
A Model Driven Approach for Automatically Improving
OLAP Legacy Applications with Security
Carlos Blanco
1
, Eduardo Fernández-Medina
2
and Juan Trujillo
3
1
GSyA Research Group, Dep. of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science,
Facultad de Ciencias, Univeristy of Cantabria, Av. de los Castros s/n. 39071, Santander, Spain
2
GSyA Research Group – Institute of Information Technologies and Systems,
Dep. of Information Technologies and Systems, Escuela Superior de Informática,
University of Castilla-La Mancha, Paseo de la Universidad, 4. 13071 Ciudad Real, Spain
3
Lucentia Research Group, Dep. of Information Languages and Systems,
Facultad de Informática, University of Alicante, San Vicente s/n. 03690, Alicante, Spain
Abstract. The majority of the organizations store its historical business
information in Data Warehouses (DW) which are queried to make strategic
decisions by using On-Line Analytical Processing (OLAP) tools. This
information has to be correctly assured for unauthorized accesses, but
nevertheless there are a great amount of legacy OLAP applications that have
been developed without considering security aspects or these have been
incorporated once the system was implemented. This work defines a reverse
engineering process that allows us to obtain the conceptual model
corresponding to a legacy OLAP application, and also analyses and represents
the security aspects that could have established. This process has been aligned
with a model driven architecture for developing secure OLAP applications by
defining the transformations needed to automatically apply it. Once the
conceptual model has been extracted, it can be easily modified and improved
with security, and automatically transformed to generate the new
implementation.
1 Introduction
The information stored in Data Warehouses (DWs) is organized by following a
multidimensional model which improves its further analysis, usually carried out by
using on-line analytical processing (OLAP) tools. In this way, the information is
organized in facts and measures which can be analyzed by different subjects called
dimensions and in different detail levels.
This information has a strategic value for the organization for making strategic
decisions and furthermore, it is use to include private data of individuals. It has to be
assured, specially focusing on information confidentiality since final users solely will
query DW’s information [19]; [22];
[20]. The security aspects have been traditionally
added to the final solution once the system has been built. Nevertheless, in order to
improve the quality and security of any information system, it is needed to identify
and incorporate security constraints from the beginning and consider them in all
stages of the development process [9]; [17].
Blanco C., Fernández-Medina E. and Trujillo J..
A Model Driven Approach for Automatically Improving OLAP Legacy Applications with Security.
DOI: 10.5220/0004609300760085
In Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Security in Information Systems (WOSIS-2013), pages 76-85
ISBN: 978-989-8565-64-8
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

On the other hand, DWs and OLAP applications can be developed by following a
Model Driven approach by using different models in the development process,
separating the system functionality from details of specific technologies and
implementations. This approach allows us to define transformations which are able to
automatically generate the intermediate models and the final implementation, saving
then on development costs and efforts. The different development stages of a DW be
aligned with the different models of a Model Driven Architecture [16]: business
models for system’s requirements (Computational Independent Model, CIM);
conceptual models (Platform Independent Model, PIM); and logical models focused
on a concrete technology (Platform Specific Model, PSM).
There are contributions on the development of secure information systems which
although they are not focused on DWs and OLAP propose interesting ideas. For
instance, UMLSec [14]; [15] which uses UML to define and evaluate security
specifications using formal semantics, or Model Driven Security (MDS) [2]; [3]
which uses the MDA approach to include security properties in high-level system
models and to automatically generate secure system architectures. On the other hand,
it can be found other proposals that take into account the specific structural and
security aspects of DWs. In this area, solely Priebe and Pernul propose a complete
methodology for develop secure DWs [19], but neither establishes the connection
between levels in order to allow automatic transformations nor deals with reverse
engineering.
Reverse engineering is very useful in the development of information systems,
since it allows us to analyze legacy systems and to obtain their models at a higher
abstraction level. Thus, to apply reverse engineering provides us a mechanism for re-
documentation, model migration, restructuring, maintenance or improvement,
tentative requirements, integration, conversion of legacy data. The model obtained by
applying a reverse engineering process are easier to understand than the
implementation of the legacy system and can be used into a modernization process in
which we can modify systems’ characteristics into the models whereas modifying the
implementation. For instance, new aspects not considered into the initial
development, such as security, could be added [18]; [6].
Although data reverse engineering field has been widely studied in literature [1];
[4];[7]; [13], there is little research on reengineering of DWs and OLAP applications
and there are no approaches that consider security and apply a model driven approach
to automate the process.
This paper defines a reverse engineering process for legacy OLAP applications that
considers both structural and security aspects. This proposal has been included in a
previously defined architecture for developing secure DWs and OLAP applications
[10]. Then, the contribution of this paper is the definition of this reverse engineering
process that is composed of two stages: the generation of logical models from legacy
OLAP implementations (considering SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) as the
source OLAP tool); and the generation of the conceptual model corresponding to the
logical model. In this way, legacy OLAP applications can be re-documented and
improved with security by modifying the conceptual model obtained. Then, the
improved system can be automatically re-implemented or migrated to other platforms
by using our model driven architecture. As a contribution of this paper the
transformations needed for automatically obtain conceptual models from legacy
OLAP applications have been implemented.
77
This paper is organized as follows: Section 2 will briefly describe our previously
defined architecture for developing secure DWs and OLAP applications; Section 3
will present the reverse engineering process proposed in this paper; Section 4 will
show an application example to validate our proposal; and Section 5 will finally
present our conclusions and future work.
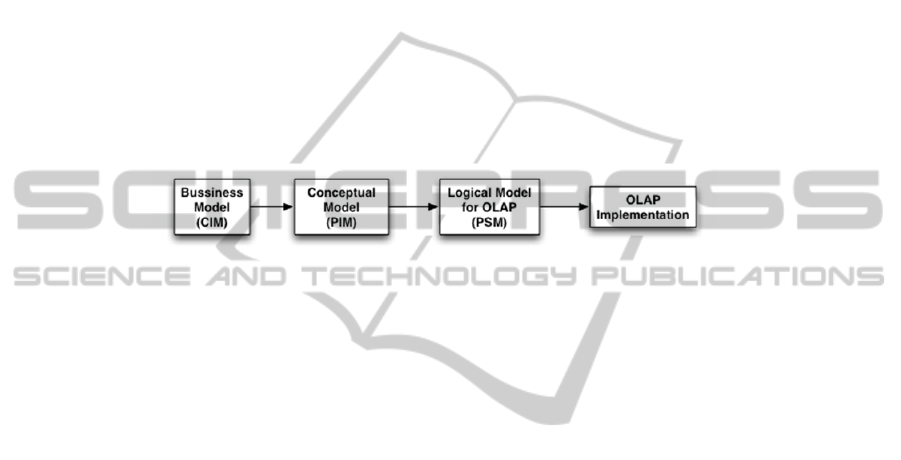
2 Our Model Driven Architecture for Secure OLAP Applications
This section briefly describes the different layers of our architecture for developing
secure DWs and OLAP applications. This architecture has been aligned with an MDA
architecture [10] providing security models at different abstraction levels (CIM, PIM,
PSM) and automatic transformations between models (Figure 1) We have defined in
previous works security models for each development stage of the secure DW and
OLAP application.
Fig. 1. Model Driven Architecture for Secure OLAP applications.
For the requirement stage (business level (CIM)) a UML profile allows us to define
security requirements associated to the DW. This profile has been [21] based on the i*
framework [23] Then, for the conceptual modeling stage (PIM), another UML profile
called SECDW [12] allows us to achieve the multidimensional modeling of the
structural aspects of the DW (facts, dimensions, bases, hierarchies, attributes, etc.)
within its security constraints defined by using an Access Control and Audit (ACA)
model focused on DW confidentiality [11].
In order to achieve the multidimensional modeling at the logical level (PSM) a
metamodel called SECMDDW focused on the OLAP technology has been defined
[5]. It extends the Common Warehouse Metamodel [8] to permit the inclusion of
security constraints and incorporates all the details needed for a further
implementation of the system into a OLAP tool.
The development process has been also automated by defining sets of
transformations between models (defining QVT rules) and towards the final secure
implementation of the OLAP application (defining MOFScript rules). In this way we
have consider SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) as the target OLAP tool.
In this paper we complete this architecture by defining the transformations needed
to automate a reverse engineering process. That is, the generation of the logical model
corresponding to a legacy implementation and the transformation from logical to
conceptual models.
3 A Reverse Engineering Process for Legacy OLAP Applications
This section describes the revere engineering process proposed in this paper (Figure
2). This process has been integrated with our MDA architecture for developing secure
78

DWs and OLAP applications (defined in previous works). That is, it uses the models
that have been defined for the different development stages and includes the
transformations needed to obtain the conceptual model corresponding to legacy
OLAP implementation. This process is composed of two stages: (1) the
transformation of the legacy OLAP implementation into a logical model and (2) the
transformation of the logical model into a conceptual model.
Fig. 2. A reverse engineering process for legacy OLAP applications.
3.1 Obtaining Logical Models
Firstly, the legacy OLAP implementation has to be analyzed in order to detect the
structural and security aspects of the OLAP application and generate its
corresponding logical model.
There are a great amount of OLAP platforms such as the solutions identified in
Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for business intelligence and analytics platforms
(www.gartner.com): Microsoft, Oracle, IBM, Microstrategy, Pentaho, Jaspersoft, etc.
In this work, we have considered that the legacy OLAP application has been
implemented into one of the platforms identified in the leaders quadrant, Microsoft
SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS).
The majority of OLAP tools represent the structural and security information as
metainformation stored in XML files: cubes, dimensions, attributes, measures,
hierarchies, roles, security permissions, etc. Nevertheless, each OLAP tool uses its
own syntax and thus has to be specifically processed. In this case, SSAS organizes
OLAP metainformation in three kind of files:
- (i) Cube files: cube, measure groups, related dimensions, classification
hierarchies and security permissions established over the cube or its measures.
- (ii) Dimension files: dimension, attributes, hierarchies, aggregation levels and
security permissions over the dimension or its attributes.
- (iii) Role files, that represent the access control policy by using an RBAC
strategy. These roles are used in the definition of security permissions.
For this stage we have implemented a parser which receives these three kind of XML
files as input, processes them by using XPath expressions and generates its
corresponding logical model according to our logical metamodel. This transformation
also processes the information in order to improve the target logical model, for
instance by grouping information that can be represented in the model together.
3.2 Obtaining Conceptual Models
In a second stage, the logical model previously generated is transformed into a
conceptual model. In order to achieve this goal a set of QVT transformations has been
defined and integrated into our MDA architecture.
79

Logical models are more concrete than conceptual models, for instance, our logical
model is focused on OLAP and manages concepts related with this concrete
technology. On the other hand, conceptual models are richer in expressiveness and
contain information independent of the platform used.
When we define a reverse engineering process, we have to take into account that
the logical model does not includes enough information “independent of the platform”
for rebuild all the aspects of the conceptual model. Then, in some occasions there are
different choices for transforming certain elements and we have to decide the best
one. In order to automate the entire process these special situations have been
analyzed and some heuristics have been implemented inside the transformations.
Figure 3 shows the main elements of the transformation defined, called
SECMDDW2SECDW. It is composed for several QVT relations grouped by its
purpose into relations for roles, cubes and dimensions.
Fig. 3. A reverse engineering process for legacy OLAP applications.
The first group generates the roles needed to represent the security configuration in
the conceptual model. Then, cubes are processed by several relations. A top relation
“Cube2SFact” serves from the remainder auxiliary rules for defining both the
structural and the security aspects related with cubes (generating facts, attributes,
security constraints, etc.).
Finally, dimensions are processed by using a top relation
“Dimension2SDimension” and auxiliary rules for the structural and security aspects
related (generating dimensions, bases, hierarchies, security constraints, etc.).
Next, two relations related with dimensions are described as examples. The first
one, called “Hierarchy2SBase” (shown in Figure 4), is related with structural aspects.
It analyses the classification hierarchies (Hierarchy) associated with each dimension
(ownedHierarchies), and for each one creates in the conceptual model a base class
(SBase) associated with the dimension implied (SDimension). It represents a
classification hierarchy composed of one aggregation level and then, the
“Level2ChilBase” is called in order to add the remainder aggregation levels of the
hierarchy.
80

Fig. 4. Hierarchy2SBase relation.
Fig. 5. DimensionMemberPermission2SConstraint relation.
Another example related with security constraints is shown in Figure 5. The
relation “DimensionMemberPermission2SConstraint” processes security permissions
defined over dimension attributes (MemberPermission) and transforms them into
security information attached to the attribute in the conceptual model. In this case, the
source security information can be transformed into four different security elements
that represent different kinds of security rules. Depending of the information included
in the source element will be better to generate one or other kind of security rule. The
heuristic needed to automatically choose the best target element has been
implemented in the where clause of the relation and depending on the source
characteristics calls the auxiliary relations needed to create the target element.
4 Application Example
This section shows our proposal applied to a legacy OLAP application implemented
into SSAS. The DW used as example is focused on analyzing sales according to
different perspectives (products, dates, customers and stores) and also considers
several security constraints. This example uses three user roles that represent security
levels with different privileges (from higher to lower privileges): secret “SLS”,
confidential “SLC” and undefined “SLU”.
81

Due to space constraints, this example has been conceived to describe how a piece
of the system has been transformed from its implementation to the conceptual model
(the dimension “Product”).
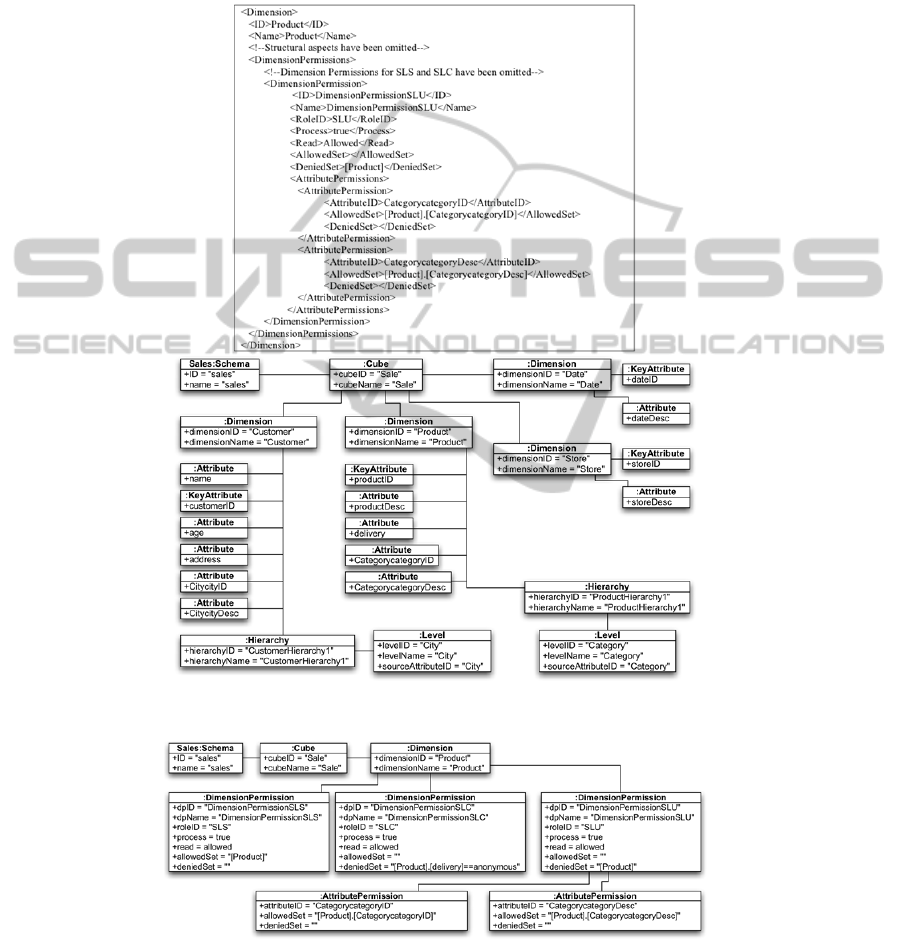
Table 1 shows a piece of code of the legacy OLAP application for the sales DW
used as example. It corresponds with the XML file for the dimension “Product” and
shows some security permissions associated with the dimension “Product” and its
attributes. Each security permission affects to a certain user role defined with the tag
“RoleID”.
Firstly, the parser developed analyses the metainformation described in XML
files and generates the logical model. Figure 6 partially shows the logical model
obtained, focusing on the structural aspects related with dimensions. It can be
observed how a schema, a cube for “Sales” and several dimensions “Customer,
Product, Date and Store” have been defined within their attributes and hierarchies.
The information needed to define these elements has been extracted from a great
number of legacy XML files (one per each cube, dimension or role) and grouped in
the same model.
Figure 7 shows the elements generated in the logical model for the security
information related with “Product” dimension, that was presented in Table 1. Our
parser has generated a dimension permission for each user role. The permission for
the role “SLS” grants access to the entire dimension. Nevertheless, the permission for
the role “SLC” denies access to certain products labeled as anonymous deliveries.
Finally, the security permission for the role “SLU” represents the information of
Table 1. It denies access to the dimension “Product” but grants access to product
information grouped by category (ID and description) by defining permissions over
attributes. The logical models corresponding with the other dimensions have been
omitted.
Next, the QVT transformation defined is applied to the logical model in order to
automatically generate the conceptual model. Figure 8 shows the model obtained. At
a first look, it can be observed how the conceptual model is smaller and easier to
understand and to modify than the logical model, and than the implementation.
Now we can easily understand how our example is composed of a central fact
“Sale” (secure fact class) with measures “amount” and “quantity”, which can be
classified by using different dimensions “Product”, “Store”, “Date” and “Customer”
(secure dimension classes). Furthermore, different aggregation levels have been
defined for “Products” which can be grouped by “Category” and for “Customers”
which can be grouped by “City”.
On the other hand, security constraints have been established over
multidimensional elements. Firstly, the security privileges needed to access fact,
dimension and base classes are defined (as tagged values): a security level of “C” is
required to access “Product”, “Store” and “Customer” dimensions; and a level of “U”
for the fact “Sale”, dimension “Date” and bases “Category” and “City”.
Moreover, several security rules complement the model. The security constraints
defined in Table 1 for the dimension “Product” were represented as several security
permissions in the logical model and finally are represented in the conceptual model
as a security rule attached to the dimension “Product”. This security rule shows all
products to the role “SLS”, hides anonymous deliveries to the role “SLC” and hides
information about all products for the role “SLU”, although role “SLU” can access
this information grouped by category (as indicates the tagged value added to the base
82
“Category”). On the other hand, an authorization rule (AUR) attached to “Customer”
allows each user to access its own customer’s information (although user’s security
privilege was lower than the required one for “Customer”, that is “SLC”).
Table 1. SSAS implementation.
Fig. 6. Logical Model (PSM). Dimensions’ structure.
Fig. 7. Logical Model (PSM). Product dimension’s security rules.
83

Fig. 8. PIM model.
5 Conclusions
The reverse engineering process presented in this paper allows us to automatically
obtain conceptual models from legacy OLAP applications. In order to achieve this
goal we have develop: (i) a parser to analyze the legacy OLAP applications’ metadata
and to generate the corresponding logical model for OLAP; and (ii) we have defined a
set of QVT transformations to obtain conceptual models independent of the platform
from logical models focused on the OLAP technology.
These models are useful for redocument existing applications and improve OLAP
applications modifying the models obtained. Another contribution of our proposal is
that the reverse engineering process also considers security aspects. That is, if the
legacy system has security constraints defined, these are extracted and represented in
the conceptual model. And once the conceptual model has been obtained, it can be
used to incorporate or to modify the security configuration. Finally, the
implementation for the modified conceptual model can be automatically obtained by
using our model driven architecture (by applying the set of transformation rules
defined in previous works for automatically generating secure OLAP code from
conceptual models).
In future work we plan to deal with more OLAP tools (such as Pentaho) and different
technologies (such as NoSQL). In this way, once the conceptual model for a legacy
system has been obtained, we would like to offer different targets to migrate the
improved systems.
Acknowledgements
This research is part of the following projects: SERENIDAD (PEII11-037-7035)
financed by the "Viceconsejería de Ciencia y Tecnología de la Junta de Comunidades
de Castilla- La Mancha" (Spain) and FEDER, and SIGMA-CC (TIN2012-36904) and
GEODAS (TIN2012-37493-C03-01) financed by the "Ministerio de Economía y
Competitividad" (Spain).
84

References
1. Aiken, P. H. (1998). "Reverse engineering of data." IBM Syst. J. 37(2): 246-269.
2. Basin, D., J. Doser, et al. (2003). Model Driven Security for Process-oriented Systems.
ACM Symposium on Access Control Models and Technologies. Como, Italy, ACM Press:
100-109.
3. Basin, D., J. Doser, et al. (2006). "Model Driven Security: from UML Models to Access
Control Infrastructures." ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology
15(1): 39-91.
4. Blaha, M. (2001). A Retrospective on Industrial Database Reverse Engineering Projects-
Part 1. Proceedings of the 8th Working Conference on Reverse Engineering (WCRE´01),
Suttgart, Germany, IEEE Computer Society.
5. Blanco, C., I. García Rodríguez de Guzmán, et al. (2010). "Defining and Transforming
Security Rules in an MDA approach for DWs." Int. J. of Business Intelligence and Data
Mining - IJBIDM 5(2).
6. Canfora, G. and M. D. Penta (2007). New Frontiers of Reverse Engineering, IEEE
Computer Society.
7. Cohen, Y. and Y. A. Feldman (2003). "Automatic high-quality reengineering of database
programs by abstraction, transformation and reimplementation." ACM Trans. Softw. Eng.
Methodol. 12(3): 285-316.
8. CWM, O. M. G. (2003). "Common Warehouse Metamodel (CWM)."
9. Fernández-Medina, E., J. Jurjens, et al. (2009). "Model-Driven Development for secure
information systems." Information and Software Technology 51(5): 809-814.
10. Fernández-Medina, E., J. Trujillo, et al. (2007). "Model Driven Multidimensional Modeling
of Secure Data Warehouses." European Journal of Information Systems 16(4): 374-389.
11. Fernández-Medina, E., J. Trujillo, et al. (2006). "Access Control and Audit Model for the
Multidimensional Modeling of Data Warehouses." Decision Support Systems 42: 1270-
1289.
12. Fernández-Medina, E., J. Trujillo, et al. (2007). "Developing Secure Data Warehouses with
a UML extension." Information Systems 32(6): 826-856.
13. Hainaut, J.-L., V. Englebert, et al. (2004). Database reverse engineering: From
requirements to CARE tools. Applied Categorical Structures. SpringerLink. 3.
14. Jurjens, J. (2004). Secure Systems Development with UML, Springer-Verlag.
15. Jurjens, J. and H. Schmidt (2011). UMLsec4UML2 - Adopting UMLsec to Support UML2.
http://hdl.handle.net/2003/27602, Technical Reports in Computer Science. Technische
Universitat Dortmund.
16. MDA, O. M. G. (2003). "Model Driven Architecture Guide."
17. Mouratidis, H. (2011). Software Engineering for Secure Systems: Industrial and Research
Perspectives, IGI Global.
18. Muller, H. A., J. H. Jahnke, et al. (2000). Reverse engineering: a roadmap.
19. Priebe, T. and G. Pernul (2001). A Pragmatic Approach to Conceptual Modeling of OLAP
Security. 20th International Conference on Conceptual Modeling (ER 2001). Yokohama,
Japan, Springer-Verlag.
20. Thuraisingham, B., M. Kantarcioglu, et al. (2007). "Extended RBAC-based design and
implementation for a secure data warehouse." International Journal of Business Intelligence
and Data Mining (IJBIDM) 2(4): 367-382.
21. Trujillo, J., E. Soler, et al. (2009). "A UML 2.0 Profile to define Security Requirements for
DataWarehouses." Computer Standards and Interfaces (CSI) 31(5): 969-983.
22. Weippl, E., O.Mangisengi, et al. (2001). An Authorization Model for Data Warehouses and
OLAP. Workshop on Security in Distributed Data Warehousing. New Orleans, Louisiana, USA.
23. Yu, E.(1997). Towards modelling and reasoning support for early-phase requirements
engineering. 3
rd
IEEE International Symposium on Requirements Engineering (RE'97),
Washington, DC.
85
