
A Dataflow-based Mobile Brain Reading System on Chip with
Supervised Online Calibration
For Usage without Acquisition of Training Data
Hendrik Woehrle
1
, Johannes Teiwes
2
, Mario Michael Krell
2
, Elsa Andrea Kirchner
1,2
and Frank Kirchner
1,2
1
Robotics Innovation Center, German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI GmbH),
Robert-Hooke-Str 5, Bremen, Germany
2
Robotics Group, University of Bremen, Bibliotheksstr. 1, Bremen, Germany
Keywords:
Brain Computer Interface, Signal Processing, Machine Learning, FPGA, Embedded Systems, Mobile
Computing.
Abstract:
Brain activity is more and more used for innovative applications like Brain Computer Interfaces (BCIs). How-
ever, in order to be able to use the brain activity, the related psychophysiological data has to be processed and
analyzed with sophisticated signal processing and machine learning methods. Usually these methods have to
be calibrated with subject-specific data before they can be used. Since future systems that implement these
methods need to be portable to be applied more flexible tight constraints regarding size, power consumption
and computing time have to be met. Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are a promising solution,
which are able to meet all the constraints at the same time. Here, we present an FPGA-based mobile system
for signal processing and classification. In addition to other systems, it is able to be calibrated and adapt at
runtime, which makes the acquisition of training data unnecessary.
1 INTRODUCTION
Brain Computer Interfaces (BCIs) became a popu-
lar research topic in the last couple of years. BCIs
are commonly used to (re-)establish communica-
tion (Wolpaw et al., 2002) or can be used to estimate
the internal mental state of humans. This is achieved
by analyzing psychophysiological signals which can
be recorded by means of different methods, like the
electroencephalogram (EEG). Although BCIs were
traditionally mainly used for rehabilitation purposes,
their application was extended to other areas (e.g.
gaming).
In contrast to traditional BCIs, brain reading
refers to a passive monitoring of the mental state.
Other approaches make use of same methods that are
applied for classical BCIs but do not interfere with
the interaction but support it more passively. For ex-
ample, for operator surveillance the operators EEG
is analyzed continuously with respect to the question
whether important stimuli are recognized (Kirchner
et al., 2010). This approach can be seen as more
difficult to accomplish compared to traditional BCIs,
since it has to work with single trial data, which is
much more noisy than time locked averaged data that
is typically used in standard BCIs. The analysis of
this data requires the application of advanced signal
processing and machine learning methods.
Before these methods can be used, they have to be
calibrated to fit subject and setup specific attributes.
Therefore, a training session has to be performed ev-
ery time before the system can be used to acquire
data for the calibration of the methods. Further-
more, the psychophysiological state of the subject
may vary over time, which can impair the system’s
performance. The training session is usually a dif-
ficult and time consuming task and stressful for the
subject. Therefore a current important research topic
is the online calibration and adaptation of the sys-
tem in order to use the systems directly without any
prior training session and to compensate the time-
dependent variations.
In an operator surveillance task there is also the
need for small and mobile devices that perform the
signal processing and classification in real time and
which can be calibrated and adapted while the system
is in use. The amount of data that has to be processed
by the system is usually very high, since usually a
46
Woehrle H., Teiwes J., Krell M., Kirchner E. and Kirchner F..
A Dataflow-based Mobile Brain Reading System on Chip with Supervised Online Calibration - For Usage without Acquisition of Training Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0004637800460053
In Proceedings of the International Congress on Neurotechnology, Electronics and Informatics (NEUROTECHNIX-2013), pages 46-53
ISBN: 978-989-8565-80-8
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

high number of electrodes (e.g. 32, 64 or even 128)
and high sampling rates (e.g. 1 kHz or 5 kHz per
electrode) are used. Recent standard mobile devices
do not provide sufficient computing power to fulfill
the timing and performance constraints at the same
time. A feasible solution is the usage of Field Pro-
grammable Gate Arrays (FPGAs), which are becom-
ing increasingly popular for digital signal processing
(Meyer-Baese, 2004; Woods et al., 2008). FPGAs
have a number of advantages compared to standard
processing architectures, like low power consumption
and high performance due to the massive parallelism
at the same time. However, their usage is usually
very difficult due to the complex programming model,
which prevents a widespread use.
1.1 Overview about the Paper
Our approach is based on the transfer of classifiers:
we investigate the change in classification perfor-
mance when a classifier is trained on data from one
subject, and transferred to another subject. We com-
pare several different online classification algorithms
regarding their classification performance when the
system is recalibrated at runtime to compensate for
this effect to increase the classification accuracy and
make preliminary training sessions obsolete. Further-
more, we present the first FPGA-based signal pro-
cessing and classification system that is able to work
with high-dimensional single trial EEG data and to
perform the recalibration process online. We inves-
tigate the amount of FPGA resources that are con-
sumed by the implementation and compare the classi-
fication performance between purely software based
and hardware-accelerated computations. The devel-
oped system is evaluated in a concrete application:
the incremental learning of single trial classification
of the P300 Event Related Potential (ERP) in an op-
erator surveillance setup.
Related work is discussed in Section 2. The used
algorithms and the architecture of our system is pre-
sented in Section 3. Section 4 describes the evaluation
scenario. The results from the experimental evalua-
tion are presented and discussed in Section 5.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 The P300 Event Related Potential
The P300 is an ERP, i.e., a brain activity pattern that
is elicited by the brain when the subject processes
subjective seldom and/or important stimuli (Polich,
2007). The P300 is widely used in BCIs (Farwell and
Donchin, 1988), since it is a relatively clear and well
understood pattern. In most approaches this signal is
used to drive a BCI, that is actively controlling a de-
vice (e.g. speller). However, much research was per-
formed to investigate its ability to predict workload
and the success in the perception of important stim-
uli during complex interaction or dual task perfor-
mance (Isreal et al., 1980; Kirchner and Kim, 2012).
It could be shown that the P300 can be used to predict
the perception of important information by an opera-
tor in single trial (Kirchner et al., 2010).
2.2 FPGAs for Signal Processing and
Machine Learning
FPGAs consist of several different configurable ele-
ments, like logic slices, memory elements and spe-
cialized resources for digital signal processing. These
elements can be configured to generate hardware ac-
celerators that accomplish a specific functionality.
Since these hardware accelerators are tailored to this
single functionality and do not have to provide the
genericness of a standard CPU, they operate very effi-
ciently regarding application speedup and power con-
sumption. Due to these reasons, FPGAs are suitable
for applications like digital signal processing (Meyer-
Baese, 2004; Woods et al., 2008).
2.3 Mobile Signal Processing and
Classification Systems for BCIs
Due to the requirement of complex processing meth-
ods there is currently only a small number of mo-
bile BCI systems available. They also only support
simple paradigms or a small number of channels (Lin
et al., 2009). Due to the advantages of FPGAs there
is some work on FPGA-based BCI systems. In (Shyu
et al., 2010), a first FPGA-based BCI was developed,
which was able to detect certain frequencies elicited
by steady state visually evoked potentials (SSVEP) on
a single channel. A first P300 FPGA BCI system was
presented in (Khurana et al., 2012), but in that case
only a simple filter was performed in the FPGAs logic
partition, while most of the processing was performed
in softcore processors.
2.4 Adaptation and Calibration of BCIs
A current major research task is the online calibra-
tion and adaptation of the system to minimize the
amount of current subject specific training data or
make the acquisition of this data in training sessions
unnecessary. These training data acquisition sessions
ADataflow-basedMobileBrainReadingSystemonChipwithSupervisedOnlineCalibration-ForUsagewithout
AcquisitionofTrainingData
47

Python
Driver Driver
SDF2
Feature
Generation
Feature
Normalization
Classification
Dimensionality
Reduction
SDF1
Filtering and
Decimation
Detrending
Python
Libraries and
Middleware
Application
Middleware
Kernel
Hardware
Figure 1: Architecture of the System. Inside the hardware-
partition the used algorithms are instantiated as dataflows
(DFs), each consisting of a chain of nodes.
are very time consuming and stressful for the sub-
ject. In (Shenoy et al., 2006) methods were evaluated,
to re-calibrate algorithms used in BCIs. The results
showed, that, e.g. by adapting the classification bias,
the non-stationarity of EEG Data could be compen-
sated by a fair amount.
3 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
3.1 General System Design
As basis of our system we use the ZedBoard
TM
eval-
uation platform which features a Xilix Zynq FPGA
(ZC7020). The Zynq platform combines a dual-core
ARM Cortex A9 with programmable logic. It is there-
fore well suited for our approach, since it allows us
to combine standard software and operating systems
with application specific hardware accelerators.
3.2 Hardware Architecture
The system is realized as System on Chip (SoC) that
consists of a generic host processor for software tasks
(the ARM CPU), and specialized hardware accelera-
tors for the signal processing methods. These hard-
ware accelerators are based on the dataflow (DF)
model of computation, as shown in Figure 1.
In this model of computation, the time-consuming
methods are realized as specialized circuits, which
are working independently from the host processor.
To execute the algorithm, the host processor simply
pushes the data into the input memory of the DF and
collects the final results from the output memory of
the DF.
We use two separate application specific accelera-
tors in our system: one for preprocessing and one to
perform the classification. Each DF is realized as a
consecutive chain of nodes, where every node imple-
ments a particular algorithm. The DFs are connected
to the system bus of the SoC and can be accessed like
a regular bus-attachment. The bus-interface utilizes
First-In-First-Out (FIFO) buffers for data input/output
and registers are used to set and get parameters of the
DF, which act as source and sink node, respectively.
Inside each flow the nodes are connected using an
AXI-Stream like protocol (i.e. data and enable/ready
signals for handshaking).
3.3 Software Architecture
The software architecture is shown in Figure 1. As
operating system (OS) we use Ubuntu Linaro (Linaro,
2013). The OS is running on a linux kernel in ver-
sion 3.6, which is adapted to the ZYNQ platform.
For high-level processing and configuration we use a
Python-based application, which depends on few ex-
ternal libraries (NumPy, SciPy and pyYAML), which
can be easily obtained using the package manager of
the operating system. The hardware accelerators re-
side in the chips logic-partition and are interfaced to
the application using the C++-based Middleware and
custom drivers. This allows us to use a Python-based
application layer for high level processing and user
configuration.
3.4 Applied Signal Processing Methods
All signal processing modules were implemented as
hardware components in the DF as well as software
components for comparison. In contrast to the soft-
ware implementation, the hardware components use
fixed point computations instead of floating point
computations. The first DF (preprocessing) applies
direct current (DC) offset removal and decimation to
the data. The DC offset removal is achieved using a
notch infinite impulse response filter which attenuates
NEUROTECHNIX2013-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
48

the 0 Hz component. Next, the data is decimated from
the initial sampling rate of 1000 Hz to 25 Hz. Before
the sampling rate reduction a finite impulse response
filter was applied to avoid aliasing effects.
The first step in the second DF (prediction) is the
application of the xDAWN (Rivet et al., 2009) spatial
filter, to reduce the number of 62 original channels to
8 signal channels. Then, the dimension of the data is
further reduced by fitting straight lines to each chan-
nel using linear regression. During feature generation
all resulting values are arranged in a single feature
vector. The feature vector is standardized by dividing
each value by the standard deviation and subtracting
the mean of the corresponding features. The classi-
fication is done using different online learning meth-
ods, which are discussed in Section 3.5. To cope with
the different amounts of instances per class the output
of the classifier is not directly mapped to the corre-
sponding class. Instead the output is compared to a
threshold score, which is used as the decision bound-
ary for the class label.
3.5 Calibration of the System using
Online Learning Methods
Online learning methods operate in rounds, which
makes them ideal for online calibration of, e.g. BCI
systems. In round t, the binary classification algo-
rithm receives an instance x
t
∈ R
d
and uses its current
prediction model to make a prediction f (x
t
), which is
mapped to the final output ˆy
t
by using ˆy
t
= sign( f (x
t
))
Subsequently, the algorithm receives the true label
y
t
∈
{
−1,1
}
and suffers a loss `(y
t
, ˆy
t
). Finally, the
algorithm updates the prediction model by using x
t
and y
t
and proceeds to the next round. Several differ-
ent online learning methods exist. An important ad-
vantage of most of these algorithms is their memory
efficiency, since they only need to store x
t
,w
t
∈ R
d
.
We compare a number of different algorithms regard-
ing their classification performance and FPGA re-
source consumption. In the following, we consider
augmented feature vectors that contain an additional
1 to be able to fit an offset term.
3.5.1 Perceptron (P) and Normalized P (NP)
The most basic learning algorithm that can be used
in an online methodology is the Perceptron algo-
rithm. In this case the prediction tries to minimize
the 0-1-loss `(y
t
, ˆy
t
) = I(y
t
6= ˆy
t
) and ˆy
t
is given by
ˆy
t
= sign(w
T
t
x
t
). The resulting update rule is given
by w
t+1
= w
t
+ ηy
t
x
t
if y
t
6= ˆy
t
. A possible modifi-
cation is the normalization of the update, which be-
comes w
t+1
= w
t
+ηy
t
x
t
||x
t
||
. Additionally, we include
an optional update coefficient η.
3.5.2 Adaline (AL) and Normalized AL (NAL)
The Adaline method is based on the squared loss
`(y
t
, ˆy
t
) =
1
2
(y
t
− ˆy
t
)
2
, where ˆy
t
is given by ˆy
t
=
w
T
t
x
t
. The corresponding update rule is w
t+1
= w
t
+
ηx
t
( ˆy
t
− y
t
) with an optional update coefficient η.
3.5.3 Passive Aggressive Algorithms
Since Support Vector Machines (SVMs) perform
well on noisy data like EEG data, we also exam-
ine the Passive-Aggressive Perceptron (PAP) algo-
rithms (Crammer et al., 2006). The PAPs have an
analogous approach to the SVM, since they try to sep-
arate the two classes by constructing a separating hy-
perplane with a maximum margin by minimizing the
hinge loss `
h
(y
t
, ˆy
t
) = max{0, 1 − y ˆy
t
}, where the lin-
ear prediction model is given by ˆy
t
= w
T
t
x
t
(see equa-
tions 2 and 3).
In contrast to SVMs, the PAPs operate in online
mode, and can therefore be used for the online cal-
ibration of the system. Different variations of PAPs
exist which are discussed in the following.
The update rule for the simplest PAP is given in
equation 1, which is called the Passive Aggressive 0
algorithm (PA0). In this case, the PAP tries to mini-
mize the cumulative hinge loss.
w
t+1
= w
t
+ η
`
h
(w
T
t
x
t
,y
t
)
||x
t
||
2
y
t
x
t
(1)
More advanced methods for the updates are given
in equation 2 and 3, which are called Passive Aggres-
sive 1 (PA1) and Passive Aggressive 2 (PA2). PA1 and
PA2 incorporate an additional aggressiveness param-
eter C that controls the aggressiveness of the update,
which can improve the generalization ability of the
obtained classifiers in the presence of noise.
w
t+1
= w
t
+ η min
C,
`
h
(w
T
t
x
t
,y
t
)
||x
t
||
2
y
t
x
t
(2)
w
t+1
= w
t
+ η
`
h
(w
T
t
x
t
,y
t
)
||x
t
||
2
+
1
2C
y
t
x
t
(3)
As in Perceptron and Adaline algorithms, we in-
clude an optional update coefficient η.
4 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
The analysis of the system was performed in an appli-
cation that monitors the conscious perception of rel-
evant messages by a subject by predicting the coin-
cidental presence of a P300 event related potential in
ADataflow-basedMobileBrainReadingSystemonChipwithSupervisedOnlineCalibration-ForUsagewithout
AcquisitionofTrainingData
49

the subjects EEG. The analysis was performed on of-
fline data.
4.1 Application Scenario
The experimental setup for the evaluation of the sys-
tem is shown in Figure 2. It allows the monitoring
of the subjects EEG while it is under a high cognitive
workload. The high cognitive workload is achieved
because the subject has to perform a dual task: play-
ing the labyrinth game and reacting to certain vi-
sual stimuli at the same time. The setup of the sce-
nario is as follows: the subject is sitting in front of a
labyrinth game which has to be actively controlled in
this scenario. The subject wears a head mounted dis-
play (HMD), which displays a simulated model of the
game as well as certain symbols, which serve as visual
stimuli for the subject. There are two kinds of stimuli:
unimportant standard stimuli, which do not require a
reaction of the subject, and different kinds of impor-
tant target stimuli, on which he has to press a buzzer
that is placed next to the game. The target stimuli are
shown infrequently among the standard stimuli in a
fixed ratio of about 1 : 6. The inter-stimulus interval
(ISI) was 1000 ms with a random jitter of 100 ms. The
used setup is of an oddball type, in which infrequent
important stimuli evoke a P300 while frequent unim-
portant ones do not. For this evaluation the task of our
Figure 2: Experimental setup of the BRIO oddball
paradigm: A subjects plays a virtualized labyrinth game
and answers on important target stimuli (target 1 and tar-
get 2 that are shown in case target 1 stimuli were missed)
by pressing a buzzer. The evoked averaged ERP after unim-
portant standard stimuli and important target 1 stimuli are
shown. Target 1 stimuli evoke a P300, standard stimuli do
not.
system is to distinguish between EEG activity evoked
by standard versus target stimuli. Hence, after a stim-
ulus has been shown in the HUD our system predicts
whether it has been perceived as a standard or target
by computing p(x
t
). The true label y is revealed from
the buzzer press, e.g. if the subject responds to a given
target stimulus.
4.2 Experimental Procedures
Six subjects (males; mean age 27.5) took part in the
experiments. The experiment was performed two
times by each subject with at least one day of rest in
between, generating two sessions per subject. In each
session, each subject performed 5 runs with 120 target
stimuli (important information) and ≈ 720 standard
stimuli. While the subject was performing the task,
the EEG was recorded (62 electrodes, extended 10-20
system with reference at FCz) using 62 channels of
a 64 channel actiCap system (Brain Products GmbH,
Munich, Germany). Impedance was kept below 5 kΩ
at each electrode. EEG signals were sampled at 1000
Hz, amplified by two 32 channel BrainAmp DC am-
plifiers and filtered with a low cut-off of 0.1 Hz.
4.3 Training and Calibration Process in
the Application
The usage of the system is divided into two different
phases: an initial training phase and a runtime cali-
bration phase. We used three of the five runs (≈ 2500
training examples) of each session as training data
for the preliminary training of the methods and the
other two runs as test data to represent the applica-
tion phase.
To evaluate the classification accuracy depen-
dence on the ability to compensate changing condi-
tions, we evaluate two different application setups:
Same Subject (SS). In this setup we use the pre-
trained methods with test data that was acquired
from the same subject on the same day. Accord-
ing to the 6 subjects and 2 sessions per subject, we
get 12 train-test combinations in this case.
Different Subject (DS). In this setup we use the pre-
trained methods with test data that was acquired
from another subject. According to the 6 subjects
and 2 sessions, we get 120 train-test combinations
in this case.
Furthermore, we analyze two different calibration
setups:
Inactive Recalibration (IR). In the IR setup, all
methods are trained on the training data and used
NEUROTECHNIX2013-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
50

without any other changes in the both the SS and
DS cases.
Active Recalibration (AR). In the AR setup we use
the pretrained methods and recalibrate them in the
application phase.
Additionally, we analyze two computing proce-
dures:
Software based Computation (SW). In the SW
procedure, all methods are evaluated purely in
software, i.e. double precision computations on a
standard processor.
Hardware-accelerated Computation (HW). In the
HW procedure, we use the described dataflow-
based hardware accelerators. Since these use
fixed point computations, an urgent question is the
stability of the recalibration process in the appli-
cation phase.
recorded
data
parameters
algorithm
loss
update
live
data
data
data
loss
update
predictiontraining
output
Figure 3: Calibration in application phase and evaluation
process using progressive validation.
For the analysis we use the progressive validation
procedure, see Figure 3. In this procedure, the test
data arrives one example x
t
at a time. The classifica-
tion algorithm performs its prediction ˆy
t
. Afterwards,
we receive the true label y
t
and we can determine
the correctness of the prediction, i.e. determine if
we made a true positive (predicted ”Target”, received
”Target”), true negative (”Standard”/”Standard”),
false positive (”Target”/”Standard”) or false negative
(”Standard”/”Target”) prediction. The label can be
deduced from the actions of the subject, e.g. if the
buzzer is pressed after a ”Target” stimulus is shown.
The used evaluation metric is the Balanced Accu-
racy, which is defined as the average of the true pos-
itive rate and the true negative rate: BA = 0.5T PR +
0.5T NR. Since the BA operates with rates, it is ap-
plicable when there are different amounts of positive
and negative examples in the data, as is the case here.
To find the optimal model regarding the η up-
date coefficient (and aggressiveness parameter C
for the PA1 and PA2 algorithms), we investi-
gated different values (10
−5
,10
−4
,.. .,1.0 for η, and
Figure 4: Classification performance in the SS setup for the
IR and AR cases and different learning algorithms (see Sec-
tion 3.5 for labels of the algorithms).
10
−5
,10
−4
,. . . , 1.0 for C) and show the best results
for each case.
5 RESULTS
5.1 The Same Subject Setup
We evaluate the performance for the different algo-
rithms regarding the same subject setup. Figure 4
shows the classification performance for different al-
gorithms and IR/AR cases. In most cases, the AR
results in a small increase of the classification perfor-
mance. Figures 5 and 6 show the development of the
classification accuracy over time.
Figures 5 and 6 show the development of the clas-
sification accuracy over time.
5.2 The Different Subject Setup
In this case, we evaluate the performance for the
different algorithms regarding the Different Subject
Setup. Figure 4 shows the classification performance
for different algorithms and IR/AR cases. In the IR
case, a significant drop of the classification perfor-
mance can be observed. This drop can be consider-
ably reduced in the AR case. The temporal develop-
ment of the classification accuracy (Fig.9) rises over
time, if the recalibration is active.
5.3 Differences
We evaluate the performance for the different algo-
rithms regarding the computing hardware. Figs. 10
and 11 shows the classification performance for the
SS and DS setups in the AP case for the SW and
HW architectures. It can be observed that there is a
small decrease in the classification performance in the
hardware-accelerated computations. A possible rea-
son for this effect is the fixed point based arithmetic of
ADataflow-basedMobileBrainReadingSystemonChipwithSupervisedOnlineCalibration-ForUsagewithout
AcquisitionofTrainingData
51
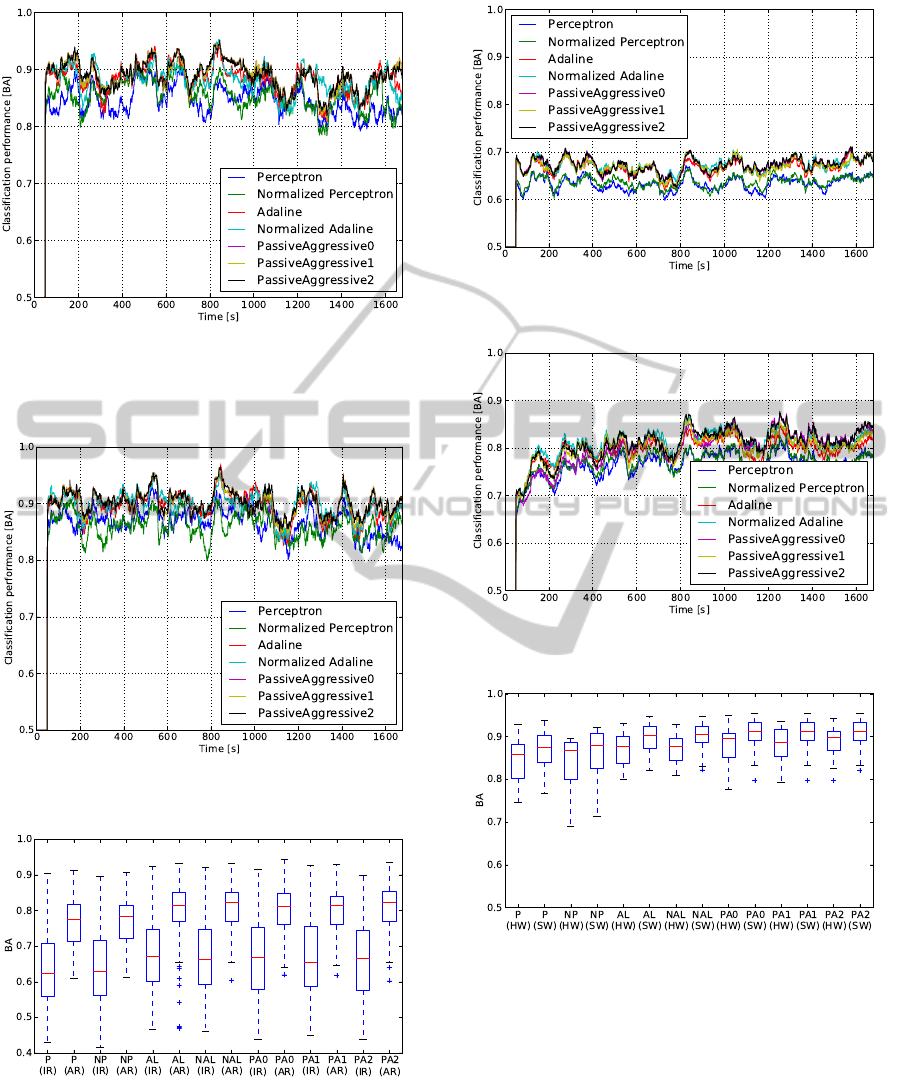
Figure 5: Time-dependent development of the classification
performance in the SS setup in the IR case for different
learning algorithms. The BA value for each algorithm is
the average over 50s and all subjects.
Figure 6: Time-dependent development of the classification
performance in the SS setup in the AR case.
Figure 7: Classification performance in the DS setup for the
IR and AR cases and different learning algorithms.
FPGAs. This effect is under investigation and might
be reduced in the future by applying more sophisti-
cated methods for floating-to-fixed point conversions
and different preprocessing methods.
Figure 8: Time-dependent development of the classification
performance in the DS setup in the IR case.
Figure 9: Time-dependent development of the classification
performance in the DS setup in the AR case.
Figure 10: Classification performance in the SS setup for
the AR case and different learning algorithms for purely
software-based double precision floating point computa-
tions (SW) and hardware accelerated computations (HW).
6 CONCLUSIONS
We presented the first FPGA-based signal processing
and classification SoC which is able to be calibrated
during the actual usage of the system. We showed
that the difference of the classification performance
of the FPGA based fixed point computations and soft-
ware based floating point performance are negligible.
NEUROTECHNIX2013-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
52
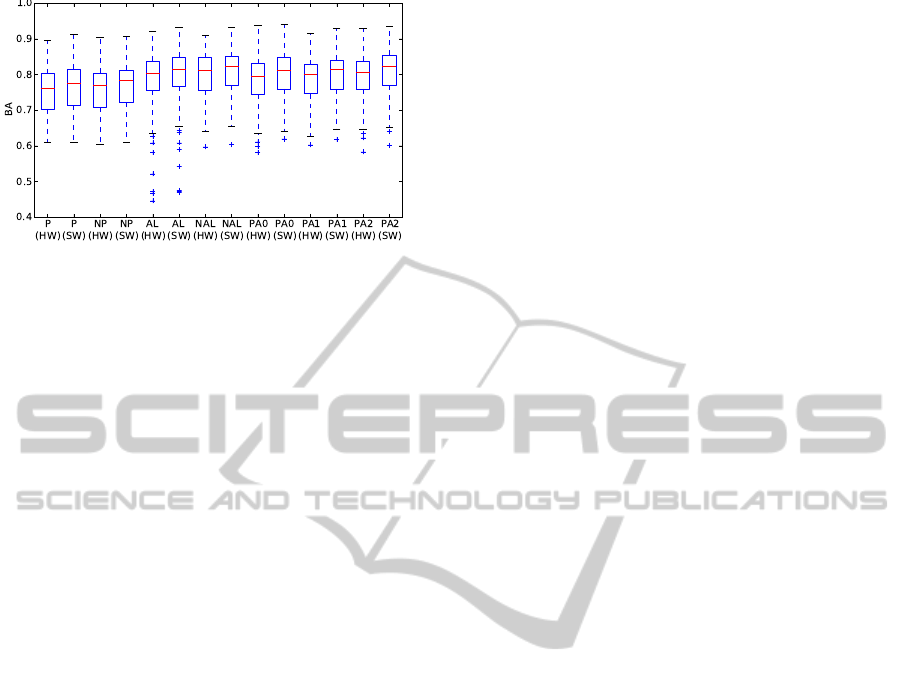
Figure 11: Classification performance in the DS setup for
the AR case and different learning algorithms for purely
software-based double precision floating point computa-
tions (SW) and hardware accelerated computations (HW).
The presented system can be used for the mobile and
portables BCIs or systems that supervise operators
EEG and mental state as it is explained here for an op-
erator surveillance system. In future, we want to im-
prove the calibration methods further, i.e. perform the
recalibration with less training examples, improve the
final classification performance and reduce the effect
of the fixed point arithmetic. Furthermore, we want
to use the system in different scenarios, like the active
control of a robot and apply the presented methodol-
ogy for the runtime calibration of different potentials,
like the Bereitschaftspotential.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was funded by the Federal Ministry of Eco-
nomics and Technology (BMWi, grant no. 50 RA
1012 and 50 RA 1011).
REFERENCES
Crammer, K., Dekel, O., Keshet, J., Shalev-Shwartz, S.,
and Singer, Y. (2006). Online passive-aggressive al-
gorithms. The Journal of Machine Learning Research,
7:551–585.
Farwell, L. A. and Donchin, E. (1988). Talking off the
top of your head: toward a mental prosthesis utiliz-
ing event-related brain potentials. Electroencephalogr.
Clin. Neurophysiol., 70(6):510–23.
Isreal, J., Chesney, G., Wickens, C., and Donchin, E.
(1980). P300 and tracking difficulty: Evidence for
multiple resources in dual-task performance. Psy-
chophysiology, 17(3):259–73.
Khurana, K., Gupta, P., Panicker, R., and Kumar, A.
(2012). Development of an FPGA-based real-time
p300 speller. In 2012 22nd International Confer-
ence on Field Programmable Logic and Applications
(FPL), pages 551 –554.
Kirchner, E. A. and Kim, S. K. (2012). EEG in Dual-Task
Human-Machine Interaction: Target Recognition and
Prospective Memory. In Proceedings of the 18th An-
nual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain
Mapping.
Kirchner, E. A., W
¨
ohrle, H., Bergatt, C., Kim, S. K., Met-
zen, J. H., Feess, D., and Kirchner, F. (2010). Towards
operator monitoring via brain reading – an EEG-based
approach for space applications. In Proc. 10th Int.
Symp. Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automa-
tion in Space, pages 448–455, Sapporo.
Lin, C., Ko, L., Chang, M., Duann, J., Chen, J., Su,
T., and Jung, T. (2009). Review of wireless and
wearable electroencephalogram systems and brain-
computer InterfacesA mini-review. Gerontology.
Linaro (2013). Open source software for arm socs. [Online;
accessed 11-April-2013].
Meyer-Baese, U. (2004). Digital signal processing with
field programmable gate arrays. Springer Verlag.
Polich, J. (2007). Updating P300: an integrative theory of
P3a and P3b. Clin Neurophysiol, 118(10):2128–48.
Rivet, B., Souloumiac, A., Attina, V., and Gibert, G. (2009).
xDAWN algorithm to enhance evoked potentials: ap-
plication to braincomputer interface. Biomedical En-
gineering, IEEE Transactions on, 56(8):20352043.
Shenoy, P., Krauledat, M., Blankertz, B., Rao, R. P. N., and
Mller, K.-R. (2006). Towards adaptive classification
for bci. Journal of Neural Engineering, 3(1):R13.
Shyu, K. K., Lee, P. L., Lee, M. H., Lin, M. H., Lai, R. J.,
and Chiu, Y. J. (2010). Development of a low-cost
FPGA-based SSVEP BCI multimedia control system.
Biomedical Circuits and Systems, IEEE Transactions
on, 4(2):125132.
Wolpaw, J. R., Birbaumer, N., McFarland, D. J.,
Pfurtscheller, G., and Vaughan, T. M. (2002). Brain-
computer interfaces for communication and control.
Clin. Neurophysiol., 113(6):767–91.
Woods, R., McAllister, J., Yi, Y., and Lightbody, G.
(2008). FPGA-based Implementation of Signal Pro-
cessing Systems. Wiley.
ADataflow-basedMobileBrainReadingSystemonChipwithSupervisedOnlineCalibration-ForUsagewithout
AcquisitionofTrainingData
53
