
Shape Segmentation using Medial Point Clouds with Applications to
Dental Cast Analysis
Jacek Kustra
1,3
, Andrei Jalba
2
and Alexandru Telea
3
1
Philips Research, Eindhoven, The Netherlands
2
Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands
3
University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands
Keywords:
Dental Cast Analysis, Surface Segmentation, Medial Axes.
Abstract:
We present an automatic surface segmentation method for dental cast scans based on the point density proper-
ties of the surface skeleton of such shapes. We produce quasi-flat segments separated by soft ridges, in contrast
to classical surface segmentation methods that require sharp ridges. We compute the surface skeleton by a fast
3D skeletonization technique followed by its regularization using surface geodesics. We segment the resulting
skeleton by a mean-shift approach and transfer the segmentation results back to the surface. We demonstrate
our results on an industrial dental-cast segmentation application and several generic 3D shape models.
1 INTRODUCTION
Segmenting 3D surfaces into their natural compo-
nents has many applications in shape analysis, com-
puter vision, shape compression, and medical imag-
ing. Segmentation requirements strongly depend on
the target application, so many segmentation meth-
ods exist. One can distinguish between patch-type
and part-type segmentation methods (Shamir, 2004).
Patch-type methods use local shape information such
as surface curvature to produce quasi-flat segments
separated by high-curvature creases or ridges. Part-
type methods are more semantically-oriented, i.e., try
to find segments that a human user would intuitively
see as distinct logical shape parts. Such segments are
not always separated by high-curvature ridges.
For some shapes, both patch-type and patch-type
methods do not yield the desired result. Consider for
example the dental cast model in Fig. 2 a, where we
want to find the separate teeth as individual segments,
and also separate them from the gums. Part-based
methods fail here, since the teeth are not clear pro-
trusions from the shape’s rump, as would be, e.g.,
the limbs sticking out of an articulated body model.
Patch-based methods also fail, since ridges separat-
ing teeth from each other and from the gums are quite
shallow. Detecting a compact, closed, and thin sep-
aration region between the segments based on curva-
ture is quite hard. Fig. 2 b illustrates this by showing
the surface’s curvature (concave=blue, convex=red).
The main motivation of this work is the need to
segment dental casts, which are tools used to cre-
ate orthodontic treatment plans for dental patients.
Advances in range imaging and 3D scanning allow
capturing dental scans directly from a patient (Atron,
Inc., 2013), and next to digitize such shapes into 3D
surface meshes of the teeth-and-gum structure. Dig-
ital casts allow the automatic assessment of several
orthodontic metrics, such as the arch length discrep-
ancy, and new opportunities towards teeth alignment
treatment planning and simulation. However, all such
analyses require a prior segmentation of the scan into
individual teeth and the gums. Typical dental scans
do not exhibit sharp creases between individual teeth
(due to scanning resolution limitations or actual teeth
touching), nor between teeth and gums. Hence, exist-
ing patch-based segmentation cannot be directly used.
For the motivating use-case of segmenting den-
tal casts, we present here a new method to compute
patch-based segmentations of 3D shapes which do not
exhibit strong creases between segments. Instead of
using local information such as curvature, we take a
global approach, based on the shape’s surface skele-
ton. Key to our method is the observation that surface
skeletons capture all input shape creases, regardless
of their sharpness. To compute a high-resolution sur-
face skeleton, we use a GPU-based method which de-
livers point-cloud skeletons for models of hundreds
of thousands of polygons in a few seconds. Next,
we regularize the surface skeleton, to eliminate small
162
Kustra J., Jalba A. and Telea A..
Shape Segmentation using Medial Point Clouds with Applications to Dental Cast Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0004688301620170
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2014), pages 162-170
ISBN: 978-989-758-009-3
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Figure 1: Algorithm workflow: A shape is transformed into
the medial domain. Its skeleton is next segmented by a
mean-shift approach. The segmentation is transferred back
to the original shape.
manifolds that do not correspond to segments large
enough to be of interest. Next, rather than segment-
ing the surface (as virtually all patch-based method
do), we segment its regularized surface skeleton, by
a mean-shift approach. Finally, we project back the
found skeletal segments onto the input surface, and
use a nearest-neighbor approach to yield a segmenta-
tion that entirely covers the input shape (Figure 1).
The structure of this paper is as follows. Section 2
reviews related work on skeletonization and dental
cast segmentation. Section 3 details our method. Sec-
tion 4 presents our results. Section 5 discusses our
method. Section 6 concludes the paper.
2 RELATED WORK
Related work can be organized into three areas:
Surface Segmentation. Patch-based segmentation
subdivides a 3D shape into non-overlapping, com-
pact, segments or patches which (a) respect desir-
able properties such as minimal size and bound-
ary smoothness, and (b) are separated by local sur-
face features, typically sharp creases. By construc-
tion, segments are much flatter than creases between
them. Many methods exist in this area. (Garland
et al., 2001) hierarchically clusters the input mesh
faces to yield a segmentation consisting of planar
segments. (Clarenz et al., 2004) propose a fuzzy
multiscale segmentation based on surface curvature.
This method often creates noisy segment boundaries
in low-curvature regions. (Borgefors et al., 2009)
compute local thickness in combination with a mul-
tiresolution structure to hierarchically segment 3D
voxel shapes. (Mangan and Whitaker, 1999) seg-
ment surfaces into similar-curvature patches by a wa-
tershed technique with curvature as the height func-
tion. (Zuckerberger et al., 2002) improved the wa-
tershed method and give many applications. (Provot
and Debled-Rennesson, 2008) segment voxel shapes
by detecting discrete planes with variable width.
Dental Segmentation. Dental cast segmentation has
been widely explored recently due to the increasing
availability of digital models. Manual segmentation
is prohibitively slow for current orthodontic practice.
Several methods have been proposed instead, ranging
from fully automated methods (Kondo et al., 2004) to
methods needing minimal user interaction (Kronfeld
et al., 2010; Zhao et al., 2005; Hirogaki et al., 2001).
(Kondo et al., 2004) avoids the 3D mesh processing
complexity by first transforming the 3D data into
a plan-view range image which is next segmented.
Recently, a snake-based approach for teeth segmenta-
tion has been proposed (Kronfeld et al., 2010). Here,
a snake is iteratively fit to the surface curvature until
it reaches local minima. However, such methods have
problems in low curvature regions, i.e., where creases
separating teeth are shallow. Also, such methods
assume a way to find the positions and amount of
teeth prior to segmentation, e.g. using the dental arch
metric. In our proposal, we do not rely on such priors.
Skeletonization. Skeletons, or medial axes, contain
the loci of maximally inscribed circles (in 2D) or
spheres (in 3D) (Blum, 1967). 2D medial axes are
collections of curves. 3D shapes admit two skeletons:
Surface skeletons are sets of curved manifolds con-
taining the loci of maximally inscribed spheres. They
fully describe the shape, i.e., the shape can be recon-
structed from the skeleton. Curve skeletons are sets
of 1D curves locally centered in the shape, accord-
ing to various heuristics. They cannot fully capture
the geometry of the input shape, and are most useful
for tubular objects (Cornea et al., 2007). Given these,
we next focus on surface skeletons. Several meth-
ods compute surface skeletons either from a meshed
surface or a volumetric (voxel) model. Volumetric
methods have significantly higher memory and speed
costs and lower accuracy. Skeletonization methods
can be divided into thinning (Pudney, 1998; Palagyi
and Kuba, 1999), geometric (Amenta et al., 2001;
Stolpner et al., 2009; Stolpner et al., 2011), and field-
based (Siddiqi et al., 2002; Pizer et al., 2003; Bouix
et al., 2005; Bouix et al., 2006; Reniers et al., 2008b).
For a survey, we refer to (Siddiqi and Pizer, 2009).
Only few 3D segmentation methods use skeletons.
(Reniers and Telea, 2008a) uses curve skeletons for
part-type segmentations of tubular shapes. (Reniers
and Telea, 2008b) use surface skeletons for part-type
segmentation of shapes with sharp edges. The latter is
of interest to us: Given a voxel shape, we compute its
surface skeleton by (Reniers and Telea, 2008a), and
next simplify it to remove small-scale details. Next,
we detect the skeleton boundary and back-project it
on the surface via the inverse feature transform (Re-
ShapeSegmentationusingMedialPointCloudswithApplicationstoDentalCastAnalysis
163
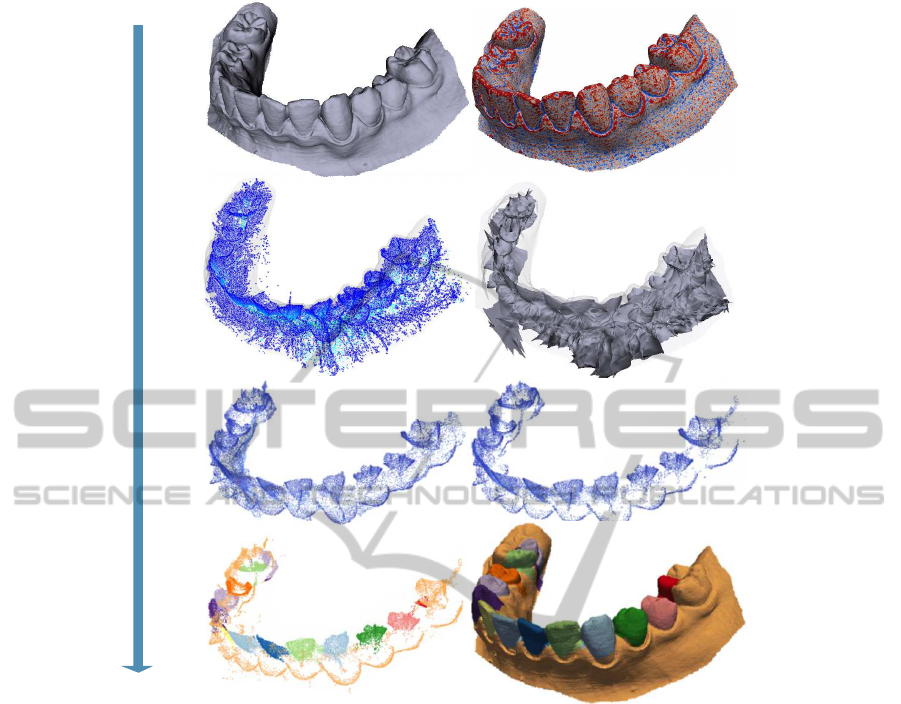
Skeletonization InitializationRegularizationSegmentation
a) input mesh
c) surface skeleton
e) thresholded importance f) seed points
g) segmented skeleton h) segmented mesh
d) reconstructed skeleton
b) surface curvature
Figure 2: Algorithm steps: Input shape (top row). Surface skeletonization (second row). Medial cloud regularization (third
row). Medial cloud segmentation and segments’ transfer to the input surface (bottom row).
niers and Telea, 2007). This robustly detects creases
between quasi-flat patches, as skeleton boundaries
correspond to the surface’s curvature maxima (Pizer
et al., 2003). Finally, we fill surface areas between
these creases to compute segments. (Reniers et al.,
2008a) use a similar relation between the skeleton and
surface to robustly find ridges of anatomical surfaces.
However, they do not actually segment the surface.
A main blocker in using surface skeletons for seg-
mentation is the difficulty to efficiently compute accu-
rate skeletons of complex models. Recently, this has
been overcome by (Ma et al., 2012) and (Jalba et al.,
2013) who compute point-cloud skeletons for meshes
of millions of polygons in seconds on the GPU. How-
ever, these methods produce an unstructured cloud
rather than a compact voxel model (as in e.g. (Reniers
and Telea, 2008a)), so they cannot be used to segment
surfaces along (Reniers and Telea, 2008b). We next
propose a shape segmentation method combining the
skeleton description power with its local point density
properties when extracted from a uniformly sampled
surface. This enables a meaningful shape segmenta-
tion based on both global and local properties.
3 METHOD
Our proposal first transforms the surface into its me-
dial domain (see Fig. 2). We next exploit skeletal
point density properties to do the segmentation in this
domain. Finally, we project the medial segmentation
back to the surface. We detail these steps next.
3.1 Skeletonization Preliminaries
Given a shape Ω ⊂ R
3
with boundary ∂Ω, we first
define its distance transform DT
∂Ω
: R
3
→ R
+
DT
∂Ω
(x ∈Ω) = argmin
y∈∂Ω
kx−yk. (1)
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
164

The skeleton of Ω is next defined as
S
Ω
= {x ∈Ω|∃f
1
, f
2
∈ ∂Ω, f
1
6= f
2
,
kx−f
1
k = kx−f
2
k = DT
∂Ω
(x)}, (2)
where f
1
and f
2
are two of the contact points with ∂Ω
of the maximally inscribed ball in Ω centered at x,
also called feature transform (FT) points (Strzodka
and Telea, 2004; Reniers and Telea, 2007). The vec-
tors f
1
−x and f
2
−x linking the skeleton points x with
their feature points are called feature vectors or spoke
vectors (Stolpner et al., 2009). In some cases, a skele-
ton point can havemore than two such feature points –
consider e.g. the center of a ball whose feature points
are the entire ball surface. For our purposes, we how-
ever need only two of these points, which are faster to
compute and store than the full feature transform.
Given a densely sampled mesh surface ∂Ω, we ex-
tract its densely sampled surface skeleton following
(Jalba et al., 2013; Ma et al., 2012). In detail, for each
point p ∈ ∂Ω having the surface normal n, we create
a ball B(s, r) of center s = −rn+ p and initial radius r
larger than the diameter of ∂Ω. The ball is iteratively
shrunk by searching the closest surface point to s until
it touches ∂Ω in exactly two points f
1
= p and f
2
. At
this moment, the center s is a newly found skeleton
point with feature points f
1
and f
2
. To remove small-
scale skeleton details created by equally small-scale
convexities (bumps) on ∂Ω, we next regularize the
skeleton. For this, we compute an importance met-
ric ρ : S → R
+
for each skeleton point. ρ(s ∈S equals
the shortest-path distance on ∂Ω between the feature
points f
1
and f
2
of s. As shown in (Reniers and Telea,
2008a; Jalba et al., 2013), ρ monotonically increases
from the skeleton boundary inwards. Thresholding it
with a small value τ yields a simplified skeleton
S
τ
= {s ∈S
Ω
|ρ(s) > τ} (3)
which captures all salient branches of S
Ω
but removes
those for surface details shorter than τ. Figure 2
shows this: From a dental cast (a), we compute the
skeleton cloud. Image (c) shows the simplified skele-
ton S
τ
for a value τ = 3% of the shape’s diameter,
colored by ρ (blue=low, red=high). We see how sim-
plification removedmany spurious skeletal points cre-
ated by small surface wiggles. Image (d) shows, for
comparison, the surface skeleton reconstructed from
the skeletal cloud following (Telea and Jalba, 2012).
Given the high resolution of the skeletal cloud, the
reconstructed skeleton also has a very complex man-
ifold structure. Robustly finding the boundaries of
these manifolds, to further apply the patch-based seg-
mentation of (Reniers and Telea, 2008b), is very chal-
lenging, as already noted in Sec. 2.
sampled convex surface
sampled skeleton
sampled concave surface
sampled skeleton
high-density medial
point clusters
Figure 3: Relationship between local surface curvature and
medial cloud density. Top: Concept sketched in 2D. Bot-
tom: High-density point clusters are formed inside positive-
curvature 3D surface areas (front teeth).
3.2 Surface Curvature vs Skeleton
Density
To further segment our skeleton cloud, we use the fol-
lowing observations linking the curvature of ∂Ω and
point density on S
Ω
. Consider a densely sampled ∂Ω.
For a positive-curvature region of ∂Ω (bump, or con-
vexity), the ball-shrinking directions rn, identical to
the feature vector directions, point inwards in a con-
verging fashion. Hence, the density of the skeletal
points for this region will be higher than the surface
density. Conversely, for a region with negative curva-
ture (a crease, or concave, region), the ball-shrinking
directions will point inwards in a diverging fashion,
so the density of the skeletal points for this region
will be lower than the surface density. Figure 3 (top)
illustrates this in 2D. Figure 3 (bottom) shows an ac-
tual example for a 3D skeletal cloud computed from
a dental cast. We observe that skeletal parts enclosed
in the front teeth present a high point density, since
these teeth are indeed convex shape parts.
3.3 Mean Shift Clustering
We now show how to use the density-related observa-
tions in Sec. 3.2 to segment the skeleton cloud.
Since the skeletal cloud exhibits strong density
variations, it should be possible to segment it into
point clusters representing the dense regions based on
a method which exploits such density variations. An
ideal such method is mean shift clustering (Comani-
ciu and Meer, 2002), which we extend to our seg-
mentation needs, as follows. We start by selecting
a set of seed points P ⊂ S
τ
from the simplified skele-
ton. The seed point selection is discussed separately
ShapeSegmentationusingMedialPointCloudswithApplicationstoDentalCastAnalysis
165

seed point
convergence
point
convergence points
a) b) c)
Figure 4: Mean shift clustering: (a) A seed point (black dot) is shifted to the centroid of its skeleton-cloud neighborhood
density until convergence (red dot). (b) Final convergence points for dental cast. (c) Segment IDs assigned to skeleton points.
in Sec. 3.4. Each seed point x ∈P is assigned a unique
‘segment id’. For each seed point x ∈ P, we aim to
find its so-called convergence point c(x) ∈ R
3
. For
this, we first find all neighbors N
ε
x
⊂ S
τ
of x within a
small fixed radius ε and determine the centroid of N
ε
x
m(x) =
∑
y∈N
ε
x
K(kx−yk)y
∑
x∈N
ε
x
K(kx−yk)
(4)
where K is a Gaussian kernel
K(x) =
1
√
2π
e
x
2σ
2
(5)
following the kernel density estimation idea in (Co-
maniciu and Meer, 2002). ε is set to a small frac-
tion (about 5%) of the model size. We next iteratively
shift the seed points x to their centroids m(x) follow-
ing Eqn. 4 (see also Fig. 4 a) until these stabilize,
i.e., move at one iteration less than a small threshold
λ = km(x)−xk, set in practice to 10
−4
. Also, for each
non-seed point (which is not shifted), we define a vot-
ing weight v(y), initialized to zero at the beginning of
the algorithm. At every mean-shift iteration, we add a
value K(k y −m(x)k) to v(y) for each non-seed point
y ∈ N
ε
x
, and also add a pointer from y to m(x), to in-
dicate that y was int he neighborhood of m(x). When
m(x) has converged, we search its neighborhood for
other existing convergence points c
′
than itself. If one
exists, we merge the ids of m(x) and c
′
. Otherwise,
we create a new convergence point c = m(x).
At the end of the mean shift, all seed points have
thus converged to a set C of convergence points (see
Fig. 4 b). The ids of the points c ∈ C give us the fi-
nal segments. Finally, to assign each non-seed point
y ∈ S
τ
to a segment, is done by assigning to y the id
of the convergence point that it is linked to and which
has the highest amount of votes within the k last iter-
ations (Fig. 4 c). Different segmentation levels can be
achieved by considering the voting of only the last k
iterations of the mean shift process. This way, only
the areas around the skeleton-cloud density peaks are
considered. This is illustrated by the dental cast mod-
els, where the gum areas remain mostly unsegmented
(Fig. 5 a-e), for which we used a value k = 20. In con-
trast, for the other shapes in Fig. 5 f-k, the full mean-
shift path has been considered for the voting, leading
to the full surface being segmented into patches.
3.4 Seed Point Detection
We find the initial seed points P used in mean shift
clustering by using the specific geometry of our den-
tal casts. We want at least one seed point in each rel-
evant segment (that is, inside each high-density clus-
ter such as the ones in Fig. 3; we do not want seed
points outside such segments. We allow more seed
points in a segment, so that finding seed points is not
parameter-critical. The definition of segment rele-
vance is application-dependent: For our dental cast
use-case, we only want the teeth segments and the
gum, i.e., we don’t want to over-segment the gum. To
achieve this, we use as seed points all skeleton points
which (a) have a low distance DT
∂Ω
(s) to the original
surface ∂Ω and (b) have a high curvature, computed
as the angle between the feature vectors f
1
−s, f
2
−s.
3.5 Segmentation Transfer to Surface
In the last step, we transfer the skeleton segmenta-
tion to the input surface, as follows. For each point
s ∈S
τ
, we copy the segment ID of s to its two feature
points f
1
and f
2
. However, this does not assign a seg-
ment ID to all points on ∂Ω, since we segmented the
simplified skeleton S
τ
rather than the full skeleton S
Ω
.
For all points p ∈ ∂Ω which are not assigned a seg-
ment ID, we search the closest surface point p
′
∈ ∂Ω
which has an ID ID(p
′
) assigned, and mark p with the
same ID(p
′
). This fills the gaps between segments on
∂Ω in distance order, yielding a full, non-overlapping,
surface segmentation.
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
166
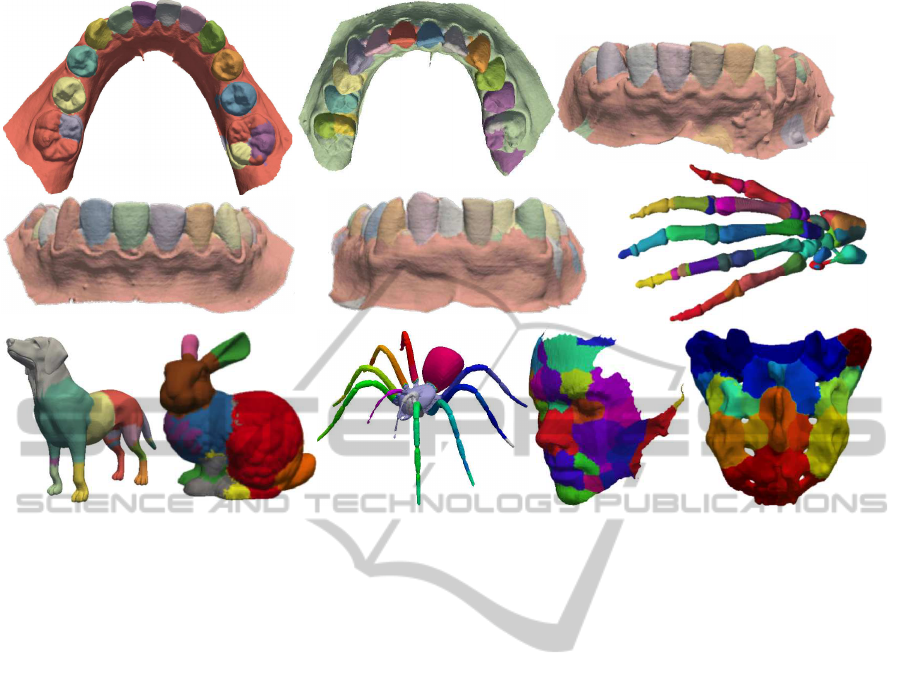
a) b) c)
d) e)
f)
g) h) i) j)
k)
Figure 5: Segmentation results for different dental casts (a-e) and other shapes (f-k).
4 RESULTS
Figure 5 shows several results. Surface segments are
colored differently, for illustration. For images (a-e),
which show dental cast scans, we see that the method
separates very well the incisives, canines, molars and
pre-molars, both from each other, and also from the
gums. We also see several problems. The molars
are over-segmented (Fig. 5 a,b), and occasionally the
gums are also oversegmented (Fig. 5 c,e). The gums
oversegmentation is not problematic for the consid-
ered orthodontic application, since users are only in-
terested to analyze the teeth, and not the gums. The
molars oversegmentation is be explained by the fact
that they (a) have a more complex geometry than the
other teeth (more internal creases) and also that, in
our models, the input surface has less points here.
Hence, the skeletal manifolds for to these detail-rich
areas are too poorly sampled to fully capture their
features. We also segmented other shapes than den-
tal casts, to get more insight in the method’s behav-
ior (Figs. 5 f-k). Several observations can be made.
For models having convex surface areas separated by
well-delimited concave ridges, such as the hand or
spider, we get the expected segmentation, just as for
the dental casts. For the other models, segments are
created around the most salient convex bumps of the
shape. These segments meet along the model concav-
ities, or creases – see e.g. the nose, eyes, and chin
of the face model (Fig. 5 j); bunny years, tail, head,
rump, and front paw (Fig. 5 h); and the convex bone
components of the sacrum model (Fig. 5 k).
5 DISCUSSION
Several aspects are relevant for our method.
Simplicity and Novelty. A key asset of our method
is its algorithmic simplicity. We use algorithms
with proven accuracy, convergence, and complexity
properties (Comaniciu and Meer, 2002; Reniers and
Telea, 2008a; Jalba et al., 2013). Our method is
the first we are aware of to use surface skeletons
computed on mesh models to segment surfaces.
Its only competitor, using more expensive and
lower-resolution voxel models, is (Reniers and Telea,
2008b). This is also the first use of mean shift to
cluster skeletons.
Robustness. The method is robust to different
surface point-sampling densities, as the segmentation
is performed based on the medial surface density
properties. We tested our method on several dental
cast models with the same parameter settings, and
ShapeSegmentationusingMedialPointCloudswithApplicationstoDentalCastAnalysis
167

Table 1: Segmentation timings.
Model dental 1 dental 2 dental 3 dog bunny bone hand spider face
# points (surface) 119594 127578 82887 18114 34834 41035 327323 29741 35437
# points (skeleton S
τ
)
6136 24339 11214 16823 10706 8271 128839 8389 8450
# seed points
339 487 373 336 535 827 644 829 1041
CPU skeletonization (sec) 51.3 48.53 22.87 34.89 10.96 10.26 151.68 5.85 12.8
GPU skeletonization (sec)
11.7 11.0 5.78 3.24 3.6 1.82 31.2 0.95 2.11
CPU segmentation (sec)
1.95 1.92 1.3 43.07 2.71 40.12 152.02 167.53 11.35
CPU total (sec) 53.25 50.45 24.17 77.96 13.67 50.38 303.7 173.38 24.15
GPU total (sec)
13.65 12.92 7.08 46.31 6.31 41.94 183.22 168.48 13.46
obtained identical results (cf. Figs. 2, 5).
Applicability. Our method is, by construction,
geared towards the segmentation of convex surface
patches separated by shallow creases. In this sense,
we stress that the skeleton simplification (Eqn. 3)
only eliminates skeleton points corresponding to
small-scale surface bumps (convexities), but no
skeleton point corresponding to a concavity (crease).
This makes our method principially more robust than
many other curvature-based segmentation methods.
Also, our method can handle non-watertight surfaces
(such as our teeth scans, which are not closed at the
base, or the face model in Fig. 5 j) with no problems.
Performance. We implemented our method in C++
using ANN (Mount and Arya, 2011) to find nearest
neighbors and the GPU skeletonization in (Jalba
et al., 2013). The latter also provides the needed
distance transform, feature points, and importance
metric (Sec. 3.1). For 3D surface supersampling, we
used Yams (Frey, 2001). Tab. 1 shows timings on a
Windows PC at 2.66 GHz with an Nvidia 690 GTX
for several shapes. Skeletonization times include
regularization (Eqn. 3); we show timings for (Jalba
et al., 2013) on both GPU and GPU. Segmentation
timings include mean shift, segment ID assignment,
and transfer on the original surface, all done on the
CPU. As expected, GPU skeletonization is much
faster than its CPU counterpart. The segmentation
cost varies in function of the actual model. For the
dental casts, this cost is quite low. Indeed, for these
models, we use only the last k iterations (Sec. 3.3),
whereas for the other models we use the full mean
shift path. The segmentation (not optimized, unlike
skeletonization) is dominated by the nearest neighbor
searches. Such searches can be massively accelerated
using GPUs, as shown in (Jalba et al., 2013), so a
GPU mean shift implementation should massively
accelerate this step.
Dental Use-case. For teeth segmentation, our method
can segment all teeth whose medial surfaces converge
to a point density maximum. Given the geometry
of the incisives, canines, molars and pre-molars,
we saw that these present the expected properties,
so are robustly segmented. Molars have a slightly
more complex geometry, including too shallow
separation creases from gums. This creates some
challenges (over-segmentation) when using the exact
same mean-shift parameters as for the other teeth
(see e.g. Fig. 2 a,b). Possible ways to overcome
this are supersampling the input mesh, leading to
a surface skeleton with better separated manifolds.
However, we stress that, even with such limitations,
our method is superior to existing alternatives in the
orthodontic industry (see references in Sec. 2), as all
such methods require a non-trivial amount of user
input to produce their segmentations.
Limitations. As seen in Fig. 5, our method cannot
be directly applied to any 3D shape. The method
is geared towards segmenting shapes whose skele-
tal manifolds exhibit clearly separated high-density
branches, each branch corresponding to one surface
segment. These are surfaces with convexpatches sep-
arated by concave ridges. As such, one should not
attempt to compare our current method with other
general-purpose surface segmentation methods. Still,
the main added value of our technique for segmenting
general shapes (apart from the segmentation of den-
tal casts) is the proof that point-cloud skeletons can
be used for segmenting complex 3D surfaces. To our
knowledge, this result has not been shown so far in
current literature. Future work is needed to study how
this result can be extended to more general surfaces.
6 CONCLUSIONS
We have presented a method for segmenting compact
convex patches of 3D polygonal surfaces from den-
tal cast scans which are separated by shallow creases.
For this, we use the properties of surface skeletons,
in particular the sampling relationship between the
skeleton and its original surface, and the correspon-
dence relationship between the two surfaces given by
the feature transform. To our knowledge, our method
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
168

is the second existing technique able to use surface
skeletons to segment 3D surfaces. In contrast to the
first published technique in this area (Reniers and
Telea, 2008b), we can directly handle meshed mod-
els without a costly voxelization step; we do not re-
quire the complex and sensitive detection of skeletal
boundaries; and we can treat significantly more com-
plex shapes than the earlier cited method in this class.
Our research is motivated by the need to create
robust and fast segmentations of dental cast models,
driven by a concrete industrial application at Philips
Research, Eindhoven, the Netherlands. We foresee
several possible extensions of our method towards
a more general-purpose surface segmentation tech-
nique. Examples are the incorporation of surface dif-
ferential properties, captured by the feature transform,
in the analysis and segmentation of the surface skele-
ton, and application-adaptive skeleton simplification
metrics that preserve or eliminate specific surface de-
tails for the purpose of more versatile segmentation.
REFERENCES
Amenta, N., Choi, S., and Kolluri, R. (2001). The power
crust. In Proc. SMA, pages 65–73. ACM.
Atron, Inc. (2013). 3D intraoral scanner. www.a-
tron3d.com/en/products/id-3d-intraoral-scanner.html.
Blum, H. (1967). A Transformation for Extracting New
Descriptors of Shape. In Wathen-Dunn, W., editor,
Models for the Perception of Speech and Visual Form,
pages 362–380. MIT Press, Cambridge.
Borgefors, G., di Baja, G., and Svensson, S. (2009). De-
composing digital 3D shapes using a multiresolution
structure. In Proc. DGCI, pages 19–28. Springer.
Bouix, S., Siddiqi, K., and Tannenbaum, A. (2005). Flux
driven automatic centerline extraction. Medical Image
Analysis, 9(3):209–221.
Bouix, S., Siddiqi, K., Tannenbaum, A., and Zucker, S.
(2006). Medial axis computation and evolution. In
Statistics and analysis of shape, chapter 1, pages 1–
28. Springer LNCS.
Clarenz, U., Griebel, M., Schewitzer, M., and Telea, A.
(2004). Feature sensitive multiscale editing on sur-
faces. Visual Computer, 20(5):329–343.
Comaniciu, D. and Meer, P. (2002). Mean shift: A robust
approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE TPAMI,
24(5):603–619.
Cornea, N., Silver, D., and Min, P. (2007). Curve-skeleton
properties, applications, and algorithms. IEEE TVCG,
13(3):87–95.
Frey, P. (2001). YAMS: a fully automatic adaptive isotropic
surface remeshing procedure. tech. rep. 0252, INRIA.
http://www.ann.jussieu.fr/ frey.
Garland, M., Willmott, A., and Heckbert, P. (2001). Hierar-
chical face clustering on polygonal surfaces. In Proc.
ACM Symp. I3D, pages 49–58.
Hirogaki, Y., Sohmura, T., Satoh, H., Takahashi, J., and
Takada, K. (2001). Complete 3-d reconstruction of
dental cast shape using perceptual grouping. Medical
Imaging, IEEE Transactions on, 20(10):1093–1101.
Jalba, A., Kustra, J., and Telea, A. (2013). Surface and
curve skeletonization of large 3D models on the GPU.
IEEE TPAMI, 35(6):1495–1508.
Kondo, T., Ong, S., and Foong, K. W. C. (2004). Tooth seg-
mentation of dental study models using range images.
IEEE Trans Med Imag, 23(3):350–362.
Kronfeld, T., Brunner, D., and Brunnett, G. (2010). Snake-
based segmentation of teeth from virtual dental casts.
CAGD, 7(2):221–233.
Ma, J., Bae, S., and Choi, S. (2012). 3D medial axis point
approximation using nearest neighbors and the normal
field. Vis. Comput., 28(1):7–19.
Mangan, A. and Whitaker, R. (1999). Partitioning 3D sur-
face meshes using watershed segmentation. IEEE
TVCG, 5(4):308–321.
Mount, D. and Arya, S. (2011). Approximate nearest neigh-
bor search software. www.cs.umd.edu/ mount/ANN.
Palagyi, K. and Kuba, A. (1999). Directional 3D thinning
using 8 subiterations. In Proc. DGCI, volume 1568,
pages 325–336. Springer LNCS.
Pizer, S., Siddiqi, K., Szekely, G., Damon, J., and Zucker,
S. (2003). Multiscale medial loci and their properties.
IJCV, 55(2-3):155–179.
Provot, L. and Debled-Rennesson, I. (2008). Segmentation
of noisy discrete surfaces. In Proc. IWCIA, volume
4958, pages 160–171. Springer LNCS.
Pudney, C. (1998). Distance-ordered homotopic thinning:
A skeletonization algorithm for 3D digital images.
CVIU, 72(3):404–413.
Reniers, D., Jalba, A., and Telea, A. (2008a). Robust classi-
fication and analysis of anatomical surfaces using 3D
skeletons. In Proc. VCBM, pages 61–68. EG Press.
Reniers, D. and Telea, A. (2007). Tolerance-based fea-
ture transforms. In Advances in Comp. Graphics and
Comp. Vision, pages 187–200. Springer.
Reniers, D. and Telea, A. (2008a). Part-type segmentation
of articulated voxel-shapes using the junction rule.
CGF, 27(7):1837–1844.
Reniers, D. and Telea, A. (2008b). Patch-type segmenta-
tion of voxel shapes using simplified surface skele-
tons. CGF, 27(7):1954–1962.
Reniers, D., van Wijk, J. J., and Telea, A. (2008b). Com-
puting multiscale skeletons of genus 0 objects using a
global importance measure. IEEE TVCG, 14(2):355–
368.
Shamir, A. (2004). A formulation of boundary mesh seg-
mentation. In Proc.3DPVT, pages 378–386.
Siddiqi, K., Bouix, S., Tannenbaum, A., and Zucker, S.
(2002). Hamilton-Jacobi skeletons. IJCV, 48(3):215–
231.
Siddiqi, K. and Pizer, S. (2009). Medial Representations:
Mathematics, Algorithms and Applications. Springer.
Stolpner, S., Whitesides, S., and Siddiqi, K. (2009). Sam-
pled medial loci and boundary differential geometry.
In Proc. IEEE 3DIM, pages 87–95.
ShapeSegmentationusingMedialPointCloudswithApplicationstoDentalCastAnalysis
169

Stolpner, S., Whitesides, S., and Siddiqi, K. (2011). Sam-
pled medial loci for 3D shape representation. CVIU,
115(5):695–706.
Strzodka, R. and Telea, A. (2004). Generalized distance
transforms and skeletons in graphics hardware. In
Proc. VisSym, pages 221–230.
Telea, A. and Jalba, A. (2012). Computing curve skeletons
from medial surfaces of 3D shapes. In Proc. TPCG
(Eurographics UK), pages 273–280.
Zhao, M., Ma, L., Tan, W., and Nie, D. (2005). Interactive
tooth segmentation of dental models. In Proc. EMBS,
pages 654–657.
Zuckerberger, E., Tal, A., and Shlafman, S. (2002). Poly-
hedral surface decomposition with applications. Com-
puters & Graphics, 26(5):733–743.
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
170
