
A Qualitative Framework for Analysing Homeostasis in Gene Networks
Sohei Ito
1
, Shigeki Hagihara
2
and Naoki Yonezaki
2
1
Department of Fisheries Distribution and Management, National Fisheries University,
2-7-1 Nagata-Honcho, Shimonoseki, Yamaguchi, Japan
2
Department of Computer Science, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 2-12-1 Ookayama, Meguro-ku, Tokyo, Japan
Keywords:
Gene Regulatory Network, Homeostasis, Temporal Logic, Realisability.
Abstract:
Toward the system level understanding of the mechanisms contributing homeostasis in organisms, a computa-
tional framework to model a system and analyse its properties is indispensable. The purpose of this work is to
provide a framework which enables testing and validating homeostatic properties on gene regulatory networks
in silico. Based on a qualitative analysis framework for gene networks using temporal logic, we proposed
a novel formulation of homeostasis by the notion of realisability. This formulation of homeostasis yields a
qualitative method to analyse homeostasis of gene networks. In this formulation, homeostasis is captured by
a response not for just an instantaneous stimulation such as dose-response relationships but for any input sce-
nario e.g. oscillating or continuous inputs, which is difficult to be captured by quantitative models. Moreover,
we can consider any number of inputs from an environment without difficulty. Such flexibility is a notable
advantage of our framework. We demonstrate the usefulness of our framework in analysing a number of small
but tricky networks.
1 INTRODUCTION
Qualitative methods in modelling and simulation of
gene networks (de Jong et al., 2003; Fages et al.,
2004; Bernot et al., 2004; Batt et al., 2005) are
useful in that we do not need quantitative informa-
tion since such information on kinetic parameters or
molecular concentrations are usually absent, as we
can see from current databases e.g. Reactome (Croft
et al., 2011), GeneCards (Safran et al., 2010), Meta-
cyc (Karp et al., 2002), Ingenuity
R
Knowledge Base
and KEGG (Kanehisa et al., 2011). Ito et al. (Ito et al.,
2010) proposeda method for analysing gene networks
using linear temporal logic (LTL) (Emerson, 1990), in
which, a gene network is modelled as an LTL formula
which specifies its possible behaviours.
Their method for analysing gene networks is
closely related with verification of reactive system
specifications (Barringer et al., 1984; Pnueli and Ros-
ner, 1989; Abadi et al., 1989; Wong-Toi and Dill,
1991; Mori and Yonezaki, 1993; Vanitha et al., 2000;
Hagihara and Yonezaki, 2006). A reactive system is a
system that responds to requests from an environment
at an appropriate timing. Systems controlling an el-
evator or a vending machine are typical examples of
reactive systems. Biological systems with external in-
puts or signals can be naturally considered as reactive
systems.
Realisability (Pnueli and Rosner, 1989; Abadi
et al., 1989) is a desirable property of reactive sys-
tem specifications which requires systems to behave
according to a specification in reaction to any input
from an environment. In terms of biological systems,
this property means that a system behaves with satis-
fying a certain property (e.g. keeping a concentration
within some range) in reaction to any input from an
environment (e.g. for any stress or stimulation). That
is to say, the system is homeostatic with respect to the
property.
Using this correspondence, we formulate the no-
tion of homeostasis by realisability of reactive sys-
tems. Our formulation captures homeostasis of not
only logical structure of gene networks but also prop-
erties of any dynamic behaviours of networks. For
example, we can analyse in our framework whether
a given network maintains oscillation over time in
response to any input sequence. This formulation
yields not only a novel and simple characterisation of
homeostasis but also provides a method to automati-
cally check homeostasis of a system using realisabil-
ity checkers (Jobstmann and Bloem, 2006; Jobstmann
et al., 2007; Filiot et al., 2009; Bloem et al., 2010).
5
Ito S., Hagihara S. and Yonezaki N..
A Qualitative Framework for Analysing Homeostasis in Gene Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0004731400050016
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms (BIOINFORMATICS-2014), pages 5-16
ISBN: 978-989-758-012-3
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
ݑ
ݑ
ݒ
ݓ
ݑ
௩
ݑ
௪
Figure 1: Regulation effect.
Based on this formulation we analyse some homeo-
static properties of a number of small but tricky gene
networks.
This paper is organised as follows. Section 2 and
3 reviews the qualitative analysis method using LTL
(Ito et al., 2010) on that our work is grounded. In sec-
tion 4, we introduce the notion of realisability and for-
mulate homeostasis by this notion. Based on this for-
mulation, we show some example networks and anal-
yse homeostatic properties of them in section 5. Sec-
tion 6 discusses some related works. The final section
offers conclusions and future directions.
2 LOGICAL
CONCEPTUALISATION OF
BEHAVIOURS
In gene regulation, a regulator is often inefficient be-
low a threshold concentration, and its effect rapidly
increases above this threshold (Thomas and Kauff-
man, 2001). The sigmoid nature of gene regulation
is shown in Figure 1, where gene u activates v and
inhibits w. Each axis represents the concentration of
products for each gene.
Some important landmark concentration values
for u are 1) the basal level, 2) the level u
v
at which
u begins to affect v, and 3) the level u
w
at which u
begins to affect w. The values u
v
and u
w
are thresh-
olds of gene u. Whether genes are active or not can
be specified by the expression levels of their regula-
tor genes. If the concentration of u exceeds u
v
then v
is active (ON), and if the concentration of u exceeds
u
w
then w is not active (OFF). This switching view of
genes leads us an abstract representation of network
behaviours, transition systems.
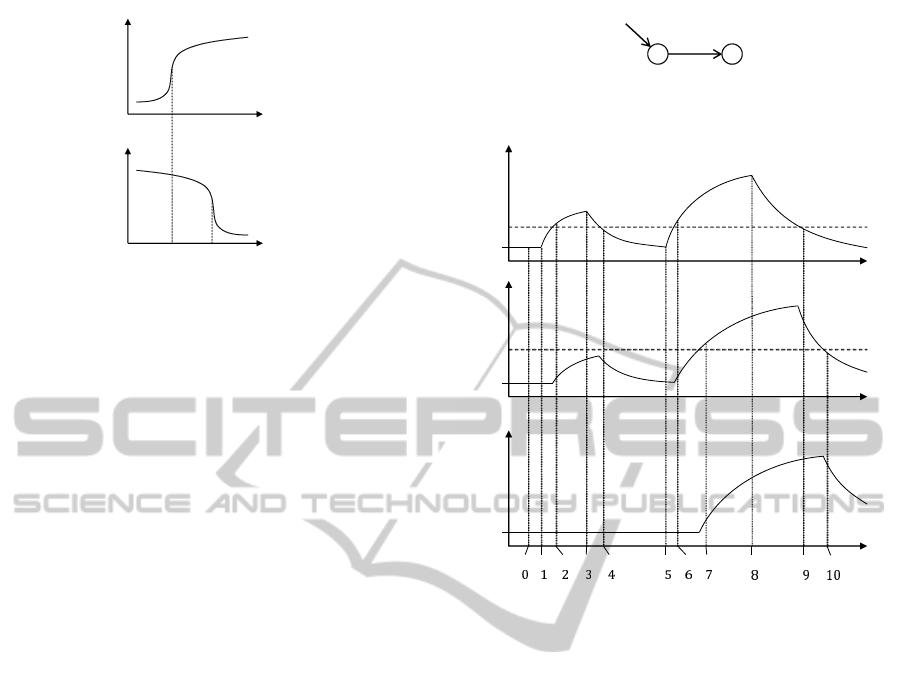
Let us consider a simple network depicted in Fig-
ure 2, in which gene x activates gene y and receives
the positive input from the environment.
x
+
input
y
+
Figure 2: A simple example.
input
x
y
t
base
base
base
ݐ
ݐ
ݐ
ݐ
ݐ
ݐ
ݐ
ݐ
ݐ
ݐ
݁
௫
ݔ
௬
t
t
ݐ
Figure 3: An example behaviour of the network in Figure 2.
We consider the behaviour depicted in Figure 3 in
which e
x
is a threshold level of the input to activate
x and x
y
a threshold of x to activate y. At time t
0
,
the input, gene x and gene y are at basal level. At
time t
1
, the input to x is coming and the level begins
to increase. At time t
2
, since the level of input to x
exceeds e
x
, gene x is being expressed. At time t
3
, the
input to x is stopped and the level begins to decrease.
At time t
4
, since the level of input to x falls below e
x
,
gene x stops being expressed; that is, the level of x is
decreasing. At time t
5
the input to x is again coming
and at time t
6
gene x is being expressed since the input
level is over e
x
. At time t
7
, gene x is expressed over
x
y
, so gene y is being expressed. At time t
8
the input
to x is stopped and at time t
9
falls below e
x
so gene x
stops being expressed. At time t
10
, since gene x falls
below x
y
, gene y stops being expressed, after which
gene x and y stay at their basal level.
This behaviour can be represented as a transition
system in Figure 4. A transition system consists of
states (represented as circles) and transitions (repre-
sented as arrows). A state represents a current sta-
tus of the system, e.g. what genes are active or what
are the expression levels of genes. A transition rep-
resents a change of states. To describe status of the
system, we introduce logical propositions that repre-
BIOINFORMATICS2014-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
6

0
݅݊
௫
݅݊
௫
݁
௫
݊
௫
݁
௫
݊
௫
݅݊
௫
݅݊
௫
݁
௫
݊
௫
݅݊
௫
݁
௫
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
݊
௬
݁
௫
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
݊
௬
ݔ
௬
݊
௬
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Figure 4: A Transition system corresponding to Figure 3.
sent whether genes are active or not (ON or OFF) and
whether concentrations of products of genes exceed
threshold values. In this network, we introduce the
propositions in
x
, on
x
, on
y
, e
x
, and x
y
1
. The meaning of
each proposition is:
• on
x
, on
y
: whether gene x or y is active,
• in
x
: whether the input to gene x is coming,
• x
y
: whether the concentration of the products of
gene x exceeds the threshold x
y
.
• e
x
: whether the level of the input to gene x exceeds
the threshold e
x
,
Propositions depicted below each state in Figure 4
shows the status of it. For example, state 2 represents
the situation that the input to gene x is coming, the
level of input is above the threshold e
x
and gene x is
ON. We can observe that state 0 represents the situ-
ation at time t
0
, state 1 represents t
1
, ... and state 10
represents t
10
.
A single state transition can represent any length
of time, since the actual duration of the transition (in
real time) is immaterial
2
in this abstraction. There-
fore, the difference between t
2
−t
0
and t
7
−t
4
, the du-
ration of the input to x in Figure 3, is not captured
directly. We, however, can see that the latter duration
is longer by comparing the propositions in state 1 to
3 and in state 5 to 9: the latter duration is sufficiently
long for x to activate y.
Note that the real values of thresholds are also ir-
relevant. Propositions such as x
y
merely represent the
fact that the concentration of x is above the threshold
at which x affects y.
In this abstraction, behaviours are identified with
each other if they have the same transition system.
This abstraction seems rather simple but preserves es-
sential qualitative features of the dynamics (Snoussi
and Thomas, 1993; Thomas and Kauffman, 2001).
Any behaviour of gene networks can be abstracted
as transition systems. Sometimes, we need more
propositions for expression levels of genes besides
threshold values. We can introduce any number of
1
Symbols e
x
and x
y
are already used to represent the
thresholds but we can clearly distinguish them from the con-
text
2
This property is called speed independence (Rabi-
novich, 1998)
them. We will see an example of such extra proposi-
tions in section 5, in which we prepare two proposi-
tions for one activation of a gene to capture a level of
the activation.
3 MODELLING BEHAVIOURS OF
GENE NETWORKS IN LTL
3.1 Linear Temporal Logic
First we introduce linear temporal logic.
If A is a finite set, A
ω
denotes the set of all infi-
nite sequences on A. The i-th element of σ ∈ A
ω
is
denoted by σ[i]. Let AP be a set of propositions. A
time structure is a sequence σ ∈ (2
AP
)
ω
where 2
AP
is
the powerset of AP. The formulae in LTL are defined
as follows.
• p ∈ AP is a formula.
• If φ and ψ are formulae, then ¬φ, φ∧ ψ, φ∨ψ and
φUψ are also formulae.
We introduce the following abbreviations: ⊥ ≡
p∧ ¬p for some p ∈ AP, ⊤ ≡ ¬⊥, φ → ψ ≡ ¬φ∨ψ,
φ ↔ ψ ≡ (φ → ψ) ∧ (ψ → φ), Fφ ≡ ⊤Uφ, Gφ ≡
¬F¬φ, and φWψ ≡ (φUψ)∨Gφ. We assume that ∧, ∨
and U binds more strongly than → and unary connec-
tives binds more strongly than binary ones.
Intuitively, ¬φ means ‘φ is not true’, φ∧ ψ means
’both φ and ψ are true’, φ ∨ ψ means ’φ or ψ is true’,
and φUψ means ‘φ continues to hold until ψ holds’. ⊥
is a false proposition and ⊤ is a true proposition. φ →
ψ means ’if φ is true then ψ is true’ and φ ↔ ψ means
’φ is true if and only if ψ is true’. Fφ means ‘φ holds at
some future time’, Gφ means ‘φ holds globally’, φWψ
is the ‘weak until’ operator in that ψ is not obliged to
hold, in which case φ must always hold. The formal
semantics are given below.
Let σ be a time structure and φ be a formula. We
write σ |= φ for φ is true in σ and we say σ satisfies φ.
The satisfaction relation |= is defined as follows.
σ |= p iff p ∈ σ[0] for p ∈ AP
σ |= ¬φ iff σ 6|= φ
σ |= φ∧ψ iff σ |= φ and σ |= ψ
σ |= φ∨ψ iff σ |= φ or σ |= ψ
σ |= φUψ iff (∃i ≥ 0)(σ
i
|= ψ and
∀ j(0 ≤ j < i)σ
j
|= φ)
where σ
i
= σ[i]σ[i + 1]. . . , i.e. the i-th suffix of σ.
An LTL formula φ is satisfiable if there exists a time
structure σ such that σ |= φ.
AQualitativeFrameworkforAnalysingHomeostasisinGeneNetworks
7

x y
+
-
+
Figure 5: An example network.
3.2 Specifying Possible Behaviours of
Gene Networks in LTL
Now we review the method proposed in (Ito et al.,
2010) to model behaviours of a given network in lin-
ear temporal logic, using an example gene network
depicted in Figure 5.
In this network gene x activates gene y and gene y
inhibits gene x. Gene x has a positive environmental
input. Let x
y
be the threshold of gene x to activate
gene y, y
x
the threshold of gene y to inhibit gene x
and e
x
the threshold of the input to activate gene x.
To specify possible behaviours of this network, we
introduce the following propositions.
• on
x
, on
y
: whether gene x and y are ON respec-
tively.
• x
y
, y
x
: whether gene x and y are expressed beyond
the threshold x
y
and y
x
respectively.
• in
x
: whether the input to x is ON.
• e
x
: whether the positive input from the environ-
ment to x is beyond the threshold e
x
.
The basic principles for characterising behaviours
of a gene network are as follows:
• Genes are ON when their activators are expressed
beyond some thresholds.
• Genes are OFF when their inhibitors are ex-
pressed beyond some thresholds.
• If genes are ON, the concentrations of their prod-
ucts increase.
• If genes are OFF, the concentrations of their prod-
ucts decrease.
We express these principles in LTL using the
propositions introduced above.
Genes’ Activation and Inactivation. Gene y is
positively regulated by gene x. Thus gene y is ON
if gene x is expressed beyond the threshold x
y
, which
is the threshold of gene x to activate gene y. This can
be described as
G(x
y
↔ on
y
)
in LTL. Intuitively this formula says gene y is ON if,
and only if, gene x is expressed beyond x
y
due to pos-
itive regulation effect of gene x toward gene y. As
for gene x, it is negatively regulated by gene y and
has positive input from the environment. A condition
for activation and inactivation of such multi-regulated
genes depends on a function which merges the multi-
ple effects. We assume that gene x is ON if gene y is
not expressed beyond y
x
and the input from the envi-
ronment to gene x is beyond e
x
; that is, the negative
effect of gene y is not operating and the positive effect
of the input is operating. Then this can be described
as
G(e
x
∧ ¬y
x
→ on
x
).
This formula says that if the input level is beyond e
x
(i.e. proposition e
x
is true) and gene y is not expressed
beyond y
x
(i.e. proposition y
x
is false; ¬y
x
is true),
then gene x is ON (i.e. proposition on
x
is true).
For the inactivation of gene x, we have choices to
specify the rule. Let us assume that gene x is OFF
when the input from the environment is under e
x
and
gene y is expressed beyond y
x
, that is, the activation
to gene x is not operating and the inhibition to gene x
is operating, in which case gene x will surely be OFF.
This is specified as
G(¬e
x
∧ y
x
→ ¬on
x
). (1)
For another choice, let us assume that the negative
effect from gene y overpowers the positive input from
the environment. Then we write
G(y
x
→ ¬on
x
), (2)
which says that if the inhibition from gene y is oper-
ating, gene x becomes OFF regardless of the environ-
mental input to gene x. Yet another choice is
G(¬e
x
∨ y
x
→ ¬on
x
) (3)
which says that gene x is OFF when the positive in-
put is not effective or negative regulation from gene
y is effective. For example, although gene y is not
expressed beyond the threshold y
x
(i.e. the negative
effect of gene y is not effective), gene x is OFF if the
positive effect of the input is not effective.
We also have several options for the activation of
gene x. The choice depends on a situation (or assump-
tion) of a network under consideration.
Changes of Expression Levels of Genes over Time.
If gene x is ON, it begins to be expressed and in some
future it will reach the threshold for gene y unless
gene x becomes OFF. This can be described as
G(on
x
→ F(x
y
∨ ¬on
x
)).
This formula means ‘if gene x is ON, in some future
the expression level of gene x will be beyond x
y
, or
otherwise gene x will become off’. This situation is
BIOINFORMATICS2014-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
8

t
x
ݔ
௬
t
x
ݔ
௬
s
0
s
2
s
1
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
s
0
s
2
s
1
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
(a) (b)
Figure 6: If gene x is ON, (a) the expression level of gene x
is over x
y
, or (b) gene x becomes OFF before gene x reaches
x
y
, where s
0
s
1
s
2
c is a time structure.
t
x
ݔ
௬
t
x
ݔ
௬
s
0
s
2
s
1
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
s
0
s
2
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
݊
௫
ݔ
௬
(a) (b)
s
1
Figure 7: If gene x is ON and the current expression level is
over x
y
, (a) the expression level of gene x keeps over x
y
, or
(b) gene x becomes OFF and as a result the expression level
may fall below x
y
.
depicted in Figure 6. If gene x is ON and expressed
beyond x
y
, it keeps the level until gene x is OFF. This
can be described as
G(on
x
∧ x
y
→ x
y
W¬on
x
).
This formula means ‘if gene x is ON and the current
expression level of gene x is over x
y
, gene x keeps its
level until gene x becomes OFF, or otherwise gene x
keeps its level always’. This situation is depicted in
Figure 7.
If gene x is OFF, its product decreases due to
degradation. Thus if gene x is OFF and the current
expression level of x is over x
y
, it will fall below x
y
in
some future unless x becomes ON again. This can be
specified as
G(¬on
x
→ F(¬x
y
∨ on
x
)).
If the expression level of gene x is under x
y
and x is
OFF then it keeps the level (i.e. it does not increase
and exceed x
y
) until x is ON. This can be specified as
G(¬on
x
∧ ¬x
y
→ ¬x
y
Won
x
).
We have similar formulae for gene y and the in-
put into gene x from the environment for increase and
decrease of them.
The conjunction of above formulae(i.e. joining by
∧ operator) is the specification of possible behaviours
of the network. In other words, time structures which
satisfy the formula are possible behaviours of the net-
work.
This method for modelling behaviours of gene
regulatory networks can be contrasted to usual quan-
titative methods like ordinary differential equation
models. We qualitatively model gene regulatory net-
works by temporal logic formulae instead of quan-
titative analytical formulae. Note that we have sev-
eral possible temporal logic specifications for a sin-
gle network depending on order of threshold values,
functions for multi-regulations and how we capture
increase and decrease of expression of genes. Inter-
ested reader may wish to consult (Ito et al., 2010; Ito
et al., 2013b) for detail.
4 REALISABILITY AND
HOMEOSTASIS
In this section we discuss the connection between re-
active systems and gene networks. Based on this con-
nection, we formulate homeostasis of gene networks
by realisability of reactive systems.
A reactive system is defined as a triple hX,Y, ri,
where X is a set of events caused by the environ-
ment, Y is a set of events caused by the system and
r : (2
X
)
+
→ 2
Y
is a reaction function. The set (2
X
)
+
denotes the set of all finite sequences on subsets of
X, that is to say, finite sequences on a set of environ-
mental events. A reaction function determines how
the system reacts to environmental input sequences.
Reactive system is a natural formalisation of systems
which appropriately respond to requests from the en-
vironment. Systems controlling vending machines,
elevators, air traffic and nuclear power plants are ex-
amples of reactive systems. Gene networks which re-
spond to inputs or stimulation from the environment
such as glucose increase, change of temperature or
blood pressure can also be considered as reactive sys-
tems.
A specification of a reactive system stipulates how
it responds to inputs from the environment. For exam-
ple, for a controller of an elevator system, a specifica-
tion will be e.g. ‘if the open button is pushed, the
door opens’ or ‘if a call button of a certain floor is
pushed, the lift will come to the floor’. It is impor-
tant for a specification of a reactive system to satisfy
realisability (Pnueli and Rosner, 1989; Abadi et al.,
1989), which requires that there exists a reactive sys-
tem such that for any environmental inputs of any tim-
ing, it produces system events (i.e. responds) so that
it satisfies the specification.
To verify a reactive system specification, it should
be described in a language with formal and rigorous
AQualitativeFrameworkforAnalysingHomeostasisinGeneNetworks
9

semantics. Widespread research in specifying and de-
veloping reactive systems lead to the belief that tem-
poral logic is the useful tool for reasoning them (Bar-
ringer, 1987; Pnueli and Rosner, 1989; Abadi et al.,
1989; Vardi, 1995). LTL is known to be one of
many other formal languages suitable for this purpose
and several realisability checkers of LTL are available
(Jobstmann and Bloem, 2006; Jobstmann et al., 2007;
Filiot et al., 2009; Bloem et al., 2010).
Now we define the notion of realisability of LTL
specifications. Let AP be a set of atomic propositions
which is partitioned into X, a set of input propositions,
and Y, a set of output propositions. X corresponds to
input events and Y to output events. We denote a time
structure σ on AP as hx
0
, y
0
ihx
1
, y
1
i. . . where x
i
⊆ X,
y
i
⊆ Y and σ[i] = x
i
∪y
i
. Let φ be an LTL specification.
We say hX,Y, φi is realisable if there exists a reactive
system RS = hX,Y, ri such that
∀ ˜x.behave
RS
( ˜x) |= φ,
where ˜x ∈ (2
X
)
ω
and behave
RS
( ˜x) is the infinite be-
haviour determined by RS, that is,
behave
RS
( ˜x) = hx
0
, y
0
ihx
1
, y
1
i. . . ,
where ˜x = x
0
x
1
. . . and y
i
= r(x
0
. . . x
i
).
Intuitively φ is realisable if for any sequence of in-
put events there exists a system which produces out-
put events such that its behaviour satisfies φ.
Example 1. Let X = {push
open
, push
close
} and Y =
{door
open
}. The specification
G(push
open
→ Fdoor
open
)
is realisable since there is a reactive system hX,Y, ri
with r( ¯xa) = {door
open
} where ¯x is any finite sequence
on 2
X
and a ⊇ {push
open
}. The specification
G((push
open
→ Fdoor
open
)∧(push
close
→ ¬door
open
))
is not realisable since for input sequence
{push
open
, push
close
}
ω
there is no output sequence
which satisfies the specification.
Realisability can be interpreted as the ability of
a system to maintain its internal condition irrespec-
tive of environmental inputs. In the context of gene
networks, realisability can be naturally interpreted as
homeostasis. For example, a network for control-
ling glucose level responds to an environmental in-
puts such as glucose increase or decrease in a manner
to maintain its glucose level within a normal range. In
the framework described in section 3, behaviour spec-
ifications of gene networks can be regarded as reactive
system specifications. Based on this connection, we
formulate homeostasis by realisability.
Let hI, O, φi be a behaviour specification of a gene
network where I is the set of input propositions, O is
the set of output propositions and φ is an LTL for-
mula characterising possible behaviours of the net-
work. Let ψ be a certain biological property of the
network. A network property ψ is homeostatic in
this network if for any input sequence x
0
x
1
. . . there
exists a reaction function r such that the behaviour
σ = hx
0
, r(x
0
)ihx
1
, r(x
0
, x
1
)i. . . is a behaviour of the
network (i.e. σ |= φ) and σ also satisfies the property
ψ (i.e. σ |= ψ). Thus we have the following simple
definition of homeostasis:
Definition 1. A property ψ is homeostatic with re-
spect to a behaviour specification hI, O, φi if φ∧ ψ is
realisable.
In this definition we consider responses of a sys-
tem not only to initial instantaneous inputs such as
dose-response relationship but also to any input se-
quences (e.g. inputs are oscillating or sustained),
which is difficult to be captured by ordinary differ-
ential models. Moreover, we have any number of en-
vironmental inputs thus we can consider homeostasis
against compositive environmental inputs.
Based on the method described in section 3 and
this formulation, we can analyse homeostasis of gene
networks using realisability checkers. In the next sec-
tion, we demonstrate our method in analysing a num-
ber of small but tricky networks.
5 DEMONSTRATION: ANALYSIS
OF HOMEOSTASIS FOR
EXAMPLE NETWORKS
First we consider the network in Figure 5 again. The
network in Figure 5 is expected to have a function that
whenever gene x becomes ON, the expression of gene
x will be suppressed afterward. This function main-
tains the expression level of gene x to its normal range
(low level). Despite of the extreme situation that the
input to gene x is always ON, the expression of gene
x inevitably ceases due to the activation of gene y and
its negative effect on gene x. Therefore this function
is expected to be homeostatic. Now we formalise this
verbal and informal reasoning with our framework.
The property ‘whenever gene x becomes ON, the ex-
pression of gene x will be suppressed afterward’ is
formally stated in LTL as:
G(on
x
→ F(¬on
x
∧ ¬x
y
)). (4)
This formula says that the property ‘if on
x
is true, it
becomes false and gene x is suppressed below x
y
in
some future’ always holds. We check whether this
formula is realisable with respect to a behaviour spec-
ification introduced in section 3.2. There are 6 propo-
sitions on
x
, on
y
, x
y
, y
x
, in
x
and e
x
for this network. The
BIOINFORMATICS2014-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
10

x y
+
-
+ -
Figure 8: The network in Figure 5 with a negative input for
gene y.
partition of input propositions and output propositions
are straightforward, that is, in
x
is the only input propo-
sition since the environment only controls the input to
gene x. Other propositions represent internal states
of the network. Note that the environment cannot
directly control the proposition e
x
, which represents
whether the level of the input exceeds e
x
. To exceed
the level e
x
, the environment needs to give the input
for a certain duration.
We had three options in the inactivation rule of
gene x, i.e. formulae (1),(2) and (3). In all choices the
property is realisable since even if in
x
is always true,
we need y
x
being false for the activation of gene x due
to the clause G(e
x
∧ ¬y
x
→ on
x
). If in
x
is always true,
gene x will be expressed beyond x
y
, and it induces
y’s expression. As a result, gene y can be expressed
beyond y
x
at which gene y inhibits gene x. Thus on
x
may not be always true. If we replace the clause for
the activation of gene x as G(e
x
→ on
x
), which says if
the input is effective gene x must be ON regardless of
the negative effect of gene y, then the property is not
realisable.
For realisability checking, we used Lily
3
(Jobst-
mann and Bloem, 2006) which is a tool for checking
realisability of LTL specifications. To use Lily, we
specify input propositions, output propositions and an
LTL formula. The result of checking (Yes or No) is
output to command-line and if it is YES, it also out-
puts a state diagram.
Now we assume gene y accepts negative input
from the environment (Figure 8). We have the extra
input proposition in
y
and output proposition e
y
. We
describe the activation rule for gene y as follows in
which gene y can be OFF by the negative input from
the environment:
G(¬e
y
∧ x
y
→ on
y
),
G(e
y
→ ¬on
y
).
Is the property (4) homeostatic with respect to this
behaviour specification? The realisability checker an-
swers ’No’. The reason is that if the input for gene
y is always ON, gene y cannot be ON, therefore the
negative effect from gene y to gene x cannot be effec-
tive. In this input scenario gene x cannot become OFF
after gene x becomes ON.
3
http://www.iaik.tugraz.at/content/research/
design verification/lily/
x y
+
+
-
Figure 9: A bistable switch.
Now we consider the next example depicted in
Figure 9. In this network we provide two thresholds
y
0
x
and y
1
x
for gene y. The threshold y
0
x
is the level
enough to activate gene x when the negative input
from the environment is not effective. The threshold
y
1
x
is the level enough to activate gene x regardless of
negative effect from the environment, that is, y
1
x
is the
threshold beyond which gene y overpowers the envi-
ronmental input. The behaviour specification for this
network will be somewhat complicated. First, we de-
scribe the fact that the threshold y
1
x
is greater than y
0
x
,
which is simply described as follows:
G(y
1
x
→ y
0
x
),
which says ’if gene y is expressed beyond y
1
x
, it is also
beyond y
0
x
(since y
1
x
> y
0
x
)’. Note that the proposition
y
1
x
means ’gene y is expressed beyond the threshold
y
1
x
’.
The activation rules and inactivation rules for gene
x are as follows:
G(¬y
0
x
→ ¬on
x
), (5)
G(e
x
∧ y
0
x
∧ ¬y
1
x
→ ¬on
x
), (6)
G(¬e
x
∧ y
0
x
→ on
x
), (7)
G(y
1
x
→ on
x
). (8)
Formula (5) says that if gene y is under y
0
x
, gene
x is OFF regardless of the environmental input. For-
mula (6) says that if gene y is in between y
0
x
and y
1
x
but the negative input is effective, gene x is OFF. For-
mula (7) says that gene x is ON when negative input
is not effective and gene y is expressed over y
0
x
. For-
mula (8) says that gene x is ON when gene y is just
expressed over y
1
x
.
The activation rule for gene y is simple:
G(x
y
↔ on
y
)
The change of the expression level of gene y when
it is ON are described as follows:
G(on
y
→ F(y
0
x
∨ ¬on
y
)), (9)
G(on
y
∧ y
0
x
→ y
0
x
W¬on
y
), (10)
G(on
y
∧ y
1
x
→ y
1
x
W¬on
y
). (11)
Formula (9) says that if gene y is ON, it will reach
the first threshold y
0
x
or otherwise it will become OFF.
Formula (10) says that if gene y is ON and the current
level is over the first threshold y
0
x
, it will keep over y
0
x
AQualitativeFrameworkforAnalysingHomeostasisinGeneNetworks
11

(this means it can be expressed beyond y
1
x
), or other-
wise gene y becomes OFF. Formula (11) says that if
gene y is ON and the current level is over the highest
threshold y
1
x
, it keeps y
1
x
or otherwise it will become
OFF.
We have similar formulae for the change of the
expression level of gene y when it is OFF.
G(¬on
y
→ F(¬y
1
x
∨ on
y
)),
G(¬on
y
∧ ¬y
1
x
→ ¬y
1
x
Won
y
),
G(¬on
y
∧ ¬y
0
x
→ ¬y
0
x
Won
y
).
For the change of the expression level of gene x
and the environmental input we have similar formulae
except they have only one threshold.
We check the bistability of the expression of gene
x, that is to say, if gene x can always be ON or always
be OFF. These properties are described as follows:
Gon
x
, (12)
G¬on
x
. (13)
By using Lily, we checked that both properties are
really homeostatic. Informal reasoning for the first
property (12) is as follows. Suppose that the input se-
quence such that the negative input to x is always ef-
fective, which is the best choice for the environment
to inactivate gene x. The system’s response to satisfy
the bistability is to start at a state in which both gene x
and y are ON and gene x and gene y are expressed be-
yond x
y
and y
1
x
, respectively. Since gene y is expressed
beyond y
1
x
, gene x can continue to be ON regardless
of negative input to x. The expression of gene y is
supported by the positive effect from gene x. For the
second property (13), we assume that the negative in-
put is always ineffective. The system’s response is
simply to start a state that both gene x and y is OFF
and gene x and y are expressed below x
y
and y
0
x
, re-
spectively. For x to be ON, we need y
0
x
being true but
the system can control gene y to be OFF since gene x
is OFF.
We expect both gene x and y are either ON or OFF
simultaneously. This can be checked by the following
properties:
Gon
x
∧ Gon
y
, (14)
G¬on
x
∧ G¬on
y
. (15)
Both properties are really homeostatic. Therefore
gene x and gene y are ‘interlocked’ in a sense.
We further investigate this ‘interlocking’ property.
Can gene x (and gene y) always be ON by its own?
That is to say, are the following properties homeo-
static?
Gon
x
∧ G¬on
y
, (16)
G¬on
x
∧ Gon
y
. (17)
x y
+
+
- -
Figure 10: A bistable switch with a negative input to gene
y.
The answers are ’No’ for both properties. To keep
gene x being ON gene x must be expressed beyond
y
x
and this prevents gene y to be always OFF. Thus
the property (16) is not homeostatic. This property is
even not satisfiable. That is to say, there is no input
sequence to satisfy the property (16). Conversely, to
keep gene y being ON gene x must be expressed be-
yond x
y
and this prevents gene x to be always OFF.
Thus the property (17) is not homeostatic and not sat-
isfiable too.
Interestingly, provided gene y accepts a negative
input from the environment (Figure 10), the proper-
ties (12) and (13) are still homeostatic. Even if both
negative inputs are always effective, each gene can be
expressed thanks to the positive effect from the other
gene. We confirmed the properties (12) and (13) are
really homeostatic with respect to the following be-
haviour specification in which we have two thresholds
for gene x (only activation rules for gene y are shown):
G(¬x
0
y
→ ¬on
y
),
G(e
y
∧ x
0
y
∧ ¬x
1
y
→ ¬on
y
),
G(¬e
y
∧ x
0
y
→ on
y
),
G(x
1
y
→ on
y
).
Moreover, the properties (14) and (15) are still
homeostatic. The properties (16) and (17) are also
not homeostatic but are satisfiable in contrast to the
previous case since if the environment appropriately
controls the inputs, gene y can be ON and OFF al-
ternately but keeps the expression level beyond y
0
x
so
that gene x can be ON indefinitely.
The last examples are anti-stress networks (Zhang
and Andersen, 2007) depicted in Figure 11. The net-
works in Figure 11 control the upper right objects
to keep them within the tolerable ranges. Though
these networks are schematic, we are just interested in
the controlmechanisms which contributehomeostasis
against environmental stresses. Let us consider the
network of Figure 11 (c). If the amount of O
2
be-
comes low, the network tries to recover the level of
O
2
. The property can be described as follows:
G(¬o
2
→ Fo
2
)
In this formula we interpret proposition o
2
as ‘the
amount of O
2
is within the tolerable range’ so ¬o
2
means it deviates the tolerable range. The behaviour
BIOINFORMATICS2014-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
12

Nrf2
Anti-electrophilic
Genes
Electrophile
Keap1
Electrophilic
stressor
-+
--
+
(a)
HSF
HSP Genes
Misfolded
Proteins
Heat
-+
+
+
(b)
Prolyl/asparaginyl
Hydroxylase
HIF
Anti-hypoxic
Genes
O
Hypoxia
++
+-
-
(c)
Figure 11: Schematic representations of anti-stress gene
regulatory networks that meditate (a) electrophilic stress re-
sponse, (b) heat shock response and (c) hypoxic response.
Prolyl/asparaginyl
Hydroxylase
HIF
Anti-hypoxic
Genes
O
Hypoxia
++
+-
-
-
Input
(c)
Figure 12: The network (c) with hypothetic negative inputs.
specification of the network is obtained as usual
4
. We
checked the property is really homeostatic.
Now we have a question: is this homeostatic func-
tion broken by the assumption that anti-hypoxic genes
receive environmental negative input? (Fig. 12) To
check this hypothesis, we modified the behaviour
specification in which anti-hypoxic genes receive a
negative input from the environment. The activation
rule for anti-hypoxic genes is modified considering
the negative input. The result of realisability check-
ing was ’No’. This analysis indicates that the home-
ostasis of this network may be broken by some envi-
4
We have ‘on’ propositions for each node and threshold
propositions for each edge.
ronmental factor which hinders the operations of anti-
hypoxic genes. Such analysis is difficult by observing
dose-response relationship based on ordinary differ-
ential models.
The homeostatic properties for other two networks
are similarly checked. Basic network topologies are
almost the same and the modification of network
specifications are minor.
6 RELATED WORK
In this section, we describe some other qualitative
methods for analysing biological systems.
BIOCHAM (Fages et al., 2004) is a language and
programming environment for modelling and simu-
lating biochemical systems, and checking their tem-
poral properties. Reactions are written as rules like
A+B=>C
, and simulations are performed by replac-
ing objects on the left-hand side with those on the
right-hand side. Since there are many possible rules
that can be applied in each state, there are many
possible successor states for each state depending
on the rule applied. After simulation, we have a
non-deterministic transition graph whose nodes are
possible states and edges are state transitions. The
set of possible behaviours of the simulation over-
approximates the set of all behaviours of the system
depending on the kinetic parameters. A biological
property is written in computation tree logic (CTL),
a type of branching time logic, and checked in the re-
sulting transition graph by the model checking tech-
nique (Clarke et al., 1999). In BIOCHAM, presence
or absence of objects is the only matter considered.
How we represent the interaction between biological
systems and environments in BIOCHAM is not pre-
sented, so it is unclear how we capture homeostasis in
BIOCHAM.
SMBioNet (Bernot et al., 2004) is a tool for for-
mally analysing temporal properties of gene regula-
tory networks. In SMBioNet, genes have concentra-
tion thresholds for activation or inhibition of each of
their regulating genes. A configuration of systems is
represented as a vector of expression values, which
are segmented by threshold. For example, if a gene
has two thresholds, then it has three levels – 0, 1, and
2. Behaviours of a network are captured as a tran-
sition system on the vectors of values for genes in
the network. Temporal evolution of a system is de-
scribed by a transition function on the vectors. Tem-
poral properties are described in CTL, and verifica-
tion of them is conducted by model checking on the
resulting transition systems. Since the models of SM-
BioNet are deterministic, it is not clear how to con-
AQualitativeFrameworkforAnalysingHomeostasisinGeneNetworks
13

sider any sequence of environmental inputs in SM-
BioNet.
GNA (de Jong et al., 2003) is a computational tool
for the modelling and simulation of gene regulatory
networks. GNA achieves simulation using piecewise
linear differential equation models and generates state
transition systems that represent possible behaviours
of networks. The qualitative dynamics of a system
are completely determined by inequality constraints
defining the ordering between thresholds and stable
equilibria of the system. Network properties of in-
terest are checked automatically using model check-
ing (Batt et al., 2005). Since the models of GNA are
based on piecewise linear differential equation, inter-
actions between biological systems and environments
over time cannot be directly captured. How we take
this essential aspect into consideration by GNA is not
clear.
As we mentioned, our work is based on the
method proposed by Ito et al. (Ito et al., 2010). For a
behaviour specification φ and a biological property ψ,
they check satisfiability of the formula φ∧ψ to know
whether there is a behaviour which satisfies the prop-
erty, or check unsatisfiability of φ ∧ ¬ψ to investigate
whether all behaviours satisfy the property. They did
not distinguish input propositions and output proposi-
tions. This means they only considered whether there
exist an input sequence to which a network can re-
spond without violating the biological property ψ.
7 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we formulated the notion of homeosta-
sis in gene regulatory networks by realisability in re-
active systems. This formulation allows the auto-
matic analysis of homeostasis of gene regulatory net-
works using realisability checkers. We analysed sev-
eral networks with our method. In the analyses we can
easily ‘tweak’ a network (such as appending extra-
inputs from the environment) and observed whether
the homeostatic properties can be maintained. Such
flexibility in analysing networks is an advantage of
our framework in the situation that we do not have
the definite network topologies. To test several hy-
pothetic networks, our method is more suitable than
quantitative approaches using ordinary differential
equation models.
There are several interesting future directions
based on this work. First is to find more interest-
ing applications in real biological examples. In as-
sociation with this topic, we are interested in ‘con-
ditional’ homeostasis which means that under certain
constraints on input sequences, a property is homeo-
static. This can be easily formulated as follows. Let
I and O be the input and output propositions respec-
tively. Let hI, O, φi be a behavioural specification and
ψ be a property. Let σ be an assumption about input
sequences e.g. ‘inputs to gene x and gene y come in-
finitely often but not simultaneously’. Then the prop-
erty ψ is conditionally homeostatic with respect to
hI, O, φi under a condition σ if hI, O, σ → φ ∧ ψi is
realisable. The motivation of this definition is that
in more realistic situation it is too strong to require a
system to respond to any input sequence.
The next topic is to develop a method to sug-
gest how we modify the model of a network when
an expected or observed property is not homeostatic
in a model. This problem is closely related to re-
finement of reactive system specifications (Aoshima
et al., 2001; Hagihara et al., 2009). We hope the
techniques developed so far for verification of reac-
tive systems can be imported to analysis of gene net-
works.
Another important future work is to develop a
method to overcome high complexity in checking re-
alisability of LTL formulae. The complexity of real-
isability checking is doubly exponential in the length
of the given specification (Pnueli and Rosner, 1989).
Thus it is intractable to directly apply our method to
large networks. To circumvent this theoretical limi-
tation we are interested in some approximate analysis
method (Ito et al., 2013b) or modular analysis method
(Ito et al., 2013a) in which a network is divided into
several subnetworks and analyse them individually.
The last topic is to extend our method with some
quantitative temporal logic (e.g. probability or real
time) (Tomita et al., 2011; Tomita et al., 2012) to en-
able quantitative analysis.
REFERENCES
Abadi, M., Lamport, L., and Wolper, P. (1989). Realiz-
able and unrealizable specifications of reactive sys-
tems. In ICALP ’89: Proceedings of the 16th Interna-
tional Colloquium on Automata, Languages and Pro-
gramming, volume 372 of LNCS, pages 1–17, Lon-
don, UK. Springer-Verlag.
Aoshima, T., Sakuma, K., and Yonezaki, N. (2001). An ef-
ficient verification procedure supporting evolution of
reactive system specifications. In Proceedings of the
4th International Workshop on Principles of Software
Evolution, IWPSE ’01, pages 182–185, New York,
NY, USA. ACM.
Barringer, H. (1987). Up and down the temporal way. The
Computer Journal, 30(2):134–148.
Barringer, H., Kuiper, R., and Pnueli, A. (1984). Now you
may compose temporal logic specifications. In Pro-
ceedings of the sixteenth annual ACM symposium on
BIOINFORMATICS2014-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
14

Theory of computing, STOC ’84, pages 51–63, New
York, NY, USA. ACM.
Batt, G., Ropers, D., de Jong, H., Geiselmann, J., Ma-
teescu, R., Page, M., and Schneider, D. (2005). Vali-
dation of qualitative models of genetic regulatory net-
works by model checking : Analysis of the nutritional
stress response in Escherichia coli. Bioinformatics,
21(Suppl.1):i19–i28.
Bernot, G., Comet, J., Richard, A., and Guespin, J. (2004).
Application of formal methods to biological regula-
tory networks: extending Thomas’ asynchronous log-
ical approach with temporal logic. J. Theor. Biol.,
229(3):339–347.
Bloem, R., Cimatti, A., Greimel, K., Hofferek, G.,
K¨onighofer, R., Roveri, M., Schuppan, V., and See-
ber, R. (2010). RATSY – a new requirements analysis
tool with synthesis. In Proceedings of the 22nd inter-
national conference on Computer Aided Verification,
volume 6174 of LNCS, pages 425–429, Berlin, Hei-
delberg. Springer-Verlag.
Clarke, E., Grumberg, O., and Peled, D. (1999). Model
Checking. MIT Press.
Croft, D., O’Kelly, G., Wu, G., Haw, R., Gillespie, M.,
Matthews, L., Caudy, M., Garapati, P., Gopinath, G.,
Jassal, B., Jupe, S., Kalatskaya, I., Mahajan, S., May,
B., Ndegwa, N., Schmidt, E., Shamovsky, V., Yung,
C., Birney, E., Hermjakob, H., D’Eustachio, P., and
Stein, L. (2011). Reactome: a database of reactions,
pathways and biological processes. Nucleic Acids Re-
search, 39(Database-Issue):691–697.
de Jong, H., Geiselmann, J., Hernandez, G., and Page, M.
(2003). Genetic network analyzer: Qualitative simu-
lation of genetic regulatory networks. Bioinformatics,
19(3):336–344.
Emerson, E. A. (1990). Temporal and modal logic. In
Handbook of Theoretical Computer Science, Volume
B: Formal Models and Sematics (B), pages 995–1072.
MIT Press.
Fages, F., Soliman, S., and Chabrier-Rivier, N. (2004).
Modelling and querying interaction networks in the
biochemical abstract machine BIOCHAM. J. Biol.
Phys. Chem., 4:64–73.
Filiot, E., Jin, N., and Raskin, J.-F. (2009). An antichain al-
gorithm for ltl realizability. In Proceedings of the 21st
International Conference on Computer Aided Verifi-
cation, volume 5126 of LNCS, pages 263–277, Berlin,
Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
Hagihara, S., Kitamura, Y., Shimakawa, M., and Yonezaki,
N. (2009). Extracting environmental constraints to
make reactive system specifications realizable. In Pro-
ceedings of the 2009 16th Asia-Pacific Software Engi-
neering Conference, APSEC ’09, pages 61–68, Wash-
ington, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Hagihara, S. and Yonezaki, N. (2006). Completeness of
verification methods for approaching to realizable re-
active specifications. In Completeness of Verification
methods for Approaching to Realizable Reactive Spec-
ifications, volume 348, pages 242 – 257.
Ito, S., Ichinose, T., Shimakawa, M., Izumi, N., Hagihara,
S., and Yonezaki, N. (2013a). Modular analysis of
gene networks by linear temporal logic. J. Integrative
Bioinformatics, 10(2).
Ito, S., Ichinose, T., Shimakawa, M., Izumi, N., Hagihara,
S., and Yonezaki, N. (2013b). Qualitative analysis
of gene regulatory networks using network motifs.
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference
on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
(BIOINFORMATICS2013), pages 15–24.
Ito, S., Izumi, N., Hagihara, S., and Yonezaki, N. (2010).
Qualitative analysis of gene regulatory networks by
satisfiability checking of linear temporal logic. In Pro-
ceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference
on Bioinformatics & Bioengineering, pages 232–237.
Jobstmann, B. and Bloem, R. (2006). Optimizations for
ltl synthesis. In Proceedings of the Formal Methods
in Computer Aided Design, FMCAD ’06, pages 117–
124, Washington, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Jobstmann, B., Galler, S., Weiglhofer, M., and Bloem, R.
(2007). Anzu: a tool for property synthesis. In Pro-
ceedings of the 19th international conference on Com-
puter aided verification, volume 4590 of LNCS, pages
258–262, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., and Tan-
abe, M. (2011). KEGG for integration and interpreta-
tion of large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids
Res.
Karp, P. D., Riley, M., Paley, S. M., and Pellegrini-Toole, A.
(2002). The MetaCyc Database. Nucleic Acids Res.,
30(1):59–61.
Mori, R. and Yonezaki, N. (1993). Several realizability con-
cepts in reactive objects. In Information Modeling and
Knowledge Bases IV, pages 407–424.
Pnueli, A. and Rosner, R. (1989). On the synthesis of a re-
active module. In POPL ’89: Proceedings of the 16th
ACM SIGPLAN-SIGACT symposium on Principles of
programming languages, pages 179–190, New York,
NY, USA. ACM.
Rabinovich, A. (1998). On translations of temporal logic
of actions into monadic second-order logic. Theor.
Comput. Sci., 193:197–214.
Safran, M., Dalah, I., Alexander, J., Rosen, N., Iny Stein, T.,
Shmoish, M., Nativ, N., Bahir, I., Doniger, T., Krug,
H., Sirota-Madi, A., Olender, T., Golan, Y., Stelzer,
G., Harel, A., and Lancet, D. (2010). GeneCards
Version 3: the human gene integrator. Database,
2010(0):baq020+.
Snoussi, E. and Thomas, R. (1993). Logical identification
of all steady states: the concept of feedback loop char-
acteristic states. B. MATH. BIOL., 55(5):973–991.
Thomas, R. and Kauffman, M. (2001). Multistationarity,
the basis of cell differentiation and memory. II. logical
analysis of regulatory networks in terms of feedback
circuits. CHAOS, 11(1):180–195.
Tomita, T., Hagihara, S., and Yonezaki, N. (2011). A proba-
bilistic temporal logic with frequency operators and its
model checking. In INFINITY, pages 79–93. EPTCS.
Tomita, T., Hiura, S., Hagihara, S., and Yonezaki, N.
(2012). A temporal logic with mean-payoff con-
straints. In Proceedings of the 14th international
conference on Formal Engineering Methods: formal
methods and software engineering, volume 7635 of
LNCS, pages 249–265, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer-
Verlag.
AQualitativeFrameworkforAnalysingHomeostasisinGeneNetworks
15

Vanitha, V., Yamashita, K., Fukuzawa, K., and Yonezaki.,
N. (2000). A method for structuralisation of evo-
lutional specifications of reactive systems. In ICSE
2000, The Third International Workshop on Intelligent
Software Engineering (WISE3), pages 30 – 38.
Vardi, M. Y. (1995). An automata-theoretic approach to fair
realizability and synthesis. In Proceedings of the 7th
International Conference on Computer Aided Verifi-
cation, volume 939 of LNCS, pages 267–278, Berlin,
Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
Wong-Toi, H. and Dill, D. L. (1991). Synthesizing pro-
cesses and schedulers from temporal specifications.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on
Computer Aided Verification, volume 531 of LNCS,
pages 272–281, London, UK, UK. Springer-Verlag.
Zhang, Q. and Andersen, M. E. (2007). Dose response rela-
tionship in anti-stress gene regulatory networks. PLoS
Comput. Biol., 3(3).
BIOINFORMATICS2014-InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsModels,MethodsandAlgorithms
16
