
Virtual Currency for Online Platforms
Business Model Implications
Uschi Buchinger, Heritiana Ranaivoson and Pieter Ballon
iMinds-SMIT, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium
Keywords: Loyalty Schemes, Virtual Currency, Business Models, Two-sided Markets.
Abstract: Since the first loyalty program was introduced in the 1980s, many sectors and industries have adopted and
configured these schemes to meet their specific requirements. But it is just recently that technological
innovation has enabled the transfer of these schemes into the online environment, and, more concretely, to
the increasing number of online platforms. Operating on two-sided markets, platforms started to deploy
loyalty programs to address customers and Third parties such as retailers or merchants alike. Additionally
they profit from the embedding in the digital environment, which enables the expansion of loyalty points to
become a Virtual Currency with the power to affect platforms’ business strategies. Based on the analysis of
four case studies, this paper focuses on the effect of the implementation of a Virtual Currency scheme on the
platforms’ organizational, financial and service business model parameters. It shows how Virtual Currency
schemes enable platforms to encourage loyalty of not only their customers but also in some configurations
of third parties, sometimes to the extent that one or both sides of the market are locked-in. Second, Virtual
Currency can be deployed as a source of revenue and thus play a role in the platform’s financial design.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since American Airlines established the first loyalty
program in the 1980s, various industries such as
hotels, retailers, financial services and leisure sectors
followed the concept of rewarding loyal customers
(O’Malley, 1998); (Palmer et al., 2000). It is
contended that this results in a positive influence on
the financial performance because of the higher
value of customer retention compared to new
customer acquisition (Christopher et al., 2008);
(Reichheld and Sasser, 1990); (Webster, 1992).
One of the most common measures is the issuing
and redeeming of company-related loyalty points
bound to a customer card which is implemented by
many industries (Wright and Sparks, 1999). Over
time loyalty programs became more and more a
standard in certain industries, which results in a loss
of its competitive advantage (Palmer et al., 2000).
While this is true for conventional businesses,
the development of Information and Communication
Technology (ICT) stimulated new industries in the
electronic business, who see a potential in the
loyalty concepts to bind customers and thus increase
the switching barriers in the online sector.
In addition, online businesses profit from the
embedding in the digital setting, where loyalty
points merge with the technology-driven rise of
digital money. Rewarded points loose their status of
simple loyalty measures to become Virtual
Currencies (VC), which have potential to change the
business’ economics. Unlike points, VC answers
multiple purposes e.g. payment methods accepted by
other Third parties and thus exceeding the sole B2C
relation.
Hence, the creator and coordinator of the VC is
on the one hand confronted with the building a
network of Third parties around the VC scheme,
while on the other hand, it aims at the original
intention of binding customers and encouraging
loyal behaviour. The purveyor can be placed as a
mediator of a two-sided market.
Platforms are already operating on two-sided or
even multi-sided markets with or without providing
own services on top of their platform activities
(Ballon, 2009); (Rochet and Tirole, 2002a). As a
platform, Rochet and Tirole (2002a) determine for
example software (videogame platforms, operating
systems), portals and media platforms or payment
systems. An essential characteristic of such markets
is that the utility for any user derived from a good or
service correlates to the number of users of this good
196
Buchinger U., Ranaivoson H. and Ballon P..
Virtual Currency for Online Platforms - Business Model Implications.
DOI: 10.5220/0004506601960206
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Data Communication Networking, 10th International Conference on e-Business and 4th
International Conference on Optical Communication Systems (ICE-B-2013), pages 196-206
ISBN: 978-989-8565-72-3
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

or service on the other side (Varian, 2000). Hence,
platforms (acting as intermediates) need to take care
of both sides in an equivalent way. The choice of the
business model is of utmost importance. Many
platforms follow the strategy of treating the two
sides differently, e. g. while one side of the market is
included for free - or is even incentivized to join -
the other side, who is interested in getting access to
the former, needs to pay (Rochet and Tirole, 2002a).
VC, which emerges from loyalty concepts but
addresses financial aspects likewise, has potential to
address both sides of the market simultaneously.
This paper will, by the analysis of four case
studies, focus on the configuration of such VC
concepts by online platforms that operate on such
two-sided of the market. This include customers on
the one hand and Third parties on the other hand.
Contrasting conventional loyalty schemes, little
research is conducted to examine how VC schemes
can affect platforms’ business models in order to
meet the two-folded objectives of online platforms,
namely to encourage loyalty (or lock-in) and open
revenue streams on one or both sides of the market.
Against this backdrop, VC strategies are thus
examined primarily upon their impact on financial
and service design parameters while also reaching
out to give insights to the organizational design via
representative value networks.
In the remainder of the paper, Section 2
describes the applied business model methodology.
Section 3 explains how platforms have taken over
loyalty points schemes invented and implemented by
various organizations. Section 4 describes in detail
how VC has been implemented in four case studies
describing the organizational design by the means of
representative value networks; Section 5 analyses
the impact of such an implementation on two further
business model parameters, the service and financial
design aspects. It thus focusing specifically on the
revenue sharing model and the loyalty concept.
Section 6 concludes and suggests ways for further
research.
2 METHODOLOGY
This paper adopts the methodology of business modelling
in order to analyse disperse interests of actors in a value
network, their respecting resources, roles and
relationships. The authors rely on the framework
developed a.o. by Ballon (2007) and Braet and Ballon
(2007), providing an holistic approach for examination of
network architectures. They define the business modelling
cycle as consisting of four parameters (see Figure 1):
organization, technology, service and finance. The
organization design corresponds to the Value network, i.e.
a framework consisting of business actors (physical
persons or corporations mobilizing tangible or intangible
resources), roles (business processes fulfilled by one or
more actors with according capabilities), relationships (the
contractual exchanges of products or services for financial
payments or other resources). The technology design
includes aspects such as modularity, distribution of
intelligence and interoperability (the technology design is
taken as granted and therefore considered with less details
in this paper). The service design refers to the intended
customer value. Finally, the finance design includes issues
related to costs and revenues.
Besides the focus on the impact of VC on the
business model parameters, the product/service offer
by the platform and Third party is taken into
consideration and linked to the VC scheme.
Figure 1: The business model cycle (Source: Braet and
Ballon, 2007).
3 DEVELOPMENT OF VIRTUAL
CURRENCY SCHEMES BY
PLATFORMS
3.1 Platforms’ Role between Customer
and Third Party
ICT markets are characterized by far-reaching
platformisation (Ballon, 2009). A platform can be
defined as a product, technology or service that is an
essential building block upon which an ecosystem of
firms can develop complementary products or
services (Gawer and Cusumano, 2002). In ICT
markets, crucial gatekeeper roles and functionalities
are often conducted by platform leaders. Various
2. TECHNOLOGY DESIGN
products & services creation
3. SERVICE DESIGN
creating customer value
1. ORGANIZATION DESIGN
mobilizing resources and
capabilities
4. FINANCE DESIGN
creating shareholder value
Leveraging resources
and capabilities
Products/service
brought to market
Resource
redistribution for
internal development
Appropriating
financial value
Consumers Consumer Groups
EXTERNAL STAKEHOLDERS
EXTERNAL ACTORS
Competitors
Suppliers
PUBLIC DOMAIN
Government, Standardizing bodies, Societal resources & institutions...
VirtualCurrencyforOnlinePlatforms-BusinessModelImplications
197

business models have emerged that help them to
exercise a form of control over the wider network,
and to add and capture significant value in the
process.
An essential characteristic of platforms is their
operation on two-sided markets. Two-sided markets
exist as soon as the utility of any customer A is
correlated to the number of customers B. These
models were first applied to credit card markets
(Rochet and Tirole, 2002b). Actually on such
markets, the higher the number of credit card
holders, the more interesting it becomes for the
shops to be equipped with devices that allow to pay
by card. Conversely, the higher the number of
equipped shops, the more utility one cardholder
derives from having such a card (Borestam and
Schmiedel, 2011).
The value network can thus be broken down to
three actors, represented in Figure 2, building the
base of each case study: the platform, which purveys
VC, the customer and the Third party. The platform
facilitates the interactions between both sides.
Relations are displayed as arrows between the
actors. In the following figures, three forms of
arrows will be depicted: black lines indicate
financial streams; dotted lines indicate
product/service streams (selling and receiving of
products or services), grey lines depict the VC
stream. Relations are bidirectional (exchange
between actors) or monodirectional (from one actor
to another).
Figure 2: A stylised representation of Two-sided markets.
Rochet and Tirole (2002a), examining the financial
relation between the actors of a two-sided market,
derive that many platforms choose either side for
revenue generation. One side of the market is then
treated as a profit centre that concurrently needs to
cover the loss (or financial neutrality) that is
accepted for the other side of the market.
It is hence a balancing act of generating revenue
and attracting and keeping stakeholders (concretely
encourage loyal behaviour or even enforce it by
locking stakeholders in). Especially in the online
environment, which is characterized by its low
switching costs (Shimizu, 2012) and the culture of
free services (Anderson, 2009), addressing this
objectives is still difficult and drives the need to find
new concepts.
3.2 From Loyalty Schemes to Virtual
Currency
The paper follows Sharp and Sharp’s (1997)
definition of loyalty program as “structured
marketing efforts which reward, and therefore
encourage, loyalty behaviour” (Sharp and Sharp,
1997, p. 474). Different types of rewards have been
developed throughout B2C sectors, notably the
implementation of incentives such as points that are
redeemable for rebates or prizes within the loyalty
scheme (Dowling and Uncles, 1997); (Sharp and
Sharp, 1997). Organizations implement according
measures to acquire competitive advantages. Such
programs however might become a standard,
diminishing the competitive edge of rewards
(Palmer et al., 2000).
One possibility to counteract this tendency is to
expand the industries or brands participating in the
loyalty program, a method pioneered once again by
various airlines. The cooperation scheme, defined
also as coalition loyalty or cross loyalty, describes
the facilitation of members’ loyalty cards at multiple
- sometimes competing - retailers. For the customer,
every industry or brand in the network adds
incentives for the customer to join (Baird, 2007).
While Baird (2007) refers particularly to the card
as the most common form of a rewarding design,
multiple approaches have arisen that changed the
establishments in the sector. An important trend is
the rise of applications allowing customers the
online coordination of loyalty programs.
Applications can have all necessary functionalities
to make a physical loyalty card obsolete. Hence,
platforms are developing adequate systems for
points collection and storage (Perez, 2012). At the
same time, they profit from the technology-driven
emergence of digital money which makes it possible
to treat loyalty points like a currency embedded in
the virtual setting. The European Central Bank
defines Virtual Currency as “unregulated, digital
money, which is issued and usually controlled by its
developers, and used and accepted among the
members of a specific virtual community”
(European Central Bank, 2012, p. 13) While this
definition raises the impression, that the community
is only the customer, in this paper it consists of both
sides of the market (customers and Third parties).
Customer
Platform
Third party
Financial or
Service flows
Legend
ICE-B2013-InternationalConferenceone-Business
198

Nevertheless, VC acts, like plain loyalty points,
as a loyalty measure towards customers by binding
them to this particular currency (and hence the
related organization). But while pure loyalty
programs are mainly implemented to reward
customer behaviour (Kumar and Shah, 2004),
Virtual Currency allows several uses, i.e. they are
tools for multiple usage options granted to the
different types of stakeholders in the Value network.
VC thus differentiates from conventional loyalty
concepts insofar as it can, besides binding customers
to the organization, have the same incorporating
effect on Third parties.
It is thus essential that the VC circulates in the
entire Value network. This can be ascribed to
whether Virtual Currency leaves a partner’s account
(i.e. a partner issues VC) enters the account (i.e. the
actors get VC) or fulfils tasks in the account.
Following options emerge:
Sell: Issuing VC in exchange of conventional
money,
Reward: Issuing or awarding VC,
Redeem: Taking back VC, i.e. accepting it as a
payment,
Create: build up and coordinate the network
around a VC,
Buy: Purchase VC for conventional money,
Spend: Using VC as a payment instrument
instead/alongside conventional money,
Get rewarded: Conduct a (qualifying) activity
that is awarded with VC,
Store: Accumulating and saving VC in personal
accounts or wallets.
Some roles can be performed by only one type of
actor in the network while others can be performed
by two or more types of actors. This paper assumes
certain preconditions: i) The creator of the VC is in
all cases represented as the platform. It manages and
coordinates the VC as well as the customer base and
user accounts and intermediated the two sides of the
market; ii) only the customer gets rewarded and
stores VC. Therefore customers need to create a
customer account on the platform; iii) Third parties
encompass all entities that sell products or services
by the means of the platform and are included in the
VC insofar as that they can either buy, reward,
redeem or sell the VC.
The exact configuration of the relationships
(organization design) and its impact on the
platform’s financial and service design will be issue
of the succeeding analysis.
4 VC IMPLEMENTATION
IN PLATFORM
SCHEMES – FOUR CASES
The section provides a detailed study of four cases
of platforms that have implemented a Virtual
Currency approach. They were selected based on
their different implementation strategies of VC and
thus the multiple options ascribed to VC
implementation that they represent. The diversity of
the actors, and their related business models, that
adopted such VC allows to draw conclusion based
on a broad view: Miles & More, Groupon Bucks,
Facebook Credits and Mobile Viking Points.
All value networks are reduced to three actors:
platform, Third party and customer. Each actor
fulfils certain roles that emerge from its daily
operations plus additional roles that emerge from the
implementation of a VC in the network. They are
illustrated as white boxes in the following value
networks and are reduced to two representative roles
for each actor: a role for product/service operations
(platform and Third parties provide products and
services, customers receive them) and VC operations
(platform creates and manages the VC, Third parties
and customers participate in the scheme). The exact
construction will be explained in a narrative way and
subject to a detailed analysis.
Relationships are displayed as arrows in the
value network including i) financial flows, ii)
product/service flows iii) Virtual Currency flows.
VC flows will also represent whether an actor
receives VC (i.e. customer gets rewarded, Third
parties buy or redeem and the platform redeem the
VC) or issues VC (i.e. customer spends VC, Third
parties and platform reward or sell VC)
The analysis of the relationship thus takes into
account: the exchange of money for products/
services, the exchange of money for VC, the
exchange of VC for products/services.
4.1 Miles
The native intention of the Miles & More program
implemented by the German airline Lufthansa is to
raise customer loyalty towards the airline while the
extension of the VC to Third parties increases its
value for customers. The platform targets both sides
of the market: Miles are rewarded to the customer
and sold to Third parties (e.g. banks, retailers,
hotels) Miles are only valid 36 month of the date of
accrual (e.g. date of flight) and expire at the end of
the respective quarter (Miles and More, n.d.). In
VirtualCurrencyforOnlinePlatforms-BusinessModelImplications
199
2011, 20 million members from 234 countries
participated in the program, with 250 partners
(Lufthansa, 2011). Figure 3 illustrates the relations.
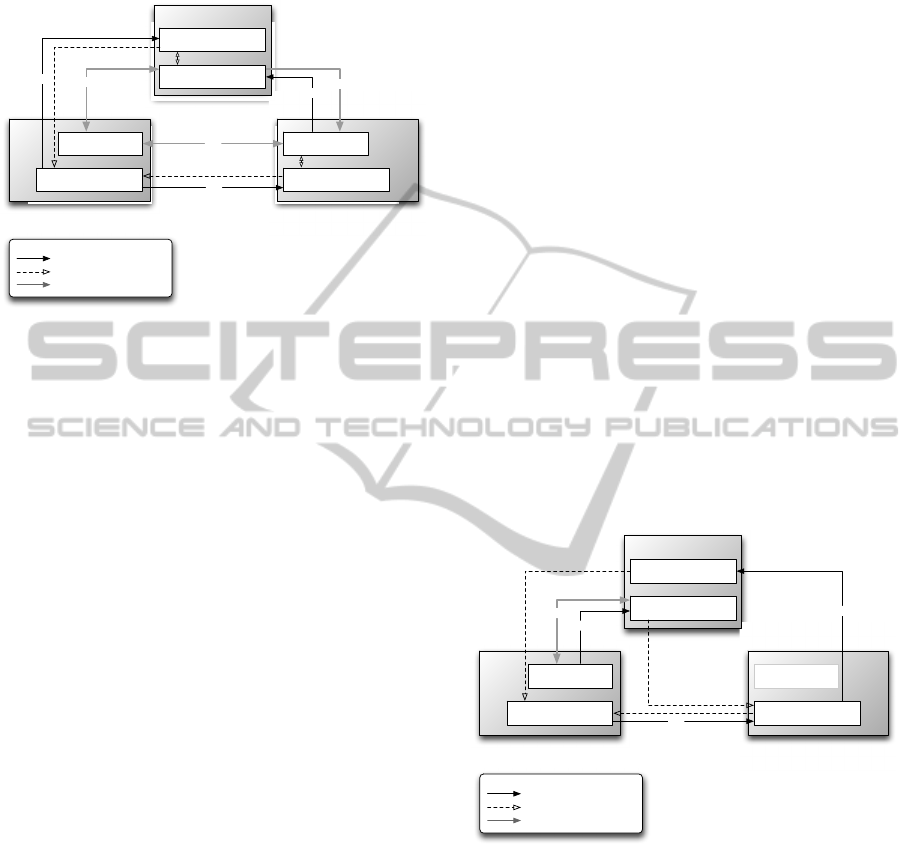
Figure 3: Miles and More Value network.
Miles & More as well as Third parties offer
products/services for selling to the customer. Money
flows from the customer to either representative role
and creates a product/service flow back (e.g. for the
receipt of a travel ticket). A purchase initiates the
rewarding of VC (arrow from product/service
provision to VC creation respectively VC program
participation and reverse: the VC can be redeemed
for products/services). The VC stream is
bidirectional between platform and customer and
customer and Third party (both partners can reward
and redeem the VC) and monodirectional between
the platform and Third parties. Third parties need to
have some form of payment agreement with the
platform (black arrow) to receive the VC that they
can reward (Mason and Barker, 1996). The
relationship between the three entities is as followed:
Platform/Customer: The primary intention of the
VC program is to reward VC to (and redeem VC
from) customers for purchases of flights. This results
in an indirect income stream for the platform –
indirect since it is unattached to the direct purchase
of miles. Customers’ purchased miles, unlike
rewarded ones, can solely be used for an immediate
redemption in form of a flight or service provided by
the airline (not by a Third party). Given the
divergent characteristics, purchases of miles are not
exposed as a possibility for the customer in the table.
Participation in the program is free for the customer,
but he/she is needs to set up a customer account.
Platform/Third Party: The platform cedes
control to Third parties by giving allowance to
reward and redeem miles. The platform generates
revenue directly by selling the VC for every mile
that the Third party rewards.
Third Party/Customer: Third parties conduct the
same rewarding process as the platform making use
of the VC acquired from the latter. They are mainly
unrestricted in their decisions upon applying terms
and conditions for rewarding (e.g. one mile for every
Euro spend on a purchase). A risk for the platform is
that none of the gathered miles are redeemed for a
ticket-purchase but merely for partner’s services.
4.2 Groupon Bucks
Groupon Bucks, executed by the group-buying
platform Groupon, solely reinforce customers’
loyalty. Groupon is an online platform that allows
Third parties to sell own products and services to
customers at a discounted price that can be set by the
means of economies of scale emerging form group
buying. Registered customers are given the
possibility to subscribe for offers that are validated
once enough customers have subscribed. Financial
movements pass via the platform. For its service,
Groupon retains a certain amount from each deal
sold but does not charge the customers to create their
customer accounts. Customers receive products or
services directly from the Third party. Groupon
Bucks do not expire (Groupon, 2012).
Figure 4: Groupon Value network.
The description of the figure is done in the following
analysis of the bilateral relations:
Platform/Customer: The platform offers its free
online service to the customer but does not have own
products for sale (dotted arrow from product/service
provision to receipt by the customer). The
implemented VC encourages solely interactions
between customers and the platform. A customer
who has performed, or participated in, a qualifying
user activity (e.g. referring someone to Groupon
who then conducts a purchase on the platform) are
rewarded with Groupon Bucks. The VC can be
Miles and More
Product/Service flow
Financial flow
Legend
€
Virtual Currency flow
VC
€
Product/Service receipt
VC program
participation
Product/Service
provision
VC creation/
management
VC program
participation
Product/Service
provision
Third party
Customer
VC
VC
€
Groupon
Product/Service flow
Financial flow
Legend
€
Virtual Currency flow
VC
€
Product/Service receipt
VC program
participation
Product/Service
provision
VC creation/
management
VC program
participation
Product/Service
provision
Third party
Customer
€
ICE-B2013-InternationalConferenceone-Business
200

redeemed for any deal at the platform. Additionally,
Bucks can be bought in form or gift cards as
presents for other customers. The redemption of the
Virtual Currency can however only pertain Third
party products/services, facilitated by the platform
(dotted line between the VC creation/management
and product/service provision of the Third party).
Platform/Third Party: The platform serves as a
mere sales channel for Third parties’ offers, not
providing services or products itself. The revenue
model consists of a fee taken by the platform on
every deal made by a Third party but yet unrelated
to the VC.
Third Party/Customer: Products/services can be
bought by the means of the platform; the VC does
not affect their relationship.
4.3 Facebook Credits
Facebook Credits, the platform’s Virtual Currency,
answer the purpose as loyalty measure towards
Third parties but moreover creates as a source of
revenue since the customers are charged for the
receipt of the VC. Credits are studied in this paper in
the case of game applications. Launched in 2004, the
free platform Facebook gathered more than 1 billion
active users in 2012. Since 2007, Third party
developers are able to provide apps, including
games, usable via the platform (The Associated
Press, 2013) while Facebook offers support in terms
of monetizing strategies. Together with the partner
company TrialPay, Facebook has implemented a
mechanism to rewarding customers for conducting
qualifying user activities (e.g. completing advertiser
offers). Credits are subject to expiration, which takes
effect when they are not used for three years. The
platform my redeem the VC for activities on behalf
of the user (sending virtual gifts to friends) or
donating it to charity. Standard redemptions fees are
however charged. Facebook Credits’ use is
constantly evolving. The paper works with the terms
and conditions of Facebook credits they were in
place in 2011/2012 (Facebook, 2013a); (Facebook,
2013b).
Platform/Customer: Facebook’s service
provision consists of the facilitation of Third party
services that can be uses via the customer accounts.
Within the game set-up, purchases of virtual in-
game items are supported, demanding however the
utilization of VC, that a customer stores in his game
items from Third party games, the actually need to
have a sufficient amount of Credits.
Figure 5: Facebook Value network.
Therefore, the customer must purchase the credits
(money stream from the VC participation to VC
creation/management and a VC flow back). The VC
cannot be redeemed at the platform itself. Besides
conscious, provident purchase of VC preliminary to
playing, it is possible to buy Facebook Credits whilst
playing when the account is not sufficiently filled.
Again Facebook Credits are bought, which are then
automatically converted into the requested item or
in-game currency. In other words, customers think
they buy the Third party’s currency whilst actually
buying Facebook Credits. Facebook thus creates a
direct revenue stream from the customer.
Platform/Third Party: While the platform creates
and operates the main service offer for the
customers, for the gaming applications it relies
mainly on the enrichment of assets via Third parties.
The platform empowers and supports Third parties
in the development of game applications and
embedding of payment mechanisms. Through the
implementation of Credits, an obligatory payment
method for gaming, Facebook has introduced loyalty
measures towards Third parties. Payments are
collected from customers. For each transaction,
Facebook credits Third parties with the proceeds
from the sale minus their service fee of 30 % + any
applicable tax (Facebook, 2013b); (Kincaid, 2011).
A partner company of Facebook enabled a
rewarding mechanism that allows Third parties to
award qualifying user activities with Facebook
Credits.
Third Party/Customer: The compulsory VC
scheme locks in game developers who want to
address and sell in-game items to the customer base
of Facebook. Customers are locked-in likewise since
they can solely purchase Third party in-game items
via Facebook Credits.
Facebook
Product/Service flow
Financial flow
Legend
€
VC
Virtual Currency flow
VC
€
Product/Service receipt
VC program
participation
Product/Service
provision
VC creation/
management
VC program
participation
Product/Service
provision
Third party
Customer
VirtualCurrencyforOnlinePlatforms-BusinessModelImplications
201

4.4 Mobile Viking Points
The MVNO (mobile virtual network operator)
Mobile Vikings implemented Viking Points as a
loyalty measure towards their customers who are
included for free in the VC program. Additionally
they incite Third parties to use this VC thus
contributing to customer loyalty towards both,
themselves and the platform. Active in Belgium and
the Netherlands, Mobile Vikings counts 160.000
members whom they sell mobile services such as
call minutes, SMS and data packages on Viking SIM
cards. The Viking Points can be exchanged in these
mobile services. Mobile Vikings additionally
operates a service to register Third party locations
(thus creating a ”Spot”). The location is thereupon
shown on a virtual map to all customers of Mobile
Vikings, with possibly related deals made available.
Information is missing about an expiration data.
Since it is however mentioned, that the customer is
free to use the VC whenever he wants, it can be
assumed, no expiration date is set (CityLive NV,
2012); (Mobile Vikings, 2013a), (Mobile Vikings,
2013b).
Figure 6: Mobile Vikings Value network.
Platform/Customer: Comparable to Miles & More,
Mobile Vikings offer products/services for their
customers (depicted as a money flow from the
customer in return for the products/services).
Regarding the VC, Viking Points set up a reward
mechanism for certain qualifying user activities (e.g.
convincing someone to join Mobile Vikings).
Optionally they can be bought in form of gift cards
mainly as a present for other users. Rewarded points
are redeemable for services/products of the platform
Mobile Vikings (bidirectional stream from the
platform to the customer).
Platform/Third Party: Solely the platform
provides the services/products that customers get in
exchange for the VC, i.e. its various mobile services.
Mobile Vikings however provides to Third parties
the possibility to gratis register venues such as shops
and stores on their virtual map. In addition, Mobile
Vikings runs a business-focused product bundle for
€ 375 (VAT incl.) per year, permitting Third parties
to create deals connected to the ”Spot”. Such deals
aim at attracting customers due to price cuts and
rebates on products. Third parties buy this tool from
the platform for their own product/service provision
(money stream from Third party’s product/service
provision and a respective service/product stream
back). With the product bundle, Third parties also
receive 3000 Viking Points that they are asked to
reward their customers with every concluded deal
(illustrated as a VC stream from the VC
participation of the Third party to the customer in
the illustration). The Third party decides upon the
height of the rebate and the volume of points
rewarded for each deal. Third parties have even
options to purchase further Viking Points for their
rewarding intentions. Mobile Viking charges then
the price for the VC plus 25% (CityLive NV, 2012).
Third Party/Customer: Third parties expand their
options with the purchase of the product bundle like
the localization and coordination of “Spots” (i.e.
shops and stores) and the creation of deals that the
customers can conduct. Third parties decide upon
the creation and exact configuration of deals. They
are obliged however to issue VC with every deal
conducted by customers.
5 VIRTUAL CURRENCY’S
IMPACT ON THE PLATFORMS’
BUSINESS MODEL
The section compares the cases studied previously to
analyse the impact of Virtual Currency on business
model parameters. The cases were chosen for their
coverage of divergent VC strategies and the disperse
sectors they are operating in. Consequently, general
conclusions are not possible. The analysis however
allows identifying of a few trends and issues that
affect the use of loyalty schemes and VC. The focus
thereby will be put on the financial- (revenue
generation and -sharing models) and the service
design aspect (strengthening of loyalty or even lock-
in on one or both sides of the market) whereas the
organizational design can be derived implicitly from
the value networks and are only described
superficially. The business model cycle of Ballon
(2007) and Braet and Ballon (2007) is used, which
Mobile Vikings
Product/Service flow
Financial flow
Legend
€
Virtual Currency flow
VC
€
Product/Service receipt
VC program
participation
Product/Service
provision
VC creation/
management
VC program
participation
Product/Service
provision
Third party
Customer
VC
VC
€
€
€
ICE-B2013-InternationalConferenceone-Business
202

consists of a further parameters, namely the
technology design. This aspect for the
implementation of VC is considered as given and
won’t be part of the analysis.
Seven characteristics are subject to comparison.
They can directly be linked up to one or more
business model parameters: the side(s) of the market
on which the VC is oriented; whether the platform
itself provides goods or services for which the VC
can be redeemed; the strength of enforcement to use
the VC in the network; whether Third parties also
redeem the VC; if the scheme rewards customer; if
the platform generates revenue by selling the VC
and if the VC has an expiration date (financial
design). For the second last point, a trade-off is
necessary between the Third parties (T.P.) and
customers (Cust.). Table 1 depicts an overview on
which characteristics are ascribed to which business
model parameters and their respective executions in
the various use cases.
Before the analysis of each parameter can be
made, this paper already revealed a general increase
in the range of roles that accompanies the
implementation of a VC stream. Expanding plain
loyalty points, VC circulation is subject to selling,
rewarding, redeeming, creating, buying, spending,
getting rewarded and storing by one or more actors
in the value network.
Regarding the organization design, one aspect is
the opening of the system to both sides of the
market. It is described as Orientation of the VC
scheme: two-sided signifies the issuance of VC
(rewarding or selling) to both sides of the market:
customers and Third parties. It applies to all cases
except of Groupon. Groupon Bucks addresses solely
the customer side but does not incorporate Third
parties in the scheme. With this limited possibilities,
loyalty through the VC is enforced on the customer
side only. The other examples are oriented on both
sides of the market, which means that the platform
needs to make a trade-off between each party’s
interests. As a result it will favour one side over the
other and thus enforce loyalty one side more. The
expansion of one side (e.g. by benefits such as free
participations or incentives) is normally an argument
to encourage the second side to join – wherefore
(payment) conditions are set. Miles & More and
Mobile Vikings initialize demand for the VC
primarily on the customer-side (free participation)
and charges the Third party. Facebook targets
principally the Third parties to implement the VC
standards (free help and support for the
implementation) and asks the customers to pay.
Multifaceted redemption describes the possibility
to redeem points at the platform as well as the Third
parties. Variety can be given throughout industries
(e.g. Third parties can be supermarkets, hotels, car
rentals, etc.) or within such (e.g. different execution
of games for Facebook). Each actor who redeems
the VC adds value to the loyalty scheme for the
customer but bears the risk that the customer does
not spend money (and shop) at the platform.
Platforms with their own products/services profit
from a system where VC, once issued, can only be
redeemed in their respective stores but limit the
choice for the customer. Consequently, platforms
need to make a trade-off between single (here:
Mobile Vikings and Groupon), or multifaceted
redemption places (Miles and More, n.d; Facebook).
The second aspect of the organization and
service design is the enforcement to use the VC in
the network. It is weak when no obligations are set
for the usage and participation is optional (Miles and
More, n.d; Groupon). In case of obligations, they
can affect both sidesb(Facebook) or one side
(Mobile Vikings) of the market. Facebook
Table 1: Characteristics of business model strategies.
Miles and More Groupon Facebook Mobile Vikings
Organization design
Orientation of the VC
scheme
two sides one side two sides two sides
Organization and
service design
Multifaceted
redemption
Y N Y N
Enforcement to use
VC
Weak Weak
Strong towards both
sides
Strong towards
Third Parties
Service design
Platform provides
services/products
Y N Y Y
Option of rewarding
Cust.
Y Y Y Y
Financial design
Direct Revenue
Platform
T.P. Cust. T.P. Cust. T.P. Cust. T.P. Cust.
Y N N Y N Y Y Y
Expiration Y N Y N
VirtualCurrencyforOnlinePlatforms-BusinessModelImplications
203

developers need to use the payment schemes if they
want to sell virtual items while customers must use
the VC for purchases. Mobile Vikings’ Third parties
are obliged to reward the VC to every customer for a
purchase. The latter can however buy products/
services from the platform for conventional money
alike.
A characteristic of the service design is the
platform proposition. Two types of platforms can be
distinguished depending on whether they have their
own products/services to exchange for the VC on
top of the platform activity. Miles & More, and
Mobile Vikings (who have their own products) are
independent of Third parties’ performance. Their
VC is still valuable for the customer without the
other side of the market. The VC of the latter
(Groupon and Facebook) has only as much value as
the Third parties (various types of merchants and
game providers) create. The platform is thus
dependent on the Third parties’ capacity and
willingness to fulfil their engagements. If Third
parties fail to meet the customer demands, the VC
looses its value.
A second characteristic of the service design is
the aspect of rewarding customers for desired user
actions. It remains a central point in the
implementation of VC strategies and presents a
consistency throughout all cases. This aspect shows
the connection to the initial loyalty schemes that aim
in building-up a (long-term) customer relationship.
Influencing the financial parameter, VC can
constitute a direct source of revenue for some
platforms. In general, platforms choose either side of
the market for creating revenue with the VC while
stimulate the other side via free (or even
incentivized) participation and benefits. In the above
cases it is the case for Miles & More and Mobile
Vikings that charge Third parties for the purchase of
VC and thus build the source of revenue for the
platform. Third parties need to compensate the
”loss” e.g. by additional sales. Facebook directly
sells the VC to customers as the only way of
receiving products/services from the Third parties.
For other platforms (here: Mobile Vikings and
Groupon) the option is given to buy VC in form of
gift cards or vouchers but it is not obligatory to use
them in order to receive products/services. Miles &
More allows customers to buy additional miles only
under the restriction that they are used for flights or
services that are provided directly from the airline.
Miles & More and Mobile Vikings allow Third
parties in fact to decide on conversion rates and
terms and conditions for rewarded VC, nonetheless,
Third parties are not allowed to sell VC (and
generate revenue).
A second parameter that affects the financial
design is the expiration date. Unused VC that
expires does not require an exchange in
products/services from the platform or Third party
and thus represents income for the respective
business without service in return. Miles & More
and Facebook implemented expiration dates, both
setting a valid period of three years before the
implemented terms and conditions take effect.
The counterpart of using VC as a source of
revenue is nevertheless that it can slow its adoption
process by Third parties or customers. The higher
the fee (e.g. per transaction using VC), the less
interesting for the customer to use the VC.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper uses the business model approach
developed a.o. by Ballon (2007) and Braet and
Ballon (2007) to draw conclusions upon the impact
of a Virtual Currency implementation on a
platform’s business features. It focuses particularly
on the organizational, financial and service design
parameters. Concretely, the paper has examined in
how far a Virtual Currency strategy is implemented
as a solution for two challenges that platform
concepts are confronted with in the online
environment, namely (i) how to attract and retain
stakeholders when switching costs tend to be at a
minimum and (ii) how to open new revenue streams.
Starting from conventional loyalty points, the
paper first has showed their adaptation to digital
requirements and expansion of functionalities. This
lays the ground for the transformation into a Virtual
Currency. VC answers in its basic functionalities the
same purposes as loyalty points. It rewards
customers and thereby binds them to a particular
platform. However, VC exceeds that by expanding
its roles for wider range of usage options than plain
loyalty points, namely selling, rewarding,
redeeming, creating, buying, spending, getting
rewarded and storing.
The paper has analysed four case studies’ value
networks: Miles & More, Groupon Bucks, Facebook
Credits, and Mobile Viking Points. Each value
network can be reduced to three actors: the platform,
customers and Third parties (i.e. partners that sell
products or services by the means of the platform).
Certain preconditions were assumed, such as the
platform as the creator and coordinator of the VC
and responsible party for the customer base. Third
parties and customer are involved twofold in the
ICE-B2013-InternationalConferenceone-Business
204

value network: on one hand in the operations of the
selling and purchasing process of conventional
products/services. On the other hand, they are
included in the VC scheme of the platform.
The four case studies were compared along
seven characteristics that are directly linked to the
organization-, service and financial design of
business models: (i) the side(s) of the market on
which the VC is oriented; (ii) whether the platform
itself provides goods or services for which the VC
can be redeemed; (iii) the strength of the
enforcement to use the VC in the network; (iv)
whether Third parties also redeem the VC; (v) if the
scheme rewards desired customer behaviour; (vi) if
and from which side of the market the platform
generates revenue by selling the VC; (vii) and if an
expiration date is introduced that can build another
income stream for the platform.
Each case follows a different strategy concerning
the implementation of VC. One consistency is
however, the purpose of strengthening loyalty
towards the platform on one or both sides of the
market. VC can be used as a tool to locked-in Third
parties and customers and thus discourage them
from switching to competitors. The realization
ranges from weak measures, where VC is handled as
benefit or bonus program, to strong measures where
loyalty is enforced by setting usage obligations in
the network.
Second the analysis revealed that all platforms
use the VC as a source of revenue, albeit to a
different extent. Purchasing VC can either be an
additional option granted to customers (besides
rewarding) or obligatory for customers or Third
parties. In line with the two-sided market theory, in
the examples where both sides are included, revenue
is generated on one side of the market while the
other one is included for free (with the option to buy
VC made available as incentive).
Although many more factors influence the
success of a platform’s business model, it can be
concluded that VC has the necessary attributes to
support platforms strategies in their service and
financial designs by encouraging loyal behaviour (or
even enforcing it by locking stakeholders in) and
opening a source of revenue for the platform.
The authors acknowledge that industries are still
in an early phase of experimenting with new
business models concerning VC strategies, in
particular with mobile devices opening up new
possibilities such as the broader use of location-
based services. Further research is thus required
reflecting the development of the market, also from
a technical point of view.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
CoMobile is an R&D project cofunded by IWT
(Agentschap voor Innovatie door Wetenschap en
Technologie), the government agency for innovation
by science and technology founded by the Flemish
Government. Companies and organizations involved
in the project are C2P – ClearPark, Alcatel-Lucent,
Netolog, CityLive – Mobile Vikings, Colibri,
Belgian Direct Marketing Association,
K.U.Leuven/COSIC, K.U.Leuven/CUO,
K.U.Leuven/ICRI, UGent/MICT, iMinds/iLab.o.
REFERENCES
Anderson, C., 2009. Free: The Future of a Radical Price,
Random House. London.
Baird, N., 2007. Coalition Loyalty programs: The next big
thing? Chain Store Age, 83(7), 14.
Ballon, P., 2007. Business modelling revisited: the
configuration of control and value. Info, 9(5), 6–19
Ballon, P., 2009. The Platformisation of the European
Mobile Industry. Communications & Strategies, (75),
15–33.
Borestam, A., Schmiedel, H., 2011. Interchange Fees in
Card Payments. ECB Occasional Paper No. 131
Retrieved from URL: SSRN: http://ssrn.com/
abstract=1927925 (accessed 26.11.2012)
Braet, O., & Ballon, P., 2007. Business Model Scenarios
for remote management. Journal of Theoretical and
Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 2(3), 62–79.
Christopher, M., Payne, A., & Ballantyne. D., 2008.
Relationship Marketing. Oxford: CRC Press.
CityLive NV, 2012. Viking Spots. URL: https://
vikingspots.com/en/ (accessed 6.2.2013)
Dowling, G. R., & Uncles, M., 1997. Do customer loyalty
Programs really Work? Sloan management review,
38, 71–82.
European Central Bank, 2012. Virtual Currency Schemes,
European Central Bank. Frankfurt am Main.
Facebook. 2013a. Facebook Sign Up. URL:
https://www.facebook.com/ (accessed 6.2.2013)
Facebook. 2013b. Facebook Developers. URL:
http://developers.facebook.com/ (accessed 6.2.2013)
Gawer, A., & Cusumano, M. A., 2002. Platform
Leadership: How Intel, Microsoft, and Cisco Drive
Industry Innovation. Boston: Harvard Business
Review Press, 1
st
edition
Groupon, 2012. Groupon. URL: http://www.groupon.com
(accessed 26.7.2012)
Kincaid, J., 2011. Facebook To Make “Facebook Credits”
Mandatory For Game Developers (Confirmed).
TechCrunch. URL: http://techcrunch.com/2011/
01/24/facebook-to-make-facebook-credits-mandatory-
for-game-developers/ (accessed: 31.10.2012)
Kumar, V., and Shah, D., 2004. Building and sustaining
VirtualCurrencyforOnlinePlatforms-BusinessModelImplications
205

Profitable Customer Loyalty for the 21st Century.
Journal of Retailing, 80(4), 317–330.
Lufthansa, 2011. Lufthansa Press Releases. Miles &
More: 20 million members. Press release archive.
URL: http://presse.lufthansa.com/en/news-releases/
singleview/archive/2011/february/11/article/1875.html
(accessed 3.7.2012)
Mason, G., & Barker, N., 1996. Buy now fly later: an
investigation of airline frequent flyer programmes.
Tourism Management, 17(3), 219–223.
Miles and More, (n.d.). Miles & More.
URL: http://www.miles-and-more.com/online/portal/
mam_com/de/homepage (accessed 6.2.2013)
Mobile Vikings, 2013a. Home. URL: https://
mobilevikings.com/bel/en/ (accessed 6th February
2013)
Mobile Vikings, 2013b. What are Viking Points? URL:
https://mobilevikings.com/bel/en/vikingpoints/
(accessed 6.2.2013)
O’Malley, L., 1998. Can loyalty schemes really build
loyalty? Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 16(1),
47–55.
Palmer, A., Mcmahon-Beattie, U., & Beggs, R., 2000.
Influences on loyalty programme effectiveness: a
conceptual framework and case study investigation.
Journal of Strategic Marketing, 8(1), 47–66.
Perez, S., 2012. PassRocket Lets Any Business Create
Loyalty Cards For Apple’s New Passbook App For
Free. TechCrunch. URL: http://techcrunch.com/
2012/09/19/passrocket-lets-any-business-create-
loyalty-cards-for-apples-new-passbook-app-for-free/
(accessed 2.10.2012)
Reichheld, F. F., & Sasser, E. W., 1990. Zero Defections:
Quality Comes to Services. Harward Business Review,
14(3), 497–507.
Rochet, J.-C., & Tirole, J., 2002a. Platform competition in
two-sided markets. Journal of the European Economic
Association, 1(4), 990–1029.
Rochet, J.-C., & Tirole, J., 2002b. Cooperation among
Competitors: Some Economics of Payment Card
Associations. The RAND Journal of Economics,
33(4), 549–570
Sharp, B., & Sharp, A., 1997. Loyalty programs and their
impact on repeat-purchase loyalty patterns.
International Journal of Research in Marketing, 14(5),
473–486.
Shimizu, K., 2012. The Cores of Strategic Management,
Routledge. New York.
The Associated Press, 2013. Hits and misses in Facebook
history over the years. The Big Story. URL:
http://bigstory.ap.org/article/hits-and-misses-facebook-
history-over-years (accessed 3.2.2013)
Varian, H.R., 2000. Introduction à la microéconomie. De
Boeck Université, Bruxelles, 4
th
edition.
Webster, F. E., 1992. The Changing Role of Marketing in
the Corporation. Journal of Marketing, 56(4), 1.
Wright, C., Sparks, L., 1999. Loyalty saturation in
retailing: exploring the end of retail loyalty cards? In
International Journal of Retail & Distribution
Management, 27(10), 429–440.
ICE-B2013-InternationalConferenceone-Business
206
