
Part-based 3D Multi-person Tracking using Depth Cue in a Top View
Cyrille Migniot and Fakhreddine Ababsa
IBISC Laboratory - University of Evry val d’Essonne, Evry, France
Keywords:
Gesture Tracking, Depth Cue, Particle Filter, Body Part, Multi-target Tracking.
Abstract:
While the problem of tracking 3D human motion has been widely studied, the top view is never taken into
consideration. However, for the video surveillance, the camera is most of the time placed above the persons.
This is due to the human shape is more discriminative in the front view. We propose in this paper a markerless
3D human tracking on the top view. To do this we use the depth and color image sequences given by a kinect.
First a 3D model is fitted to these cues in a particle filter framework. Then we introduce a process where the
body parts are linked in a complete 3D model but weighted separately so as to reduce the computing time
and optimize the resampling step. We find that this part-based tracking increases the accuracy. The process is
real-time and works with multiple targets.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the fundamental problems in computer vision
is estimating the 3D motion of humans. A lot of re-
search has been devoted to develop markerless meth-
ods which can track the motion of characters without
interfering. The great majority of the methods in the
literature use a model adapted to a front view of the
person because the shape of a person is much more
discriminative on this orientation. Furthermore the
color of the skin and the elements of the face is sel-
dom available in a top view. But the top view is often
used in video-surveillance so as to better separate the
persons, reduce the occlusions and evaluate the dis-
placement of persons. The well known Viola-Jones
face detector (Viola and Jones, 2004) provides for ex-
ample an accurate estimation of faces localization in
the front view. Nevertheless, in the application of the
video-surveillance, the camera is frequently installed
above the persons. The tracking on a top view needs
a feature more descriptive than color: the depth. The
kinect is one of the more popular devices used to pro-
vide it. It has sensors that capture both rgb and depth
data. Here, we simulate the installation of kinect cam-
eras in the ceiling of a supermarket. The goal is to
analyze the behaviors of the customers during their
buying acts within the shelves. The first step is track-
ing the pose of a customer. Then existing treatments
could be adapted to our particular context for human
activity recognition (Xu et al., 2012; Escalera, 2012).
Particle filtering (Isard and Blake, 1998a) pro-
vides a robust Bayesian framework for human mo-
tion capture. It estimates the current pose from a
sample of possible states weighted from a likelihood
function that represents the probability that a model
corresponds to the observation (here the depth and
the rgb image). As a person is articulated, most of
tracking methods use as model a skeleton that com-
prises of a set of appropriately assembled geometric
primitives (Deutscher and Reid, 2005; Hauberg et al.,
2010; Horaud et al., 2009). Variations on the frame-
work come from the choice of the likelihood function.
Skin color (Gonzalez and Collet, 2011) and contour
(matched to the chamfer distance (Xia et al., 2011))
are the most useful features. Kabayashi (Kobayashi
et al., 2006) inserts results of classifiers in the likeli-
hood function.
Some new methods introduce optimization at the
propagation level. Shan (Shan and Wei, 2007) uses
a Mean-Shift to place the particles in local minima of
the likelihood function. Nevertheless, new particle set
can not be used directly for particle filtering otherwise
the whole concept of a Bayesian approach would be
lost. But it can be used without destroying the original
distribution by adopting the technique called impor-
tance sampling (Isard and Blake, 1998b). Importance
sampling is too used by Cai (Cai et al., 2006) and
by Bray (Bray et al., 2004) with a Stochastic Meta-
Descent optimization. ISPF (Li et al., 1998) incre-
mentally draws particles and uses an online learned
pose estimator to iteratively tune them to their neigh-
boring best states.
All poses of the skeleton are not possibles in prac-
tice. For example the head can not rotate over 360
◦
.
419
Migniot C. and Ababsa F..
Part-based 3D Multi-person Tracking using Depth Cue in a Top View.
DOI: 10.5220/0004648204190426
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2014), pages 419-426
ISBN: 978-989-758-009-3
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

The sampling can be constrained by a projection on
the feasible configuration space (Hauberg et al., 2010)
or by stochastic Nelder-Mead simplex search (Lin and
Huang, 2004).
Finally, transformation can be applied to provide
an unimodal likelihood model that allows using a
Kalman filter. Larsen (Larsen et al., 2011) uses stereo
data to disambiguate depth and Brox (Brox et al.,
2010) tracks interest points provided by SIFT.
The likelihood function computing is the most
time consuming operation because it has to be done
once at every time step for every particle. Some
adaptations are needed to obtain a real time process-
ing. Gonzales (Gonzalez and Collet, 2011) realizes a
tracking for each sub-part of the body so as to use only
simple models. A hierarchical particle filter (Yang
et al., 2005) simplifies the likelihood function. The
annealed particle filtering (Deutscher and Reid, 2005)
reduces the required number of particles. (Navarro
et al., 2012) use layered particle filters to realize the
tracking of pixels of skin from multiple views. Finally
Kjellstr
¨
om (Kjellstr
¨
om et al., 2010) considers interac-
tion with objects in the environment to constrain the
pose of body and remove degrees of freedom.
In this paper, we describe a human gesture track-
ing from a top view by particle filtering. Relevant in-
formation is given by the depth provided by a kinect.
The skeleton allows to model the interaction and the
links into body parts. But the large number of degrees
of freedom leads to a too large possible states repre-
sentation to be well sampled by the particle filtering.
Our main contributions are first to introduce adapted
weighting of each degree of freedom depending on
the part of the body that it is related to. Secondly,
we use our treatment in the top view that is a sel-
dom studied perspective but often used in the video
surveillance or buying behavior context. Finally we
transpose our method to the multi-target tracking.
2 PARTICLE FILTER
IMPLEMENTATION
2.1 Observation
The Xtion Pro-live camera produced by Asus is used
to simultaneously acquire the depth and the color
cues. All the points that the sensor is not able to mea-
sure depth are offset to 0 in the output array. We re-
gard it as a kind of noise. Moreover we only model
the up part of the body. Thus, we threshold the image
to only take into consideration the pixels recognized
as an element of the torso, arms or head. It provides a
first segmentation of region of interest (ROI). A cali-
bration step associates each pixel of the depth image
to its corresponding in the color image.
One of the most interesting advantages of employ-
ing depth is the possibility of matching model and ob-
servation in the 3D space. A pixel p visible on the
depth image can be expressed in two ways : in the 2D
space of the image (figure 1(left)) and in the 3D space
(figure 1(right)). In the 2D spatial space, the point is
defined by: p
2D
= {x
2D
, y
2D
, d} where x
2D
and y
2D
are the position of the pixel on the depth image and
d is the depth value of this pixel. Calibration param-
eters computed by learning provide its corresponding
in the 3D space defined by: p
3D
= {x
3D
, y
3D
, z
3D
}.
Figure 1: The kinect records simultaneously color and
depth images (on the left). Each pixel visible in the 2D
space of these images can be transposed in the spatial 3D
space (on the right with projections on the XZ and YZ
planes).
2.2 The Particle Filter
The particle filter, also called CONDENSATION (Is-
ard and Blake, 1998a), is a method based on
the Monte-Carlo simulation that provides a suitable
framework for state estimation in a nonlinear, non-
Gaussian system. At moment k, let x
k
be the state of
the model and y
k
be the observation. Particle filter re-
cursively approximates the posterior probability den-
sity p(x
k
|y
k
) of the current state x
k
evaluating obser-
vation likelihood based on a weighted particle sample
set {x
i
k
, ω
i
k
}. Each of the N particles x
i
k
corresponds
to a random state propagated by the dynamic model
of the system and weighted by ω
i
k
. There are 4 basic
steps:
• resampling: N particles {x
0i
k
,
1
N
} ∼ p(x
k
|y
k
) from
sample {x
i
k
, ω
i
k
} are resampled: large weight parti-
cles are duplicated while low weight particles are
deleted.
• propagation: particles are propagated using the
dynamic model of the system p(x
k+1
|x
k
) to obtain
{x
i
k+1
,
1
N
} ∼ p(x
k+1
|y
k
).
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
420

• weighting: particles are weighted by a likelihood
function that defines the correspondence between
the model and the new observation. The new
weights ω
i
k+1
are normalized so that :
N
∑
i=1
ω
i
k+1
=
1. It provides the new sample {x
i
k+1
, ω
i
k+1
} ∼
p(x
k+1
|y
k+1
).
• estimation: the new pose is approximated by:
x
k+1
=
N
∑
i=1
ω
i
k+1
x
i
k+1
2.3 The 3D Model
Our study focuses on the part of the body from the hip
to the head that is visible in a top view. Our model is a
skeleton with 6 rigid parts (figure 2(a)): the head, the
torso with the shoulders, each arm and each forearm
with the hand. We make the hypothesis that the neck
has 2 degrees of freedom, each shoulder has 3 degrees
of freedom and each elbow has 2 degrees of freedom
(figure 2(c)). The pose of the torso is determined by
3 spatial coordinates and a rotation at the pelvis level
(if the customer is bent down to catch a product at
the bottom of the shelve). Overall, our 3D model has
17 degrees of freedom. That represents a very large
possible states space that is hard to well-sample with
a little number of particles and low time-processing.
The state vector that defines the pose of the model is
given by: V
3D
= {x
t
, y
t
, z
t
, θ
z
, θ
ne
x
, θ
ne
z
, θ
r.sh
x
, θ
r.sh
y
,
θ
r.sh
z
, θ
r.el
x
, θ
r.el
z
, θ
l.sh
x
, θ
l.sh
y
, θ
l.sh
z
, θ
l.el
x
, θ
l.el
z
}. To rep-
resent the volume, geometrical primitives are added.
Arms and forearms are modeled by truncated cylin-
ders, torso by an elliptic cylinder and finally the hands
by rectangular planes (figure 2(b)).
Figure 2: Our 3D model: skeleton is composed of 6 rigid
parts (a), geometrical primitives form the volume (b) and
angles related to the articulations define the pose (c).
2.3.1 The Depth-based Likelihood
In the weighting process, the likelihood function gives
the probability that a state of the model corresponds to
the pose of the person. A particle defines a 3D model
pose and the pixel of the depth image provides a set of
3D points ∆
3D
. The likelihood function describes the
matching between these two 3D datasets. Let d
ch
i
be
the average 3D euclidean distance from the points of
∆
3D
to the model state defined by the particle i. The
likelihood function is defined by :
ω
i
= e
−d
ch
i
(1)
2.3.2 The Color-based Likelihood
While the color is not discriminative of human class,
it gives interesting hint on the body parts. Indeed the
color of each part (color of the hair, of the skin, of
the clothes, etc.) is constant in the time. We define
the color-based likelihood with the Bhattacharyya dis-
tance (Nummiaro et al., 2002). For each part, a color
histogram is computed for each particle and compared
with the one computed for the estimation at the pre-
vious instant. The sum of the corresponding Bhat-
tacharyya distance is named d
bh
i
. The likelihood func-
tion of equation 1 is updated by:
ω
i
= e
−(d
ch
i
+d
bh
i
)
(2)
2.4 The Part-based Tracking
A part-based study has various advantages. First, the
number of pixels visible on a top view for each part is
not well-balanced: most of the pixels of ROI belong
to the head or the shoulders. Thus, good positions of
the head and the shoulders have most importance in
the weighting and the resampling do not well follow
the positions of the arms. Separating the weighting of
each part provides a relevant estimation for each ones.
Secondly, the number of degrees of freedom related
to a part is lower than the one of the whole model.
Hence, a lowest number of particles is required and
the computing time is reduced.
We separate the model in 5 parts P : the head, the top
part of the shoulders, the torso and each arm (figure
3). Each of the 17 degrees of freedom is related to one
part in table 1.
Table 1: Set of degrees of freedom related to each part.
Part Degrees of freedom
Head θ
ne
x
, θ
ne
z
Shoulders x
t
, y
t
, z
t
Torso θ
to
x
, θ
z
Right arm θ
r.sh
x
, θ
r.sh
y
, θ
r.sh
z
, θ
r.el
x
, θ
r.el
z
Left arm θ
l.sh
x
, θ
l.sh
y
, θ
l.sh
z
, θ
l.el
x
, θ
l.el
z
For a particle i and a part p, the weight ω
i.p
is defined
by the depth and color-based likelihood function used
previously but for the pixels of ROI whose p is the
Part-based3DMulti-personTrackingusingDepthCueinaTopView
421
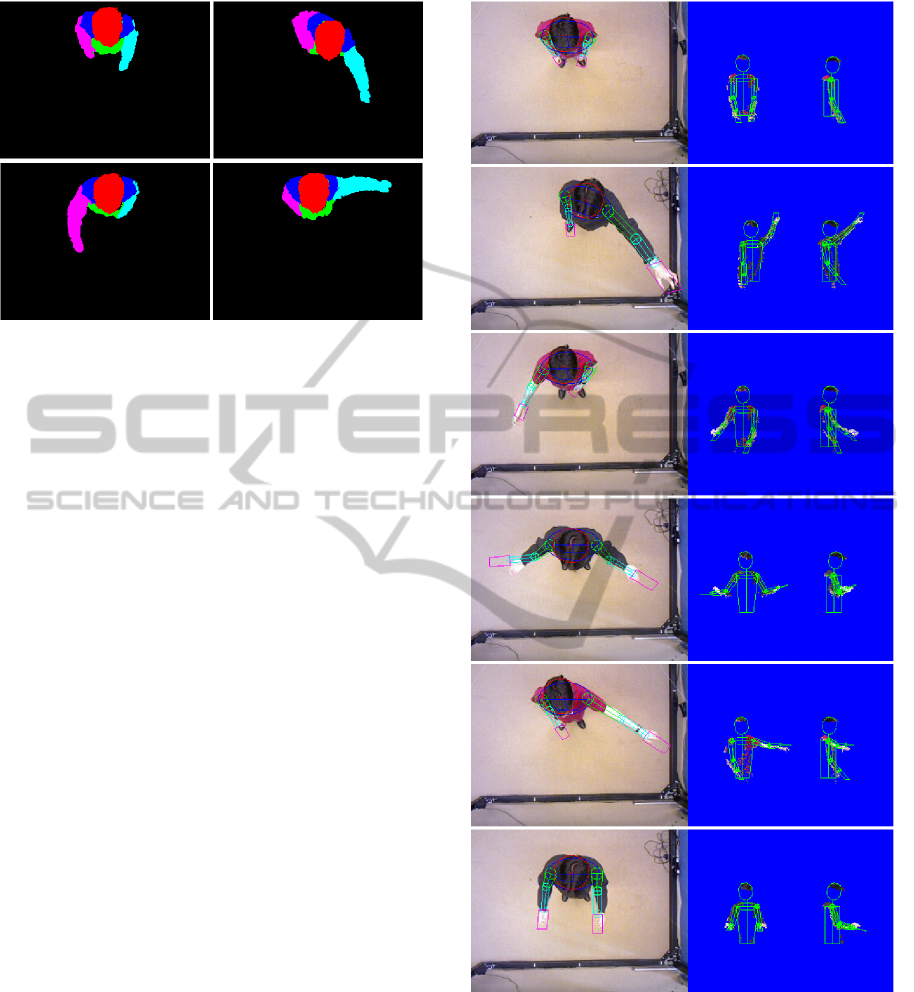
Figure 3: Each pixel of the ROI is associated with the near-
est part of the model. The five parts are: the head (in red),
the top part of the shoulders (in blue), the torso (in green),
the right arm (in magenta) and the left arm (in cyan).
nearest part for the model state given by i in the 3D
space. The sample is now defined by:
{x
i
k
= [x
i,p
k
, p ∈ P ],ω
i
k
= [ω
i,p
k
, p ∈ P ]} (3)
In the resampling step, as we have different weights
for each part, the elements x
i,p
k
duplicated or deleted
do not correspond to the same particles. Moreover,
the combination of tested poses have to be diversified.
That’s why we shuffle each part of the state vector.
The new sample is defined by:
{x
i
k
= [x
f
p
(i),p
k
, p ∈ P ],ω
i
k
= [ω
f
p
(i),p
k
, p ∈ P ]} (4)
where f
p
is a permutation from [1, N] to [1, N].
3 PERFORMANCES
Two sequences with various motion of the arms are
used to test the robustness and efficiency of our track-
ing algorithm. The first one (S
1
) is made of 450
frames (>1min) and follows the movements of a per-
son with dark clothes. Indeed, most of the time, peo-
ple wear dark clothes that are not easy to distinct from
the other elements. But we want to estimate the influ-
ence of the color in the process. Therefore, the second
sequence (S
2
) is made of 300 frames (≈43s) and fol-
lows the movements of a person with flashy clothes.
These sequences are recorded in experimental condi-
tions with a Xtion Pro live camera produced by Asus
and installed 2.9 m from the floor that corresponds to
the top of the shelves of a supermarket and is relevant
with the depth sensor range (between 0.8m and 3.5m).
The fitting between the estimation and the obser-
vation is first visualized by the projection of the esti-
mated model state on the color image (figure 4 on the
Figure 4: The tracking provides the pose of the person: on
the left the model in the color image and on the right the
model in the 3D space (the pixels in white correspond to
the points given by the depth image).
left) and on the 3D space (figure 4 on the right). We
note the good correspondence of our results and the
efficient pose description by our 3D model.
To asses the accuracy of our method and estimate
the improvement provided by the part-based process-
ing, we need to quantitatively evaluate our results. We
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
422

want that the 3D points corresponding to the pixels of
the person in the depth image are the closest of the 3D
model state. However the arms are the most difficult
part to track. The head and shoulders represents the
most of the pixels and are rather well tracked. That
leads to biases the evaluation. Thus we evaluate here
only the tracking of the arms. The set of pixels of the
arms ∆
arms
are manually annotated on all the frames
of the two sequences to create a groundtruth. Then let
ε be the average 3D euclidean distance between the
points of ∆
arms
and the estimated model state. A low
value of ε indicates a good correspondence between
the model and the observation and a good estimation.
A large number of particles best samples the possi-
ble states space and improves the estimation. Conse-
quently increasing the number of particles improves
the accuracy of the tracking. But it increases the com-
puting time. We display the curve of ε in a function of
the average computing time for a frame so as to find
an acceptable compromise. The processing times are
obtained with a non-optimized C++ implementation
running on a 3,1GHz processor.
Figure 5: Performances of the two models on the sequences
S
1
et S
2
. The part-based process improves the tracking.
The figure 5 shows explicitly that using a part-
based process improves the tracking. The results are
stable over the same computing time (approximately
150ms) but are much more accurate with the part-
based process. Then, adding the color cue slightly
improves the tracking (figures 6). It is more obvious
on the 3D model. Indeed the color cue recognizes the
various parts of the person that is already done by the
part-based 3D model. The improvement produced by
the color cue clearly depends on the video features: it
is most marked when the colors are more flashy as in
sequence S
2
.
The particle survival rate α denotes if the weights
Figure 6: Performances with and without the color cue on
the 3D (top) and the part-based 3D (bottom) models track-
ing. In favorable case (sequence S
2
), adding the color cue
increases slightly the accuracy of the tracking and particu-
larly with the 3D model.
of the particle are equally divided or not. A low value
of α means that a little number of particles are favored
by the weighting. That increases the resampling pro-
cess. In the figure 7, we notice that the arms are the
fewer rate. Thus the likelihood function is the more
efficient for these parts. Indeed it is for the arms that
the 3D shape is the more descriptive. Moreover the
color cue increases the description but decreases the
efficiency of the likelihood function.
4 MULTI-PERSON TRACKING
Multi-target tracking has been studied extensively in
the literature to estimate the position of a person but
Part-based3DMulti-personTrackingusingDepthCueinaTopView
423

Figure 7: Particle survival rate evolution on the 3D model
(in black) and for each part of the part-based 3D model: the
arms are the most descriptive parts and adding the color cue
decreases the efficiency of the likelihood function.
not to estimate his gesture. Object tracking that usu-
ally deals with targets of identical appearance, can be
ranged by learning individual target models (Breiten-
stein et al., 2011; Shu et al., 2012; Liem and Gavrila,
2009; Wu and Nevatia, 2007) but using classifiers is
time-consuming. To avoid the problem produced by
the overlapping of different targets, Gonzales (Gon-
zalez and Collet, 2011) uses the exclusion principle
introduced by MacCormick and Blake (MacCormick
and Blake, 1999). At each step, the observation (the
pixels of the recorded image) is split between the tar-
gets. Xing (Xing et al., 2009) selects the best subset
of current observations which corresponds to visible
parts to update particle weights. Blocking methods
penalize particles that overlap zones with other tar-
gets (Canton-Ferrer et al., 2008). Hence each traker
is associated to the revelant observation and can be
performed almost independantly.
Concatening the data of the all targets in a single
state vector increases dramatically the complexity of
the sytem and the computing time. Applying the ex-
clusion principle to track each target independtly is
relevant to obtain a real-time processing. For each
moment k and target t, a prediction of the model state
ˆx
t,k
is computed from the previous estimation x
t,k−1
and the dynamic of the system. Each prediction de-
fines a 3D shape related to a model state. Let T be
the set of tracked targets. We assign each pixel of the
observation (ROI) to the target whose the model state
is the nearest in the 3D space. The assignation a(u)
of the pixel u is defined by:
a(u) = argmin
t∈T
(d
E
(u, ˆx
t,k
)) (5)
where d
E
is the euclidean distance from a point to a
model state in the 3D space.
With this configuration, the tracking of each per-
son is processed as previously (figure 8).
Figure 8: To deal with multi-person tracking, the observa-
tion corresponding to each target is split (bottom left). Then
each target is tracked as previously.
We have recorded a new sequence S
3
of 214 frames
(≈ 30s) that contains two persons whose the arms are
frequently crossing and overlaped. That causes inter-
person occlusions. On this sequence, the rate of cor-
rectly assigned pixel of the ROI ∆
3D
is 99,56%.
In practice, the tracking will be used for behavior
recognition. The main challenge is to define the acts
of the person. In the multi-target tracking, it means
that the spatial proximity between two targets and the
possible inter-person occlusion it causes must not per-
Figure 9: Evolution on our estimation of the location of
the moving wrist for the two persons in the x, y, z coordi-
nates and of the distance between the two wrists. Thanks to
the exclusion principle, the two tragets are tracked indepen-
dently.
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
424
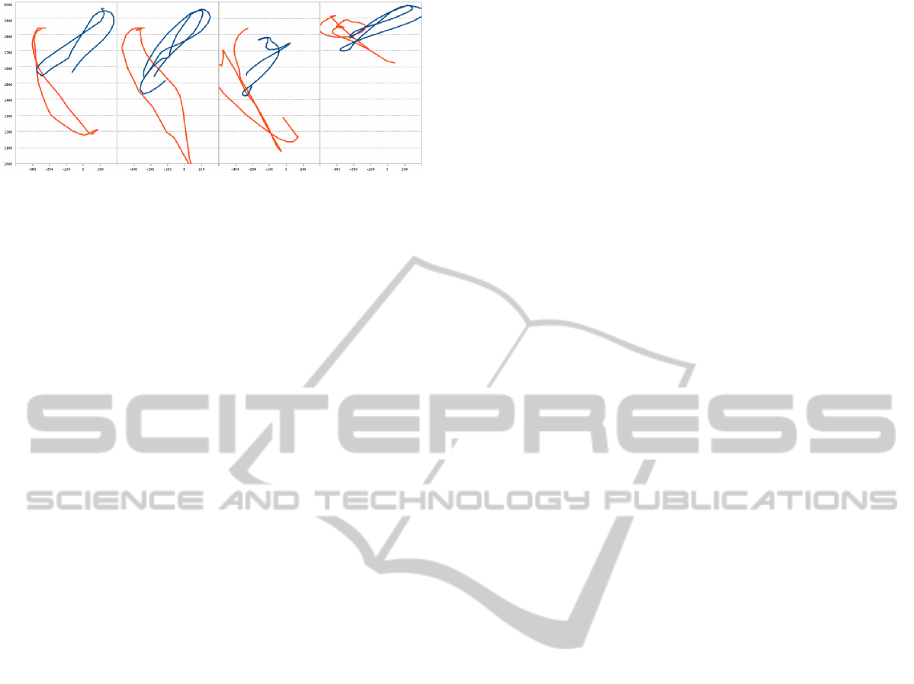
Figure 10: Trajectories of the moving wrist for the two per-
sons on our estimation projected in the XZ plane during the
four quarters of the sequence S
3
. The two arms often over-
lap in the recorded 2D image but they are correctly tracked
in the 3D space.
turbs the movement estimation of each target. Con-
sequently, we have displayed the evolution over time
of the 3D location of the wrists (well-descriptive of
the arm movement) of the two persons in sequence S
3
(figures 9 and 10). We notice that the method keep
tracking the arm regularly in case of occlusion and
that the two trajectories have independant evolutions.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have proposed a new 3D track-
ing method based on the well known particle filter
method. To be efficient in the particular case of the
top view, the new Asus camera records the depth and
color cue. Then we have introduced a particle filtering
where the elements of the state vector are weighted
separately but linked by the complete 3D model. Ex-
perimental results show that this part-based process
improves the efficiency of the tracking. The resulting
application is real time and works for multi-person
tracking by the application of the exclusion principle.
The color of the skin visible for the hands is well
descriptive of the human class. The detection of the
hands could constraint the model in future works and
reduce the number of degrees of freedom. Then, the
tracking is only the first step of the human behav-
ior. Our method could be introduced in an action
recognition process. A camera pose estimation (Di-
dier et al., 2008; Ababsa and Mallem, 2008; Ababsa,
2009) could insert our work in a Augmented Real-
ity context with a moving camera. Finally a coupled
tracking and segmentation method would give more
information for the following of the processing and
prevent wrong estimations of each of the two treat-
ments.
REFERENCES
Ababsa, F. (2009). Robust extended kalman filtering for
camera pose tracking using 2d to 3d lines correspon-
dences. IEEE/ASME Conference on Advanced Intelli-
gent Mechatronics, pages 1834–1838.
Ababsa, F. and Mallem, M. (2008). A robust circular
fiducial detection technique and real-time 3d cam-
era tracking. International Journal of Multimedia,
3(4):34–41.
Bray, M., Koller-Meier, E., and Van Gool, L. (2004). Smart
particle filtering for 3d hand tracking. IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture
Recognition, pages 675–680.
Breitenstein, M., Reichlin, F., Leibe, B., Koller-Meier,
E., and Van Gool, L. (2011). Online multiper-
son tracking-by-detection from a single, uncalibrated
camera. IEEE Transaction on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, XXXIII:1820–1833.
Brox, T., Rosenhahn, B., Gall, J., and Cremers, D. (2010).
Combined region and motion-based 3d tracking of
rigid and articulated objects. IEEE Transaction on
Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, pages
402–415.
Cai, Y., De Freitas, N., and Little, J. (2006). Robust visual
tracking for multiple targets. European Conference on
Computer Vision, pages 107–118.
Canton-Ferrer, C., Salvador, J., Casas, J. R., and Pard
`
as,
M. (2008). Multi-person tracking strategies based on
voxel analysis. Multimodal Technologies for Percep-
tion of Humans, pages 91–103.
Deutscher, J. and Reid, I. (2005). Articulated body motion
capture by stochastic search. International Journal of
Computer Vision, 2:185–205.
Didier, J., Ababsa, F., and Mallem, M. (2008.). Hybrid
camera pose estimation combining square fiducials
localisation technique and orthogonal iteration algo-
rithm. International Journal of Image and Graphics,
8(1):169–188.
Escalera, S. (2012). Human behavior analysis from depth
maps. In International Conference on Articulated Mo-
tion and Deformable Objects, pages 282–292.
Gonzalez, M. and Collet, C. (2011). Robust body parts
tracking using particle filter and dynamic template. In
IEEE International Conference on Image Processing,
pages 529 – 532.
Hauberg, S., Sommer, S., and Pedersen, K. S. (2010).
Gaussian-like spatial priors for articulated tracking. In
European Conference on Computer Vision, pages 425
– 437.
Horaud, R., Niskanen, M., Dewaele, G., and Boyer, E.
(2009). Human motion tracking by registering anartic-
ulated surface to 3d points and normals. IEEE Trans-
action on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,
XXXI:158–163.
Isard, M. and Blake, A. (1998a). Condensation - conditional
density propagation for visual tracking. International
Journal of Computer Vision, XXIX:5 – 28.
Isard, M. and Blake, A. (1998b). Icondensation - unifying
Part-based3DMulti-personTrackingusingDepthCueinaTopView
425

low-level tracking in a stochastic framework. Euro-
pean Conference on Computer Vision, I:893–908.
Kjellstr
¨
om, H., Kragic, D., and Black, M. J. (2010). Track-
ing people interacting with objects. In IEEE Confer-
ence on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.
Kobayashi, Y., Sugimura, D., Sato, Y., Hirasawa, K.,
Suzuki, N., Kage, H., and Sugimoto, A. (2006). 3d
head tracking using the particle filter with cascaded
classifiers. In British Machine Vision Conference,
pages 37 – 46.
Larsen, A., Hauberg, S., and Pedersen, K. (2011). Un-
scented kalman filtering for articulated human track-
ing. Scandinavian conference on Image analysis,
pages 228–237.
Li, M., Tan, T., Chen, W., and K., H. (1998). Efficient ob-
ject tracking by incremental self-tuning particle filter-
ing on the affine group. IEEE Transactions on Image
Processing, XXI:1298–1313.
Liem, M. and Gavrila, D. (2009). Multi-person tracking
with overlapping cameras in complex, dynamic envi-
ronments. British Machine Vision Conference, pages
1–10.
Lin, J.Y. Wu, Y. and Huang, T. (2004). 3d model-based hand
tracking using stochastic direct search method. IEEE
International Conference on Automatic Face and Ges-
ture Recognition, pages 693–698.
MacCormick, J. and Blake, A. (1999). A probabilistic ex-
clusion principle for tracking multiple objects. Inter-
national Journal on Computer Vision, I:572–578.
Navarro, S., L
´
opez-M
´
endez, A., Alcoverro, M., and Casas,
J. R. (2012). Multi-view body tracking with a
detector-driven hierarchical particle filter. In Inter-
national Conference on Articulated Motion and De-
formable Objects, pages 82–91.
Nummiaro, K., Koller-Meier, E., and Van Gool, L. (2002).
An adaptive color-based particle filter. Image and Vi-
sion Computing, XXI:99–110.
Shan, C., T. T. and Wei, Y. (2007). Real-time hand tracking
using a mean shift embedded particle filter. Pattern
Recognition, XXXX:1858–1970.
Shu, G., Dehghan, A., Oreifej, O., Hand, E., and Shah, M.
(2012). Part-based multiple-person tracking with par-
tial occlusion handling. IEEE Conference on Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1815–
1821.
Viola, P. and Jones, M. (2004). Robust real-time face de-
tection. International Journal of Computer Vision,
LVII(2):137–154.
Wu, B. and Nevatia, R. (2007). Detection and tracking of
multiple, partially occluded humans by bayesian com-
bination of edgelet based part detectors. International
Journal on Computer Vision, LXXV:247–266.
Xia, L., Chen, C.-C., and Aggarwal, J. K. (2011). Human
detection using depth information by kinect. Inter-
national Workshop on Human Activity Understanding
from 3D Data.
Xing, J., Ai, H., and Lao, S. (2009). Multi-object track-
ing through occlusions by local tracklets filtering and
global tracklets association with detection responses.
IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, pages 1200–1207.
Xu, R., Agarwal, P., Kumar, S., Krovi, V. N., and Corso, J. J.
(2012). Combining skeletal pose with local motion for
human activity recognition. In International Confer-
ence on Articulated Motion and Deformable Objects,
pages 114–123.
Yang, C., Duraiswami, R., and Davis, L. (2005). Fast multi-
ple object tracking via a hierarchical particle filter. In
International Conference on Computer Vision, pages
212 – 219.
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
426
