
Fast Semi-automatic Target Initialization based on Visual Saliency for
Airborne Thermal Imagery
C¸a˘glar Aytekin
1
, Emre Tunalı
2
and Sinan
¨
Oz
2
1
Middle East Technical University, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Ankara, Turkey
2
Image Processing Department, ASELSAN Inc. Microelectronics, Guidance and Electro-Optics Division, Ankara, Turkey
Keywords:
Real-time Target Initialization, Saliency, Distinctive Feature Selection, Long-term Tracking, Center-surround
Histogram Difference, Error Compensation.
Abstract:
In this study, a semi-automatic target initialization algorithm is introduced based on a recently proposed visual
saliency approach. First, a center-surround difference based initial window selection is utilized around the
input point coordinate provided by the user, in order to select the window which is most likely to contain
the actual target and background satisfying piecewise connectivity. Then, a recently proposed visual saliency
algorithm is exploited in order to detect the bounding box encapsulating the most salient part of the object.
The experiments support that the saliency based tracking window initialization is capable of handling marking
errors, i.e. erroneous user inputs, and boosts the performance of several tracking algorithms in terms of the
number of frames in which successful tracking is achieved, when compared with several fixed window size
initializations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Target tracking is a classical problem and has many
important applications such as surveillance, activity
or behavior detection. Hence, a diverse set of track-
ing algorithms are proposed in the literature. Majority
of tracking algorithms assume predetermined target
location and size for initialization of tracking (Shi
and Tomasi, 1994; Sand and Teller, 2006; Ramanan
et al., 2007; Dowson and Bowden, 2005; Kwon and
Lee, 2010; Bibby and Reid, 2008; Grabner et al.,
2010; Collins et al., 2005a; Avidan, 2007; Grabner
and Bischof, 2006; Babenko et al., 2009; Grabner
et al., 2008; Stalder et al., 2009). In many appli-
cations, target size and location are required as in-
put from human-users. Therefore, target initialization
can drastically change the performance of the tracker
since this initial window determines for the tracker
what to track, i.e. the features (Shi and Tomasi,
1994; Sand and Teller, 2006), appearance (Ramanan
et al., 2007; Dowson and Bowden, 2005; Kwon and
Lee, 2010), contours (Bibby and Reid, 2008). Hence,
any insignificant or false information, i.e. parts of ob-
jects similar to common background or patches from
background, may result in a mislearning of target ap-
pearance. Some tracking algorithms (Grabner et al.,
2010; Collins et al., 2005a; Avidan, 2007; Grabner
and Bischof, 2006; Babenko et al., 2009; Grabner
et al., 2008; Stalder et al., 2009) try to deal with
this problem inherently: They classify the foreground
and background of the selected window by defining
the regions close to selected window as foreground
samples, and the ones distant from the selected win-
dow as background priors. Still, this attempt does not
completely compensate the false initialization, specif-
ically in scenarios with high clutter or in crowded
scenes. Hence, false target initialization is still a prob-
lem. Indeed, in most of the real-time applications,
erroneous input is usually provided by the user due
to obligation to mark the target instantly. This er-
roneous input usually results in track losses prema-
turely. Therefore, if long-term tracking performance
desired to be achieved this erroneous input should be
compensated. Moreover, even in the case that user
provides a perfect bounding box or the center of the
target to be tracked, depending on the appearance of
the target; this initialization may not always be pre-
ferred. For example, in Fig. 1(a) an object with a
similar appearance with the background is illustrated.
An initialization like that of in Fig. 1(b) may result in
redundant features or deceptive appearance depend-
ing on the type of tracker, which may not provide
long-term tracking. Therefore, we propose that tar-
get should be selected as the most salient part of an
490
Aytekin Ç., Tunalı E. and Öz S..
Fast Semi-automatic Target Initialization based on Visual Saliency for Airborne Thermal Imagery.
DOI: 10.5220/0004668904900497
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2014), pages 490-497
ISBN: 978-989-758-009-3
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

(a) (b) (c)
Figure 1: (a) A thermal image containing a car as a target,
(b) The actual bounding box including the whole target is
indicated as red, (c) The bounding box detected by the pro-
posed target initialization algorithm.
object, most distinctive segment from background, as
in Fig. 1(c), in order to achieve long-term tracking
performance.
In many industrial applications the initialization
of target needs to be done in real time and most of
the time the only user interaction is just a marking
operation on the object. Using only marking input,
many systems initialize target, being target center at
the marked point with predefined discrete bounding
box sizes. In this study, a real-time target initializa-
tion framework is proposed which takes a single (x, y)
image coordinate from the user and returns the most
salient region bounding box in the neighborhood. It
is also shown that this initialization results in bet-
ter discriminative targets with respect to background
and provides a long-term tracking even in trackers
that claim to deal with discrimination problem during
tracking.
Automatic target initialization methods exist in
the literature, with several limitations. One main ap-
proach is motion detection (Veeraraghavan et al.,
2006) which cannot deal with stationary targets. A
more systematic approach is used in (Toyama and
Wu, 2000), however it requires a target model. There
are other existing methods (Mahadevan and Vascon-
celos, 2011; Yilmaz et al., 2003) that can handle pre-
viously mentioned issues. These algorithms process
exhaustive search over the entire image to extract tar-
gets which takes a lot of time, thereby making them
inappropriate for real-time applications. Hence, we
do not prefer exploiting these works and we follow a
semi-automatic approach instead, since we are con-
centrated on real-time applications. Furthermore, we
avoided using object window detector as (Alexeet al.,
2010) or segmentation algorithms with user interac-
tion (Rother et al., 2004), since we have obligation
to select the initial bounding box in real-time and we
only retain a coordinate input.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: The
proposed target initialization method is explained in
Section 2, the conducted experiments are analyzed in
Section 3, finally the study is concluded in Section 4
where discussions were made.
2 PROPOSED METHOD
The target initialization method proposed in this study
consists of three main steps: First, an initial window
selection method based on center-surround histogram
difference is processed, then saliency map in this win-
dow is calculated by the method (Wei et al., 2012)
and the saliency map is thresholded. Finally, the
connected component having maximum total saliency
with minimum distance to the center is selected as ini-
tial target location. These steps are extensively ana-
lyzed in this chapter.
Figure 2: Three main steps of the proposed initial target
window selection algorithm.
2.1 Initial Window Selection
The motivation of selecting an initial window is to in-
clude the foreground and to provide a feasible back-
ground for the saliency evaluation method (Wei
et al., 2012) which assumes that most of the im-
age boundaries belong to the background and the
background patches are piecewise connected. This
makes the saliency detection sensitive to the image
boundaries; hence a proper window selection is re-
quired. The main approach to an initial window se-
lection is based on the well-known center-surround
histogram difference (CSD). First, we calculate the
center-surround histogram distances in windows of
multiple sizes around the pixel marked by the user.
In order to ensure the piecewise connectivity assump-
tion in the saliency detection, we choose the window
which gives the first local maximum of histogram dis-
tance HD vector which is defined as follows:
HD(i) = K (B
w
i
+ F
w
i
), (1)
where K is a distance measure between B
w
i
and F
w
i
which are the foreground and background histograms
of window w
i
and i = (1, 2, ., N).
Local maxima other than the first one can have a
larger CSD. Actually, these maxima appear in win-
dows with layered background patches, where the
background region may correspond to only some
patches of real background, whereas the foreground
window may cover the actual foreground together
with another layer of background (See Fig. 3). How-
ever, we wish to obtain an initial window where back-
ground patches are piecewise connected, which may
not be case in some local maxima other than the first
FastSemi-automaticTargetInitializationbasedonVisualSaliencyforAirborneThermalImagery
491

(a)
(b)
Figure 3: (a) Three window sizes and blue and red win-
dows indicating the foreground and background region bor-
ders respectively, (b) Histogram distance of foreground and
background regions obtained at each window number.
Figure 4: Foreground (blue),deadzone (red) and back-
ground borders for several window selections.
one. Therefore, we select the window corresponding
to first local maximum of HD(i).
During the selection of initial window, various ob-
ject shapes are desired to be handled also. However,
since the foreground and background regions of each
window are selected as square boxes, objects with
shapes deviating from a square can be problematic.
For example, if foreground window is selected as en-
capsulating the whole target in Fig. 4, this square win-
dow also includes regions from backgroundwhich de-
crease CSD. To compensate this effect we introduce a
dead-zone region when calculating CSD. Empirically
we choose the foreground and background to cover
the 25 and 20 percent of the selected window area re-
spectively and the remaining area to be a dead-zone.
This selection is realized to help dealing with targets
with large deviation from square shape (Fig. 4).
Another issue is the calculation of histogram dis-
tances of foreground and background. For this pur-
pose, quadratic-chi histogram distance (Pele and
Werman, 2010) is utilized, since it suits to the prob-
lem in two aspects. First, it is capable of handling
quantization effects that occurs when close intensity
values are mapped into different histogram bins by
using similarity matrix which is taking care of cross-
bin relationship. Second, it suppresses the distances
resulting from bins with high values. Formulation of
quadratic-chi histogram distance is given in Eqn. 2
as:
QC
A
m
(P, Q) = (2)
s
∑
ij
(P
i
− Q
i
)
(
∑
c
(P
c
+ Q
c
)A
ci
)
m
(P
j
− Q
j
)
(
∑
c
(P
c
+ Q
c
)A
cj
)
m
A
ij
,
where P and Q represent N dimensional nonnega-
tive bounded foreground and background histograms,
”i,j” are histogram bins, A is the nonnegative sym-
metric bin similarity matrix which is NxN and m is
the normalization factor retaining distance due to high
bin values.
2.2 Saliency Map Calculation
The saliency map of the window, selected by the al-
gorithm above, is extracted by a recently proposed
fast saliency extraction method (Wei et al., 2012) in
which the saliency problem is tackled from different
perspective by focusing on background more than the
object. Although there are various saliency detection
algorithms (Hou and Zhang, 2007; Achanta et al.,
2009; Goferman et al., 2010; Cheng et al., 2011), the
main motivation of using this method is its capability
of extracting a saliency map within few milliseconds;
however, it has two basic assumptions that should be
guaranteed, namely boundary and connectivity. The
boundary assumption is reflection of a basic tendency
that photographer/cameraman do not crop salient ob-
jects among the frame. Therefore, the image bound-
ary is usually background. The connectivity assump-
tion comes from the fact that background regions are
generally tend to be large and homogenous, i.e. sky,
grass. In other words, most image patches can be eas-
ily connected to each other piecewisely. Satisfying
these two conditions, the salient regions are assumed
to be the patches that are extracted by downscaling
or by any super pixel extraction algorithm with high
geodesic distance from the boundaries of the image
that is assumed to correspond to piecewise-connected
background regions. The geodesic saliency of a patch
p is the accumulated edge weights along the shortest
path from p to virtual background node b in an undi-
rected weighted graph p ∈ {υ, ε},
S(p) = min
p
1
=p, p
2
,..., p
n
=b
n−1
∑
i=1
weight(p
i
, p
i+1
), (3)
s.t. (p
i
, p
i+1
) ∈ ε,
For this purpose a shortest path algorithm is ex-
ploited (Toivanen, 1996) in order to calculate the
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
492

shortest distance to the image boundaries from each
patch. The higher this value is the more salient the
patch. Furthermore, since patches close to the center
of the image requires a longer path in order to reach
the background, accumulation of weights tend to be
larger in the center patches. Therefore, this method
also favors the center image regions as more salient
which is reasonable since salient regions tend to oc-
cur around the center of image.
2.3 Binarization of Saliency Map
Since we look for a fast target initialization, we wish
to keep the computational cost at minimum even in
the binarization step. Hence, a fast binarization ap-
proach is proposed here exploiting the local max-
ima of saliency map. The threshold is selected by
a weighted average of local maxima of the saliency
map (Eqn. 4). In this sense, for fast binarization
process, fast local maxima detection is required. In
order to achieve fast local maxima detection, a fast
local maxima detection algorithm (Pham, 2010) is
used. After detection of local maxima, we form a
vector LocalMax
sorted
by sorting the local maxima
in descending order, and the normalized laplacian of
this vector is used as weights for local maxima. This
is meaningful since the local maxima with higher
laplacian represent a distinctive fall within local max-
ima. We shall favor these values when calculating
the threshold level since distinctive falls are indicators
of split between regions with higher saliency with re-
spect to their surroundings. Hence, a threshold would
be suitable for binarization around the most distinc-
tive fall; greatest weight is given to that local maxi-
mum in the weighted average of local maxima.
Thr = LocalMax
T
sorted
.∇
2
norm
(LocalMax
sorted
), (4)
where
∇
2
norm
( f) =
∇
2
( f) − min
∇
2
( f)
∑
i
∇
2
( f)|
i
− min(∇
2
( f))
, (5)
In order to sort the local maxima in a fast man-
ner, we generate a binary tree with heap property in
the phase of local maxima selection. Then, sorting is
accomplished in classical sense by selecting the first
element,highest, and then re-ordering the heap at each
turn until all local maxima are sorted.
After thresholding the saliency map, the con-
nected component maximizing the regularization en-
ergy given by Eqn. 6, i.e. the most salient region with
minimum distance to the center, is selected as the tar-
get.
argmax
c
i
c
T
i
s
sqrt
(x
i
− x
c
)
2
+ (y
i
− y
c
)
2
, (6)
where C
i
is the vectorized form obtained by raster
scanning the 2D label matrix with values 1 and 0
as foreground and background respectively, S is the
saliency map vectorized similarly and (x
i
, y
i
), (x
c
, y
c
)
are the centers of each connected component and the
inital window respectively.
Based on the explainations above, the entire initial
target window selection algorithm is summarized in
Algorithm 1.
Algorithm 1: Semi-Supervised Target Initialization.
Input: (x, y) coordinates from user indicating the target
location roughly
Initial window selection: Given input (x, y), select a
square window which is most likely to include actual target
and the background satisfying piecewise connectivity from
a set of windows W ∈ {w
1
, , w
n
};
Initialize Dist = {};
for W ∈ {w
1
, , w
n
} do
Obtain histogram of square foreground window
F
W
: 25% of area(W), centered at (x, y)
Obtain histogram of background window
B
W
: 20% of area(W), from the boundaries of W
Calculate quadratic-chi histogram distance
HD(W) = QC
A
m
(F
W
, B
W
)
Dist = Dist ∪ HD(w);
end for
return window size that corresponds to 1st local
maximum of Dist as initial window size
Saliency Map Calculation: Given the initial window size
return saliency map using Eqn. 3
Binarization of Saliency Map: Given the saliency map
Find local maxima and sort in descending order to
obtain LocalMax
sorted
Calculate normalized laplacian of LocalMax
sorted
using Eqn. 5
Obtain the threshold Thr using Eqn. 4
Select the connected component satisfying Eqn. 6
Output: Target bounding box enclosing the selected
connecting component.
3 EXPERIMENTS
The proposed method was tested for two aspects with
two different procedures. For both stages, in ini-
tial window selection phase, nine window sizes from
20x20 to 100x100 with regular grid were used and his-
togram bin number was selected as 25. In the calcu-
lation of histogram difference, the parameters m and
bin similarity matrix A were selected empirically as m
FastSemi-automaticTargetInitializationbasedonVisualSaliencyforAirborneThermalImagery
493
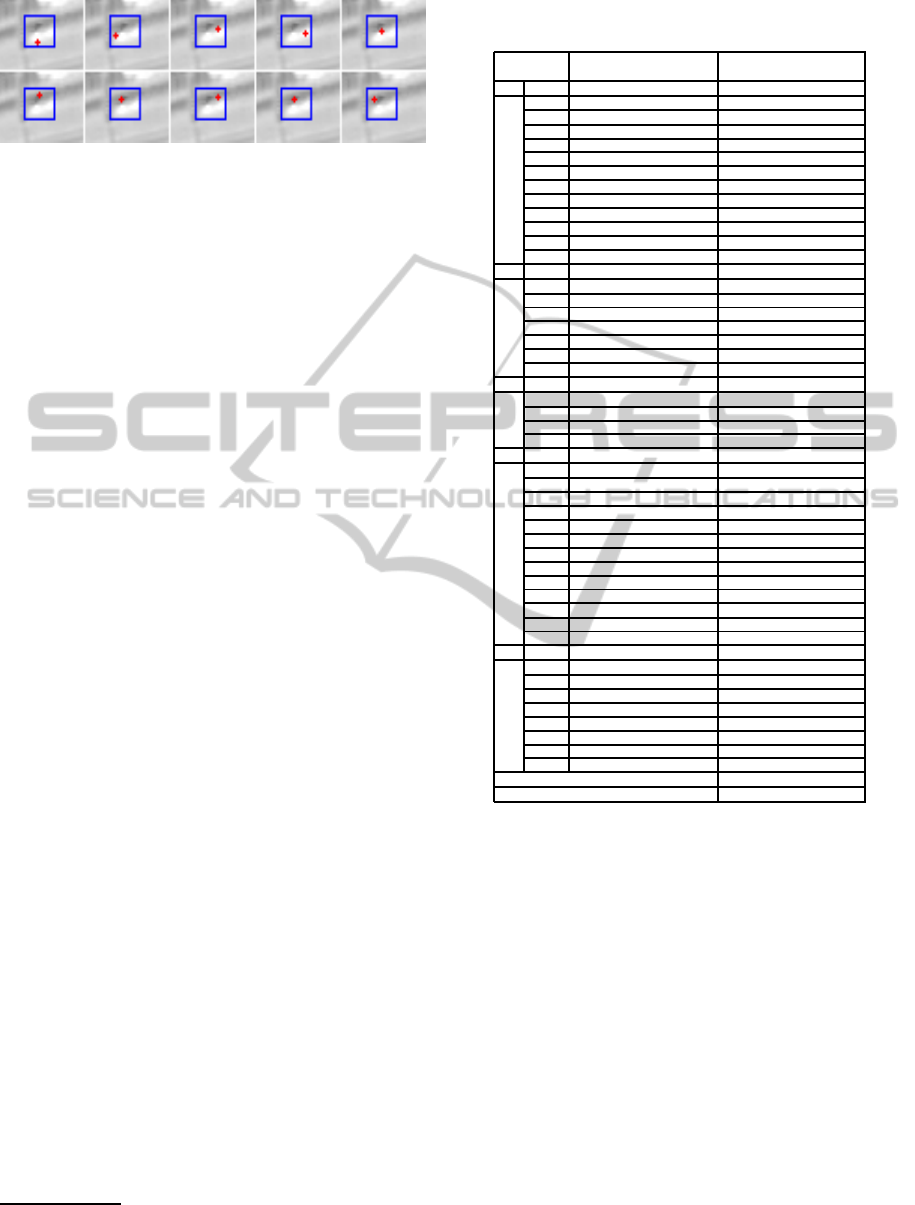
Figure 5: Erroneous marking input (red dot) and the output
target window (blue bounding box).
is to be 0.5 and A to be in 5 bin neighborhood which
cover one fifth of total number of bins. It should be
noted that increase in the number of bins of histogram
results in better resolution; therefore, better discrim-
inability between foreground and background. How-
ever, it also yields increase in computational com-
plexity which reduces time efficiency. Considering
the compromise between time efficiency and resolu-
tion, histogram bin number was decided to be 25. The
same consideration is also valid for the saliency map
calculation in which 2x2 patches were used for mean
intensity computation. Thus, these parameters may
be modified according to system in use.
At the first experiment, proposed target initializa-
tion method and its error compensation capability, i.e.
robustness to marking errors, were tested. Ground
truth for performance evaluation was generated by 10
different users. 5 specific images
1
illustrated in Ap-
pendix were given to all users. They were kindly
requested to generate bounding box for anything in
the image that appears to them as target. After the
bounding box generation, we selected targets among
the images generated by at least 6 different users as
targets and the ground truth of target bounding boxes
were decided to be the average of all bounding boxes
generated by users. Input marks were given as the
summation of the center coordinates of ground truth
bounding box and uniformly distributed pseudo ran-
dom integers, representing marking errors, for each
direction as illustrated in Fig 5.
The noise amount was decided to be 5 pixels at
maximum for the targets that are smaller than 20 pix-
els, however for the targets which are greater than 20
pixels noise amount becomes one fourth of the target
size. For each selected target, the target initialization
algorithm was run for 10 times with erroneous input
and numbers of successful initializations were noted.
The success measure for initialization is the ratio of
intersection and union of the ground truth and the tar-
get bounding box (overlap measure) and successful
initialization assumed to be achieved when the mea-
sure is higher than 0.5 as it is used in many different
1
To obtain detailed results and the input images, please
contact with the authors.
Table 1: Performance of proposed method for target initial-
ization and marking error compansation.
Image& # of Succesful Target Max # of Fully Matched
Target No Initilization (for 10 trial) Target Window
1 1 10 10
2 10 10
3 10 10
4 9 9
5 10 10
6 10 10
7 0 X
8 9 2
9 10 10
10 10 10
11 6 5
12 9 2
13 0 X
2 1 10 10
2 9 9
3 10 10
4 9 5
5 7 6
6 0 X
7 10 10
8 10 10
3 1 0 X
2 0 X
3 9 7
4 10 10
5 0 X
4 1 10 10
2 10 8
3 10 10
4 10 10
5 10 10
6 10 10
7 10 10
8 10 10
9 9 3
10 10 10
11 0 X
12 10 10
13 10 10
14 0 X
5 1 10 8
2 7 7
3 10 6
4 5 5
5 0 X
6 10 7
7 3 3
8 10 6
9 10 6
Initialization Performance: 75.7
Robustness: 87.3
applications. Since, the purpose is to obtain exactly
same target bounding box for erroneous user input,
we counted the maximum number of target bounding
boxes which are exactly matched among the target
bounding boxes that are considered as successfully
initialized and their ratio is used for robustness mea-
sure. It should be noted that in most of cases (≈ 87%)
the input error was compensated by the proposed al-
gorithm and robust target initialization(exactly same
target bounding box) was achieved. Results of the
first part are given in Table 1.
At the second stage of experiments we tested the
effect of our target initialization algorithm on tracking
by evaluating the tracking performance of three track-
ing algorithms (Grabner and Bischof, 2006; Grab-
ner et al., 2008; Stalder et al., 2009) in terms of the
number of frames that the tracker successfully tracks
against the condition that the distance from the center
of the object to be tracked to the target window center
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
494

does not change more than 5 pixels. The marking in-
put was given with a random error similar to previous
stage but in this case initialization and tracking was
executed only once. We compared the performance
of the proposed algorithm with that of fixed window
size initializations, which is the case for many real-
time applications. 16x16, 32x32 and 64x64 window
sizes were used whose centers marked by the user. It
should be mentioned that initializing the target 5 pix-
els wider than extracted window by the proposed al-
gorithm at each direction helps the trackers to learn
the model of foreground better, hence we chose the
initial windows wider. The experiments were con-
ducted over various datasets from the work of Collins
et al. (Collins et al., 2005b) with several scenar-
ios which includes airborne videos. Before compar-
ing the tracking performances, we first analyzed the
location of the initialization window determined by
the proposed algorithm when initial marks provided
by the user were erroneous, i.e. far from the cen-
ter of the target. In Fig. 6 the marks and the pro-
posed target windows are illustrated. As it is real-
ized, the algorithm is quite tolerant to erroneous input
and achieves high performance of selecting the salient
part of the target. On the other hand, when the track-
ing window was selected with fixed size target initial-
ization, the initial window tended to include various
parts of background image, decreasing the tracking
performance. The tracking performance evaluations
in terms of unsuccessful frame numbers are given in
Table 2. In this sense, 0 means target is successfully
tracked throughout the scenario.
We observed that the proposed initialization
achieved high mean performance over the scenarios
when compared with that of each fixed size initial-
izations, and it gave comparable results with each
single window initialization almost in each scenario.
The performance boost achieved with the proposed
algorithm results from handling a subset of scenarios
very well such as crowded scenes, where target is sur-
rounded with many objects; or a small part of back-
ground around the neighborhood of the target includ-
ing very strong, discriminative features. In the former
case, a erroneous initialization may result in tracking
”jumps” where the tracker starts to track the other tar-
get, whereas in the latter case, the tracker may learn
the discriminative features as the ones that belong to
background and not the actual target. Both cases oc-
cur if the window is selected large or localized at an
erroneous position from wrong marking. On the other
hand, a small window initialization may prevent the
tracker to learn the features discriminative enough to
track the target, resulting in the loss of track. The
proposed initialization is able to compensate for such
Figure 6: Some examples of target initialization windows:
(black)64x64 window, (green) 32x32 window, (red) 16x16
window, (blue) window extracted by the proposed method
and the red asterisk is the click input provided by the user.
effects and achieves good performance. Furthermore,
in cases of occlusion and illumination changes, we
observed that the tracker is more likely to redetect the
target and continues tracking. Although redetecting
target is a trait of the tracking algorithm itself, a more
discriminative initial target window selection is ob-
served to help boosting the performance in these sce-
narios.
The algorithm is applicable to real-time and a
C++ implementation of the proposed target initial-
ization algorithm takes about 12 ms on average in
TMS320C6713 Floating-Point Digital Signal Proces-
sor @270 MHz which is enough to achieve target ini-
tialization in a frame for 60 fps systems.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, we have shown that target initializa-
tion can dramatically change the performance of the
tracker, since the initial window determines for the
tracker what to track. In order to achieve a better
tracking performance; we proposed a fast, saliency
based algorithm for target initialization. Performance
boost of tracker is mainly based on two key fea-
tures of target initialization algorithm: It is capable
of compensating erroneous user input; also select-
ing the most distinctive, salient part of object as tar-
get, so better discrimination is achieved between the
target and background. Experimental results show
that tracking performance is boosted in scenarios, in
which the tracking is initialized by the proposed algo-
rithm. Very low computational cost and requirement
of only a point coordinate as input in the neighbor-
hood of the target make this approach preferable in
real time tracking applications.
FastSemi-automaticTargetInitializationbasedonVisualSaliencyforAirborneThermalImagery
495

Table 2: Performance comparison of proposed method and fixed sized windows for three different trackers.
BooostingTracker SemiBooostingTracker BeyondSemiBooostingTracker
Scenario (Grabner and Bischof, 2006) (Grabner et al., 2008) (Stalder et al., 2009)
Initial
Sequence Frame Frames Proposed 16x16 32x32 64x64 Proposed 16x16 32x32 64x64 Proposed 16x16 32x32 64x64
1.pktest01 0 450 315 310 307 210 274 314 299 191 157 178 275 241
2.pktest01 1110 350 76 316 0 155 14 74 63 194 80 160 78 344
3.pktest02 0 470 431 434 433 438 213 437 376 197 202 206 231 193
4.pktest02 770 450 0 0 0 388 360 372 275 373 0 192 102 33
5.pktest02 1185 330 32 279 96 103 5 8 52 262 84 148 273 116
6.egtest03 0 300 0 300 267 16 237 300 300 240 29 300 39 72
7.pktest03 290 230 191 190 185 188 196 192 103 184 139 197 139 199
8.egtest01 0 150 0 150 150 0 0 150 150 0 59 150 150 40
9.egtest03 0 150 0 11 137 77 52 57 141 71 47 150 74 38
10.pktest03 0 415 86 86 80 122 83 88 118 210 94 410 88 186
Average number of frames
with track loss 116.11 221.11 175.00 175.00 150.11 211.56 195.44 190.22 88.56 186.78 151.22 141.78
Although a dead zone was introduced in order to
deal with elongated objects, the proposed window se-
lection method may not be effective for all elongated
objects. Specifically, when significant amount of the
object pixels flood into the background zone together
with background pixels in foreground zone affect tar-
get initialization adversely and may yield erroneous
target initialization, which may be the case for elon-
gated objects. Even though the experiments are exe-
cuted in thermal data sets in which target objects has
smooth transition due to heat diffusion equation, the
suggested solution may be well generalized to other
imaging devices.
REFERENCES
Achanta, R., Hemami, S., Estrada, F., and Susstrunk, S.
(2009). Frequency-tuned salient region detection.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009.
CVPR 2009. IEEE Conference on, pages 1597–1604.
Alexe, B., Deselaers, T., and Ferrari, V. (2010). What is an
object? In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
(CVPR), 2010 IEEE Conference on, pages 73–80.
Avidan, S. (2007). Ensemble tracking. Pattern Analy-
sis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on,
29(2):261–271.
Babenko, B., Yang, M.-H., and Belongie, S. (2009). Vi-
sual tracking with online multiple instance learning.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009.
CVPR 2009. IEEE Conference on, pages 983–990.
Bibby, C. and Reid, I. (2008). Robust real-time visual track-
ing using pixel-wise posteriors. In Proceedings of
the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision:
Part II, ECCV ’08, pages 831–844, Berlin, Heidel-
berg. Springer-Verlag.
Cheng, M., Zhang, G., Mitra, N. J., Huang, X., and Hu,
S. (2011). Global contrast based salient region detec-
tion. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR ’11,
pages 409–416, Washington, DC, USA. IEEE Com-
puter Society.
Collins, R., Liu, Y., and Leordeanu, M. (2005a). On-
line selection of discriminative tracking features. Pat-
tern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Trans-
actions on, 27(10):1631–1643.
Collins, R., Zhou, X., and Teh, S. K. (2005b). An open
source tracking testbed and evaluation web site. In
IEEE International Workshop on Performance Evalu-
ation of Tracking and Surveillance (PETS 2005), Jan-
uary 2005.
Dowson, N. D. H. and Bowden, R. (2005). Simultaneous
modeling and tracking (smat) of feature sets. In Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2005. CVPR
2005. IEEE Computer Society Conference on, vol-
ume 2, pages 99–105.
Goferman, S., Zelnik-Manor, L., and Tal, A. (2010).
Context-aware saliency detection. In Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2010 IEEE Confer-
ence on, pages 2376–2383.
Grabner, H. and Bischof, H. (2006). On-line boosting
and vision. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recog-
nition, 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on,
volume 1, pages 260–267.
Grabner, H., Leistner, C., and Bischof, H. (2008). Semi-
supervised on-line boosting for robust tracking. In
Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on
Computer Vision: Part I, ECCV ’08, pages 234–247,
Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
Grabner, H., Matas, J., Van Gool, L., and Cattin, P. (2010).
Tracking the invisible: Learning where the object
might be. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion (CVPR), 2010 IEEE Conference on, pages 1285–
1292.
Hou, X. and Zhang, L. (2007). Saliency detection: A spec-
tral residual approach. In Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition, 2007. CVPR ’07. IEEE Conference
on, pages 1–8.
Kwon, J. and Lee, K. M. (2010). Visual tracking decompo-
sition. In CVPR, pages 1269–1276.
Mahadevan, V. and Vasconcelos, N. (2011). Automatic ini-
tialization and tracking using attentional mechanisms.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Work-
shops (CVPRW), 2011 IEEE Computer Society Con-
ference on, pages 15–20.
Pele, O. and Werman, M. (2010). The quadratic-chi
histogram distance family. In Proceedings of the
11th European conference on Computer vision: Part
II, ECCV’10, pages 749–762, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Springer-Verlag.
Pham, T. Q. (2010). Non-maximum suppression using
fewer than two comparisons per pixel. In Blanc-Talon,
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
496

J., Bone, D., Philips, W., Popescu, D., and Scheun-
ders, P., editors, Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vi-
sion Systems, volume 6474 of Lecture Notes in Com-
puter Science, pages 438–451. Springer Berlin Hei-
delberg.
Ramanan, D., Forsyth, D., and Zisserman, A. (2007).
Tracking people by learning their appearance. Pat-
tern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Trans-
actions on, 29(1):65–81.
Rother, C., Kolmogorov, V., and Blake, A. (2004). ”grab-
cut”: interactive foreground extraction using iterated
graph cuts. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2004 Papers, SIG-
GRAPH ’04, pages 309–314, New York, NY, USA.
ACM.
Sand, P. and Teller, S. (2006). Particle video: Long-
range motion estimation using point trajectories. In
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2006 IEEE
Computer Society Conference on, volume 2, pages
2195–2202.
Shi, J. and Tomasi, C. (1994). Good features to track. In
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1994. Pro-
ceedings CVPR ’94., 1994 IEEE Computer Society
Conference on, pages 593–600.
Stalder, S., Grabner, H., and Van Gool, L. (2009). Beyond
semi-supervised tracking: Tracking should be as sim-
ple as detection, but not simpler than recognition. In
Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), 2009
IEEE 12th International Conference on, pages 1409–
1416.
Toivanen, P. J. (1996). New geodesic distance trans-
forms for gray-scale images. Pattern Recogn. Lett.,
17(5):437–450.
Toyama, K. and Wu, Y. (2000). Bootstrap initialization of
nonparametric texture models for tracking. In Pro-
ceedings of the 6th European Conference on Com-
puter Vision-Part II, ECCV ’00, pages 119–133, Lon-
don, UK, UK. Springer-Verlag.
Veeraraghavan, H., Schrater, P., and Papanikolopoulos, N.
(2006). Robust target detection and tracking through
integration of motion, color, and geometry. Computer
Vision and Image Understanding, 103(2):121–138.
Wei, Y., Wen, F., Zhu, W., and Sun, J. (2012). Geodesic
saliency using background priors. In Proceedings of
the 12th European conference on Computer Vision -
Volume Part III, ECCV’12, pages 29–2, Berlin, Hei-
delberg. Springer-Verlag.
Yilmaz, A., Shafique, K., and Shah, M. (2003). Target
tracking in airborne forward looking infrared imagery.
Image and Vision Computing, 21(7):623 – 635.
APPENDIX
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
Figure 7: Thermal image dataset.
FastSemi-automaticTargetInitializationbasedonVisualSaliencyforAirborneThermalImagery
497
