
Parameter Estimation and Equation Formulation in Business Dynamics
Marc Drobek
1,2
, Wasif Gilani
1
and Danielle Soban
2
1
SAP UK Ltd., Belfast, U.K.
2
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Queens University Belfast, U.K.
{marc.drobek, wasif.gilani}@sap.com, d.soban@qub.ac.uk
Keywords:
System Dynamics, Business Dynamics, Parameter Estimation, Equation Formulation, Non-linear Dynamic
Equations, Machine Learning, Big Data, Modelling, Classification and Regression Trees.
Abstract:
System Dynamics enables modelling and simulation of highly non-linear feedback systems to predict future
system behaviour. Parameter estimation and equation formulation are techniques in System Dynamics, used
to retrieve the values of parameters or the equations for flows and/or variables. These techniques are crucial
for the annotations and thereafter the simulation. This paper critically examines existing and well established
approaches in parameter estimation and equation formulation along with their limitations, identifying perfor-
mance gaps as well as providing directions for potential future research.
1 INTRODUCTION
As the world increases in complexity, so too do the
myriad systems that comprise it: from products such
as mobile phones and automobiles, to large and small
scale businesses, to our transportation system and
even to climate change. These complex systems can
be characterized as multi-dimensional, highly non-
linear, and containing dynamic feedback. The field of
System Dynamics has long been used to model, un-
derstand, and predict the behaviour of these complex
systems. Business Dynamics, a specialized offshoot
of System Dynamics, has been particularly success-
ful in examining and analysing the complex business
models of todays commerce (Sterman, 2000). For
example, envision a business analyst whose goal is
to try and predict the behaviour of customers, par-
ticularly their trend in returning to business. Using
the Systems Dynamics approach, she starts by famil-
iarising herself with the business, including all im-
portant processes and strategic goals. She then col-
lects all influencing elements on the customer and
connects them together to create a meaningful Sys-
tems Dynamics model. After some reiterations and
further discussions with the process owners, prod-
uct managers, and customers, she finally has a suf-
ficiently accurate model to address the returning cus-
tomer scenario. Up to this point, she has leveraged
her skill and expertise in defining and understanding
the problem, and has stayed well within her bound-
ary of knowledge and capability. The next critical
step, however, involves defining the parameter values
and equations in her model, which drive the simula-
tions. Even though she has access to stored business
data, as well as some stock estimation techniques, she
still needs to manually determine the parameters and
equations in her model (Peterson 1976). This process
has traditionally been found to be time consuming,
cumbersome, resource intensive, and often necessi-
tates a level of mathematical and technical expertise
that may or may not be consistent with the analysts
basic knowledge set of the initial problem. In addi-
tion, by virtue of this process being a manual one, the
opportunity for error increases dramatically.
This process, called Parameter Estimation and
Equations Formulation (PEEF), is arguably the most
critical step in the entire modelling process, since it is
key to reliable and sufficient system behaviour simu-
lations. But it is also one of the most challenging tasks
in the traditional System Dynamics process. This pa-
per begins with a survey of the state of the art ap-
proaches to parameter estimation and equation for-
mulation in a System Dynamics model. A detailed
overview of these concepts is provided, and advan-
tages and limitations are then summarized and dis-
cussed. The paper concludes by making a strong case
for the automation of the PEEF process, in order to ul-
timately improve the overall efficiency, accuracy, and
effectiveness of the System Dynamics approach.
166
Drobek M., Gilani W. and Soban D.
Parameter Estimation and Equation Formulation in Business Dynamics.
DOI: 10.5220/0004775101660176
In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design (BMSD 2013), pages 166-176
ISBN: 978-989-8565-56-3
Copyright
c
2013 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 BACKGROUND
This section contains a brief explanation of the Sys-
tem Dynamics concept. The authors introduce the
eight step modelling process by Burns, and discuss
PEEF.
2.1 Overview of System Dynamics
Concepts and Modelling Processes
The concept of System Dynamics has been widely ap-
plied to a large variety of fields, be it the simulation
and modelling of enterprises in ”Industrial Dynam-
ics” and city growth in ”Urban Dynamics” as shown
by (Forrester, 1961) and (Forrester, 1971), the world
population in ”Limits to Growth” (Meadows et al.,
1972), the System Dynamics National Model as sim-
ulation of social and economic change in countries
(Forrester et al., 1976) or the decline of the Mayan
empire in history (Hosler et al., 1977), among others.
These systems under study are highly non-linear dy-
namic systems which are continuously changing over
time. They consist of both static parameters, which
never change during each simulation run, and vari-
ables which may or may not change during simula-
tions. These parameters and variables are mostly in-
terdependent, meaning that there are circular depen-
dencies in the system under study. System Dynamics
modellers incorporate the circular dependencies by
modelling feedback loops to visualise cause and ef-
fect with causal loop diagrams (CLD) and/or state and
flow diagrams (SFD). The figures 1 and 2 illustrate a
CLD and an SFD representing an economic problem
of returning customers, which also contains a feed-
back loop. A feedback loop in a system can either be
characterised as balancing or reinforcing. Balancing
loops drive the system behaviour sooner or later to-
wards a steady state, thus equilibrium, whereas rein-
forcing loops emphasise the growth itself, either pos-
itive or negative in each iteration of the loop. The
CLD and SFD are widely accepted in the System Dy-
namics community and support the modellers under-
standing of the system under study, as explained by
Lane (Lane, 2000). Whereas the CLDs main purpose
focusses on the identification of basic elements (quan-
tities) and their connections (couplings) in the system
under study, the SFD is used to map the system to
a set of stocks (levels), rates, variables (auxiliaries),
constants (parameters), flows and connections (infor-
mation couplings). The SFD, furthermore, visualises
the resources or materials flowing through the system
under study. Such resources/materials are determined
by the system and might be, for instance, money, pol-
lution, population, water or customers as explained in
Figure 1: A causal loop diagram (CLD).
the introduction example. The previously mentioned
System Dynamics model types CLD and SFD have
been formally defined by Burns (Burns, 1977), who
relied on the concept of set theory to provide for-
mal definitions of all elements. The steps involved in
modelling a specific system using the System Dynam-
ics approach have been discussed for decades (Burns,
1977; Ford, 1999; Binder et al., 2004). Burns gave
the following procedure:
1. Determine the concrete problem which shall be
modelled and the system boundaries.
2. Identify quantities in the system which reflect the
system (e.g. by considering smaller components
of the system) .
3. Blue-print the causal diagram by addressing de-
pendencies of previous defined quantities using a
set of connections.
4. Migrate the causal diagram into a schematic
(flow) diagram to highlight the resources or ma-
terial flowing through the modelled system.
5. Formulate the model equations and estimate pa-
rameters with the help of the schematic diagram
and expert knowledge.
6. Transform equations into a machine program to
simulate the model.
7. Run the simulation and verify/validate the simula-
tion output with observed or expected real world
behaviour of the system.
8. Gain insights of simulation output, identify possi-
ble consequential policies and give client recom-
mendations.
In the early days of System Dynamics, Forrester
was for instance starting the modelling process with
an SFD and used the CLD close to the end of a
whole modelling process to summarise and visualise
the dominant loops in the current model. But later
Parameter Estimation and Equation Formulation in Business Dynamics
167
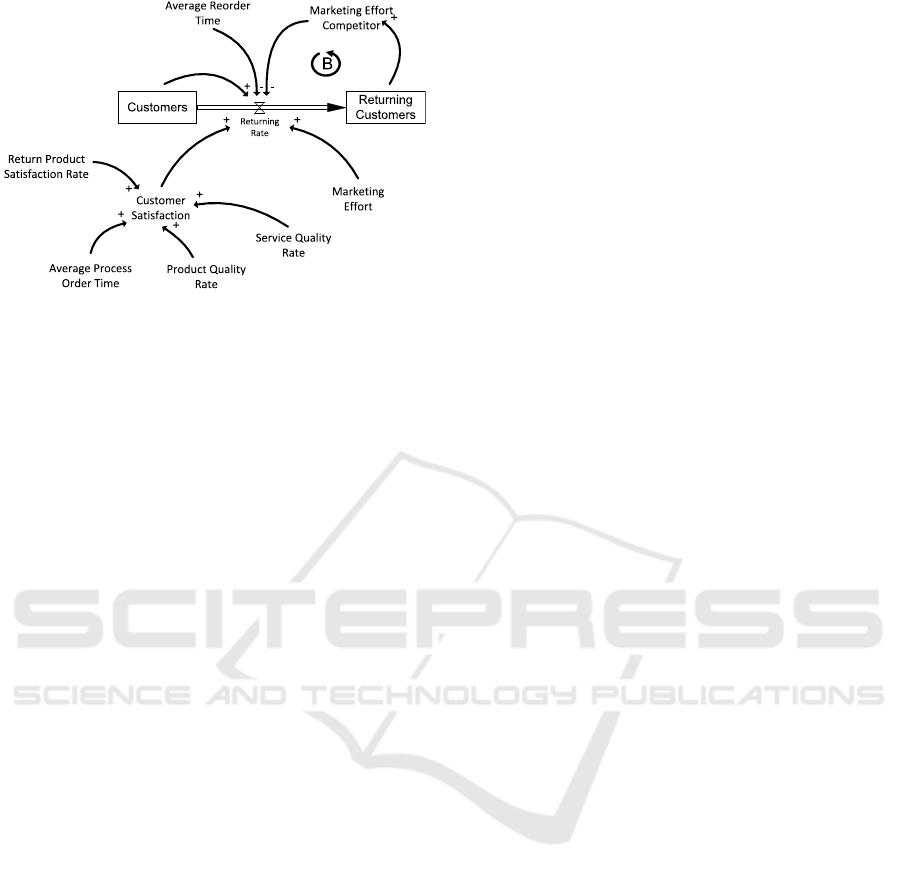
Figure 2: An economical state/flow diagram (SFD).
on it was stated by other researchers, e.g. Haraldsson
(Haraldsson, 2000), that it might come handier to start
with the CLD to get a better understanding of the in-
volved quantities and their connections. Even though
the order of the previously defined modelling process
might change from time to time, the general process
of modelling is still valid after more than 40 years.
2.2 PEEF (Parameter Estimation and
Equation Formulation)
The System Dynamics modeller has to rely upon a
huge knowledge base to identify the systems main
connections and the way in which the quantities are
influencing each other. Forrester stated that the qual-
ity of one model highly depends on the usage of
all known information about the system under study
(Forrester, 1991). This statement also holds for an-
notating a created SFD model with parameters and
equations. He divided the types of available knowl-
edge into three different classes, namely the mental
data base (experience and knowledge of humans), the
written data base (natural language text, written in-
structions) and the numerical data base (numbers in
a table). It was stated in the introduction section
that one of the critical phases in System Dynamics
is the computation of parameters and equations in the
model. There are existing approaches in place that
address this phase. However, these approaches either
lack automation, are very focussed towards specific
problems or are unable to fully exploit all available
data. Therefore, a clear potential exists for ground-
breaking research on ”Equation formulation and pa-
rameter estimation”, which corresponds to step 5 in
the traditional modelling process (see previous sec-
tion). The authors believe that PEEF is one of the ma-
jor requirements to systematically run the simulations
and predict model behaviour. Furthermore, the pro-
cess should be automatically supported and it should
be able to leverage all available data sources. The
available memory and computation power, which un-
til recently were considerable constraints to an auto-
mated process, are no longer an issue with the current
availability of cloud infrastructures and data centres.
Leveraging this new technology allows the modeller
to use all resources that might necessarily support her
in creating accurate simulation output.
3 STATE OF THE ART
This section discusses System Dynamics with respect
to PEEF, which is, after roughly 40 years, still mostly
manually done by the modeller. Relying on modeller
experience, assumptions and the knowledge of do-
main experts, if available, the initial parameters and
equations of resulting models are usually not provid-
ing satisfactory results after simulating the model. In
most cases, eventually a series of try (adjust parame-
ters/equations) and fail (rerun the simulation) replays
will deliver acceptable results in the end (see (For-
rester, 1991; Graham, 1981; Richardson, 1992)), but
this trial and error process is expensive and inefficient.
Nonetheless a lot of excellent research has been done
in these fields (Senge, 1974; Peterson, 1976; Burns,
1977; Graham, 1980; Chen and Jeng, 2002; Medina-
borja and Pasupathy, 2007). To simplify further ex-
planation of these concepts, we will borrow the defi-
nition of a very simple system from Peterson.
X(t) = A ∗ X(t − 1) +W (t) (1)
Z(t) = X (t) +V (t) (2)
Let X be the state of the system, A an unknown
parameter which has to be estimated, Z the actual
measured state of the system, W the equation error
(driving noise) and V the measurement error. Addi-
tionally
ˆ
Z is defined as the simulated state of the sys-
tem. In the now following subsections, we are going
to summarise the approaches of the former named re-
searchers.
3.1 Estimation through Simulation
The concept of imitating a real-world process over
time, so called simulation, is widely used in a variety
of technical fields, such as aeroplane design, build-
ing constructions, weather forecast etc. It is also one
of the common methods for parameter estimation in
System Dynamics. Senge and Peterson showed the
estimation of a parameter A by consecutively rerun-
ning the system simulation with new assumptions of
A until the simulation produces satisfying results. Pe-
terson called this method the Naive Simulation (NS).
Third International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design
168
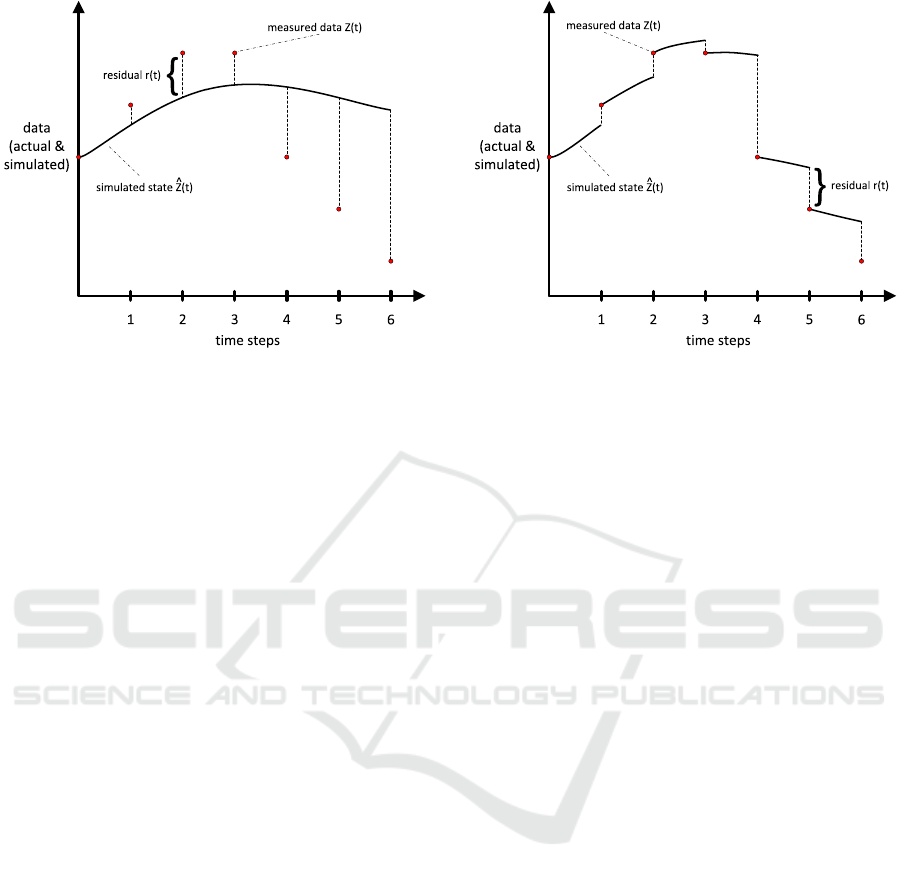
Figure 3: The naive simulation.
It is mostly accomplished by determining an initial
value for the parameter A (e.g. by guessing), run-
ning the simulation to get new results
ˆ
Z, calculating
the difference between
ˆ
Z and Z (so called residuals r)
and finally repeating this methodology until a value
for A has been found which causes the simulation
to produce acceptable results. To measure the suc-
cess of the parameter estimation, they were initially
using the Least squares method invented by Gauss
(Aldrich, 1998). This statistical concept is mostly
used in over-determined systems with more equations
than variables to estimate. The idea is to minimise
the sum of all squared residuals to get the best fit for
the estimated parameter. Figure 3 shows an exam-
ple simulation and the residuals to be minimised with
the least squares approach. The NS approach works
very well in perfect systems not being influenced by
external circumstances (reflected in the equations as
driving noise W ). In fact Peterson has shown that
for systems containing driving noise W the NS ap-
proach might deliver completely wrong parameter es-
timations, because most of the available data is sim-
ply ignored and the system might completely drift
away from the simulation result (Peterson, 1975). In
such cases where driving noise is present, but mea-
surement errors are still absent, an advanced NS ap-
proach might deliver better results. Whenever a new
data point is available, Peterson referred to the Ordi-
nary Least Squares (OLS) method to reset the current
system state when simulating to counteract the drift
(Peterson, 1976). The method delivers satisfying re-
sults for modelled systems with driving noise W , but
it is easy to understand that measurement errors V of
each available data point will also end in unsatisfy-
ing parameter estimations due to the wrong state of
the system when resetting the system. One can ar-
gue that nowadays the quality of stored data in ware-
Figure 4: The ordinary square simulation.
houses and data bases is considerably more accurate
than back in the days, but at the time Peterson formu-
lated these ideas, stored data was rare and mostly not
checked automatically for quality or the observed data
was even retrieved manually. An excellent idea of
preventing the problem of high influence from mea-
surement errors to the estimation of parameter A is Pe-
tersons idea of the Full-Information Maximum Likeli-
hood (FIMLOF) algorithm. It is based on the Kalman
filtering technique (Kalman, 1960). FIMLOF was de-
signed to determine the most likely state of the system
at each time t where data is available, by considering
all given measured, simulated and expected error data.
Whereas the measured and simulated data will be the
same input as by NS and OLS, the expected error data
is additionally computed by using the standard devia-
tion for the predicted state
ˆ
Z and the variance for the
measured data Z. Given the two most likely cases
that either V is high and W is low (high measurement
errors, but low driving noise) or V is small and W is
high (the prediction is incorrect, but the observed data
has high quality) the algorithm will behave as follows:
In the first case, FIMLOF will choose a value close to
the predicted output for the current time step, whereas
in the second case, the algorithm tends to choose a
value close to the measured data point. Either way,
FIMLOF has a very high chance to choose the most
likely value of the current system for the next simula-
tion step. This specific characteristic increases the ac-
curacy of the parameter estimation, because the more
accurate the predicted system state can be retrieved,
the fewer errors are passed through the parameter esti-
mation. Nevertheless, each of these approaches forces
the modeller to rerun the whole simulation several
times until finally computing a satisfying estimation
of parameter A. The simulation approach is therefore
no end-to-end process and works on hard assumptions
Parameter Estimation and Equation Formulation in Business Dynamics
169
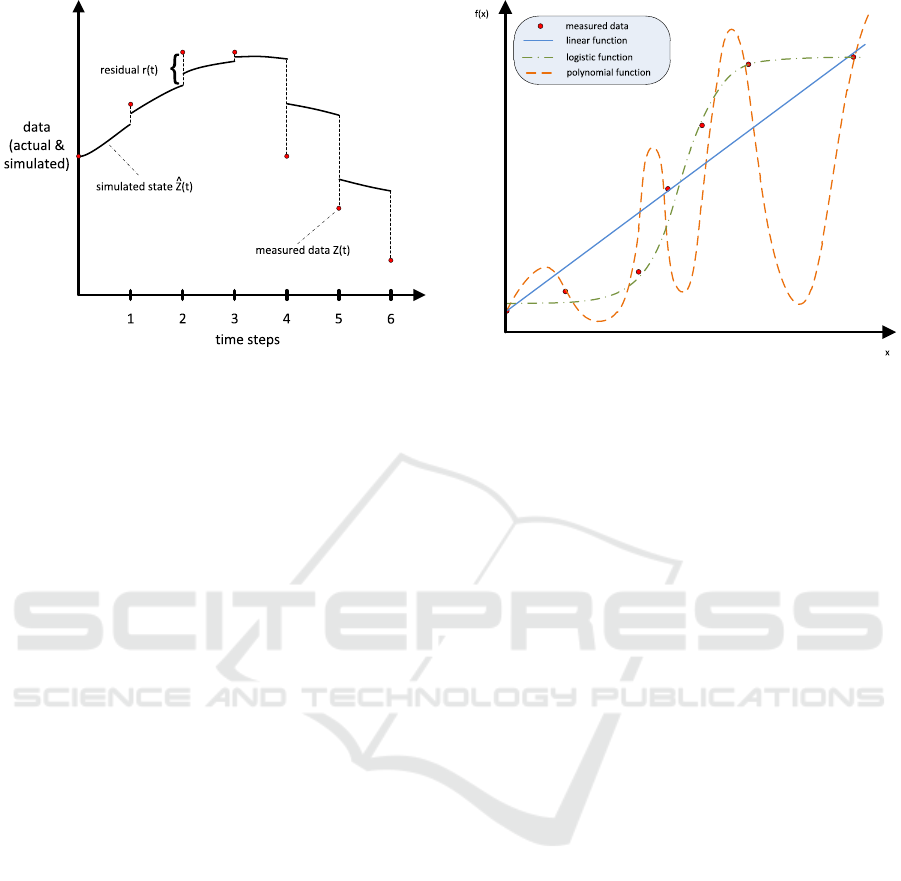
Figure 5: The FIMLOF simulation.
for the inital values of A, which is summarised in the
limitations L1 and L5.
3.2 Estimation by Data Type
Graham divided the model quantities into representa-
tions of data below the level of aggregation and data
at the level of aggregation (Graham, 1980). Data be-
low the level of aggregation (also called disaggregated
data) refers to observations and measurements made
in the real world which can be directly addressed and
therefore conforms to a specific observable character-
istic. Examples are the number of sold items in a mar-
ket at a specific time or the amount of vacation days
of one specific employee in a year. On the other hand,
data at the level of aggregation describes quantities
which are accumulated out of a number of different
basic values and are not atomic, e.g. the time for a
TCP/IP packet sent from one client machine to an-
other client machine. The main problem with data at
the level of aggregation is that it hides the main root
causes which are driving and influencing the aggre-
gated data. Graham shows different approaches of pa-
rameter estimation for data below the level of aggre-
gation and data at the level of aggregation (Graham,
1980).
The actual approach for estimating parameters
from disaggregated data depends on the available ob-
served data. If few data points are observed, the mod-
eller is able to determine a parameter by choosing a
value between the given observed limits. Dependent
on the size of the limit interval, the modellers guess
of parameter A might be more or less accurate. For
more available data points, Graham proposed to use
a table function with specific interpolations to deter-
mine the parameter A. The trick in this case is to iden-
tify the right interpolation to get slopes with smooth
Figure 6: Equation calculation with statistical analyses like
regression.
curves between the normal observed values and the
extreme observed values. And last, if the modeller
has access to numerical estimates or process obser-
vations which represent the modelled quantity, this
data might be used to calculate the actual value of
the modelled quantity. Graham uses the example of
the rabbit birth rate in an ecological model to explain
this methodology. Even though the modeller might
not have an observed value for the rabbit birth rate it-
self, she is at least in the position to acquire observed
behaviour about rabbit reproduction to calculate the
rabbit birth rate. In every case, parameter estima-
tion for disaggregated data never uses actual model
equations to retrieve parameters but instead relies on
statistical approaches like regression (linear or poly-
nomial). Figure 6 shows that by using statistical ap-
proaches an optimal fit for a given data set might be
computed, but without background knowledge about
the analysed data set the resulting function might be
completely misleading for future data points. This
problem is covered with limitation L4 and fully ap-
plies to the concept of estimation via disaggregated
data.
Graham additionally explains the concepts of
Equation estimation and Model estimation to estimate
parameters from aggregated data. Both methods rely
on model equations and transposition (usage of alge-
bra) to estimate the parameters. Using equation esti-
mation, the modeller manipulates exactly one model
equation which consists of aggregated quantities like
stocks, flows and variables to compute a value for one
parameter A. The methodology of model estimation
involves transposition of all model equations to cal-
culate parameters. In both cases, the modeller would
start to transpose the chosen model equation(s) up to
the point where A can be simply computed by insert-
Third International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design
170

ing the aggregated data values and resolving the equa-
tion(s). But working with aggregated data and model
equations usually involves assumptions made by the
modeller (see limitation L1), which in return gives
room for possible errors (Graham, 1980). However,
the quality of the parameter estimation for these meth-
ods is obviously highly dependent on the accuracy of
the underlying model equation(s) transposed and used
for calculation. Additional data of further involved
variables or rates, accessible by the modeller, is not
at all incorporated in the parameter calculation. This
approach is therefore only working on a possible frac-
tion of the available and accessible background data.
The two limitations L2 and L3 are described in the
limitation section.
3.3 Equations by Dimensions
Burns explained the approach of transforming a pre-
viously created causal diagram D (as in figure 1) into
a state/flow model by using a square ternary matrix
(STM) and modified square ternary matrix (MSTM)
as intermediate steps (Burns, 1977). The STM con-
tains all quantities q
i
as rows and q
j
as columns of
a given causal diagram and defines either −1, 0 or 1
for a connection from q
i
to q
j
or no connection (usu-
ally empty cells), as shown in table 1 for the example
of the returning customers. The sign in front of a 1
indicates the influence of q
i
to q
j
, which is either neg-
ative or positive. After identifying a set of definitions
(D1 - D9) and a set of axioms (A1-A7) which reflect
the structure of a SFD according to Forrester, Burns
was able to create systematic algorithmic rules. These
rules, when applied to a STM, deliver an SFD. The
SFD might also be represented visually with a modi-
fied STM (so called MSTM), as shown in table 3. The
MSTM differs from the STM in the representation of
the connections. Instead of having −1 and 1 as nega-
tive or positive connection, the MSTM contains either
−F, F or −I, I to indicate whether the represented
connection is an out- or inflow or a negative/positive
information coupling. Having the MSTM and the di-
mensions (dim) of each quantity enables the modeller
to retrieve equations for stocks, rates and variables
as follows. Stock equations are apparently trivial to
identify, because all stock equations are of the form:
calculate the difference between the inflow r
in
and the
outflow r
out
for the current time step ∆t and add this
value to the last value of stock x
i
, which translates to
the general equation:
x
i
(t + ∆t) = x
i
(t) + ∆t(r
in
− r
out
) (3)
The specific equations for each stock of a model
are therefore easily retrievable from the MSTM by
identifying the inflow and outflow of each stock. The
System Dynamics expert is furthermore able to de-
termine rate and variable equations by investigating
the MSTM and the dimensions (units) of these quan-
tities. Having a closer look to the MSTM columns
reveals the affecting quantities A
q
(q
i
) for each vari-
able or rate quantity q
i
. As a matter of fact, q
i
has
to be at least calculated from its affected quantities,
otherwise the given causal diagram must have been
incorrect. Burns defined this relation with equation 5
(see (Burns, 1977) pp. 705 for further information).
His mathematical function f is a mapping from all af-
fecting quantities q
j
∈ A
q
(q
i
) to the quantity q
i
(see
equation 4).
f : Q
n
→ Q (4)
q
i
= f [{A
q
(q
i
)}]
q
i
= f [{q
j1
,q
j2
,. ..,q
jn
}]
q
i
= q
j1
⊗ ·· · ⊗ q
jn
(5)
The goal of f is to establish dimension consis-
tency between all affecting quantities q
j
and the target
quantity q
i
. This is achieved by applying the math-
ematical operators (+, −, ∗, /), abbreviated by the
⊗ operator, to all affection quantities q
j
as shown in
equation 5. Because of the given mathematical oper-
ators, the equation defined in f is always of a linear
form. This method apparently fails at the point when
some affecting quantities of q
i
are dimensionless or
the dimensions are not fitting together. In this case,
Burns proposed to assume a table function for the af-
fecting quantities A
q
.
Apart from the limited linear form of the extracted
equations (see limitation L6), the expressions in each
equation are also not decorated with weighting fac-
tors and therefore might lead to inaccurate simulation
results. For example in the business world we can
easily build cases having one or more variables with
weighted dependencies: The price p and the quality q
of a product are both influencing the amount of sold
product units u
de f
, and can therefore be connected to
each other with the ⊗ operator as shown in equation
6. Since their dimensions are not fitting, a table func-
tion T , which maps the result to product units, has to
be applied.
u
de f
= T (p ⊗ q) (6)
But dependent on the product, we can fairly as-
sume that either the price or the quality of the prod-
uct have more influence on the amount of sold units
and should be weighted with weights ω
1
and ω
2
. The
equation 7 shows the weighted connection of the price
and the quality,
u
wei
= T ((ω
1
∗ p) ⊗(ω
2
∗ q))
(7)
where ω
1
,ω
2
∈ [0,1.0] and ω
1
+ ω
2
= 1.0.
Parameter Estimation and Equation Formulation in Business Dynamics
171
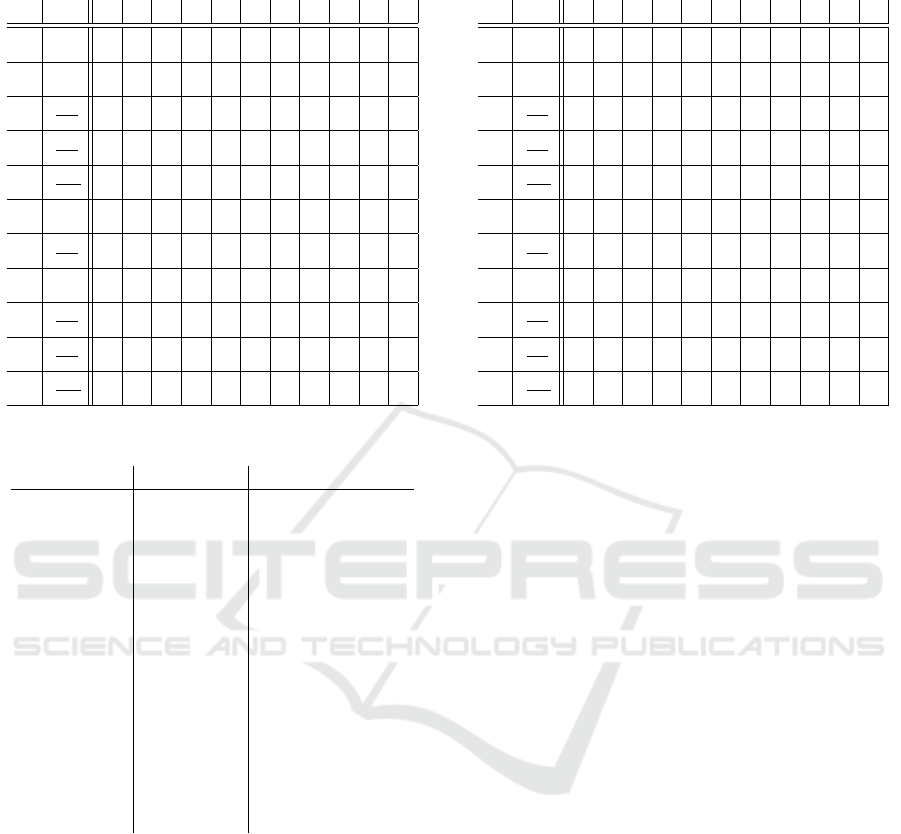
Table 1: Square ternary matrix for the example of the re-
turning customers causal diagram.
dim 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
0 CO 1
1 CO 1
2
CO
TU
-1 1
3
1
TU
-1
4
MU
TU
-1
5 - 1
6
O
TU
1
7 - 1
8
RP
TU
1
9
CC
TU
1
10
MU
CO
1
Table 2: Description of used dimensions.
abbreviation name description
CO customers the amount of
customers in the
system
TU time unit a unit of time rel-
ative to the over-
all system time
MU monetary
unit
standard currency
unit in the system
O orders all processed or-
ders
RP returned
products
all returned prod-
ucts in the sys-
tems
CC customer
complaints
all customer com-
plaints for orders
3.4 Equations with Surrogate Modelling
The sheer complexity of the System Dynamics do-
main including modelling, parameter estimation,
equation formulation, confidence checking, etc., can
be addressed by borrowing ideas and techniques from
other well established domains.
Surrogate Modelling is one such potential inter-
disciplinary field, which can be employed in the Sys-
tem Dynamics domain to address the complex equa-
tion formulation part. By blending the concepts from
the domains of Machine Learning and Statistics, Sur-
rogate Modelling offers a technique to create a surro-
gate function ˆg(x) for an unknown real function g(x)
by applying an analyses algorithm to a given train-
Table 3: Modified square ternary matrix for the example of
returning customers.
dim 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
0 CO I
1 CO I
2
CO
TU
-F F
3
1
TU
-I
4
MU
TU
-I
5 - I
6
O
TU
I
7 - I
8
RP
TU
I
9
CC
TU
I
10
MU
CO
I
ing dataset. Dependent on the chosen analysis algo-
rithm different equations can be formulated, e.g. low-
order polynomials with the least-squares regression
algorithm, neural networks with a back-propagation
training algorithm or classifications with support vec-
tor machines. Since ˆg(x) is only a substitute of the
real function g(x), it does not necessarily produce the
same outputs for the same given inputs. A calcu-
lated surrogate function ˆg(x) might therefore be ei-
ther more accurate (computational intensive) or more
computational efficient (less accurate) depending on
the given constraints (time, computation power, etc.).
Forrester et al. and Vapnik have provided an excellent
overview of Surrogate Modelling and available analy-
ses algorithms (Forrester et al., 2008; Vapnik, 1998).
However, research effort in this direction was initiated
by Chen & Jeng (Chen and Jeng, 2002) based on the
work of Dolado (Dolado, 1992). Chen and Jeng dis-
cussed the usage of artificial neural networks (ANN)
for System Dynamics as another representation of an
SFD in the first place. ANNs were first pioneered by
McCulloch & Pitts in the early 1940s and further im-
proved by Rosenblatts perceptron theory, Hopfields
energy approach and Werbos back-propagation learn-
ing algorithm (McCulloch and Pitts, 1943; Rosen-
blatt, 1962; Hopfield, 1982; Werbos, 1974). Chen and
Jeng used one partial recurrent neural network (PRN)
to represent a complete system dynamics model and
introduced a transformation from SFD to PRN. To en-
able such a transformation, there has to be a mapping
of System Dynamics elements (quantities and con-
nections) to neural network elements as follows. A
stock variable is transformed into an input, state and
output neuron. The input and output unit handle the
Third International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design
172

input and output function of a stock, whereas the state
unit serves as storage. Flows and their rates are repre-
sented by a hidden unit and the connection between a
hidden unit and an output unit, which is part of a stock
representation. Auxiliary variables are not mapped as
such, because Chen and Jeng argue that these vari-
ables might be expressed as subdivided parts of a rate
equation (”a rate in front of another rate” (Chen and
Jeng, 2002)). Furthermore, parameters (constants) are
either imitated with stocks without having a connec-
tion to hidden neurons to prevent changes in the sim-
ulation or parameters are treated as multipliers in rate
equations and therefore are not specially represented
with a neuronal network element. Finally informa-
tion couplings are illustrated with links between hid-
den and state neurons. Given these transformation
rules Chen and Jeng present a transformation algo-
rithm (FD2PRN) to convert a given SFD into a PRN.
They are furthermore applying standard algebra to the
activation functions of the PRN to proof the mathe-
matical compliance of the transformed PRN and the
typical stock, rate, initialisation and constant equa-
tions.
Up to this point the ANN is only used to illus-
trate any SFD and is therefore just another represen-
tation of a SFD like Burns MSTM. But as mentioned
earlier, ANNs have the ability to unveil hidden pat-
terns in a given dataset and therefore are capable of
providing predictions for the future development of
the dataset. The neural network mimics the equation
which produces the values of the given dataset. Hav-
ing this equation enables a modeller to predict future
values. In other words, if there is input data avail-
able for a given ANN, the ANN can be trained and
afterwards used to predict results. This statement also
holds for Chens & Jeng’s created PRN and they lever-
age this concept by training the raw untrained PRNs
of their System Dynamics test models with previously
simulated data. The trained PRNs might then be used
to predict the system behaviour, similar to simulation
runs of SFDs. The results for training of the PRN in
their paper are quite promising and given the learn-
ing ability of ANNs, they are highly adjustable to ex-
ternal changes in the system under study. These in-
sights motivate for deeper research in this field and
we, the authors, believe that the concepts of Surro-
gate Modelling and Machine Learning in general are
very well suited to tackle the problem of automated
PEEF in System Dynamics. We are especially high-
lighting this, because these concepts are embodying
the least of our addressed limitations. Nevertheless,
there are open questions arising from Chen & Jengs
work. For instance, the prediction accuracy for known
worse neural network equations like alternating be-
haviour might not be appropriately represented by a
neural network.
3.5 Formulation via Decision Trees
For decades the System Dynamics community relied
on Forresters recommendations of the three different
models explained in the beginning of this paper on
how to retrieve knowledge for building System Dy-
namics models. Forrester values the mental model
far above the written and numerical model, because
there was simply not enough data to replace the hu-
man mind of the modeller and domain experts. This
guideline is still valid, but in the modern business
world where every digital step of each customer is
monitored and stored in huge databases, the written
and numerical models are becoming more and more
useful and relevant. Research communities in the area
of business intelligence and business process manage-
ment are exploiting this huge amount of available data
and proposing enhanced solutions in the area of busi-
ness decision support. For instance, Medina-borja &
Pasupathy are leveraging this data for semi-automated
model creation and equation formulation (Medina-
borja and Pasupathy, 2007). They are showing two
statistical approaches to identify predictors of model
variables from a given data set and afterwards one
algorithm to leverage these dependencies and reveal
their mathematical representations. Classification and
Regression Trees (CART) and Chi-Square Automatic
Interaction Detection (CHAID) are both decision tree
methods which are used to divide the given data set
into groups and subgroups to assign them to nodes.
After the tree has been grown and possibly pruned,
most of the remaining nodes in the tree represent im-
portant independent variables. Common usages in the
literature for CART and CHAID are the identifica-
tion of predictors for customer behaviour and market
segmentation, direct marketing to group customers
in classes or the field of processing mining to clas-
sify process instances. On the other hand Structural
Equation Modelling (SEM) is a statistical approach
of validating or exploring a predefined model with
a given data set, see for instance (Hayduk, 1985) or
(Pearl, 2000). One idea to use SEM is to first cre-
ate a model which supposedly fits the given data set
and afterwards applying the SEM algorithm to the de-
fined model and given data set to figure whether the
model fits the data and if so, how much. The model
consists of measured variables (indicators) and unob-
served/abstract variables (latent variables). The out-
come of SEM is the cause and effect sizes (structural
coefficients) which might be used for equation for-
mulation. The idea proposed by Medina-borja & Pa-
Parameter Estimation and Equation Formulation in Business Dynamics
173

Figure 7: A regression tree for the problem of returning
customers.
supathy is to use CART or CHAID to uncover the de-
pendencies of a given data set and create a model us-
ing the generated decision tree. Afterwards SEM can
be used to determine the fit of the model to the data
and to provide the structural equations of the model.
The resulting model and its equations can be used as
a SDM and eventually fed into simulation/analyses
tools. Unfortunately SEM is only capable of creat-
ing linear structural equations and is thus subject to
limitation L6. However this concept shows a semi-
automated procedure from a given data set to final
simulation results.
4 GENERAL LIMITATIONS
All of the above stated approaches are extremely
helpful for a System Dynamics expert to either
retrieve parameter values or gain help in formulating
equations in a System Dynamics model. As each of
these concepts require specific prerequisites, there
are certain minor or major limitations associated
with these algorithms and additional questions arise
which need further research to be answered. We have
identified and collected a number of these limitations
(L1 - L6) which are either stated by the authors of the
algorithms themselves or are obvious when applying
the algorithms.
L1. Assumptions. We have observed that some of the
algorithms are working with hard assumptions, for in-
stance to guess initial values. Assumptions generally
lead to errors because there is always room to spec-
ulate. This limitation also implies a decrease in the
quality of the retrieved parameters/equations.
The algorithm works on assumptions.
L2. Predefined Equations. The availability of System
Dynamics model equations is a strong prerequisite for
simulations. For instance, in the case of the estimat-
ing by data type approach, model equations have to
be manually provided to start transposing them and
finally resolving parameters. This possesses a sig-
nificant limitation for the applicability of the algo-
rithm, because the equation formulation requires a
huge amount of effort and domain expertise. Given
the fact that the modeller is particularly interested in
the simulation result output, she is forced to addition-
ally perform the complex equation retrieval process
by hand.
Model equation information needed by the algorithm
restricts its usage and forces the modeller to deal
with additional intermediate steps.
L3. Limited Data Utilisation. Many of the algo-
rithms have a very restricted view on the available
data sets; they only consume a fraction of the avail-
able data. Good examples are observed in the equa-
tions by dimensions algorithm where only the dimen-
sions of all quantities are incorporated and in the esti-
mation through simulation algorithm where only the
historical measured data sets are captured. Histori-
cal measured data, for instance in the equations by
dimensions approach could be readily used to further
refine the retrieved equations with weights. The lim-
ited data view drives towards inaccurate equation for-
mulations and thereby misleading simulation results.
Limited data utilisation leads to inaccurate equation
formulations.
L4. Interpolation. Many algorithms (especially sta-
tistical algorithms) are very much capable of provid-
ing optimal equations that fit a given data set (see
polynomial regression algorithm figure 6). However,
these algorithms do not incorporate the actual seman-
tics hidden in the data while interpolating a given data
set. The resulting equations are therefore lacking the
accuracy to compute future data points outside the
given data set range.
The algorithm does not capture hidden patterns and
semantics.
L5. Automation. None of the algorithms support an
automated end-to-end process for PEEF. When us-
ing these algorithms, there are always intermediate
manual steps involved. For example, determining
the interpolation approach, aggregating data, provid-
ing basic equations for further refinement, creating a
model from a given decision tree, training the algo-
rithm. Manual execution of an algorithm or inter-
vention while the algorithm is executed is not only
tedious and requires a lot of domain knowledge, but
also slows down the actual process and raises addi-
tional possibilities for failures.
Third International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design
174
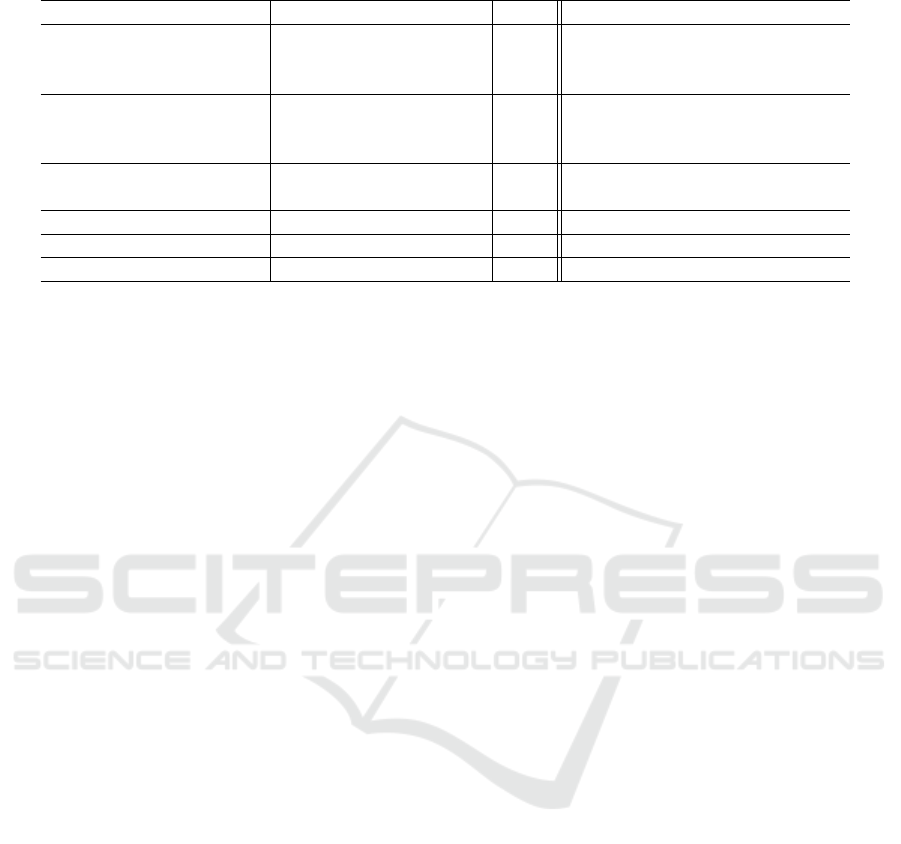
Table 4: Overview of concepts for PEEF and their limitations.
Method Algorithm Type L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6
Simulation NS PE X X ◦ ◦ X n.a.
OLS PE X X ◦ ◦ X n.a.
FIMLOF PE ◦ X ◦ - X n.a.
Data type (disaggregated) Estimate between limits PE X - X X X n.a.
Estimate table functions PE X X ◦ X X n.a.
Calculate numerical data PE ◦ X - X ◦ n.a.
Data type (aggregated) Equation estimation PE X X X X X n.a.
Model estimation PE ◦ X ◦ X X n.a.
Dimension STM/MSTM EF - - X X X X
Surrogate Modelling FD2PRN EF - - - - ◦ -
Decision trees CART, CHAID, SEM EF ◦ - - ◦ ◦ X
The algorithm is not designed to operate in an
end-to-end fashion without manual intervention.
L6. Non-linearity. Linear equations can describe the
system properly, but as stated in L4 a wrongly se-
lected interpolation leads to inaccurate simulation re-
sults. Additionally, in the business world were we
have to deal with highly non-linear behaviour, algo-
rithms are needed, that are capable of computing non-
linear equations. A good example is that of the return-
ing customers (presented in figure 2). Since some of
its influencing factors, such as the average process or-
der time, can’t be written as independent linear com-
binations, the returning customers problem is a non-
linear system. The reason is that there are so many in-
fluencing factors like marketing effort, the number of
one-time customers or even the average process order
time indirectly linked via customer satisfaction to the
returning rate. These variables and the flow can more
precisely be captured with complex non-linear cubic,
logarithmic, exponential, etc. equations. We observed
that, not all analysed algorithms, which are intended
for equation formulation, are capable of producing the
non-linear equations that can optimally capture the
system behaviour.
The algorithm is not capable of extracting non-linear
equations.
All identified limitations are summarised in table 4.
For all analysed algorithms the following three sym-
bols are used to indicate how much the limitation ap-
plies to the current algorithm.
1. The hyphen symbol (-) implies that this limitation
does not apply at all.
2. A circle symbol (◦) suggests that this limitation is
partly valid.
3. The check mark symbol (X) shows that this limi-
tation completely holds.
The table contains a method column which de-
scribes the methodology used by the algorithm to
compute its results, an algorithm name, a type column
which either contains the abbreviation PE (parameter
estimation) or EF (equation formulation) to show the
main usage of the algorithm, and one column for each
defined limitation, respectively.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper the authors have analysed methodolo-
gies and techniques for PEEF in the domain of Sys-
tem Dynamics. These methodologies have facilitated
the work of System Dynamics modellers to run and
simulate the models and finally get output for future
system behaviour. Researchers like Burns, Graham
and Senge have developed concepts to estimate pa-
rameters and to formulate equations for System Dy-
namics models from the early 70s/80s. Neverthe-
less, each of the studied approaches is embodying
specific limitations which are posed by the very na-
ture of the concept itself or these approaches were
not originally meant to be used for PEEF in the first
place. Especially for the equation formulation none
of the algorithms offers an end-to-end process from
model and data to annotated, ready to simulate model.
The authors believe that this concept of an end-to-
end automatic PEEF process is worthwhile to be re-
searched, because it would significantly decrease the
manual workload of the modeller to retrieve param-
eters/equations. Chen & Jeng and Medina-borja &
Pasupathy have shown, that machine learning and
classification approaches are very much suitable to
first create the formal models and afterwards anno-
tate them with parameters and equations. Since nowa-
days more and more business data is generated and
stored, we see high potential especially in the surro-
gate modelling concepts to leverage this data for Busi-
ness Dynamics. Our future goal is to create a semi-
automated framework which is capable of transform-
ing business data into ready-to simulate SFDs. For
Parameter Estimation and Equation Formulation in Business Dynamics
175

this, we will have to incorporate an automated version
of PEEF within our planned framework. This will free
up the analyst from doing unnecessary tasks of man-
ual PEEF, allowing her to focus more on her actual
modelling tasks. We further plan to reuse and em-
bed the existing machine learning and classification
approaches in our framework. We will invest further
research to help automate most of the crucial steps of
System Dynamics.
REFERENCES
Aldrich, J. (1998). Doing Least Squares: Perspectives
from Gauss and Yule. International Statistical Review,
66(1):61–81.
Binder, T., Vox, A., Belyazid, S., Haraldsson, H. V., and
Svensson, M. (2004). Developing System Dynamics
models from Causal Loop Diagrams. Technical re-
port, University of Luebeck, Germany; Lund Univer-
sity, Sweden.
Burns, J. R. (1977). Converting signed digraphs to For-
rester schematics and converting Forrester schematics
to Differential equations. IEEE Transactions on sys-
tems, man, and cybernetics, 10:695–707.
Chen, Y.-T. and Jeng, B. (2002). Yet another Representation
for System Dynamics Models , and Its Advantages. In
System Dynamics Society Conference.
Dolado, J. J. (1992). Qualitative Simulation and System
Dynamics. System Dynamics Review, 8(1):55–81.
Ford, A. (1999). Modeling the environment: An Intro-
duction to System Dynamics Models of Environmental
Systems. Island Press, Washington, D.C.
Forrester, A., Sobester, A., and Keane, A. (2008). Engi-
neering Design Via Surrogate Modelling: A Practical
Guide. Wiley-Blackwell.
Forrester, J. W. (1961). Industrial Dynamics. MIT Press;
currently available from Pegasus Communications;
Waltham, MA, Cambridge, MA.
Forrester, J. W. (1971). Urban Dynamics. Pegasus Com-
munications, Waltham, MA.
Forrester, J. W. (1991). System Dynamics and the Lessons
of 35 Years. pages 1–35.
Forrester, J. W., Mass, N. J., and Ryan, C. J. (1976).
The system dynamics national model: Understanding
socio-economic behavior and policy alternatives.
Graham, A. K. (1980). Parameter formulation and estima-
tion in System Dynamics Models. Elements of the Sys-
tem Dynamics Method, pages 143–161.
Graham, A. K. (1981). Lessons on modeling from the Sys-
tem Dynamics National Model. In 1981 System Dy-
namics Research Conference.
Haraldsson, H. V. (2000). Introduction to Systems and
Causal Loop Diagrams. Technical Report January,
Department of Chemical Engineering, Lund Univer-
sity, Lund.
Hayduk, L. A. (1985). The Conceptual and Measurement
Implications of Structural Equation Models. Cana-
dian Journal of Behavioural Science, 17.
Hopfield, J. J. (1982). Neural Networks and Physical Sys-
tems with Emergent Collective Computational Abili-
ties. In In Proc. National Academy of Science, pages
2554–2558.
Hosler, D., Sabloff, J. A., and Runge, D. (1977). Simulation
model development: a case study of the Classic Maya
collapse. Academic Press: London.
Kalman, R. E. (1960). A new approach to linear filtering
and prediction problems. Journal of Basic Engineer-
ing, 82:35–45.
Lane, D. C. (2000). Should System Dynamics be Described
as a ‘ Hard ’ or ‘ Deterministic ’ Systems Approach?
Systems Research and Behavioral Science, 22(June
1999):3–22.
McCulloch, W. S. and Pitts, W. (1943). A Logical Calculus
of Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity. Bull. Mathe-
matical Biophysics, 5:115–133.
Meadows, D. H., Meadows, D. L., Randers, J., and Behrens,
W. (1972). The Limits to Growth. Universe Books,
New York, NY.
Medina-borja, A. and Pasupathy, K. S. (2007). Uncovering
Complex Relationships in System Dynamics Model-
ing: Exploring the Use of CART , CHAID and SEM.
In System Dynamics Society Conference, pages 1–24.
Pearl, J. (2000). Causality: Models, Reasoning and Infer-
ence. Cambridge University Press.
Peterson, D. W. (1975). Hypothesis, Estimation and Vali-
dation of Dynamic Social Models. PhD thesis, MIT,
Cambridge, Mass.
Peterson, D. W. (1976). Statistical Tools for System Dy-
namics. Elements of the System Dynamics Method,
pages 841–871.
Richardson, G. P. (1992). Problems for the Future of System
Dynamics. Technical report, Rockefeller College of
Public Affairs and Policy, University Albany.
Rosenblatt, R. (1962). Principles of Neurodynamics. Spar-
tan Books, New York.
Senge, P. M. (1974). An experimental evaluation of gener-
alized least squares estimation. In System Dynamics
Group Memo.
Sterman, J. D. (2000). Business Dynamics: Systems think-
ing and modeling for a complex world. McGraw-Hill,
New York, NY.
Vapnik, V. N. (1998). The Nature of Statistical Learning
Theory. Springer, 2nd edition.
Werbos, P. (1974). Beyond Regression: New Tools for Pre-
diction and Analysis in the Behavioral Sciences. PhD
thesis, Harvard University.
Third International Symposium on Business Modeling and Software Design
176
