
Learning Semantic Attributes via a Common Latent Space
Ziad Al-Halah, Tobias Gehrig and Rainer Stiefelhagen
Institute for Anthropomatics, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany
Keywords:
Semantic Attributes, Object Classification, Latent Space, Partial Least Squares Analysis.
Abstract:
Semantic attributes represent an adequate knowledge that can be easily transferred to other domains where lack
of information and training samples exist. However, in the classical object recognition case, where training
data is abundant, attribute-based recognition usually results in poor performance compared to methods that
used image features directly. We introduce a generic framework that boosts the performance of semantic
attributes considerably in traditional classification and knowledge transfer tasks, such as zero-shot learning.
It incorporates the discriminative power of the visual features and the semantic meaning of the attributes
by learning a common latent space that joins both spaces. We also specifically account for the presence of
attribute correlations in the source dataset to generalize more efficiently across domains. Our evaluation of the
proposed approach on standard public datasets shows that it is not only simple and computationally efficient
but also performs remarkably better than the common direct attribute model.
1 INTRODUCTION
Visual recognition via attribute-based models has
proven to be quite effective and robust especially in
cases where training samples are scarce or even not
available. Because they are defined by human lan-
guage, semantic attributes shifted the focus of vi-
sual recognition from object naming to description,
and provided a plausible way to efficiently apply the
acquired knowledge from one domain to another to
recognise previously unseen categories for example.
Since their introduction (Ferrari and Zisserman,
2008), semantic attributes were successfully applied
in many disciplines of computer vision. They en-
abled new tasks in the object recognition field like
unusual/missing attribute detection (Farhadi et al.,
2009), detection of novel classes (Farhadi et al., 2009;
Farhadi et al., 2010; Lampert et al., 2009), aiding
object naming and localization (Wang and Forsyth,
2009; Wang and Mori, 2010), relative comparison of
objects (Parikh and Grauman, 2011) and face verifi-
cation (Kumar et al., 2011) to name a few. Recently,
they were employed in action recognition showing re-
markable performance both in video-based (Liu et al.,
2011; Fu et al., 2012) and image-based (Yao et al.,
2011) action classification.
The unique property of semantic attributes is of
being both machine detectable and human under-
standable in comparison to raw image features. This
enables them to be adequate pieces of knowledge that
can be easily transferred across categories to closely
related classes that can be described using the same
vocabulary. Nevertheless, attribute-based models by
themselves could not compete with the typical object
classifiers that are built via supervised learning on im-
age features, and they are rather used along with other
models to aid the recognition performance. For ex-
ample, (Farhadi et al., 2009) used both semantic and
discriminative attributes for multi-class classification,
where the discriminative attributes are based on ran-
dom binary comparisons between sub-groups of the
classes. They use random splits between groups of
one to five classes and train a linear SVM classifier
for each split. In their experiments, 1000 discrimi-
native attributes are used to boost the attribute-based
object recognition. (Wang and Mori, 2010), on the
other hand, use a rather more sophisticated method.
They jointly model object classes, global attributes,
attributes-attributes interaction and attributes-object
interaction. Additionally, they use a latent SVM for-
mulation and introduce a loss function that is sensitive
to the mean per class accuracy, hence, it can handle
datasets with unbalanced training samples per class.
They show that their discriminative latent model re-
sults in a significant improvement over state of the art
in multi-class classification. In (Liu et al., 2011), the
authors used data-driven attributes learned directly
from image features by clustering them based on the
mutual information loss. Then, they incorporate both
attributes (semantic and data-driven) in a joint model
48
Al-Halah Z., Gehrig T. and Stiefelhagen R..
Learning Semantic Attributes via a Common Latent Space.
DOI: 10.5220/0004681500480055
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2014), pages 48-55
ISBN: 978-989-758-004-8
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Head
Ears
Furry
Nose
Eyes
Skin
...
Image
Head
Ears
Furry
Nose
Eyes
Skin
...
✔
Has head
✔
Has ears
✔
Has nose
✔
Has eyes
✔
Has skin
✔
Furry
✔
...
Partial least
squares
analysis
Latent
attribute
space
Semantic
attribute classifier
(SVM)
Semantic
attribute classifier
(SVM)
Semantic
attribute classifier
(SVM)
Semantic
attribute classifier
(SVM)
Semantic
attribute classifier
Image features
De-correlate attributes
Attribute predictions
Figure 1: Summary of our approach. First, a common latent space between image features and attributes is discovered, then
the semantic attribute classifiers are trained on this intermediate space to predict attributes.
similar in spirit to (Wang and Mori, 2010) to classify
actions.
All the mentioned methods tried to boost the poor
performance of the semantic attribute classifiers by
adding additional models like data-driven attributes,
object model or/and attribute interaction model. How-
ever, these additional models, although helped in the
typical multi-class classification task, they increased
the complexity and computational cost of the model
and they are, on the other hand, not beneficial in cases
of zero- or n-shot learning, since this type of knowl-
edge does not hold a direct semantic meaning and can
not be transferred to another domain in a similar easy
fashion as semantic attributes.
In (Duan et al., 2012), an iterative system is pro-
posed to discover both discriminatively powerful and
semantically meaningful attributes. In each iteration,
the system finds the most confused categories based
on the attributes discovered before and select a set
of local candidate attributes that can best discriminate
the confused categories. Then, based on a recommen-
dation system, the model chooses the attributes that
most likely have a semantic meaning to present for
a human operator to name the attribute. While this
system models the semantic and data-driven attributes
jointly, it requires human intervention, and is intended
to mine good attributes for classification and does
not deal with the case of already labeled data. (Fu
et al., 2012) suggested to learn a semi-latent attribute
space to classify complex social activities. The la-
tent space incorporates user defined attributes, class-
conditional attributes and non-discriminative back-
ground attributes that are learned jointly from the
data using an LDA framework. They leverage the
use of latent attributes in zero-shot learning by us-
ing the k most confident results returned using the
semantic attributes to learn a new prototype of the
novel class in the full latent space, in other words
an attribute-based zero-shot learning followed by a
latent-attribute-based k-shot learning. Our work dif-
fers from theirs in the sense that we do not extend the
attribute space to include other complementary types
of attributes, rather we focus on learning a latent space
that enhances the predictive power of the semantic at-
tributes. Hence, in contrast to the previous work, we
do not require additional annotations, like class labels,
and the latent space is learned from the features and
the defined attributes only.
We introduce a novel model to learn the semantic
attributes that results in a substantially better perfor-
mance in both the traditional recognition settings, like
multi-class classification, and knowledge transfer-
based tasks, like zero-shot learning. The model em-
ploys a multi-layer approach where a suitable latent
attribute space, that combines both the semantic at-
tribute and visual feature spaces, is first discovered
and then the attribute classifiers are learned accord-
ingly. The model is simple and robust against at-
tribute correlations and has a low computational cost
while achieving high performance. It can be easily
integrated in more complex systems that make use of
semantic attributes to improve the performance even
further when needed.
2 APPROACH
Using separate models of data-driven and seman-
tic attributes increases the complexity of the system
and reduces its ability to generalise well across data
sets. Data-driven attributes, although discriminatively
powerful, are semantically meaningless, hence it’s
difficult to use them for across data set recognition
or zero-shot learning.
In our approach, we implicitly combine both types
of attributes in one model, where the data-driven at-
tributes are extracted in a way to aid the recognition
of semantic attributes. We assume that there is a com-
mon space that bridges the gap between the image
features and attribute spaces and contains the best pre-
dictive ”latent” attributes to estimate the semantic at-
tributes. In other words, we introduce an intermediate
LearningSemanticAttributesviaaCommonLatentSpace
49

layer between image features and semantic attributes
(Figure 1), the latent attribute space, that improves the
performance of the semantic attribute classifiers sub-
stantially over the common direct approach while at
the same time reduces the computational complexity
of attribute-based recognition. We also enhance the
generalisability of the latent space for across-category
prediction and zero-shot learning by proposing an in-
termediate step to decorrelate the semantic attributes
in the source domain.
2.1 Latent Attribute Space
In order to enhance the generalizability of the at-
tributes model, we suggest to learn a common latent
space that learns the fundamental relations between
two spaces, the visual features and the semantic at-
tributes. In other words, a space that extracts a set
of latent variables from the feature space which have
the best predictive power to distinguish semantic at-
tributes. To derive this common space we use partial
least squares analysis (PLS).
Originally proposed for the field of econometrics
and widely used in the field of chemistry, PLS was
applied successfully in the recent years also for com-
puter vision problems. There, it was used to estimate
a common compact intermediate space for multiple
modalities, e.g in face recognition and head pose es-
timation (Sharma and Jacobs, 2011; Haj et al., 2012;
Schwartz et al., 2010), simultaneous age, gender, and
ethnicity estimation (Guo and Mu, 2011), or facial ex-
pression analysis (Gehrig and Ekenel, 2011).
In this work, we use PLS to estimate a common
compact space of latent attributes which relates the
visual features and the attributes. This is achieved by
maximizing the covariance between the projections of
features and attribute descriptions in the latent space.
A PLS model will try to find the multidimensional
direction in the feature space that explains the max-
imum multidimensional variance direction in the at-
tribute space (Figure 2). Hence, it derives a com-
pact representation of a dataset, that takes not only
the image features into account but also the corre-
sponding attributes and tries to find the most repre-
sentative components explaining the variance of the
given dataset. This allows for a very general lower di-
mensional space, where the information of interest, in
our case the presence of specific semantic attributes,
is usually present in the first few latent variables.
Other methods e.g. the principal component anal-
ysis, unlike PLS, just consider the input space to ex-
plain the variance of the data. That probably leads to
the case where the first few principal components are
not the most suitable candidates to discriminate the
output space.
Learning a Common Space via PLS. Assum-
ing that we have n samples in our training set,
linear PLS models the relationship between the
n × N-dimensional centered image features X =
[x
1
, . . . , x
n
]
T
and the corresponding n× p-dimensional
latent variables T = [t
1
, . . . , t
p
], respectively the n ×
M-dimensional centered semantic attributes Y =
[y
1
, . . . , y
n
]
T
and their latent representations U =
[u
1
, . . . , u
p
] as follows (Rosipal and Kr
¨
amer, 2006):
X = TP
T
+ E (1)
Y = UQ
T
+ F (2)
where P and Q are the N × p and M × p loading ma-
trices, respectively. E and F are the residual matrices
modelling the projection error.
The relationship between the latent projections of
the image features and the semantic attributes is then
modelled by the inner relation:
U = TD + H (3)
where D is a p × p diagonal matrix and H is again a
residual matrix.
To estimate the appropriate matrices, PLS uses the
following optimization criterion:
[cov(t, u)]
2
= [cov(Xw, Yc)]
2
= max
|r|=|s|=1
[cov(Xr, Ys)]
2
(4)
where cov(t, u) ∝ t
T
u represents the sample covari-
ance between the score vectors t and u. The latter are
column vectors of T and U, and they are the projec-
tions of X and Y using the column vectors w and c of
the projection matrices W and C, respectively. r and
s are the candidates for w and c over which we seek to
maximize the covariance, finally resulting in the best
candidates w and c.
In our experiment, we adopt the SIMPLS algo-
rithm for partial square analysis (de Jong, 1993). This
also restricts the score vectors t to be orthogonal, i.e.
t
T
j
t
i
= 0 for i > j. Thus, the resulting score matrix T
is orthonormal and will be in the further process used
as the latent attributes representation.
To project image features into this latent attribute
space, SIMPLS estimates the projection or weighting
matrix W, so that:
T = XW (5)
2.2 Correlated Attributes
In general, the attribute description will have some
correlation, which might be either due to the com-
position of the database or a general correlation be-
tween these attributes. To make the classifier gener-
alize better to unknown data, e.g. other categories or
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
50

Semantic attribute space
(has head, furry, metal...)
Visual feature space
(HoG, texture descriptors..)
Latent space
WC
XY
Figure 2: A latent space between image features and at-
tributes is learned by maximizing the covariance between
the projections of features and attributes into the latent
space using partial least squares analysis.
in the case of zero-shot learning, and improve conver-
gence, we want to remove that correlation. Addition-
ally, we want to give each decorrelated attribute equal
importance by normalizing it to have unit variance.
To achieve this, we propose to whiten the semantic
attributes description matrix Y.
Whitening is a linear transformation, which multi-
plies a whitening matrix Ψ to the attribute description
matrix Y (Hyv
¨
arinen and Oja, 2000; Comon, 1994)
resulting in the whitened semantic attributes descrip-
tion matrix:
˜
Y = YΨ (6)
such that the covariance matrix cov(Y) = E(yy
T
) for
the zero-mean normalized semantic attributes is trans-
formed into the identity matrix:
cov(
˜
Y) = E(
˜
y
˜
y
T
) = Ψ
T
E(yy
T
)Ψ = I (7)
We can see from Eq. (7) that Ψ should be the in-
verse of the square root of cov(Y). This problem can
be solved by means of an eigen-value decomposition
(EVD) or more numerically reliable using a singular
value decomposition (SVD):
E(yy
T
) = VΣV
T
(8)
where V and Σ are the matrix of eigenvectors and
eigenvalues, respectively. The whitening matrix thus
is estimated by:
Ψ = VΣ
−
1
2
(9)
so that
cov(
˜
Y) = Σ
−
1
2
T
V
T
E(yy
T
)VΣ
−
1
2
= Σ
−
1
2
T
V
T
VΣV
T
VΣ
−
1
2
= I (10)
So if we apply whitening to the semantic attribute
descriptions, Eq. (2) changes to:
˜
Y = UQ
T
+ F (11)
2.3 Semantic Attributes
Once the latent space is determined, the attribute clas-
sifiers can then be learned using linear support vector
machines over the latent attributes (Figure 1) by min-
imizing the objective function:
1
2
kw0k
2
+C
∑
i
max(0, 1 − y
i
. f (x
i
))
where f (x
i
) = w0ϕ(x
i
)
= w0(x
T
i
W) (12)
The dimensionality of the latent attribute space is usu-
ally much lower than the image feature space. This
allows to train the numerous attribute classifiers very
fast compared to direct approaches.
3 EVALUATION
We evaluate our approach on the common attribute-
based recognition settings, namely the attribute pre-
diction for within and across category, multi-class
classification and zero-shot learning. We test on the
a-Pascal / a-Yahoo datasets, introduced by (Farhadi
et al., 2009).
The a-Pascal dataset is based on the Pascal VOC
2008 dataset (Everingham et al., 2008), it contains
various types of object classes from three main cat-
egories (animals, vehicles, and artefacts). The dataset
has 6340 training images and 6355 test images for
20 object classes. The a-Yahoo dataset has 2644
samples collected from Yahoo images for 12 object
classes. The classes in a-Yahoo are selected to have
some similarity with the categories in a-Pascal in or-
der to evaluate the attributes generalization properties
in across category recognition. The images in these
two datasets are annotated with 64 semantic binary
attributes. They describe the shape (2D boxy, round,
...), parts (tail, head, wheel, ...), and material (metal,
plastic, ...) of the object.
In the following experiments, we follow the setup
suggested by the authors for training and testing. We
also use the image features (or base features) pro-
vided with the datasets to have a fair comparison with
(Farhadi et al., 2009). The base features are made up
of histograms of HOG, color, edge and local texture
descriptors that are joined together in a 9751 dimen-
sional feature vector.
LearningSemanticAttributesviaaCommonLatentSpace
51

5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
a-Pascal
PLS
wPLS
# Latent Attributes
AUC
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
a-Yahoo
PLS
wPLS
# Latent Attributes
AUC
Figure 3: The performance of our model with and without the attribute whitening step in relation to the number of latent
attributes (wPLS and PLS, respectively). The average AUC over all attribute classifiers is reported for within (left) and across
(right) category prediction.
3.1 Attributes Prediction
We check the effectiveness of our model in learning
uncorrelated attributes in two protocols. The within
category prediction, where attributes are learned
and tested on the same dataset (a-Pascal[train],
a-Pascal[test]) and the across category prediction,
where attributes are learned and tested on two dif-
ferent datasets (a-Pascal[train], a-Yahoo), hence they
have different correlation statistics. We report the av-
erage area under the receiver operating characteristic
(ROC) curve of the binary attribute classifiers in rela-
tion to different number of latent attributes.
Attribute Generalization. Figure 3 shows the per-
formance of our model with and without the attribute
decorrelation step explained in Section 2.2. When
considering within category prediction, both models
have similar performance with a slight edge to the
model with the correlated attributes. This is due to the
fact that both train and test datasets have similar cor-
relation statistics, hence it’s beneficial to incorporate
this information in the latent space. However, the per-
formance of the model deteriorates much more when
moving to across category prediction compared to the
one with the decorrelation components.
Figure 3 right presents the performance of the
model on a-Yahoo, where using the decorrelation suc-
cessfully improves performance up to 3% on aver-
age which gives the model a clear advantage over
the basic one regarding generalization across datasets.
We also observe that when the number of latent at-
tributes increases, the performance of both methods
have the tendency to decline for across category pre-
diction with a clear advantage of the whitened over
the correlated-attributes model. We speculate that this
may be the result of unnecessary information from the
source dataset (a-Pascal) being incorporated in the la-
tent space, showing that the few first latent attributes
represent the most appropriate knowledge to transfer
across datasets.
Number of Latent Attributes. One of the main pa-
rameters of our approach is the dimensionality of the
attribute latent space. The method for choosing the
optimal number of latent attributes is depending on
the targeted task of the system. For example, if the
focus is on the performance for within category tasks,
the number of attributes can be determined by simply
doing n-fold cross validation on the training set, and
if the across category performance is favoured, then
a leave N class out technique would be more suitable
to get the number of latent attributes. For our exper-
iments, we choose the number of latent attributes by
splitting the a-Pascal training set into a development
and validation set (50/50) and picking the number of
latent space dimensions that results in the best seman-
tic attribute classifiers when tested on the validation
set. The validation results in selecting 35 latent at-
tributes which we use in the rest of our experiments
and report the performance accordingly.
Attribute Prediction vs. Baseline. We compare the
attribute prediction performance of our model against
the baseline model (Farhadi et al., 2009). In the
attribute-baseline model, the attribute classifiers are
trained directly on the base features. We train both
models on the a-Pascal training set and evaluate on
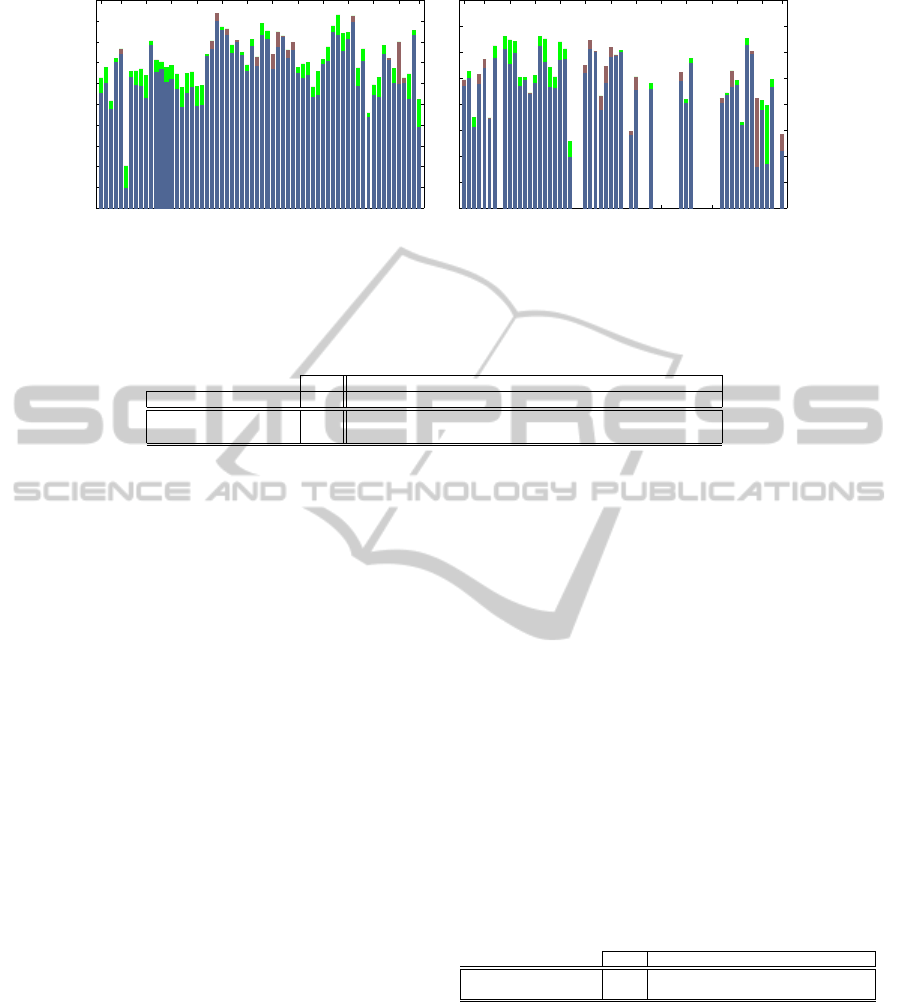
the a-Pascal test set. In Figure 5 left, we see that
most of the attribute classifiers (49 out of 64) bene-
fit from our model with up to 6.6% increase in terms
of area under curve of ROC. On average, our model
achieves 85.35% area under the ROC curve compared
to 83.54% of the baseline (our implementation of the
baseline system is slightly better than the one reported
in (Farhadi et al., 2009) with 83.4% average AUC).
When testing using across category protocol (test on
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
52
−0.02 −0.015 −0.01 −0.005 0 0.005 0.01 0.015 0.02 0.025 0.03
−0.02
−0.01
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
t1
t2
HeadLight
VertCyl
Ear
(a) First two dimensions for wPLS.
−20 −10 0 10 20 30
−30
−20
−10
0
10
20
30
t1
t2
HeadLight
VertCyl
Ear
(b) First two dimensions for PCA.
−0.02
−0.01
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
−0.02
0
0.02
0.04
−0.04
−0.03
−0.02
−0.01
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
t1
t2
t3
HeadLight
VertCyl
Ear
(c) First three dimensions for wPLS.
−20
−10
0
10
20
30
−20
0
20
−20
−10
0
10
20
30
t1
t2
t3
HeadLight
VertCyl
Ear
(d) First three dimensions for PCA.
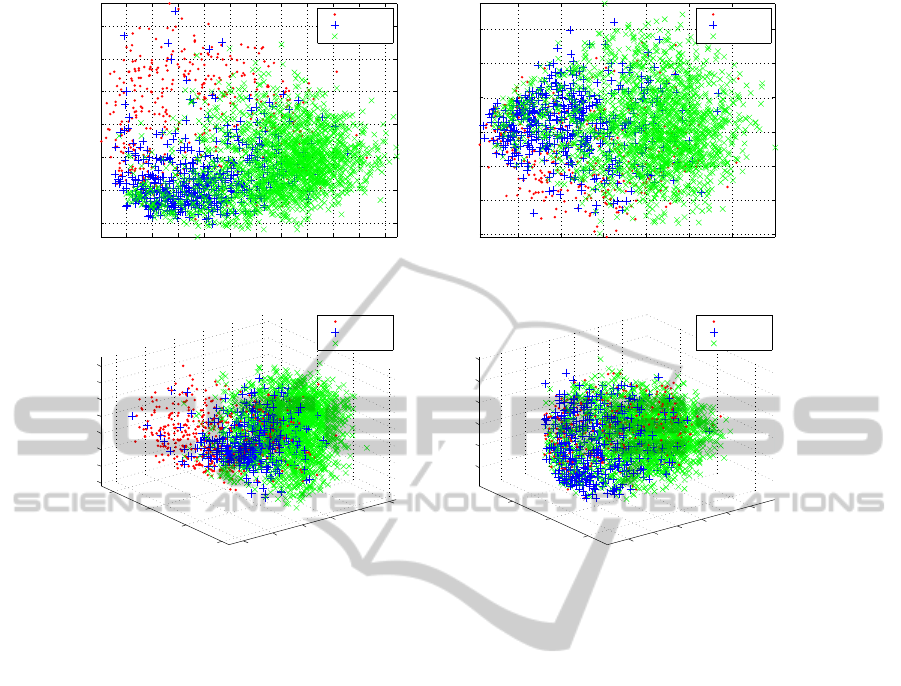
Figure 4: (a) and (b) visualize the first two, and (c) and (d) the first three learned dimensions in the latent space and PCA,
respectively. The points are labelled according to three of the semantic attributes for a better view of the sample distributions
after projection to the latent space. (Best viewed in color.)
a-Yahoo which has 10 different classes). We can
see in Figure 5 right, that our model has on average a
better prediction performance than the baseline (58%
of the classifiers have better performance with an in-
crease up to 23% in terms of AUC compared to the
baseline) although we have selected the number of
latent attributes that favour within category predic-
tion. Hence, our semantic attribute classifiers outper-
form the model that learns directly from image feature
space in both within category and across category pre-
diction.
To have a closer look at the learned latent space,
we visualize the directions learned by the model. In
Figure 4(a) and Figure 4(c), the first two and three la-
tent variables projected from the visual feature space
are displayed. The projections are labelled with
three semantic attributes (Headlight, VerticalCylin-
drical and Ear). The figure shows intuitively that the
model learns meaningful discriminant directions in
the latent space that bring distinct semantic attributes
into compact clusters. In contrast, the unsupervised
PCA learns a latent space that best explains the vari-
ance in the feature space which is usually not suit-
able enough to learn the semantic attributes as seen in
Figure 4(b) and Figure 4(d).
3.2 Multi-class Classification
Most of the systems that use attributes in multi-class
classification use them as a sub-model of a more
complicated system since using just the semantic at-
tributes didn’t result in comparable performance to
the baseline-models that learn the classes directly
from image features. We show here that our model
outperforms both the baseline-model of objects and
attributes. Using our approach presented in Section 2,
we train the semantic attribute classifiers based on the
latent attribute space using linear SVMs. We use the
predicted semantic attributes afterwards to train a lin-
ear multi-class SVM (Chang and Lin, 2011). For all
SVM classifiers, the parameters are selected using a
5-fold cross validation on the training data set of a-
Pascal. We report the overall and the mean per class
accuracies, because the dataset is heavily biased to-
wards the ”person” class (with 2500 out of 6340 train
samples).
Table 1 shows the performance of our approach
compared to (Farhadi et al., 2009). It outperforms the
LearningSemanticAttributesviaaCommonLatentSpace
53
1 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 64
0.5
0.55
0.6
0.65
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
a−Pascal
Attribute Index
AUC
1 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 64
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
a−Yahoo
Attribute Index
AUC
Figure 5: Comparison between the direct approach and ours for attribute classifiers prediction performance on the datasets
a-Pascal(left) and a-Yahoo(right). The green bars indicate an improvement of our model over the baseline while the red bars
indicate a reduction in performance (best viewed in color).
Table 1: The multi-class classification accuracies of our approach compared to the models proposed by (Farhadi et al., 2009)
on the a-Pascal dataset.
Ours Base features Semantic attr. Semantic + Discriminative attr.
# Dimensions 64 9751 64 1064
Mean overall accuracy 59.6 58.5 56.1 59.4
Mean per class accuracy 40.9 35.5 34.3 37.7
class-based (base features) and attribute-based (se-
mantic attr.) models with up to 3.5% in terms of over-
all accuracy, 5.4% and 6.6% with regard to the per
class accuracy. The best result reported in (Farhadi
et al., 2009) uses, in addition to semantic attributes,
1000 discriminative attributes along with a feature se-
lection method. Our method still performs better with
a 3.2% absolute increase in per class accuracy.
Due to the high dimensionality reduction when
learning semantic attributes via latent attribute space,
our model is computationally very efficient. Using a
computer with core i7 @ 3.20 GHz, we trained our
model in 20.2 minutes, which includes the validation
time to get the proper latent attributes number (15.8
min.), getting the latent attribute space and learning
the semantic attributes with linear SVMs and 5-folds
cross validation for parameter selection (4.4 min.). In
comparison, the baseline model, that learns attributes
directly from the raw features space, trained in 13.77
hours (826.65 min.). The computational efficiency,
simplicity and the higher performance of our model
make it a good candidate for large scale visual recog-
nition.
3.3 Zero-shot Learning
One of the important properties of the attribute-based
recognition is the ability to generalize across do-
mains. It enables zero-shot learning of novel cate-
gories based on the semantic description of the cat-
egory. We test our approach on zero-shot learn-
ing by performing multi-class classification on a-
Yahoo based on category-level attribute descriptions
of the 10 classes in a-Yahoo and using attribute clas-
sifiers trained on a-Pascal.
In (Farhadi et al., 2009) category-level attributes
are not provided, in order to test for zero-shot learn-
ing we get the attribute description for each of the
classes in a-Yahoo by calculating the attribute-class
frequency matrix over all classes in the dataset and
thresholding using the average frequency.
For classification, we use the first nearest neigh-
bour (1NN) classifier to find out the nearest class de-
scription to the predicted attributes. Table 2 shows
that our model outperforms the baseline model, that
uses the base feature space to learn the semantic at-
tributes, with an absolute accuracy increase of 1.51%
and 2.03% in overall and per class accuracy, respec-
tively.
Table 2: Results of zero-shot learning on the a-
Yahoo dataset, comparing our approach to a baseline model
that learns the semantic attributes directly from image fea-
tures.
Ours Semantic attr. on base features (baseline)
Mean overall accuracy 25.53 24.02
Mean per class accuracy 23.94 21.91
4 CONCLUSIONS
We have introduced a combined model of latent and
semantic attributes. The layered approach uses partial
least squares to find a suitable latent attribute space to
learn the semantic attributes. The experiment results
show that different tasks based on attribute recog-
nition benefit clearly from our model. The model
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
54

outperforms the direct approach model in within and
across category attribute prediction, multi-class clas-
sification and zero-shot learning. In addition, our
model is simple and computationally more efficient
than methods that use the base feature space.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study is funded by OSEO, French State agency
for innovation, as part of the Quaero Programme.
REFERENCES
Chang, C.-C. and Lin, C.-J. (2011). LIBSVM: A library
for support vector machines. ACM Transactions on
Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2:27:1–27:27.
Comon, P. (1994). Independent component analysis, A new
concept? Signal Processing, 36(3):287–314.
de Jong, S. (1993). SIMPLS: An alternative approach to
partial least squares regression. Chemometrics and In-
telligent Laboratory Systems, 18(3):251–263.
Duan, K., Parikh, D., Carndall, D., and Grauman, K.
(2012). Discovering localized attributes for fine-
grained recognition. In CVPR.
Everingham, M., Van Gool, L., Williams, C. K. I., Winn,
J., and Zisserman, A. (2008). The PASCAL Visual
Object Classes Challenge 2008 (VOC2008) Results.
Farhadi, A., Endres, I., and Hoiem, D. (2010). Attribute-
Centric Recognition for Cross-category Generaliza-
tion. In CVPR.
Farhadi, A., Endres, I., Hoiem, D., and Forsyth, D. (2009).
Describing Objects by their Attributes. In CVPR.
Ferrari, V. and Zisserman, A. (2008). Learning Visual At-
tributes. In NIPS.
Fu, Y., Hospedales, T. M., Xiang, T., and Gong, S. (2012).
Attribute Learning for Understanding Unstructured
Social Activity. In ECCV.
Gehrig, T. and Ekenel, H. K. (2011). Facial Action Unit
Detection Using Kernel Partial Least Squares. In 1st
IEEE Int’l Workshop on Benchmarking Facial Image
Analysis Technologies (BeFIT 2011).
Guo, G. and Mu, G. (2011). Simultaneous Dimensional-
ity Reduction and Human Age Estimation via Kernel
Partial Least Squares Regression. In CVPR.
Haj, M. A., Gonz
`
ales, J., and Davis, L. S. (2012). On
Partial Least Squares in Head Pose Estimation: How
to simultaneously deal with misalignment. In CVPR,
Providence, RI, USA.
Hyv
¨
arinen, A. and Oja, E. (2000). Independent component
analysis: algorithms and applications. Neural net-
works : the official journal of the International Neural
Network Society, 13(4-5):411–30.
Kumar, N., Berg, A., Belhumeur, P. N., and Nayar, S.
(2011). Describable Visual Attributes for Face Verifi-
cation and Image Search. In PAMI, pages 1962–1977.
Lampert, C., Nickisch, H., and Harmeling, S. (2009).
Learning to detect unseen object classes by between-
class attribute transfer. In CVPR.
Liu, J., Kuipers, B., and Savarese, S. (2011). Recognizing
Human Actions by Attributes. In CVPR.
Parikh, D. and Grauman, K. (2011). Relative Attributes. In
ICCV.
Rosipal, R. and Kr
¨
amer, N. (2006). Overview and recent
advances in partial least squares. In Saunders, C.,
Grobelnik, M., Gunn, S., and Shawe-Taylor, J., ed-
itors, Subspace, Latent Structure and Feature Selec-
tion, pages 34–51. Springer.
Schwartz, W., Guo, H., and Davis, L. (2010). A robust
and scalable approach to face identification. In ECCV.
Springer.
Schwartz, W. R. and Davis, L. S. (2009). Learning discrim-
inative appearance-based models using partial least
squares. In XXII Brazilian Symposium on Computer
Graphics and Image Processing, pages 322–329.
Schwartz, W. R., Kembhavi, A., Harwood, D., and Davis,
L. S. (2009). Human detection using partial least
squares analysis. In ICCV.
Sharma, A. and Jacobs, D. (2011). Bypassing Synthesis:
PLS for Face Recognition with Pose, Low-Resolution
and Sketch. In CVPR.
Wang, G. and Forsyth, D. (2009). Joint learning of visual
attributes, object classes and visual saliency. In ICCV.
Wang, Y. and Mori, G. (2010). A Discriminative Latent
Model of Object Classes and Attributes. In ECCV.
Yao, B., Jiang, X., Khosla, A., Lin, A. L., Guibas, L.,
and Fei-Fei, L. (2011). Human action recognition by
learning bases of action attributes and parts. In ICCV.
LearningSemanticAttributesviaaCommonLatentSpace
55
