
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Knowledge Management based on
k-Workflow, on Conversion and Knowledge Flow
The Case of the National Land Transport Agency in Brazil
Luiziana Rezende
1,2,4
, Maria Angela Lobão
2,5
, Joel de Lima Pereira Castro Junior
2,3
,
Luiz Angelo Merino
2
, Soraia Alves Rocha
2
, Carlos Alberto Malcher Bastos
2
1
Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
2
GtecCom / Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, Brazil
3
PPGAd / Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, Brazil
4
Post DocPPEngProd / Fluminense Federal University, Niterói, Brazil
5
IBMEC Faculty, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Keywords: Knowledge Management, Knowledge Workflow, Conversion and Knowledge Flow, Innovation.
Abstract: This paper presents the main contributions of the Iterative Model for Knowledge Management proposed by
Universidade Federal Fluminense (UFF) in cooperation with the Brazilian Agency for Land Transport
Regulation (ANTT). The method’s great innovation is to combine to the KM diagnosis and prognosis, the
concepts of conversion and knowledge flow, with the application of the 5W1H method and Enterprise
Architect (EA) software to integrate the models built, also allowing its graphical representation. The models
and products obtained have allowed: to understand the culture of the Agency's current KM; view existing
gaps and needs in their knowledge flow construction and in the process of converting knowledge; propose a
set of KM practices and tools appropriate to their reality and predict future actions of improvement that
impact on the efficiency of the regulatory process.
1 INTRODUCTION
Currently, organizations have several computerized
systems to support the implementation of its
processes and activities without a structured
information and knowledge model. In this scenario,
some problems were identified: the absence of an
information critical analysis culture; low level of
information integration between sectors; absence of
a formal structuring information process to
facilitate/enable the fulfillment of the institutional
mission; dispersed knowledge and with difficult
access, requiring transformation of tacit knowledge
into explicit and provision /sharing explicit
knowledge to decision making process.
ANTT, National Land Transport Agency in
Brazil, is an entity linked to the Ministry of
Transportation and the regulation Agency of the
exploitation of federal railway and highway
infrastructure activity and land transportation
provision activity in Brazil.
In order to fulfill its mission, the Agency needs
to have its information and knowledge identified,
mapped, integrated and available to those who may
need it effectively building an Information and
Knowledge Management Model (MGIC).
In order to develop a MGIC for an organization
there are some necessary preliminary steps which
are essential: information assets identification,
information and knowledge flows and knowledge
and skills mapping.
The major difference of MGIC is that it uses, in
an innovative way, a specific methodology that
brings together several theories, methods and tools
embodied in the information and knowledge
management.
This paper is a step of the building process of a
MGIC and the result of the academic and scientific
research; with the application of a case study
conducted in the Brazilian land transportation
Agency (Bastos et al., 2011).
Based on these products and aimed at creating a
fertile environment for new ideas and problem
413
Rezende L., Lobão M., de Lima Pereira Castro Junior J., Merino L., Alves Rocha S. and Malcher Bastos C..
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Knowledge Management based on k-Workflow, on Conversion and Knowledge Flow - The Case of the National Land
Transport Agency in Brazil.
DOI: 10.5220/0004550104130418
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval and the International Conference on Knowledge
Management and Information Sharing (KMIS-2013), pages 413-418
ISBN: 978-989-8565-75-4
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

solving, another goal is to make proposals and
suggestions for improvements in knowledge
management in ANTT.
The phases presented in this work are
specifically modeling, analysis and representation of
knowledge management in one Organizational Unit
of the ANTT, providing details on methodology and
method.
This paper is organized as follow. The next
section presents the Knowledge Models
Development Phases; the section 3 the Analysis of
the Models and Generated Products, the fourth
section shows Diagnosis of the current status of
Knowledge Management, finally the fifth section
shows the conclusion of the work in progress.
2 KNOWLEDGE MODELS
DEVELOPMENT PHASES
For developing of an Information and Knowledge
Management Model (MGIC), the first phase is the
knowledge and skills mapping using a specific
method, which enables to build a knowledge tree,
knowledge and skills topography and a unified
knowledge database, which enable a descriptive and
analytical approach to knowledge management in
the organization.
For building a MGIC, there have been
specifically adopted the following integrated
methodologies and scientifically proven in the
literature: Zarifian (2005) and Fleury and Fleury
(2004) with the concept of mobilization of
knowledge and skills; Rezende (2007) with the
Iterative Method for Mapping and Analysis of
knowledge and Skills; Nonaka and Takeuchi (1995,
2009) with the SECI Model explaining the processes
of knowledge conversion and the knowledge spiral;
Michael Authier and Pierre Lévy (1992) with the
concept of the knowledge tree for knowledge
dynamic structuring .
It is worth mentioning that the initial part that
composes the MGIC: Information Asset
identification and modeling, Information Flow and
Ontology model, as well as the final phase of
construction of the architecture and implementation
of knowledge management in the organization, are
described in a more complete methodology for the
construction of MGIC (Bastos et al., 2011).
The relevance of the method lies in the fact that,
while it maps knowledge/skills/professionals, it also
analyzes the flow and the processes of knowledge
conversion in the organization, supporting the
construction of architecture and a tool proposition
for knowledge management.
The method application allows the organization
to identify the relevant sources of information and
knowledge and set the strategy for its collection and
methods for its analysis; to implement a culture of
research, collection, recording and analysis of
knowledge within an organizational context; to
know what types of knowledge exist and where they
are located, to manage them, integrate them and
organize them, in order to make the most of their
extraction for decision-making; support to the
organization through knowledge sharing and
integration among employees, enabling the
transformation of tacit knowledge into explicit;
improve the localization and exploitation process of
new knowledge that, despite having it, the
organization is not able to identify, thus enriching
creativity and generating competitive intelligence; to
identify experts (inside professionals) to give
technical support for analysis; to support the
construction of communication forms, conversation,
learning, training community work, structuring
individual and teams experiences, facilitating access
to ideas and solutions.
In the phases of knowledge and skills
identification and collection, initially, there were
mapped the procedures for carrying out the
information flows activities and related to explicit
and tacit knowledge, as well as the skills of the
professionals involved. In this process we created a
Knowledge Workflow (k-workflow), an innovation
in modeling process and knowledge management
created especially for the MGIC.
For knowledge and skills mapping and
representation and k-workflow building, there were
used a methodology based on research developed by
Rezende (2011), the methodology 5W1H (Ikeda et
al., 1997) and the software Enterprise Architect (EA)
for the models integration and reports generation.
For visualization in a hierarchical form of shared
and specialized knowledge, the Treebolic (2007)
software was used for the construction the
knowledge tree (Authier and Lévy, 1992).
From the construction of knowledge and skills
topographies and an integrated database, it was
possible to generate descriptive graphs that enable
statistical analysis.
An important level of analysis is the
identification of gaps in knowledge flow (Figure 1)
and the process of knowledge conversion (SECI
Model), proposed by Nonaka and Takeuchi (1995;
2009), which allows to have a vision of KM as a
process.
KMIS2013-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
414

From the knowledge gaps identification during
the analysis phase there were suggested techniques,
practices and tools that allow the organization to
capture, mobilize and innovate knowledge as an
input for the development of intellectual capital and
social capital through effective services.
Figure 1: Knowledge flow.
The models developed, Iterative Method for
Knowledge Mapping and Management in Enterprise
Environments, indicating the different steps
performed: 1) information collection; 2) knowledge
and skills survey; 3) classification; 4) representation
and 5) analyzing, during which several products are
generated.
The first stage of information collection was
conducted through open interviews with managers
and employees, chosen by the nature of their
functions and specializations potentially useful to
participate in the collective knowledge development
process.
This step has two well featured phases, the first
phase is inputs consolidation at the information level
and needed knowledge to start modeling, where it
was taking into consideration: a) all documents
provided to assist the agency understanding, b)
existing systems at the agency, c) the list of
information assets and d) the actors/workers
identified at the generated models in the previous
stages of MGIC construction.
From the consolidation phase of the inputs, the
professionals list to be interviewed was identified. A
script was prepared for interviews considering all the
knowledge previously gathered in information
flows.
The interviews, which were carried out openly
and transcribed manually searched to identify the
existing explicit and tacit knowledge and skills
needed to perform the activities.
The method generates a table that shows a sketch
with the demographic data of the interviewed
employees that can allow to analyze the expertise
level and realize their correspondence to operational
skills at the Organizational Unit (OU).
The workflow, was made based on 5W1H method
(Ikeda, Okumura and Muraki, 1997), led to the
breakdown of activities to be undertaken for the
management of an information asset. The method
also generates an outline of working groups identified
in the information assets.
Thus, the collection stage enabled the
construction of the k-workflow containing
procedures for implementation of information asset
and their knowledge, their skills and their related
working groups, the information asset matrix x
interviewed x working group and the listing of
demographics data of the interviewed professionals
(Figure 2).
The second stage was to survey, which allowed
the mobilized knowledge definition and the skills
needed to perform the activities of an information
asset by working group. Consequently it was
possible to generate knowledge and skills lists.
After information collecting phase the
knowledge and skills of an information asset were
identified. The materials collected in the interviews,
documents provided and the existing systems
applied were used to define the knowledge and
skills.
In this phase it was performed the knowledge
Topography composed of the following steps:
identification, description and classification (nature,
relevance and level).
By analyzing the knowledge topography, it was
identified that the majority of processes are well
structured for employees.
All identified knowledge was of explicit nature,
with well-defined location, but without a systematic
storage, retrieval, update, dissemination and
recreation.
In this phase it was performed the skills
topography, consisting of the following steps:
identification, description, relevance and skills
representation (Rezende, Lobão, Burmann, Castro
Júnior, Merino, Rocha and Bastos, 2012).
The third stage, the classification, aims to
construct the knowledge and skills topographies.
The knowledge topography consists in classification
in nature terms (tacit or explicit), relevance
(irrelevant, little irrelevant, relevant and very
relevant), knowledge level (basic, intermediate and
advanced) and its location. Based on these ratings
the relationships map was constructed from
information assets x activities x working groups.
From knowledge and skills topographies and the
relationship matrix it was prepared the basis for
DiagnosisandPrognosisofKnowledgeManagementbasedonk-Workflow,onConversionandKnowledgeFlow-The
CaseoftheNationalLandTransportAgencyinBrazil
415
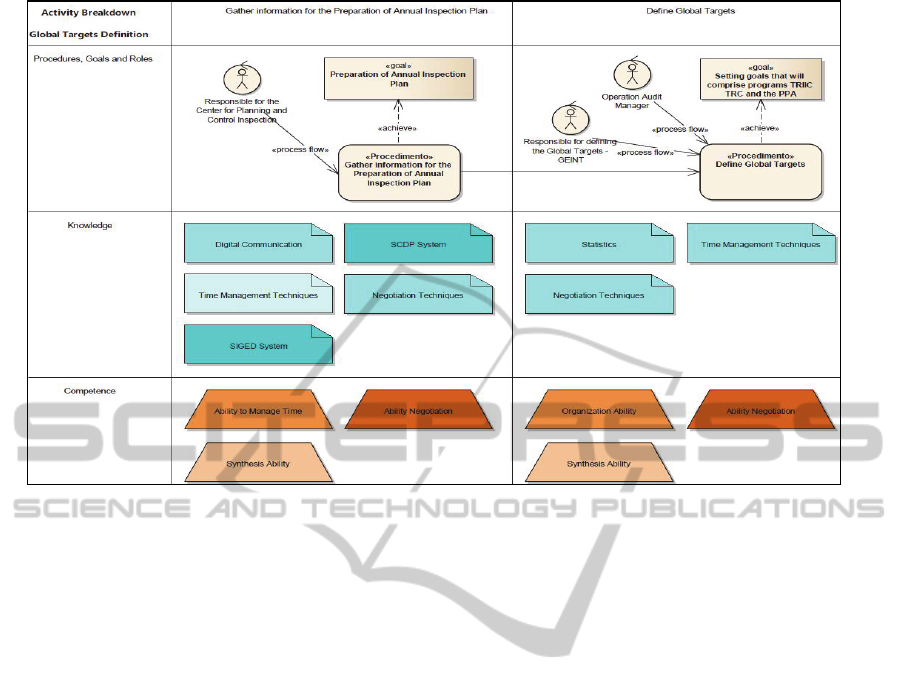
Figure 2: Knowledge workflow and map of knowledge/skills/work groups.
construction of knowledge /skills / professionals
map.
The fourth step was the representation, which
consisted of the knowledge/ skills/professionals map
(through the use of EA software) and the knowledge
tree (using the Treebolic software).
To view in a hierarchical way the knowledge
gathered the knowledge tree was used as graphic
representation. This visual instrument to represent
knowledge is easy to handle and allows any user to
explore a whole information structure without
feeling lost in its hierarchy.
The organization can use the knowledge tree as a
support tool to help: the elaboration of a training
plan and capacity building; locating expertise;
sharing information; indicating knowledge gaps.
In the final stage of model analysis there were
constructed descriptive charts, showing the different
possible groupings of the information and
knowledge gathered, classified, represented and
mapped. Gaps were identified in relation to the
knowledge flow (Figure 1) and the SECI Model
(Nonaka and Takeuchi, 1995, 2009).
Yet it was possible to investigate the correlations
between skills and knowledge that indicate new
relationships associated with information assets,
activities and working groups.
The following section presents outlines of
models and generated products at each stage of the
method and its application.
3 ANALYSIS OF THE MODELS
AND GENERATED PRODUCTS
Several analyses can be performed from the models
and generated products. With the knowledge basis
built it is possible to identify: the existing working
groups in the organization, the working groups
associated with an information asset, the working
groups associated with different information assets
activities; the technical knowledge ordered by the
relevance; correlations between activities /
knowledge /skills; specializations by working groups
and vice versa; specialized and shared knowledge
and data intersections of interest to the organization.
The analysis of the technical knowledge of an
information asset by relevance may influence the
profile definition of knowledge that an employee
must have to perform his activities efficiently.
Another application may be the use of these analyses
as an additional tool for the process of evaluating the
employee performance.
The analyzes of the activities numbers of the
working groups in the implementation process of an
information asset within the Organizational Unit
may help in assessing the OU assessing the number
of activities performed by a particular working
group.
It should be noted that other possible analysis
may be performed from the knowledge basis such
KMIS2013-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
416

as: a) working groups in ANTT by area; b)
information asset associated to working groups; d)
technical expertise ordered by relevance; e)
correlations between activities/ knowledge/skills; f)
expertise by working group and vice versa; g)
specialized and shared knowledge. Therefore, the
Agency has a strong management tool to define
projects teams, employees recruitment process,
development of training courses for the different
working groups, monitoring and evaluation of
performance of its employees, among others.
4 DIAGNOSIS OF THE CURRENT
STATUS OF KNOWLEDGE
MANAGEMENT
Throughout the processes of data collection,
mapping and modeling, information and knowledge
inputs were consolidated provided by the Agency to
understand the business processes, ANTT's mission
and how their activities contribute to achieving the
Agency’s goals.
Based on these inputs a diagnosis of Knowledge
Management was built in the following categories:
People; Knowledge Management; Organization/
Procedures.
Regarding the People category, we evaluate the
experience and the educational of the Agency staff.
As far as the Organization and Procedures for
Knowledge Management category is concerned, we
evaluate the knowledge required for the execution of
information assets, if it is formalized in documents
and is integrated by systems. We are also interested
if the Agency promotes knowledge sharing and if it
includes dissemination activities for training new
employees. The K-workflow procedures for carrying
out the necessary activities for implementing their
information assets helped us to understand its
operation and identify its working groups. It is
noteworthy that the most of employees interviewed,
participate in more than one working group. We are
particularly interested to know if the environment is
adequate for the implementation of methods and
techniques of knowledge management.
Knowledge management has the function to
strengthen the individual and organizational
knowledge basis. In the category related to
Knowledge Management, we evaluate if the stages
of knowledge flow are properly covered, associated
to the steps of knowledge capture, mobilization and
consequently to innovation steps.
We evaluate if documents and reports
standardization support the implementation of
information assets and if storage and documents
protection are done in an unique way.
Regarding the mobilization stage, we evaluate if
overall and specific goals from previous years are
used as inputs for the creation of the new documents
and information assets. It is also verified if the
Agency promotes sharing and dissemination among
stakeholders.
We also evaluate if there are some gaps in the
steps of knowledge capture and mobilization that
can compromise the innovation stage.
We also evaluate if the four models of
knowledge conversion: socialization,
externalization, combination and internalization are
performed systematically in stages of knowledge
flow for implementing identified information assets.
The socialization process is regarding individual
and collective experiences sharing to create new
tacit knowledge. In the organizational, it occurs
through training, customer interactions, informal
sessions, brainstorms. So, we are interested in
identify the need to intensify the integration among
actors involved and to socialize knowledge and
successful practices.
The externalization process consists of
knowledge creation through new and explicit models
from tacit knowledge. We are interested to check if
tacit knowledge is been explicit and registered and if
knowledge is mapped and organized to be used.
In the combination process, which occurs
through the exchange and combination of different
sets of explicit knowledge, and that in the
Organization is acquired especially by means of
documents, meetings or computer network, it has
been found that the absence of a knowledge database
centralized, integrated and consolidated causes
avoidance of explicit knowledge thus making it hard
the activities related to analysis, reporting and
consultation documents. In order to have quality and
efficiency in the activities performance, it is
necessary to ensure that the skills are available for
the application, reuse and creation.
The internalization process occurs in conversion
of explicit knowledge into tacit, by "learning by
doing". So we are interested to check if information
from prior years is used as support for the
development of new reports and documents and if
knowledge is internalized and therefore used for the
construction of new explicit knowledge.
In order to accomplish the prognosis of methods,
techniques and tools for Knowledge Management,
each category used in KM diagnosis is then analyzed
and some improvements recommendations are
DiagnosisandPrognosisofKnowledgeManagementbasedonk-Workflow,onConversionandKnowledgeFlow-The
CaseoftheNationalLandTransportAgencyinBrazil
417

proposed in order to eliminate the gaps identified in
knowledge flow and knowledge conversion
processes.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The Iterative Method proved to be effective in its
application, allowing to identify, collect, map,
analyze and represent tacit and explicit knowledge,
skills and professionals mobilized and involved in
the construction of information assets, besides
analyzing the knowledge flow in all stages.
Mapping will facilitate the activity of allocation,
reallocation and professional training according to
the activity to be performed, besides facilitating the
location of key people, those that have the most
relevant knowledge on a particular subject.
Critical success factors identified and their
enablers in KM may assist managers in their
decision making process in different situations, such
as: process improvement using techniques and tools
of knowledge management; identification of
knowledge gaps in professional activities; perception
of opportunities for new training courses and
competences building; identification of gaps
between individual's professional knowledge and
skills needed to perform activities.
The method developed can be applied to other
domains of different areas, constituting a knowledge
basis for Knowledge Management.
KM models developed for the Agency based on
its information assets are implementable in the short
or medium term, through the use of best practices
and tools (intermediate results) or from the
application of KM architecture still under
construction (final results).
From knowledge basis constructed throughout
modeling process it is possible to make more
descriptive analysis such as: working groups
associated with one or several information assets and
vice versa; working groups associated with different
activities of an information asset, correlations among
activities/skills/abilities of one or more working
groups and vice versa. The managers have at their
disposal an incremental basis of knowledge, unique
to the Agency, which enable different analysis
depending on the need and the decision to be made.
With mapping and modeling built it will be
possible to structure the KM architecture of the
Agency and define proper methods, techniques,
technologies and tools for their effective knowledge
management, allowing it to fulfill its mission more
effectively.
REFERENCES
Authier, M., Lévy, P., 1992. Les arbres de connaissances.
Paris: La Découverte.
Bastos, C.A.M.; Rezende, L; Caldas, M.F.; Garcia, A;
Mecena Filho, S.; Sanchez, M.L.D.; Castro Junior, J.;
Burmann, C.R., 2011. Building up a model for
management information and knowledge: the case-
study for a Brazilian regulatory agency. In:
Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on
Software Knowledge - SKY / IC3K. Paris.
Fleury, A.C.C., Fleury M.T., 2004. Estratégias
empresariais e formação de competências. 3 ed. São
Paulo: Atlas.
Ikeda, T., Okumura A., and Muraki, K., 1998. Information
Classification and Navigation Based on 5W1H of the
Target Information, Proceedings of the 17th
International Conference on Computational
Linguistics - Volume I, Montreal, Quebec, Canada. pp.
571-577.
Nonaka, L.; Takeuchi, H., 2009. Gestão do Conhecimento.
1ed. Porto Alegre: Bookman.
Nonaka, L.; Takeuchi, H., 1995. The knowledge creating
company: how Japanese companies create the
dynamics of innovation. New York: Oxford University
Press, pp. 284, ISBN 978-0-19-509269-1.
Rezende, L., Lobão, M. A., Burmann, C. R. N., Junior, J.
L. P. C., Merino, L. A., Rocha, S. A. and Bastos, C. A.
M. (2012). Modelling and Knowledge Management in
the Field of Road Infrastructure Operation and
Regulation - Study on the Methods Application in an
Organizational Unit. KMIS 2012: 265-268. Barcelona,
Spain.
Rezende, Luiziana, 2011. Iterative method for the
mapping of knowledge and competencies in
corporative scenarios. Technical Report of Post-
Doctoral Internship. Rio de Janeiro: Departamento de
Engenharia de Produção/GtecCom/UFF.
Rezende, Luiziana, 2007. Iterative method for the analysis
of competences required for the egress in computer
sciences – A case study in Rio de Janeiro, PhD
Thesis. Rio de Janeiro: COPPE/UFRJ.
Treebolic., 2007. Available at url
http://treebolic.sourceforge.net/. Acessed on
08/25/2012. WALTERS, David; RAINBIRD, Mark.
The Value Chain. Palgrave Macmillan, 2007.
Zarifian, P., 2005. O modelo da competência: trajetória
histórica, desafios atuais e propostas. Rio de Janeiro:
SENAC.
KMIS2013-InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeManagementandInformationSharing
418
