
Human-like Sensor Fusion Mechanisms in a Postural Control Robot
Georg Hettich, Vittorio Lippi and Thomas Mergner
Neurocenter, Neurological University Clinic, Breisacher Str. 64, 79106 Freiburg, Germany
Keywords: Sensor Fusion, Postural Control, Sensory Feedback, Humanoid Robot.
Abstract: In humans, maintaining body posture is a basis for many activities such as standing, walking or reaching.
Human posture control involves multi-sensory integration mainly of joint angle, joint torque, vestibular and
visual inputs. This integration provides humans with high flexibility and with robustness in terms of fail-
safety. Roboticists may draw inspirations from the human control methods when building devices that
interact with humans, such as prostheses or exoskeletons. This study presents a multisensory control method
derived from human experiments, which is re-embodied in a biped postural control robot. The robot uses
ankle and hip joints for balancing in the sagittal plane during external disturbances such as support surface
motion. For the balancing, the robot estimates the external disturbances that have impact on its body by
fusing the sensory signals. It then uses these estimates in negative feedback to command the local joint
controls to compensate for the disturbances. This study describes the human sensor fusion mechanisms and
their implementation into the robot, and it compares robot and human responses to support surface tilt.
Measured balancing responses of the robot resemble in the main characteristics those of the human subjects,
suggesting that the described sensor fusion mechanisms capture important aspects of human balancing.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sensors play a fundamental role in the sensorimotor
behaviors of animals and humans. Use of sensors
offloads computational burdens to the periphery and
early processing stages of the central nervous system
(CNS; e.g. Wehner, 1987). Furthermore, fusion of
sensory data represents an important step in the
perceptual reconstruction of the external world
events having impact on the body (Mergner, 2002).
Motion control of mechatronic systems, such as
humanoid robots, still face many unsolved research
problems, therefore roboticists show an increasing
interest to unravel the human sensorimotor control,
together with neuroscientists. This research aims to
adopt principles from biological signal processing
and sensorimotor control in humanoid robots, so that
these can (i) show more human-like characteristics
such as robustness in terms of fail-safety, versatility,
and energy efficiency; (ii) show mechanical
compliance to ensure safety in human-robot
interactions; and (iii) serve as guidelines for
constructing medical devices such as neural
prostheses and exoskeletons.
Neuroscientists often distinguish between
proactive and reactive sensorimotor control. The
term proactive refers to feed forward control of
voluntary actions, dealing with foreseen or self-
produced disturbances. The term reactive refers to
sensory feedback control in response to unforeseen
disturbances. A prototype of reactive control is
balancing of upright posture during unforeseen
external disturbances. Human control of this posture
involves sensory feedback mainly from joint
proprioception, vestibular system and vision (see
Horak and MacPherson, 1996). The underlying
neural sensor fusion mechanisms, often called multi-
sensory integration, allow humans to adapt posture
control to changes in the environment and to the
availability of sensory information. Depending on
the external conditions, the relative contributions of
sensors to balance vary considerably, which has
been called ‘sensory reweighting’ (Nashner and
Berthoz, 1978); (Peterka, 2002); (Mergner et al.,
2003); (Maurer et al., 2006); (van der Kooij and
Peterka, 2011). The sensory integration and
reweighting mechanisms are still the topic of on-
going research. This paper presents a novel posture
control concept that builds mainly on sensor fusion
mechanisms and is currently implemented in a
humanoid robot that balances even when subjected
to changing external disturbances.
Previous bipedal robots that perform sensor
152
Hettich G., Lippi V. and Mergner T..
Human-like Sensor Fusion Mechanisms in a Postural Control Robot.
DOI: 10.5220/0004642701520160
In Proceedings of the International Congress on Neurotechnology, Electronics and Informatics (SensoryFusion-2013), pages 152-160
ISBN: 978-989-8565-80-8
Copyright
c
2013 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

fusion often used Kalman filters for multisensory
integration (Tahboub and Mergner, 2007);
(Mahboobin et al., 2008); (Klein et al., 2011).
Corresponding simulation models of sensor fusion in
the postural control also used Kalman filters (van
der Kooij et al., 1999); (Kuo, 2005). Common to
these models is a ‘sensory integration center’ in
which multiple sensory signals are combined with
centrally generated information (‘efference copy’).
The aim of combining this information is to find the
most accurate sensory representation for a given
environmental situation. These solutions were
primarily inspired by the technical evolution rather
than the biological evolution.
A different approach was used by Mergner and
colleagues (Mergner et al., 2003); (Maurer et al.,
2006); (Mergner, 2010). These authors investigated
fusion of vestibular and proprioceptive sensory
signals in human psychophysical experiments on
self-motion perception using an open loop systems
analysis approach. They found that humans use
several processing steps to combine the signals,
which originate from several sensory transducers
and finally result in a few estimates of the external
disturbances that have an impact on body posture.
The underlying fusion mechanisms are rather
simple, in that they don’t require use of a full
dynamic model of human biomechanics and of
iterative processing.
The inferred fusion mechanisms were then
implemented into a stance control model, having in
mind that normally a high congruency between
perception and action exists (Mergner, 2002). In
model simulation, a close correspondence between
simulated and experimentally observed postural
responses to external disturbances has then been
observed (Mergner et al., 2003); (Maurer et al.,
2006). Noticeably, the implemented sensor fusion
mechanisms provide a means for automatic sensory
re-weightings and for reducing effects of sensory
noise. The model was implemented and successfully
tested so far on a 1 degree of freedom (DOF) robot
with ankle joint actuation (Posturob I; Mergner et
al., 2009).
The implementation of human-inspired posture
control concepts in this robot mimics to a large
extent the human balancing of moderate external
disturbances in the sagittal plane, which uses mainly
the ankle joints (‘ankle strategy’; Nashner and
McCollum, 1985); (Horak and Nashner, 1986). The
simplification of human biomechanics as a single
inverted pendulum (SIP) was also helpful in
modeling studies (e.g. Peterka, 2002). However, the
SIP simplification is no longer applicable when
humans use other joints in addition to the ankle
joints, such as the hip joints, as one typically
observes when strong transient disturbances are
applied (‘hip strategy’; Nashner and McCollum,
1985); (Horak and Nashner, 1986).
In this study we extend the human-inspired
postural control model to deal with the double
inverted pendulum (DIP) biomechanics of humans
and a 2 DOF robot (hip and ankle joint). The focus
is here, however, not so much on involving the hip
joints during strong disturbances, but rather another
aspect. During many activities such as walking, the
secondary task ‘head stabilization in space’ is
superimposed on the primary task of maintaining
equilibrium using the ankle joints. This secondary
task uses the hip joint to maintain a given trunk (and
head) orientation in space to stabilize the
workspaces of gaze, arms and hands and is thought
to improve under dynamic conditions sensory
feedback from the vestibular and visual cues arising
in the head (Bronstein, 1988); (Pozzo et al. 1991).
In the following, a model of sensorimotor control
is explained, which was used to interpret human SIP
balancing responses around the ankle joints. Then
the concept is extended to control a DIP by
including the hip joints. The implementation of the
control model into a humanoid robot and the
comparison between robot and human subjects is
described. In the final section, it is concluded that
the human-inspired sensorimotor control concept
can be used in the form of a modular control
architecture for humanoid robots that are expected to
show human-like characteristics when interacting
with humans behaviorally or in the form of
prostheses or exoskeletons.
2 METHODS
A model for controlling hip and ankle joint torques
during balancing of external disturbances was
developed using human-inspired sensor fusion
mechanisms. These fusion mechanisms provide
estimates of the external disturbances, which are
used for disturbance compensation by feeding back
the estimates rather than the raw sensory signals
(disturbance estimation and compensation, DEC,
concept). First, the sensor fusion underlying the
DEC concept will be briefly reviewed.
2.1 Basic Aspects of Sensor Fusion in
the DEC Concept
The DEC concept involves essentially two steps of
Human-likeSensorFusionMechanismsinaPosturalControlRobot
153

fusion. In the first step, information from several
sensory transducers is fused to obtain measures of
physical kinematic and kinetic variables. In the
second step, these physical variables are combined
to yield estimates of the external disturbances.
2.1.1 Sensory Transducer Data Fusion
An example of the first step is the human sense of
joint angle proprioception. It combines information
from several sensory transducers such as muscle
spindles, Golgi Tendon organs and cutaneous
receptors (Gandevia et al., 2002). Also the human
perception of head on trunk rotation is derived from
such combinations, even with rotations across
several segments of the cervical vertebral column.
The result is a sense of angular head-on-trunk
velocity and position, as if a rate sensor and a
goniometer were measuring head-trunk rotation and
speed about a single joint (Mergner et al., 1983);
(Mergner et al., 1991).
Another example for the first step, better known
to engineers, is the fusion of angular and linear
accelerometers in an inertial measuring unit (IMU).
There is a problem with linear accelerometers, as
they do not distinguish between inertial and
gravitational forces (i.e. between linear acceleration
and tilt of the sensor). There is also a problem with
angular accelerometers (often used in the form of
gyroscopes that measure angular velocity), as they
show signal drifts over time. Both problems can be
solved for the earth vertical planes by fusing the
inputs from the two sensors in an appropriate way.
This has an analogy in the human vestibular system
that is located in the inner ears. Its otholith organs
and canal systems represent biological equivalents
of linear and angular accelerometers, respectively
(Mergner et al., 2009). The canal-otolith and gyro-
accelerometer fusions require information of the
gravitational vector, however. Therefore, spatial
orientation in the horizontal translational and
rotational planes requires further information. In
technical systems, often a Global Positioning System
(GPS) is used. Humans usually use the visual system
for this specific purpose.
In the following we will speak of joint angle and
angular velocity sensors and mean corresponding
virtual sensors that result from step one. The same
applies when we refer to the vestibular sensor and its
three output measures, i.e. 3D angular velocity and
linear acceleration in space and orientation with
respect to the gravitational vertical. It is known from
animal studies that neural signals coding local and
global physical variables already exist in low
processing levels of the CNS such as the spinal cord
(Bosco and Poppele, 1997; Poppele et al., 2002).
The measures of the physical variables represent the
inputs to the second step of sensor fusion.
2.1.2 Disturbance Estimation
In the second step, the signals of these variables are
combined to reconstruct disturbances that have
impact on the body. This step was motivated by
reports of human subjects in the psychophysical
experiments and by simple plausibility related to
mechanics. An example from the psychophysical
experiments is that a subject, asked to report his
percept when passively turned on a rotation chair, is
typically not reporting a sensation of head in space
rotation stemming from the vestibular system, but a
rotation of the chair, which is the underlying cause
of the head rotation. Without being aware of it, the
subject internally reconstructs the physical cause by
using the vestibular head-in-space signal and
combines it with proprioceptive information on the
trunk rotation relative to the head, thereby obtaining
the percept of trunk in space rotation, which during
sitting is in haptic connection with the chair. This
percept can formally be described in terms of a
coordinate transformation by which the trunk is
referenced to the vestibular derived notion of space
(Mergner et al., 1997).
Another intuitive example of a reconstruction of
an external disturbance by sensor fusion in step two
concerns gravity as a field force. For field forces in
general, it is known that subjects presented with a
new aspect of a field force perceive and readily learn
to counteract its impact on the body and then no
longer perceive it consciously (Lackner and DiZio,
1994). Considering specifically gravity, during body
lean it tends to accelerate the body away from the
vertical. Stabilizing the body posture then requires a
compensatory ankle torque. With small body
excursions, this torque is proportional to the body
COM angle in space. On the sensory side, the body
lean is directly measured by the vestibular system.
Knowing the vestibular signal, the body mass and
the COM height, the gravitational ankle torque can
be estimated and directly compensated. As before
with the estimation of a rotation of the chair (support
surface), neck proprioceptive signals allow to
reference the body lean to the vestibular notion of
space.
Interestingly, it suffices to add to the just
described two disturbances, i.e. to (a) support
surface rotation and (b) field forces such as gravity,
two more disturbances, which are (c) support surface
NEUROTECHNIX2013-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
154
translational acceleration and (d) contact forces such
as a push or pull, in order to cover all the external
disturbances that may have impact on the body
during balancing. The latter two external
disturbances also can be estimated by sensor fusion
in simple, non-iterative ways (Mergner, 2010).
Furthermore, it was shown that the four estimates
may be implemented in a feedback control to
compensate for the disturbances.
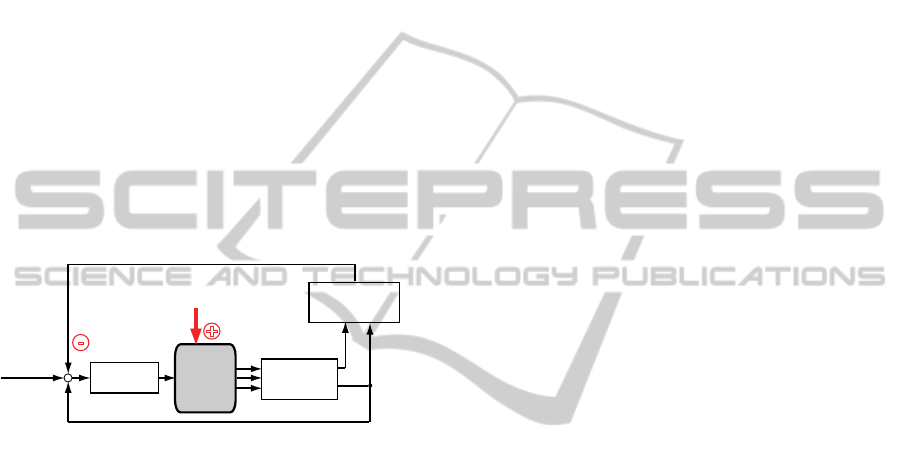
Implementation of both steps of sensory fusion
into a feedback model is shown schematically in
Figure 1. The figure shows that the first fusion step
(Transducer Fusion) applies to two distinct feedback
loop systems. In the lower loop of the scheme, it
provides a kind of local state feedback in the form of
a proprioceptive signal of joint angle. In addition,
the first fusion step provides inputs to the upper loop
system where the external disturbances are estimated
using the second fusion step (Disturbance
Estimation).
Figure 1: Simplified scheme of the Disturbance Estimation
and Compensation (DEC) concept.
The lower loop in Figure 1 represents a short-
latency local mechanism for regulating a joint in the
form of a simple ‘servo control’. It receives a
voluntary input signal (Set Point Signal) of the
desired joint position. The controller (with a
proportional and a derivative factor; PD controller)
provides the motor command that is transformed by
the muscles (not shown) into joint torque. Passive
stiffness and viscosity, stemming from intrinsic
properties of the musculoskeletal system contribute
a minor part to the joint torque (also not shown).
Proprioceptive feedback, biomechanics, and
controller values are adjusted to account for the
moment of inertia of the plant such that the actual
displacement trajectory corresponds to the desired
trajectory. Therefore, no feed forward of plant
dynamics (e.g. through an inverse of plant
dynamics) is required.
Noticeably, the P and D factors identified in
human stance control experiments (Peterka, 2002;
Alexandrov et al., 2005; Maurer et al., 2006) are
surprisingly low. In a SIP scenario, they appear to be
geared to the body mass m of the pendulum, the
height h of the mass and gravitational acceleration g
(mgh; P ≈ mgh; D ≈ mgh/4). The human identified
values are only slightly higher than these values.
The upper loop in Figure 1 stands for a more
time consuming feedback loop from the disturbance
estimates (identified lumped time delay of both loop
systems, ≈180 ms; Peterka, 2002); (Maurer et al.,
2006). The upper loop commands the servo loop to
compensate the effects that the external disturbances
have on the body (note that sign of upper loop is
opposite to that of the disturbances). By this, for
example, the gravitational torque in the SIP joint is
compensated for, in that the corresponding estimate
commands the servo accordingly. The loop gain (at
the level of the controller) is raised by this additional
feedback. However, this increase occurs only at the
time of the disturbance and to the extent of its
impact. Interestingly, the compensation applies even
with superposition of several disturbances as well as
with superposition of the disturbances with
voluntary movements (Mergner et al., 2009).
It has been shown by comparisons between
human data and model simulations that the DEC
concept describes the human balancing in a variety
of disturbance scenarios. This even applied when the
model was implemented in a 1 DOF humanoid robot
(PostuRob I), including human time delays, and was
tested in the human laboratory (overview Mergner,
2010). These testings demonstrated that the control
method is robust against real world problems such as
inaccurate and noisy sensors, mechanical dead
zones, etc.
2.2 Sensor Fusion in Hip and Ankle
Joints
Current work on the DEC concept, described below,
deals with the questions (1) how the disturbance
estimates and their compensation might deal with
the DIP biomechanics, (2) how the head/trunk
stabilization task is achieved, (3) how inter-
segmental coupling torques are dealt with, and (4)
how movement synergies are generated in the DEC
control. The approach proceeds from the assumption
that the DEC concept is realized in a multi-
segmental system in the form of a modular control
architecture. By controlling each DOF with one
DEC module, the whole control would be easily
scalable to changes in the number of DOFs.
2.2.1 Dip Biomechanics
The DIP biomechanical model is shown in Figure 2.
-
-
Disturbance Compensation
+
External
Disturbances
Proprioceptive Feedback
Controller
Plant
Disturbance
Estimation
Set Point
Signal
Transducer
Fusion
Human-likeSensorFusionMechanismsinaPosturalControlRobot
155

In Figure 2A, COM
T
, COM
L
and COM
B
stand for the
COM of the trunk, leg and whole body, respectively.
Leg length is given by l
L
, the trunk and leg COM
heights are given by h
T
and h
L
, respectively. Figure
2B shows the angular excursion of the trunk and leg
segments with respect to earth vertical (trunk-space
angle α
TS
, leg-space angle α
LS
). Angular excursion of
COM
B
is defined as body-space angle α
BS
. The foot
has firm contact with the support surface, therefore
platform tilt angle equals foot angle with respect to
earth horizontal (foot-space angle α
FS
). The trunk-
leg joint angle is α
TL
and the leg-foot joint angle is
α
LF
. In perfectly erect position all angles are 0°.
Angular speed during reactive human balancing can
be assumed to be slow enough such that the Coriolis
and centrifugal forces can be neglected; the model
can be linearized using the small angle
approximation, assuming that the subject is
maintaining his upright position close to the vertical.
Figure 2: DIP biomechanics.
Maintaining upright stance in the situation of a
support surface tilt in the sagittal plane requires
corrective joint torque in the ankle and hip joints.
This torque can be expressed by the following
equations for hip torque T
H
∝
∝
∝
,
(1)
and for ankle torque T
A
∝
∝
∝
∝
∝
(2)
where ∝
, ∝
and ∝
represent angular
accelerations, g is the gravitational acceleration, m
L
and m
T
are the segment masses, and J
L
and J
T
the
segment moments of inertia (details in AlBakri,
2008).
In the DEC concept for the DIP, the hip joint is
used for balancing the head-trunk segment and the
ankle joint for balancing the whole-body using two
separate controls. The co-operation between the two
joint controls is achieved by extending the afore-
mentioned second step of sensory fusion in a form
that the control of the lower segments benefits from
the fusion in the upper control and, vice versa, the
upper control benefits from the fusion in the lower
control.
The vestibular signals used for controlling the
DIP are: the trunk-space angle ∝
, trunk-space
angular velocity ∝
and head translational
acceleration
. The proprioceptive signals are:
the trunk-leg angle ∝
and the trunk-leg angular
velocity ∝
; the leg-foot angle ∝
and the leg-foot
angular velocity ∝
. Uppercase letters in the angle
subscripts were used to indicate physical angles,
while lowercase letters were used to indicate sensory
derived representations of the same angles.
2.2.2 Hip Joint Control
The control of the trunk segment at the hip joint
reflects a DEC control as described above for the
SIP biomechanics. In the considered support surface
tilt scenario, the leg segment is not perfectly
stabilized in space, but rotates somewhat with the
platform. Because the legs represent the support
base for the trunk, their rotation causes the following
disturbances in the hip joint:
(a) Tilt of the support base for the trunk during leg
rotation,
. Intrinsic properties of the
musculoskeletal system (passive stiffness and
viscosity) then generate a hip torque that tends to
move the trunk along with the legs (
_
).
(b) Hip translational acceleration x
during the leg
rotation. This tangential acceleration produces a
hip torque in relation to the trunk’s moment of
inertia (T
_
). Here treated as if it were an
external disturbance rather than an inter-
segmental coupling effect.
(c) Gravitational hip torque (T
_
) arises when the
trunk is rotated off the vertical.
The three disturbances are estimated by the sensor
fusion mechanisms in the DEC-based module of the
hip (Figure 3) in the following form:
(i) Estimation of leg tilt ∝
. This estimate is
derived from fusing the vestibular velocity signal
∝
with the proprioceptive velocity signal ∝
in the
form of ∝
∝
∝
. (Assumption: such
NEUROTECHNIX2013-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
156
coordinate transformations are performed as vector
summations separately for the three body planes).
The estimate ∝
is obtained by applying to the
signal a detection threshold and a mathematical
integration.
(ii) Estimation of hip translational acceleration
. The estimate is derived from fusing vestibular
signals ∝
and
in the form
∝
.
(3)
This kinematic estimate
is, in turn, used to
estimate the inertial disturbance torque in the form
of
_
.
(4)
(iii) Estimation of gravitational hip torque
_
. Using the vestibular signal ∝
,the third
term of equation (1) becomes
_
∝
.
(5)
2.2.3 Ankle Joint Control
This balance control stabilizes the whole body above
the ankle joint, which includes the leg and the trunk
segments. Correspondingly, the ankle DEC-based
module combines the leg and trunk angular
excursions in the form of whole-body COM
excursion in space, ∝
. In this respect, also the
DEC module for the ankle joint can be viewed as
dealing with a SIP. The three disturbances that have
impact on the ankle torque during support surface
tilts are:
(a) The support surface tilt
. It evokes the passive
ankle torque
_
.
(b) The gravitational ankle torque
_
. It arises
from COM
B
angular excursion in space ∝
.
(c) Inter-segmental coupling torque in the ankle joint
_
. It arises through angular acceleration of
the trunk segment.
For disturbance estimation, the ankle joint DEC
module fuses sensory signals from the vestibular
system and the hip and ankle joint proprioception.
To this end, sensory signals from the hip DEC
module are transmitted (“down-channeled”) to the
ankle joint DEC module. This leads to the following
disturbance estimates:
(i) Estimation of foot-space rotation ∝
. This
estimate uses a down-channeled version of ∝
and
combines it with the ankle joint velocity signal ∝
in the form
∝
∝
∝
.
(6)
Analogous to the hip module, the estimate ∝
is
obtained by applying to the signal a detection
threshold and a mathematical integration.
(ii) Estimation of gravitational ankle torque
_
. This estimate relates to the fourth and fifth
terms of equation (2), which are mathematically
combined in the COM
B
excursion ∝
. From this,
the gravitational torque is obtained as follow
_
∝
(7)
where m
B
represents whole-body mass and h
B
COM
B
height. Small angular excursions allow
approximating h
B
by a constant value.
(iii) Estimation of the inter-segmental coupling
torque
_
. This torque arises upon rotational
acceleration of the trunk and evokes a leg counter-
motion. It may be estimated on the basis of the first
three terms of equation (2). Previous work showed,
however, that leg motion in the same direction
already results from stabilizing the COM
B
, often
referred to as trunk-leg synergy (compare
Alexandrov et al., 2005). This suggests, and model
and robot simulation confirm that one can refrain
from compensating this torque, at least in the
framework of the human balancing (Hettich et al.,
2011).
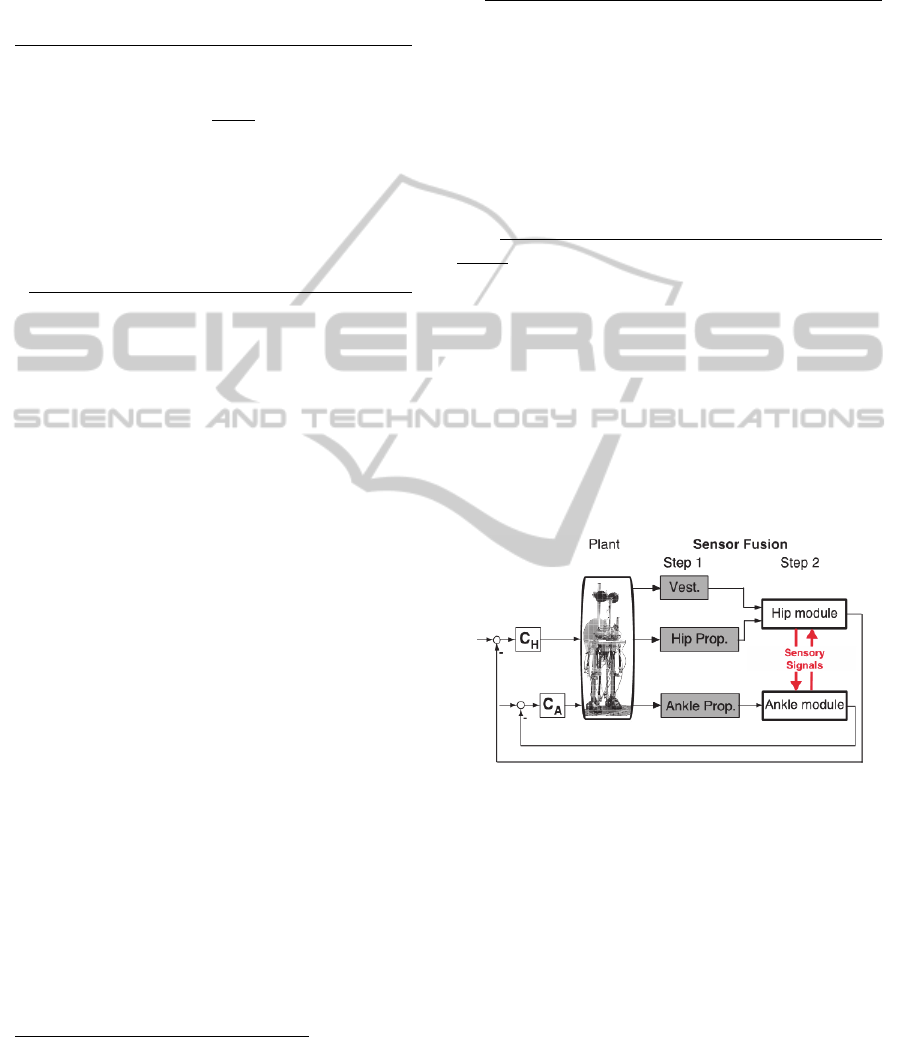
Figure 3: Basic aspects of control concept of PostuRob II.
C
H
and C
A
are hip and ankle controllers, Vest. is the
vestibular input while Hip Prop. and Ankle Prop. are the
proprioceptive inputs.
The combination of the hip and ankle control
modules and the mutual exchange of sensory
information are shown schematically in Figure 3.
Details of the “up-channeled” sensory information
will be given in a forthcoming publication.
2.3 PostuRob II
The two-module control concept was implemented
in PostuRob II. This robot consists of mechanical,
mechatronic, and computer control parts. The
mechanical part comprises one trunk segment, two
Human-likeSensorFusionMechanismsinaPosturalControlRobot
157
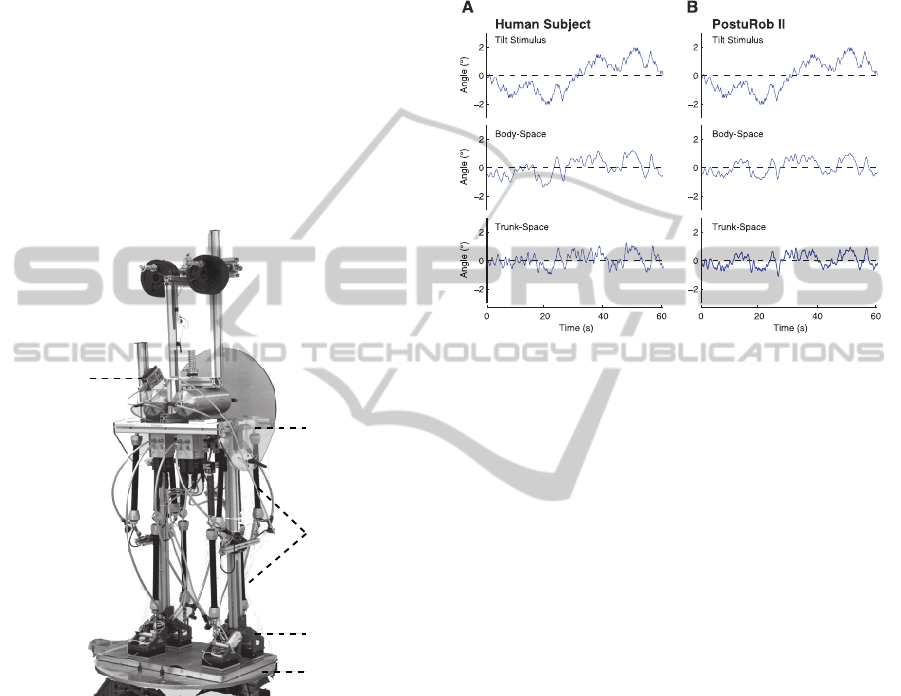
legs and two feet, with a total mass of 59 kg and a
total height of 1.78 m. Two hip joints and two ankle
joints connect the segments (4 DOF in the sagittal
plane; Figure 4). The mechatronic part comprises an
artificial vestibular sensor (see Mergner et al., 2009)
that is fixed to the trunk segment. Artificial
pneumatic ‘muscles’ (FESTO, Esslingen, Germany;
Typ MAS20) connected with serial springs (spring
rate 25 N/mm) are used for actuation. An electronic
inner torque control loop ensures that actual torque
equals approximately desired torque. Sensory
signals are sampled at 200 Hz via an acquisition
board. Computer control is performed through a real
time PC that executes a compiled Simulink model
using Real-Time Windows Target (The Math Works
Inc., Natick, USA).
Figure 4: PostuRob II. The robot consists of trunk, leg,
and foot segments interconnected by the hip joints (a) and
ankle joints (b). Sensory information stems from artificial
vestibular system (c) and ankle and hip joint angle sensors.
Actuation is through pneumatic ‘muscles’ (d). PostuRob II
stands freely on a motion platform (e).
2.4 Human and Robot Experiments
The two-module control concept was tested by
comparing human responses with robot responses to
support surface tilt in the sagittal plane in a human
posturography laboratory. For this study, seven
healthy human subjects (3 female; mean age, 28 ± 3
years) gave their informed consent. The subjects
(with eyes closed) and the robot stood freely on a
motion platform (see Figure 4). The experiment
consisted of six successive pseudorandom ternary
tilt sequences, each 60.5 s long, with peak-to-peak
amplitude of 4° (PRTS stimulus; frequency range
0.017 – 2.2 Hz; Peterka, 2002). The first rows in
Figure 5A,B shows one 60.5 s long tilt stimulus
sequence.
Figure 5: Tilt stimulus and angular excursion responses of
one representative subject (A) and of PostuRob II (B).
Trunk, leg, and COM
B
angular excursions in
space were calculated on the basis of opto-
electronically measured markers (Optotrak 3020®;
Waterloo, Canada) that were recorded with a
sampling frequency of 100 Hz. Data analysis took
into account human anthropometric measures
(Winter, 1990) and was performed using custom-
made software programmed in Matlab (The
MathWorks, Natick, USA). The responses were
expressed as gain and phase from the frequency
response function (Peterka, 2002) in a form where
zero gain means no body excursion and unity gain
means that body angular excursion equals platform
tilt. Phase represents the temporal relationship
between stimulus and response. Variability of
averaged values was expressed as 95% confidence
limits (Otnes and Enochson, 1972).
3 RESULTS
Subjects and PostuRob II balance the support
surface tilts in similar way. Time series of the
responses of one subject and the robot are shown in
Figure 5. Note that their responses are similar both
for the body (COM
B
) and the trunk angles. The
mean gain and phase curves are also very similar
between the human subjects and the robot as it is
shown in Fig. 6. The gain and phase values vary
c
a
b
d
e
NEUROTECHNIX2013-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
158
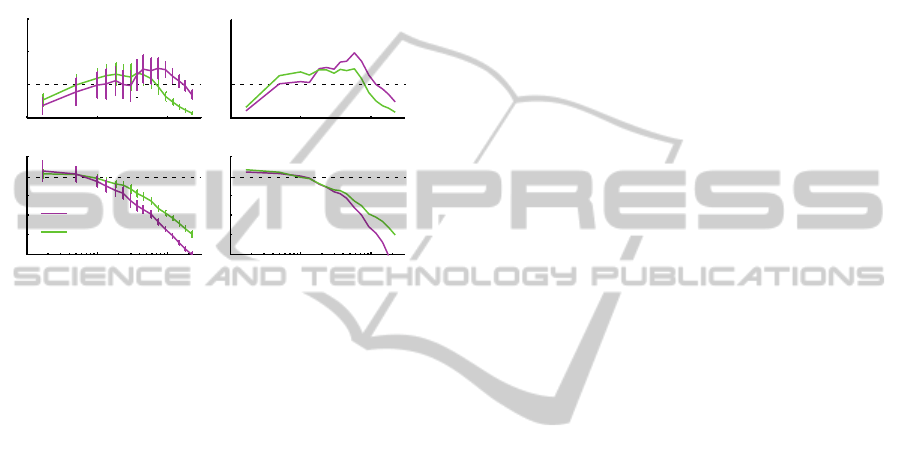
with stimulus frequency. In the low frequency range
(< 0.3 Hz) trunk in space (TS) gain is lower than
body in space (BS) gain. In the high frequency range
(> 0.3 Hz) TS gain exceeds BS gain, while the phase
shows a larger phase lag.
The good match of the data between the human
subjects and PostuRob II suggests that the proposed
sensor fusion mechanisms capture important aspects
of human balancing.
Figure 6: Tilt responses in terms of gain, phase and
coherence of human subjects (A) and PostuRob II (B).
4 CONCLUSIONS
The presented posture control system takes
advantage of sensor fusion mechanisms derived
from findings in human experiments. The sensor
fusion proceeds in two steps. In the first step,
sensory transducer signals are fused to obtain
physical variables. In the second step, the physical
variables are combined to estimate external
disturbances. This is performed without integrating
any dynamic model of the whole body in the control
architecture.
Balancing upright stance using hip and ankle
joints in terms of a DIP requires the integration of
sensory signals from the whole body. For instance,
to estimate a support surface tilt, the vestibular
information of head-space angular velocity (here in
the absence of head-trunk excursions equivalent to
trunk-space velocity ∝
) is fused with co-planar
proprioceptive signals to obtain the angular speed of
foot in space ∝
. This value is then integrated to
obtain ∝
. Before the integration, ∝
is filtered
through a nonlinear operation, which is a deadband
threshold. This works as a filtering system
stabilizing the estimate ∝
based on the noisy
vestibular signal (Mergner et al., 2009). The
threshold also explains the nonlinear responses of
human subjects upon increase of the external
disturbances (Maurer et al., 2006), which reflects an
important aspect of the automatic sensory re-
weighting. Another aspect is that the control
automatically adjusts to changes in disturbance type
and sensor availability (Mergner, 2010).
The presented sensor fusion system proved to be
efficient enough to stabilize a humanoid robot in the
presence of external disturbances. The control
system based on this approach is modular in that it
controls every joint as a SIP. Although optimizing
the control parameters of the DEC concept is still a
topic under research, the concept proved to have
several promising features. These include: (i) a
computationally very simple implementation, since
almost all sensor fusions are based on algebraic
operations; (ii) the control complexity scales linearly
with the number of joints, since every joint is
controlled as a SIP; (iii) noise rejection makes it
possible to fuse the input of an high number of
sensors; and lastly (iv) the system, originally
proposed for its predictive power of human
behaviour, can be employed to control actuated
prostheses and exoskeletons to preserve a natural
feeling in the user.
Future work comprises fusion of sensor-derived
disturbance estimates with expected disturbance
estimates and further validation of the concept by
implementing it in a robot with a higher number of
DOF.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Supported by the European Commission (FP7-ICT-
600698 H2R).
REFERENCES
AlBakri, M. (2008). Development of a mathematical
model and simulation environment for the postural
robot (PostuRob II). Retrieved June 12, 2013, from
http://www.posturob.uniklinik-freiburg.de.
Alexandrov, A. V., Frolov, A. A., Horak, F. B., Carlson-
Kuhta, P. and Park, S. (2005). Feedback equilibrium
control during human standing. Biol Cybern, 93, 309–
322.
Bosco, G. and Poppele, R. E. (1997). Representation of
multiple kinematic parameters of the cat hindlimb in
spinocerebellar activity. J Neurophysiol, 78, 1421–
1432.
Bronstein, A. M. (1988). Evidence for a vestibular input
contributing to dynamic head stabilization in man.
Acta Otolaryngol, 105, 1–6.
Gain
200
0
Phase (°)
Frequency (Hz)
0.01 0.1 1
0.01 0.1 1
A
TS
1
2
3
-200
0
Frequency (Hz)
0.01 0.1 1
0.01 0.1 1
B
1
2
3
BS
Human subjects PostuRob II
Human-likeSensorFusionMechanismsinaPosturalControlRobot
159

Gandevia, S. C., Refshauge, K. M. and Collins, D. F.
(2002) Proprioception: peripheral inputs and
perceptual interactions. Adv Exp Med Biol, 508, 61-8.
Hettich, G., Fennell, L. and Mergner, T. (2011). Double
inverted pendulum model of reactive human stance
control. Multibody Dynamics Conference 2011
(available http://www.posturob.uniklinik-freiburg.de).
Horak, F. B. and Nashner, L. M. (1986). Central
programming of postural movements: adaptation to
altered support-surface configurations, J Neurophysiol,
55, 1369–1381.
Horak, F. B. and Macpherson, J. M. (1996). Postural
Orientation and Equilibrium. Rowell, L., & Shepherd,
J., Handbook of physiology. Vol. 1. New York: Oxford
University Press.
Klein, T. J., Jeka, J., Kiemel, T. and Lewis, M. A. (2011).
Navigating sensory conflict in dynamic environments
using adaptive state estimation. Biol Cybern, 105, 291-
304.
Kuo, A. D. (2005). An optimal state estimation model of
sensory integration in human postural balance. J
Neural Eng, 2, 235–249.
Lackner, J. R. and DiZio, P. (1994). Rapid adaptation to
Coriolis force perturbations of arm trajectories. J
Neurophysiol, 72, 299–313.
Mahboobin, A., Loughlin, P. J., Redfern, M. S., Anderson,
S. O., Atkeson, C. G. and Hodgkins, J. K. (2008)
Sensory adaptation in balance control: lessons for
biomimetic robotic bipeds. Neural Netw, 21(4), 621–
627.
Maurer, C., Mergner, T. and Peterka, R. J. (2006).
Multisensory control of human upright stance, Exp
Brain Res, 171, 231–250.
Mergner, T., Nardi, G. L., Becker, W. and Deecke, L.
(1983). The role of canal-neck interaction for the
perception of horizontal trunk and head rotation. Exp
Brain Res, 49, 198-208.
Mergner, T., Siebold, C., Schweigart, G. and Becker, W.
(1991). Human perception of horizontal trunk and
head rotation in space during vestibular and neck
stimulation. Exp Brain Res, 85, 389-404.
Mergner, T., Huber, W. and Becker, W. (1997).
Vestibular-neck interaction and transformations of
sensory coordinates. J Vestibul Res-Equil, 7, 119–135.
Mergner, T. (2002). The Matryoshka Dolls principle in
human dynamic behavior in space—A theory of linked
references for multisensory perception and control of
action. Curr Psychol Cogn, 21, 129–212.
Mergner, T., Maurer, C. and Peterka R. J. (2003). A
multisensory posture control model of human upright
stance, Prog Brain Res, 142, 189-201.
Mergner, T., Schweigart, G. and Fennell, L. (2009).
Vestibular humanoid postural control. J Physiol
(Paris), 103, 178–194.
Mergner, T. (2010). A neurological view on reactive
human stance control. Annu Rev Control, 34, 177-198,
2010.
Nashner, L. M. and Berthoz, A. (1978). Visual
contribution to rapid responses during postural control.
Exp Brain Res, 150, 403–407.
Nashner, L. and McCollum, G. (1985). The organization
of human postural movements: a formal basis and
experimental synthesis. Behav Brain Sci, 8, 135–172.
Otnes, R. K. and Enochson, L. D. (1972) Digital Time
Series Analysis. New York: Wiley.
Peterka, R. J. (2002). Sensorimotor integration in human
postural control. J Neurophysiol, 88, 1097–1118.
Poppele, R. E., Bosco, G. and Rankin, A. M. (2002).
Independent representations of limb axis length and
orientation in spinocerebellar response components. J
Neurophysiol, 87, 409–422.
Pozzo, T., Berthoz, A., Lefort, L. and Vitte, E. (1991).
Head stabilization during various locomotor tasks in
humans. II. Patients with bilateral peripheral vestibular
deficits. Exp Brain Res, 85, 208– 217.
Tahboub, K. A. and Mergner, T. (2007) Biological and
engineering approaches to human postural control.
Integ. Comput Aid Eng, 13, 1–17.
van der Kooij, H., Jacobs, R., Koopman, B. and
Grootenboer, H. (1999). A multisensory integration
model of human stance control. Biol Cybern, 80, 299–
308.
van der Kooij, H. and Peterka R.J. (2011) Non-linear
stimulus-response behavior of the human stance
control system is predicted by optimization of a
system with sensory and motor noise. J Comput
Neurosci, 30(3), 759-778.
Wehner, R. (1987). Matched Filters - Neural models of the
external world, J Comp Physiol A, 161, 511-531.
Winter, D. A. (1990). Biomechanics and motor control of
human movement (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
NEUROTECHNIX2013-InternationalCongressonNeurotechnology,ElectronicsandInformatics
160
