
Effective Business Plan Evaluation using an Evolutionary Ensemble
G. Dounias, A. Tsakonas, D. Charalampakis and E. Vasilakis
Management and Decision Engineering Laboratory, Department of Financial Engineering and Management,
University of the Aegean, 41 Kountouriotou Street, 82100 Chios, Greece
Keywords:
Decision Making, Ensemble Building, Genetic Programming, Fuzzy Systems, Business Plan Evaluation.
Abstract:
The paper proposes the use of evolving intelligent techniques, for effective business decision making related
to strategic management. Under the current competitive environment, business plans appraisal arises as an im-
portant task for bankers, investors, venture capital fund managers and consultants among others. The process
of business plans assessment requires various technical competencies, market awareness and adequate expe-
rience, thus increasing the relevant operating costs. A conceptual model for the evaluation of business plans
is being proposed, with the use of both numerical and qualitative parameters, clustered under four headings.
The input data is processed with the comparative use of ensembles of evolutionary classifiers, and an intelli-
gent model of business plans’ appraisal is built. The reliability and the accuracy of the results are considered
satisfactory by the subject matter experts.
1 INTRODUCTION
The evaluation of business plans is a process which
demands proper technical and managerial compe-
tences, market and industrial awareness as well as
professional expertise. Moreover, this multi-task ana-
lytical procedure is regarded as a time consuming ac-
tivity. These capabilities and prerequisites are rais-
ing high the resources that must be committed from a
consultancy or a venture capital fund, taking into con-
sideration the need to analyse and assess hundreds of
business plans annually. In addition, high-skilled and
expert human resources shall be employed and com-
pensated, in order to undertake this difficult to stan-
dardize activity.
In recent years, business tasks and analyses be-
come more and more demanding requiring advanced
computational techniques for modelling related de-
cisions. Advanced intelligent techniques, often em-
bodying hybrid mechanisms or adaptive schemes, are
proven useful and reliable in business decision mak-
ing and knowledge management. One important task
to fulfil in business decision making, is the analysis
and evaluation of business strategy and policy data,
mainly business plans, but also marketing plans, fea-
sibility studies and competition analysis.
The well-known advantages of intelligent tech-
niques for modelling and analysing several business
applications are:
• The ability to easily cope effectively with various
types of data (quantitative and qualitative, contin-
uous and discrete etc) with sparse data matrices
and structures including blank (i.e. unknown or
dont care) entries, with huge collections of data
and complex solution spaces.
• The ability to produce comprehensible knowledge
structures with a high degree of generalization,
solutions ready for immediate use for the domain
experts, but even for non-expert decision makers
in some cases.
Two types of risk are involved in the business plan
evaluation problem:
• Propagated Risk: Refers to the risk accumulated
from the primary data sets that compose the data
base of the system. The measurement value of
this risk does not differentiate from the risks value
that is generated through the business plans man-
ual evaluation by the expert.
• Regression risk: Is the risk involved during the
validation of the model due to its accuracy rate.
For encountering the regression risk the following
measures have been implemented:
– In each question that the system responses, the
accuracy rate is displayed. By this, the expert
user is provided with a primary estimation of
the accuracy rate.
97
Dounias G., Tsakonas A., Charalampakis D. and Vasilakis E..
Effective Business Plan Evaluation using an Evolutionary Ensemble.
DOI: 10.5220/0004491400970103
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Data Technologies and Applications (DATA-2013), pages 97-103
ISBN: 978-989-8565-67-9
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

– For each case of assessment, a set of five in-
dependent evaluators is deployed, that imple-
ments different methodologies of validation.
Full or partly full consensus of the evaluators,
strengthens explicitly the accuracy of the result.
Considering the aforementioned factors, the intelli-
gent model proposed in this work, supports the de-
cision making of entrepreneurs looking for funds to
finance their own start-up Small-Medium Enterprises
(SME), as well as for investors and business angels
searching innovative and promising business ideas.
The system incorporates data driven technologies for
the construction of classification models, and its out-
put is a result of learning from actual, real-world
cases.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: The
next section includes a literature review in the re-
spective domains. Section 3 presents the intelligent
methodology proposed for building a classification
and decision model for business plan evaluation tasks,
and sketches the general methodological scheme of
the approach. Then results on the application domain
and the business plan data are presented, followed by
a short discussion in Section 4. The paper concludes
in Section 5 with a summary and a discussion on po-
tential future research.
2 BACKGROUND
The use of computational intelligence approach in
business applications is not new. Several applica-
tions exist, either carefully gathering and then in-
telligently analysing large business data collections,
or implementing generalized methodologies that can
cope with complex business concepts, rules and prin-
ciples in order to obtain powerful managerial decision
analysis tasks. In this context papers can be found
which perform demanding business tasks with the aid
of sophisticated intelligent techniques.
In (Wen et al., 2008), the authors present the im-
plementation of a knowledge based decision support
system for measuring enterprise performance, based
in various financial data, in future total sales predic-
tion using neural nets, but also using knowledge rea-
soning for evaluating enterprise performance. Strate-
gic planning support by judgment of internal and
external decision factors using a fuzzy-multicriteria-
CBR methodology is given by (Royes and Bastos,
2003).
In (Fowler, 2000), the authors propose the devel-
opment of a knowledge value-chain (KVC) concept
into a closed loop knowledge activity cycle. Busi-
ness self-assessment through a multiple criteria de-
cision analysis software tool is described by (Xu et
al., 2006). In (Changchien and Lin, 2005) the au-
thors present the design and implementation of a case-
based reasoning system for marketing plans. Feature
selection is used by (Chen and Hsiao, 2008), to diag-
nose a business crisis by using a real GA-based sup-
port vector machine. The application of a multi-agent
intelligent approach for profitable customer segmen-
tation is proposed by (Lee and Park, 2005).
There is a growing number of research demon-
strating the effectiveness of ensemble systems over
their respective individual estimators. A general theo-
retical framework for improving regression estimates
by ensemble methods has been proposed in (Perrone
and Cooper 1993), where it is demonstrated that an
ensemble may provide better results that those of its
independent predictors. The idea of creating hierar-
chical mixtures of experts has been proposed in (Jor-
dan and Jacobs, 1993) where generalized linear mod-
els were effectively used as coefficients and compo-
nents.
Improved generalization for ensembles of classi-
fiers has been demonstrated in (Tumer and Ghosh,
1996), where focus is given on data selection and clas-
sifier training methods, aiming to improve classifier
complementarity by effectively reducing their corre-
lation. The effect of diversity in neural network en-
sembles for classification has also been studied re-
cently in (Brown et al.,(2005)). These ensembles
are constructed using the negative correlation learn-
ing approach (Eastwood and Gabrys 2007), and an
evolutionary approach is used to calculate the basic
parameter of the algorithm γ. Their result denotes that
γ tends to be problem-dependent and bounds for this
value are provided.
Zhou et al.(Zhou et al., 2001) examine the rela-
tionship between the generalization ability of the neu-
ral network ensemble and the correlation of the indi-
vidual neural networks. They propose a model that
employs a genetic algorithm to select an optimum
subset of individual trained neural networks. Their
approach shows better performance as compared to
averaging the neural networks. Genetic Programming
(Koza 1992)(Whigham, 1996a), is an an evolving in-
telligent algorithmic approach, in fact an extension of
Genetic Algorithms (GAs), where chromosomes have
been replaced by variable length decision tree pro-
grams, while the well-known genetic operators such
as crossover and mutation remain the same in prin-
ciple. Special syntax principles can be used for so-
lution encoding, commonly expressed in grammar-
based restrictions (Whigham, 1996b)(Tsakonas and
Dounias, 2002a). The applied restrictions are then
able to produce very complex forms of output (Koza,
DATA2013-2ndInternationalConferenceonDataManagementTechnologiesandApplications
98
1997b)(Koza, 1997c).
3 SYSTEM DESIGN
The objective of this work was the design and imple-
mentation of a novel intelligent application support-
ing the decision makers and evaluators of business
plans in innovative sectors. During this work, a se-
ries of methodological tools were identified, whereas
the effectiveness of the following two methodologies
were validated and comparatively deployed through
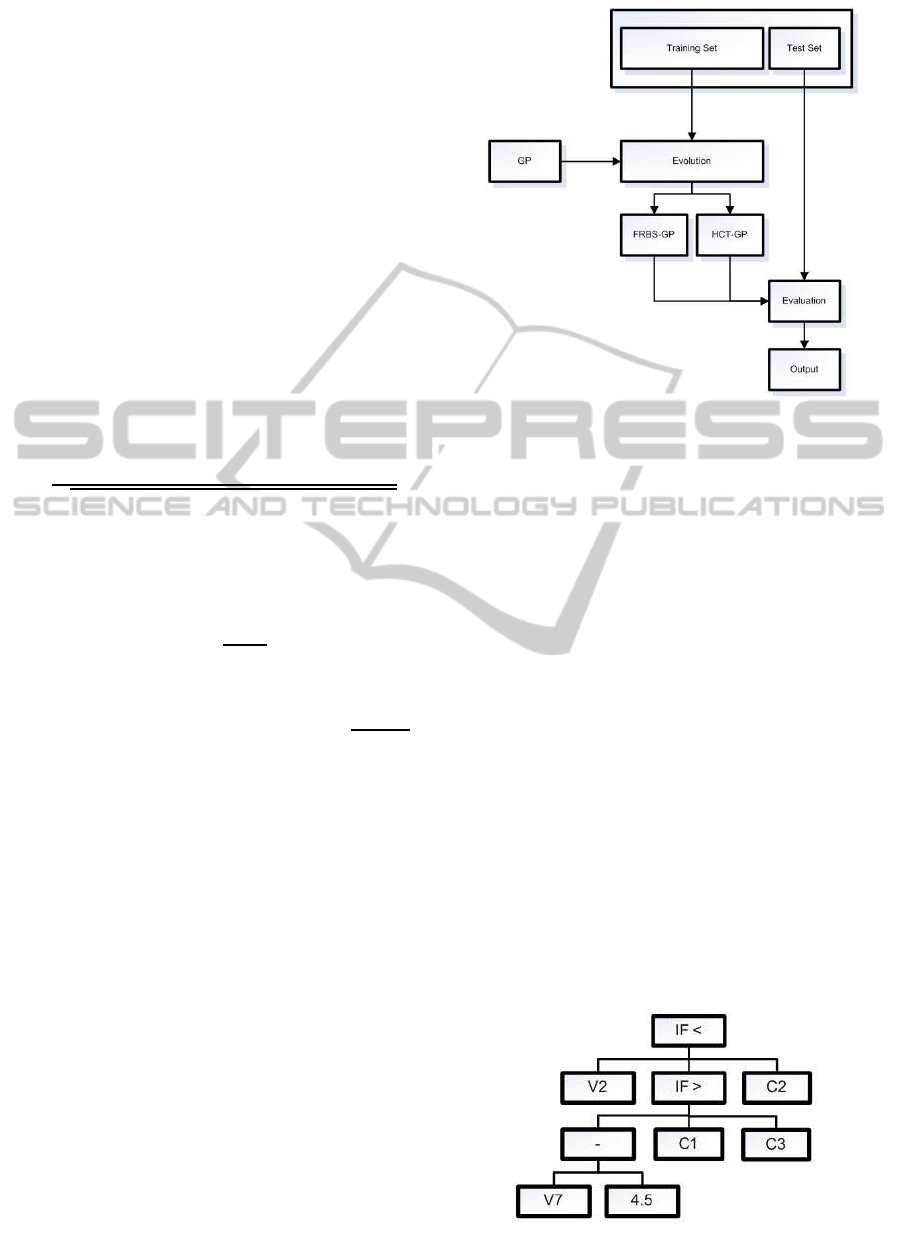
various pilot tests. The process to train each of the
models is shown in Fig. 1. For each of the predictive
model outputs a 5-fold cross-validation process was
used for training. As fitness value, the Matthews cor-
relation coefficient was used for the binary tasks 1, 2
and 4 (see Section 4), aiming to reduce any training
bias potentially imposed by inequivalent classes:
M
cc
=
TP× TN − FP× FN
p
(TP+ FP)(TP+ FN)(TN + FP)(TN + FN)
(1)
where TP: True positiveclassifications, TN: True neg-
ative, FP: False positive and FN: False negative. For
the nominal task 3, the Geometric mean of the recall
values of all classes was used (Sun et al., 2006):
G
mean
=
n
s
n
∏
1
R
i
(2)
where R
i
is the Recall value for class i, R
i
=
TP
i
TP
i
+FN
i
and n the total classes number (e.g. the number of the
nominal values in our problem). Two computational
intelligence models were used:
• Hierarchical classification trees using grammar
guided genetic programming (GGGP).
• Fuzzy rule-based systems represented as GGGP
trees.
The first approach produces hierarchical classification
trees with the aid of genetic programming (Tsakonas
and Dounias, 2002b). Such an example tree is shown
in Fig. 3. This tree corresponds to the following deci-
sion rule:
IF V2 < 0 THEN
(IF V7-4.5 > 0 THEN
C1
ELSE C3)
ELSE C2
where Cn implies a class. The second approach
implements Mamdani fuzzy rule based systems
(Zadeh, 1965) also by means of genetic program-
ming (Tsakonas et al., 2004). Furthermore, a
Figure 1: Training process for the predictive models in this
work.
<CLAUSE> ::= <CLASS>|<IF_OPER>
<IF_LESS> ::= IF_LESS <EXPR> <EXPR> <CLAUSE>
<CLAUSE>
<IF_OPER> ::= IF_LT | IF_GT | IF_EQ | IF_LTE |
IF_GTE
<EXPR> ::= <ATTR> | <NUMB> | <OPER>
<OPER> ::= <OPS> <EXPR> <EXPR>
<OPS> ::= + | - | * | PDIV
<NUMB> ::= Real
<ATTR> ::= X1 | X2 | X3 | ... | Xn
<CLASS> ::= CLASS1 | CLASS2 | ... |
CLASSn
Figure 2: Grammar for evolving hierarchical classification
trees using GGGP.
majority-voting system of the two above-mentioned
approaches was incorporated, in order to reduce the
training bias and increase the robustness of the sys-
tem. The grammar for the hierarchical trees is shown
in Fig. 2.
The definition of the BNF Grammar for evolv-
ing Mamdani fuzzy rule-based systems is shown in
Fig. 4 (Tsakonas et al., 2004). In this work, triangu-
lar membership functions were applied. The evalua-
tion of business plans demands the generation of four
sub-systems, each requiring their own classification
task. For every sub-system, an independent ensemble
Figure 3: Example hierarchical classification tree by GP.
EffectiveBusinessPlanEvaluationusinganEvolutionaryEnsemble
99

Table 1: Parameters of structural and contextual analysis of the business plans assessment methodology.
Parameter group Parameter
Profile (of the Prior expertise and sector of activity
Entrepreneur and Educational level
the start-up SME) Professional experience
Years of professional activity in the sector
Financial results
Net profit the past three years
Return on Investment the past three years
Average growth rate of the sales, past 3 years
Own versus Funded capital ratio
Own resources invested (proportionally)
Sector Analysis
Type of sector
Sectors growth rate
Sectors attractiveness
Level of competition
Perspectives and
features of the Funding sources
business activity Return on Investment horizon
Annual projected net profit for the next five years
Net Present Value
Investments life expectation
Core competence(s)
SWOT analysis effectiveness
Pricing policy
Launching strategies
Markets sales perspectives
Products/services distribution
Products/services positioning
Business Analyst
Assessment fields Technical and structural characteristics
of the business plan
Overall evaluation of business model
Business plans projections efficiency
Business plans scenario planning
system is created, consisted of five fuzzy-ruled based
systems and five hierarchical classification trees. Dur-
ing the voting procedure, in case of equality between
two options, the output with the higher average confi-
dence level of their Mamdani fuzzy-rule based predic-
tors is promoted. The ensemble architecture is shown
in Fig. 5. Regarding the technical settings of the evo-
lutionary framework, the reader is referred for further
details to (Tsakonas and Dounias, 2002b)(Tsakonas
et al., 2004).
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The clusters of the qualitative and quantitative param-
eters that feed the model, and compose the structural
and contextual analysis of the business plan assess-
<TREE> ::= <RL> | <RULE>
<RL> ::= RL <TREE> <TREE>
<RULE> ::= RULE <COND> <CLASS>
<COND> ::= <IF> | <AND>
<IF> ::= IF <ATTR> <FS>
<AND> ::= AND <COND> <COND>
<CLASS>::= THEN <OUT> <CLASS>
<FS> ::= SMALL | MEDIUM | LOW
<ATTR> ::= X1 | X2 | X3 | ... | Xn
<CLASS>::= CLASS1 | CLASS2 | ... | CLASSn
<OUT> ::= Y
Figure 4: Grammar for evolving Mamdani fuzzy rule-based
systems using GGGP.
ment methodology as well as of the entrepreneurs
profile are illustrated in Table 1. The data was stan-
dardized in [−1, 1] and the parameter Net Present
DATA2013-2ndInternationalConferenceonDataManagementTechnologiesandApplications
100

Figure 5: Overall ensemble architecture.
value was transformed to logarithmic scaling. Fif-
teen (15) out of the forty two (42) decision variables
related to business plan evaluation were continuous,
seven (7) were discrete with three or five different in-
teger values each and finally, twenty (20) were binary
variables. The initial decision problem was divided to
four sub-problems, each of which aimed at finding the
relation of every dependent variable in question, from
the total set of decision parameters.
The reliability of the intelligent model was val-
idated against the average accuracy of 120 business
plans of Greek innovative start-ups and succeeded the
following average accuracy results:
• Completeness of technical and structural charac-
teristics of the business plan. This is a binary vari-
able. The accuracy rate in test data was 86.4%.
• Overall evaluation of the business model (quality
of work of the business plan). This is also a binary
variable. The system managed 76.4% accuracy
rate.
• Business plans projections efficiency (quality of
assumptions and estimations made in the study).
This is a 5-scale nominal variable. In this task, a
value of 86.4% was achieved as accuracy rate.
• Business plans scenario planning (existence of
possible alternative plans). It is a binary variable
and the accuracy rate here was 80%.
As it can be seen, the response of the system was
designed to be given at four levels, three of which
were corresponding to binary responses and one was
a linguistic characterization corresponding to low,
medium/neutral, or high prospects carried with ev-
ery new submitted business plan. The overall evalua-
tion of the response was made with the human subject
matter expert using a penalty function scheme (f.ex.
business plans with high prospects rated from the de-
cision system as low prospects business plans, are pe-
nalized higher than a neutral prospects response, etc.).
A presentation of a detailed evaluation scheme and
the comparative experimentation of this step is be-
yond the scope of this work.
According to the above-mentioned evaluation
scheme, the overall average performance of the sys-
tem (classification accuracy for new business plans,
submitted to the system) is calculated to be 76.4%,
which is considered a very satisfactory performance
by the subject matter experts. The response for the
evaluation of each new business plan was given from
the system in four output parameters, accompanied by
a confidence level for each of them, according to the
number of the predictors that agreed to the output. In
Fig. 6, a segment of one hierarchical classification
tree for parameter 1 (i.e. completeness of technical
EffectiveBusinessPlanEvaluationusinganEvolutionaryEnsemble
101

(IF < -0.22 (IF< CLIN -0.13 (IF< CLIN
-0.01 (IF< YRS -0.70 (IF< CLIN
-0.18 (IF< OWN -0.77 (IF< DISR -0.18
ACC (IF< CLIN -0.01 (IF< EXP -0.09
(IF< CLIN -0.10 (IF= DISR -0.19 ACC REJ) [..]
Figure 6: Evolved hierarchical classification tree for busi-
ness plan evaluation (segment of the first predictor for pa-
rameter 1).
and structural characteristics of the business plan) is
presented.
5 CONCLUSIONS
AND FURTHER RESEARCH
This work presented a system for effective evaluation
of business plans. The proposed system is consisted
of four sub-systems, each of them classifying a dif-
ferent parameter for the assessment of the plans. For
every sub-system, an ensemble was built, consisted
of five hierarchical classification trees and five Mam-
dani fuzzy rule-based systems. To generate these pre-
dictors, the genetic programming paradigm was used,
guided by respective context-free grammars. The re-
sults of the system are considered very satisfactory by
the subject matter experts and they assist business an-
alysts and investors in the respective evaluation tasks.
Further research will be directed in both the busi-
ness plan evaluation domain and the technical aspects
of the application. Applying the proposed architec-
ture in other classification tasks from the economic
and financial domain, such as bankruptcy prediction
and price prediction for on-line air tickets, will be
considered. The incorporation of other computational
intelligent predictors in the ensemble such as deci-
sion trees, multilayer perceptron neural networks and
Fuzzy Petri-nets is also a potential line of research.
Finally, considering the application of diversity fac-
tors during the ensemble building process, aiming to
increase the generalization ability, consists one of our
future tasks.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research leading to these results has received
funding from the General Secretariat for Research
and Technology (GSRT), Hellenic Republic, within
the Programme for the Development of Industrial Re-
search and Technology (PAVET) under grant agree-
ment 05-PAB-150.
REFERENCES
Brown G., Wyatt J., Harris R., Yao X., Diversity creation
methods: a survey and categorisation, Inf. Fusion, 6,
pp. 5-20, Special issue on diversity in multiple classi-
fier systems (2005)
Changchien S.W. and Lin M-C.: Design and implementa-
tion of a case-based reasoning system for marketing
plans, Expert Systems with Applications (Elsevier),
Vol. 35, 1145–1155 (2005)
Chen L-H. and Hsiao H-D.: Feature selection to diagnose a
business crisis by using a real GA-based support vec-
tor machine, Expert Systems with Applications (Else-
vier), 28, 43–53 (2008)
Eastwood M. and Gabrys B.: The Dynamics of Negative
Correlation Learning, Journal of VLSI Signal Pro-
cessing, 49:2, pp 251–263 (2007)
Fowler A.: The role of AI-based technology in support of
the knowledge management value activity cycle, Jour-
nal of Strategic Information Systems (Elsevier) Vol. 9,
pp. 107–128 (2000)
Gleiber. F. Royes and Golber F. Royes.: A hybrid-fuzzy-
multicriteria-CBR methodology for strategic planning
support, In: IEEE-NAFIPS 2004s, Alberta, Canada,
June 27-30, 2004, pp. 208–213 (2004)
Jordan M. I. and Jacobs R. A.: Hierarchical mixtures of
experts and the EM algorithm, In IJCNN 93, Proceed-
ings of 1993 International Joint Conference on Neural
Networks. Volume 2, JNNS, pp.1339-1344 (1993)
Koza J.R.: Genetic Programming: On the Programming of
Computers by Means of Natural Selection, MIT Press,
Cambridge, MA (1992)
Koza J.R., Bennett III F.H., Keane M.A., Andre D.: Evo-
lution of a time-optimal fly-to controller circuit using
genetic programming, in Koza J.R., Deb k., Dorigo
M., Fogel D.B., Garzon M., Iba H., Riolo L. (Eds.),
Genetic Programming 1997: Proceedings of the Sec-
ond Annual Conference, 207–212, Stanford Univer-
sity, Morgan Kaufmann (1997)
Koza J.R., Bennett III F.H., Hutchings J.L., Bade S.L.,
Keane M.A., Andre D.: Evolving sorting networks us-
ing genetic programming and rapidly reconfigurable
field-programmable gate arrays, in Higuchi T. (Ed.),
Workshop on Evolvable Systems, International Joint
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 27–32 (1997)
Koza J.R., Bennett III F.H., Lohn J., Dunlap F., Keane M.A.,
Andre D.: Automated synthesis of computational cir-
cuits using genetic programming, in Proceedings of
the 1997 IEEE International Conference on Evolu-
tionary Computation, pp. 447-452, Indianapolis, IEEE
Press (1997)
Lee J-H and Park S-C.: Application of a multi-agent intel-
ligent approach for profitable customer segmentation,
Expert Systems with Applications (Elsevier), Vol. 29,
pp. 145–152 (2005)
Perrone, M. P., Cooper, L. N.: When networks disagree:
Ensemble methods for hybrid neural networks, in R.
J. Mammone (ed.), Neural Networks for Speech and
Image Processing, Chapman-Hall, London, pp 126-
142 (1993)
DATA2013-2ndInternationalConferenceonDataManagementTechnologiesandApplications
102

Royes G.F., Bastos R.C..: Applicants’ selection applying a
fuzzy muticriteria CBR methodology, Journal of In-
telligent and Fuzzy Systems, 14(4), 167–180 (2003)
Sun Y., Kamel M.S., Wang Y., Boosting for Learning Mul-
tiple Classes with Imbalanced Class Distribution, Pro-
ceedings of the Sixth International Conference on
Data Mining (ICDM’06), IEEE Computer Society
(2006)
Tsakonas A. Dounias G.: A Scheme for the Evolution of
Feedforward Neural Networks using BNF-Grammar
Driven Genetic Programming, in Proc. of Eunite-02
Conf., European Network of Excellence for Intelligent
Technologies, Algarve (2002)
Tsakonas A., Dounias G.: Hierarchical Classification Trees
Using Type-Constrained Genetic Programming, in
Proc. of 1st Intl. IEEE Symposium in Intelligent Sys-
tems, Varna (2002)
Tsakonas A, Dounias G, Jantzen J, Axer H, Bjerregaard B,
von Keyserlingk DG.:Evolving rule-based systems in
two medical domains using genetic programming, Ar-
tif Intell Med., 32(3):195-216 (2004)
Tumer K., Ghosh J.: Error Correlation and Error Reduction
in Ensemble Classifiers, Connection Science, Taylor
& Francis, 8:3/4, pp 385–404 (1996)
Wen W., Chen Y.H., Chen I.C.: A knowledge-based deci-
sion support system for measuring enterprise perfor-
mance, Knowledge Based Systems (Elsevier) Vol, 21,
pp. 148–163 (2008)
Whigham P.A.: Search bias, language bias and genetic
programming, Genetic Programming 1996: Pro-
ceedings of the First Annual Conference, J.R.Koza,
D.E.Goldberg, D.B.Fogel, R.L.Riolo (Eds.), 410–415,
Stanford University, CA, MIT Press (1996)
Whigham P.A.: Grammatical Bias for Evolutionary Learn-
ing, Ph.D. Thesis, University of New South Wales,
Australian Defence Force Academy (1996)
Xu D-L, McCarthy G., Yang J-B.: Intelligent decision sys-
tem and its application in business innovation self as-
sessment, Decision Support Systems Vol. 42, (Else-
vier), 664–673 (2006)
Zadeh L.A.: Fuzzy sets, Information Control, 8, pp. 338-
353 (1965)
Zhou Z., Wu J., Jiang Y., S. Chen, R.: Genetic algorithm
based selective neural network ensemble, In Proc. of
17
th
Int’l Joint Conf. Artif. Intell. , USA, Morgan
Kaufmann, pp 797–802 (2001)
EffectiveBusinessPlanEvaluationusinganEvolutionaryEnsemble
103
