
Efficient 3D Control for Needle Steering
using Duty-cycled Rotation
Xiao Li
1
, Craig A. Lehocky
2
and Cameron N. Riviere
3
1
Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213, U.S.A.
2
Dept. of Biomedical Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213, U.S.A.
3
The Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213, U.S.A.
Keywords: Medical Robotics, Path Planning, Path Tracking, Controls, Needle Steering, Surgical Simulation.
Abstract: Bevel-tipped flexible needles can be steered to reach clinical targets along curvilinear paths in 3D while
avoiding obstacles. Steering by duty-cycled rotation increases the versatility of this approach by providing
proportional control of trajectory curvature. This paper presents computationally efficient techniques for
path planning and path-following control for this application, using a 3D simulated brain environment. Path
planning algorithms for this class of steerable needles have been developed using Rapidly-exploring
Random Trees (RRTs). This paper expands on these methods, using quaternions for representation of
rotation, and enhancing computational efficiency through use of interpolation, and by relaxing the entry
constraint. For path-following, a look-ahead proportional controller for position and orientation is
presented. Simulations in a 3D brain-like environment demonstrate the performance of the proposed planner
and path-following controller. The look-ahead is seen to improve path-following performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
Needle insertion is an important aspect of numerous
medical diagnoses and treatments (Abolhassani et
al., 2007). In the brain, deep needle insertion has the
potential to become an important means for delivery
of chemotherapeutic drugs to tumors (National
Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
(NINDS) and National Cancer Institute, 2000).
Traditional needles are limited to straight
trajectories, whereas the ability to follow curved
trajectories could increase targeting versatility while
also improving the ability to avoid blood vessels and
other critical structures. These capabilities could
also be advantageous for deep brain stimulation
(DBS) (Frasson et al., 2010). Bevel-tipped flexible
needles naturally curve during insertion, due to their
asymmetry; this phenomenon has been exploited in
order to steer the needles by controlling the
orientation of the needle shaft (Webster III et al.,
2006). An additional technique, duty-cycled rotation
during insertion, first developed by our group (Engh
et al., 2006a); (Engh et al., 2006b), augments this
method by providing proportional control of path
curvature.
For clinical use, it is generally desirable to
pre-plan a path for the needle to follow during
insertion to a target. Numerous path-planning
algorithms for steerable needles have been
developed (Alterovitz, 2005); (Alterovitz et al.,
2009); (Park et al., 2005); (Xu et al., 2008); (Patil
and Alterovitz, 2010); (Bernardes et al., 2011),
(Bernardes et al., 2012), many of which involve
Rapidly-exploring Random Trees (RRT) (Xu et al.,
2008); (Patil and Alterovitz, 2010); (Bernardes et al.,
2011), (Bernardes et al., 2012). RRT is a random
search algorithm that is widely used in robot path
planning problems. However, the motion of a
flexible needle has numerous kinematic constraints,
such as smoothness of the path and bounded
curvature, meaning that the needle tip can only move
into a certain zone at each motion step. The basic
RRT algorithm must be constrained appropriately in
order to be applied to steerable needle path planning
(Patil and Alterovitz, 2010). Once a feasible path is
determined, closed-loop path-following control is
needed in order to execute the desired trajectory
safely and effectively. Of the relevant literature on
path planning, some papers do not address control
explicitly; some others include it; some others treat
replanning essentially as control.
As noted earlier, a steerable needle could be used
192
Li X., A. Lehocky C. and N. Riviere C..
Efficient 3D Control for Needle Steering using Duty-cycled Rotation.
DOI: 10.5220/0004456501920199
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2013), pages 192-199
ISBN: 978-989-8565-71-6
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

as a guide wire for DBS. In some DBS cases,
surgeons start near Kocher’s point (2.5 cm off the
midline at the level of the coronal suture) and aim
for the subthalamic nucleus. The corticospinal tract
is nearby and is to be avoided. This scenario is
assumed here in order to form a simulation
environment. Figure 1 illustrates the environment,
which includes a simplified set of anatomical
obstacles, including the basal ganglia, corticospinal
tracts, and the thalamus. The Albany Medical
College Virtual Brain Model software was used for
brain images (Lindsley, 2009).
Figure 1: The path planner pre-computes feasible paths in
a human brain environment from entry zone to the target
point located in the area of the subthalamic nucleus
(indicated by a highlighted black bounding box), while
avoiding anatomical obstacles along the paths. We try
different target points (randomly generated) to test the
planner. A: Overview of the environment. B: Close-up of
the anatomical obstacles.
1.1 Related Work
Some researchers have used the Finite Element
Method to design needle paths in 2D, considering
the interactions between the flexible needle and the
work environment (Alterovitz et al., 2005);
(Alterovitz et al., 2009). Park et al. used a diffusion-
based approach for path planning in an obstacle-free
3D environment (Park et al., 2005). Xu et al. and
Patil et al. have developed a 3D RRT algorithm for
needle path planning while avoiding obstacles (Xu et
al., 2008); (Patil and Alterovitz, 2010), but this work
considered only open-loop control inputs, and did
not explicitly account for uncertainty in state
estimation.
Bernardes et al. recently used explicit geometry
to obtain an Arc-based RRT algorithm to connect
two searched points in path planning; this planner is
sufficiently fast to replan the path interactively
during insertion, but is limited to 2D (Bernardes et
al., 2011), (Bernardes et al., 2012). Van den Berg et
al. presented an LQG-based approach to 3D
planning and control that incorporates process and
measurement noise, and linearizes the nonlinear
motion and sensor models locally along the path
(Van den Berg et al., 2010). Unlike Van den Berg et
al., our work uses quaternions to represent rotations,
and therefore does not require the assumption that
the deviation from the path is small; on the other
hand, our computationally simple control approach
does not offer the optimality of the LQG method.
1.2 Contributions of the Paper
The main contribution of this work is a
computationally efficient approach to path-following
control for steerable needles while considering
uncertainties in state estimation, with a
computationally efficient approach to path planning
included as well. In simulation, Gaussian noise is
added to needle tip position estimation to simulate
uncertainty in image-based state estimation; good
triangulation is assumed in this study. This paper
derives a set of formulae to build the feasible path,
using quaternions to represent orientations, and
incorporating interpolation of points along the path,
to decrease search time while maintaining path-
following accuracy. Each point on the path contains
both position and quaternion information. Then a
look-ahead closed-loop control law is introduced,
considering both position error and heading error. A
constraint is imposed on maximum curvature, to
enhance the realism of the simulation.
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2
gives a formal problem statement. Section 3 presents
the kinematic model of steerable needles actuated by
duty-cycling. In the sequence, in sections 4 and 5
present the 3D RRT-based algorithm in path
planning and control law in path-following,
respectively, and simulation results are provided in
these two sections. Finally, Section 6 presents the
discussion and future work.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
To make the problems well defined, we make the
assumptions below. These assumptions are
discussed further in Section 6.
1). The metallic bevel-tip flexible needle is
torsionally rigid, so rotating the needle at the
base will not change its position in the
workspace and the body will follow the tip
Efficient3DControlforNeedleSteeringusingDuty-cycledRotation
193
motions exactly;
2). tissue deformation is neglected, and the
workspace is defined as a 3D cuboid;
3). Anatomical obstacles are composed of spheres,
cylinders, and truncated cones.
With the above assumptions, the needle steering
problem can be stated as follows.
Problem 1. (path planning): Given a target
position and an entry zone, determine a feasible path
between them while keeping the needle inside the
workspace and avoiding the obstacles.
Inputs: Boundaries of the workspace, maximum
curvature of the bevel-tipped flexible needle,
locations and geometrical characteristics of the
obstacles, entry zone and target locations, segment
length used in RRT algorithm, and the biased
sampling term.
Output: A sequence of points from entry zone to
the target that compose the path, including the
position and quaternion information of each point.
Problem 2. (path-following): Given a
predetermined feasible path from entry zone to the
target, let the needle track the reference points on
path with acceptable position errors and reach the
target. In this case, we considered the sensing noise
in image-based needle tip position measurement, and
random deviations from the predetermined entry
configuration.
3 NEEDLE KINEMATIC MODEL
Bevel-tipped flexible needles bend when inserted
into tissue because of asymmetric forces on the tip.
The nonholonomic kinematics of this process have
been described by Webster et al. (Webster III et al.,
2006).
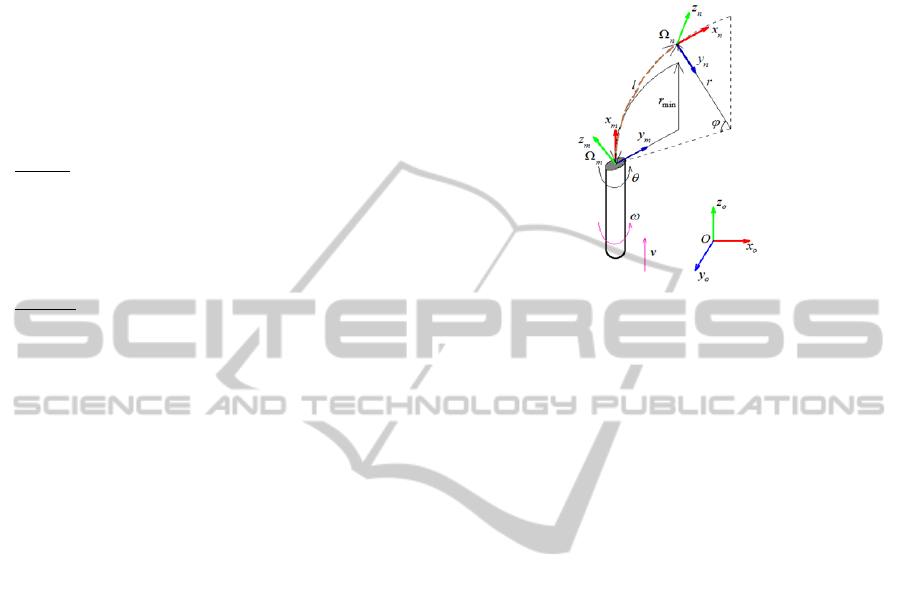
As presented in Fig. 2, a body coordinate frame
Ω is rigidly attached to the needle tip. The body x-
axis is the direction of forward motion, the y-axis is
the bending direction, and the z-axis is determined
by the right-hand rule. Inserting the needle causes
the tip to move along the x-axis with velocity v and
rotate about the z-axis with angular velocity v/r.
The maximum possible curvature is κ
max
=1/r
min
; r
min
is the minimum radius that corresponds to insertion
without axial rotation (ω = 0). Through duty-cycled
spinning, the needle can achieve any curvature
between 0 and κ
max
.
Each duty-cycle period in the 3D insertion
motion consists of a segment (variable in length) of
insertion without rotation followed by a fixed
segment length of insertion while rotating one full
cycle. For each period, a triplet is used to describe
the needle motion. The triplet consists of the shaft
orientation angle when not rotating, the length of the
inserted arc (shown in brown), and the effective
curvature.
Figure 2: Needle coordinate system and control inputs.
The body coordinate frame is attached to the needle tip.
The needle path is composed of segments of arcs, and
each arc (shown in brown) is parameterized as a triplet.
In our implementation, for the path planning part,
we have two discrete feasible points in space, and
use a function (
,,
)=
GET_TRIPLET(P
m
,P
n
,length) (introduced later in
Alg. 1) to solve for the parameters that compose this
path segment, in which P
m
and P
n
represent the 3D
positions for two consecutive points and length is
the fixed distance between these two points. For the
path-following part, we use function
X
n
=MOVE( ,,, X
m
) to make this movement
happen, in which is the rotation angle before
insertion (Wood et al., 2010), is the arc length, and
is the effective curvature. X
m
contains both
position and quaternion information of a point (7-
dimensional vector), as also does X
n
(the new state).
4 ARC-BASED RRT FOR PATH
PLANNING
We present an effective RRT-based path planning
algorithm, considering obstacles and kinematic
constraints. For computational efficiency, we
introduce a biased sampling term and set a relatively
large segment length for the tree, which will make
the tree grow faster towards the target. After
determination of the path, linear interpolation of
position and spherical linear interpolation of
quaternions between two connected points are used
in order to increase the density of points for better
path-following. Though the interpolation introduces
some error, the accuracy is acceptable if the step size
ICINCO2013-10thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
194

is small enough.
With an initial configuration, after one cycle
period, the next configuration of the needle tip must
satisfy the following local constraint (Patil &
Alterovitz, 2010), in which p
x
, p
y
, and p
z
are the
Cartesian coordinates of the new point relative to the
previous point in 3D space:
22 22
min
2( )( ).
xyzyz
p r pp pp
(1)
In practice, the surgeon requires that insertion begin
from a specified entry zone, but the entry
configuration of the needle is less critical. We use
an RRT path planning algorithm with bias, λ, toward
a small entry zone to compute feasible trajectories in
the reverse direction, beginning from the final target.
This method reduces the computation time greatly
compared with searching a path from one fixed entry
point to the target point. When generating a point in
3D space, the bias specifies the probability of
choosing the target point (in this case, a point
located inside the entry zone) as a new state instead
of a random point when expanding the tree. An
appropriate bias term value can help decrease the
search time. However, with greedier sampling, i.e.,
increasing the probability that the random state is the
goal state, the path can get stuck in local minima for
some complicated environments. The RRT
algorithm used is outlined in Alg. 1.
Alg. 1.
SET PARAMETERS
1. MAX_CURVATURE=
2. MAX_ITERATION=K
3. SEGMENT_LENGTH=L
4. BIASED_SAMPLING_PARAMETER=∈0,1
5. START_NODE=TARGET
BUILD_RRT(START_NODE,END_CONDITION)
1. WHILE(TREE∩END_CONDITION==∅∩
2. TREE=EXTEND_TREE(TREE); k=k+1
EXTEND_TREE()
1. WHILE(FLAG==0)
2. IF(RAND(1)<)
3. NEW_POINT=RAND_POINT_IN_ENTRYZONE
4. ELSE
5. NEW_POINT=RAND_POINT_IN_SPACE
6. PARENTPOINT=NEAREST(NEW_POINT,TREE)
7. NEW_POINT=PARENT_POINT+
__
__
∙
8. IF(REACHBLE AND COLLISION_FREE)
9.
,,
GET_TRIPLET(PARENT_POINT,NEW_
POINT,L)
10. NS_NEW=MOVE(PARENTPOINT,,,)
11. TREE=[TREE;NS_NEW]; FLAG=1
The formulae used in the GET_TRIPLET() function
are shown below.
2
,
22
(2)
IF()
0;;
ELSE
1
;∙1
2
;
The returned results of the MOVE() function
provide position and quaternion information as well.
In line 8 of function EXTEND_TREE(),
“reachable” means the new needle tip state satisfies
inequality (1), and NS means “needle state.”
Figure 3: Eight feasible paths calculated by the above
RRT algorithm.
Using Matlab with an Intel Core 2 desktop
computer, the computing time ranges from 4 s to
132 s, with an average of 50 s. Table 1 shows more
trials with different parameters. The average
iterations and average CPU time are computed based
on the successful runs. The proposed RRT planner is
considerably faster than the 3D RRT planner in (Xu
et al., 2008). The planner is slower than that in (Patil
and Alterovitz, 2010), possibly due to a more
complicated search environment and different CPU
speed. The success rate can be expected to vary
with the anatomical environment. In this brain
model, the target is quite near to some obstacles,
which has an impact on success rate.
The values chosen for
in this work (Table
1) are similar to values exhibited by PTFE needles
under investigation in our laboratory.
Efficient3DControlforNeedleSteeringusingDuty-cycledRotation
195

Table 1: Path Planner Performance.
No.
trials
κ
max
(mm
-1
)
λ
Avg.
iterations
Avg.
CPU
time (s)
Success
rate
(%)
20
1/20 0.1 309 76 80
20 1/20 0 348 59 50
20 1/25 0.1 237 100 70
20 1/30 0 273 97 55
20 1/30 0 267 211 40
For the feasible path (red) which is the most
computationally time-consuming among the eight
paths in Fig. 3, Fig. 4 shows the searched points and
the path after point interpolation. For the quaternion,
we use spherical linear interpolation.
Figure 4: A: Searched points (start from zero in x
direction). B: Reversed the world coordinate system,
interpolated points along a feasible path, each point on
path contains its positions and quaternion.
5 LOOK-AHEAD
PATH-FOLLOWING CONTROL
5.1 Concepts
Compared with open-loop control, closed-loop
feedback control provides better path-following
performance. Our control approach is based on the
error calculation between the current needle tip
position and the nearest point on the path. A
proportional controller takes a weighted average of
position error (or “cross-track error” (Thrun et al.,
2006)) and heading error and returns the parameters
(
,,
) for the next motion step. Our group has
demonstrated this approach experimentally in 2D
(Wood et al., 2010), and extended it to 3D in (Wood
et al., 2013). However, this “look-down” control
law considers only the nearest point on the planned
path, resulting in lag on curved paths, as well as
oscillations in cases of initial position offset. In the
present work, in order to improve performance, we
have incorporated look-ahead control (Ünyelioğlu et
al., 1997). Simulation results show that it can
reduce average position error on anatomically
realistic trajectories.
5.2 Controller
The errors include position error and heading error.
As shown in Fig. 5, the green point on the path is a
point ahead of the nearest point with look-ahead
distance L with respect to the current needle tip
position. Vector x
n
is the error vector measured in
needle coordinates, and the heading error is the
angle difference between the current needle body x-
axis and x
n
. The control law is outlined in Alg. 2.
Figure 5: Path-following error description.
Alg. 2
1. ds = duty_cycle_step_size
2. k
1
=proportional_gain_for_cross_tracking_error
3. k
2
=proportional_gain_for_heading_error
4. x = [1;0;0]
5. x
tra
=atan2(x
n
(z), x
n
(y))
6.
7. K
h
=k
2
tan(heading_error)
8. hve=qvrot(quaternion_error, x)
// deviation vector from 1;0;0
// qvrot(Q,V) rotates vector V by Q (St. Pierre, 2009)
9. h
ax
=cross(x,hve) // compute orthogonal vector
10. h
ra
=atan2(-h
ax
(2),h
ax
(3))
11. x=cos(x
tra
)·K
ct
+cos(h
ra
)·K
h
y=sin(x
tra
)·K
ct
+sin(h
ra
)·K
h
12. rotation
angle
=atan2(y,x)
curvature=min(sqrt(x
2
+y
2
),κ
max
)
The returned rotation angle and curvature are the
control variables that used to determine the motion
for the next step. Duty cycle is related to effective
curvature by
∙(1-DC)
(3)
ICINCO2013-10thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
196
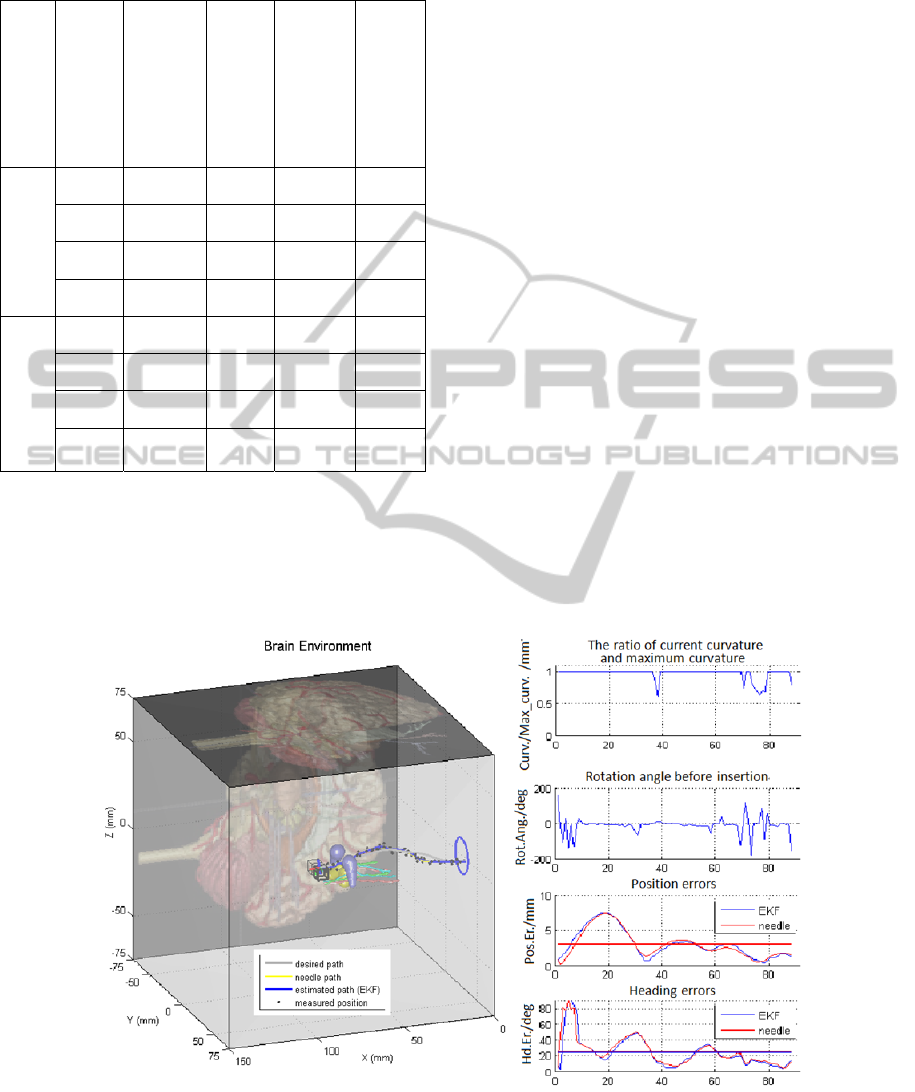
Table 2: Path-Following Performance at Various Look-
Ahead Distances.
Path
No.
trials
L (mm)
Avg.
pos.
error
along
path
(true)
(mm)
Avg.
pos.
error
along
path
(estim.
via
EKF)
(mm)
Avg.
final
target
pos.
error
(mm)
A
20
0
2.9±0.
9
2.6±0.5 2.0±0.7
20 3
1.8±0.
7
1.4±0.4 1.1±0.9
20 6
1.7±0.
6
1.5±0.3 1.0±0.8
20 9
2.5±0.
5
2.1±0.4 1.7±0.9
B
20 0
3.2±0.
6
2.8±0.5 2.5±0.8
20 3
1.9±0.
8
1.2±0.3 2.2±1.1
20 6
1.6±0.
8
1.0±0.3 1.8±1.0
20 9
2.0±0.
8
1.4±0.4 2.1±0.9
where DC is defined as the ratio of the rotation
period to the cycle period, where the cycle period is
the sum of the rotation period and the translation
period (Wood et al., 2010).
5.3 State Estimation
It is infeasible for the vision system to detect the
axial orientation of the needle tip because of its
small size. The vision system exhibits some
measurement noise. Studies have shown that the
steerable needle system is completely controllable
and observable by controlling its insertion speed and
rotation angle and speed around its base while
measuring only tip position over time, due to the
nonholonomic kinematics (Kallem and Cowan,
2009); (Hall, 2009). In the case of physical
experimentation, two cameras are used to capture
images, and triangulation is used to obtain the needle
tip positions (x,y,z) in 3D. (Clinically, a medical
imaging modality such as fluoroscopy is used
(Wood et al., 2010).) To cope with measurement
errors in position and to estimate the six states by
observing only three of them, Extended Kalman
Filter-based estimation is implemented (Wood et al.,
2010). In the present work, uncertainty in state
estimation was simulated by incorporation of
Gaussian noise.
In the simulation, we assigned a non-zero
variance to the initial configuration of the needle tip
and the feedback image sensing noise, which obeys
a zero-mean Gaussian distribution with standard
deviation σ = 1 mm in the x, y, and z directions.
Figure 6: Path-following without look-ahead control (i.e., L=0). The final needle tip position is inside the bounded region.
The actual needle trajectory shows oscillation behaviour and is more likely to hit the obstacles. The absolute final needle tip
position error is 1.85mm from the target point [72.76, 2.97, -5.22]. EKF estimation (shown in blue) is very close to the
actual needle states (actual path is shown in yellow, and actual errors are shown in red). The average actual needle position
error and EKF estimated position error are 3.06mm and 3.11mm, respectively.
Efficient3DControlforNeedleSteeringusingDuty-cycledRotation
197

Figure 7: Path-following with look-ahead control. The initial configuration is the same as in Fig. 7. The look-ahead
distance is L = 6 mm. The final tip position error is with respect to the target is 0.83 mm. EKF estimation (shown in blue)
is very close to the actual needle states (actual path is shown in yellow, and actual errors are shown in red). In this case,
both the average actual needle position error and EKF estimated position error are 1.00 mm.
5.4 Simulation Results
To test the performance of the proposed look-ahead
control law, we chose two paths (A and B) at several
different look-ahead distances and compared the
average position errors for several different look-
ahead distances. Error is measured by the needle tip
position and the closest point on path, and the
average final needle tip position errors, which is
measured by the actual needle tip position and the
target position (although we will never know the
actual needle position in reality). Table 2 shows the
error comparisons. For each path, the first row
indicates the performance of the earlier look-down
algorithm (L=0) (Wood et al., 2013),
Figures 6 and 7 compare path-following
simulations without and with look-ahead
implementation. The fourth and fifth columns
represent the true average error and the EKF-
estimated error (as shown in Figs. 6 and 7)
calculated based on 20 trials, respectively, along the
needle path (the true error would be unknowable in
experiment, but is known here, in simulation). The
final column shows the average final error between
the needle tip and the target point. Look-ahead
control shows a higher success rate and better error
performance. In the simulations in Figs.6 and 7, the
maximum attainable curvature is set at 1/25 mm
−1
.
6 DISCUSSION
This paper presents techniques for both path
planning and path-following control in 3D for bevel-
tipped steerable needles using duty-cycled rotation.
Path planning is based on the popular RRT
algorithm. The computational expense of the
algorithm was reduced by reversing the coordinate
system and relaxing the entry constraint from a
single entry point to a slightly larger entry zone, as
well as by the use of interpolation. This work uses
positions and quaternions to describe the path,
increasing the generalizability of the technique.
Uncertainty in state estimation via imaging is
explicitly included in the simulation by
incorporation of noise. Simple and effective path-
following is provided by a look-ahead proportional
controller for position and heading, inspired by an
autonomous vehicle controller (Thrun et al., 2006).
Prior to this work, experimental insertions of the
needle in question were performed in gelatine
samples with fiducial beads included. Image
analysis of the resulting video stream confirmed that
tissue deformation during these insertions was
negligible. Therefore, tissue deformation was
neglected in these simulations.
As noted earlier, this simulation did not account
for torsional windup of the needle. Such windup will
ICINCO2013-10thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
198

undoubtedly occur. However, its inclusion in
simulation is problematic, because we do not have
ground truth that can be used. In physical
experimentation, a feedforward model of torsional
windup can be included (Reed et al., 2009), but
simulation of this effect is very difficult because of
the lack of an estimate separate from the
feedforward model itself, which could be used to
generate an error signal for a realistic simulation.
For this reason, treatment of torsional windup has
been deferred until physical experimentation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Partial funding for this work was provided by the
U.S. National Institutes of Health (grant no.
R21EB012209).
REFERENCES
Abolhassani, N., Patel, R. and Moallem, M. (2007) Needle
insertion into soft tissue: a survey. Med. Eng. Phys. 29
(4), 413–431.
Alterovitz, R., Goldberg, K. and Okamura, A. (2005)
Planning for steerable bevel-tip needle insertion
through 2D soft tissue with obstacles. In: Proc. IEEE
Int. Conf. Robot. Autom. 2005 pp. 1652–1657.
Alterovitz, R., Goldberg, K. Y., Pouliot, J. and Hsu, I.-C.J.
(2009) Sensorless motion planning for medical needle
insertion in deformable tissues. IEEE Trans. Inform.
Technol. Biomed. 13 (2), 217–225. Available from:
doi:10.1109/TITB.2008.2008393.
Van den Berg, J., Patil, S., Alterovitz, R., Abbeel, P., et al.
(2010) LQG-based planning, sensing, and control of
steerable needles. In: D. Hsu (ed.). Algorithmic
Foundations of Robotics IX. Berlin, Springer-Verlag.
pp. 373–389.
Bernardes, M. C., Adorno, B. V., Poignet, P. and Borges,
G. a. (2012) Semi-automatic needle steering system
with robotic manipulator. In: IEEE Int. Conf. Robot.
Autom., pp. 1595–1600.
Bernardes, M. C., Adorno, B. V., Poignet, P., Zemiti, N.,
et al. (2011) Adaptive path planning for steerable
needles using duty-cycling. In: Proc. IEEE/RSJ Int.
Conf. Intell. Robot. Syst. pp. 2545–2550.
Engh, J. A., Minhas, D. S., Kondziolka, D. and Riviere, C.
N. (2010) Percutaneous intracerebral navigation by
duty-cycled spinning of flexible bevel-tipped needles.
Neurosurgery. 67 (4), 1117–22.
Engh, J. A., Podnar, G., Khoo, S. Y. and Riviere, C. N.
(2006a) Flexible needle steering system for
percutaneous access to deep zones of the brain. In:
Proc. 32nd IEEE Northeast Bioeng. Conf. 2006 pp.
103–104.
Engh, J. A., Podnar, G., Kondziolka, D. and Riviere, C. N.
(2006b) Toward effective needle steering in brain
tissue. In: Proc. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol.
Soc. 2006 pp. 559–562.
Frasson, L., Ko, S. Y., Turner, A., Parittotokkaporn, T., et
al. (2010) STING: a soft-tissue intervention and
neurosurgical guide to access deep brain lesions
through curved trajectories. Proc Inst Mech Eng H.
224 (6), 775–788.
Hall, K. (2009) Attitude estimation and maneuvering for
autonomous obstacles avoidance by miniature air
vehicles. Brigham Young University.
Kallem, V. and Cowan, N. J. (2009) Image guidance of
flexible tip-steerable needles. IEEE Trans. Robot. 25
(1), 191–196.
Lindsley, T. A. (2009) Virtual Brain Model software.
(http://www.amc.edu/academic/software.)
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
(NINDS) and National Cancer Institute (2000) Report
of the Brain Tumor Progress Review Group. (NIH
Publication Number 01-4902).
Park, W., Kim, J. S., Zhou, Y., Cowan, N. J., et al. (2005)
Diffusion-based motion planning for a nonholonomic
flexible needle model. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf.
Robot. Autom. 2005 pp. 4611–4616.
Patil, S. and Alterovitz, R. (2010) Interactive Motion
Planning for Steerable Needles in 3D Environments
with Obstacles. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Biomed. Robot.
Biomechatron. pp. 893–899.
St. Pierre, J. (2009) Quaternion Toolbox. 2009.
(http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchan
ge/1176-quaternion-toolbox.)
Reed, K. B., Okamura, A. M. and Cowan, N. J. (2009)
Modeling and control of needles with torsional
friction. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 56 (12), 2905–
2916.
Thrun, S., Montemerlo, M., Dahlkamp, H., Stavens, D., et
al. (2006) Stanley: the robot that won the DARPA
Grand Challenge. J. Field Robot. 23 (9), 661–692.
Ünyelioğlu, K. A., Hatipoğlu, C. and Özgüner, Ü. (1997)
Design and Stability Analysis of a Lane Following
Controller ¨. IEEE Trans. Contr. Syst. Technol. 5 (1),
127–134.
Webster III, R. J., Kim, J. S., Cowan, N. J., Chirikjian, G.
S., et al. (2006) Nonholonomic modeling of needle
steering. Int. J. Robot. Res. 25 (5-6), 509–525.
Wood, N., Lehocky, C. A. and Riviere, C. N. (2013)
Algorithm for three-dimensional control of needle
steering via duty-cycled rotation. In: Proc. IEEE Int.
Conf. Mechatron. pp. 1–5.
Wood, N., Shahrour, K., Ost, M. C. and Riviere, C. N.
(2010) Needle steering system using duty-cycled
rotation for percutaneous kidney access. In: Proc.
Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. pp. 5432–
5435.
Xu, J., Duindam, V., Alterovitz, R. and Goldberg, K.
(2008) Motion planning for steerable needles in 3D
environments with obstacles using rapidly-exploring
Random Trees and backchaining. In: Proc. IEEE Int.
Conf. Autom. Sci. Eng. pp. 41–46.
Efficient3DControlforNeedleSteeringusingDuty-cycledRotation
199
