
Fuzzy Cognitive Map Hierarchical Triage Decision Support
for the Elderly
Voula C. Georgopoulos
1
and Chrysostomos D. Stylios
2
1
School of Health and Welfare Professions, TEI of Western Greece, Patras, Greece
2
Dept. of Informatics and Communications Technology, TEI of Epirus, Artas, Greece
Keywords: Medical Decision Support, Health System, Modelling, Soft computing.
Abstract: Fuzzy Cognitive Maps (FCMs) is a soft computing technique that has successfully been used to model
complex systems and to develop Medical Decision Support Systems for many medical discipline
applications. FCMs have a great ability to handle complexity, uncertainty and abstract inference as is the
case in the health care sector. In this work a Hierarchical structure is introduced within an integrated health
system where the Supervisor is modelled as an abstract FCM to support the triaging procedure. At the lower
level, the FCM-ESI DSS is used to estimate the Triage ESI level of every patient. This FCM-ESI DSS is
developed based on a novel approach, which ensures a high degree of inferring from human experts.
1 INTRODUCTION
The significant difficulty of making decisions in the
health care area of Emergency Department (ED)
service delivery is due to the inherent complexity
and intrinsic uncertainty of EDs and their dynamic
nature. Taking into consideration the aging
population increasingly seeking services at the ED in
combination with the limited resources and
increased costs lead to the need for development of
decision making tools that will effectively and
efficiently provide patient care in a timely fashion.
Emergency Departments (EDs) vary from
country to country both in terms of range of services
offered as well as patients arriving for care in EDs.
However, a recent definition provides the essence of
what goes on in EDs: “Emergency departments
provide unscheduled care for a wide variety of
persons for reasons that range from life-threatening
conditions to problems that could be treated in a
primary care setting” (Nawar et al., 2007).
Triaging involves an initial sorting of patients
who arrive at the emergency room, usually called
emergency department (ED), by rapidly identifying
patients requiring immediate care due to urgent, life-
threatening conditions as well as assessing the
severity of the problem so as to ensure that care is
appropriate and timely (ENA, 2001).
Patients are categorized according to the level of
urgency (Fernandes et al., 2004); (Travers et al.,
2002), based on their complaints, their general
condition, a brief examination and physiological
factors. In this way triage systems permit
minimizing of the waiting time for treatment of the
most urgent patients, while those not in need of
urgent treatment are placed in a waiting area.
Given the constantly increasing age of a
population this leads to increased numbers of visits
of elderly patients to the ED and as a result to an
increased burden on the EDs (Yim et al., 2009). The
elderly often have multiple and complex diseases
(Aminzadeh and Dalziel, 2002) and, as a general
rule, undergo more diagnostic testing and have
longer length of stays than younger patients. The
elderly frequently visit the ED because of their
increased prevalence to chronic-degenerative
diseases, susceptible to frequent exacerbations.
It is significant to mention that in study of a
sample of 50 randomly selected cases of ED
admissions patients 65 years or older, discrepancies
were found between the medical staff and expert
nurses in 20 cases: where staff nurses had
undertriaged 13 patients and overtriaged 7 patients
(McCall, et al.,2009). According to another study
(Grossmann et al., 2012) of patients over 65,
undertriage occurred in 22.5% cases. Main reasons
were neglect of high-risk situations and failure to
appropriately interpret vital signs.
Since all patients presenting to the ED are not of
equal severity and complexity, those that do not
577
C. Georgopoulos V. and D. Stylios C..
Fuzzy Cognitive Map Hierarchical Triage Decision Support for the Elderly .
DOI: 10.5220/0004634105770583
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (HA-2013), pages
577-583
ISBN: 978-989-8565-69-3
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

have a severe/and or life threatening condition will
have to wait to receive care. For the elderly
population where the complexity of problems is
increased, a long wait may cause deterioration of
their condition. Therefore it is important that
patients are also prioritized after the triage
classification within their classification category and
not be tended to on a first-come first-served basis.
Emergency rooms are extremely complex not
only in the patient and treatment protocols, but also
due to the high level of automation and
instrumentation, huge volume of information, and
interdisciplinary coordination that is necessary
(Christian et al., 2006). As such the triage decision
can be modelled using soft computing modelling
techniques such as Fuzzy Cognitive Maps discussed
in the next section.
In this paper, a two-level Decision Support
System is discussed to automatically assist in the
triage classification as well as assign and update
priority for patients which must wait according to
their classification.
2 FUZZY COGNITIVE MAPS
Fuzzy Cognitive Maps with their modifications
integrate aspects of fuzzy logic, neural networks,
semantic networks, expert systems and they are
usually supplemented by other soft and hard
computing methodologies. An FCM is illustrated as
a causal graphical representation consisting of
interrelated concepts. FCMs are fuzzy signed
directed graphs permitting feedback, where the
weighted edge w
ij
from causal concept C
i
to affected
concept C
j
describes the degree by which the first
concept influences the latter. FCMs are
characterized as fuzzy feedback models of causality,
where the weighted interconnections between
concepts of the FCMs present causality between
concepts by creating an interconnected network of
interrelated entities, like an abstract mental model.
Feedback interconnections are permitted along with
if- then inferencing; that permits FCMs to model
complex nonlinear dynamic systems. FCMs have the
ability to include hidden nonlinear dynamics.
The concepts of the Fuzzy Cognitive Model
stand for the main characteristics of an abstract
model of any system, each concept of the FCM
represents a granular entity such as state, variable,
input, output, event, action, goal, trend of the system
that is modeled as an FCM. The value of every
concept
C
i
is A
i
and it results from the
transformation of the fuzzy real value of the
system’s variable, for which this concept stands for,
in the interval [0,1]. This produces the initial
concept value which is then updated as it is
computed through the interaction of the
interconnected concepts with the corresponding
weight. Generally, between two concepts there are
three possible types of causal relationships that
express the type of influence from one concept to the
other. The weight of the arc between concept
C
i
and
concept
C
j
could be positive
)0(
ij
W
which
means that an increase in the value of concept
C
i
leads to the increase of the value of concept
C
j
, and
a decrease in the value of concept
C
i
leads to the
decrease of the value of concept
C
j
. When there is
negative causality
)0(
ij
W
which means that an
increase in the value of concept
C
i
leads to the
decrease of the value of concept
C
j
and vice versa.
Finally, there can be no causality
)0(
ij
W
.
The value
i
A
of concept
i
C
expresses the
degree of its corresponding physical value. FCMs
are used to model the behavior of systems; during
the simulation step, the value
i
A
of a concept
i
C
is
calculated by computing the influence of the
interconnected concepts
j
C ’s on the specific
concept
i
C
following the calculation rule:
N
j
ij
ji
k
j
k
i
k
i
)wAf(AA
1
)(
1
(1)
where
)1( k
i
A is the value of concept
i
C
at
simulation step
1
k
,
)(k
j
A
is the value of concept
j
C at simulation step
k
,
ji
w is the weight of the
interconnection from concept
j
C to concept
i
C
and
f
is the sigmoid threshold function:
x
e
f
1
1
(2)
where
0
is a parameter that determines its
steepness. In this approach, the value
1
has
been used. This function is selected since the values
i
A
of the concepts must lie in the interval [0,1].
Fuzzy Cognitive Maps have been used to
develop Medical Decision Support Systems
(MDSS). A specific type for Medical Diagnosis is
the Competitive Fuzzy Cognitive Map (CFCM)
(Georgopoulos et al., 2003); (Georgopoulos et al.,
SIMULTECH2013-3rdInternationalConferenceonSimulationandModelingMethodologies,Technologiesand
Applications
578

2005); (Georgopoulos and Stylios, 2008) which
consists of two main types of concepts: diagnosis-
concepts and factor-concepts. Figure 1 illustrates an
example CFCM model that is used to perform
medical diagnosis. Here, the concepts of the FCM
and the causal relations among them that influence
concepts and determine the value of diagnosis
concepts indicating the final diagnosis are
illustrated.
In the CFCM model each diagnosis concept
represents a single diagnosis, which means that these
concepts must be mutually exclusive because the
main intention is to always infer only one diagnosis.
This is the case of most medical applications, where,
according to symptoms, medical professionals
conclude to only one diagnosis and then decide
accordingly concerning the treatment. Actually, this
comes from the medical axiom: “every patient has
only one disease” but may represent many
symptoms related to different diseases but all are
results of the primitive disease. The general
diagnosis procedure is a complex process that has to
take under investigation a variety of interrelated
factors, symptoms and functions. In accomplishing
any diagnosis process, some of these factors are
complementary, others are similar and even others
are conflicting.
Figure 1: A CFCM model for Medical Diagnosis.
In the Competitive Fuzzy Cognitive Map model, the
factor-concepts can be considered as inputs into the
MDSS from patient data, observed symptoms,
patient records, experimental and laboratory tests
etc, which can be dynamically updated based on the
system interaction, whereas the decision-concepts
are considered as outputs where their estimated
values outline the possible diagnosis for the patient.
3 ESI TRIAGE SYSTEM
When a patient first arrives in the Emergency
Department, the first stop is triage where a trained
and experienced registered nurse typically prioritizes
each patient's condition into one of five general
categories. This is done according to the Emergency
Severity Index (ESI) which was designed for use in
ED triage by the US Department of Health &
Human Services. The ESI is a five-level
categorization algorithm that prioritizes patients into
five groups from 1 (most urgent) to 5 (least urgent)
on the basis of severity and the number of resources
that the patient may need to receive proper care
(Wuerz, 2001).
In particular, the ESI uses the following scale
based on decision points to determine its categories
(Gilboy et al., 2005); (Barbee et al., 2010):
ESI category 1- Emergent: patient intubated,
without pulse or respiration, or unresponsive. i.e
the patient requires immediate life-saving
intervention so as to prevent loss of life, limb, or
eyesight,
ESI category 2- Urgent: patient is in a high-risk
situation, or confused, lethargic or disoriented, or
in severe pain, or danger zone vital signs.
ESI category 3- Acute: patient is in need of many
resources to be taken care of. These may include,
for example, Laboratory Tests, ECG, X-rays, CT-
MRI-ultrasound-angiography, IV fluids, specialty
consultation, com-plex procedures etc.
ESI category 4- Routine: patient is in need of one
resource.
ESI category 5- Non urgent: patient is in need of
no resources.
Due to the dynamic and uncertain nature of the
overall triage process in addition to the
differentiation difficulty, methods are needed to help
the triage nurse to be efficient in making
prioritization among the patients with the same
acuity classification. Triage is a dynamic process in
decision-making and the determination of who needs
the most immediate care must be reassessed as
contextual factors change and additional patient
information becomes available [Patel, et al., 2008].
The triaging procedure requires a continuously
monitoring and keeping track of patients waiting to
be seen and a prompt assessment of each new
patient who arrives at the triage area. All the above
mentioned factors have to be taken into
consideration and they contribute to the complexity
of decision-making and create a degree of
uncertainty for the triage procedure. Therefore a
Decision Support System on Fuzzy Cognitive Maps
FuzzyCognitiveMapHierarchicalTriageDecisionSupportfortheElderly
579
for ESI Triage is developed in the next section.
4 FUZZY COGNITIVE MAPS
MODEL FOR THE 5-LEVEL
ESI TRIAGE SYSTEM
In an ED triage system each patient is assigned one
of the 5 ESI levels and therefore, the Fuzzy
Cognitive Map ESI will include 5 Decision
Concepts (DC) each one for every ESI level:
DC1 ESI Level 1;
DC2 ESI Level 2;
DC3 ESI Level 3;
DC4 ESI Level 4;
DC5 ESI Level 5.
The FCM development procedure is based on
human experts who have to define the factor
concepts that are represented at the FCM. There is
group of experts who are asked to select the main
factors based on which they conclude to an ESI
triage; everyone expert replies with a set of 3-5
factors or even more sometimes.. The frequency
with which each factor was chosen by the group of
experts as a whole determined the importance
weight (
iw
) between a factor concept and a
decision concept.
The 22 factor concepts (FC1-FC22) of the FCM
are and their
iw
have been detailed reported in
(Georgopoulos and Stylios, 2012); (Georgopoulos
and Stylios, 2013) and are mentioned in Table 1.
Moreover, the experts are asked to evaluate the
triage stage of specific cases and based on their
assessment we infer additional information, which
leads to a complementary second weight, the
“influence to specific decision” specific weight-
sw
, which represents how much the specific factor
leads towards a specific decision / diagnosis. The
procedure to calculate the
sw is the following:
every expert who considers one factor as important
and takes it into consideration, is asked to present
the degree with which this specific factor leads the
expert to select one decision. Every expert describes
the degree of influence of one factor towards one
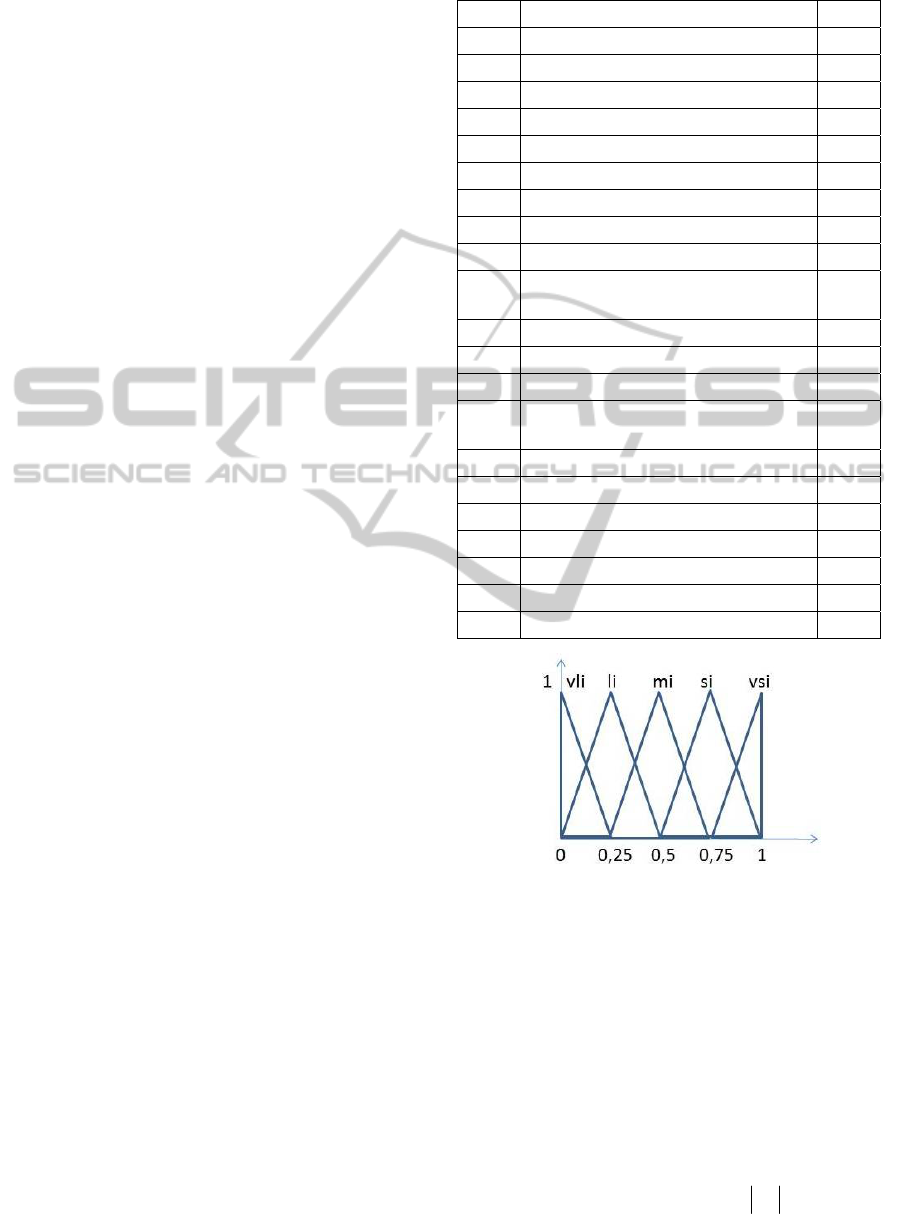
decision using a linguistic variable, such as “very
strong influence
vsi”, “strong influence, si”,
“medium influence,
mi”, “weak influence wi”, “very
weak influence vwi”, as it is depicted at Figure 2.
Thus, every expert describes the specific weight
of each interconnection with a fuzzy linguistic
variable from the above mentioned set, which stands
for the relationship between the two concepts and
Table 1: Factors of the FCM.
FC1 Life threatening 0.45
FC2 Limb threatening 0.40
FC3 Patient chief complaint 0.67
FC4 Vital signs 0.4
FC5 Medical history 0.35
FC6 Other factor 0.32
FC7 Expected # of resources 0.31
FC8 Patient age 0.16
FC9 Required timely intervention 0.15
FC10 Weakness 0.20
FC11 Additional symptoms other than chief
complaint
0.14
FC12 Severe pain or distress 0.12
FC13 Patient referred to ED from outside 0.08
FC14 Behavioral or psychiatric issue 0.07
FC15 No additional symptoms to chief
complaint
0.05
FC16 Absence of medical history 0.05
FC17 Patient medications 0.05
FC18 Hospital or ED discharge<3 days 0.04
FC19 Patient immune-compromised 0.04
FC20 Alcohol or illicit drug use 0.03
FC21 No recent change mental state 0.75
FC22 Patient can walk or sit 0.12
Figure 2: The positive fuzzy linguistic weights.2
determines the grade of causality between the two
concepts. Then, all the proposed linguistic weights
for one interconnection suggested by experts, are
aggregated using the SUM method and an overall
linguistic weight is produced. The overall lingustic
weight with the defuzzification method of Center
Of Gravity (COG), is transformed to a numerical
weight , belonging to the interval [-1, 1].
Then, the overall weight describing the influence
from one factor concept towards a decision concept
is calculated using the form:
swliwlsww
ji
**)sgn(
21
(4)
SIMULTECH2013-3rdInternationalConferenceonSimulationandModelingMethodologies,Technologiesand
Applications
580

where the two parameters are introduced to
represent the participation of the importance weight
and the specific weight, on the overall weight
describing the influence of every factor concept
towards the decision/diagnosis concept. It is
mentioned that the value of has to be normalized in
the interval [-1, 1], where the weight takes values.
The previously developed FCM-ESI model did
not provide for interactions between the various
factor concepts. However, because the decision is
very complex and there are always cause effect
relationships between factors contributing to the
triage decision, it is important to extend the previous
FCM-ESI DSS system to include such connections
between factor nodes.
In the current model these are as follows:
Vital signs (FC4) and Patient chief complaint
(FC3) Vital signs (FC4) and Patient immuno-
compromised (FC19) – for example patients that
are experiencing fever and are on chemotherapy.
Over the counter medications (F15) and chief
complaint (FC3) – patients using over the counter
pain medication may have decrease in their pain
level and as a result the severity indicated
concerning their chief complaint may be decreased
Figure 3: The FCM-ESI model for triaging.
Over the counter medications (F15) and vital signs
(FC4) – over the counter medications may change
vital signs, e.g. reduced fever, increased blood
pressure etc
Experts were asked to identify the possible
interactions among Factor Concepts. At first, every
expert is asked to determine the pair of concepts that
are coupled. Thus, a set of possible paired factors
concepts is created and then all the experts are asked
to suggest the degree (using a linguistic weight) of
coupling/ influencing among the previously
identified pairs of factor concepts. A set of five
fuzzy linguistic values are used.
The complete FCM-ESI is illustrated in Figure 3
where the 5 central nodes are the decision nodes
(ESI levels). The decision node with the maximum
value is the level at which a patient is triaged.
The FCM-ESI for every patient takes the concept
factor values from measurements, laboratory test and
examination and these values are transformed in the
interval [0,1] where concepts take values and then
the values of Decision Concepts are calculated, so
that to infer the ESI level.
5 PRIORITY BETWEEN
EQUALLY TRIAGED
PATIENTS
FOR ESI LEVELS 3-5
An important issue after initial triage for patients
with ESI levels 3-5 in an overcrowded ED is the
priority with which patients receive care. Usually,
this is on a first come – first served basis. However,
this can change over time. For example, in some
cases injuries and illnesses that need medical and
nursing intervention are time sensitive. The longer
the wait, the more damage may occur because of
changes for example such in oxygen, blood,
electrolytes (potassium, sodium, etc.), sugar, etc.
Failure to prioritize triaged patients appropriately
may result in very sick patients at risk for
deterioration while waiting. Since this is also
difficult and critical decision for the personnel in the
ED, a supervisory level has been added on the
FCM-ESI DSS model, where the outcome is
changes in priority for patients within the same ESI
level.
In order to develop the supervisor priority FCM-
ESI Decision Support Systems, there are selected the
most essential factor concepts that may influence the
patient status. The supervisor priority FCM-ESI
consists of the concepts (Figure 4):
Change in vital signs (FC4).
FuzzyCognitiveMapHierarchicalTriageDecisionSupportfortheElderly
581

Patient report of worsening symptoms.
Change in mental state (FC21).
Change in patient can walk or sit (FC22).
Triage ESI level.
Time in waiting area.
Therefore, for each patient where a particular ESI
Decision Concept had the maximum value (i.e. the
ESI Level with which the patient was characterized)
this decision node interacts dynamically with other
FC nodes as new information is provided over time
and is checked every half hour.
This leads to prioritizing of the patients that have
equal or almost equal ESI status in order to avoid
adverse events after triage due to long wait in
overcrowding. Thus the supervisor priority FCM-
ESI is called to prioritize among patients with the
same ESI level.
6 CASE STUDY
A 72-year-old woman presented to a busy
emergency department (ED). During triage she told
the triage nurse that she experienced face and tongue
swelling in the last two days. The vital signs at
triage, including respiratory rate and oxygen
Figure 4: The supervisor priority FCM-ESI DSS.
saturation, were normal. No previous history
indicated this condition, the patient had not taken
medications, was not in any pain, and there were no
problems with the patient’s mental state, Also the
patient was able to sit and walk. Both a triage nurse
and the FCM-ESI resulted in ESI-Level 3.
The patient sat in the waiting room for more than
2 hours after which she was placed in a room in the
ED. After an additional hour a doctor evaluated her.
In the meantime, her tongue and throat had swollen
substantially, and she was having difficulty
breathing. She was diagnosed with angioedema and
required emergency intubation, a potentially
dangerous and high-risk procedure accompanied by
aggressive treatment with intravenous epinephrine.
On the other hand, using the supervisor priority
FCM-ESI DSS, when the patient after 1.5 hours
experienced substantial swelling and difficulty
breathing the triage the patient priority was
increased to Very-Very High and thus, the patient
received immediate care without the need for
intubation.
7 SUMMARY
This paper is an extension of previous work and it
presents an integrated methodology for developing a
hierarchical Decision Support System for ESI
Triage. Usually at the Emergency Department (ED)
of hospitals medical staff has to cope with many
patients, asking for urgent treatment and so they
have to assess their health condition under
significant time constrains. The case of elderly
patients has great importance as they usually are
admitted quite frequently at the ED suffering from
chronic problems, their health condition is
characterized by complementarity and/or
controversy and usually with a lack of interaction
and low level communication ability. Thus triaging
of elderly people is characterized by high
complexity and it makes a difficult task the
assessment and decision about health condition.
For such cases, Soft Computing methodologies
are rather suitable and so Fuzzy Cognitive Maps
(FCMs) are proposed here to model and develop a
Decision Support Systems for the ESI Triage, which
is a significant procedure during patient admission at
the Emergency Department (ED) of hospitals.
Generally, FCMs have been successfully applied to
develop Medical Decision Support Systems for
many discipline fields.
Here, there is further expansion of a recently
proposed methodology to develop FCMs exploiting
SIMULTECH2013-3rdInternationalConferenceonSimulationandModelingMethodologies,Technologiesand
Applications
582

and combining knowledge and experience of human
experts along with information and bibliographic
data. Moreover, a hierarchical two level structure is
introduced consisting of a FCM at each level. The
introduction of the abstract FCM supervisor
prioritizes among the different patients and increases
the efficiency of the MDSS.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the E.U. FP7–
PEOPLE–IAPP–2009, Grant Agreement No.
251589, Acronym: SAIL.
REFERENCES
Aminzadeh, F. & Dalziel, W. B., 2002. Older adults in the
emergency department: a systematic review of patterns
of use, adverse outcomes, and effectiveness of
interventions, Ann Emerg Med, 39:238-47.
Barbee, G. A. et al., 2010. The effect of provider level
triage in a military treatment facility emergency
department. Journal of Emergency Primary Health
Care (JEPHC), 8:Article 990386.
Christian, C. K. et al., 2006. A prospective study of patient
safety in the operating room, Surgery, 139:159–173.
Emergency Nurses Association (ENA), 2001. Making the
right decision: A triage curriculum (2nd ed.). Des
Plaines, IL.
Fernandes, C. et al., 2004. Five level triage: A report from
the ACEP/ENA Five Level Triage Task Force. JEN
31(1):39-50.
Grossmann, F. F. et al. 2012. At risk of undertriage?
Testing the performance and accuracy of the
emergency severity index in older emergency
department patients, Annals of Emergency Medicine,
60(3):317–325.e3.
Georgopoulos, V. C., Malandraki G. A., & Stylios, C. D.,
2003. A Fuzzy Cognitive Map Approach To
Differential Diagnosis of Specific Language
Impairment, Journal of Artificial Intelligence in
Medicine 29(3):261-278.
Georgopoulos, V. C. & Stylios, C. D., 2005. Augmented
Fuzzy Cognitive Maps Supplemented with Case Based
Reasoning for Advanced Medical Decision Support,
In: Soft Computing for Information Processing and
Analysis Enhancing the Power of the Information
Technology. M. Nikravesh, L. A. Zadeh and J.
Kacprzyk (Eds.) Studies in Fuzziness and Soft
Computing, Springer-Verlag, Vol. 1, pp. 391-405
Georgopoulos, V. C. & Stylios, C. D., 2008.
Complementary case-based reasoning, competitive
Fuzzy cognitive maps for advanced medical decisions.
Soft Computing, 12: 191-199.
Georgopoulos, V. C. & Stylios, C. D., 2012. Introducing
Fuzzy Cognitive Maps for Developing Decision
Support System for Triage at Emergency Room
Admissions for the Elderly. Proceedings of the 8th
IFAC Symposium on Biological and Medical Systems,
29-31 August 2012, Budapest, Hungary.
Georgopoulos, V. C. & Stylios, C. D., 2013. Fuzzy
Cognitive Map Decision Support System for
Successful Triage to Reduce Unnecessary Emergency
Room Admissions for the Elderly. In Fuzziness and
Medicine: Philosophical Reflections and Application
Systems in Health Care, pp. 415-436, Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Gilboy, N. et al., 2005. Emergency Severity Index, Vers.
4: Implementation Handbook. Agency for Healthcare
Research & Quality, Publication No. 05-0046-2,
Rockville, MD. http://www.ahrq.gov/research/esi/
McCall, B. et al., 2009. Mistriage of elderly in the
emergency de-partment, Connecting the Dots:
Geriatric Nursing, Education, and Clinical
Simulation, Chapel Hill, NC, 2009.
Nawar, E. W., Niska, R. W., & Xu J., 2007. National
Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2005
emergency department summary, Adv Data, 386:1-32.
Patel, V. L. et al., 2008. Calibrating urgency: triage
decision-making in a pediatric emergency department.
Advances in health sciences education, 13(4):503-520.
Travers, D. A. et al., 2002. Five-level triage system more
effective than three-level in tertiary emergency
department, JEN 28(5):395-400.
Wuerz, R., 2001. Emergency severity index triage
category is associated with six-month survival. ESI
triage study grou, Academic Emergency Medicine,
8:61–64.
Yim, V. W., Graham, C. A., & Rainer, T. H., 2009. A
comparison of emergency department utilization by
elderly and younger adult patients presenting to three
hospitals in Hong Kong, Int J Emerg Med, 2:19-24.
FuzzyCognitiveMapHierarchicalTriageDecisionSupportfortheElderly
583
