
Mathematical Modelling of Smooth and Precise Adaptive Train
Braking System
A. Potapov, M. Gorobetz and A. Levchenkov
Institute of Industrial Electronics and Electrical Engineering, Riga Technical University, Kalku Street 1, Riga, Latvia
Keywords: Adaptive Systems, Intelligent Control, Railway Transport Braking Systems, Modelling.
Abstract: This position paper provides a new insight into the smooth and precise adaptive railway transport braking
system design. The first phase of the development is described and includes a development of a necessary
mathematical and computer model. Components of new adaptive braking system and their interactions are
defined. Mathematical model contains equations that describe the movement of the train and the pneumatics
braking system of the train, as well as offering new features of the developed system, which will adaptively
adjust the service brake modes and will perform real-time system diagnostics without any human
interaction. The computer model and simulation results are described in this position paper.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays the industry of railway transport is
developing new solutions for increasing a capacity
and speed of the railway. These actions are followed
by various problems that connected with railway
transport movement safety, which has to be at least
at the same or higher level than before (Wang, Wang
et al., 2012).
Authors are solving the safety problem and
propose to develop new smooth and precise adaptive
braking system of the rolling stock. This new system
is aimed to reduce various deficiencies of existing
railway safety systems. The purpose of the system is
an automatic braking of the rolling stock using
service braking and previously developed safety
functions (Gorobecs, Greivulis et al., 2009), which
allow to stop the train before another railway
vehicle, before a level-crossing where a road vehicle
is stuck or before the signal with restrictive aspect.
Usage of emergency braking has negative effect and
not recommended if regular service braking might
be performed. Therefore, the new proposed system
is based on authors’ previously developed railway
safety systems and may increase safety level of the
train and the railway system as a whole.
After real field test experiments (Potapovs,
Gorobetz et al., 2012) authors concluded that
efficiency of the previously developed railway
safety system is not sufficient, because the system
does not adapt to various working environment
conditions and may work imprecise if the rolling
stock contains various wagons.
Therefore, the research and development of new
smooth and precise adaptive train braking system,
which is now patented (Potapovs, Levchenkov et al.,
2013), is going on. This process contains some
development stages and the first one is described in
this paper.
2 PURPOSE AND TASKS
Main goal of the research is to develop a new
smooth and precise train braking control system
based on adaptive algorithms and neural networks.
Main tasks for the goal achievement are
following:
1) Development of the mathematical model and the
computer model of train movement and work of
the pneumatics braking system;
2) Development of the adaptive control algorithm
using neural networks, for the new braking
control system, based on the developed
mathematical un computer models;
3) Simulation of self-organization of the adaptive
braking control system using developed
algorithms;
4) Development of prototypes of the new adaptive
braking control system, testing in laboratory
conditions and performance of field tests.
204
Potapov A., Gorobetz M. and Levchenkov A..
Mathematical Modelling of Smooth and Precise Adaptive Train Braking System.
DOI: 10.5220/0004592602040209
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH-2013),
pages 204-209
ISBN: 978-989-8565-69-3
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

In this paper the mathematical model and the
computer model of train movement and pneumatic
braking system is described.
3 PRINCIPLES AND NOVELTY
OF NEW SMOOTH AND
PRECISE ADAPTIVE TRAIN
BRAKING SYSTEM
Main functions of the new smooth and precise
adaptive train braking system are following:
Automatic train stopping in a target point using
regular service braking modes;
Definition of the target point according to
existing routing data, such as a stop at the
defined platform point, or to safety reasons, such
as a risk of collision or a risk of trespassing the
restrictive signal aspect;
Real-time diagnostics of train pneumatic braking
system during the operation and self-learning for
precise braking;
Sending alarms to the driver about possible
failures of a train pneumatic braking system.
Advantages of the new smooth and precise adaptive
train braking system using are following:
The system does not disturb work of existing
pneumatics braking system;
The system does not disturb a train driver to
perform his duties and no manual input is needed
from the driver;
The system does not need the installation of
additional embedded sensors, because it would
cause the reconfiguration and recertification
process.
Main components of the braking system of the train
and the adaptive braking control system are divided
in four groups.
The first group contains pneumatics elements of
the existing braking system (Fig. 1. shown in blue):
Compressor (K);
Main reservoirs (GR);
Driver’s control valve (MK);
Electropneumatic valve (EPV);
Feeding main line (BM);
Braking main line (BrM);
Compressed air relay (GSR);
Air splitters (GS);
Braking cylinders (BC).
The second group contains proposed mechanical
elements of new braking control system (Fig. 1.
shown in yellow):
New connections of braking main line;
High-pressure tubes and flexible connectors;
Electropneumatic valves (V1 and V2);
Analogue electrical manometer (AMN);
Protective valve (DrV) to control pressure at
maximum allowed level;
Emergency valves (AV1 and AV2) used in
emergency situation to shunt specific parts of
braking main line.
The third group has electronic components and
electric extension modules: (Fig. 1. shown in olive
green):
Programmable logic controller (PLC), which
performs main calculation and control functions;
Input/output modules for devices (IM);
Power supply unit (BB);
Wireless communication module (BSM);
Satellite positioning module (GPM);
Driver interface module (IIM).
From the one side PLC usage in this case needs to
meet requirements of various railway safety
standards such as EN 50126, EN 50128, EN 50129.
From the other side usage of programmable devices
in many years proved its workability in different
fields and safety systems and provides great
possibilities for improvement of the system
functionality.
The fourth group contains software components
of the PLC:
Initialization function;
Satellite global positioning system data
processing function;
Wireless communication function;
PLC input/output control functions;
Adaptive control function based on neural
networks – realizes self-learning of control
system by analysing of the train braking system
and performs control of the system.
Figure 1 provides the principle scheme of the new
smooth and precise adaptive train braking system
integrated in existing braking system.
MathematicalModellingofSmoothandPreciseAdaptiveTrainBrakingSystem
205

Figure 1: Main nodes of new smooth and precise adaptive train braking system.
4 MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF
TRAIN BRAKING SYSTEM
NODES
In the first approximation of train movement and
pneumatics model, the rolling stock is considered as
whole moving object without wagon details. This
step allows removing uncertainties of various wagon
types, cargo load and different braking modes of
individual wagons. But in spite of such
simplification, increasing of the longitudinal loads of
train and other factors influencing the activity of
brake system should be taken in account.
Following equations are proposed to use for
simplified train movement mathematical model.
Taking in account that the train is moving, the train
deceleration a
br
may be calculated as following:
m
FF
a
frictbrak
br
,
(1)
where, Fbrak – braking force of train pneumatic
braking system, N;
Ffrict – train friction force, N;
m – mass of whole train, kg.
From the literature (Shuleshenko, 1985) we know
that other forces influences movement of the train,
but as these forces are variable, uncontrollable and
minor, it is proposed to use the most important of
them.
Train friction force F
frict
is calculated using train
movement specific resistance
0
:
mF
frict
0
(2)
where m – mass of the train, t.
The specific resistance of train movement
0
defined by equation:
"
00
x
.
(3)
The specific resistance of the locomotive
x
defined by the formula:
2
00035,0009,04,2 VV
x
.
(4)
But the specific resistance of wagons
"
0
calculated
by formula:
0
2
"
0
0025,01,08
7,0
q
VV
,
(5)
where V – speed of train, km/h;
0
q
- axle load.
Formulas defined for long-welded track and taking
SIMULTECH2013-3rdInternationalConferenceonSimulationandModelingMethodologies,Technologiesand
Applications
206

in account that rolling stock contains four-axle cargo
wagons with axle load more than 6 t (during the
simulation it is possible to use another equations,
describing another track type or wagons).
The braking force of the rolling stock Fbrak may
be defined by known train specific braking force
T
B
:
Tbrak
BF
.
(6)
Specific braking force
T
B
is calculated using the
equation:
calccalcT
nbaKB
1000
,
(7)
where
calc
K
- rated pressure force to one slipper;
a – number of slippers at one axle;
b – axle number in a wagon;
n – number of wagons in a rolling stock;
calc
- rated friction coefficient of a slipper.
Braking coefficient
apr
shows the proportion of
total slippers pressure force to the mass of the rolling
stock. A lot of parameters are needed to calculate
calc
(Shuleshenko, 1985) and it is impossible to get
the values of these parameters without additional
data input. Therefore, the value of these parameters
should be defined as minimally allowed value before
adaptive self-learning.
By the model
calc
is calculated by equation:
1005
100
27,0
V
V
calc
.
(8)
As the pneumatic braking system of the rolling stock
is going through the whole length of rolling stock is
has working inertia, rated pressure force
calc
K
can
not be set as the same maximum value at the
moment when the braking mode is activated.
According to the distribution (Vencevich, 2006)
approximation of pressure force along the rolling
stock the equation for a percentage of full
%calc
K
is
got:
%calc
K
=
3028,2855,1
2
calccalc
KK
.
(9)
Similar process happens when releasing the
brakes after full service braking. The value of
calc
K
reduces from its maximum to zero in 35-38 s in the
first wagons of the train and in 55-60 s in the last
wagons of the train.
Minimal allowed value of coefficient
calc
in
cargo train is 0,33 (Vencevich, 2006). But it is
necessary to calculate the precise value of this
parameter to perform precise and smooth braking
control.
Therefore, the main task for adaptive system and
neural network is a detection of the braking
coefficient
apr
. It must be calculated automatically
during the train movement.
For this case, authors propose to input a new
parameter in the model – coefficient of train braking
system efficiency
ef
BS
.
This coefficient is defined by following
functional dependency:
),;;;(
stabbrakef
ttiVPfBS
,
(10)
where,
P
- changing of the air pressure in the
braking main realizing one braking step
V
– changing of the railway transport speed
realizing one braking step;
i – slope of the track profile, %;
tstab – time of stabilisation of braking system
pressure;
tbrak – braking time, s.
A parameter
P
defines pressure changes in braking
main line from initial value to stabilized value after
braking starting.
constPPP
01
,
(11)
where P1 – pressure in a braking main line after the
braking step;
P0 – pressure in a braking main line before
braking.
Stabilization time tstab depends on a selected
braking mode and various factors such as leakage in
braking system, length of the rolling stock, outdoor
temperature etc.
For calculation of
V
parameter initial speed
V0 and speed after braking step V1,
when
constP
.
01
VVV
.
(12)
MathematicalModellingofSmoothandPreciseAdaptiveTrainBrakingSystem
207
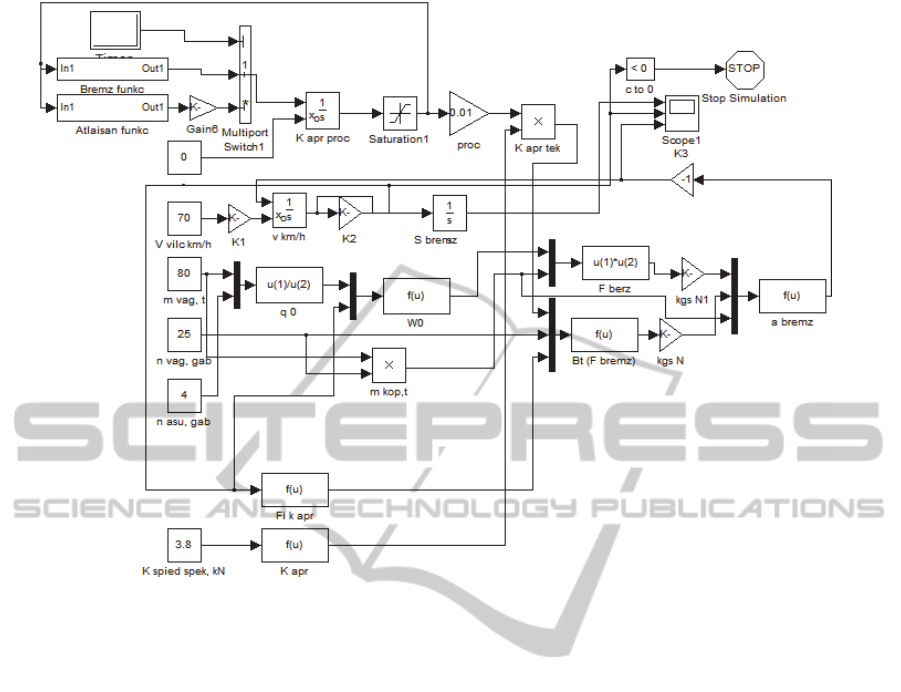
Figure 2: Computer model of train braking system behaviour.
Slope may be received from the database in PLC
memory.
The theoretical braking distance using service
braking may be calculated after the calculation of
the coefficient of train braking system efficiency.
),;;( iVTBSfS
trainoutefbr
,
(13)
where T
our
– outdoor temperature, which has
influence on cohesion between wheels and rails,
C
;
V
train
– train movement speed, km/h.
Using S
br
it is possible to calculate point at which
automatic service braking must be started to stop the
train in the target point.
Outputs of adaptive algorithm and neural
network should be time moments when braking and
release of braking is necessary. Calculation of
theoretical curves and obtained data about the
pneumatic braking system during the train
movement will be the base of calculation. The
following constraints must be taken in account:
Maximum braking time;
Planned time for P
1
achievement (braking and
releasing brakes);
Train speed V
train
;
Train physical parameters (longitudinal loads in
the rolling stock);
Outdoor temperature influencing cohesion and
pressure change time.
5 COMPUTER MODEL OF
TRAIN BRAKING
The first approximation of the computer model of
train braking system behaviour is developed in
Matlab/Simulink environment and shown in Figure
2. The computer model allows setting up following
initial parameters:
Train speed V, km/h;
Mass of one wagon, t;
Number of wagons, n;
Pressure force of braking slippers
K
, N/t;
Function of
%calc
K increasing and decreasing
according to the train length.
The model contains realization of two service
braking modes: braking mode and release mode. For
these modes function „Bremz funkc” un „Atlasan
SIMULTECH2013-3rdInternationalConferenceonSimulationandModelingMethodologies,Technologiesand
Applications
208
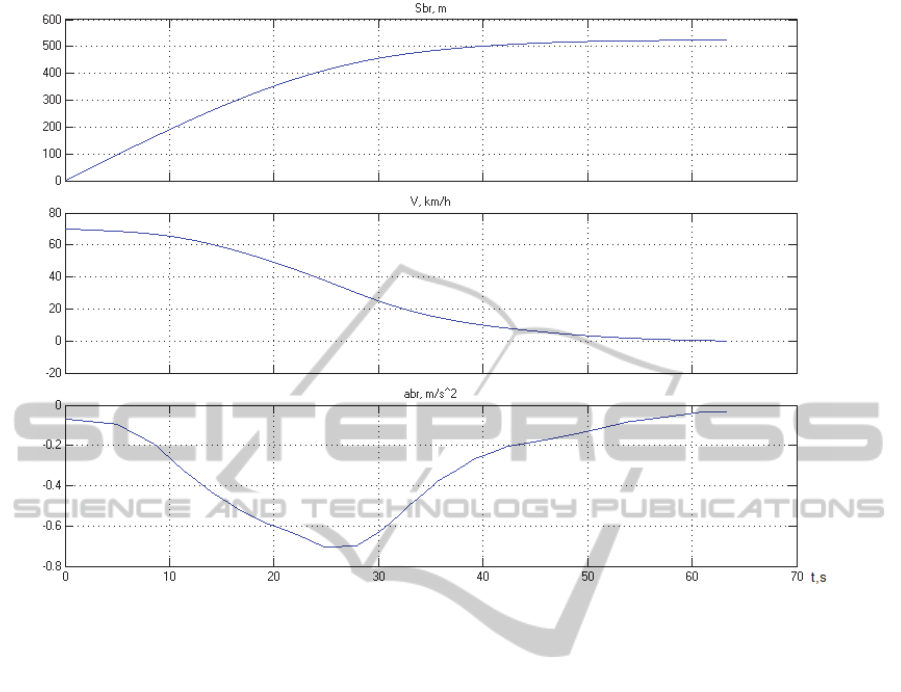
Figure 3: Computer model simulation results.
funkc” are developed.
Graphical simulation results are representing the
case of braking the rolling stock with a mass 2000 t
from initial speed 70 km/h and release brakes at 25th
second. The total length of the braking way is 523 m
and braking time 63 seconds.
6 RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
Following results are achieved:
The mathematical model is created for train
service braking modes;
The computer model is created for simulation of
train behaviour when breaking and releasing
brakes;
Graphical simulation results obtained.
Developed mathematical model of smooth and
precise adaptive braking control in the first
approximation allows creating the computer model,
which is precise enough to get reliable simulation
results. Reliability of obtained results has been
checked by theoretically and practically obtained
data described in the literature.
Further stages of smooth and precise adaptive
train braking control system development will be
presented in next publications.
REFERENCES
Wang, J. F., Wang, H. H., & Lin, Z. (2012). Research on a
new type of train control system used at 350km/h. WIT
Transactions on the Built Environment, 127, 51-60.
Gorobecs M., Greivulis J., Ļevčenkovs A., Balckars P.,
Ribickis L., 2009. Train Emergency Braking Device.
Patent Nr. LV13978.
Potapovs A., Gorobetz M., Levchenkov A., 2012.
Intelligent electronic embedded systems for the
protection of railway transport from accidents,
ITELMS-2012.
Potapovs A., Levchenkov A., Gorobetz M., Holodov S.,
Birjulin I., 2013, Train smooth and precise automatic
braking device. Patent Application Nr. P-13-43.
Shuleshenko F., 1985. Rules of traction calculations for
train operation. Moscow “Transport”.
Vencevich L., 2006. Train movement safety devices and
decoding of their information data. Moscow
“Marshrut”.
MathematicalModellingofSmoothandPreciseAdaptiveTrainBrakingSystem
209
