
The Significance of Data Governance in Healthcare
A Case Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital
Sarah Alofaysan, Bandar Alhaqbani, Rana Alseghayyir and Maryam Omar
College of Health Informatics, King Saud Bin AbdulAziz University for Health Sciences, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Keywords: Data Governance, Data Warehouse, Healthcare Analytics, Corporate Data Quality, Data Accuracy and
Completeness, Data Rules and Policies, Healthcare Data, Key Performance Indicators, Kpis.
Abstract: The paper investigates the importance of data governance to healthcare organizations. First, the paper
introduces the main pillars of data governance namely, data quality, compliance, and business
transformation. The paper then outlines the perceived challenges that may affect the adoption of data
governance strategies. The paper then proposes a new framework for data governance within healthcare
organizations. More importantly, the paper presents a case study on a leading tertiary care hospital in the
Middle East in order to investigate the impact of absence of data governance. 179,450 patients’ data records
were analysed within three outpatient clinics. Discrepancies in the total numbers of seen patients were
discovered between electronic data records and manually collected data. The main sources of the
discrepancies were identified within each clinic and were rooted to the violation of hospital policies, the
disregard to data related rules and policies and the lack of accountability on the data entered into the
electronic systems. Finally, the paper concludes with identifying research directions that requires further
investigation in this area.
1 INTRODUCTION
The sheer numbers of separated data sources in
healthcare organizations are growing in volume each
year, which makes the control of vital patients data
an unattainable goal. Understanding that data can
lead to better healthcare decisions, which ultimately
lead to better business, shifts organizations to a new
era of consuming patients’ data rather than only
producing it.
One of the mistakes in healthcare is approaching
data as technology assets not as corporate assets,
where in fact it must be treated as being as important
as corporate financial assets (Fisher, 2009). This
leads to many significant data problems such as
losing accountability, poor quality, and
noncompliance with external regulations. It is also
noticeable that healthcare data have fragmented
ownership with little authority and non-existent
standards, policies, and procedures. Consequently,
patients’ data could be exposed to exploitation
potentially resulting in bad decisions being made,
money being wasted, and business opportunities
being ignored (Sarsfield, 2009).
Data governance is the remedy for such data
problems. Data governance in simple words is the
process of controlling patients’ data by identifying
who is the data governor, what are the data rules,
how to enforce these rules, and how to monitor
compliance improvement. This control must
maintains a balance between dual core objectives of
data governance that are 1) limiting access to
patients' data to ensure privacy and security, and 2)
sharing patients' data between systems for
integration and decision-making purposes.
Conceptually, data governance has three main
interrelated modules which are administrative,
technical, and business module (Orr, 2011). The
administrative module represents the formal
governors who are responsible for defining the
governance scope and policies, resolving issues, and
assigning stewardships roles and responsibilities.
The business module represents stewardships that
are responsible for data standardizations and
definitions, and compliance with data policies,
business rules and processes. Lastly, the technical
module represents IT personnel who are responsible
for technical aspects of data governance such as data
integration rules and data modelling standards.
178
Alofaysan S., Alhaqbani B., Alseghayyir R. and Omar M..
The Significance of Data Governance in Healthcare - A Case Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital.
DOI: 10.5220/0004738101780187
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2014), pages 178-187
ISBN: 978-989-758-010-9
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Proper collaboration between business and IT is the
cornerstone for data governance initiatives in
healthcare (Russom, 2008).
It is important to distinguish between data
governance and data management. In general, data
management is about making decisions and
implementing them in the organization while data
governance concerns who is authorized to make
these decisions and based on which rules and
policies. Data governance completes data
management but never replace it (The Data
Management Association, 2009). Well-established
data governance programs can guarantee that other
data-driven projects such as data warehousing and
business intelligence will produce maximum value
to the organization (Kooper et al., 2011).
2 DATA GOVERNANCE
AND HEALTHCARE
ORGANIZATIONS
In the following sections, we discuss the areas that
yield massive benefits from data governance
program in healthcare environments.
2.1 Focus Area 1: Data Quality
Many healthcare organizations are facing data
quality challenges due to the complexity of the
clinical-systems’ data structure, massive growth in
clinical data volume and the lack of standardization
between the clinical systems in terms of naming and
modelling. Undoubtedly, poor data quality has a
tremendous impact on the efficiency and
effectiveness of the healthcare organizations, at both
operational and strategic levels (Brown and Khatri,
2010). As reported by The Data Warehousing
Institute (TDWI), problems of data quality cost US
businesses more than 600 billion dollars every year
(Batini et al., 2010).
All data problems are attributed to the absence of
effective governance. The data governance program
helps healthcare organizations to pinpoint the root
causes of data quality issues and identify the best
remedy that tackle all the problem dimensions
(Eppler, 2006). In the Electronic Medical Record
system (EMR), for example, data could be entered
through templates such as dropdown lists or
checkboxes. Physicians point out that this method of
data capturing does not allow them to describe
patients’ condition specifically. Rather, it has the
potential to negatively impact the accuracy and
completeness of patients’ documentation. It is
extremely important to determine under which
conditions structured data entry is appropriate
(AHIMA, 2008).
Similarly, healthcare organizations wrestle with
the inconsistency of naming and terms. For example,
one department in a hospital refers to “inpatient”
while another refers to “hospitalized” are both
departments referring to the same activity! One
system uses “pain killer” another uses “analgesic”.
The need for a unified data dictionary is critical for
end users of information in order to assure them that
the data they rely on for making-decisions is exactly
what they expected (Soares, 2010). A study was
conducted in a tertiary care hospital that experienced
a failure implementation of an enterprise data
warehouse showed that the absence of data
dictionary compromised the data quality and
reliability (Househ et al, 2011). Correspondingly, Fu
et al. reviewed seven systems that are widely used in
predictive toxicology, with a meticulous focus on
their data governance aspect. They found that
toxicology data were entered in different formats
with no systematic and standard measures for
checking data quality. Also, they reported that
systems’ metadata is crucial for toxicology
prediction; however, it was totally absent (Fu et al.,
2011). In response to predictive toxicology data
quality problems, Palczewska et al. proposed a data
governance model that address and mitigate the
significant gaps in toxicology data (Palczewska et
al., 2013).
2.2 Focus Area 2: Privacy, Security
and Compliance
Many healthcare organizations establish data
governance rules to ensure compliance with internal
privacy and security policies, as well as complying
with externally legislated regulations, such as Health
Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
(HIPAA) and the Privacy Act. However, while most
healthcare organizations have formal policies that
describe how and when privileged users may access
healthcare systems, they do not have an effective
mechanism to enforce, monitor, control, and audit
the privileged users’ actions (Wende, 2007). As a
result, accountability becomes an impossible
mission, especially with busy privileged clinicians
who are sharing their system-access credentials with
their workmates. Security and privacy compliance in
fact is one of the top ten issues that might cause
significant risks within the general field of
healthcare (Rishel, 2001). Data governance role here
TheSignificanceofDataGovernanceinHealthcare-ACaseStudyinaTertiaryCareHospital
179

is to transform compliance with hospital internal
policies and external regulations from manual audits
to automated, real-time checks and change-driven
business processes that instantly assess and mange
risks.
2.3 Focus Area 3: Business
Transformation
Business transformation is a change in the healthcare
management strategy to align people, processes and
technologies more closely with its business strategy.
Business transformation is a facilitator to achieve
compliance, quality improvement and business
integration through managing changes in term of
data ownership and data usage (Lenzerini, 2002).
Business transformation is a nightmare to any
healthcare organization where a recent research
shows that the failure rate of transformation program
is considered high, up to 70-80% while the
organizations that adopt effective data governance
approach can obtain almost 80% success (RapidBI,
2007).
All healthcare organizations have to change the
way of accessing patients' data and define who is
allowed to access what type of data in order to
comply with external regulations (HIPAA, for
example). Also, healthcare organizations have to
change the ownership of the data as it move toward
using data as an enterprise assets (Russom, 2008). In
the beginning of establishing any data governance
program, it is very crucial to locate one primary
legal owner of the data. In reality, there is a great
debate on who owns the data (Alkouri, 2012). Is it
the data creator (physicians or other healthcare
providers)? Is it the patient? Or is it the organization
itself (where the data has been created)? According
to HIPPA, the patient has a medical record, which is
owned by his/her medical provider (Shay, 1999).
But, if the medical provider died, fired or transferred
to other healthcare organization we lost the real data
owner. In fact, the ownership of healthcare data is
still in a grey area.
As one of the big conceptual challenges that faced
a tertiary care hospital while they were
implementing data warehouse project is identifying
the ownership of the systems, data, and Key
Performance Indicators (KPIs) (Bergeron et al,
2007). Data warehousing is one of the data-intense
business initiatives that required well-structured data
governance to enforce business transformation.
3 PERCEIVED CHALLENGES
The benefits of strong data governance initiative are
many and diverse and so are the challenges. The
core challenges in data governance are
fundamentally not about technologies but about
people and processes (Nigel, 2012). The first
challenge is political leadership to establish
governing council office. The lack of business
involvement and executive level sponsorship is also
one of the biggest challenges. In fact, the
commitment of executives is difficult because the
governance of data is often perceived as a
mysterious issue, rather than as a program that
delivers business measures (Hsu, 2009). As reported
by The Data Warehousing Institute (TDWI) survey
of data governance, the second leading barrier is the
lack of people understanding of governance which
includes non-sustainable executive sponsorship as
well as lack of business justification (Russom,
2008). Lastly, the lack of data ownership, resistance
to change, and resistance to accountability are focal
barriers.
4 DATA GOVERNANCE
FRAMEWORK FOR
HEALTHCARE
ORGANIZATIONS
There is a great need to compose a model that treats
data as a strategic enterprise asset. There is also lack
of data governance models in the market. The Data
Governance Institute (DGI) framework and IBM
framework are the only models currently available.
However, both frameworks are very generic. They
are not industrial oriented, which creates gaps when
they are implemented in a specific industry. In
addition, both frameworks fail to define a clear
governance cycle that proactively puts into place
data rules and policies, monitors and measures the
on-going services, and reactively resolves issues.
The business obstacles and needs in the healthcare
industry are totally different from those of other
industries. Physicians’ and clinicians’ resistance, for
example, is significantly high. For this reason,
change management becomes an important on-
going process in the healthcare data governance
framework. In addition, the compliance with the
healthcare regulations and standards is crucial. The
proposed framework in Figure 1 illustrates how the
healthcare organization governs its data on the
organizational and operational levels. This
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
180
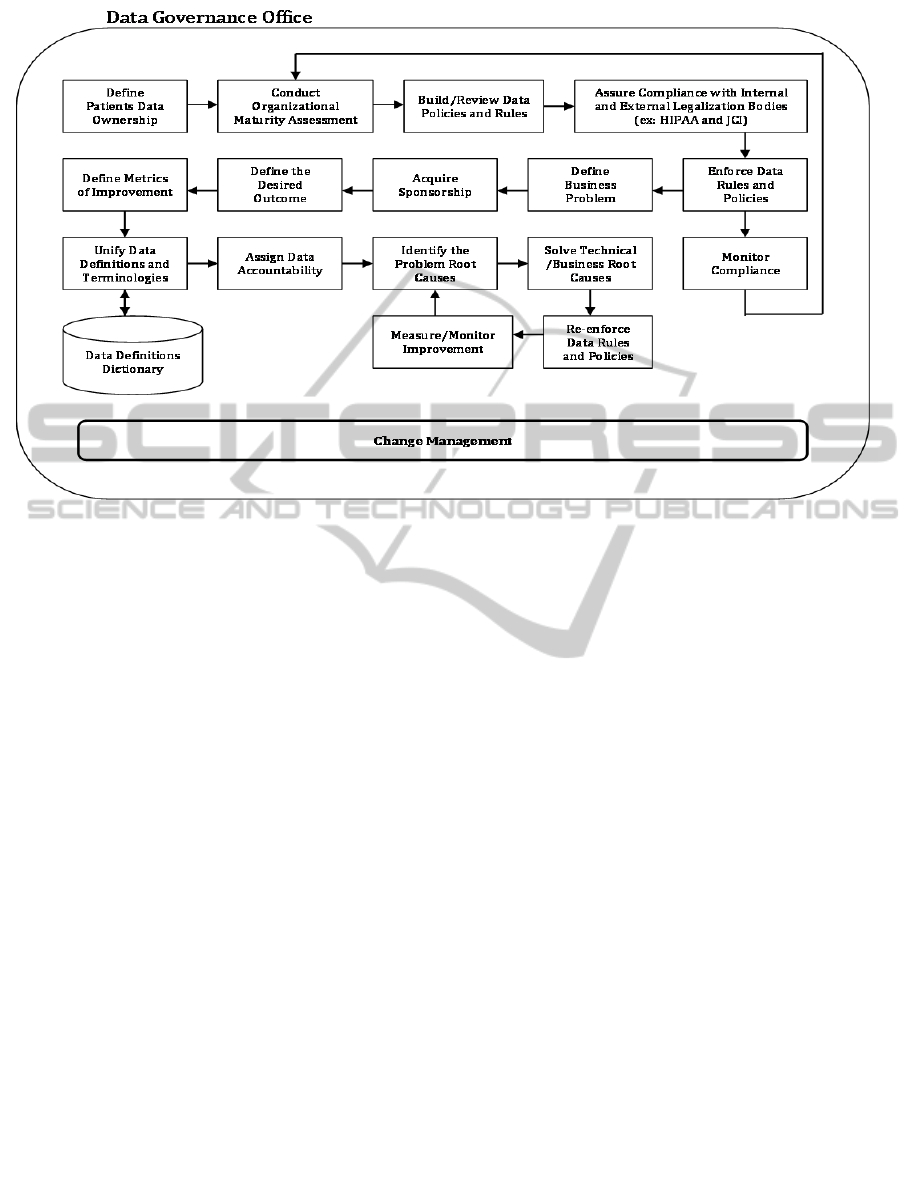
Figure 1: A New Data Governance Framework for Healthcare Organizations.
framework can be directly implemented after
establishing the data governance office, appointing
data governors, and defining their decision rights.
The proposed model starts with the agreement on
who owns the data, followed by an understanding of
the maturity level of the organization, in terms of
data governance. The goal is to build a clear
understanding of the organization’s current state
and define the gap between the current and the
desired state. It is advised to conduct this
assessment on a yearly basis in order to measure the
progress of the governance initiative. On the
operational level, data governors define business
problems and assign a sponsor for each. Then, the
governors and the sponsor define performance
measurement metrics to assess the improvements
over time. Then, they assign accountability for data
that is related to this business problem in order to
limit data problems in the future. After that, they
work to identify and resolve the technical and
business root causes of each problem. The defined
metrics in each business area helps the accountable
person to monitor improvements and breaches of
data rules and policies. Any adjustment/addition or
deletion of data rules or policies must be escalated
to the board of data governors in the data
governance office for reviewing and approval.
5 A CASE STUDY ON DATA
GOVERNANCE IN A
TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
In this section, we introduce a data governance
exercise based on our proposed model. This exercise
was conducted in a leading healthcare organization
within the Middle East. In the study, we investigate
the root causes of patients’ data quality problems
and summarize the main findings.
5.1 General Background
This research was conducted in one of the leading
tertiary healthcare organizations in the Middle East,
with more than 2,200 beds and around 12,000
employees. This organization serves all eligible
patients around the country through four main sites
in different regions. In the capital city, the average
yearly outpatients’ visits exceeded 485,000 visits,
while the average yearly inpatients’ admissions and
discharges is around 40,000 admissions/discharges.
This organization has 15 core clinical and
administrative systems that were running smoothly
to serve all clinical and non-clinical needs. The core
clinical system, which is the Electronic Medical
Record system (EMR), is integrated between all the
remote sites of the hospital. In 2007, the data
TheSignificanceofDataGovernanceinHealthcare-ACaseStudyinaTertiaryCareHospital
181
warehouse initiative began. A massive amount of
data were captured, transferred, and loaded into the
data warehouse. The average number of data records
that are transferred daily to the data warehouse from
the EMR system is about 5,832,000 records a day.
Electronic data measures and dashboards showed
significant discrepancies when compared with the
organizational manually collected reports.
5.2 Research Aim
This research aims to identify the root causes of
patients’ data discrepancies in the chosen
organization and investigates the effectiveness of the
proposed data governance model.
5.3 Research Design
This research was conducted in the Ambulatory Care
Services division (ACS). ACS has eighteen different
outpatient clinics that run nine hours a day, five days
a week. The high-volume of patients visiting the
ambulatory care clinics in addition to the different
processes implemented in each clinic contribute to
the complexity of data discrepancies.
Three out of eighteen clinics were selected vigilantly
based on their flexibility of accepting walk-in
patients, their volume of booked and referred
patients, the number of physician-clinics and nurse-
clinics in a single specialty, and how strict they were
in using the EMR system. The three chosen clinics
were: the Employee Health Clinic, the Obstetric and
Gynaecology Clinic, and Ophthalmology Clinic. We
then formed a group of nurses, physicians, and
clinical statisticians for each clinic and gave them
the responsibility of producing their clinic’s manual
statistics. The role of these groups was to provide
researchers with yearly manual statistics, as well as
the manual log files for patients’ visits in each clinic.
Also, these groups were responsible for clarifying
the KPIs definitions and formulas they used in
producing their manual statistics. The list of KPIs,
along with the definitions and formulas, were
communicated to the data warehouse representative
who was responsible of extracting each clinic’s
electronic data directly from the data warehouse.
Table 1 illustrates a list of terminologies and
definitions, as agreed upon by the formed groups.
We collected both manual and electronic data in
the period between January 2011 and December
2012 for the three selected clinics. Both data sets
were analysed in different timeframes in order to
validate that the discrepancies in the clinical data
was a phenomenon and not a coincidence.
Table 1: Unified List of Definitions.
Terms Definitions
Manual
Data
Data that is collected manually by
nurses in a clinic using paper and pen
Electronic
Data
Data that is captured from an electronic
source of data such as Data Warehouse
Nurse-
Clinic
Outpatients clinic that is run by a nurse
Physician-
Clinic
Outpatients clinic that is run by a
physician
Booked
Appt.
Patients who did register an
appointment for consultation
Kept Appt.
Patients who did attend their registered
appointments and had their consultation
Walk-in
Patients
Patients who attended a clinic without
an appointment being made
No-Show
Patients
Patients who did not attend their
appointments
Seen
Patients
Patients who visited the clinic as a
walk-in or with an appointment. The
total seen patients are equal to the total
walk-in patients plus total kept
appointments
Seen Patients = (Walk-in + Kept
Appointments)
5.4 Research Findings
In this section, we explore the data discrepancy’s
root causes in the three selected clinics.
5.4.1 Employee Health Clinic (EHC)
Background
The EHC is designated to provide primary
healthcare services to the hospital employees and
their dependents. This clinic is subdivided into two
main categories: family physician-clinics and nurse-
clinics. As a general practice, the EHC accepts
patients as walk-in patients. Some patients are
granted a booked appointment if their family
physician asks for a follow-up on a specific date.
Experimental Results
We analysed the EHC manual collected data and
electronic data from January 2011 to July 2011. The
manuals reveal a higher number of seen patients
than electronic data records, an up to 4.6%
difference. Figure 2 below shows a bar chart of the
total number of seen patients of both manually
collected data and electronic data records, denoted
by (M) and (E) respectively.
The total number of seen patients in EHC
constitutes the sum of the numbers of all seen
patients in both nurse and physician clinics. Thus,
the discrepancy in the EHC data is a result of
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
182
discrepancy in either the nurse-clinics data or the
physician-clinics data or in both. Starting with
physician-clinics, we analysed the number of
patients who visited these clinics as walk-ins or as
booked appointments. The difference between both
data sets is negligible as illustrated in Figure 3.
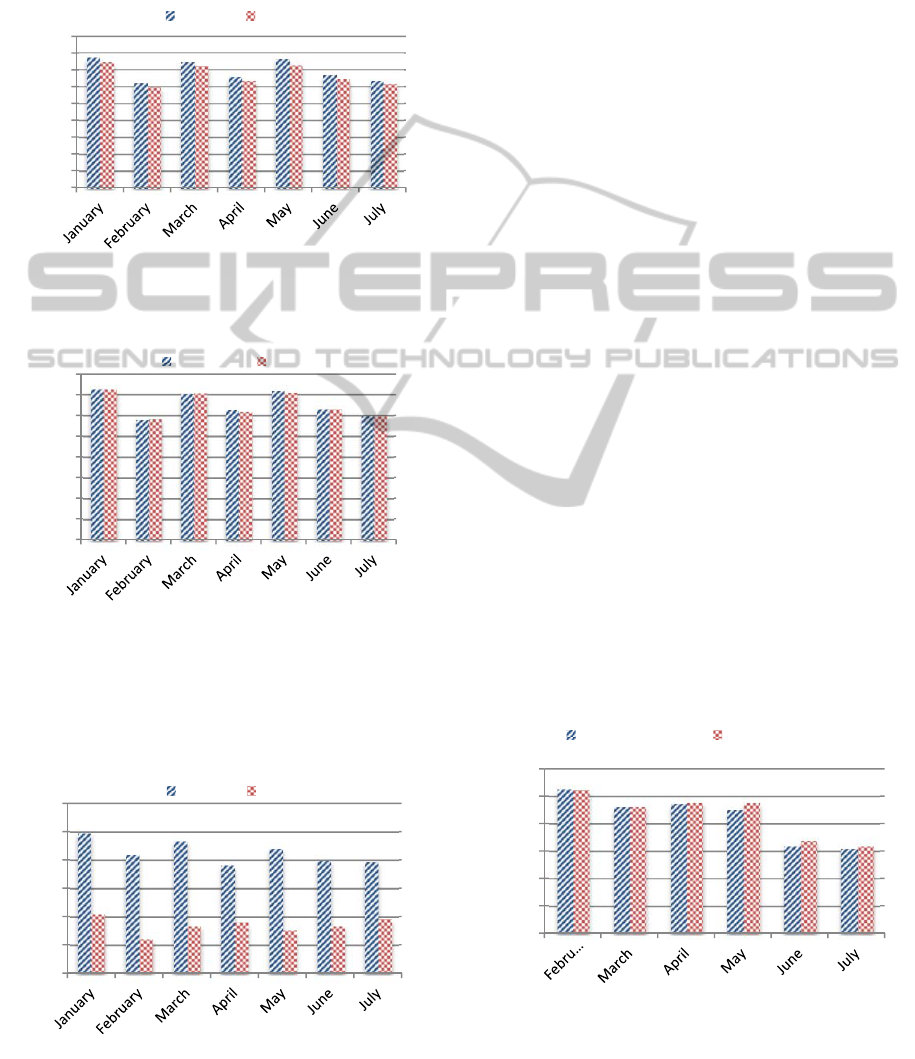
Figure 2: Total Seen Patients in EHC Clinics from January
to July 2011.
Figure 3: Total Seen Patients in EHC Physician-Clinics
from January to July 2011.
Next, we examined the number of patients who
visited the nurse-clinics as walk-ins or as booked
appointments. The difference between both data sets
Figure 4: Total Seen Patients in EHC Nurse-Clinics from
January to July 2011.
is very significant as illustrated in Figure 4. The data
warehouse provided up to 70% fewer data in
comparison with manually collected data for this
case. Thus, clearly, the discrepancy observed in the
EHC total seen patients (Figure 2) is a result of a
discrepancy in the nurse-clinics data (Figure 4).
Core Reasons for Discrepancies
Nurses in the nurse-clinics are not using the EMR
system to register all visits they encounter. The
practice of using papers instead of using the EMR
system is a large violation of the hospital’s policy.
5.4.2 Ophthalmology Clinics
Background
The Ophthalmology clinics provide patients with
full range of eye care starting from routine eye
check-up to complex surgical procedures. Unlike
EHC, all Ophthalmology clinics are specialist
physician-clinics. All patients should book their
appointments prior to their actual visits. Walk-in
patients, however, are accepted under certain
conditions.
Experimental Results
The analysis of a random six-month timeframe data
reveals discrepancies in the total number of seen
patients. The electronic data provided up to 20%
fewer records than the manually collected data. The
total number of seen patients is the sum of both,
walk-in patients and kept appointments. Thus,
discrepancies were due to either errors in the number
of walk-in patients or the in the number of patients
that kept their booked appointments, or in both. The
numbers of total kept appointments from both data
sources were found to be almost matching as
illustrated in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Total Kept Appointments in Ophthalmology
Clinics.
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
NumberofVisits
Yearof2011
Seen(M) Seen(E)
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
NumberofVisits
Yearof2011
Seen(M) Seen(E)
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
NumberofVisits
Yearof2011
Seen(M) Seen(E)
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
NumberofVisits
Yearof2012
KeptAppt(M) KeptAppt(E)
TheSignificanceofDataGovernanceinHealthcare-ACaseStudyinaTertiaryCareHospital
183

On the other hand, the differences in the
numbers of walk-in patients were significantly high.
The electronic data showed up to 95% fewer records
than manually collected data as shown in Figure 6.
Clearly, the discrepancy observed in total number of
seen patients is a result of not recording walk-in
visits in the electronic data source.
Figure 6: Total Walk-in Patients in Ophthalmology
Clinics.
Core Reasons for Discrepancies
Nurses are not registering walk-in patients in the
EMR system. Not using the electronic system for
patients’ encounters is an unforgivable violation of
the hospital’s policy.
5.4.3 Obstetrics and Gynaecology Clinics
(OB-GYN)
Background
The OB-GYN department offers complete
obstetrical and gynaecological services for female
patients. It is the busiest department around the year.
The OB-GYN clinics are divided into two groups,
physician-clinics and nurse-clinics.
Experimental Results
We randomly selected a timeframe of seven months,
from September 2011 to March 2012, to study the
statistical inconsistencies. The analysis of both
manual and electronic data sets shows similarities in
the total number of seen patients as shown in Figure
7. An accurate measure on the clinical level does not
necessarily mean that all sub-measures are accurate.
Further analysis of both data sets is essential. In
physician-clinics, the manual collected data
provided up to 14% more records of seen patients as
illustrated in Figure 8. On the other hand, the nurse-
clinics indicate a significant difference between both
data sets where the electronic data gave up to 45%
more records of seen patients as shown in Figure 9.
However, through analysing differences and
similarities in both nurse-clinics and physician-
clinics, we noticed that the variances between the
manually collected data and the data from the
electronic source followed the same trend. The
difference in the total number of seen patients in
nurse-clinics was the same as the difference in the
total number of seen patients in the physician-clinics
as illustrated in Figure 10.
Figure 7: Total Seen Patients in OB-GYN Clinics from
September 2011 to March 2012.
Figure 8: Total Seen Patients in OB-GYN Physician-
Clinics from September 2011 to March 2012.
Figure 9: Total Seen Patients in OB-GYN Nurse-Clinics
from September 2011 to March 2012.
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
February March April May June July
NumberofVisits
Yearof2012
Walk‐in(M) Walk‐in(E)
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
NumberofVisits
Yearof2011and2012
Seen(M) Seen(E)
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
NumberofVisits
Yearof2011and2012
Seen(M) Seen(E)
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
NumberofVisits
Yearof2011and2012
Seen(M) Seen(E)
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
184

Core Reasons for Discrepancies
The OB-GYN is the busiest department around the
year. All physician-clinics’ schedules are fully
booked for six months in advance. Physicians in the
OB-GYN department need to follow-up with
patients who have critical cases on a regular base.
To avoid moving these patients to the waiting list,
physicians booked them follow-up appointments
under the nurse-clinics. As a result, when measures
were taken from the electronic data system, it
revealed a higher number of seen patients in nurse-
clinics and a fewer number of seen patients in
physician-clinics.
Figure 10: Differences in Numbers of Seen Patients in
Physician-Clinics and Nurse-Clinics.
5.5 Results after Implementing the
New Data Governance Model
We selected the Ophthalmology clinic to represent
the implementation model of our new data
governance framework (Figure 1). In June 2013, we
started enforcing data policies and rules as well as
monitoring compliance improvement. We also
provided direct and indirect educational sessions to
key clinicians in the Ophthalmology department, as
small steps toward change management. By the end
of November 2013, we investigated the changes that
happened in patients’ data during the four months of
governance. The analysis of both data sets reveals
improvement in total numbers of walk-in patients.
The electronic data provided up to 21% fewer
records than the manually collected data as shown in
Figure 11. The electronic data was used to provide
up to 95% fewer walk-in records as illustrated
previously in Figure 6.
Figure 11: Total Walk-in Patients in Ophthalmology
Clinics after Implementing our New Data Governance
Framework.
6 DISCUSSION
This study helped the chosen healthcare organization
to identify the root causes of their patients’ data
quality issues. The study reveals how the different
business processes implemented in each clinic affect
the data outcomes. The EHC physician-clinics, for
example, had a robust walk-in business process in
place. As a result, the measures of walk-in patients
in this clinic were precise, even though the number
of walk-in patients dropping by the clinic fluctuated
over the year (due to seasonal changes). On the other
hand, 95% of the Ophthalmology clinic’s walk-in
patients were omitted from the Electronic Medical
Record system. This is due to the absence of a well-
defined walk-in business process, and the weak
enforcement of the hospital’s policies, as well as the
lack of education and training on the Electronic
Medical Record system.
The study also provides evidence on how data
outcomes were affected by nurses and physicians
misconduct. 70% of patients seen by EHC nurse-
clinics were not entered into the Electronic Medical
Record system as a result of nurses’ negligence.
This misbehavior of not entering data into the
electronic system is a breach of the hospital policy.
Similarly, the malpractice of OB-GYN physicians
in booking more appointments for their patients
under the nurse-clinics resulted in discrepancies in
the Electronic Medical Record system. This
conduct, which was discovered through this data
governance exercise, is a violation of the hospital’s
administrative policies and procedures. More
importantly, the study provides evidence on the
importance of adapting a robust data governance
framework that designed primarily for healthcare
needs. The proposed framework shows
effectiveness on resolving patients’ data issues
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
NumberofVisits
DifferencesinPhysician‐Clinics
DifferencesinNurse‐Clinics
TheSignificanceofDataGovernanceinHealthcare-ACaseStudyinaTertiaryCareHospital
185

within a short period of time. This model helped to
proactively control data, reactively resolve data
issues, and monitor breaches of data rules and
policies. However, it still needs more
experimentation.
This research has clearly shown evidence of data
errors that are related to the absence of data
governance. Such data errors resulted from the lack
of data privacy and security rules, the lack of data
policies, and the absence of accountability on the
data entered into the Electronic Medical Record
system. The outcomes of this study were presented
to the board of decision-makers in the chosen
healthcare organization. The board decided to
formally start two initiatives: Data Governance
Project and Book of Measures Project, the latter of
which aimed to build an enterprise dictionary of
KPIs, terminologies, and definitions in order to unify
the language used in the hospital.
7 CONCLUSIONS
We believe that applying data governance in
healthcare will provide a solid start for data-driven
projects such as data quality improvement, data
warehousing, healthcare analytics, and business
intelligence. The analytical measures of data alerts,
data quality improvement, policy violation
provenance, rules monitoring, and authority
monitoring will increase the reliability and
transparency of data governance for all users and
regulatory bodies. Studying and comparing the
outcomes of different data governance framework is
an essential piece of future work. This research is a
starting point that directly impacts many interesting
research disciplines pertaining to healthcare data
governance such as business governance, strategic
decisions effectiveness, data error tracking and
assessments of improvements to data quality.
REFERENCES
AHIMA. 2008. Quality Data and Documentation for
EHRs in Physician Practice. Journal of AHIMA, 79(8),
43-48.
Alkouri, A. 2012. DATA OWNERSHIP: WHO OWNS
'MY DATA'?. International Journal of Management
and Information Technology, 2(1). Available from:
<http://www.slideshare.net/alkhouri/data-ownership-
who-owns-my-data>.[10 August 2013].
Batini, C., Mecella, M., & Viscusi, G. 2010. Information
Systems for EGovernment (1sr Edition ed.): Springer.
Bergeron, B., AlDaig, H., Hoque, E., AlBawardi, F. S., &
Alswailem, O. 2007. Developing a Data Warehouse
for the Healthcare Enterprise: Lessons from the
Trenches: HIMSS.
Brown, C. V., & Khatri, V. 2010. Designing Data
Governance. Communications of the ACM, 53(1), 148-
152.
Eppler, M. J. 2006. Managing Information Quality. Berlin,
Heidelberg: Springer
Fisher, T. 2009. The Data Asset: How Smart Companies
Govern Their Data for Business Success (1 ed.):
Wiley; 1 edition (June 22, 2009).
Fu, X., Wojak, A., Neagu, D. Ridley, M., & Travis, K.
2011. Data governance in predictive toxicology: A
review. Journal of Cheminformatics, 3(1). doi:
10.1186/1758-2946-3-24
Househ, M. S., & AlTuwaijri, M. 2011. Early Development
of an Enterprise Health Data Warehouse. In
Borycki,E.,M. et al. (Eds.), International Perspective in
Health Informatics (Vol. 164, pp. 122-126). doi:
10.3233/978-1-60750-709-3-122
Hsu, V. 2009. How Technology Enables Data
Governance. Available from: <http://www.oracle.com/
us/products/applications/master-data-management/
042941.pdf>. [23 August 2013].
Kooper, M. N., Maes, R., & Lindgreen, E. R. 2011. On the
governance of the information: Introducing a new
concept of governance to support the management of
information. International Journal of Information
Management, 31(3), 195-200. doi:10.1016/
j.ijinfomgt.2010.05.009
Lenzerini, M. 2002. Data integration: A theoretical
perspective. Proc. of the 21st ACM SIGMOD-SIGART
Symposium on Principles of Database<p> Systems
(PODS).
Nigel, C. 2012. Data governance. Health Informatics
Society of Australia. 1. Available from:
<http://www.hisa.org.au/?page=thought_lship>.[13
July 2013].
Orr, J. C. 2011. Data Governance for the Executive.
Colorado Springs: Senna Publishing, L.L.C.
Palczewska, A., Fu, X., Trundle, P., Yang, L., Neagu, D.,
Ridley, M., Travis, K. (2013). Towards model
governance in predictive toxicology. International
Journal of Information Management, 33(3),567–582.
Available from: <http://www.inf.brad.ac.uk/~mick/
papers/IJIM1227.pdf>.[1 September 2013].
RapidBI 2007. Business Transformation – a change
strategy. Available from: <http://rapidbi.com/
created/businesstransformation/>.[10 August 2013].
Rishel, W. 2001. HIPAA: An Industry Progress Report.
Available from: <http://www.ehcca.com/presentations
/HIPAA3/202.pdf>. [27 July 2013].
Russom, P. 2008. Data Governance strategies Helping
your Organization Comply, Transform, and Integrate.
TDWI Best Practices Report.
Sarsfield, S. 2009. Data Governance for Imperative.
Cambridge, UK: IT Governance Publishing.
Shay, E. F. (1999). Legal implications of the informatics
revolution. Physician's News Digest. Available from:
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
186

<http://www.physiciansnews.com/computers/399shay
dv.html>. [27 July 2013].
Soares, S. 2010. The IBM Data Governance Unified
Process. Ketchum: MC Press Online, LLC.
The Data Management Association. 2009. The DAMA
Guide to Data Management Body of Knowledge.
Bradley Beach, US :Technics Publications,LLC.
Wende, K., A. 2007. A Model for Data Governance –
Organising Accountabilities for Data Quality
Management. Paper presented at 18th Australasian
Conference on Information Systems, Australia,
Toowoomba: ACIS 2007 Proceedings.
TheSignificanceofDataGovernanceinHealthcare-ACaseStudyinaTertiaryCareHospital
187
