
Creating New Teaching Techniques with ITCs following
the Montessori Method for Uneducable Young Students
Habib M. Fardoun
1
, Abdullah AL-Malaise AL-Ghamdi
1
and Antonio Paules Cipres
2
1
King Abdulaziz University, Faculty of Computing and Information Technology,
Information Systems Department, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
2
University of Castilla-La Mancha, Polytechnic School,
Information Systems Department, 02071 Albacete, Spain
Abstract. Nowadays, it is important to help students’ critical and independent
thinking skills development by promoting the capacity to resolve problems on
an individual or group basis. Cognitive development is the term used by experts
to describe the learning process, mind expansion and the capacity to resolve
problems happening inside students’ minds when working on their own or with-
in groups while interacting with their peers. In this paper we present the design
and development of a system for the students to work at schools as well as at
home following the “Montessori” method using technologically enhanced
learning sensory. We have implemented the Montessori suggested patters by
designing and developing a system, also having the capacity to monitor and
measure students’ evaluation and actual grading. The proposition is directed
towards the first cycle of primary education, where basic skills are acquired.
1 Introduction
Nowadays a great number of educational games for students exist aiming at develop-
ing their personal skills such as [1]. The students can play these games individually as
they work through the action and reaction process even for students less than 6 years
old. These educational applications do exist for digital tablets. In Spain for example,
there is a wide use of the educational software Pipo [2]. Games can complement a
more conventional master class (for example a traditional method) to enhance a stu-
dent’s associated cognitive levels. For example, we may consider the traditional edu-
cative Montessori Method developed by María Montessori (1850-1952) in 1912. At
that time, the schools consisted of one teacher who had to work with a great number
of students from different educational levels simultaneously, and the uneducable
students had to be sent to special centers those days [3]. While working on one of
these schools, the author observed that the uneducable students of the specific institu-
tion were playing with the crumbs of food, as there were no other objects in the room.
“She saw that they didn’t eat them but they manipulated them and she realize that
they need objects to manipulate. This is because the human being has the necessity of
activity, of reality, of developing their intelligence and personality”[4].
M. Fardoun H., AL-Malaise AL-Ghamdi A. and Paules Cipres A..
Creating New Teaching Techniques with ITCs following the Montessori Method for Uneducable Young Students .
DOI: 10.5220/0004607401090114
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Interaction Design in Educational Environments (IDEE-2013), pages 109-114
ISBN: 978-989-8565-65-5
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

So we may find a situation that can facilitate the development of educational pat-
terns for the specific didactical method. During our research, we did not find educa-
tional platforms or software applications for home use, allowing teachers to track
successful methodologies that improve uneducable students’ learning process. How-
ever, we have found a lot of games focused on the action and reaction stimuli engag-
ing the students’ senses and attention while playing. Surprisingly, babies and very
young students seem to have been programmed to learn to play in such environments
(regardless if they tend to be educated or not). In addition, actions that adults see like
gaming, in reality, they can work to stimulate the uneducable students’ learning pro-
cess. There are also several easy to use measurements we may consider to utilize for
these experiences to become more efficient in order to improve students’ cognitive
development.
In this paper we present a system’s design and development that allows teachers
and parents to perform and control educational work using didactics methods at
school as well as at home. In addition, the validation of this system with such peda-
gogical features has been performed using current technological devices and systems
everyone uses.
2 System Features and Attributes
The proposed methodology anchored in the Montessori Method was developed by
taking into account the cognitive structures and the social development; the main
features are [3]:
Teachers must perform their work without obstacles inside the classrooms. The
students are active participants in the learning process.
The environment and the Montessori Method promote the internal individual dis-
cipline.
Personal learning and group learning are adapted to the individual student’s learn-
ing style.
Students of different ages are grouped together.
Students are motivated to teach, collaborate and help each other.
The students choose their own work according to their individual interest and
skills, as to formulate their own concepts based on autodidact material.
Each student chooses his/her own step in the learning process and path as well as
the learning speed.
The student discovers his own errors through the material feedback.
Repeating one specific learning activity leading the student at receiving a success-
ful positive feedback and feeling reinforces the learning process.
Each student can work where s/he feels comfortable, where s/he moves freely and
talks secretly without disturbing his/her partners. Group work is optional.
The educational patterns that can be determined for these ages [4], emphasize
basic values in collaborative work and the necessity for the students to interact and
work together based on the use via action and reaction of their senses and stimuli
within the environment, accessed from the school as well as from home interacting
110

with each other using a platform. Therefore, we present a set of selected patterns for
these educational levels following the features of the aforementioned methodology, in
order to cover the uneducable students’ new needs. In addition, we accompany each
pattern with the device to help each student’s performance. These attributes function
as behavioral patterns and are the following:
Motivation: This pattern performs motivation-stimulating activities for the unedu-
cable student; it activates students’ senses, their individual integration and mobility
[5] [6]. To carry out this pattern, there is a need for audio and video systems to im-
prove student’s interaction with his/her environment. This pattern must also in-
clude sensory-based actions so to stimulate reactions; while using ICTs, those
senses are: Sight (color, size, position and movement), Hearing, Touch, Smell and
Taste.
Collaboration: This pattern compliments motivation necessities towards collabo-
ration among the students and their peers, so they can learn to help each other.
Selection: The uneducable student chooses his/her own work according to the
individualized purposes and skills.
Temporization: the student establishes studying times inside the selected projects
and structures in his/her own time by performing this activity.
Feedback: The student learns by trial and error. This pattern controls the mistakes
performed by the student during the learning process. When the system detects an
error, it uses this information to plan activities to reinforce student’s learning,
based on the specific error.
Repetition: The student repeats the activity to reach a successful action and there-
fore feeling.
Daily activities: This model organizes activities related to the self- and environ-
mental care. These social skills are needed inside the system; thus, the student au-
tomatically acquires the necessary basic competences.
The system was developed using HTML5, which ensures its portability among the
different operative systems, and guarantees its maintenance.
3 Personal Assistant Design and Development
The uneducable student of an infantile course must perform a set of exercises aiding
at developing sensorial learning and peer-to-peer collaboration and learning. To sup-
port this, we have planned a scenario where the students need to work collaboratively
taking into account the developed patterns anchored in the Montessori Method. When
the student enters the systems, s/he finds a graphic user interface, which is friendly,
comfortable and attractive; it is also enhanced with a “Personal Assistant” to support
the student with his/her individual interaction with the system. This is a virtual char-
acter with capacities depending on the specific device connected to the system allow-
ing the student to easily interact, as in Figure 1.
Once the student initiates the application, the system selects the programmed ac-
tivities controlled by the teacher or the parents. After that, the student selects the
111
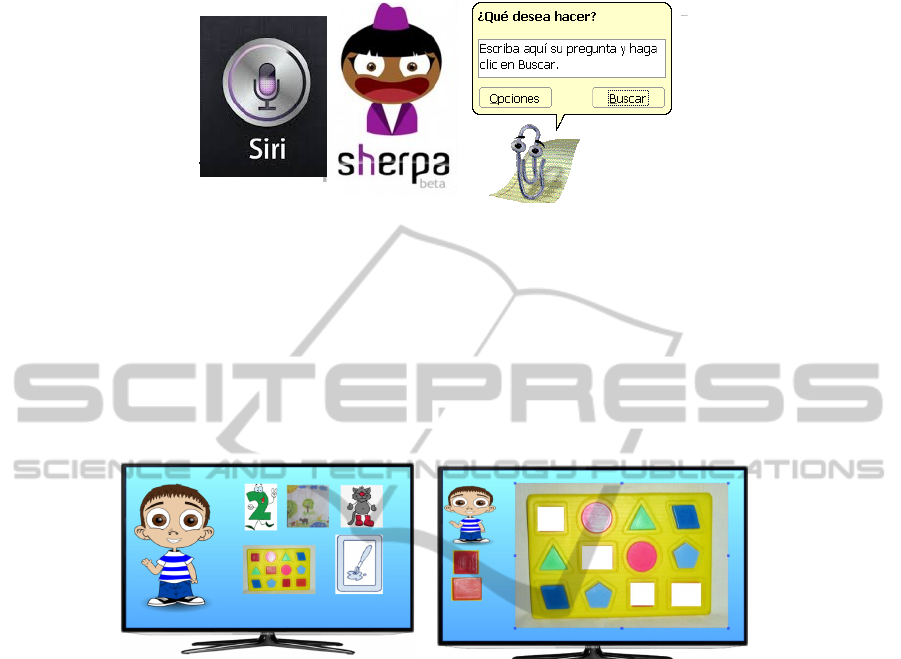
Fig. 1. Examples of Personal Assistants.
activities from a specific category anchored in the official curriculum for infantile
education [7]. The process is straightforward and easy to handle; the student only
clicks on the corresponding icon and then on the virtual character to start performing
the activity. Instantly, the virtual character starts interacting with the student by
providing personalized activities step by step performed in a way so to complete the
targets of the learning activity. As an example, this student decides to perform the
activity related to geometric forms on his own as personal work as well as interacting
with his peers as collaborative work, as in Figure 2.
Fig. 2. Educative game selection.
The collaborative work is conducted by the interchange of “tokens” that appears
on the screen on an individual and group basis so to fill in all the gaps in the table
presented on the screen. If the student does not know which token to send to which
one of his peers, the virtual character helps him with this task, as in Figure 3. This
performed exercise takes into consideration the satisfactory presentation and business
logics for user interface design. This is completely oriented to reach and evaluate the
goals targeted for each of the previous presented attributes.
The design of the educational game can be personalized according to the age of
the student, and his requirements. The tutor (teachers and parents) has to select an
activity from a set of games available to them according to the student needs, to en-
sure by this the correct application of the educational games.
3 Conclusions and Future Work
During our research about educative applications and systems, we discovered great
112

Fig. 3. Educative game selection.
discrepancies regarding educative methodologies that could fit the uneducable stu-
dents’ needs. Based on this vision, we conducted extensive research for appropriate
methodologies to fit these needs; apparently, we found that the Montessori method,
which is related to sensorial learning and is widely recommended by teachers at
schools to fit our purpose. As a result, we started searching for patterns that cover the
specific actions these students need to perform and their relation with technological
hardware devices. For now we want to focus on students with special needs of just
one type: Children with problematic and not friendly behavior with other children
similar to their ages.
During the system design and development, we have noticed the simplicity related
to user interface design and development specifically for these ages, as the students
press over objects with their finger within a virtualized solution developed using
HTML5. Currently 7 students in the CEP Juan XXIII educational centre of Huesca
are using this system, and until now the intervention was successful and widely ac-
cepted by the teachers and parents. The evaluation of this test will be presented in our
future research work.
For the system implementation we are studying to apply Model-Based User Inter-
face development environment to give the system the possibility to be independent to
work over any type of platform and using any type of interactive device.
References
1. Aleven, Vincent, et al. "Toward a framework for the analysis and design of educational
games." Digital Game and Intelligent Toy Enhanced Learning (DIGITEL), 2010 Third
IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2010.
2. Asqui, G., & Matilde, L. (2012). Incidencia Del Software Educativo Pipo Multimedia En
La Enseñanza Aprendizaje De La División De Los Numeros Naturales De Los Estudiantes
113

Del Cuarto Año Educación Básica De La Escuela Benjamín Araujo Durante El Periodo
2009-2010 (Doctoral Dissertation).
3. Montessori, M. (1912). The montessori method. Frederick A. Stokes Co.
4. Romero Lopez, S.; Fardoun, H. M.; Alghazzawi, D. M., "Coaching for students: Parents
tutoring children as part of their educational process," Computer Science and Information
Systems (FedCSIS), 2012 Federated Conference on , vol., no., pp.863,870, 9-12 Sept. 2012
5. Herrero Jiménez, A. B. (2000). Intervención psicomotriz en el Primer Ciclo de Educación
Infantil. Revista interuniversitaria de formación del profesorado, (37), 87-102.
6. Mérida, R. (2002). Una nueva forma de trabajar en educación infantil: los mapas pre con-
ceptuales A new approach to preschool education: Conceptual maps. Cultura y Educación,
14(1), 99-123.
7. Cipres, A. P.; Fardoun, H. M.; Mashat, A., "Cataloging teaching units: Resources, evalua-
tion and collaboration," Computer Science and Information Systems (FedCSIS), 2012 Fed-
erated Conference on, vol., no., pp.825,830, 9-12 Sept. 2012
114
