basin and DCP. As is clearly follows
from the comparison between the two schemas in
Figure 4 and Figure 5, the use of spatial attributes
improves representation of the meteorology SDW
(and, in turn, its “visual quality”) by achieving a
more compact one, as six dimensions are no longer
modeled (i.e., Basin Location, DCP Location, State,
Meso Region, Micro Region, City).
On the other hand, from Figure 4 it also follows
that the meta-model proposed by (Fidalgo et al.,
2004; Times et al., 2009; da Silva et al., 2010) does
not mix the DW modeling concepts with the OLAP
data cube ones, similarly to the proposed meta-
model SDWM. This is, indeed, a positive
contribution.
Summarizing, from the results of this analysis we
can conclude that, with respect to the meta-model
proposed by (Fidalgo et al., 2004; Times et al., 2009;
da Silva et al., 2010), the proposed meta-model
SDWM is capable of achieving equivalent SDW
schemas in a much more compact and concise way,
thanks to the fact it can immerse spatial attributes
(and their geometries) directly into dimensions,
hence the expressive power of the SDWM proposal
is clearly higher.
5 COMPARISON WITH
(MALINOWSKI & ZIMÁNYI,
2007)
Malinowski & Zimányi (2007; 2009) propose a
SDW meta-model that introduces dimensions,
hierarchies, levels and measures, which all can be
ComparativeAnalysisofState-of-the-ArtSpatialDataWarehouseMeta-models-CatchingtheExpressivePowerofSDW
Schemas
305
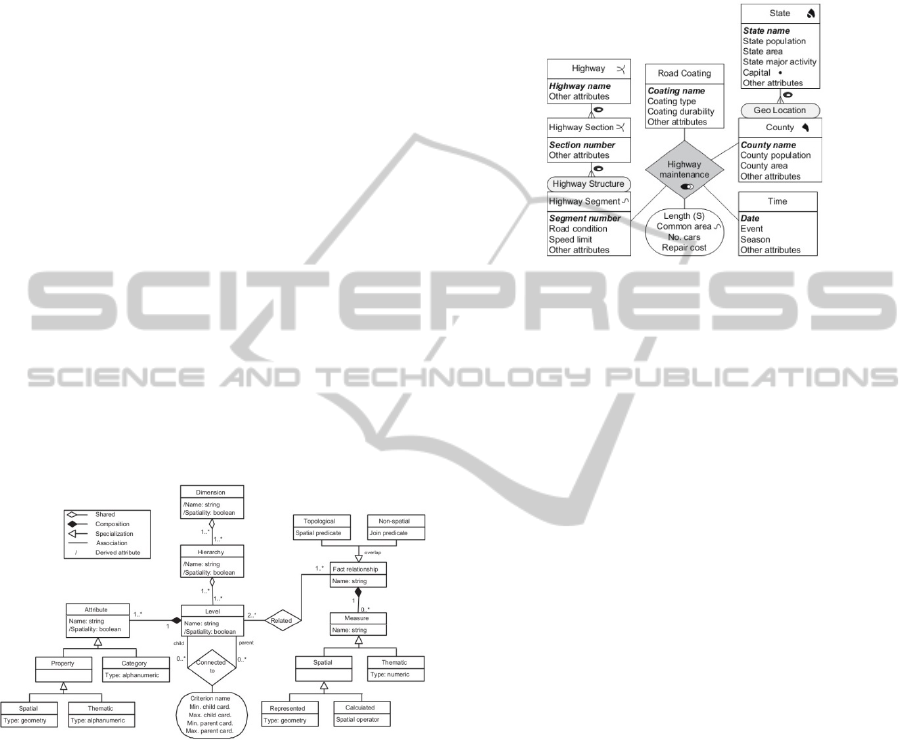
spatial or not by simply declaring a Boolean
specifying state variable called Spatiality. The SDW
logical models adhering to such a meta-model are
represented as suitable extensions of the classical ER
model. Figure 6 (Malinowski & Zimányi, 2009)
shows the UML class diagram for the meta-model
proposed by Malinowski & Zimányi (2007; 2009).
As it follows from Figure 6, this meta-model mixes
DW modeling concepts with OLAP data cube
modeling ones, and it does not provide support for
the following DW modeling techniques: degenerated
dimensions, bridge tables (many-to-many
relationships) and role-playing dimensions. As a
consequence, the meta-model by Malinowski &
Zimányi (2007; 2009) does not allow a full
modeling of the homicide SDW of the running
example (see Section 3). In fact, this meta-model
neither allows specifying whether the geometry of a
spatial attribute can be normalized and/or shared nor
provides support for modeling the previously-
mentioned DW modeling techniques (which are
frequent cases in real-life SDW settings). Moreover,
to the best of our knowledge, there is no a CASE
tool based on this meta-model. This is another
relevant limitation of the proposal by Malinowski &
Zimányi (2007; 2009).
Figure 6: UML class diagram of the SDW meta-model
proposed by (Malinowski & Zimányi, 2007).
Figure 7 (Malinowski & Zimányi, 2007) shows
the logical model of a highway SDW according to
the proposal due to Malinowski & Zimányi (2007;
2009). As shown in Figure 6, the SDW schema
introduces one fact table, called Highway
Maintenance, with is characterized by conventional
and spatial measures (e.g., No. cars and Common
area), and dimensions/levels (e.g., Highway and
Highway Segment) with conventional and spatial
information (e.g., Road condition and State). From
Figure 7, it follows that representation of levels as
entities (it should be reminded that in this case ER
extensions are considered), besides being not
correspond to an intrinsic concept of DW, it does not
provide a concise representation/notation, as,
according to this approach, it is necessary to create
an entity for each level, hence polluting the SDW
schema significantly.
Figure 7: Highway SDW according to (Malinowski &
Zimányi, 2007).
Figure 8 shows the highway SDW of Figure 7
modeled by means of SDWCASE according to
SDWM. Again, the two schemas are equivalent.
Since, from Figure 7, it is not possible to know
whether the geometry of a spatial object is
normalized or shared, in the logical model of the
highway SDW according to SDWCASE of Figure 8,
we simply define all geometries as not normalized
and not shared. As a consequence, the SDW schema
of Figure 8 is characterized by significant
redundancy of geometric information, which, in
turn, increases the whole data volume of the final
SDW and, in addition to this, the SDW
administration itself becomes more difficult.
Similarly to the case of the comparison of SDWM
with the meta-model proposed by (Fidalgo et al.,
2004; Times et al., 2009; da Silva et al., 2010) (see
Section 4), here we again observe the clear
advantages deriving from immersing spatial
attributes (and their geometries) into dimensions
directly. In fact, in the highway SDW according to
SDWM (see Figure 8) we employ four dimensions
only whereas in the highway SDW according to
Malinowski & Zimányi (2007; 2009) (see Figure 7)
seven dimensions are necessary to represent the
same knowledge. This comparison clearly is in favor
of SDWM, which is capable of representing the
same knowledge in a more compact and concise
way.
Summarizing, from the results of this analysis we
can conclude that, with respect to the meta-model
proposed by Malinowski & Zimányi (2007; 2009),
the proposed meta-model SDWM exposes a clearly-
higher expressive power, as the meta-model due to
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
306

Malinowski & Zimányi (2007; 2009) does not
address some important DW modeling techniques
(i.e., degenerated dimensions, bridge tables and role-
playing dimensions) and also it does not allow to
specify whether the geometry of a spatial attribute
can be normalized and/or shared among dimensions,
thus preventing a full modeling of our running
example on the homicide SDW. In addition to this,
the meta-model due to Malinowski & Zimányi
(2007; 2009) introduces an entity for each
dimensional level, hence it clearly reduces the
clarity and the comprehensibility of final SDW
schemas (this drawback is much more evident with
real-life SDW schemas that are usually characterized
by high numbers of dimensions and dimensional
attributes). Finally, Malinowski & Zimányi (2007;
2009) do not propose any CASE tool adhering to
their meta-model, like the SDWM proposal.
Figure 8: Highway SDW according to SDWM.
6 COMPARISON WITH (GLORIO
& TRUJILLO, 2008)
Glorio & Trujillo (2008; 2009) extend the UML
meta-model in order to define a UML profile
enriched with a set of stereotypes for dimensions,
facts, conventional measures, spatial measures,
degenerated dimensions, conventional levels and
spatial levels. Figure 9 (Glorio & Trujillo, 2009)
shows the obtained SDW-aware UML profile.
Moreover, based on the proposed UML profile, they
also build a CASE tool whose components adhere to
their meta-model. Figure 10 (Glorio & Trujillo,
2009) shows the logical models of a sale SDW
according to the proposal due to Glorio & Trujillo
(2008; 2009). As shown in Figure 10, the SDW
schema mixes DW modeling concepts with OLAP
data cube ones and it does not provide support for
the following DW modeling techniques: role-playing
dimensions and bridge tables. Also, it is not possible
to define whether the geometry of spatial attributes
can be normalized and/or shared. As a consequence,
similarly to the other two meta-model proposals due
(Fidalgo et al., 2004; Times et al., 2009; da Silva et
al., 2010) (Section 4) and Malinowski & Zimányi
(2007; 2009) (Section 5), the meta-model by Glorio
& Trujillo (2008; 2009) does not allow a full
modeling of the homicide SDW of the running
example (see Section 3).
Figure 9: SDW-aware UML profile by (Glorio & Trujillo,
2008).
Looking again to Figure 10, we observe that the
sale SDW schema modeled according to the
methodology by Glorio & Trujillo (2008; 2009)
exposes one fact table, called Sales, which is
characterized by conventional measures only (e.g.,
cost and total) and three dimensions: Store, Product
and Client, equipped with levels having
conventional and spatial attributes (e.g., category
and geometry_polygon). This means, again, mixing
concepts from different contexts (i.e., DW and
OLAP). Also, similarly to the previous meta-models
investigated in our analysis, the solution by Glorio &
Trujillo (2008; 2009) does not provide a concise and
compact notation. In fact, again one class (it should
be reminded that in this case UML extensions are
considered) is introduced for each dimensional level.
Figure 11 shows the sale SDW of Figure 10
modeled by means of SDWCASE according to
SDWM. Again, the two schemas are equivalent.
Similarly to the case of the highway SDW (see
Section 5), in the logical model of the sale SDW
according to SDWCASE of Figure 11, we simply
define all geometries as not normalized and not
shared, hence again obtaining redundancy, high data
volumes and difficult SDW administration. Just like
the previous case, we observe that, contrary to this,
the SDWM meta-model offers a more concise and
compact solution (five dimensions in the SDWM’s
case – see Figure 11 – vs eight dimensions in the
ComparativeAnalysisofState-of-the-ArtSpatialDataWarehouseMeta-models-CatchingtheExpressivePowerofSDW
Schemas
307

Glorio & Trujillo's (2008; 2009) case – see Figure
10).
Figure 10: Sale SDW according to (Glorio & Trujillo,
(2008).
Summarizing, from the results of this analysis we
can conclude that, with respect to the meta-model
proposed by Glorio & Trujillo (2008; 2009), the
proposed meta-model SDWM exposes a clearly-
higher expressive power, along with more concise
and compact schemas, according to similar
consideration given in Section 4 and Section 5.
Figure 11: Sale SDW according to SDWM.
7 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
RESULTS
In this Section, we provide the results of the
comparative analysis on the proposed meta-model
SDWM against the related ones we discussed in the
previous Sections.
Table 1 summarizes the results of our analysis.
As it follows from Table 1, all comparison
approaches allow us to design spatial measures.
However, no proposal except the SDWM one
addresses spatial attributes. As a consequence,
comparison approaches do not support determining
whether the geometry of a spatial attribute should be
normalized and/or shared among different
dimensions. As highlighted in previous Sections, it
should be recalled here that normalizing and sharing
spatial attributes has the beneficial effect of reducing
the whole data volume of SDW and making the
SDW administration simpler.
Moreover, among comparison approaches, only
the proposal by (Fidalgo et al., 2004; Times et al.,
2009; da Silva et al., 2010) (i) disassociates DW
modeling concepts from OLAP data cubes modeling
concepts, and (ii) addresses the degenerated
dimension modeling technique. Unfortunately, for
what regards bridge tables and role-playing
dimensions, no comparison approach addresses
these yet-useful constructs.
Also, contrary to the SDWM approach, where
we make use of suitable spatial attributes to
represent spatial information, (Fidalgo et al., 2004;
Times et al., 2009; da Silva et al., 2010) model
spatial information as dimensions, Malinowski &
Zimányi (2007; 2009) as ER entities, and Glorio &
Trujillo (2008; 2009) as UML classes.
Finally, as highlighted throughout the paper,
comparison approaches are clearly not capable of
providing concise and compact SDW schemas like
the SDWM approach.
Table 1: Results of the comparative analysis among SDW
meta-modeling approaches.
(Fidalgo
et al.,
2004)
(Malinowski
& Zimányi,
2007)
(Glorio &
Trujillo,
2008)
SDWM
DW vs OLAP
Modeling
YES NO NO YES
CASE
Tool
YES NO YES YES
Degenerated
Dimensions
YES NO YES YES
M-N
Relationships
(Bridge Tables)
NO NO NO YES
Role-Playing
Dimensions
NO NO NO YES
Spatial
Attributes
NO NO NO YES
Spatial
Measures
YES YES YES YES
Concise
Notation
NO NO NO YES
Normalized
Geometry.
NO NO NO YES
Shared
Geometry.
NO NO NO YES
Yes (%) 40 10 30 100
NO (%) 60 90 70 0
ICEIS2013-15thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
308

8 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we have provided a comparative
analysis of the SDWM approach (Del Aguila et al.,
2011; Cuzzocrea & Fidalgo, 2012a; Cuzzocrea &
Fidalgo, 2012b) against the state-of-the-art SDW
meta-model proposals (Fidalgo et al., 2004;
Malinowski & Zimányi, 2007; Glorio & Trujillo,
2008). Results of our analysis clearly state that the
SDWM proposal exposes a higher expressive power
and allows us to obtain more concise and compact
SDW schemas.
Future work is oriented towards enriching
SDWM with novel aspects such as security and
privacy of SDW, in line with recent results in the
context of security and privacy of DW and OLAP
(e.g., (Cuzzocrea & Bertino, 2011; Cuzzocrea et al.,
2012; Cuzzocrea & Saccà, 2012)).
REFERENCES
Bédard, Y., Merrett, T., & Han, J. 2001. Fundamentals of
spatial data warehousing for geographic knowledge
discovery. Geographic data mining and knowledge
discovery, vol. 2, pp. 53-73.
Del Aguila, P. S. R., Fidalgo, R. N. & Mota, A., 2011.
Towards a more straightforward and more expressive
metamodel for SDW modeling. In Proceedings of the
ACM 14th international workshop on Data
Warehousing and OLAP. New York, NY, USA: ACM,
pp. 31-36.
Cuzzocrea, A., & Bertino, E., 2011. Privacy Preserving
OLAP over Distributed XML Data: A Theoretically-
Sound Secure-Multiparty-Computation Approach.
Journal of Computer and System Sciences 77(6), pp.
965-987.
Cuzzocrea, A., Bertino, E., & Saccà D., 2012. Towards a
theory for privacy preserving distributed OLAP. In:
EDBT/ICDT Workshops 2012, pp. 221-226.
Cuzzocrea, A. & Fidalgo, R. N., 2012a. Enhancing
Coverage and Expressive Power of Spatial Data
Warehousing Modeling: The SDWM Approach. In A.
Cuzzocrea & U. Dayal, eds. Data Warehousing and
Knowledge Discovery. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg,
pp. 15-29.
Cuzzocrea, A. & Fidalgo, R. N., 2012b. SDWM: An
Enhanced Spatial Data Warehouse Metamodel. In M.
Kirikova & J. Stirna, eds. CAiSE Forum. CEUR-
WS.org, pp. 32-39.
Cuzzocrea, A., & Saccà, D., 2012. A Theoretically-Sound
Accuracy/Privacy-Constrained Framework for
Computing Privacy Preserving Data Cubes in OLAP
Environments. In: OTM Conferences 2012, pp. 527-
548.
Fidalgo, R. N. et al., 2004. GeoDWFrame: A Framework
for Guiding the Design of Geographical Dimensional
Schemas. In Y. Kambayashi, M. Mohania, & W. Wöß,
eds. Data Warehousing and Knowledge Discovery.
Springer Berlin / Heidelberg, pp. 26-37.
Glorio, O. & Trujillo, J., 2008. An MDA Approach for the
Development of Spatial Data Warehouses. In I.-Y.
Song, J. Eder, & T. Nguyen, eds. Data Warehousing
and Knowledge Discovery. Springer Berlin /
Heidelberg, pp. 23-32.
Glorio, O. & Trujillo, J., 2009. Designing Data
Warehouses for Geographic OLAP Querying by Using
MDA. In O. Gervasi et al., eds. Computational
Science and Its Applications – ICCSA 2009. Springer
Berlin / Heidelberg, pp. 505-519.
Gray, J. Chaudhuri, S., Bosworth, A., Layman, A.,
Reichart, D., Venkatrao, M., Pellow, F. & Pirahesh H.,
1997. Data Cube: A Relational Aggregation Operator
Generalizing Group-by, Cross-Tab, and Sub Totals.
Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 1(1), pp. 29-
53.
Malinowski, E. & Zimányi, E., 2009. Advanced Data
Warehouse Design: From Conventional to Spatial and
Temporal Applications (Data-Centric Systems and
Applications), Springer.
Malinowski, E. & Zimányi, E., 2007. Logical
Representation of a Conceptual Model for Spatial Data
Warehouses.
GeoInformatica, 11(4), pp.431-457.
da Silva, J. et al., 2010. Modelling and querying
geographical data warehouses. Information Systems,
35(5), pp.592-614.
Times, Valéria Cesário et al., 2009. A Metamodel for the
Specification of Geographical Data Warehouses. In S.
Kozielski et al., eds. New Trends in Data Warehousing
and Data Analysis. Springer US, pp. 1-22.
Zghal, H. B., Faïz, S. & Ghézala, H. B., 2003. CASME : A
CASE Tool for Spatial Data Marts Design and
Generation. In Proceedings of Design and
Management of Data Warehouses. Berlin, Germany,
pp. 1-11.
ComparativeAnalysisofState-of-the-ArtSpatialDataWarehouseMeta-models-CatchingtheExpressivePowerofSDW
Schemas
309
