
Self-organizing Agents for an Adaptive Control of Heat Engines
J
´
er
´
emy Boes, Fr
´
ed
´
eric Migeon and Franc¸ois Gatto
Institut de Recherche en Informatique de Toulouse, Universit
´
e Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France
Keywords:
Multi-Agent Systems, Self-organization, Intelligent Control Systems.
Abstract:
Controlling heat engines imposes to deal with high dynamics, non-linearity and multiple interdependencies.
A way handle these difficulties is enable the controller to learn how the engine behaves, hence avoiding the
costly use of an explicit model of the process. Adaptive Multi-Agent Systems (AMAS) are able to learn and
to adapt themselves to their environment thanks to the cooperative self-organization of their agents. A change
in the organization of the agents results in a change of the emergent function. Thus we assume that AMAS
are a good alternative for complex systems control, reuniting learning, adaptivity, robustness and genericity.
In this paper, we present an AMAS for the control of heat engines and show several results.
1 INTRODUCTION
Over the years, the complexity of car engines has been
growing up, with new sophistications like Exhaust
Gas Recirculation or particle filters. Moreover our ex-
pectations about their efficiency are becoming more
important due to the strengthening of environmen-
tal norms, while the need for economic competitivity
leads to a need for easily instantiable controllers. The
emergence of software and electronic devices helps
to tackle these challenges but the development of En-
gine Control Unit (ECU) remains a difficult and time
consuming task.
The goal of this paper is to introduce a non-
classical approach of the control of car engines, based
on Adaptive Multi-Agent Systems (AMAS), that aims
to provide a quickly instantiable controller, avoiding
a heavy parametrization work. Based on learning and
adaptiveness skills of AMASs, our approach consid-
ers the engine and its ECU as a black box. The con-
troller modifies ECU parameters in order to obtain the
desired values on the engine outputs. This work is
part of a national project named Orianne.
Our motivation for working on a non-classical ap-
proach comes from the difficulties to build and fit an
efficient model of the engine we intend to control.
Humans fulfill this control task in their everyday life.
A child learning to drive a bike is a good example.
He has the ability to move his legs in order to walk
and run. He does not have any knowledge about bike
gears or inertia theory. While he is experiencing his
first ride, his most used skill is the ability to adapt and
to coordinate his movements in a new situation. This
adaptation requires learning, which is certainly not an
instantaneous process. Following a practice period,
the child eventually ends up acquiring the ability to
control the bike but still did not get in touch with any
theoretical concept and did not build any analytical
model of the bike inside his head. Furthermore, he
never stops learning: each new ride will improve his
mastering of the bike, and he will be able to adapt to a
new bike. This analogy is meant to explain the point
of view we adopted: the use of an explicit analytical
model is not necessary to the control of an engine.
Section 2 introduces usual control methods. We
follow with an introduction to self-organization and
to the Adaptive Multi-Agent Systems (AMAS) the-
ory. Section 3 describes the design of a Multi-Agent
System before going deeper in the agents behavior in
section 4. Then section 5 shows some results, before
section 6 concludes with our perspectives.
2 RELATED WORKS
In this section the main approaches of control are
presented before self-organization and the Adaptive
Multi-Agent Systems theory are briefly introduced.
2.1 Complex Systems Control
Controlling systems is a generic problem that can be
expressed as finding which modifications are needed
to be applied on the inputs in order to obtain the de-
243
Boes J., Migeon F. and Gatto F..
Self-organizing Agents for an Adaptive Control of Heat Engines.
DOI: 10.5220/0004483302430250
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO-2013), pages 243-250
ISBN: 978-989-8565-70-9
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

sired effects on the ouputs. The main approaches are
presented in the next paragraphs.
2.1.1 PID
Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers are
well-known and widely used. They base the control
on the calculation and the combination of three terms,
corresponding to the error (P), its duration (I) and its
variation rate (D) (Astrom and Hagglund, 1995). The
instantiation of a PID controller to a particular system
is a heavy procedure despite adjustement methods
like (Tyreus and Luyben, 1992). Besides, PID con-
trollers are not always efficient with non-linear sys-
tems, they need to be complemented with other mech-
anisms like fuzzy logic (Visioli, 2001). Also, a PID
controller can only handle one input with one retroac-
tion signal, which is a severe drawback for complex
systems control.
2.1.2 Adaptive Control
The dynamic nature of complex systems imposes to
adapt the controller as the system evolves. Model-
based approaches like Model Identification Adaptive
Control (MIAC) (Soderstrom and Stoica, 1988) or
Model Reference Adaptive Control (MRAC) (Kreis-
selmeier and Anderson, 1986) are regrouped under
the name of Model Predictive Control (MPC) (Niko-
laou, 2001). A model able to forecast the behavior of
the process is used in order to help the controller find-
ing the optimal control scheme. These approaches
successfully handle several inputs of dynamic non-
linear systems. They are used in particular in the do-
main of car engines (Dabo et al., 2008) but are limited
by the construction of the model on one hand, and
its parametrization on the other hand, which can take
several years.
2.1.3 Intelligent Control
Intelligent control can be seen as a part of adaptive
control. It regroups control approaches that use Ar-
tificial Intelligence methods to enhance the controller
adaptiveness. Among these methods we can find neu-
ral networks (Hagan et al., 2002), fuzzy logic (Lee,
1990), expert systems (Stengel, 1991) and bayesian
controllers (Colosimo and Del Castillo, 2007). Neu-
ral networks provide great genericity but they require
an offline learning step with a considerable amount
of data. Even if this enable an efficient control, they
remain sensible to perturbations and cannot adjust
themselves to the evolution of the system.
Expert systems are composed of a knowledge
base and an inference engine. They lack of generic-
ity and are hardly adaptable to highly dynamic non-
linear systems. That is why they are often com-
bined with fuzzy logic. Bayesian controllers are
based on bayesian probabilities, the most common are
the Kaman filter based controllers (Lee and Ricker,
1993). Yet, the bayesian approach does not deal with
the problem of control itself but with a sub-problem
which is the observation of the process. These meth-
ods can also be easily combined one with another, or
with more classical control approaches.
Finally agents-based techniques have been applied
in various fields, for example in the case of voltage
control (Wang, 2001) or manufacturing control (Clair
et al., 2008).
2.2 Self-organizing Software
The next paragraphs introduce the notion of self-
organization along with the Adaptive Multi-Agent
Systems theory.
2.2.1 Self-organization
The notion of self-organization refers to the fact that
the organization of a system results from internal
mechanisms and local interactions without any ex-
plicit external control (Camazine et al., 2003). Var-
ious artificial systems show this property, such as
swarms (Montresor et al., 2003) or some multi-
agent systems (O’Hare and Jennings, 1996). Self-
organization brings robustness and scalability, and
allows the engineering of underspecified software
(Di Marzo Serugendo et al., 2011).
2.2.2 Adaptive Multi-Agent Systems
The Adaptive Multi-Agent Systems (AMAS) the-
ory is a basis for the design of multi-agent systems
where cooperation is the engine for self-organization
(Georg
´
e et al., 2011). As cooperative entities, AMAS
agents try to reach their own goals as well as they
try to help other agents to achieve their goals. More-
over, an agent will modify its behavior if it thinks that
its actions are useless or detrimental to its environ-
ment. Such situations are called Non-Cooperative Sit-
uations (NCS). Some behavioral rules are specific to
NCSs, they allow agents to avoid or to solve these sit-
uations. By solving NCSs in regard to their own local
goals, cooperative agents collectively find a solution
to the global problem. Therefore one can consider the
global behavior of an AMAS as emergent.
AMAS principles have been applied by (Videau
et al., 2011) for the control of bioprocesses, avoid-
ing the use of a specific model and dealing with the
ICINCO2013-10thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
244
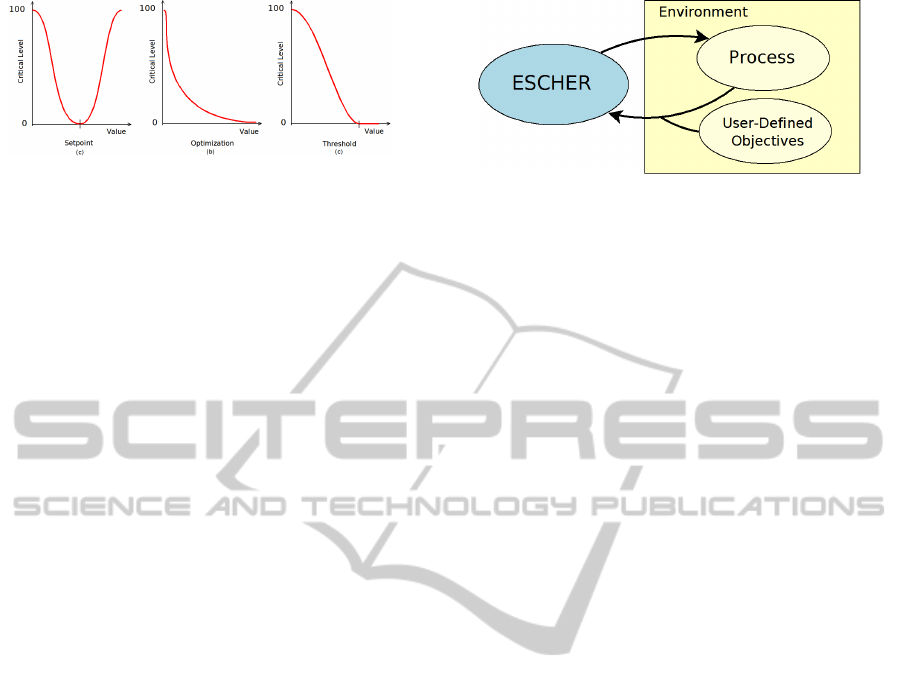
Figure 1: Criticality Functions.
evolution of the process over time, since an AMAS is
perpetually adjusting itself to its environment.
The next two sections describes the agents of our
controller, how they perform control and how they
self-organize.
3 CONTROLLER OVERVIEW
In this section we present the required abilities of a
complex system controller, and what are the agents of
our controller that enable them.
3.1 Basic Behavior
The next paragraphs describe how our multi-agent
system, called ESCHER (Emergent Self-adaptive
Controller for Heat Engine Regulation), works when
it is already adapted to the engine. The mechanisms
that lead to this adaptation will be explained further.
3.1.1 Observing the Process
If we intend to control an engine, it is obvious that we
need to be able to observe it. A specific agent type is
in charge of perception, called Variable Agent. Each
input and each output of the controlled black box has
a corresponding Variable Agent. These agents per-
ceive their value from the black box and send it to
other agents that need this information. Also, Vari-
able Agents can embed noise reduction algorithms if
this problem is not handled by a third party system.
3.1.2 Representing Objectives and Constraints
The controller needs to know what is the desired state
of the engine. This state is represented by a set of
Constraint Agents and possibly by additional Variable
Agents.
There are three types of Constraint Agents:
Threshold, Setpoint and Optimization. A Threshold
Constraint Agent expresses the will to keep a vari-
able either below or above a threshold specified by
a Variable Agent. This Variable Agent can either
correspond to a process variable or to a user-defined
value. In a similar way, a Setpoint Constraint Agent
Figure 2: ESCHER and its Environment.
expresses the will to set a process variable to a partic-
ular value specified by a Variable Agent. Finally, an
Optimization Constraint Agent represents the will to
minimize or maximize a process variable.
Using the functions shown in figure 1, each Con-
straint Agent computes a critical level that varies from
0 (the agent is satisfied) to 100 (the agent is far from
satisfied). The critical level depends on the value of
the variable on which the constraint is applied and
can be parametrized by a second Variable (in the case
of a threshold or a setpoint constraint). The critical-
ity function of an Optimization Constraint Agent is
asymptotic to zero, since we always try to minimize or
maximize the value. For instance, if the user desires
to set the rotational speed to 5000rmp, the Variable
Agent RotSpeedCommand (corresponding to “user-
defined setpoint on rotational speed”) will be set to
5000 and a setpoint Constraint Agent will be created.
Its critical level will be zero if the value of the Vari-
able Agent RotSpeed equals the value of RotSpeed-
Command, and will increase with the difference be-
tween RotSpeed and RotSpeedCommand.
It is clear that decreasing the critical levels means
solving the constraints, and the only way to do so is
to perform the adequate actions on the engine inputs.
Finding these actions implies to be able to analyze the
current sate of the environment. The engine and the
user desires are considered as the environment of the
multi-agent system.
3.1.3 Analyzing the State of the Environment
As shown in Figure 2, ESCHER environment is the
engine as well as the user-defined setpoints, thresh-
olds and optimizations. Thanks to Variable Agents
and Constraints Agents, the ESCHER has a represen-
tation of its environment. Before it can perform con-
trol, it must be able to extract relevant information
from this representation. This is the role of agents
called Context Agents.
A Context Agent memorizes the effects, on ev-
ery critical level, of an action applied to one partic-
ular input of the engine. It also memorizes the state
of the environment when the action was applied. To
represent this state the Context Agent maintains a set
Self-organizingAgentsforanAdaptiveControlofHeatEngines
245

of validity ranges, containing one range per Variable
Agent. A Context Agent also maintains a set of values
that are the observed and memorized effects of the ac-
tion on each of the critical levels. This set is called the
forecasts. In other words, a Context Agent represents
the information that if every Variable Agent value is
inside the Context Agent validity range, and if its ac-
tion is applied, then the effects on every critical level
will be similar to the Context Agent forecasts.
A Context Agent is said valid when the environ-
ment is in a state that matches its validity ranges, i.e.
every perceived variable is inside the corresponding
validity.
When valid, a Context Agent sends a notification
with its action and forecasts to the appropriate Con-
troller Agent, which will be explained in the next part.
3.1.4 Selecting the Adequate Action
Each controlled input of the engine is associated with
a Controller Agent. The role of a Controller Agent is
to apply the most adequate action in order to reduce
the critical levels. It will base the choice of the action
(ie increment, decrement or stay put) on the informa-
tion it receives from Context Agents, picking the ac-
tion that will provoke the biggest decrease of the crit-
ical levels. When an action is picked, the Controller
Agent notifies every Context Agents who proposed it.
For instance, the Controller Agent of the mass fuel
injected may receive two notifications from two Con-
text Agents. Context Agent A says if you apply a
decrease of 0.5 the critical levels will not change ex-
cept for the Constraint Agent Torque Optimization
that will rise of 3.5. Context Agent B says if you apply
an increase of 0.5 the critical levels will not change
except for the Constraint Agent Torque Optimization
that will drop of 1.5. In this case, the Controller Agent
obviously chooses to increase the mass fuel injected.
There are several cases where the Controller
Agent is unable to make a good decision, because
of incomplete or incorrect information from Con-
text Agents. These cases are Non-Cooperative Situa-
tions (NCS). They happen when ESCHER is not well
adapted to the engine yet. When a NCS occurs, the
cooperative behavior of involved agents is triggered
in order to solve it. This will be explained in section
4. For now, we continue with the architecture of the
system.
3.2 Topology
The four ESCHER’s agent types were introduced in
the previous paragraphs. Figure 3 shows the topol-
ogy of their interactions. We can see that, while it is a
MAS itself, ESCHER is also an aggregation of several
MASs, each constituted by a Controller Agent and its
set of Context Agents. The environment of these sub-
MASs is composed of the Variable Agents, the Con-
straint Agents, and the environment of ESCHER. In-
deed, each Controller Agent is not directly in interac-
tion with other Controller Agents. The only link be-
tween them are their environment (the engine they are
controlling, via the Variable and Constraint Agents).
Actions from one Controller Agent will have conse-
quences on the engine that will be reflected by Vari-
able and Constraint Agents, and Controller Agents
share the same environment, hence we can expect
them to progressively synchronize their actions. Fur-
thermore, Context Agents never directly interact with
each other (even inside the same set) but only with
their associated Controller Agent.
The question is now how can the system create
and adjust Context Agents in order to deal with an
unknown process? The next section gives an answer.
4 CONTEXT AGENTS LEARNING
AND ORGANIZATION
This section explains how the set of Contexts Agents
is built and how they self-organize to provide an accu-
rate representation of the explored part of the process’
state space.
4.1 Non-cooperative Situations
In this part, we explain how agents solve the Non-
Cooperative Situations they face. Since they provoke
changes in the agents behavior, NCSs are the key of
the adaptiveness of Adaptive Multi-Agent Systems.
Each agent locally solves its own NCSs when they
occur, by changing its own local behavior, and thus
of the global behavior of the system. The NCSs of
ESCHER concern the Controller Agents and the Con-
text Agents, and trigger behaviors that correct Context
Agents’ forecasts and validity ranges.
4.1.1 No Adequate Action in Suggestions
This NCS occurs when the suggestions list of a Con-
troller Agent contains only forecasts of increasing
critical levels. Whatever the Controller Agent may
chose, it believes it will deteriorate the constraints.
There are two cases: either all the possible actions are
already suggested (i.e. increase the value, decreasethe
value and stay put) or some actions are not suggested.
In the first case, the only choice left is to accept the
suggestion with the less bad forecasts. In the second
case, a new action is chosen among those which are
ICINCO2013-10thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
246

Figure 3: ESCHER Topology.
not suggested, and a new Context is created with this
action.
4.1.2 Empty Suggestions List
This NCS happens when a Controller Agent has to
apply an action, but finds its suggestion list empty.
It will be unable to find an adequate action with cer-
tainty, but it can make some hypothesis to try one. If
the last applied action had reduced the higher critical
level, the same action is reproduced. If not, the op-
posite action is applied (e.g. if the last action was an
inscrease of the input value, the new action will be a
decrease). If no action has ever been applied, the so-
lution is to randomly chose the action. In any case a
new Context Agent is created with the applied action.
After its creation, a Context Agent extends its validity
ranges as long as its action is applied and observe the
variations of the critical levels to set its forecasts.
4.1.3 Wrong Forecast
When a Context Agent is selected and its action ap-
plied, it oberves the variations of the critical levels to
check if they matches its forecasts. If the forecasts
are wrong (i.e. a critical level evolves in the opposite
direction of the forecast), the Context Agent consid-
ers that it should not have been valid when the ac-
tion was suggested. Thus it reduces its validity ranges
but does not modify its forecasts. A Context Agent
dies if one of its ranges is reduced to an amplitude of
zero. If the forecasts are simply inexact (i.e all the
critical levels evolve in the forecasted direction, but
not with the forecasted amplitude), the Context Agent
considers that its validity was relevant. Thus it does
not modify its validity ranges but adjusts its forecasts
to match its observation.
This NCS also impacts the Controller Agent that
had selected the Context Agent with the wrong fore-
casts. When a Controller Agent notices that the
critical levels variations don’t match the forecast, it
stop applying the current action, notifies the Context
Agent that its action is no longer applied, and looks
for a new action in its suggestion list.
4.2 Self-organization
Context Agents are able to evaluate their own behav-
ior and to adjust it (by modifying their forecasts and
their validity ranges) if necessary. Thus we can say
that a Context agent is self-adaptive. Moreover, Con-
text Agents are created at runtime. Each of them fol-
lows simple and local behavioral rules. These rules
lead to the formation of a coherent set of Context
Agents where each agent occupies a portion of the en-
vironment state space for which its forecasts on crit-
ical levels are correct. Thus we can say that the set
is the result of the self-organization of the Context
Agents. It is also intersting to note that all the Con-
text Agents of a given set put together give a good
approximation of the criticality functions.
There is another, more subtle, level of self-
organization. Each Controller Agent makes its own
decisions about the action to apply on its effec-
tor, other Controller Agents are never consulted.
Nonetheless, it appears that they manage to synchro-
Self-organizingAgentsforanAdaptiveControlofHeatEngines
247
nize their actions and efficiently reduce the critical
levels, solving the constraints. This is possible be-
cause each process input corresponding to a Con-
troller Agent is also represented as a Variable Agent.
Context Agents suggestions for one Controller Agent
are therefore conditionned by the current state of
other Controller Agents corresponding process input.
As they all try to lessen the critical levels, they even-
tually find a synergy and the global behavior of ES-
CHER (the actions on all the controlled inputs) is co-
herent.
5 RESULTS
Generated black-boxes (Boes et al., 2013) were used
for the first tests to check ESCHER’s abilities to deal
with multiple inputs and outputs, to find compro-
mises between several objectives, and to adapt to un-
expected changes of behavior of the controlled pro-
cess. These tests are not detailed here due to space
limitations.
Several tests have been driven on a 125cc mono-
cylinder fuel engine in various steady operating points
of rotational speed and load. Those presented here
have been driven at 5000rpm and 870mbar of pressure
in the inlet manifold. The goal of ESCHER is here
to maximize the indicated mean effective pressure
(IMEP), an output variable that reflects the torque. In
other words, the goal is to minimize the critical level
of an Optimization Constraint Agent associated to the
IMEP. Injected mass fuel (IMF) and ignition advance
are controlled by ESCHER, which has no other pre-
vious information about the engine than the variation
interval of the variables. Each test has been super-
vised and validated by domain experts.
5.1 Controlling Mass Fuel Injection
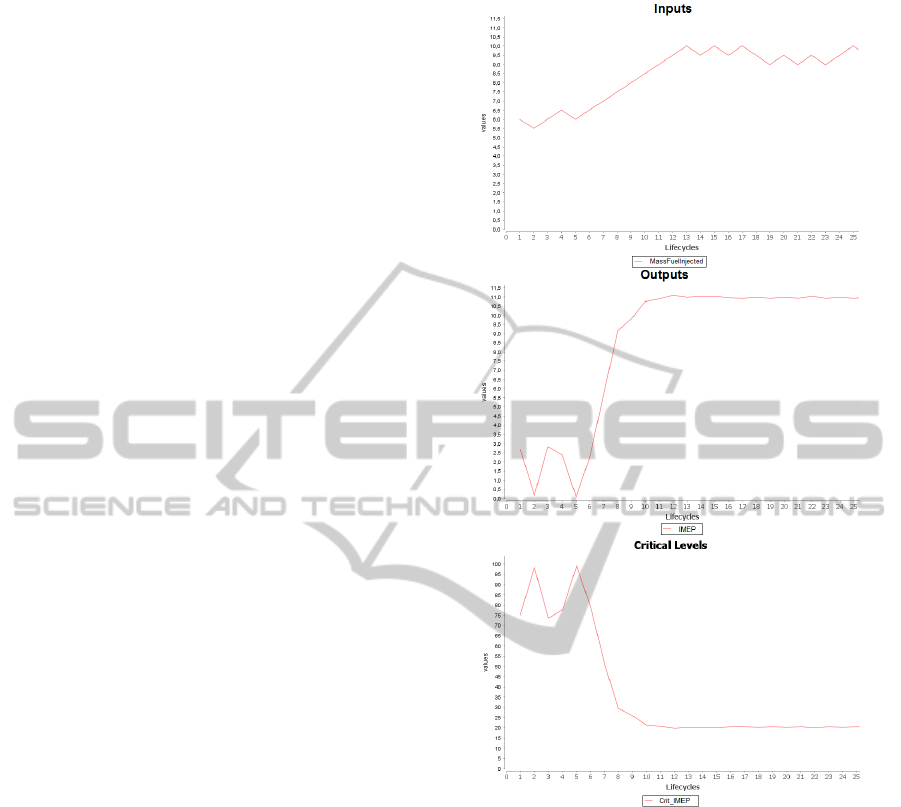
Figure 4 shows ESCHER controlling the IMF to max-
imize the IMEP. At the beginning of the test, ES-
CHER does not know anything about the controlled
process. It first decreases the IMF, but it is a mistake:
the critical level rises (first lifecyle). The error is cor-
rected by increasing the IMF. The critical level drops,
so ESCHER keeps this action (lifecycles 2 and 3).
Then it perceives that while the IMF is rising, the crit-
ical level of the IMEP is rising too. But it is due to the
noise on the IMEP. This causes ESCHER to mistak-
enly decrease the IMF. The error is rapidly detected
and ESCHER eventually finds that it has to increase
the IMF in order to reduce the critical level (lifecycles
5 to 13). Once the maximal IMEP has been reached,
ESCHER oscillates around the IMF value that keeps
Figure 4: Controlling Injected Mass Fuel to Maximize
IMEP.
the critical level at its minimum. During this test, five
Contexts Agents were created and the optimum value
was reached in 12 lifecycles.
5.2 Controlling Mass Fuel Injection
and Ignition Advance
In this test, ESCHER controls the ignition advance in
addition to the IMF. Figure 5 shows the curves of this
test. Results are similar to the previous test, with ES-
CHER first committing a mistake on both of the con-
trolled inputs, causing a rise of the critical level. Then
the error is corrected, before the controller stabilizes
the engine around the maximum IMEP.
The optimum IMEP was reached in 18 lifecycles.
During the 30 lifecycles of the test, ESCHER created
ICINCO2013-10thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
248

Figure 5: Controlling Injected Mass Fuel and Ignition Ad-
vance to Maximize IMEP.
19 Context Agents (10 were created by Mass Fuel In-
jected Controller Agent and 9 by Ignition Advance
Controller Agent).
The main challenge with the real engine compared
to generated black boxes is to deal with noise and la-
tency. As ESCHER quickly reacts to errors, the noise
is handled naturally. To overcome the latency be-
tween an action and its effects, ESCHER waits during
a parametrizable period of time between its actions
and its observations. For each test on the engine, a
lifecycle was executed every three seconds.
5.3 Discussion
ESCHER finds optimum values for all of the tested
operating points. As it is impacted by the noise on
the variables, the time taken to converge may vary.
The biggest differences were observed at 4000rpm
and 700mbar of pressure in the inlet manifold where it
took from 100 seconds up to 400 seconds to converge.
But it remains quicker than human experts doing it by
hand as it is currently the case in the industry. More
tests are planned, with more objectives and more si-
multaneously controlled variables.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORKS
In this paper, we presented an Adaptive Multi-Agent
System, called ESCHER, which controls heat en-
gines, basing its behavior on self-organizing agents.
We detailed its architecture and the agents interac-
tions.
ESCHER is based on the idea that the complete
understanding of how an engine works is not neces-
sary to its control. All the controller needs to know
is how the engine behaves. In other words our con-
troller is of black-box type: ESCHER only perceives
the engine’s inputs and outputs, but not its internal
mechanisms. The basic principle of our controller is
the following: the state of the engine inputs/outputs is
memorized when an action is applied and the conse-
quences of this action are recorded. This information
will be used to decide whether this action was good or
not in regard of the user-defined desired engine state.
This means that the quality of the control improves
over time: at the begining the controller knows noth-
ing about the engine, but it perpetually learns from
its actions and quickly manages to control it. The
learning is parallel to the control, so ESCHER con-
tinuously self-adapts to the process.
No prerequisite knowledge other than the inten-
tions of the user (i.e. some criticality functions)
is needed by ESCHER. It is also able to satisfy
multi-criteria constraints on multiple inputs and out-
puts. Moreover, the independence between Controller
Agents gives a certain modularity to ESCHER. Each
Controller Agent (and its related Context Agents) is
a stand-alone MAS that can be plugged on a process
input. Regardless on what is controlling the other in-
puts, it will be able to synchronize its actions to per-
form a correct control.
We showed that ESCHER is able to deal with non-
linearity and multiple inputs and outputs, and that it
handles the noise and latency of a real engine, without
heavy knowledge about the engine. The only required
instantiation work is the translation of the user’s ob-
jectives into criticality functions.
By focusing on its learning skills, we consider to
Self-organizingAgentsforanAdaptiveControlofHeatEngines
249

make the ESCHER generic enough to be easily ap-
plied to all kind of systems. Multi-Agent Systems us-
ing a similar pattern have already been successfully
applied to the control of the temperature of a biopro-
cess (Videau et al., 2011) and are currently being ap-
plied in the contexts of ambiant systems (Guivarch
et al., 2012) and energy management of buildings.
Secondly, the behavior itself needs some improve-
ments. New mechanisms for a better resolution of the
problem of latency between the actions and their ef-
fects are required. Moreover, in large processes, some
inputs may not affect some outputs. The learning
of the process behavior could be enhanced by taking
into account this fact. Finally, the main limitation to
the application of ESCHER is the need for predefined
criticality functions. Self-defined criticality functions
could simplify make our controller even easier to in-
stantiate.
REFERENCES
Astrom, K. J. and Hagglund, T. (1995). PID Controllers:
Theory, Design, and Tuning. Instrument Society of
America, Research Triangle Park, NC, second edition.
Boes, J., Glize, P., and Migeon, F. (2013). Mimicking Com-
plexity: Automatic Generation of Models for the De-
velopment of Self-Adaptive Systems. In International
Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodolo-
gies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH),
Reykjavik. INSTICC Press.
Camazine, S., Deneubourg, J.-L., Franks, N. R., Sneyd,
J., Theraulaz, G., and Bonabeau, E. (2003). Self-
Organization in Biological Systems. Princeton Uni-
versity Pres.
Clair, G., Kaddoum, E., Gleizes, M.-P., and Picard, G.
(2008). Self-regulation in self-organising multi-agent
systems for adaptive and intelligent manufacturing
control. In Second IEEE International Conference on
Self-Adaptive and Self-Organizing Systems.
Colosimo, B. M. and Del Castillo, E., editors (2007).
Bayesian Process Monitoring, Control and Optimiza-
tion. Taylor and Francis, Hoboken, NJ.
Dabo, M., Langlois, N., Respondek, W., and Chafouk, H.
(2008). NCGPC with dynamic extension applied to a
Turbocharged Diesel Engine. In Proceedings of the
International Federation of Automatic Control 17th
World Congress, pages 12065–12070.
Di Marzo Serugendo, G., Gleizes, M.-P., and Karageorgos,
A., editors (2011). Self-organising Software - From
Natural to Artificial Adaptation. Natural Computing
Series. Springer.
Georg
´
e, J.-P., Gleizes, M.-P., and Camps, V. (2011). Co-
operation. In Di Marzo Serugendo, G., editor,
Self-organising Software, Natural Computing Series,
pages 7–32. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Guivarch, V., Camps, V., and Pninou, A. (2012). Context
awareness and adaptation in ambient systems by an
adaptive multi-agent approach. In International Joint
Conference on Ambient Intelligence, Italy.
Hagan, M. T., Demuth, H. B., and De Jesus, O. (2002). An
introduction to the use of neural networks in control
systems. International Journal of Robust and Nonlin-
ear Control, 12(11):959–985.
Kreisselmeier, G. and Anderson, B. (1986). Robust model
reference adaptive control. IEEE Transactions on Au-
tomatic Control, 31(2):127 – 133.
Lee, C. C. (1990). Fuzzy logic in control systems: Fuzzy
logic controller. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man
and Cybernetics, 20(2):404–418.
Lee, J. H. and Ricker, N. L. (1993). Extended kalman filter
based nonlinear model predictive control. In Ameri-
can Control Conference, pages 1895–1899.
Montresor, A., Meling, H., and Babaolu, z. (2003). Mes-
sor: Load-balancing through a swarm of autonomous
agents. In Moro, G. and Koubarakis, M., editors,
Agents and Peer-to-Peer Computing, volume 2530 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 125–137.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Nikolaou, M. (2001). Model predictive controllers: A criti-
cal synthesis of theory and industrial needs. Advances
in Chemical Engineering, 26:131–204.
O’Hare, G. M. and Jennings, N. R. (1996). Foundations of
distributed artificial intelligence. Wiley-Interscience.
Soderstrom, T. and Stoica, P. (1988). System identification.
Prentice-Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA.
Stengel, R. F. (1991). Intelligent failure-tolerant control.
IEEE Control Systems, 11(4):14–23.
Tyreus, B. D. and Luyben, W. L. (1992). Tuning PI con-
trollers for integrator/dead time processes. Industrial
& Engineering Chemistry Research, 31(11).
Videau, S., Bernon, C., Glize, P., and Uribelarrea, J.-L.
(2011). Controlling Bioprocesses using Cooperative
Self-organizing Agents. In Demazeau, Y., editor,
PAAMS, volume 88 of Advances in Intelligent and Soft
Computing, pages 141–150. Springer-Verlag.
Visioli, A. (2001). Tuning of PID controllers with fuzzy
logic. IEE Proceedings - Control Theory and Appli-
cations, 148(1):1–8.
Wang, H. (2001). Multi-agent co-ordination for the sec-
ondary voltage control in power-system contingen-
cies. Generation, Transmission and Distribution,
IEEE Proceedings, 148(1):61 –66.
ICINCO2013-10thInternationalConferenceonInformaticsinControl,AutomationandRobotics
250
