
Recovering RSA Private Keys on Implementations with Tampered LSBs
Constantinos Patsakis
Distributed Systems Group, School of Computer Science and Statistics, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland
Keywords:
SAT Solvers, Partial Key Exposure, Integer Factorization, RSA, Public-key Cryptography.
Abstract:
The theoretical security that modern encryption algorithms are providing, leads researchers to new attack
scenarios which are more implementation centric. By discovering hardware or software flaws that can recover
some information about the decryption key, cryptanalysts try to exploit this knowledge. Therefore, many
side channel attacks have appeared, illustrating that the concept of having secure code or even embedding
all cryptographic functions in hardware modules, in many cases in not adequate. The aim of this work is to
illustrate how partial information can be used to exploit the extracted information, leading to full reconstruction
of the private key of RSA, for some implementations of the algorithm where the LSB has been selected to fit
several constraints. More precisely, we study the case where the LSB half of the primes is identical or when
there is a linear equation that mixes the LSB halves of the two primes.
1 INTRODUCTION
Encryption for centuries was a strictly and detained
art of the privileged. However, recent advances in
telecommunications and computer science havetrans-
formed it into a science, which is used by everyone
with a wide range of applications. It is important to
highlight that cryptography provides a layer in all the
applications that use it that people take for granted.
People when using an application are sure that their
information cannot be intercepted, altered or forged
by other entities, something that is provided by cryp-
tography. Simultaneously, the advances in the fiels
enable users to enjoy the benefits, without needing to
come in direct contact with it or understand how it
works. Therefore, in most cases we can talk about
seamless integration of built-in cryptographic primi-
tives.
In many attack scenarios, the attacker can be con-
sidered to have physical access to the information sys-
tem. To justify the validity of such scenarios we have
to consider the extended use of portable and mobile
devices. Moreover, we have to take into considera-
tion the determination of attackers that want to attack
an information system and manage to enter the server
room. A measure to counter the impact of such at-
tacks on is to use encrypted partitions, this way, even
if the attacker can have physical access to the storage,
he will not be able to recover the stored information.
Breaking a modern encryption algorithm like AES-
128 can be considered infeasible, nevertheless if the
attacker can guess the first 100 bits, then brute-forcing
the rest 28 bits can be considered a trivial task.
The question that rises is how could the attacker
find these 100 bits and how feasible could this be.
The answer is the implementation of the algorithm.
If there are flaws in the implementation of the algo-
rithm, the attacker may extract bits by measuring sev-
eral things like:
• How much time does it take the algorithm to en-
crypt/decrypt?
• How much power does the processor use?
• What is the pool of randomness that is being used
to create the keys?
Depending on the answers to these questions, the at-
tacker will use a different technique to extract as many
key bits as possible.
While in many cases we consider the attacker, as
the malicious entity, in many scenarios, this is the
exact opposite. The wide adoption of cryptography
has enabled both “good” users as well as malicious
ones to use it. Therefore, frequently malware is us-
ing encryption to to attack or to hide its trails. Ex-
tortion software use cryptographic algorithms to en-
crypt user’s files and afterwards demand monetary
exchanges to disclose the decryption key belong. In
other cases, computer viruses and backdoors, encrypt
the code of their body and their traffic, making their
presence undetectable from antivirus programs.
453
Patsakis C..
Recovering RSA Private Keys on Implementations with Tampered LSBs.
DOI: 10.5220/0004534904530460
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT-2013), pages 453-460
ISBN: 978-989-8565-73-0
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

In this context, it becomes essential, even for dig-
ital forensics, to study how to much information is
needed to reconstruct a decryption key out of some
information that is provided. This work is studying
the special case of RSA, highlighting that even if the
RSA problem or the problem of integer factorization
are very difficult to be solved, having partial access
to random bits of the keys, leads to an easier problem
that can be solved much easier.
1.1 Contributions
The main contribution of this work is a set of fast real
world attacks on two implementations of RSA with
random known bits with high success rate. The first
case that is studied is the LSBS-RSA, a special imple-
mentation of RSA for smartcards, where the primes
share their least significant bits. Extending this attack,
we focus on RSA where there is a known linear rela-
tionship between the LSB halves of the two primes.
This work extends the results of (Patsakis, 2013) for
these use case, illustrating the powerful attacks that
can be launched using SAT solvers.
1.2 Structrure of this Work
The rest of the paper is organizedas follows. The next
section provides an overview of the previous work re-
garding RSA key reconstruction and partial key ex-
posure. The third section is presenting the results
from attacks using SAT solvers. More precisely, we
present the results for the general case of LSBS-RSA
and afterwards, we focus on the case where the pub-
lic exponent is equal to three. The following section
discusses these results, their significance and feasibil-
ity. Finally, we end this work with some remarks and
ideas for future work.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 SAT Solvers in Cryptanalysis
SAT solvers are programs that try to solve the boolean
satisfiability problem, that is given a boolean formula
to find whether there the variables can take true/false
values so that the given expression evaluates to true.
The problem is very well known to be a NP-complete,
actually, it was the first one to be proved belonging in
this category, nevertheless, several instances can be
solved. The need for solutions in industrial problems,
led to the creation of SAT solvers, which nowadays
are very efficient.
Massacci was the first one to use them in crypt-
analysis, introducing logical cryptanalysis (Massacci,
1999) and later trying to attack DES(Massacci and
Marraro, 2000). The development of more effi-
cient SAT solvers in the coming years, led sev-
eral researcher to explore the possibility of using
SAT solvers as a tool for cryptanalysis, leading
to more cryptanalytic-friendly versions like (Soos,
2010; Soos, 2009; Soos et al., 2009). Therefore, it
was a mater of time for SAT based attacks to emerge
like (Eibach et al., 2008; Golle and Wagner, 2007;
Mironov and Zhang, 2006; Morawiecki and Srebrny,
2010; Erickson et al., 2010; Homsirikamol et al.,
2012; De et al., 2007; Courtois et al., 2008; Mo-
hamed et al., 2011; Kamal and Youssef, 2010). How-
ever these attacks are focusing on symmetric key al-
gorithms and hash functions, for the case of public
key algorithm the main attacks can be found in (Fior-
ini et al., 2003; Dylkeyt et al., 2007; Faizullin et al.,
2009; Patsakis, 2013).
2.2 LSBS-RSA
RSA is the most widely used public keyencryptional-
gorithm, however, due its design, there are many cal-
culations that have to be made, hence, when it comes
to performance, it cannot be compared to any sym-
metric algorithm. Moreover, since these calculations
in many cases demand serious processing, deploying
it for mobile devices or for low processing devices
like smart-cards, is very difficult.
In order to provide a more efficient implementa-
tion Steinfield and Zheng proposed the use of slightly
altered scheme for RSA in (Steinfeld and Zheng,
2001). Instead of just selecting two prime numbers
that meet the criteria of typical RSA, the researchers
proposed the selection of primes that have in com-
mon the α least significant bits. This way, they en-
able fast and secure public-server-aided RSA decryp-
tion/signature generation. Even if one could claim
that this may create a new backdoor, specially us-
ing the BDF attack (Boneh et al., 1998), the authors
showed that this attack is not more powerful against
their proposedscheme. Nevertheless, several cryptan-
alytic attacks havealready been reported, highlighting
weak families of keys or improving the BDF attack
for this specific key generation procedure (Sun et al.,
2008b; Sun et al., 2008a; Zhao and Qi, 2007; Meng
and Bi, 2011).
According to their scheme, in the key generation,
we select two prime numbers which have α bits in
common and proceed generating n, e, φ(n) and d
as in common RSA. However, the public key key is
n,e,αd
pub
and the secret key is d
sec
, where:
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
454

d
sec
= (2
−2α
n/2−1
∑
i=2α
2
i
d
i
)
d
pub
= d −2
2α
d
sec
and d
i
represents the i−th bit of d. On input message
m the signature σ = H(m)
d
mod n is generated as fol-
lows:
1. The server computes:
β
1
≡ H(m)
d
pub
mod n
β
2
≡ H(m)
2
2α
mod n
and sends them to the client.
2. The client computes:
σ ≡ β
1
β
d
sec
2
mod n
which demands significantly less computations.
In this case, we have one multiplication modulo
n and one exponentiation, which is half the size of
the original one.
2.3 Cold Boot Attacks
Cold boot attacks are a special category of attacks that
is being more and more studied the past few years.
The concept of the attack is that the attacker gains
physical access to a device that implements an en-
cryption algorithm. Using several ways, from clean-
ing air canisters to liquid nitrogen, the attacker can
quickly decrease the temperature of RAM many de-
grees below zero. He then closes the device and boots
up with special software that dumps the memory to
a storage device (hard disk, usb etc). This memory
dump contains the decryption key, or a corrupted ver-
sion of it. The reason is that RAM is not instantly
deleted, but it is gradually corrupted. Depending on
the manufacturer and the model of the DIMM bits are
either turning from 0 to 1 or the opposite. By freezing
the DIMM the attacker manages to delay the corrup-
tion, hence from the memory dump he can be sure that
if for example the degration is from 0 to 1, whenever
he sees a 0 the value is correct. The implications of
such attacks can be found in (Halderman et al., 2009).
2.4 RSA Key Reconstruction
The problem of RSA key reconstruction was firstly
studied by Rivest and Shamir. According to their ap-
proach, we can query a random oracle which can re-
ply with a yes or no to our questions. Based on that,
they built up an attack which recovers the RSA pri-
vate key given 2/3 of the LSBs of one of the primes
(Rivest and Shamir, 1985).
Later, Coppersmith provided a very well crafted
polynomial time algorithm, that can recover small
roots of polynomials modulo N, when the factoriza-
tion of N is unknown, based on LLL algorithm (Cop-
persmith, 1996). Using this theorem, it can be shown
that if the attacker knows 1/2 of the MSBs of one of
its primes, then he can factor n in polynomial time.
Afterwards, Boneh et al. showed that the above
result can be achieved if the attacker is given 1/2 of
the LSBs of one of its primes, or
logn
4
bits of d (Boneh
et al., 1998).
Heninger and Shacham in (Heninger and
Shacham, 2009), provided a methodology, that
reconstructs the RSA private key from random bits, if
one the following is disclosed:
• 27% of the bits of p, q, d, d
p
, and d
q
, or
• 42% of the bits of p, q, and d, or
• 57% of the bits of p and q.
The above methodologies however have a basic lim-
itation, we assume that the bits that have been dis-
closed are all correct. Even if one of them is wrong,
the attack will not be successful. Since in cold boot
attacks, some of the bits can be flipped, Henecka et
al. studied a more close to reality scenario, how to re-
construction the RSA private key when all the bits are
given to the attacker, butwith some known probability
of error for the bits (Henecka et al., 2010). Maitra et
al. use lattices, so that given only knowledge of ran-
dom bits in the LSB halves of the primes, or blocks of
bits in the MSB halves of the primes, the attacker can
reconstruct the key (Maitra et al., 2010). Sarkar stud-
ied the case where the attacker is given a pattern in
the unknown corrupted version of d, so most of d is
considered known but only some contiguous blocks
are unknown (Sarkar, 2011). In another attack, the
attacker reconstructs the private key, using partial in-
formation with error for the MSBs of the secret pa-
rameters (Santanu et al., 2011).
In (Paterson et al., 2012), the researchers follow a
code theoretic approach, that enables them to launch a
series of attacks for a wide range of cold boot attacks
setups. More interestingly, they set the lower bounds
on how much information is needed to perform such
attacks efficiently and the success probability of their
attacks. Since the range of attacks that they cover is
wide, and covers setups that are not possible with the
current work, we only focus on the results on erasure
channels where they manage to recover the keys, for
the following cases:
• 33% of random bits of p, q and d with 34% suc-
cess rate in around 25.9 seconds
• 50% of random bits of p and q with 69% success
rate in around 7.23 seconds.
RecoveringRSAPrivateKeysonImplementationswithTamperedLSBs
455
3 THE SAT APPROACH FOR
RECONSTRUCTION
A novel approach for RSA key reconstruction was
proposed in (Patsakis, 2013). Even if in many cases
SAT solvers were proved to be at least inefficient
for integer factorization problem, several tweaks as
well as the random known bits enable the attacker
to launch powerful attacks against RSA implemen-
tations where the public exponent is equal to three.
Their major issue was that they couldn’t take advan-
tage of the underlying algebraic structures, therefore,
they ended up doing random walks among possible
keys, which will find the prime decomposition in
√
n
time.
Based on the Python implementation of Yuen and
Bebel (Yuen and Bebel, 2011), the prime decompo-
sition problem of the RSA modulo n is converted to
a SAT problem. Since this implementation is quite
generic, allowing the primes to be on range of 2 to
n/2, the author added the needed equations to make it
fit more to the RSA case. Hence, the upper
logn
2
bits of
the primes are set to zero, the last significant bits are 1
as well as the bits at position
logn
2
−1. Even if simplis-
tic, these tweaks drastically improve the performance
of the SAT solver, compared to the original one. For
the special case where e = 3, half of the bits of d (the
upper ones) are disclosed, therefore, the aforemen-
tioned information is supplied to the DIMACS file.
Finally, appending the known bits to the system, re-
sulted to a very powerful attack. More precisely, the
attacker can recover the private key in around 45 secs
with almost 98% success rate, given either 53-59% of
the bits of p and q or 38-44% of the bits of p, q and
d.
In order to decrease the file size of the DIMACS
file, enable testing for keys beyond 1024 bits and
work on Lonsdale cluster
1
, where each core has 2GB
of RAM, several improvements had to be made on
the initial implementation. Therefore, the current im-
plementation is making the multiplication on integers
which are each of half size of the product, reducing
drastically the file size of the DIMACS file. As it be-
comes apparent from Table 1, the space requirements
have been reduced by a factor of around 4. For a key
of 1024 bits the measurements for the CNF conver-
sion of the problem are illustrated in Table 2. The
measurements of the aforementioned table clearly in-
dicate that the system is not trivial at all and that the
SAT solver is really managing to solve a problem that
demands lot of resources. Therefore, it cannot be re-
garded as a random or trivial incident.
1
http://www.tchpc.tcd.ie/resources/clusters/lonsdale
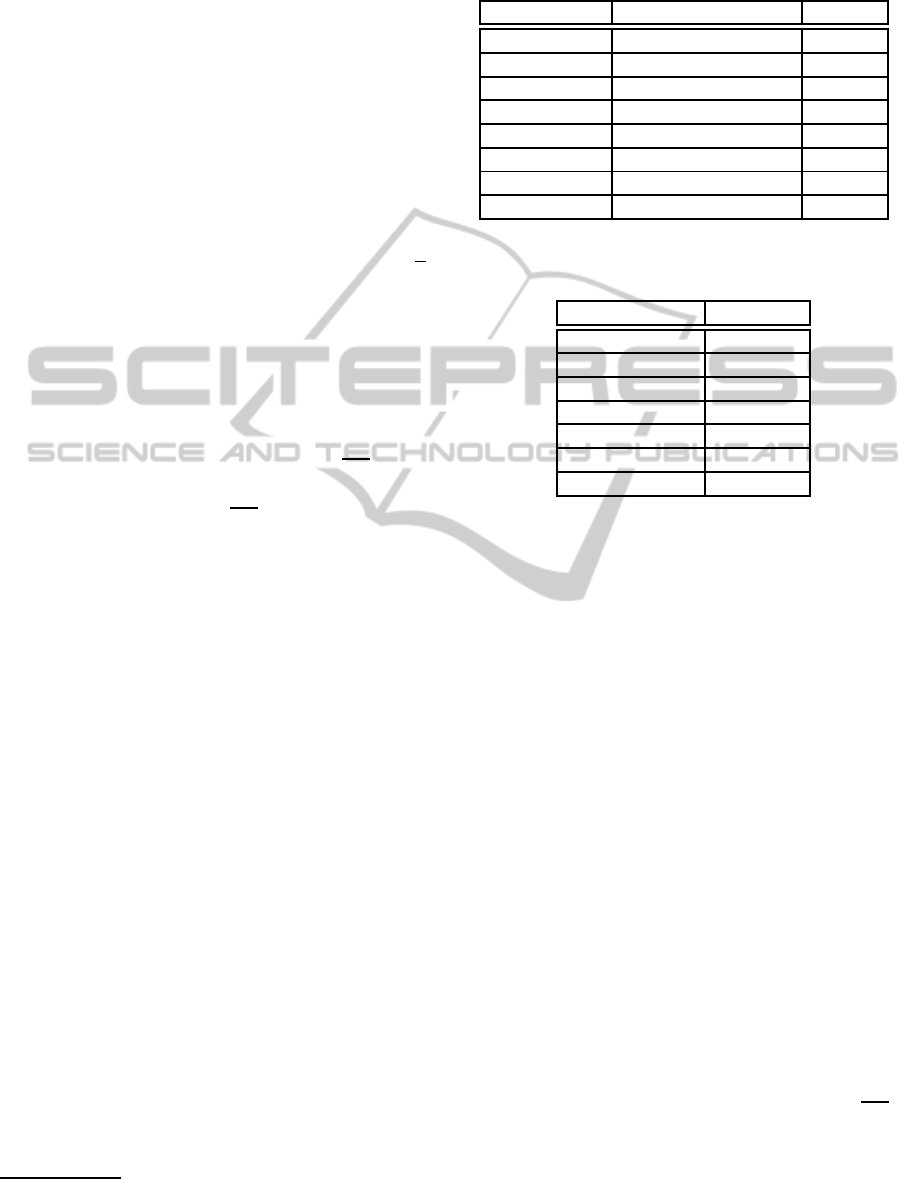
Table 1: Space requirements for creating systems of CNFs
before and now.
RSA key size Space needed before Now
128 bits 8.5MB 2MB
256 bits 36MB 8.2MB
384 bits 84MB 19MB
512 bits 150MB 36MB
768 bits 355MB 83MB
1024 bits 650MB 150MB
1536 bits 1.5 GB 355MB
2000 bits NA 617MB
Table 2: Typical measurements for a run of a 1024 RSA
key.
Measure Value
Variables 2904473
Clauses 6605492
Restarts 62
Conflicts 15632
Decisions 166656
Propagations 28649977
Conflict literals 405316
The conversion of the problem from algebraic to
CNF is quite straight forward. Each bit of the primes
is represented as a variable p
i
and q
i
and we try to
multiply these N/2 bit numbers as we would nor-
mally do for an embedded system. This means that
the multiplication is broken down to full adders and
half adders. The main difference is that the carries and
sums that are generated on each operation are stored
independently, therefore, they become new variables
to our system of equations, increasing the original
number of N/2 + N/2 = N variables at each opera-
tion.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Building on top of the results in (Patsakis, 2013), we
tried to focus on other implementations of RSA and
LSBS-RSA is one of them. For this case, we imple-
mented an attack where d is completely blinded, alter-
ing the key generation algorithm to create the proper
keysand appendedthe required CNFs to the DIMACS
file to make the lower bits common. In order, to de-
crease the processing time, the CNFs for the product
n = p × q were made for up to bit in position
logn
2
.
This created less constraints, therefore, less process-
ing time, however, the cost is more solution candi-
dates and probable false positives. This means that
the SAT solver returned a solution, but since it didn’t
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
456

meet all the necessary constraints, it was wrong. To
find the proper solutions, which decompose n as a
product of primes, we checked the upper halves of the
solutions. If these are correct, then the decomposition
can be achieved using Coppersmith’s theorem.
Since the attack was quite successful, the attack
was generalized to other probable RSA implementa-
tions. Since on LSBS-RSA we have the last bits to
be equal, we generalized this assumption. Therefore
the attack focused on implementations where the LSB
halves of the two primes are related with a known lin-
ear equation. This means that previously we knew
that
p
i
= q
i
, ∀ i, 0 ≤ i <
log n
2
now we have that
p
i
+ q
i
= x
i
, ∀ i, 0 ≤ i <
log n
2
with known x
i
.
The experiments were made on Lonsdale cluster.
Each node has 8 cores and 16GB of RAM running on
64-bit Opteron processors clocked at 2.30GHz. Each
experiment was run on one of the cores. The cluster
is running on 2.6.18 64 bit kernel and the SAT solver
used was miniSAT2.
The experiments were made for RSA keys from
128 bits up to 1024 bits. The amount of random
known bits was 30%, 35%, 40% and 45%. In each
case all the bits of the primes were entered in a pool,
and only the regarding amount of bits was selected,
the rest of the bits were blinded. For each category
of the attack 500 tests were made. This means that
totally there where 2 ×4×5 ×500 = 20000 tests ex-
ecuted.
The results of the experiments are illustrated in
Tables 3 and 4 and Figures 1 and 2. It is obvious
that the success rate of the attack is very high and ad-
ditionally, the attacks can be launched within reason-
able time, less than 2.5 minutes. The amount of infor-
mation to launch these attacks is quite low. We should
note here that for the case of LSBS-RSA we have to-
tally, N/2 + N/4 = 3N/4 variables, from which we
know in some attacks the 30% thus:
0.3
0.75
= 40% of
the variables, if we want to compare it with full RSA.
However,the attack can still be launched successfully,
with high success rate, indicating that it can take ad-
vantage of the underlying structure better than other
methods.
It is obvious from the tables that the more infor-
mation is disclosed, the less time is needed to solve
the system, the more successful the attack becomes.
In order to choose the proper SAT solver, an ini-
tial experimentation was conducted. More precisely,
128 256 512 768 1024
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
Key size
Time Elapsed (in secs)
Figure 1: Summary of the results for all bit sizes for LSBS-
RSA.
128 256 512 768 1024
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
Key size
Time Elapsed (in secs)
Figure 2: Summary of the results for all bit sizes for RSA
with related LSB halves.
SATzilla
2
was downloaded, that contains all the final-
ists of the 2012 SAT Challenge
3
. Each executable of
the competition was tested for some instances of the
1024 bit keys. Quite surprisingly, miniSAT outper-
formed all the other competitors, in many cases with
significant difference, therefore, it was chosen for the
final experiments.
2
http://www.cs.ubc.ca/labs/beta/Projects/SATzilla/
3
http://baldur.iti.kit.edu/SAT-Challenge-2012/results.html
RecoveringRSAPrivateKeysonImplementationswithTamperedLSBs
457

Table 3: Results for LSBS-RSA.
128 256 512 768 1024
mean success mean success mean success mean success mean success
30 4.83 96.75 40.27 99.99 95.8 99.99 158.55 99.99 162.3 100
35 1.83 96.75 20.99 99.98 59.35 99.98 111.02 99.99 141.64 100
40 0.68 100 21.28 100 53.9 99.99 113.65 99.99 157.32 100
45 0.34 99.99 7.84 100 47.75 99.99 90.79 99.99 142.52 100
Table 4: Results for RSA when the LSBs are related.
128 256 512 768 1024
mean success mean success mean success mean success mean success
30% 0.22 49.9 1.51 51.56 13.4 50.16 48.88 49.04 145.08 45.45
35% 0.18 66.14 1.43 60.52 12.78 60.49 50.84 59.62 134.83 59.35
40% 0.13 86.66 1.4 68.95 12.81 67.07 44.8 66.43 162.67 62.94
45% 0.11 95 0.9 88.13 11.49 65.32 54.49 75.69 168.33 70.99
5 DISCUSSION
The experimental results clearly indicate that the pro-
posed methodology can provide very powerful at-
tacks, outperforming (Heninger and Shacham, 2009)
and comparable to (Paterson et al., 2012). The pro-
vided information is significantly decreased as the
prime bits are related. In any case, it should be
noted that the proposed approach to key reconstruc-
tion has very high success rate and reasonable time
needed to execute the experiments allowing compar-
isons in terms of efficiency with the two aforemen-
tioned works. It should be highlighted, that the above
results apply to a specific implementation of RSA and
exploit its features, illustrating that some presump-
tions that we make regarding what kind of access can
the attacker gain, may have huge impact in the secu-
rity of the implementation of a generally secure algo-
rithm. Further decrease in the amount of given infor-
mation, resulted to huge delays in the output or many
false positives, validating the information bounds of
the aforementioned works. Additionally, we have to
highlight the exponential tendency of the needed time
to launch the attack that is depicted in Figures 2, that
is not the same as in Figure 1. The average needed
time in this case is multiplied by a factor around 10,
when the bits of the key are doubled. Finally, even if
the needed time for the LSBS-RSA is in most cases
greater that the related LSBs, the success rate is al-
most 100%. The explanation for this is probably be-
cause the resulting system is more strict, due to the
constraints.
Since in this attack we are targeting towards the
upper part of the primes, one could argue that the
amount of the provided information, is given at the
Figure 3: Knowing bits of p and q that “fit”.
upper halves of the primes with overwhelming prob-
ability. For example one could assume that the values
of the bits that are disclosed form the upper part of
the primes as in Figure 3. To make it more clear, let
p
i
and q
i
be bits of the two primes, then one could
recover in polynomial time all the missing bits, if
they could could ‘ fit perfectly”. Since both are odd
primes the last bit is 1. If this is not given in q then
we correct it. Now if we know the second bit for q
but not for p then it can be easily calculated since
n mod 2
2
≡ p mod 2
2
×q mod 2
2
. Since we know the
value q mod 2
2
and p mod 2, the value of p mod 2
2
can be easily calculated. The above scenario can be
generalized showing that if we do not have informa-
tion for any of the primes in k positions, then we need
to brute force 2
k
values. Additionally, we deduce that
if we are given information in the same position for p
and q, we do not extract significant information.
Firstly, we have to note that for the highest prob-
ability which is 40%, we expect 20% of the bits to
be on the upper half and 20% on the lower part.
Moreover, we expect 0.4
2
= 16% of collisions, that
is 8% on the upper part and 8% on the lower part.
Taking the above into consideration, we expect that
20%+ 20%−8% = 32% of the bits of the upper part
of the primes to be disclosed. Quantifying it, means
that for a key of 1024 bits, the SAT solver, if it was
just a brute force attack it would need 2
512×0.28
= 2
143
attempts. Definitely, this amount of calculation is be-
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
458

yond by any chance feasible and not comparable with
our experimental results.
More generally, let’s assume that 2ν bits of the to-
tal 2N bits of the primes have been disclosed. More-
over, we assume that brute forcing k bits is possible.
Let λ
1
and λ
2
be the bits of each of the two primes that
have been disclosed on the most significant halves re-
spectively. Then the possibility of being able to brute
force the most significant halves is:
∑
k
1
,k
2
∈ [0,k]
k
1
+ k
2
≤ k
∑
λ
1
,λ
2
∈ [0,
N
2
]
λ
1
+ λ
2
= 2ν
2
N
2
−k
1
λ
1
N
2
−k
2
λ
2
N
2
N
2
−λ
1
N
2
N
2
−λ
2
2N
2ν
From the above, we can safely deduce two major re-
sults. The first is that only using the provided infor-
mation, it is extremely improbable to extract all the
needed upper halves. Moreover, the provided infor-
mation is extremely improbable to allow us to extract
the upper halves through brute force as well. Hence,
the SAT solvers manage to solve the provided equa-
tions very efficiently and do not perform just a brute
force attack, but take advantage of the generated equa-
tions very efficiently.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Even if we are facing one of the strongest problems in
mathematics, prime decomposition or more precisely
the RSA problem, additional information regarding
the implementation of the algorithm, may allow the
attacker to break specific instances. With the constant
increase of side channel attacks and the discovery of
leaks within the implementation of encryption algo-
rithms, several attacks have been deployed escalat-
ing small leaks to complete disclosure. Within this
context, this work illustrates how a small amount of
random known bits of the private key of specific im-
plementations of RSA, may lead to full disclosure of
the private key with the use of SAT solvers. The as-
sumption for LSBS-RSA that the algorithm is secure
because it is immune to the standard BDF attack, does
not mean by any chance that the algorithm or its im-
plementations can be considered secure as well. As it
is shown in this work, the same applies of course for
the case where the LSBs of the two primes are related
with an arbitrary linear equation.
The basic limitation of the attack is that it does not
apply to real-world cold boot attacks, where some of
the known bits could be wrong, something that is cov-
ered in (Paterson et al., 2012). Nevertheless, the time
needed to launch the attack as well as the amount of
information needed clearly indicate that for the same
attack scenarios, they are at least comparable in terms
of time and success rate. Baring in mind that the re-
search on this field has recently started showing sig-
nificant results, we should expect in the near future
the development of even more efficient attacks and for
more algorithms. Finally, these attacks should force
everyone who is implementing cryptographic algo-
rithms to deploy them with more caution, trying to
detect all possible leaks of information.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
All calculations were performedon the Lonsdale clus-
ter maintained by the Trinity Centre for High Perfor-
mance Computing. This cluster was funded through
grants from Science Foundation Ireland.
REFERENCES
Boneh, D., Durfee, G., and Frankel, Y. (1998). An attack
on rsa given a small fraction of the private key bits. In
ASIACRYPT, pages 25–34.
Coppersmith, D. (1996). Finding a small root of a univariate
modular equation. In EUROCRYPT, pages 155–165.
Courtois, N. T., Bard, G. V., and Wagner, D. (2008). Fast
software encryption. chapter Algebraic and Slide
Attacks on KeeLoq, pages 97–115. Springer-Verlag,
Berlin, Heidelberg.
De, D., Kumarasubramanian, A., and Venkatesan, R.
(2007). Inversion attacks on secure hash functions us-
ing sat solvers. In Proceedings of the 10th interna-
tional conference on Theory and applications of satis-
fiability testing, SAT’07, pages 377–382, Berlin, Hei-
delberg. Springer-Verlag.
Dylkeyt, V. I., Faizullin, R. T., and Khnykin, I. G. (2007).
Reducing the problem of asymmetric ciphers crypt-
analysis to solving satisfiability problems.R In Pro-
ceedings of the XIII All-Russian Conference Mathe-
matical Methods in Pattern Recognition, pages 249–
251. MAKC press.
Eibach, T., Pilz, E., and V¨olkel, G. (2008). Attacking
bivium using sat solvers. In Proceedings of the 11th
international conference on Theory and applications
of satisfiability testing, SAT’08, pages 63–76, Berlin,
Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
Erickson, J., Ding, J., and Christensen, C. (2010). Alge-
braic cryptanalysis of sms4: gr¨oebner basis attack and
sat attack compared. In Proceedings of the 12th inter-
national conference on Information security and cryp-
tology, ICISC’09, pages 73–86, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Springer-Verlag.
Faizullin, R. T., Khnykin, I. G., and Dylkeyt, V. I. (2009).
The sat solving method as applied to cryptographic
analysis of asymmetric ciphers. The Computing Re-
search Repository, abs/0907.1755.
RecoveringRSAPrivateKeysonImplementationswithTamperedLSBs
459

Fiorini, C., Martinelli, E., and Massacci, F. (2003). How to
fake an rsa signature by encoding modular root find-
ing as a sat problem. Discrete Applied Mathematics,
130(2):101–127.
Golle, P. and Wagner, D. (2007). Cryptanalysis of a cog-
nitive authentication scheme (extended abstract). In
Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Symposium on Secu-
rity and Privacy, SP ’07, pages 66–70, Washington,
DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Halderman, J. A., Schoen, S. D., Heninger, N., Clarkson,
W., Paul, W., Calandrino, J. A., Feldman, A. J., Ap-
pelbaum, J., and Felten, E. W. (2009). Lest we re-
member: cold-boot attacks on encryption keys. Com-
munications of the ACM, 52(5):91–98.
Henecka, W., May, A., and Meurer, A. (2010). Correct-
ing errors in rsa private keys. In Proceedings of
the 30th annual conference on Advances in cryptol-
ogy, CRYPTO’10, pages 351–369, Berlin, Heidel-
berg. Springer-Verlag.
Heninger, N. and Shacham, H. (2009). Reconstructing rsa
private keys from random key bits. In In CRYPTO,
pages 1–17.
Homsirikamol, E., Morawiecki, P., Rogawski, M., and Sre-
brny, M. (2012). Security margin evaluation of sha-3
contest finalists through sat-based attacks. In Com-
puter Information Systems and Industrial Manage-
ment, volume 7564 of Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence, pages 56–67. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Kamal, A. and Youssef, A. (2010). Applications of sat
solvers to aes key recovery from decayed key sched-
ule images. In Emerging Security Information Systems
and Technologies (SECURWARE), 2010 Fourth Inter-
national Conference on, pages 216 –220.
Maitra, S., Sarkar, S., and Sen Gupta, S. (2010). Fac-
toring rsa modulus using prime reconstruction from
random known bits. In Proceedings of the Third
international conference on Cryptology in Africa,
AFRICACRYPT’10, pages 82–99, Berlin, Heidel-
berg. Springer-Verlag.
Massacci, F. (1999). Using walk-sat and rel-sat for crypto-
graphic key search. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth In-
ternational Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
IJCAI ’99, pages 290–295, San Francisco, CA, USA.
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.
Massacci, F. and Marraro, L. (2000). Logical cryptanalysis
as a sat problem. J. Autom. Reason., 24(1-2):165–203.
Meng, X. and Bi, J. (2011). Weak keys in rsa with primes
sharing least significant bits. In Information Security
and Cryptology, pages 278–287. Springer.
Mironov, I. and Zhang, L. (2006). Applications of sat
solvers to cryptanalysis of hash functions. In Proceed-
ings of the 9th international conference on Theory and
Applications of Satisfiability Testing, SAT’06, pages
102–115, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
Mohamed, M., Bulygin, S., and Buchmann, J. (2011). Us-
ing sat solving to improve differential fault analysis of
trivium. pages 62–71. Springer.
Morawiecki, P. and Srebrny, M. (2010). A sat-based
preimage analysis of reduced keccak hash func-
tions. http://eprint.iacr.org/2010/285. pawelm@wsh-
kielce.edu.pl 14742 received 13 May 2010.
Paterson, K., Polychroniadou, A., and Sibborn, D. (2012).
A coding-theoretic approach to recovering noisy rsa
keys. Advances in Cryptology–ASIACRYPT 2012,
pages 386–403.
Patsakis, C. (2013). Rsa private key reconstruction from
random bits using sat solvers. IACRCryptology ePrint
Archive, 2013:26.
Rivest, R. L. and Shamir, A. (1985). Efficient factoring
based on partial information. In EUROCRYPT, pages
31–34.
Santanu, S., Sourav Sen, G., and Subhamoy, M. (2011). Re-
construction and Error Correction of RSA Secret Pa-
rameters from the MSB Side. In WCC 2011 - Work-
shop on coding and cryptography, pages 7–16, Paris,
France.
Sarkar, S. (2011). Partial key exposure: Generalized frame-
work to attack rsa. In Progress in Cryptology - IN-
DOCRYPT 2011, volume 7107 of Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, pages 76–92. Springer Berlin /
Heidelberg.
Soos, M. (2009). Cryptominisat - a sat solver for cryp-
tographic problems. http://planete.inrialpes.fr/∼soos/
CryptoMiniSat2/index.php.
Soos, M. (2010). Grain of Salt — an Automated Way
to Test Stream Ciphers through SAT Solvers. In
Tools’10: Proceedings of the Workshop on Tools for
Cryptanalysis 2010, pages 1–2, RHUL.
Soos, M., Nohl, K., and Castelluccia, C. (2009). Extending
sat solvers to cryptographic problems. In Proceedings
of the 12th International Conference on Theory and
Applications of Satisfiability Testing, SAT ’09, pages
244–257, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
Steinfeld, R. and Zheng, Y. (2001). An advantage of low-
exponent rsa with modulus primes sharing least signif-
icant bits. Topics in Cryptology-CT-RSA 2001, pages
52–62.
Sun, H., Wu, M., Wang, H., and Guo, J. (2008a). On the
improvement of the bdf attack on lsbs-rsa. In Infor-
mation Security and Privacy, pages 84–97. Springer.
Sun, H.-M., Wu, M.-E., Steinfeld, R., Guo, J., and Wang,
H. (2008b). Cryptanalysis of short exponent rsa with
primes sharing least significant bits. In Franklin, M.,
Hui, L., and Wong, D., editors, Cryptology and Net-
work Security, volume 5339 of Lecture Notes in Com-
puter Science, pages 49–63. Springer Berlin Heidel-
berg.
Yuen, H. and Bebel, J. (July 18, 2011). Toughsat. http://
toughsat.appspot.com.
Zhao, Y. and Qi, W. (2007). Small private-exponent attack
on rsa with primes sharing bits. Information Security,
pages 221–229.
SECRYPT2013-InternationalConferenceonSecurityandCryptography
460
