
Self-other Agreement on Influence Attempts in Virtual Organizations
Do Agents and Peers See Eye to Eye?
Henning Staar
1
and Monique Janneck
2
1
Department of Psychology, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
2
Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Luebeck University of Applied Sciences, Luebeck, Germany
Keywords: Influence Tactics, Micro-politics, Self-other Agreement, Virtual Organizations.
Abstract: The aim of the study was to determine the convergent and discriminant validity of self-peer reports from
three different sources on the use of influence tactics in virtual organizations. Therefore, directly related
triads of network members were analyzed. First, members (agents) should describe how they try to
influence a certain person (target) in the joint collaboration. Second, the defined target and another network
member (non-target) described how they perceive the agent’s influence attempts. All sources rated nine
types of influence tactics. The resulting multitrait-multimethod design was analyzed with 243 sets of triads
using structural equation modeling (SEM). Results supported evidence for convergence of agents’ and
peers’ reports on influence attempts and confirmed the multidimensionality of micro-political behavior in
virtual organizations.
1 INTRODUCTION
During the last decade, factors such as globalization
and technological advancements have led to new
organizational structures. Most notably, several
forms of virtual organizations and networks have
emerged as possible solutions to these new
challenges. However, little is known about social
influence processes between individual members of
virtual networks (Elron and Vigoda-Gadot, 2006),
especially when influence is mediated through an
expanding variety of information and
communication technologies (ICT) that separate the
parties spatially and/or temporally (Barry & Fulmer,
2004). In ‘traditional’ managerial settings such
mutual influence processes–often referred to as
micro-politics–have been acknowledged as being “a
pervasive aspect of organizational life” (Blickle,
2003, p. 40). Given the lack of established
leadership theories in virtual organizational settings,
influence tactics can thus be viewed as a ‘vital tool’
for members to get their way in network issues
(Greer and Jehn, 2009).
However, current empirical findings on social
influence processes in virtual collaboration setting
solely rely on self-rating scales. Thereby,
respondents are asked to evaluate the use of several
influence strategies when trying to achieve their
aims within the network. As a result, the insights
into micro-political behavior in virtual networks
have been limited so far to the actor’s perspective.
Consequently, it remains unclear whether micro-
political agents actually manage to create the image
that they seek when interacting with their network
partners via ICT. According to this, influence targets
could have a totally different account of what
happens when an agent tries to cause him or her to
do something. Therefore, the purpose of the present
study was to evaluate the convergence of agents’
and peers’ reports on micro-political influence
attempts in virtual networks.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Virtual Networks
There is a wide variety of forms that are embraced
by the term ‘virtual organizations’ (Travica, 2005).
However, the wide majority of definitions agree that
virtual organizations are forms of “inter-
organizational, cross-border ICT-enabled
collaboration between legally independent entities,
usually with a specific economic goal” (Pitt,
Kamara, Sergot and Artikis, 2005, p. 373).
Especially horizontal forms of collaboration are
551
Staar H. and Janneck M..
Self-other Agreement on Influence Attempts in Virtual Organizations - Do Agents and Peers See Eye to Eye?.
DOI: 10.5220/0004495505510560
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (STDIS-2013), pages 551-560
ISBN: 978-989-8565-54-9
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

important for freelancers or small and medium-sized
enterprises that might be in danger of losing their
competitiveness in a globalized market. However, at
the same time, network members often still act as
individual competitors on the market and as such are
caught between cooperation and competition–a
potential field of conflict which has also been
labeled as ‘coopetition’. Beyond that, most virtual
organizations can be described as being polycentric,
i.e., highly distributed through loosely coupled
associations with high degrees of autonomy of their
members, brought together through intense use of
ICT (e.g., Travica, 2005).
2.2 Micro-politics
Given the lack of formal hierarchies and roles as
well as a distributed leadership over distance, it is
sensible to assume that informal actions of
individual network members play a crucial role in
shaping and governing the network. In
organizational science, so-called micro-political
processes are understood as strategies of individuals
to achieve their goals, realize ideas, or push certain
interests (e.g. Yukl and Falbe 1990). In their
research, Janneck & Staar (2011) have identified a
number of typical informal behavioral patterns–so-
called micro-political tactics–being used in virtual
organizations (table 1).
An important differentiation among these tactics
aims at their range of influence. The first six tactics
are more or less restricted to dyadic influence
attempts, i.e., an agent is attempting to directly
influence a certain target person in a given
interpersonal setting. This dyadic perspective on
social influence in virtual settings has been prevalent
so far (e.g., Barry & Fulmer, 2004). However,
beside direct dyadic relations of inter-personal
influence, some authors have emphasized the
importance of indirect structural tactics. These are
related to the individual’s position within the
network as a whole rather than on mere influence
dyads. In their set of tactics, Janneck & Staar (2011)
have considered Mediating, Proactive Behavior and
Visibility as indirect attempts to gain influence.
Former research on political processes in virtual
organizations suggests that technology-based
interactions may be especially susceptible to
informal influence processes (Wilson, 2003).
Moreover, ICT used by inter-organizational
networks might not only contribute to but even
constitute micro-political processes, as technology
serves both: making existing processes and
structures more explicit and bringing forth new roles
Table 1: Micro-political tactics in virtual organizations.
Direct tactics
Rational
Persuasion
Spreading information to the network
partner(s) to clarify one’s concerns.
Assertiveness
Engaging in open confrontation with
or putting pressure on the network
partner(s).
Exchange
Offering to do a network partner a
favour in return; Signalising to
reciprocate for the network partner’s
support
Inspirational
Appeals
Calling upon the common vision, the
basic idea of a network; emphasizing
the need to pull together for being
successful.
Self-Promotion
Emphasizing one’s efforts regarding
the network collaboration or one’s
value for the network.
Inspiring Trust
Trying to appear open-minded about
the network partners’ concerns;
purposefully presenting oneself as a
network partner who is willing to share
information and resources.
Indirect tactics
Visibility
Trying to show presence via electronic
media; Purposefully using all available
channels to call attention to one’s
concerns.
Proactive
Behavior
Looking for opportunities to play an
additional part in the network beyond
the primary role; taking over new tasks
and/or roles within the network to
extend one’s scope of action.
Mediating
Trying to mediate between partners
during negotiations and discussions;
Keeping a non-committed position in
discussions and controversies instead
of taking sides with a party straight
away.
and rules (Janneck and Staar, 2011). However, these
relations remain artificial if the targets’ perceptions
of influence attempts are not evaluated in relation to
the agent’s original intention.
2.3 Agent-target Convergence
Focusing on intra-organizational influence attempts,
some studies have examined the convergence of
agents’ and targets’ reports. In summary, most
results confirm significant agent-target convergence,
albeit only at a moderate level (for an overview, see
Blickle, 2003). The development of new
organizational settings such as virtual organizations
rises the question whether technology-based
interaction has an effect on processing and
understanding of interpersonal influence (Okdie and
WEBIST2013-9thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
552

Guadagno, 2008; Wilson, 2003). Whereas in
‘traditional’ intra-organizational face-to-face
interaction, influence agent and target(s) share the
same physical location, can see and hear one
another, receive messages in real time as they are
produced, and send and receive information
simultaneously and in sequence, this is seldom the
case for distributed parties as in virtual
organizations. So far, empirical micro-political
research on self-peer agreement in intra-
organizational and industrial settings has been
reduced to same time same place conditions
(Blickle, 2003). Few research attention has been
paid to the question of how technology-mediated
interaction affects the targets’ perception of an
agent’s influence attempts (Barry and Fulmer,
2004).
Based on the premises of Social Impact Theory
(Latané et al., 1996), some authors have suggested
that the impact of influence on a target decreases
with increasing distance (e.g., Elron and Vigoda-
Gadot, 2006). Similar arguments come from
Driskell, Radtke and Salas (2003) who conclude that
in virtual settings the opportunity for political agents
to transmit, and for targets to access the subtlety,
nuance, connotation inherent in interpersonal
influence messages would be rather low as they do
not experience “the immediacy of interacting and
being involved with a physically present team
member” (Driskell et al., 2003, p. 298). Similarly,
Greer and Jehn (2009) suppose that in computer-
mediated communication (CMC) or other leaner
mediums than face-to-face, traditional non-verbal
clues within influence attempts may not be as easily
captured.
Some researchers reply that conversation via ICT
does not significantly disrupt conversational control
and understanding. From an agent’s perspective,
Abele (2011) notes that ICT-mediated interactions
offer much more opportunities for deliberative
action. Similarly, Okdie et al. (2011) point out that
individuals interacting via CMC “have time to
rethink, edit, and possibly censure the information
they convey to their interaction partners ensuring
they are perceived the way they intend” (p. 154).
Finally, most research agrees that virtual contexts
tend to make people feel free to express themselves
in a manner decoupled from traditional social mores
and restrictions leading to more uninhibited behavior
(Tidwell and Walther, 2002).
Based on the theoretical discussion above, the
following conclusions emerge. So far, the vast
majority of studies that have evaluated micro-
political influence in virtual organizations offer a
restricted perspective, namely that from an agent’s
view. However, neglecting the target’s (or more
general: peer’s) perception of an agent’s behavior,
only a fragmented extract of social influence
processes within these settings can be expected. In
addition, it has become clear that research on
influence behavior in virtual networks should go
beyond mere dyads of inter-personal influence
situations: In most virtual organizations members
are not only loosely connected with each other but
they rather build a tight network of mutual relations.
Accordingly, some influence tactics might not be
restricted to a single chosen target but address the
network and its members as a whole. As a
consequence, for a reliable examination of the
convergent and discriminant validity of agents’ and
peers’ reports on direct and indirect micro-political
influence attempts, real groups of agents, targets and
non-targets as well as parallel scales are needed. In
this study, we will examine self-other agreement of
nine influence tactics used in virtual networks.
3 METHOD
3.1 Subjects
Participants were acquired by means of a systematic
internet research or through online business
platforms such as XING. All persons were asked if
they would care to participate in a study on
communication and cooperation in virtual networks.
As an incentive to participate in the study, all
members were offered an analysis of the age
structure of their network. Furthermore, we raffled
small gifts such as ipods and guaranteed a report on
the results of the study.
Since convergence between different raters
should be analyzed using Structural Equation
Modeling (SEM), a sample size of at least 200
complete sets was needed. Following Marsh, Ballah
and MacDonald (1988), this sample size is necessary
for a meaningful interpretation of the models’ fit-
indices. For this study, a total of 243 complete sets
consisting of agent-target-non-target-triads could be
acquired. The vast majority of respondents worked
as freelancers with a lot of experience in virtual
working being reflected in an average network
membership of more than one year. More than half
of the networks had less than 10 members (55%),
31% had 10-20 members, and 14% had more than
20 members. Most respondents were male (73%),
mean age was 38,8 years. The respondents worked
mainly in Media (36%) or IT (30%) business, 21%
Self-otherAgreementonInfluenceAttemptsinVirtualOrganizations-DoAgentsandPeersSeeEyetoEye?
553

worked in the Health sector (13% other).
Concerning the degree of virtuality, i.e., the
frequency and variety of ICT-usage, the sample was
homogenous: All triads reported to interact first and
foremost via different ICT. Further, network-
exclusive or open groupware were used in most
cases and served as the linchpin to mutual
interactions.
3.2 Research Design
First, members of virtual networks were asked with
whom they were currently working on a common
project and had interacted regularly for the last
months. Without knowing about the study’s focus on
influence, participants should list at least three
persons belonging to their virtual network. As most
of the data was assessed via online questionnaires,
we were able to benefit from dynamically generated
contents. To avoid systematic effects such as
sympathy, one of the listed network partners was
chosen randomly. Then the questionnaire consisting
of the nine influence tactics was presented in
randomized order and the participants (agents) were
requested to rate their own influencing attempts on
the person chosen (target). After completing the
questionnaire, the agents were asked to distribute
two links (that led to a parallel version of the agent’s
questionnaire) which should be sent to the target
person and a further network member (non-target)
who was randomly chosen out of the list of partners
put together by the agent at the beginning. To collect
matched triads of agents, targets and non-targets, a
code was generated at the end of the agent’s
questionnaire, which should be sent to the target and
non-target. When targets and non-targets
participated, they were asked to describe to which
degree the identified agent uses certain types of
influence attempts in an effort to influence the target
(or the peer respectively). After both peers had
finalized their questionnaires, their ratings were
matched with the agents’ questionnaires through the
common code numbers.
One approach to methodically determine the
convergent and discriminant validity of agents’,
targets’ and non-targets’ reports on different micro-
political tactics can be found within the framework
of a multitrait-multimethod (MTMM) design by
which multiple traits are measured by multiple
methods.
Generally, traits are defined as hypothetical
constructs that relate to stable characteristics such as
personality attributes. Methods refer to multiple test
forms or specific measurement methods (Byrne,
2011). However, MTMM-designs have been applied
not only to traits but to influence tactics as well (e.g.,
Blickle, 2003). Further, treating different raters
(such as self-report or specific informants) as
method factors has become a common modification,
too.
In the seminal work of Campbell and Fiske
(1995), the inspection of the correlation matrices of
scores from all variables was analyzed to determine
convergent and discriminant validity. Alternatively,
confirmatory factor analyses (CFA) offer a more
systematic way to deal with multitrait-multimethod
matrices. Especially the Correlated Traits
Correlated Methods (CTCM) approach to MTMM
data has been used as the most widely alternative to
the ‘informal’ approach of analyzing MTMM
matrices. This is particularly attractive because the
model’s structure directly corresponds to Campbell
and Fiske’s original conceptualization of the
MTMM matrix. The CTCM-model offers separate
trait and method factors that are assumed to be freely
correlated, but trait factors are assumed to be
independent of method factors. The rationale behind
this model is that high loadings on trait factors
would suggest convergent validity; high loadings on
the method factors would indicate common method
effects, and moderate correlations among different
trait factors would support evidence of discriminant
validity (Kline, 2005).
The basic CTCM-model was specified as
follows: First, three latent method factors were
defined, i.e., self-, target- and non-target-ratings.
Each of the latent method factors had nine
indicators, i.e., the ratings of the nine influence
tactic scales. In addition, nine latent trait factors
were formulated, representing the ratings of
influence tactics with three indicators each. To test
the models, maximum likelihood estimates were
applied. AMOS 6 was used for calculations.
3.3 Instruments
Influence tactics were measured with an inventory
that captured the nine tactics based on the work from
(Janneck and Staar, 2011, see table A.1 in the
appendix). The original version was used for agent
respondents. Targets and non-targets were given a
slightly adjusted version to assess the agent’s tactical
behavior from three different views. In the agent
version the respondent rated his or her own
influence attempts on the defined target (e.g., “I use
rational arguments to convince [name of the
target]”). The target, in turn, was asked to evaluate
the agent’s use of influence tactics when trying to
WEBIST2013-9thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
554

cause him or her to do something (e.g., “[Name of
the agent] uses rational arguments to convince me”).
Finally, the non-target version contained a global
peer view on the agent’s influence behavior in
network issues (e.g., “[Name of the agent] uses
rational arguments to convince his network
partners”). The 6-point-likert scale ranged from 1 =
“never” to 6 = “always”. As a filtering question,
agents were first asked if they were part of a for-
profit network in which projects are realized in
cooperation with other people from the same branch.
Furthermore, all participants were asked to indicate
their sex, age, educational level and actual
profession. Additionally, all members were asked to
indicate network-specific data such as the name,
size, length of cooperation and branch of their
virtual network.
4 RESULTS
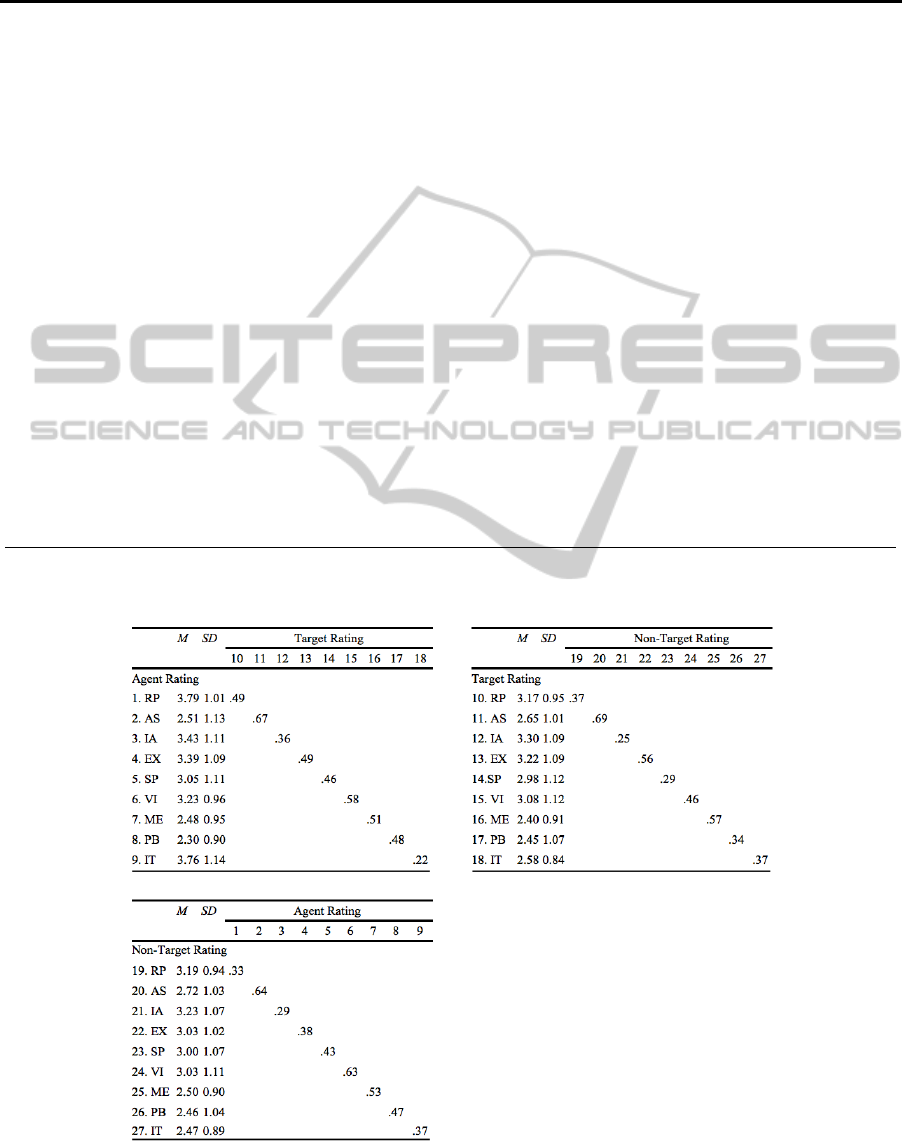
The agent-target-non-target correlation matrices as
well as the scale means, standard deviations and
reliabilities are documented in table A.2 (see
appendix).
Table 2: Parameter Estimates for Model 1 (CTCM) (n = 243): Tactic and Source Loadings.
a
RP AS IA EX SP VI ME PB IT AR TR NR
Agent Rating (AR)
Rational Persuasion (RP) .63* .23*
Assertiveness (AS) .85* .44*
Inspirational Appeals (IA) .93* .17*
Exchange (EX) .60* -.02
Self-Promotion (SP) .78* .10
Visibility (VI) .86* -.10
Mediating (ME) .68* -.09
Proactive Behavior (PB) .92* .20*
Inspiring Trust (IT) .65* .01
Target Rating (TR)
Rational Persuasion (RP) .69* .20*
Assertiveness (AS) .94* -.04
Inspirational Appeals (IA) .38* .27*
Exchange (EX) .82* -.08
Self-Promotion (SP) .59* -.03
Visibility (VI) .66* .24*
Mediating (ME) .77* .09
Proactive Behavior (PB) .52* -.06
Inspiring Trust (IT) .36* .48*
Non-Target Rating (NR)
Rational Persuasion (RP) .49* .20*
Assertiveness (AS) .73* -.11
Inspirational Appeals (IA) .32* -.11
Exchange (EX) .69* .34*
Self-Promotion (SP) .55* .27*
Visibility (VI) .72* .24*
Mediating (ME) .75* -.09
Proactive Behavior (PB) .48* -.13
Inspiring Trust (IT) .57* .21*
Note.
a
Standardized estimates; *
p < .05.
Self-otherAgreementonInfluenceAttemptsinVirtualOrganizations-DoAgentsandPeersSeeEyetoEye?
555

4.1 Goodness of Tested Models
To test the convergent validity of the different
source ratings from agents, targets and non-targets
on nine influence tactics, four structural equation
models were calculated. Following Byrne (2011),
we included the CTCM-model as the general CFA
model and additionally specified two nested models.
Model 2 was specified without method factors but
with correlated traits (CT), Model 3 differed from
Model 1 only in the absence of correlations among
method factors (CTUM). Following Byrne’s
recommendations, the set of models was completed
with the CU-model (Correlated Uniqueness).
The goodness-of-fit indices show that Model 1
yields an acceptable global fit (χ
2
(259) = 342,139, p
= .057). Furthermore, relevant fit-indices such as
CFI (.942) and RMSEA (.039) revealed a good fit to
the data, too (Hu & Bentler, 1999). Similar estimates
were found for Model 3. In contrast, goodness-of-fit
indices for the CU-model proved to be
comparatively poor (χ
2
(180) = 263.109, p = .025;
CFI = .942; RMSEA = .046), Model 2 revealed an
even worse fit. On the whole, the stable solution and
acceptable fit indices of Model 1 support a tenability
of this model. Accordingly, we will focus on this
general CFA-model in the subsequent analyses.
4.2 Analysis of Convergent
and Discriminant Validity
An assessment of self-other agreement on different
tactics can be ascertained by analyzing the
individual parameter estimates. Specifically, the
factor loadings and factor correlations of Model 1
provide the focus here. The completely standardized
estimates for the factor loadings are summarized in
Table 2. Trait and method factor correlations can be
found in Table 3.
In examining these individual parameters,
convergent validity is reflected in the magnitude of
the trait loadings. As Table 2 shows, all trait
loadings are statistically significant with magnitudes
ranging from .315 (non-target-ratings of
Inspirational Appeals) to .944 (target-ratings of
Assertiveness). Moreover, when comparing factor
loadings across traits and methods, it becomes clear
that the proportion of trait
variance exceeds that of
method variance for all but one of the target-ratings
(Inspiring Trust). This means that in the evaluation
of all nine tactics agents’, targets’ and non-targets’
reports converged to a considerable degree.
Beside the basic confirmation of the assumptions
made, a more in-depth examination at the individual
parameter level reveals that some of the trait
loadings are significant indeed but the explained
variances tend to be rather low on a considerable
Table 3: Trait (Tactic) and Method (Source) Factor Correlations for Model 1 (CTCM).
a
Tactics Sources
Measures RP AS IA EX SP VI ME PB IT AR TR NR
Rational Persuasion (RP) 1.00
Assertiveness (AS) -.21* 1.00
Inspirational Appeals (IA) -.11* -.08* 1.00
Exchange (EX) -.19* -.10* -.02* 1.00
Self-Promotion (SP) -.05* -.20* .17* -.06 1.00
Visibility (VI) --.32* -.04* -.05* -.04 .03* 1.00
Mediating (ME) -.13* -.11** -.14*-.08 -.03*-.02* 1.00
Proactive Behavior (PB) -.09* -.08* -.13*-.01 -.04* .35* -.03 1.00
Inspiring Trust (IT) -.08* -.18* -.13*-.13 .04 .16* -.13*-.13* 1.00
Agent Rating (AR) 1.00
Target Rating (TR) .39* 1.00
N
on-Target Rating (NR) .36* .14 1.00
Note.
a
Standardized estimates; *
(p < .05).
WEBIST2013-9thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
556

number of trait loadings. Finally, correlations among
trait factors provide an evaluation of the
distinctiveness of self-other agreement and of the
multidimensionality of micro-political behavior.
Most latent trait factors correspond only to a low
degree. Rational Persuasion yields significant
correlations with Visibility (r = .32, p < .05) and
Assertiveness (r = -.21, p < .05). The latter, in turn,
is negatively related to Self-Promotion (r = -.20, p <
.05), and Proactive Behavior correlates with
Visibility at r = .35 (p < .05). In total, these results
support evidence for discriminant validity and the
multidimensionality of micro-political-behavior.
An examination of method factor correlations
reveals significant correlations between agent-
ratings and target-ratings (r = .39, p < .05) and non-
target ratings (r = .36, p < .05) respectively, which
detracts from a discriminability of methods. Possible
explanations for these findings will be discussed
below.
5 DISCUSSION
Do micro-political agents reach to create the image
that they seek when interacting with their partners in
virtual organizations? Or do peers with whom the
agent is interacting rather have a totally different
account of how the agent is trying to exert
influence? To find answers, the aim of the present
study was to determine the convergent and
discriminant validity of agents’ and peers’ reports on
influence attempts in virtual network settings. We
wanted to know whether agents, targets and non-
targets as three different sources are on the same line
when evaluating the agents’ influence attempts in
form of nine micro-political tactics. Despite the fact,
that the main focus was set on convergence, and
hypotheses were formulated according to that effect,
the MTMM-model accounted for the evaluation of
discriminant validity, too, i.e., the extent to which
independent sources diverge in their measurement of
different tactics (cf. Byrne, 2011).
On the whole, the results support the convergent
as well as the discriminant validity of the inventory
being used in the present study. All trait loadings
showed significant estimations, most of them of
considerable magnitude. Moreover, beside high trait
loadings, almost all loadings on method factors were
marginal. In addition, correlations among trait
factors were mainly low. These findings support
strong evidence for a discriminability of the nine
tactics. Interestingly, contrary to our implicit
assumptions, there was no big difference between
the targets’ and non-targets’ ability to perceive direct
influence tactics.
Two conclusions can be drawn from these
results. The first explanation follows from the
ongoing discussion concerning an agent’s influence
style. On that note, some researchers argue that
agents are far from being ‘micro-political
chameleons’, which adjust their influence strategies
to a respective person or situation (cf. Ferris et al.,
2002). Rather, an agent’s choice of tactics appears to
vary only within a certain corridor when attempting
to influence different targets (cf. Barbuto and Moss,
2006). Following the perspective of a relatively
stable inter-individual influence style, convergence
not only between agent and a specific target can be
expected. The rationale behind this view can be
explained through the fact that although non-targets
were not the direct aim of influence within the
present study’s design, they rated their own
experiences with the agent's behaviors, therewith
producing a second ‘target rating’. In doing so, he or
she could have drawn upon recurrent actions of the
agent that are similar to the target’s perceptions.
Another explanation for the convergence of all
three sources on direct influence tactics might be
found in the ‘open playground’ available when
groupware is used. If ICT guarantee an open
information flow between all network members, the
model of dyadic influence attempts might become
ineffective and obsolete. By using open groupware
strategically the whole network can be addressed
simultaneously. Therefore, convergence between all
three parties could have emerged through such a
‘glass-house-effect’. However, we did not control
for the communication channels that were used.
Accordingly, we were not able to differentiate
between influence situations where open forms of
ICT where used vs. those where communication was
masked to others and only certain persons were
addressed (e.g., through e-mail use). This aspect will
be further critically reviewed below.
Compared to most deflating results from intra-
organizational research where agents and targets
meet same time, same place the convergence of
different sources that we have found in virtual
settings can be interpreted as fairly good. How can
this be understood? Some studies on self-other
agreement in personality judgments have shown that
virtual groups were better able to selectively present
aspects of themselves and could better manage their
self-presentation via CMC than those who were
engaged in physical face-to-face interactions (Okdie
et al., 2011). In addition, social and normative
contexts may be of even greater importance in
Self-otherAgreementonInfluenceAttemptsinVirtualOrganizations-DoAgentsandPeersSeeEyetoEye?
557

virtual organizations when compared to intra-
organizational face-to-face interactions. For
example, it can be assumed that the negotiation of
norms and the evaluation of the persons’ network fit
are of more substantial importance in virtual
organizations as in traditional industrial settings.
Especially when formalized routines are missing, the
networks’ members have to rely on a common sense
in their decisions about the persons they want to
work with. Before de facto collaboration occurs,
potential partners have put each other to the test in
terms of trust, engagement, and the others’
willingness to reciprocity. Accordingly, it is
reasonable to assume that most of the members in
virtual organizations know each other very well,
which would provide an explanation for high self-
peer-agreements. Even if information available via
ICT is fragmented, incomplete, or ambiguous,
perceivers can resort to their previous knowledge of
each other.
A more in-depth view to the results, however,
reveals some shortcomings of the tested model.
Almost half of the error variances that were
specified in the CTCM-model were of considerable
height. Within error variances, ‘the rest of the world’
can be found which is not explained through
specified trait or method factors. It can be assumed
that additional variables which had not been
specified within this model may be of crucial
importance to better understand the model’s
interrelations. One important factor could lie in the
variety of ICT used within the participants’ virtual
organizations. As mentioned in the description of the
sample, the vast majority of triads used a wide
variety of ICT to coordinate workflows and to
communicate with each other. As we have
mentioned above, we did not further differentiate
with respect to media usage. Nevertheless, it is
obvious that some mediating technologies may be
more effective for some kinds of tasks than others.
Therefore, situational and contextual factors created
through different communication media are likely to
affect the selection of influence strategies as well as
the peers’ interpretation of the actors’ behavior
(Sussman et al., 2002). Therefore, future research
should take a closer look on how and for what
purposes the teams’ technologies are used when
trying to influence a target person and control for
different ICT. Furthermore, the effect on the target
will be especially dependent on how politically
skilled and media-savvy the agent is.
In addition to aspects related to the variety of
ICT in carrying influence processes one must take
into consideration the social nature of networks
which might have contributed to considerable
variations in the ratings. To broaden the picture,
future research in this field should address relational
aspects such as the quality of the relationship
between agent and target, their respective network
positions and the degree to which political behavior
is addressed openly. Further, individual-level aspects
such as the political skills of the agent and several
other personal competencies might substantially
contribute to a deeper understanding of the inner
dynamics of virtual networks.
The present study offers some methodical
limitations. Since at least 90 parameters were to be
estimated for model calculations, the sample size of
243 data sets was relatively small (Kline, 2005).
Even if samples of n = 200 have been set as a
benchmark by some authors (e.g., Marsh et al.,
1988) a sample of at least n = 250 rather meets the
recommendations of most authors. Another
limitation is set by the selection of the sample.
Despite the fact that targets and non-targets were
randomly selected, they had been listed by the agent
before, and thus belong to a specific pool of network
members. Consequently, effects of sympathy or
other inter-individual preferences may have led to a
selective set of triads. This leads directly to another
important limitation. In fact only cliques within the
network have been evaluated but not the whole
network. However, research on virtual organizations
would require a consideration of the multiple mutual
relations that actually build the network. Thus,
analyses of triads provide only a first step to gain
insights into social influence processes.
Beside these limitations, the study offers
important insights into the social nature of virtual
collaborations: Obviously, peers are aware of the
agent’s influence attempts in virtual networks. So
does being caught in the act blow the agent's cover?
With a view to career advancement some authors
have pointed out that micro-political influence
attempts cannot be carried out as an overt act in
order to be effective (Elron and Vigoda-Gadot,
2006). On this note, it could be argued that covert
influence attempts that are not perceived as such
may even be more powerful, because the target
cannot put up resistance. In our study we
concentrated solely on the observed influence
attempts and refrained from evaluating the success
of influence attempts. Accordingly, questions
concerning the relationship between the obviousness
of tactics and realized effects towards influence
targets cannot be answered. However, at least from a
theoretical point of view, one might assume that in
virtual organizations dealing with influence is
WEBIST2013-9thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
558

different. Given the lack of formalized leadership
hierarchies in most virtual organizations, leadership
at its most basic level is the ability to influence
others. Influence tactics can thus be viewed as a
vital–if not necessary–tool for members to get their
way in network issues (Greer and Jehn, 2009). This
dilemma–working at eye level without the formal
authority to give directives but getting work done
together at the same time–requires any form of
informal influence behavior. In the absence of
leadership alternatives, mutual influence is thus
beside joint decisions and collective processes not
only tolerated but often the only leadership
instrument available.
REFERENCES
Abele, S. (2011). Social interaction in cyberspace, Social
construction with few constraints. In Z. Birchmeier, B.
Dietz-Uhler & G. Stasser (Eds.), Strategic Uses of
Social Technology. An Interactive Perspective of
Social Psychology (pp. 84-107). New York:
Cambridge University Press.
Barbuto, J. E. & Moss, J. A. (2006). Dispositional Effects
in Intra-Organizational Influence Tactics: A Meta-
Analytic Review. Journal of Leadership &
Organizational Studies, 12(3), 30-48.
Barry, B. & Fulmer, I. S. (2004). The medium and the
message: The adaptive use of communication media in
dyadic influence. Academy of Management Review,
29, 272-292.
Blickle, G. (2003). Convergence of agents' and targets'
reports on intraorganizational influence attempts.
European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 19(1),
40-53.
Byrne, B. M. (2001). Structural Equation Modeling With
Amos: Basic Concepts, Applications, and
Programming. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Campbell, D. T. & Fiske, D. W. (1959). Convergent and
discriminant validation by the multitrait-multimethod
matrix. Psychological Bulletin, 56, 81-105.
Driskell, J. E., Radtke, P. H. & Salas, E. (2003). Virtual
teams: Effects of technological mediation on team
performance. Group Dynamics: Theory, Research and
Practice, 7, 297–323.
Elron, E. & Vigoda-Gadot, E. (2006). Influence and
political processes in cyberspace: The case of global
virtual teams. International Journal of Cross-Cultural
Management, 6(3), 295-317.
Ferris, G., Hochwarter, W., Douglas, C., Blass, F.,
Kolodinsky, R. & Treadway, D. (2002). Research in
Personnel and Human Resources Management (pp.
65-127). Stanford: Elsevier.
Greer, L. L. & Jehn, K. A. (2009). Follow me: Strategies
used by emergent leaders in virtual organizations.
International Journal of Leadership Studies, 5, 102-
120.
Hu, L. & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit
indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional
criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation
Modeling, 6, 1-55.
Janneck, M., Staar, H. (2011). Playing Virtual Power
Games: Micro-political Processes in Inter-
organizational Networks. International Journal of
Social and Organizational Dynamics in Information
Technology, pp. 46-66.
Kline, R. B. (2005). Principles and practice of structural
equation modeling. New York: Guilford.
Latané, B., Liu, J. H., Nowak, A., Bonevento, M. &
Zheng, L. (1996). Distance Matters: Physical Space
and Social Impact. Personality & Social Psychology
Bulletin, 21, 795-805.
Marsh, H. W., Ballah, J. R. & MacDonald, R. (1988).
Goodness-of-fit indices in confirmatory factor
analysis: The effect of sample size. Psychological
Bulletin, 88, 245-258.
Okdie, B. M. & Guadagno, R. E. (2008). Social Influence
and Computer Mediated Communication. In K. St.
Amant & S. Kelsey (Eds.), Handbook of Research on
Computer Mediated Communication (pp. 477-491).
Hershey, PA: IGI Global.
Okdie, B. M., Guadagno, R. E., Bernieri, F. J., Geers, A. J.
& Mclarney-Vesotski, A. R. (2011). Getting to know
you: Face-to-face vs. online interactions. Computers in
Human Behavior, 27, 153-159.
Pitt, J., Kamara, L., Sergot, M. & Artikis, A. (2005).
Formalization of a voting protocol for virtual
organizations. In Proceedings of the Fourth
international Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents
and Multiagent Systems (pp. 373-380). New York:
ACM.
Sussman, L., Adams, A., Kuzmits, F. & Raho, L., (2002).
Organizatonial politics: tactics, channels, and
hierarchical roles. Journal of business ethics. 40(4),
313-331.
Tidwell, L. C. & Walther, J. B. (2002). Computer-
mediated communication effects on disclosure,
impressions, and interpersonal evaluations. Human
Communication Research, 3, 317-348.
Travica, B. (2005). Virtual organization and electronic
commerce. SIGMIS Database 36(3), 45–68.
Wilson, E. (2003). Perceived effectiveness of
interpersonal persuasion strategies in computer-
mediated communication. Computers in Human
Behavior, 19(5), 537-552.
Yukl, G. & Falbe, C. M. (1990). Influence tactics and
objectives in upward, downward and lateral influence
attempts. Journal of Applied Psychology, 75(2), 132-
140.
Self-otherAgreementonInfluenceAttemptsinVirtualOrganizations-DoAgentsandPeersSeeEyetoEye?
559
APPENDIX
Table A.1.: English Version of the Virtual Politics Inventory.
To achieve my goals within the network…
Rational Persuasion
I try to convince others with my knowledge in that matter.
I use rational arguments to convince my network partners.
I describe in detail the reasons for my concerns.
I spread information to the network partners to clarify my
concerns.
Assertiveness
I clearly express my displeasure towards my network
partners.
I engage in open confrontation with my network partners.
I put pressure on my network partners.
Inspirational Appeals
I try to highlight that we are all in the same boat.
I call upon our common vision, the basic idea of a network.
I emphasize the need to pull together for being successful.
Self-Promotion
I emphasize my efforts regarding the network collaboration.
I emphasize my value for the network.
I refer to positive outcomes due to my work and/or the
central position of my company within the network.
Exchange
I affirm that I would show my gratitude for a partner’s
favor.
I offer to do my network partner a favor in return.
I promise to reciprocate for my network partner’s support.
Mediating
I achieve my goals better when I behave neutrally towards my partners.
I try to stay neutral and mediate between partners during negotiations
and discussions.
I keep a non-committed position in discussions and controversies
instead of taking sides with a party straight away.
I try to be the mediating tie in cases of disagreement.
Claiming Vacancies
I look for opportunities to play an additional part in the network beyond
my primary role.
I adopt some additional tasks as they turned out to be advantageous.
I take over new tasks and/or roles within the network to extend my
scope of action.
Being Visible
I always try to show presence via electronic media.
I purposefully use electronic media to call attention to my concerns.
I always try to be available and present on all communication channels.
Inspiring Trust
I try to appear open-minded about my network partners’ concerns from
the very beginning.
I purposefully try to show that I am a good and worthy network partner
(showing mutual exchange, trustworthiness, etc.).
I purposefully present myself as a network partner who is willing to
share information and resources.
Right from the start I tried to show my reliability towards the other
network members.
Table A.2.: Multitactic-Multisource-Matrix: Scale Means, Standard Deviations and Convergent Validity Coefficients (n =
729; 243 triads).
WEBIST2013-9thInternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
560
