
The Effects of Edge Weights on Correlating Dynamical Networks
Comparing Unweighted and Weighted Brain Graphs of nervus opticus Patients
Christian Moewes and Rudolf Kruse
Faculty of Computer Science, Otto-von-Guericke University, Universit
¨
atsplatz 2, 39106 Magdeburg, Germany
Keywords:
Dynamical Networks, Regression, Vector Autoregression Weighted Graph.
Abstract:
We are interested in the regression analysis of dynamical networks. Our goal is to predict real-valued function
values from a given observation which is manifested as series of graphs. Every observation is described
by a set of dependent variables that we want to predict using the dynamical graphs. These graphs change
their edges over time, while the set of nodes is assumed to be constant. Such settings can be found in many
real-world applications, e.g., communication networks, brain connectivity, microblogging. We apply several
measures to every graph in the series to globally describe its evolution. The resulting multivariate time series
is used to learn vector autoregressive (VAR) models. The parameters of these models can be used to correlate
them with the dependent variables. The graph measures typically depend on the type of edges, i.e., weighted
or unweighted. So do the VAR models and thus the regression results. In this paper we argue that it is
beneficial to keep edge weights in this setting. To support this claim, we analyze electroencephalographic
(EEG) networks from patients suffering from visual field defects. The edge weights are in the unit interval and
might be thresholded. We show that dynamical network models for weighted edges lead to similar regression
performances compared to those of unweighted graphs.
1 INTRODUCTION
Complex networks be constructed from any set of
objects that “interact” with each other. So, based
on the large number different objects with this prop-
erty, complex networks can be found in nearly ev-
ery part of our world, e.g., in social science (Wasser-
mann and Faust, 1994), computer science (Faloutsos
et al., 1999), medicine (Pereira-Leal et al., 2004), bi-
ology (Fischhoff et al., 2007), neuroscience (Sporns,
2010), and the World Wide Web (Kleinberg et al.,
1999). Many researchers in these and other fields
think that the analysis of complex networks may be
useful to extract their intrinsic regularities, causal re-
lations, and other useful pieces of information.
Probably the most complex network in the uni-
verse is the human brain. Since (Varela et al., 2001),
if not earlier, it became very common in neuroscience
to analyze functional networks. One property of these
complex networks is their nature to dynamically—
sometimes even chaotically—change their edges over
time. They are typically obtained from neuroimaging
methods, e.g., electroencephalography (EEG), elec-
trocorticography (ECoG), magnetoencephalography
(MEG), or functional magnetic resonance imaging
(fMRI). These methods record the activity of different
brain regions—on the skull, on the brain meninges, or
even inside the brain.
Whenever two brain regions, i.e., the nodes of the
brain graph, are co-active, they are functionally con-
nected to each other. These connections lead to a
complex brain network which represents a high-level
abstraction of the biological nervous cells. The analy-
sis of these brain networks has already led to a better
understanding of the functionality of different brain
centers and the brain as a whole (Sporns, 2010).
Most research on complex graphs—no matter if
neuroscientific or not—has mainly focused on static
graphs. Such a static network is simply obtained by
averaging the connections over time. Of course, it is
far easier to analyze static networks than a series of
networks. Nevertheless averaging diminishes an im-
portant property, i.e., the dynamics of such complex
networks.
We argue that the dynamical nature of networks
can also be exploited to analyze complex networks
and some of their functions. Some first findings sup-
port this claim, at least for “damaged” human brain
webs: In (Moewes et al., 2013) patients’ EEG has
been correlated to the size of visual field deficits that
279
Moewes C. and Kruse R..
The Effects of Edge Weights on Correlating Dynamical Networks - Comparing Unweighted and Weighted Brain Graphs of nervus opticus Patients.
DOI: 10.5220/0004641402790284
In Proceedings of the 5th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (FCTA-2013), pages 279-284
ISBN: 978-989-8565-77-8
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

resulted from optic nerve damages (W
¨
ust et al., 2002).
The authors identified a relation between the extend
of the vision loss and the dynamics of the functional
brain connectivity. More precisely, the authors of this
paper propose the first model-based approach to cap-
ture the relevant features of a dynamical complex net-
work (Moewes et al., 2013).
In the above-mentioned work of the authors, un-
weighted graphs have been constructed to facilitate
the computation of the network models. There-
fore some patient-independent threshold for the edge
weights had to be identified. The question we ad-
dress in this paper is whether the tedious and some-
what arbitrary choice can be omitted. We thus claim
that it is beneficial to use weighted graphs instead of
unweighted ones.
To support this hypothesis, we analyze the same
kind of EEG networks used in (Moewes et al., 2013).
We apply different thresholds to the weighted edges to
obtain an unweighted graph. Eventually we show that
dynamical network models for weighted edges lead
to similar if not better regression results than those of
unweighted graphs. Thus the tedious and somewhat
arbitrary choice of an edge weight threshold is super-
fluous.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Sec-
tion 2 introduces the concept of dynamical networks
to describe functional brain connectivity. Section 3
describes the experimental setup we have used to
compare the regression performance of weighted and
unweighted graphs. The results of this experiment are
listed in Section 4. Finally, Section 5 concludes the
paper.
2 DYNAMICAL NETWORK
ANALYSIS
Having defined the functional connectivity of two
brain regions, the corresponding dynamical brain net-
work can be obtained. We remark that functional
connectivity is just a statistical relationship between
brain regions without implying any causal coher-
ence (Pearl, 2009). There exist many ways to com-
pute functional connectivity. We refer the interested
reader to (Wendling et al., 2009) for a review on EEG
connectivity measures.
2.1 Synchronization Likelihood
Out of these methods, we have used the synchroniza-
tion likelihood (SL) (Stam and van Dijk, 2002) since
it has been used in the literature to study the relation-
ship between structural network damage and func-
tional connectivity (Stam et al., 2007).
Consider a multivariate time series (e.g. a multi-
channel EEG recording) of length N with n variables.
Let measurement x
i,k
be observed at timestamp i in
channel k. For the SL, a time-delay embedding is
computed by
X
i,k
=
x
i,k
,x
i+L,k
,x
i+2·L,k
,...,x
i+(m−1)·L,k
where L is the lag and m the dimension of the embed-
ding. The state vectors X
i,k
shall capture the relevant
patterns of the signal.
Now consider two channels A,B. The probability
that X
i,k
are closer to each other than ε is
P
ε
i,k
=
1
2(W
2
−W
1
)
N
∑
j
W
1
<|i− j|<W
2
θ(ε − d(X
i,k
,X
j,k
))
where d is the Euclidean distance (or any other dis-
tance measure). For each k and i, a critical distance
ε
i,k
is computed such that P
ε
i,k
i,k
= p
ref
whereas p
ref
1
is some user-defined threshold. For each pair of points
in time (i, j) within W
1
< |i − j| < W
2
, the number of
channels H
i, j
for which d(X
i,k
,X
j,k
) < ε
i,k
is computed
by
H
i, j
= θ(ε
i,A
− d(X
i,A
,X
j,A
)) + θ(ε
i,B
− d(X
i,B
,X
j,B
))
where θ(x) = 0 if x ≤ 0 and θ(x) = 1 for x > 0. Then
the synchronization likelihood is then given by
SL
i
=
1
2p
ref
(W
2
−W
1
)
N
∑
j
W
1
<|i− j|<W
2
(H
i, j
− 1). (1)
Now the final brain graph can be computed. Note that
only two of these the parameters are needed to com-
pute SL if prior information about the frequency range
and temporal resolution of the signal are given (Mon-
tez et al., 2006).
2.2 Graph Measures
We remark that any functional connectivity measure
based on a sliding window will change its value over
time. So do the edge weights of the corresponding
brain graph. In (Moewes et al., 2013) the authors
described these changes by learning how graph mea-
sures evolve.
Therefore we consider a set of different graph
measures, i.e., the number of cliques, the density, and
the squared distance between the current graph and
the previous one (Bunke, 1997).
IJCCI2013-InternationalJointConferenceonComputationalIntelligence
280

2.3 Vector Autoregressive Models
Vector autoregressive (VAR) models (L
¨
utkepohl,
2005) have been shown to capture a high proportion
of variance in these data.
A VAR model with p lags is given by
~x
t
= c +
p
∑
i=1
A
i
~x
t−i
+ ε
t
.
where c is a constant, A
i
is a matrix storing the rela-
tionships between every pair of variable at point t − i,
and ε
t
is white noise. Flattening the coefficients A
i
to a feature vector is beneficial for statistical learning
methods.
3 EXPERIMENTS
In our experiments we used EEG data from 33 vi-
sually impaired subjects suffering from optic nerve
damages (W
¨
ust et al., 2002). For every patient, sev-
eral optometric tests had been performed to describe
the location and the size of the optic nerve damage
for both eyes (Sabel et al., 2011). Among them are
high resolution perimetry (HRP) (Kasten et al., 1998),
static perimetry, kinetic perimetry, and the assessment
of visual acuity (Bailey and Lovie, 1976). Based on
these tests an expert defined the following clinical
variables relevant to quantify the vision loss of both
eyes:
• detection accuracy in HRP visual field (%),
• foveal threshold in static perimetry (dB),
• mean threshold in static perimetry (whole 30
◦
vi-
sual field, dB),
• mean eccentricity in kinetic perimetry (
◦
),
• visual acuity of near vision (LogMAR scale),
• visual acuity of far vision (LogMAR scale).
Nearly every optometric test is very tiring, time-
consuming, and error-prone. Each one of them served
as variable assumed to be depended from the dynam-
ics in the EEG. It is our motivation to find good corre-
lates of the EEG signal and these tests. If successful,
a good prediction model may determine the size of
the optic nerve damage by solely looking at EEG data
that can be recorded much faster.
To preprocess the EEG data we did the following
steps in EEGLAB (Delorme and Makeig, 2004):
• manually removal of noisy time frames at begin-
ning/end of each recording,
• removal of uncommon EEG channels across all
subjects (28 were used),
• high-pass filtering with cutoff frequency at 1 Hz to
remove slow movements,
• notch filtering 50 Hz to remove the European
power line frequency,
• low-pass filtering with cutoff frequency at 95Hz,
• re-referencing by the average electrode,
• down-sampling to 250Hz to reduce the costs of
SL computation,
• manual removal of biological artifacts using in-
dependent component analysis (Makeig et al.,
1996).
Biological artifacts that stem from electromyographic
(EMG) or electrocardiograph (EKG) signal appear as
noise in the recorded EEG signal in all variations. To
remove EMG and ECG signals ICA was applied to
very carefully remove noisy components.
We applied FIR filters to obtain the conventional
frequency bands. They are associated with differ-
ent brain states (Edwards, 2007). These bands are
δ: f ∈ (1, 4] Hz, θ: f ∈ (4,7] Hz, α: f ∈ [8,12] Hz,
β: f ∈ [13,30] Hz, and γ: f ∈ [30, 50] Hz. We ex-
pect the optometric variables to explainable by the dy-
namics of functional connectivity in these frequency
bands. Functional connectivity was computed by
the synchronization likelihood (Stam and van Dijk,
2002): We used an outer window length of W
2
= 3s
and a reference probability of p
ref
= 0.02. To cap-
ture most of the dynamics, the sliding window shifted
every 0.5 s, i.e. an overlay of
1
/6. Note that the analy-
sis of the averaged graphs did not result in any useful
model (Held et al., 2012).
We applied the measures mentioned in Section 2
to every brain graph. We used the Python package
igraph (Cs
´
ardi and Nepusz, 2006) to accomplish this
task. This resulted in a multivariate time series for
each subject and each frequency band. Every time
series was then fitted by a VAR model with p = 1,2
for simplicity. Eventually we obtained p · 3 · 3 = 9 and
18 parameters, respectively, describing the dynamics
of the corresponding multivariate time series.
4 RESULTS
We used ordinary least-squares regression and com-
puted its leave-one-out (LOO) estimation of the true
error. All models have been fit using the Python pack-
ages sklearn (Pedregosa et al., 2011) and statsmod-
els (Seabold and Perktold, 2010). Both the VAR pa-
rameters and the optometric variables have been z-
score normalized, i.e., we subtracted the mean and di-
vided by the standard deviation. The regression per-
TheEffectsofEdgeWeightsonCorrelatingDynamicalNetworks-ComparingUnweightedandWeightedBrainGraphsof
nervusopticusPatients
281
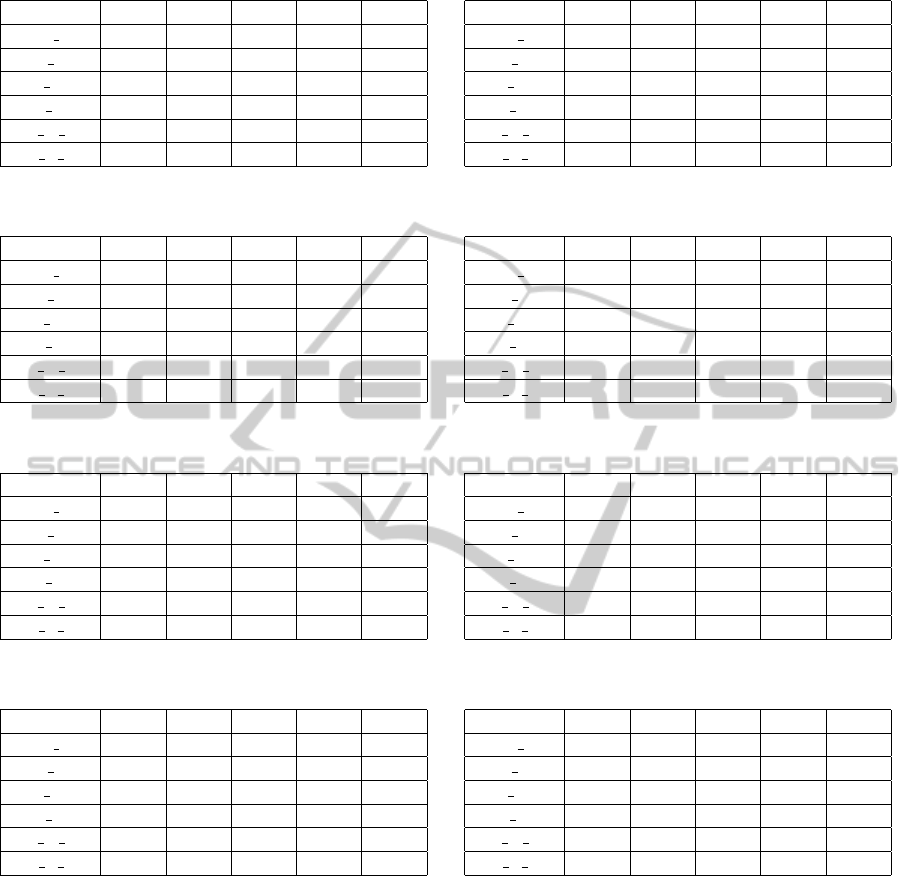
Table 1: Mean-squared errors (MSE) of the VAR models to describe the vision loss of the right eye. The results from the
weighted networks are shown on the left-hand side, the ones from the unweighted network are shown on the right-hand side.
weighted δ θ α β γ
HRP DA 0.963 1.297 1.055 1.403 2.015
SP FT 1.335 1.447 1.330 1.142 1.869
SP MT 1.134 1.542 0.897 1.436 2.087
KP ME 1.259 1.559 1.369 1.354 1.844
VA N log 1.235 1.229 1.385 1.313 1.532
VA F log 1.209 1.283 1.348 1.254 1.431
SL ≥ 0.5 δ θ α β γ
HRP DA 1.337 1.291 1.448 1.204 2.440
SP FT 1.202 0.941 1.571 2.159 1.627
SP MT 1.197 1.140 1.396 2.261 1.949
KP ME 1.318 1.601 1.435 2.329 1.245
VA N log 1.215 1.365 1.483 2.115 1.779
VA F log 1.181 1.411 1.580 2.656 1.411
Table 2: Mean-squared errors (MSE) of the VAR models to describe the vision loss of the right eye. The results from two
unweighted networks that used different thresholds are shown on both sides of the table.
SL ≥ 0.7 δ θ α β γ
HRP DA 1.371 1.580 1.144 1.148 0.979
SP FT 1.314 1.275 1.385 1.070 0.807
SP MT 1.336 1.546 1.282 0.857 1.055
KP ME 1.493 1.518 1.626 0.971 1.081
VA N log 1.270 1.321 1.292 1.183 0.752
VA F log 1.256 1.242 1.325 1.295 0.838
SL ≥ 0.2 δ θ α β γ
HRP DA 0.963 1.485 1.290 1.422 1.187
SP FT 1.335 1.375 1.751 0.992 1.175
SP MT 1.134 1.280 1.130 1.358 1.244
KP ME 1.259 1.459 1.476 1.575 1.428
VA N log 1.235 1.143 1.959 0.733 1.136
VA F log 1.209 1.169 2.199 0.758 1.014
Table 3: Mean-squared errors (MSE) of the VAR models to describe the vision loss of the left eye. The results from the
weighted networks are shown on the left-hand side, the ones from the unweighted network are shown on the right-hand side.
weighted δ θ α β γ
HRP DA 1.580 1.572 1.450 1.629 1.397
SP FT 1.511 1.239 1.089 1.873 1.647
SP MT 1.259 1.559 1.369 1.354 1.844
KP ME 1.534 1.103 1.305 1.456 1.471
VA N log 1.541 1.140 1.298 2.193 1.578
VA F log 1.425 1.117 1.433 1.913 1.682
SL ≥ 0.5 δ θ α β γ
HRP DA 1.164 0.760 1.398 1.217 1.054
SP FT 1.490 1.178 1.253 1.368 1.434
SP MT 1.080 1.021 1.065 1.109 1.189
KP ME 1.286 1.011 1.221 1.047 1.222
VA N log 1.568 1.064 1.299 1.328 1.347
VA F log 1.551 1.465 1.412 1.527 1.359
Table 4: Mean-squared errors (MSE) of the VAR models to describe the vision loss of the left eye. The results from two
unweighted networks that used different thresholds are shown on both sides of the table.
SL ≥ 0.7 δ θ α β γ
HRP DA 1.357 1.259 1.401 0.665 3.353
SP FT 1.423 1.524 1.283 1.698 1.412
SP MT 1.230 1.267 1.122 1.502 1.056
KP ME 1.283 0.987 1.324 1.037 0.992
VA N log 1.484 1.173 1.413 1.520 1.391
VA F log 1.454 1.325 1.387 1.414 1.378
SL ≥ 0.2 δ θ α β γ
HRP DA 1.580 0.967 1.174 1.755 1.783
SP FT 1.511 1.128 1.451 1.166 1.234
SP MT 1.291 0.931 0.745 1.344 1.367
KP ME 1.534 1.106 1.471 1.651 1.299
VA N log 1.541 1.091 1.726 1.367 1.124
VA F log 1.425 1.257 1.717 1.340 1.240
formance of the normalized data was measured by the
mean-squared error (MSE).
Tables 1 and 2 on the next page summarize our
analyzes for the right eye. Weighted networks lead to
MSE that are competitive to the ones of the thresh-
olded networks. For low-frequency bands (i.e., δ,
θ, α), the weighted networks produce even smaller
errors. This is in line with the previous results in
(Moewes et al., 2013) where 8 subjects less have been
used. Equivalently, the results for the left eye are
shown in Tables 3 and 4. They do confirm the find-
ings.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We have advocated not to threshold edge weights
when analyzing dynamical networks. The choice of
a threshold to obtain an unweighted graphs can be
omitted if the graphs are used for regression models.
To show this we have analyzed EEG networks from
patients suffering from visual field defects. We have
thresholded the edge weights using several different
values. Still, the models describing the weighted dy-
namical network lead to similar errors compared to
those of unweighted graphs.
IJCCI2013-InternationalJointConferenceonComputationalIntelligence
282

We plan to enlarge the data set to further increase
the quality of our models. We also want to establish a
way to combine the optometric tests of both eyes. A
comparison of brain networks to classical EEG rep-
resentations is in preparation. Furthermore we are
working on the creation of different data sets, e.g.,
communication networks and microblogs, to general-
ize our findings.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The first author thanks Carolin Gall and her students
from the Medical Faculty for collecting the EEG data.
We give thanks to Hermann Hinrichs from the Medi-
cal Faculty for pointing out several hints to preprocess
the EEG data. Last not least we thank Bernhard A.
Sabel and Michał Bola for fruitful discussions while
preparing this paper.
REFERENCES
Bailey, I. L. and Lovie, J. E. (1976). New design principles
for visual acuity letter charts. Am J Optom Physiol
Opt, 53(11):740–745.
Bunke, H. (1997). On a relation between graph edit distance
and maximum common subgraph. Pattern Recognit
Lett, 18(8):689–694.
Cs
´
ardi, G. and Nepusz, T. (2006). The igraph software
package for complex network research. InterJournal
Complex Systems, 1695.
Delorme, A. and Makeig, S. (2004). EEGLAB: an open
source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dy-
namics including independent component analysis. J
Neurosci Methods, 134(1):9–21.
Edwards, E. (2007). Electrocortical Activation and Human
Brain Mapping. PhD thesis, University of California,
Berkeley, CA, USA.
Faloutsos, M., Faloutsos, P., and Faloutsos, C. (1999).
On power-law relationships of the internet topology.
In Proceedings of the conference on Applications,
technologies, architectures, and protocols for com-
puter communication, SIGCOMM ’99, pages 251–
262, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Fischhoff, I. R., Sundaresan, S. R., Cordingley, J., Larkin,
H. M., Sellier, M., and Rubenstein, D. I. (2007).
Social relationships and reproductive state influence
leadership roles in movements of plains zebra, equus
burchellii. Anim Behav, 73(5):825–831.
Held, P., Moewes, C., Braune, C., Kruse, R., and Sabel,
B. A. (2012). Advanced analysis of dynamic graphs in
social and neural networks. In Borgelt, C., Gil, M.
´
A.,
Sousa, J. M. C., and Verleysen, M., editors, Towards
Advanced Data Analysis by Combining Soft Comput-
ing and Statistics, pages 205–222. Springer-Verlag.
Kasten, E., Wst, S., Behrens-Baumann, W., and Sabel, B. A.
(1998). Computer-based training for the treatment of
partial blindness. Nat Med, 4(9):1083–1087.
Kleinberg, J. M., Kumar, R., Raghavan, P., Rajagopalan,
S., and Tomkins, A. S. (1999). The web as a graph:
measurements, models, and methods. In Proceedings
of the 5th annual international conference on Com-
puting and combinatorics, COCOON’99, pages 1–17,
Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
L
¨
utkepohl, H. (2005). New Introduction to Multiple Time
Series Analysis. Econometrics / Statistics. Springer-
Verlag, Berlin / Heidelberg, Germany.
Makeig, S., Bell, A. J., Jung, T., and Sejnowski, T. J. (1996).
Independent component analysis of electroencephalo-
graphic data. In Touretzky, D. S., Mozer, M. C.,
and Hasselmo, M. E., editors, Advances in Neural In-
formation Processing Systems, volume 8, pages 145–
151, Cambridge, MA, USA. MIT Press.
Moewes, C., Kruse, R., and Sabel, B. A. (2013). Analysis of
dynamic brain networks using var models. In Kruse,
R., Berthold, M. R., Moewes, C., Gil, M.
´
A., Grze-
gorzewski, P., and Hryniewicz, O., editors, Synergies
of Soft Computing and Statistics for Intelligent Data
Analysis, pages 525–532. Proc. of the 6th Int’l Conf.
on Soft Methods in Probability and Statistics (SMPS-
2012), 4–6 Oct. 2012, Konstanz, Germany.
Montez, T., Linkenkaer-Hansen, K., van Dijk, B. W.,
and Stam, C. J. (2006). Synchronization likelihood
with explicit time-frequency priors. Neuroimage,
33(4):1117–1125.
Pearl, J. (2009). Causal inference in statistics: An overview.
Stat Surv, 3:96–146.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, and et al. (2011).
Scikit-learn: Machine learning in python. JMLR,
12:2825–2830.
Pereira-Leal, J. B., Enright, A. J., and Ouzounis, C. A.
(2004). Detection of functional modules from protein
interaction networks. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinf,
54(1):49–57.
Sabel, B. A., Fedorov, A. B., Naue, N., Borrmann, A., Her-
rmann, C., and Gall, C. (2011). Non-invasive alternat-
ing current stimulation improves vision in optic neu-
ropathy. Restor Neurol Neurosci, 29(6):493–505.
Seabold, S. and Perktold, J. (2010). Statsmodels: Econo-
metric and statistical modeling with python. In van der
Walt, S. and Millman, J., editors, Proceedings of the
9th Python in Science Conference (SciPy 2010), pages
57–61.
Sporns, O. (2010). Networks of the Brain. MIT Press, Cam-
bridge, MA, USA.
Stam, C., Jones, B., Nolte, G., Breakspear, M., and Schel-
tens, P. (2007). Small-World networks and functional
connectivity in alzheimer’s disease. Cerebral Cortex,
17(1):92–99.
Stam, C. J. and van Dijk, B. W. (2002). Synchronization
likelihood: an unbiased measure of generalized syn-
chronization in multivariate data sets. J Phys D: Non-
linear Phenom, 163(3-4):236–251.
Varela, F., Lachaux, J., Rodriguez, E., and Martinerie, J.
(2001). The brainweb: phase synchronization and
TheEffectsofEdgeWeightsonCorrelatingDynamicalNetworks-ComparingUnweightedandWeightedBrainGraphsof
nervusopticusPatients
283

large-scale integration. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2(4):229–
239.
Wassermann, S. and Faust, K. (1994). Social Network Anal-
ysis: Methods and Applications, volume 8 of Stuctural
Analysis in the Social Sciences. Cambridge University
Press, Cambridge, UK.
Wendling, F., Ansari-Asl, K., Bartolomei, F., and Senhadji,
L. (2009). From EEG signals to brain connectivity: A
model-based evaluation of interdependence measures.
J Neurosci Methods, 183(1):9–18.
W
¨
ust, S., Kasten, E., and Sabel, B. A. (2002). Blindsight af-
ter optic nerve injury indicates functionality of spared
fibers. J Cogn Neurosci, 14(2):243–253.
IJCCI2013-InternationalJointConferenceonComputationalIntelligence
284
