
Multiobjective Memetic Algorithms applied to University Timetabling
Problems
Nuno Leite
1,2
, Fernando Mel
´
ıcio
1,2
and Agostinho Rosa
2,3
1
ISEL - Lisbon Polytechnic Institute, R. Conselheiro Em
´
ıdio Navarro, 1, 1959-007 Lisboa, Portugal
2
LaSEEB-System and Robotics Institute, Av. Rovisco Pais 1, TN 6.21, 1049-001 Lisboa, Portugal
3
Department of Bioengineering/IST, TU-Lisbon, Av. Rovisco Pais, 1, 1049-001 Lisboa, Portugal
1 STAGE OF THE RESEARCH
1.1 Introduction
The present document describes the Ph.D. thesis pro-
posal of Nuno Leite, doctoral candidate in Electrical
and Computer Engineering at the Technical Univer-
sity of Lisbon (IST/TU-Lisbon). The thesis is titled
“Multiobjective Memetic Algorithms applied to Uni-
versity Timetabling Problems” and is supervised by
Drs. Agostinho Rosa (IST/TU-Lisbon) and Fernando
Mel
´
ıcio (ISEL/Polytechnic Institute of Lisbon). The
research work is developed in the LaSEEB (Evolu-
tionary Systems and Biomedical Engineering Lab) at
the IST/TU-Lisbon. The five year doctoral program
enrolled by Nuno Leite started in December 2010 and
ends in December 2015. The curricular part of the
doctoral program include the realization of four Ph.D.
courses.
1.2 Scope of Research
Nuno’s thesis concerns the study and implementation
of population based metaheuristics for solving uni-
versity timetabling problems, e.g. the examination
timetabling and post-enrolment course timetabling
problems. The study will be focused in approaching
these problems as single and multiobjective problems
using memetic algorithms.
1.3 Developed Work
Nuno has now completed three of the four Ph.D.
courses. These courses are: Nonlinear Optimization
(completed), Intelligent Optimization (completed),
Multiobjective Optimization with Evolutionary Al-
gorithms (completed), and Statistical Learning (not
completed yet). Related to the thesis work, Nuno has
published one conference paper (Leite et al., 2012).
This paper was further selected so that a revised and
extended version of this paper will be published by
Springer-Verlag in a SCI Series book (Leite et al.,
2013b). In May 2013, the authors submitted a po-
sition paper to the IJCCI/ECTA 2013 (Leite et al.,
2013a), which was accepted for publication as a short
paper. In the paper (Leite et al., 2012), the authors
present a bi-objective memetic algorithm for solv-
ing a real instance of the uncapacitated examination
timetabling problem from the ISEL/Polytechnic Insti-
tute of Lisbon. The automatic algorithm implemented
was able to produce feasible timetables with lower
number of conflicts in students’s exams compared
with the manual solution, and in a shorter time. In
the paper (Leite et al., 2013b), the previous work was
further extended to solve the capacitated case. Also,
rooms are allocated automatically by the algorithm.
In the novel work (Leite et al., 2013a), the applica-
tion of a recently proposed single-objective memetic
algorithm (known as SFLA – Shuffled Frog-Leaping
Algorithm) to the examination timetabling problem is
studied. The proposed adaptation was evaluated on
the standard Toronto benchmark datasets with com-
parable results to the state-of-the-art algorithms. We
now intend to study forms of improving the proposed
algorithm which include: (i) implement a diversity
management procedure in order to control the popu-
lation diversity, (ii) study the problem landscape char-
acteristics and propose efficient neighbourhood oper-
ators to be incorporated in the local search step of
the algorithm, and (iii) propose an extension of the
algorithm by managing multiple objectives and ex-
periment with the Toronto and the 2nd International
Timetabling Competition (ITC2007) benchmark data.
29
Leite N., Melício F. and Rosa A. (2013).
Multiobjective Memetic Algorithms applied to University Timetabling Problems.
In Doctoral Consortium, pages 29-37
Copyright
c
SCITEPRESS

2 OUTLINE OF OBJECTIVES
2.1 General Objectives
The research work undertaken has the following ob-
jectives:
1. Solve hard multiobjective combinatorial opti-
mization problems by approaching them with
Multiobjective Memetic Algorithms. The study
will focus on University Timetabling Problems
such as the Examination timetabling problem or
the Post-enrolment course timetabling problem.
2. Propose a novel multiobjective problem for-
mulation and benchmark data for examination
timetabling problem instances found in Por-
tuguese universities.
3. Implement the proposed algorithms in a parallel
way using existing frameworks and libraries.
4. Implement an application with a graphical user
interface that helps the timetable planner in
the multiobjective (many-objective) optimization
process.
2.2 Description
The following items describe in more detail the ob-
jectives of the research work.
1. Study university timetabling problems in its dif-
ferent dimensions: as scalar (single-objective) and
as multiobjective optimization problems. Typi-
cally, multiobjective approaches solve intermedi-
ate scalar versions of the problem at hands (e.g.
multiobjective evolutionary algorithms that use
decomposition, MOEA/D (Zhang and Li, 2007)).
In particular, in examination timetabling, we will
consider the following problems:
- single-objective problems of Toronto
1
and
ITC2007
2
benchmark datasets;
- bi-objective problems of Toronto benchmark
datasets;
- many-objective problems of ITC2007 bench-
mark datasets.
2. Propose scalar and multiobjective memetic algo-
rithms that can efficiently solve the studied prob-
lems. Compare the proposed algorithms with cur-
rent state-of-the-art algorithms.
1
University of Toronto benchmark data proposed
in (Carter et al., 1996).
2
2nd International Timetabling Competition benchmark
data (McCollum et al., 2012).
3. Propose a model and benchmark data for a new
multiobjective examination timetabling problem
found typically in Portuguese universities. This
model extends the ITC2007 model and cover a
more realistic model comprising:
- different interrelated examination sessions that
include intermediate evaluation tests (usually
two or three tests or a global test in some cases)
during the academic semester or year. These
are followed by a final examination period,
which is formed, normally, by two examination
sessions;
- consider more hard and soft constraints. Some
characteristics of the problem are the follow-
ing. The intermediate evaluation tests during
the semester should take place in the days of
one of the classes. In this scenario the classes’s
timetables have to be considered in order to
know the days of each class for schedule the
evaluation tests. For examinations with few
students (e.g. less than 100), the examina-
tions should take place in the rooms of one of
the classes. Otherwise, if the examination has
a large number of students, then it should be
scheduled into examination special rooms. The
date of the last intermediary examination test
must be far apart from the corresponding first
final examination date. Also, all examinations
should be spread out for each student, number
of used periods minimized, among other con-
straints.
This new problem will be also solved by the pro-
posed multiobjective algorithm.
4. Study and design a multiobjective memetic algo-
rithm parallel implementation.
5. Study forms of interacting with the decision
maker in many-objective optimization. Design an
interactive multiobjective memetic algorithm and
an application with a graphical user interface that
expose the algorithm functionality.
In the following section, we describe the research
problem in detail.
3 RESEARCH PROBLEM
In this thesis we address the class of university
timetabling problems, which include problems such
as course scheduling and examination timetabling.
The problem will be approached in a generic way but
we intend to conduct practical experiments on spe-
cific problems such as the examination timetabling
IJCCI2013-DoctoralConsortium
30

problem (ETTP) found in universities. The univer-
sity timetabling problems belong to the general class
of NP-complete Combinatorial optimization prob-
lems (Lewis, 2008). This implies that deterministic
exact algorithms, which guarantee finding of optimal
solutions, can only be applied to small sized prob-
lem instances. Due to this, there’s a growing inter-
est in using metaheuristics (Glover and Kochenberger,
2003), (Gendreau and Potvin, 2010) to solve real in-
stances of these hard combinatorial problems.
The university timetabling is a subset of the gen-
eral family of timetabling and scheduling problems.
The aim of these problems is to assign a set of en-
tities (e.g. tasks, events, people, vehicles) to limited
number of resources over time, respecting a set of pre-
defined schedule requirements (Lewis, 2008). In this
sense, the university timetabling problem is generi-
cally defined as the task of assigning a number of
events, such as lectures, exams, or meetings, to a lim-
ited set of timeslots and rooms, satisfying a set of con-
straints. A categorization of typical constraints can
be found in (Lewis, 2008). The constraints are fur-
ther classified in hard and soft constraints. The first
ones are related to the feasibility of the timetable (e.g.
a teacher cannot be scheduled to give two different
lectures at the same timeslot in course timetabling, or
a student cannot take two different exams at the the
same timeslot, in examination timetabling), and can-
not be violated. The soft constraints should be satis-
fied, if possible, as they contribute to the improvement
of the timetable quality for the different stakehold-
ers (students, institution, professors/invigilators, etc.),
but they could be violated. An example of a soft con-
straint is the Period spread (McCollum et al., 2012)
in examination timetabling, with the aim of spreading
the exams for all students as much as possible.
Real instances of university timetabling problems
encountered in practice, such as the ETTP, have sev-
eral hard and soft constraints. As in many other prob-
lems in scheduling and other areas, these constraints
can be seen as multiple objectives, conflicting or not,
which means that university timetabling problems are
multiobjective optimization problems (MOPs) in na-
ture. Due to the associated extra complexity, in prac-
tice these problems have been approached mainly as
single-objective problems and very few studies con-
sider multiobjective approaches.
The approaches found in literature to solve the
ETTP were first categorised by Carter (Carter, 1986)
into four types: sequential methods, cluster methods,
constraint-based methods and generalised search.
Later, Petrovic and Burke (Petrovic and Burke,
2004) added more categories: hybrid evolutionary al-
gorithms, metaheuristics, multi-criteria approaches,
case based reasoning techniques, hyperheuristics and
adaptive approaches.
Evolutionary approaches are well suited to tackle
multiobjective problems because a population of so-
lutions is already maintained, therefore a set of non-
dominated solutions (trade-off solutions) could be
determined at the end of one generation of the al-
gorithm. The Multiobjective Evolutionary Algo-
rithms (MOEAs) have been extensively studied in
the last 20 years (Van Veldhuizen and Lamont,
2000) (Zhou et al., 2011). It is well known that
combining a local search procedure into an evolution-
ary algorithm greatly improves the algorithm’s perfor-
mance. These algorithms were named Memetic Algo-
rithms (MAs) (Moscato and Norman, 1992) (Neri and
Cotta, 2012). Recently, researchers began combin-
ing the ideas of MOEAs with memetic evolution, and
propose several Multiobjective Memetic Algorithms
(MOMAs). These were used recently for solving hard
Combinatorial optimization problems with good suc-
cess (Jaszkiewicz et al., 2012). Hybridizations of evo-
lutionary algorithms with other techniques other than
local search metaheuristics, for instance with exact
algorithms, seem also to be very promising (Raidl,
2006). In (Ehrgott and Gandibleux, 2008) the au-
thors survey Multiobjective (meta)heuristics for solv-
ing multiobjective combinatorial optimization prob-
lems, focusing on recent approaches, where meta-
heuristics are hybridized with exact methods.
In Multiobjective Optimization (MOO), the prob-
lems are usually classified in two categories. If the
number of objectives is below three or four, the op-
timization problem is termed simply as MOP; other-
wise, if for a number of objectives greater than three
or four, the problem is termed Many-objective opti-
mization problem (Zhou et al., 2011).
The early algorithms proposed for Evolutionary
Multiobjective Optimization (EMO), such as NSGA-
II (Deb et al., 2002), don’t work well for the many-
objective case (Ishibuchi et al., 2008) (Zhou et al.,
2011). As such, many-objective problems pose new
challenges for algorithm design, visualisation and im-
plementation.
Multiobjective optimization involves three
phases (Coello et al., 2006), (Branke et al., 2008):
model building, optimization, and decision making.
So, converting a MOP into a single-objective problem
puts the decision making task before optimization,
and before the existing alternatives are known.
The task of a multiobjective algorithm, as shown
in Figure 1, is to find a good approximation of
the true Pareto front to the decision maker (DM).
Three aspects of the solution set quality are usually
considered:
MultiobjectiveMemeticAlgorithmsappliedtoUniversityTimetablingProblems
31
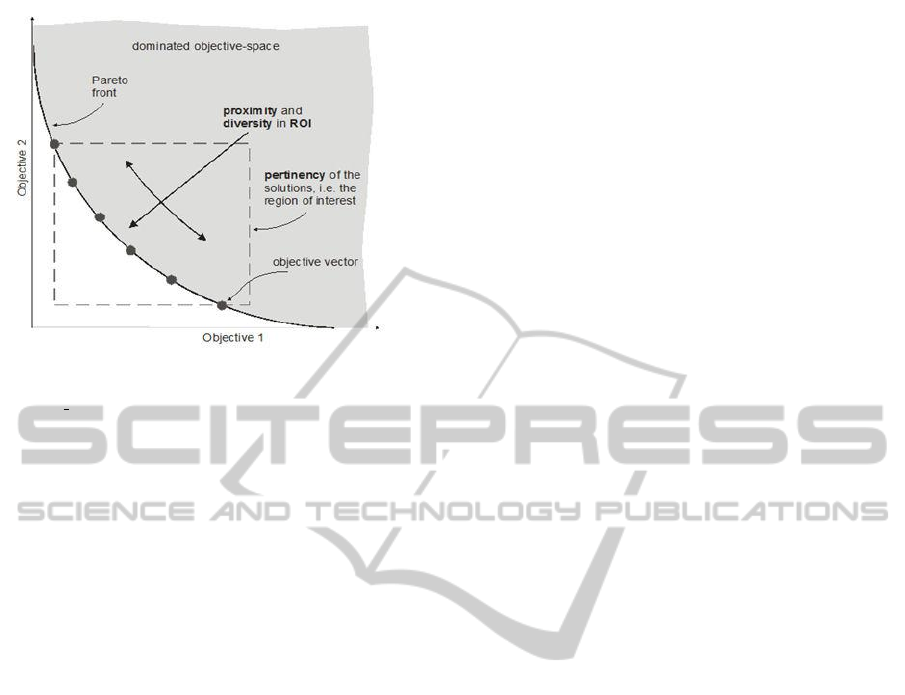
Figure 1: Requirements of a MOEA. (Illustration from
Prof. Peter J. Fleming site, http://www.shef.ac.uk/acse/
staff/peter fleming/manyoo).
1. Proximity, the produced set should contain solu-
tions close to the true Pareto set.
2. Diversity, the solutions in the approximated set
should be well distributed.
3. Pertinency, the produced set should contain solu-
tions in the DM’s region of interest (ROI). The
definition of a ROI is especially relevant as the
number of objectives increase, because the num-
ber of solutions of the approximated set also in-
creases, thus increasing the difficulty of the DM
to analyse all the alternatives.
4 STATE OF THE ART
4.1 Single-objective Approaches to the
ETTP
The development of systems to automate the con-
struction of university examination timetables has
begun in the 1960 decade. The paper (Qu et al.,
2009) constitute a survey of the recent (from 1995
to 2008) techniques and algorithmic approaches used
to solve this problem. Lewis (Lewis, 2008) sur-
veys metaheuristic-based techniques applied to Uni-
versity Timetabling problems. These two surveys
describe techniques applied to Toronto, Nottingham
and Melbourne benchmarks. M
¨
uller (M
¨
uller, 2009)
and Gogos (Gogos et al., 2012) propose two efficient
scalar optimization techniques to the ITC2007 bench-
mark data (these authors were the winner and second
classified in the ITC2007 competition, respectively).
M
¨
uller’s algorithm is based on a general Constraint
solver developed by the author which was adapted to
the ETTP. Gogos apply a multi-stage algorithm com-
prising several metaheuristics and also a step where a
Branch & Bound based method was applied.
Researchers recognized that next to the algorithm
used to optimize this problem, the way the neighbour-
hoods are constructed and sampled is important (De-
meester et al., 2012) (Abdullah et al., 2010). The
Kempe chains, introduced by Morgenstern (Morgen-
stern, 1989) for solving graph colouring problems,
is one of the most successful neighbourhoods. The
Kempe chain-based neighbourhood was first applied
on the ETTP by Thompson and Dowsland (Thomp-
son and Dowsland, 1998), which used the Simulated
Annealing metaheuristic. The Kempe chain heuris-
tic maintains feasibility by swapping infeasible exams
between time slots. The simple neighbourhood intro-
duced in Burke and Bykov (Burke and Bykov, 2008)
is also frequently used. This heuristic swaps all exams
of two randomly chosen time slots, and so it maintains
feasibility.
4.2 Multiobjective Approaches to the
ETTP
More recently, the ETTP has been approached like a
Multiobjective/Multi-criteria Optimization problem,
recognizing the true dimensions of real world prob-
lems, that typically have many facets to consider
(proximity costs between student exams, timetable
lengths, room assignment, invigilator availability,
etc.). Silva et al. (Silva et al., 2004) present
an overview on multiobjective timetabling meta-
heuristics. Multi-criteria techniques were proposed
in (Burke et al., 2001) and (Petrovic and Bykov,
2003). Pais and Amaral (Pais and Amaral, 2009)
also approach ETTP (Toronto benchmark) as a mul-
tiobjective problem, and consider the four objec-
tives studied in (Petrovic and Bykov, 2003). Other
recent works (C
ˆ
ot
´
e et al., 2004), (Wong et al.,
2004), (Cheong et al., 2009) and (Mumford, 2010),
applied MOEAs to solve the ETTP. The current au-
thors propose in (Leite et al., 2012) a MOEA based
on NSGA-II and applied it to a real problem instance
of a Portuguese university. The crossover and muta-
tion operators were adapted from the ones in (Cheong
et al., 2009). A computational analysis involving
MOEAs for the ETTP is given in (Paquete and Fon-
seca, 2001). Burke et al. (Burke et al., 2008) and
later (McCollum et al., 2012) present the ITC2007
problem as an MOP. They consider four objectives,
each representing a compromise between the various
interested parties or stakeholders. These parties are:
(1) student interests for a good individual timetable,
(2) interests of exam invigilators (and students), (3)
IJCCI2013-DoctoralConsortium
32

the front load (representing the desire of the exam
markers to receive the largest exams as soon as pos-
sible so as to have more time for marking), and (4)
the estate management interests in avoiding the use
of some rooms and periods. Due to the complexity
of this four objective problem, in Burke et al. (Burke
et al., 2008) work the objectives are further grouped
in two objectives concerning the students interests and
the administration interests. The authors then apply a
solver (CPLEX solver) to solve smaller versions of
the real datasets. It is mentioned that due to the unop-
timized formulation used, the full instances could not
be solved.
4.3 Parallel Metaheuristics
Alba et al. (Alba et al., 2013) present recent ad-
vances and new trends on Parallel metaheuristics.
Talbi (Talbi and Hasle, 2013) present an editorial re-
view of the application of metaheuristics on GPUs.
Coello et al. (Coello et al., 2006) also dedicate a chap-
ter to MOEA parallelization. In (Nebro and Durillo,
2010), a MOEA/D parallel implementation was pro-
posed.
4.4 Many-objective Optimization
Algorithms
In addition to the previous referred research on
multi and many-objective optimization, we include
some recent developments on the NSGA-II and the
MOEA/D algorithms. In (Deb and Jain, 2012), the
authors propose a many-objective NSGA-II (MO-
NSGA-II). Recently (Jain and Deb, 2013), the same
authors present an improved MO-NSGA-II. In (yan
Tan et al., 2013), it is proposed an improved MOEA/D
for many-objective optimization.
5 METHODOLOGY
I’m developing a portable library containing single-
objective and multi-objective algorithms. The lan-
guage used is the C++ programming language. In or-
der to reuse some code and to implement the parallel
MOEA we are using the ParadisEO library (Cahon
et al., 2004).
5.1 Neighbourhood and Variation
Operators
I intend to implement some efficient neighbourhoods
such as Kempe chains and time slot swaping, men-
tioned in Subsection 4.1. We will extend the re-
cently developed Shuffled Frog-Leaping Algorithm to
include these neighbourhoods. We will analyse and
implement other neighbourhoods and variation oper-
ators such as the ones proposed in (Abdullah et al.,
2010) and (Cheong et al., 2009). The performance
of these operators will be studied first on the smaller
dataset (Leite et al., 2012), in order to visualize its op-
eration on the timetables produced, and later we will
test with the bigger datasets of Toronto and ITC2007
benchmarks.
5.2 Hybrid EMO Methodology
As mentioned in the objectives outline, we in-
tend to tackle the university timetabling prob-
lems using EMO algorithms combined with other
(meta)heuristics, forming the so called memetic algo-
rithms.
We intend to extend the recently proposed SFLA
algorithm and implement a multiobjective SFLA.
Some efforts have been done in this path (Rahimi-
Vahed and Mirzaei, 2007).
For the local search we intend to explore several of
the most successful techniques in the literature such
as Hill Climbing, Simulated Annealing, Tabu Search,
among others. The acceptance criteria implemented is
very important as shown, for example, by the method
implemented by (Burke and Bykov, 2008), which
achieves the best results on some Toronto datasets.
Other idea will be explored in the final project of
the fourth and last doctoral course, yet to be com-
pleted. In this project I intend to implement a learning
algorithm, called STAGE (Boyan and Moore, 2001),
and use it to solve the ETTP. The STAGE algorithm
works by learning an evaluation function that pre-
dicts the outcome of a local search algorithm, such
as hillclimbing, from features of states visited dur-
ing search. The learned evaluation function is then
used to bias future search trajectories toward better
optima on the same problem. In (Boyan and Moore,
2001) the authors use the STAGE algorithm to solve
several known large-scale optimization domains, such
as bin-packing, channel routing, cartogram design or
Boolean satisfiability problem.
We intend to study the application of the STAGE
algorithm on the ETTP and test it with the bench-
marks available. We also want to study other re-
gression strategies such as SVM (Support Vector Ma-
chines) regression.
MultiobjectiveMemeticAlgorithmsappliedtoUniversityTimetablingProblems
33

5.3 Variable Timetable Length
Solutions
One of the typical objectives of timetabling opti-
mization is to find solutions with the lower num-
ber of time slots. This was explored in some
single-objective (Carter et al., 1996) (Caramia et al.,
2008) and multiobjective methods (C
ˆ
ot
´
e et al.,
2004) (Cheong et al., 2009) for the Toronto bench-
mark. Manipulating variable timetable length solu-
tions, by creating new time slots needed to accommo-
date infeasible exams generated by the variation oper-
ators, and then trying to repair those solutions, seems
another tool for conveniently exploring the search
space. Associated to this are the methods proposed
in the graph colouring literature, specifically for solv-
ing the Minimum Vertex Colouring problem. As anal-
ysed in the timetabling literature, the ETTP consider-
ing just the student clash hard constraint with k time
slots is equal to the k−vertex colouring problem. So,
graph colouring heuristics are also of interest to our
analysis. One example of an effective memetic algo-
rithm for tackling the graph colouring problem is the
work (L
¨
u and Hao, 2010).
So, we intend to create operators that vary the
time slots as needed in order to rearrange the exams.
Repairing schemes and specific constraint-handling
techniques to handle infeasible solutions will be de-
vised.
5.4 Algorithm Comparison and
Performance Measures
For a fair algorithm comparison of the proposed al-
gorithms on benchmark data for the Toronto dataset,
we intend to use similar computers to those tested in
the literature. For the ITC2007 data, the organizers of
the competition provided an application for estimat-
ing the CPU time available for running the optimiza-
tion algorithm (for single-objective/non-parallel algo-
rithm comparison purposes). This application only
applies to single CPU machines.
Desirable characteristics of a MOEA include gen-
eration of nondominated set close as much as possi-
ble to the true Pareto front, and, secondly, that solu-
tions in the obtained nondominated set should be dis-
tributed in a diverse and uniform manner. For eval-
uating these two aspects we will consider the use of
performance metrics suggested in the literature (Zit-
zler et al., 2003) and that are used by researchers in
this field to compare the several MOEAs.
5.5 Activity Plan until December 2015
In the next months, I intend to explore thoroughly
the concepts mentioned earlier about many-objective
optimization. At the same time, we will improve
(by exploring the described points mentioned in the
earlier sections) and extend the single-objective pro-
posed in (Leite et al., 2013a) to the ITC2007. Next,
we will study forms of extending it to a multiobjec-
tive framework and implement also a parallel version
of the algorithm. The last objective mentioned of cre-
ating a graphical interface for the MOEA is optional
in this phase of the work.
5.5.1 Goals for Publication
We intend to prepare in the mean time commu-
nications and articles to submit to related confer-
ences and journals. We are considering the follow-
ing international conferences: Evolutionary Compu-
tation, Theory and Applications (IJCCI-ECTA), Prac-
tice and Theory of Automated Timetabling (PATAT),
Multidisciplinary International Scheduling Confer-
ence (MISTA). For the journals we are considering
the following ones: Elsevier’s European Journal of
Operational Research (EJOR), Springer’s Journal of
Scheduling (JSched), Springer’s Annals of Opera-
tions Research (AOR) and IEEE Transactions on Evo-
lutionary Computation (TEVC).
6 EXPECTED OUTCOME
With the realization of this Ph.D. thesis I expect to
give novel contributions to the study of the University
Timetabling field. The expected outcome of the thesis
is:
• Extend the study of university timetabling prob-
lems, exploring them as multiobjective problems,
which they are in nature. The majority of the ex-
isting studies consider single-objective problems
and very few consider two-objective problems.
We will extend this framework by considering for-
mulations with three and more objectives.
• Contribute to the understanding of the search
space of the analysed timetabling problems.
• Provide efficient neighbourhood operators for the
selected problems.
• Provide efficient multiobjective memetic algo-
rithms that improve upon the results of the state-
of-the-art algorithms for the multiobjective and
single-objective problem instances of the anal-
ysed problems.
IJCCI2013-DoctoralConsortium
34

• The proposed algorithms should be optimized in
terms of time performance due to the their parallel
implementation. This provides for efficient usage
of the multicore machines available in nowadays
mainstream market, and, more importantly, pro-
vide for new modifications to a given timetable
to be done in a much short period of time. The
parallelism is also important because multiobjec-
tive optimization algorithms are more complex
and manipulate more data compared to single-
objective optimization algorithms.
• New multiobjective examination timetabling
problem formulation and benchmark data from
practical problem found in Portuguese universi-
ties.
• Publish research results in related refereed confer-
ences and journals.
• User application providing a graphical user inter-
face that helps the decision maker to search inter-
actively given a selected set of objectives, guiding
the search process towards a preferred Pareto sub-
set.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Nuno Leite’s work is partially supported by the FCT
SFRH/PROTEC/67953/2010 grant. The authors work
is also supported by the PEst-OE/EEI/LA0009/2011
grant.
REFERENCES
Abdullah, S., Turabieh, H., McCollum, B., and McMullan,
P. (2010). A tabu-based memetic approach for exami-
nation timetabling problems. In Yu, J., Greco, S., Lin-
gras, P., Wang, G., and Skowron, A., editors, RSKT,
volume 6401 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
pages 574–581. Springer.
Alba, E., Luque, G., and Nesmachnow, S. (2013). Paral-
lel metaheuristics: recent advances and new trends.
International Transactions in Operational Research,
20(1):1–48.
Boyan, J. and Moore, A. W. (2001). Learning evaluation
functions to improve optimization by local search. J.
Mach. Learn. Res., 1:77–112.
Branke, J., Deb, K., Miettinen, K., and Słowi
´
nski, R., edi-
tors (2008). Multiobjective Optimization: Interactive
and Evolutionary Approaches. Lecture Notes in Com-
puter Science. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin,
Heidelberg.
Burke, E., Bykov, Y., and Petrovic, S. (2001). A Mul-
ticriteria Approach to Examination Timetabling. In
Burke, E. and Erben, W., editors, Practice and Theory
of Automated Timetabling III, volume 2079 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 118–131. Springer
Berlin / Heidelberg.
Burke, E. K. and Bykov, Y. (2008). A Late Acceptance
Strategy in Hill-Climbing for Exam Timetabling Prob-
lems. In PATAT ’08 Proceedings of the 7th Interna-
tional Conference on the Practice and Theory of Au-
tomated Timetabling.
Burke, E. K., McCollum, B., McMullan, P., and Parkes,
A. J. (2008). Multi-objective aspects of the exami-
nation timetabling competition track. Proceedings of
PATAT 2008.
Cahon, S., Melab, N., and Talbi, E.-G. (2004). ParadisEO:
A Framework for the Reusable Design of Parallel and
Distributed Metaheuristics. J. Heuristics, 10(3):357–
380.
Caramia, M., Dell’Olmo, P., and Italiano, G. F. (2008).
Novel local-search-based approaches to university ex-
amination timetabling. INFORMS Journal on Com-
puting, 20(1):86–99.
Carter, M., Laporte, G., and Lee, S. Y. (1996). Examina-
tion Timetabling: Algorithmic Strategies and Appli-
cations. Journal of the Operational Research Society,
47(3):373–383.
Carter, M. W. (1986). A survey of practical applications
of examination timetabling algorithms. Oper. Res.,
34(2):193–202.
Cheong, C., Tan, K., and Veeravalli, B. (2009). A Multi-
objective Evolutionary Algorithm for Examination
Timetabling. Journal of Scheduling, 12:121–146.
Coello, C. A. C., Lamont, G. B., and Veldhuizen, D. A. V.
(2006). Evolutionary Algorithms for Solving Multi-
Objective Problems (Genetic and Evolutionary Com-
putation). Springer-Verlag New York, Inc., Secaucus,
NJ, USA.
C
ˆ
ot
´
e, P., Wong, T., and Sabourin, R. (2004). Application of
a Hybrid Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithm to
the Uncapacitated Exam Proximity Problem. In Pro-
ceedings of the 5th International Conference on Prac-
tice and Theory of Automated Timetabling (PATAT
2004), pages 151–167.
Deb, K. and Jain, H. (2012). Handling many-objective
problems using an improved NSGA-II procedure.
In Evolutionary Computation (CEC), 2012 IEEE
Congress on, pages 1–8.
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., and Meyarivan, T. (2002).
A Fast and Elitist Multiobjective Genetic Algorithm :
NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Com-
putation, 6(2):182–197.
Demeester, P., Bilgin, B., Causmaecker, P. D., and Berghe,
G. V. (2012). A hyperheuristic approach to exami-
nation timetabling problems: benchmarks and a new
problem from practice. J. Scheduling, 15(1):83–103.
Ehrgott, M. and Gandibleux, X. (2008). Hybrid Metaheuris-
tics for Multi-objective Combinatorial Optimization.
In Blum, C., Aguilera, M., Roli, A., and Sampels, M.,
editors, Hybrid Metaheuristics, volume 114 of Stud-
ies in Computational Intelligence, pages 221–259.
Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
MultiobjectiveMemeticAlgorithmsappliedtoUniversityTimetablingProblems
35

Gendreau, M. and Potvin, J.-Y. (2010). Handbook of Meta-
heuristics. Springer Publishing Company, Incorpo-
rated, 2nd edition.
Glover, F. W. and Kochenberger, G. A. (2003). Handbook
of Metaheuristics. Springer.
Gogos, C., Alefragis, P., and Housos, E. (2012). An im-
proved multi-staged algorithmic process for the solu-
tion of the examination timetabling problem. Annals
OR, 194(1):203–221.
Ishibuchi, H., Tsukamoto, N., and Nojima, Y. (2008). Evo-
lutionary many-objective optimization: A short re-
view. In IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computa-
tion, pages 2419–2426. IEEE.
Jain, H. and Deb, K. (2013). An improved adaptive ap-
proach for elitist nondominated sorting genetic algo-
rithm for many-objective optimization. In Purshouse,
R. C., Fleming, P. J., Fonseca, C. M., Greco, S., and
Shaw, J., editors, EMO, volume 7811 of Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 307–321. Springer.
Jaszkiewicz, A., Ishibuchi, H., and Zhang, Q. (2012). Mul-
tiobjective memetic algorithms. In Neri, F., Cotta, C.,
and Moscato, P., editors, Handbook of Memetic Algo-
rithms, volume 379 of Studies in Computational Intel-
ligence, pages 201–217. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Leite, N., Mel
´
ıcio, F., and Rosa, A. C. (2013a). Solving
the Examination Timetabling Problem with the Shuf-
fled Frog-Leaping Algorithm. Accepted on the IJCCI-
ECTA 2013 conference as a position paper.
Leite, N., Neves, R. F., Horta, N., Mel
´
ıcio, F., and
Rosa, A. C. (2012). Solving an Uncapacitated Exam
Timetabling Problem Instance using a Hybrid NSGA-
II. In Rosa, A. C., Correia, A. D., Madani, K., Filipe,
J., and Kacprzyk, J., editors, IJCCI, pages 106–115.
SciTePress.
Leite, N., Neves, R. F., Horta, N., Mel
´
ıcio, F., and
Rosa, A. C. (2013b). Solving a Capacitated Exam
Timetabling Problem Instance using a Bi-objective
NSGA-II. In Madani, K., Correia, A. D., Rosa, A. C.,
and Filipe, J., editors, IJCCI (Selected Papers), Stud-
ies in Computational Intelligence. Springer (in press).
Lewis, R. (2008). A survey of metaheuristic-based tech-
niques for university timetabling problems. OR Spec-
trum, 30(1):167–190.
L
¨
u, Z. and Hao, J.-K. (2010). A memetic algorithm for
graph coloring. European Journal of Operational Re-
search, 203(1):241 – 250.
McCollum, B., McMullan, P., Parkes, A. J., Burke, E. K.,
and Qu, R. (2012). A New Model for Automated
Examination Timetabling. Annals of Operations Re-
search, 194:291–315.
Morgenstern, C. (1989). Algorithms for General Graph
Coloring. PhD thesis, Department of Computer Sci-
ence, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New
Mexico.
Moscato, P. and Norman, M. (1992). A “Memetic” Ap-
proach for the Traveling Salesman Problem Imple-
mentation of a Computational Ecology for Combina-
torial Optimization on Message-Passing Systems. In
Proceedings of the International Conference on Par-
allel Computing and Transputer Applications, pages
177–186. IOS Press.
M
¨
uller, T. (2009). ITC2007 solver description: a hybrid ap-
proach. Annals of Operations Research, 172(1):429–
446.
Mumford, C. (2010). A Multiobjective Framework for
Heavily Constrained Examination Timetabling Prob-
lems. Annals of Operations Research, 180:3–31.
Nebro, A. J. and Durillo, J. J. (2010). A Study of the
Parallelization of the Multi-Objective Metaheuristic
MOEA/D. In Blum, C. and Battiti, R., editors, LION,
volume 6073 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
pages 303–317. Springer.
Neri, F. and Cotta, C. (2012). A primer on memetic algo-
rithms. In Neri, F., Cotta, C., and Moscato, P., edi-
tors, Handbook of Memetic Algorithms, volume 379
of Studies in Computational Intelligence, pages 43–
52. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Pais, T. C. and Amaral, P. A. (2009). Weight aggre-
gation in a multiobjective approach for exams
timetabling problems. Centro de Matem
´
atica e
Aplicac¸
˜
oes. Pre-print CMA 4-2009, available on:
http://www.cma.fct.unl.pt/sites/www.cma.fct.unl.pt/
files/documentos/publicacoes/pdf
2009/CMA%204-
2009.pdf.
Paquete, L. F. and Fonseca, C. M. (2001). A study of exam-
ination timetabling with multiobjective evolutionary
algorithms. Proceedings of the 4th Metaheuristics In-
ternational Conference (MIC 2001), pages 149–154.
Petrovic, S. and Burke, E. (2004). University timetabling.
In Handbook of Scheduling: Algorithms, Models,
and Performance Analysis, chapter 45. Chapman
Hall/CRC Press.
Petrovic, S. and Bykov, Y. (2003). A Multiobjective Opti-
misation Technique for Exam Timetabling Based on
Trajectories. In Burke, E. and Causmaecker, P., ed-
itors, Practice and Theory of Automated Timetabling
IV, volume 2740 of Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence, pages 181–194. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Qu, R., Burke, E., McCollum, B., Merlot, L. T. G., and
Lee, S. Y. (2009). A Survey of Search Methodologies
and Automated System Development for Examination
Timetabling. Journal of Scheduling, 12:55–89.
Rahimi-Vahed, A. and Mirzaei, A. H. (2007). A hy-
brid multi-objective shuffled frog-leaping algorithm
for a mixed-model assembly line sequencing prob-
lem. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 53(4):642
– 666.
Raidl, G. (2006). A Unified View on Hybrid Metaheuristics.
In Hybrid Metaheuristics, pages 1–12.
Silva, J. D. L., Burke, E. K., and Petrovic, S. (2004).
An introduction to multiobjective metaheuristics for
scheduling and timetabling. In Gandibleux, X., Se-
vaux, M., S
¨
orensen, K., and T’kindt, V., editors,
Metaheuristics for Multiobjective Optimisation, vol-
ume 535 of Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathe-
matical Systems, pages 91–129. Springer Berlin Hei-
delberg.
Talbi, E.-G. and Hasle, G. (2013). Metaheuristics on gpus.
J. Parallel Distrib. Comput., 73(1):1–3.
IJCCI2013-DoctoralConsortium
36

Thompson, J. M. and Dowsland, K. A. (1998). A robust
simulated annealing based examination timetabling
system. Computers & Operations Research,
25(78):637 – 648.
Van Veldhuizen, D. A. and Lamont, G. B. (2000). Multiob-
jective evolutionary algorithms: Analyzing the state-
of-the-art. Evol. Comput., 8(2):125–147.
Wong, T., C
ˆ
ot
´
e, P., and Sabourin, R. (2004). A Hybrid
MOEA for the Capacitated Exam Proximity Problem.
In Congress on Evolutionary Computation, volume 2,
pages 1495 – 1501.
yan Tan, Y., chang Jiao, Y., Li, H., and kuan Wang, X.
(2013). MOEA/D + uniform design: A new ver-
sion of MOEA/D for optimization problems with
many objectives. Computers & Operations Research,
40(6):1648 – 1660.
Zhang, Q. and Li, H. (2007). MOEA/D: A Multiobjective
Evolutionary Algorithm Based on Decomposition.
IEEE Trans. Evolutionary Computation, 11(6):712–
731.
Zhou, A., Qu, B.-Y., Li, H., Zhao, S.-Z., Suganthan, P. N.,
and Zhang, Q. (2011). Multiobjective evolutionary al-
gorithms: A survey of the state of the art. Swarm and
Evolutionary Computation, 1(1):32 – 49.
Zitzler, E., Thiele, L., Laumanns, M., Fonseca, C. M., and
da Fonseca, V. G. (2003). Performance assessment
of multiobjective optimizers: an analysis and review.
IEEE Trans. Evolutionary Computation, 7(2):117–
132.
MultiobjectiveMemeticAlgorithmsappliedtoUniversityTimetablingProblems
37
