
Key-point Detection with Multi-layer Center-surround Inhibition
Foti Coleca
1
, Sabrina Z
ˆ
ırnovean
1,2
, Thomas K
¨
aster
1,3
, Thomas Martinetz
1
and Erhardt Barth
1
1
Institute for Neuro- and Bioinformatics, University of L
¨
ubeck, Ratzeburger Allee 160, L
¨
ubeck 23562, Germany
2
University ”POLITEHNICA” of Bucures¸ti, Splaiul Independent¸ei 313, 060042, Bucures¸ti, Romania
3
Pattern Recognition Company GmbH, Innovations Campus L
¨
ubeck, Maria-Goeppert-Straße 3, 23562 L
¨
ubeck, Germany
Keywords:
Object Recognition, Pet Recognition, Sparse Representations, End-stopped Operators, Higher-order Decorre-
lation, Deep Multi-layer Networks.
Abstract:
We present a biologically inspired algorithm for key-point detection based on multi-layer and nonlinear center-
surround inhibition. A Bag-of-Visual-Words framework is used to evaluate the performance of the detector
on the Oxford III-T Pet Dataset for pet recognition. The results demonstrate an increased performance of our
algorithm compared to the SIFT key-point detector. We further improve the recognition rate by separately
training codebooks for the ON- and OFF-type key points. The results show that our key-point detection algo-
rithms outperform the SIFT detector by having a lower recognition-error rate over a whole range of different
key-point densities. Randomly selected key-points are also outperformed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Various object-recognition and tracking approaches
rely on the detection of object key-points (Lowe,
1999; Csurka et al., 2004). Regions around such
key-points are expected to contain the information
needed for matching and recognition. Although some
have argued that a dense sampling of randomly se-
lected points can replace or even outperform recog-
nition algorithms based on key-points (Nowak et al.,
2006), the benefits of appropriate key-points and re-
lated saliency measures are obvious since they re-
duce the amount of information that needs to be pro-
cessed and often, as in many cases including ours,
lead to better recognition performance, see (Vig et al.,
2012a) for a recent example. The standard for key-
point detection is the SIFT algorithm, which selects
key-points as the local maxima of the Difference-of-
Gaussians (DoG) operator (Lowe, 1999).
We here show how SIFT key-point selection can
be improved by introducing a few biologically in-
spired extensions and new features. The DoG oper-
ator has been often used to model lateral inhibition, a
key feature of early visual processing. However, some
essential properties of biologically realistic lateral in-
hibition are usually ignored and it turns out that three
of them fit our purpose of improving key-point selec-
tion. The first property is that of nonlinearity, which is
here modeled as a simple one-way rectification (clip-
ping) of the DoG. The second property is that of
ON/OFF separation, i.e. the distinct representation
of bright-on-dark versus dark-on-bright features. The
third property is that of multiple layers, i.e., the fact
that lateral inhibition occurs repeatedly in successive
layers of early visual processing. All these features
have been considered in (Barth and Zetzsche, 1998),
where the authors have shown that iterated and non-
linear lateral inhibition generates representations of
increasing sparseness and converges to end-stopped
representations, i.e., representations of only 2D fea-
tures like corners and junctions. In other words: the
linear DoG operator eliminates 0D regions, which are
uniform, and the iteration of the clipped DoG then
eliminates 1D regions, i.e., straight edges and lines.
This approach, however, has not been used for key-
point selection in the context of object recognition.
Operators that extract 2D features, called end-
stopped operators in vision, are thought to provide an
efficient representation by eliminating redundancies
in images and videos (Zetzsche and Barth, 1990; Vig
et al., 2012b). This works well because 0D and 1D
regions are redundant in a geometrical sense (Mota
and Barth, 2000). Statistical approaches consider a
representation to be efficient if statistical dependen-
cies in the signal are reduced. Linear operators such
as the DoG, however, can only decorrelate the signal
386
Coleca F., Zîrnovean S., Käster T., Martinetz T. and Barth E..
Key-point Detection with Multi-layer Center-surround Inhibition.
DOI: 10.5220/0004743103860393
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2014), pages 386-393
ISBN: 978-989-758-003-1
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

and nonlinear operations such as those advocated in
(Zetzsche and Barth, 1990) are needed to deal with
higher-order dependencies. However, isotropic oper-
ators such as the DoG, even when combined with sim-
ple nonlinearities, are limited in their ability to deal
with higher-order dependencies.
Although the principle of iterating the nonlinear
DoG has been shown to provide 2D representations,
this insight was only supported by simulations. How-
ever, the computational power of linear-non-linear
(LNL) structures has been further analyzed in (Zet-
zsche and Nuding, 2007) and it has been shown how
LNL networks can reduce the statistical dependen-
cies in natural images. The idea is to learn the linear
part of the LNL sandwich, e.g., by PCA for decor-
relation, then apply a simple nonlinearity that would
introduce new correlations (since the nonlinearity can
map higher-order dependencies to second-order de-
pendencies), which can then be removed in the next
linear stage. These results can explain why the iter-
ation of the nonlinear DoG can progress towards re-
moving more and more redundancies.
More recently, deep learning algorithms have per-
formed very well in object-recognition tasks (Cires¸an
et al., 2010; Bengio, 2009; Hinton, 2007). The first
layers of these deep multi-layer networks are meant
to provide efficient representations and are trained
by unsupervised learning. When applied to natural
images, these algorithms often provide representa-
tions that exhibit an increasing degree of sparseness
as one proceeds from the first to the subsequent lay-
ers. Based on the above considerations one can thus
interpret the multiple layers of the deep networks as
providing an increasing degree of higher-order decor-
relation, which reduce the statistical dependencies be-
tween the components of a representation vector. In
this context, one can interpret the iterated DoG pro-
posed here as an hard-wired implementation of a deep
multi-layer network where the linear decorrelating
operations are not learned but simply implemented as
a DoG.
Given the above considerations, we evaluate the
performance of our key-point detectors for different
numbers of layers and different numbers of selected
key-points. We use a Bag-of-Words approach on a
pet-recognition benchmark and the popular SIFT al-
gorithm as a base line.
2 SALIENCY OPERATORS
Key-points are usually selected randomly or accord-
ing to some saliency measure. We base our key-point
detection algorithm on the iterated nonlinear inhibi-
tion operator presented in (Barth and Zetzsche, 1998).
There it is shown how iterations of a simple nonlinear
operator can exhibit an increasing end-stopping be-
havior, making it an obvious candidate for key-point
detection. The balance between 1D and 2D features
that may lead to key points depends on the number of
iterations.
2.1 Multi-layer nonlinear inhibition
We define the nonlinear inhibition of a by b (a,b ∈ R)
as
N[N[a] − N[b]] (1)
where N[ ] is a nonlinearity in the form of half-wave
rectification
N[x] = Max(x, 0). (2)
The multi-layer (iterated) nonlinear Difference-
of-Gaussian (INDoG) operator is defined by taking a
and b to be the outputs of Gaussian low-pass filters of
different spatial extent:
f
i+1
= N[N[g
1
⊗ f
i
] − N[g
2
⊗ f
i
]]; i = 0, . . . , M (3)
where i is the layer index, ⊗ denotes convolution,
and g
1
, g
2
are Gaussian convolution kernels with vari-
ances σ
1
< σ
2
, the inhibitory filter being larger. Ini-
tially f
0
is equal to the image intensity.
2.2 ON/OFF Separation
As the INDoG operator exhibits responses only for
certain features (responds strongest at bright corners
and blobs, i.e. like an ON-type operator), one needs to
define a pair of operators in order to obtain ON/OFF
separation, i.e., distinct responses to bright and dark
features.
Accordingly, the CON operator is defined as
f
i+1
= N[N[g
1
⊗ f
i
] − N[g
2
⊗ f
i
]]; i = 0, . . . , M (4)
while the COFF type operator is obtained by
f
1
= N[N[g
2
⊗ f
0
] − N[g
1
⊗ f
0
]]
f
i+1
= N[N[g
1
⊗ f
i
] − N[g
2
⊗ f
i
]]; i = 0, . . . , M
(5)
i.e. by reversing the inhibition at the first iteration.
The responses of these operators on synthetic and
natural images over M = 8 iterations are shown in
Fig. 1. For the two squares, it can be seen how
the edge response gets progressively weaker and dis-
appears at the end, leaving only the corners to have
distinct peaks. In the natural image one can observe
the features becoming more separated over the itera-
tions. Larger features can be detected by running the
iterations in a DoG scale space, i.e., a collection of
different-scale responses are shown in Fig. 3.
Key-pointDetectionwithMulti-layerCenter-surroundInhibition
387

(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
(f)
(g)
(h) (i)
(j)
Figure 1: Synthetic (a) and natural (f) images, and their ON/OFF responses (b)-(e), (g)-(j) after 1, 2, 4 and 8 iterations of the
INDoG algorithm on a single scale of the frame. Top row: squares are 100 × 100 pixels in size, taken from octave 2, scale 3
of the DoG scale space (σ
1
= 12.8, σ
2
= 16.08 pixels). Bottom row: picture size is 180 × 160 pixels, taken from octave 0,
scale 4 of the DoG scale space (σ
1
= 4.02, σ
2
= 5.05 pixels). The ON responses are shaded in white, and the OFF responses
in black.
3 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
Evaluations of features are often done via a descriptor
repeatability or matching score (Mikolajczyk et al.,
2005). However, this is more suitable for key-point
detector evaluations used in image matching applica-
tions. In our case, we want to evaluate how much the
key-points contribute to object recognition and there-
fore use a object-recognition benchmark.
3.1 The Oxford III-T Pet Dataset
The dataset consists of 2371 pictures of cats and 4978
pictures of dogs. The images are further split into spe-
cific breeds, 25 of which are dogs and 12 are cats. The
images have been downloaded from various websites
on the Internet and therefore exhibit a high degree
of variation, the pets being photographed in various
poses, at different illumination levels, and the pictures
themselves being at different resolutions. Adding to
this is a high amount of intra-class variation due to the
different breed types being represented.
The dataset was used in (Parkhi et al., 2012) re-
sulting in recognition rates from 83% to 96% for cat-
versus-dog classification. We do not use these as a
baseline, as their methods are not comparable with
ours (multiple regions are defined which are densely
sampled, yelding a 20,000 dimensional feature vector
in the simplest approach). Also, although annotations
in the form of bounding boxes and pet silhouettes are
available, we do not use the additional data since we
only wish to asses the contribution of the different
types of key-points in general, and for a difficult tasks.
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 2: Sample image from the Oxford III-T Pet Dataset,
along with face (b) and foreground/background/contour (c)
annotations.
3.2 Key-point Detectors
For evaluation, we compare our algorithm to Lowe’s
(Lowe, 1999) SIFT key-point detector as imple-
mented in the VLFeat (Vedaldi and Fulkerson, 2010)
library. The SIFT detector is also based on a DoG
scale-space analysis of the image, along with some
enhancements that suppress low contrast and straight-
edge responses. The SIFT keypoints that were used
in the evaluation were outputted by the unmodified
VLFeat package with the default parameters.
In order to make the comparison as close as possi-
ble, the INDoG detector was implemented as a mod-
ification of the open-source VLFeat package by re-
placing the usual DoG pyramid used in the SIFT de-
tector with our own INDoG CON/COFF frames and
skipping the principal curvature analysis for edge sup-
pression. The INDoG algorithm was run 4 times, for
1, 2, 4 and 8 iterations. As shown in Equations (4)
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
388

(a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
(f)
(g)
(h) (i)
(j)
Figure 3: Different scales of the ON/OFF responses on synthetic (a)-(d) and natural (f)-(i) images, and the key-points found
by the INDoG algorithm (the first 100 as ordered by their magnitude). Both rows: frames are taken from iteration 4 of the
INDoG algorithm, at octaves 0, 1, 2 and 3, scale 4 of the DoG scale space (σ
01
= 4.03, σ
02
= 5.07 pixels, σ
s+1
= 2σ
s
).
and (5), the first iteration is directly equivalent to the
SIFT algorithm, but without the edge suppression en-
hancements. All parameters, e.g., for the Gaussian
kernels, the numbers of scales etc. are the same as
the defaults used by the SIFT detector in all cases.
This way, the main differences between the SIFT key-
points and ours are the iterations (multiple layers) and
the ON/OFF separation, and we can study the effect of
the number of layers on the recognition performance.
As a control, we included randomly generated
key-points at strides of 4, 6, 8 and 10 pixels. The
randomly chosen key-points are used to extract SIFT
features of random scales ranging from 12 to 30 pixels
width per bin with the help of the VL Feat framework.
The orientation of the features is also calculated as in
the VL Feat framework implementation of the SIFT
features.
3.3 The Bag-of-Visual-Words
Framework
We evaluate the performance of our detector using a
Bag-of-Visual-Words (BoVW) framework. First, the
few images that are of excessive size (more than 1000
pixels horizontally or vertically) are discarded. The
positives (cats) and negatives (dogs) are randomized
and split into 80% training and 20% testing groups.
The detector is run on the images and the key-
points that have been found are ordered by their mag-
nitude. The total number of key-points is then limited
at 0.25% of the picture size for all detectors, the rest of
the key-points being discarded. Note that key-points
that return multiple orientation for the same location
are only counted as one towards the total number of
key-points allowed (i.e. only key-points at differing
locations are counted).
SIFT features are extracted at the key-point loca-
tions, using the rotation and scaling provided by the
detector for each key-point. In order to evaluate the
discriminative power of sparse key-points, a number
of subsets are created by discarding a portion of the
features, creating a total of 9 training/test sets con-
taining the top 100%, 50%, 30%, 20%, 10%, 5%, 3%,
2% and 1% key-points (as ordered by their magni-
tude) of the maximum number of allowed key-points
per frame.
The BoVW codebook is created using an online
K-means algorithm on all the extracted features in
each feature subset separately. The number of clusters
in each codebook was empirically set as the square
root of the number of key-points in that particular
subset (i.e. for 1 million key-points, which was ap-
proximately the allowed size of the full positive train-
ing set, we would set k = 1000). This codebook is
used to generate keyword histograms for each image
in the current set. The histograms are then normalized
with the l
1
norm and used in a support vector machine
(SVM) for training and classification. We use a linear
kernel SVM with the softness parameter C set to 128
for all tests. This value has been chosen based on
several test runs, and it did not influence the relative
performance of the different methods tested here.
The above steps are repeated 5 times with a differ-
ent subset of the positive/negative images for a 5-fold
cross validation scheme, the resulting error rates be-
ing averaged at the end. Note that the codebooks are
generated from scratch for every set and subset sepa-
rately, no codebooks being reused at any point during
the performance evaluation.
3.4 Further Enhancements
There are many ways of enhancing the VBoW ap-
Key-pointDetectionwithMulti-layerCenter-surroundInhibition
389
68
70
72
74
76
78
80
Kept descriptors, %
Recognition rate, %
SIFT
INDOG 1 iteration
INDOG 2 iterations
INDOG 4 iterations
INDOG 8 iterations
Random sampling
1
10
100
(a)
68
70
72
74
76
78
80
Kept descriptors, %
Recognition rate, %
SIFT
INDOG 1 iteration
INDOG 2 iterations
INDOG 4 iterations
INDOG 8 iterations
Random sampling
1
10
100
(b)
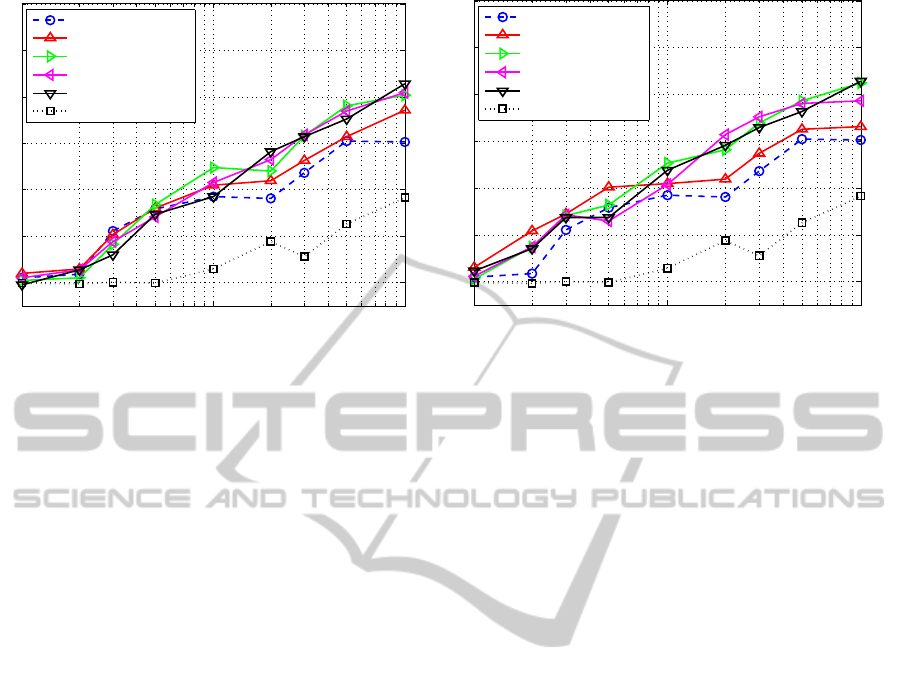
Figure 4: (a) Results for INDoG, SIFT and random key-point sampling at different key-point densities; (b) Results for the
INDoG algorithm with separate CON/COFF codebooks versus SIFT and random sampling (same as in (a)). The number of
key-points on the right (100%) is equal to 0.25% of the total number of pixels in the image.
proach, e.g. by improving the codebook creation step.
Here we propose a very simple extension, which is to
separate the ON- and OFF-type key-points, see Sec-
tion 2.2. This is implemented by separately training
two codebooks for the CON and COFF key-points.
We expect the recognition rate to improve due to the
additional information pertaining to the scene struc-
ture that was extracted at that particular key-point.
A further motivation for ON/OFF separation is that
ON/OFF streams are segregated in biological vision
systems.
As mentioned in section 3.1, the dataset contains
additional annotations such as bounding boxes and
pet silhouettes. An obvious improvement therefore
would be to restrict the codebook generation and
learning process only on the relevant portions of the
images, which has been shown to boost the recogni-
tion rate on this dataset (Parkhi et al., 2012). How-
ever, as we are interested in evaluating the overall per-
formance of the detectors in a general sense (i.e. with-
out a priori information about the object location), we
do not use these annotations.
4 RESULTS
The results are detailed in Table 1, together with
the variance (1σ) obtained by performing a five-way
cross validation (for clarity, error bars were not in-
cluded in Figure 4). Note that the average perfor-
mance of the INDoG algorithm surpasses the SIFT
key point detector as well as the random sampling
when using the maximum allowed number of key
points, and is more apparent at lower key point densi-
ties.
From Figure 4 it can be seen that, in general, the
recognition performance increases with the number
of key-points. When comparing the different curves,
one finds a significant improvement due to the use of
several layers instead of just one layer of lateral in-
hibition, SIFT key points and randomly selected key
points are outperformed by multi-layer key-point de-
tectors. The right plot in Figure 4 demonstrates a
further improvement, which is obtained by separat-
ing the ON/OFF responses as describe in Sections 2.2
and 3.4. This improvement is also greater and more
consistent at lower key point densities, as seen in Ta-
ble 1.
In Figure 5 the spatial distribution of the found key
points is shown, within a typical example of an un-
cluttered picture from the dataset. It is interesting to
note that the key points found by the SIFT detector as
well as the first iterations of the INDoG algorithm are
more spread throughout the picture, even in the uni-
form background area. In an uncluttered frame such
as the one shown, one could expect to see results sim-
ilar to the higher iterations of the INDoG algorithm,
i.e. key points concentrated on the object of interest,
as it exhibits the highest variations.
We can speculate that one of the reasons for the
increased performance would be the distribution of
key points on only the subjects in uncluttered frames,
i.e., the detector avoiding detection of key points in
uniform areas. Another reason might be an optimal
balance, controlled by the number of iterations, in the
allocation of key points to 1D and 2D features. Both
factors would lead to better codewords and an overall
improved performance of the BoVW framework.
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
390

Table 1: Results for SIFT, INDoG 1, 2, 4, and 8 iterations (with and without CON/COFF separation) and random sampling.
The best results in each column are printed in bold type.
Descriptors kept 1% 2% 3% 5% 10% 20% 30% 50% 100%
SIFT 68.2% 68.3% 70.2% 71.1% 71.7% 71.6% 72.7% 74.1% 74.0%
±1σ 0.42 0.33 0.69 0.73 0.90 0.31 0.70 1.71 1.56
INDoG, 1 iteration 68.3% 68.6% 70.0% 71.2% 72.2% 72.3% 73.2% 74.3% 75.4%
±1σ 0.42 0.36 0.72 1.18 0.77 0.82 0.40 1.01 0.59
ON/OFF separation 68.6% 70.1% 70.9% 72.1% 72.2% 72.4% 73.5% 74.5% 74.6%
±1σ 0.32 0.89 0.46 0.87 0.88 1.80 1.17 0.81 1.30
INDoG, 2 iterations 68.1% 68.2% 69.7% 71.4% 72.9% 72.8% 74.3% 75.6% 76.0%
±1σ 0.22 0.10 0.44 0.75 1.17 1.13 0.81 1.16 1.17
ON/OFF separation 68.1% 69.5% 70.8% 71.3% 73.0% 73.6% 74.7% 75.7% 76.5%
±1σ 0.54 0.35 0.30 0.46 1.05 0.67 1.80 0.63 1.02
INDoG, 4 iterations 68.2% 68.5% 69.7% 70.8% 72.3% 73.2% 74.4% 75.4% 76.2%
±1σ 0.22 0.47 0.38 0.62 0.62 0.32 0.75 1.38 0.83
ON/OFF separation 68.2% 69.5% 70.9% 70.6% 72.1% 74.3% 75.0% 75.6% 75.7%
±1σ 0.33 0.58 0.70 0.54 0.47 0.45 0.84 0.41 1.10
INDoG, 8 iterations 67.9% 68.6% 69.2% 70.9% 71.7% 73.6% 74.3% 75.0% 76.6%
±1σ 0.53 0.65 0.55 0.60 1.02 0.72 0.87 1.35 1.01
ON/OFF separation 68.5% 69.4% 70.7% 70.7% 72.7% 73.8% 74.6% 75.3% 76.5%
±1σ 0.42 0.60 0.60 0.38 1.59 1.09 0.64 1.14 1.47
Random sampling 67.9% 67.9% 68.0% 68.0% 68.4% 70.1% 69.6% 70.7% 71.8%
±1σ 0.08 0.06 0.15 0.10 0.71 1.59 0.91 1.45 0.66
5 DISCUSSION
Although the improvements in performance relative
to SIFT key-points are not huge, our results show
that a very simple, biologically plausible, lateral-
inhibition scheme can be used successfully for key-
point detection. The computations have low com-
plexity and can be implemented as a parallel network.
Moreover, they can be implemented as neuromorphic
hardware on retina-like image sensors (Indiveri et al.,
2011), and it seems an interesting results that looping
the image through such a hardware will lead to key
points.
Unfortunately, as with other deep-networks, an
thorough analytical treatment and a deeper under-
standing of the nonlinear iterative computations is
currently missing and we therefore had to rely on
some heuristics, such as the notion of higher-order
decorrelation, to explain our results.
Various extensions and improvements are possi-
ble. As already suggested in (Barth and Zetzsche,
1998), one can replace the DoG with a RoG, i.e., a
ratio of Gaussians. The resulting INRoG is sensitive
to image contrast as opposed to difference in image
intensity. Furthermore, one can optimize the ratio be-
tween the two Gaussians, which has been here taken,
for better comparison, from the SIFT implementation,
although more stable results are obtained with a larger
surrounds (Barth and Zetzsche, 1998). Finally, exten-
sions to spatio-temporal DoGs, i.e., to moving images
are possible.
6 CONCLUSIONS
We have shown that the introduction of multiple lay-
ers provides a saliency measure and derived key-
points that enhance recognition performance relative
to just one layer of lateral inhibition. The enhance-
ment seems to be due to the fact that straight edges
are progressively suppressed as the number of layers
increases.
Key-pointDetectionwithMulti-layerCenter-surroundInhibition
391

Figure 5: Comparison between keypoints generated by SIFT (first row) and the INDoG algorithm (next rows, from top to
bottom: 1, 2, 4 and 8 iterations). From left to right, the first 20%, 50% and 100% of the maximum number of keypoints
allowed per image (defined as 0.25% of the total number of pixels in the image, i.e. the same number of keypoints column-
wise), sorted by magnitude. The background picture has had its brightness and contrast lowered to facilite the viewing of the
keypoints.
Surprisingly, performance is enhanced relative to
the SIFT key-points, which use second order deriva-
tives and the determinant of the Hessian to suppress
straight edges in the saliency measure.
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
392

By using the arguments outlined in the Introduc-
tion, the role of the multiple layers can be under-
stood as a form of higher-order decorrelation of the
input, which leads to more efficient representations
with increased sparseness and more representative
key-points.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is supported by the Graduate School for
Computing in Medicine and Life Sciences funded by
Germany’s Excellence Initiative [DFG GSC 235/1].
We thank the reviewers for their constructive com-
ments.
REFERENCES
Barth, E. and Zetzsche, C. (1998). Endstopped operators
based on iterated nonlinear center-surround inhibition.
In Human Vision and Electronic Imaging III, volume
3299 of Proc. SPIE, pages 67–78, Bellingham, WA.
Bengio, Y. (2009). Learning deep architectures for ai. Foun-
dations and trends
R
in Machine Learning, 2(1):1–
127.
Cires¸an, D. C., Meier, U., Gambardella, L. M., and Schmid-
huber, J. (2010). Deep, big, simple neural nets for
handwritten digit recognition. Neural computation,
22(12):3207–3220.
Csurka, G., Dance, C., Fan, L., Willamowski, J., and Bray,
C. (2004). Visual categorization with bags of key-
points. In Workshop on statistical learning in com-
puter vision, ECCV, volume 1, page 22.
Hinton, G. E. (2007). Learning multiple layers of represen-
tation. Trends in cognitive sciences, 11(10):428–434.
Indiveri, G., Linares-Barranco, B., Hamilton, T., van
Schaik, A., Etienne-Cummings, R., Delbruck, T., Liu,
S.-C., Dudek, P., H
¨
afliger, P., Renaud, S., Schem-
mel, J., Cauwenberghs, G., Arthur, J., Hynna, K.,
Folowosele, F., Saighi, S., Serrano-Gotarredona, T.,
Wijekoon, J., Wang, Y., and Boahen, K. (2011). Neu-
romorphic silicon neuron circuits. Frontiers in Neuro-
science, 5:1–23.
Lowe, D. G. (1999). Object recognition from local scale-
invariant features. In Computer vision, 1999. The pro-
ceedings of the seventh IEEE international conference
on, volume 2, pages 1150–1157. Ieee.
Mikolajczyk, K., Tuytelaars, T., Schmid, C., Zisserman, A.,
Matas, J., Schaffalitzky, F., Kadir, T., and Van Gool,
L. (2005). A comparison of affine region detectors.
International journal of computer vision, 65(1-2):43–
72.
Mota, C. and Barth, E. (2000). On the uniqueness of curva-
ture features. In Dynamische Perzeption, volume 9 of
Proceedings in Artificial Intelligence, pages 175–178,
K
¨
oln. Infix Verlag.
Nowak, E., Jurie, F., and Triggs, B. (2006). Sampling strate-
gies for bag-of-features image classification. In Com-
puter Vision–ECCV 2006, pages 490–503. Springer.
Parkhi, O. M., Vedaldi, A., Zisserman, A., and Jawahar, C.
(2012). Cats and dogs. In Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition (CVPR), 2012 IEEE Conference on,
pages 3498–3505. IEEE.
Vedaldi, A. and Fulkerson, B. (2010). Vlfeat: An open
and portable library of computer vision algorithms. In
Proceedings of the international conference on Multi-
media, pages 1469–1472. ACM.
Vig, E., Dorr, M., and Cox, D. (2012a). Saliency-based
selection of sparse descriptors for action recognition.
In Image Processing (ICIP), 2012 19th IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on, pages 1405 – 1408.
Vig, E., Dorr, M., Martinetz, T., and Barth, E. (2012b). In-
trinsic dimensionality predicts the saliency of natural
dynamic scenes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Anal-
ysis and Machine Intelligence, 34(6):1080–1091.
Zetzsche, C. and Barth, E. (1990). Fundamental lim-
its of linear filters in the visual processing of two-
dimensional signals. Vision Research, 30:1111–1117.
Zetzsche, C. and Nuding, U. (2007). Nonlinear encoding in
multilayer LNL systems optimized for the represen-
tation of natural images. In Human Vision and Elec-
tronic Imaging XII, volume 6492 of Proc. SPIE, pages
649204–649204–22.
Key-pointDetectionwithMulti-layerCenter-surroundInhibition
393
