
Optimization of Endoscopic Video Stabilization by Local Motion
Exclusion
Thomas Gross, Navya Amin, Marvin C. Offiah, Susanne Rosenthal, Nail El-Sourani
and Markus Borschbach
Competence Center Optimized Systems, University of Applied Sciences (FHDW),
Hauptstr. 2, 51465 Bergisch Gladbach, Germany
Keywords:
Endoscopy, Foreground Moving Objects, Global Motion, Local Motion, Outlier Rejection, Image Composi-
tion, Video Stabilization.
Abstract:
Hitherto video stabilization algorithms for different types of videos have been proposed. Our work majorly
focuses on developing stabilization algorithms for endoscopic videos which include distortions peculiar to
endoscopy. In this paper, we deal with the optimization of the motion detection procedure which is the most
important step in the development of a video stabilization algorithm. It presents a robust motion estimation
procedure to enhance the quality of the outcome. The outcome of the later steps in the stabilization, namely
motion compensation and image composition depend on the level of precision of the motion estimation step.
The results of a previous version of the stabilization algorithm are here compared to a new optimized version.
Furthermore, the improvements of the outcomes using the video quality estimation methods are also discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
As discussed in (Offiah et al., 2012) endoscopic
videos include a variety of distortions making it diffi-
cult for the surgeon to have a better view of the region
of interest. These may be the movement of the or-
gans,foreground moving objects such as scalpels, or
body fluids secreted during the operation. Of all the
distortions, the foreground moving objects contribute
majorly to affect the quality of stabilization. This is
because, the endoscopic videos have the camera lens
held very close to the region of interest. Thus the fore-
ground objects consume major part of the captured
video frame. In contrast to the global motion, wherein
each image pixel (px) from frame to frame experience
the same speed and direction, the direction and speed
of the local motion in a local area is different from the
co-existing motion in the frame. The estimated mo-
tion from our previous motion estimation procedure
is majorly influenced by these foreground moving ob-
jects. This makes it essential to separate these local
motions from the global motion to determine a global
camera path for further stabilizing the video. In the
following, approaches for local motion detection are
presented. Depending on the application field, this
research area is sometimes referred to as foreground
object detection (Liyuan Li et al., 2003) or local mo-
tion segmentation (Flores-Mangas and Jepson, 2013),
(Bradski1 and Davis2, 2002).
2 PREVIOUS WORK
The local motion detection plays an important role
in a variety of fields, namely object tracking, video
surveillance or in the field of video coding (MPEG)
(Berna and Faouzi, 2000), (Georgia et al., 2009).
Previous approaches for segmentation of local image
changes included the subtraction of consecutivevideo
frames where stationary background objects remain
in the same position and moving objects change their
position from frame to frame. The image frames are
then subtracted and only areas with a local change ap-
pear in the resultant image. However, this method has
the disadvantage that the camera must be located at a
fixed position, so that the background is always in the
same position. For this reason, this method proved to
be unsuitable for our purpose.
Another method for motion detection is to use the
optical flow (OF) field, which determines motion vec-
tors for all image px based on the image intensities
(Shafie et al., 2009). Motion vectors with different
directions and lengths represent the local changes in
64
Gross T., Amin N., C. Offiah M., Rosenthal S., El-Sourani N. and Borschbach M..
Optimization of Endoscopic Video Stabilization by Local Motion Exclusion.
DOI: 10.5220/0004745900640072
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2014), pages 64-72
ISBN: 978-989-758-009-3
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

the video frame. The exact calculation of the opti-
cal flow is limited by the following restrictions: First,
the image intensities may differ slightly between suc-
cessive frames which is not often the case in endo-
scopic videos. Second, because of the small light
source of the endoscope, the lighting conditions of-
ten vary within a video sequence. A further disadvan-
tage of the OF is that large movements in the image
cannot be well determined. But motion changes in
endoscopic recordings can be quite large. Also, the
frames must be noise-free, which is not the case in
endoscopic videos.
Another technique for motion detection is the
feature-based method, which detects feature points in
a frame and tracks the feature points in the next frame
(Han et al., 2006). This method is well suited for this
approach of this work because it is based on feature
points. The local motion detection can be directly
integrated into our video stabilization algorithm En-
dostabf2f.
3 MOTION ESTIMATION
The process of video stabilization includes three ma-
jor steps: motion estimation, motion compensation
and image composition. The quality of the resultant
video completely depends on the precision of these
three steps. However, motion estimation influences
the quality majorly. The process of estimating mo-
tion vectors from the extracted features is influenced
by certain distractions which need to be dealt with to
obtain the optimal motion vectors. To do so, the fol-
lowing approaches are used to first exclude the out-
liers and further the local motion vectors to attain the
global camera path:
3.1 Outlier Removal
Feature detection using Shi-Tomasi corner detection
algorithm (Shi and Tomasi, 1994) and looking for
matching features in the next frame using KLT tracker
(Kanade-Lucas-Tomasi feature tracker) (Tomasi and
Kanade, 1991) generate point matches tracking the
best match for spatial intensity information. However,
changes in the corresponding frame such as lumi-
nance variations, out of plane rotations lead to some
false matches called ’outliers’ which corrupt the re-
sults of stabilization. This complicates the estimation
of geometric transformation leading to jittery videos
with added shakes. Some of these irregularities can be
solved by performing an outlier rejection method us-
ing RANSAC (Zhao et al., 2009) on the correspond-
ing point matches. Figure 1 shows the results of the
RANSAC outlier analysis and removal. The image
on the left shows two frames, current and next over-
layed on each other. The red circles and green crosses
represent the features and the connecting yellow lines
show matching features between the two images. The
left image shows some false matches between distant
points in the respective frames. The image on the
right of Figure 1 shows perfect matches left after the
application of the outlier removal procedure.
3.2 Local Motion Detection
Our motion estimation approach algorithm includes
local motion detection and foreground moving object
detection. In the first step, the image is divided into
mxn large sectors called grid cells. The feature points
(FPs) determined in the subsequent steps are assigned
to a cell and the local movement of a cell is measured.
Different cell sizes can be selected and typically a
size of 10x10 px is used. Since the video record-
ings have different resolutions such as 384x288 px
to 1280x1024 px for HD videos, the cell size can be
chosen dynamically, depending on the image resolu-
tion. Once the FPs were determined using the KLT
method in frame A and tracked in frame B, the un-
traceable FPs are deleted from the feature point ma-
trix. As a result, only valid FPs, which correspond in
the two frames, are kept (Frame A: reference points,
Frame B: tracked points). Next, all the FPs are as-
signed to their respective grid cell. An index matrix is
created to indicate the cell belonging to its respective
FP. Then, the local motion for individual cell is de-
termined by calculating an average of motion values
from all FPs within the respective cell. More specif-
ically, the change of the x and y position from frame
A to frame B for each FP within a cell c
i
is measured.
The change of the position of each image px rep-
resents the movement in a frame. The median of all
measured x- and y changes is calculated for each cell
and stored in a local cell movement matrix. Cells with
too large local translation in the + / - or x + / - y di-
rections, are marked as outliers by using the Median
Absolute Deviation from the median (MAD). MAD
is a robust estimate of the spread, and calculates the
maximum permissible deviation of the position (+ / -
x and y) of a cell compared to the overall movement
of all the cells in the x or y direction. The MAD is
defined as follows (Walker, 1999):
MAD = median
i
|c
i
− median
j
(c
j
)| (1)
where, c
i
is motion of an individual cell and c
j
is the
set of motion values of all cells.
The cells labelled as outlier cells are excluded
from the calculation of the global camera path. In Fig-
ure 2 the left image with the red vector arrows show
OptimizationofEndoscopicVideoStabilizationbyLocalMotionExclusion
65
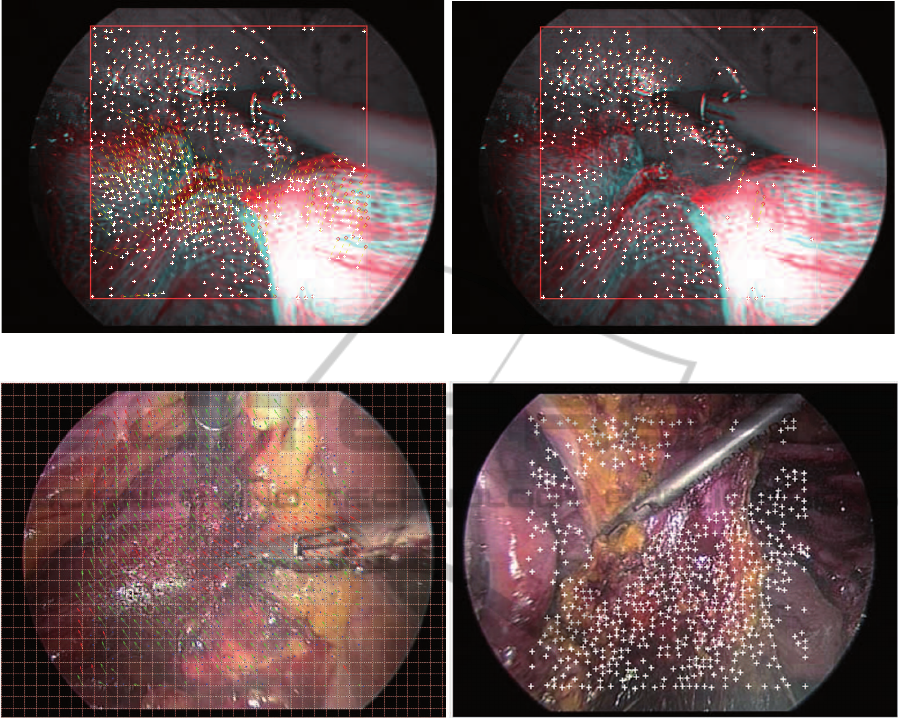
Figure 1: Outlier Rejection. Left: Original image consisting of outliers Right: Resultant one after filtering.
Figure 2: Local motion estimation. Left: Grid Map with global and local motion vectors from the tracked FPs. The red arrows
on the moving scalpel are the excluded local motions. Right: FPs after local motion exclusion.
the local movements of the scalpel. In contrast, the
green vector arrows represent the movements of the
camera. The local motions are excluded for global
motion estimation as shown in the right image of Fig-
ure 2. where the tracked feature points of a video are
represented by white crosses. In the region of the
moving scalpel illustrated by red arrows, only local
movements are detected by the algorithm and the FPs
in this region are excluded from the complete set of
tracked FPs. From the x/y translation values from all
inlier cells, the median is calculated, which represents
the global camera motion of the endoscope as shown
in Figure 3 for the y direction. The Y-axis of the graph
describes the motion of the px in the y direction, the
X-axis indicates the frame number in the video.
Unlike our previous method of motion compensation
where we smoothened the raw global camera path and
further used this smoothened path for image composi-
tion, our current method uses an optimized approach.
Here the difference between the original camera mo-
tion and the smoothened camera path is used for im-
age composition. In most cases, the intense move-
ments are in the range of +/- 15 px called the high-
frequencyjitter. The peaks in the motion curve caused
by sudden movement of the endoscope (Figure 4) re-
sult in a jerky stabilized video which can be a dis-
advantage for the subsequent creation of the crop-
ping mask (see next section Image Composition 4).
In order to mitigate the impact of these peak values,
the values which are above a selected threshold are
smoothened. As a threshold +/- 12 px is chosen. To
sort out the peak values, the difference curve between
the original and smoothened camera motion is calcu-
lated as shown in red in figure 4. Thereafter, the dif-
ference curve is smoothened where the peak values
are reduced as shown in figure 6. Subsequently, all
the values in the difference curve (red) which exceed
the threshold value are replaced by the values of the
smoothened difference curve (green curve). The blue
curve in Figure 6 shows the new difference motion
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
66
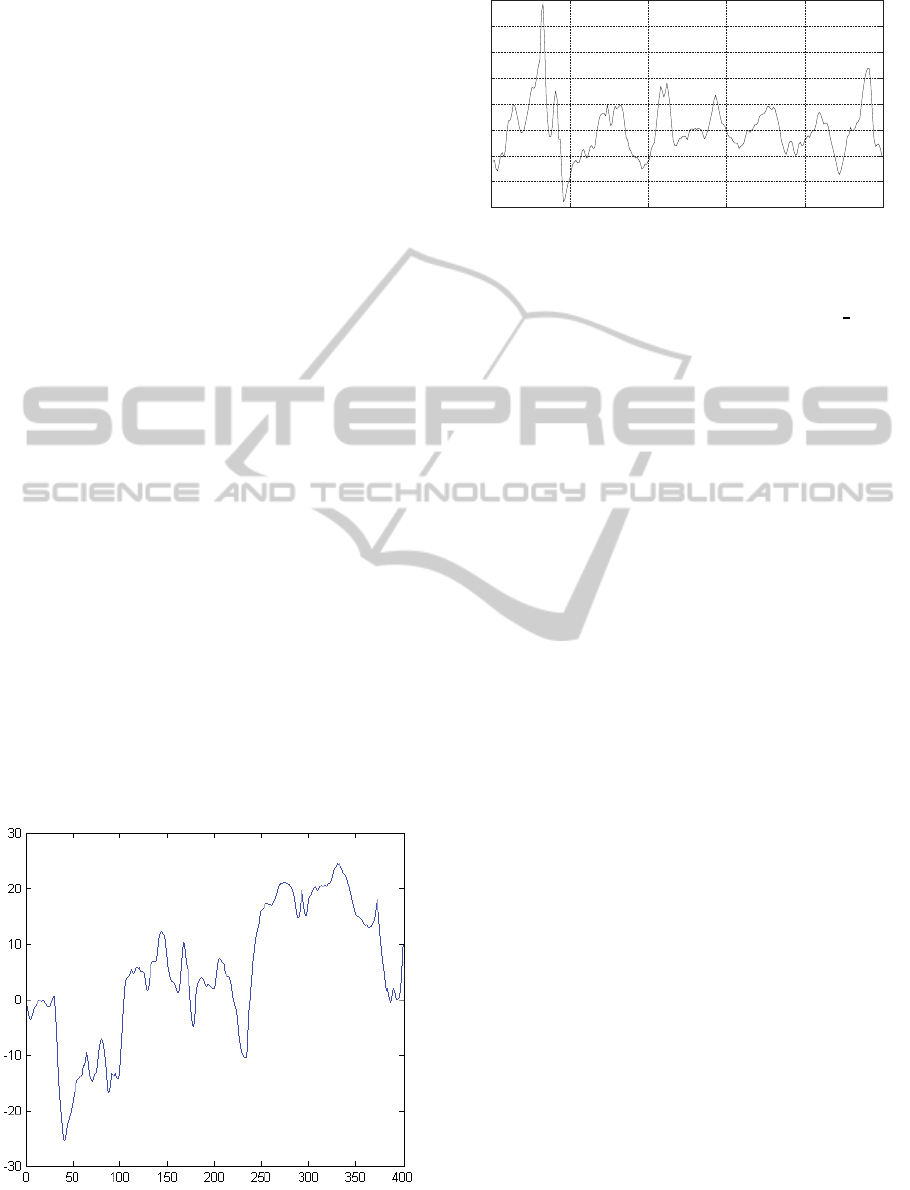
which is used for the transformation in the subsequent
image composition procedure.
4 IMAGE COMPOSITION
As mentioned in the previous section the smoothened
difference curve is used for transformation of the
video frames. Affine transformation, inspite of hav-
ing two added degrees of freedom when compared to
Similarity Transformation does not produce expected
results as mentioned in (Grundmann et al., 2011),
(Zhou et al., 2013). We used the similarity transfor-
mation for transformingthe video frames according to
the smoothened difference curve. Further the frames
are cropped such that the stabilized video is devoid of
black borders which are a result of the motion com-
pensation. In the previous step, the motion values in
the video are reduced to a maximum allowed value.
This makes it possible to calculate a cropping mask,
which discards the black area around the stabilized
video. The maximum movement in the video is the
maximum value used for the cropping area. How-
ever, it would be better to divide the video into scenes
and not crop the entire video with the maximum value
because individual scenes often have different move-
ments.
5 EXPERIMENT
The complete workflow of the stabilization process
in described in detail in (Amin et al., 2014). The
motion estimation part of the previous algorithm de-
scribed in this paper is optimized by excluding the
Figure 3: Camera motion (Pixel) in y-direction over 400
frames.
0 50 100 150 200 250
−15
−10
−5
0
5
10
15
20
25
Pixelmotion in y
Frames
Figure 4: Difference of motion between Original Global
Camera Motion and Smoothened Global Camera Motion.
local motion vectors in the current Endostabf2f
LME
algorithm. The stabilization algorithm EndoStabf2f
with Local Motion Exclusion (LME) and without
LME is applied to two datasets: Dataset 1 includ-
ing 15 non-distortion-specific videos (provided by the
Forschungszentrum Borstel (Frey, 2012) and Leipzig
(HTWK Leipzig, 2013)) and dataset 2 including 52
gastroscopic distortion-specific test video sequences
from human surgery that were provided by the Charit´e
Berlin (Charit´e Berlin, 2013).
The test video sequences of dataset 2 were taken
from a large database of over 1400 videos. These
videos are of varying file sizes, durations and frame
numbers and have a resolution of 364x288 px (in-
cluding, in part of the cases, black regions around
the medical ROI), while the medical ROI generally
covers at least three quarters of each video frame.
They are available as MPEG files and are converted
to MP4 (25 frames and 2208 kb per second). A list of
11 different distortion types (see appendix) is defined
that follows from the previously described and refer-
enced types of distortions in endoscopic videos. The
1400 videos are also manually screened to identify
further distortion types that flow into this list. A sec-
ond manual screening process by members of the sci-
entific team goes through each distortion type of this
list and identifies appropriate videos that contain that
distortion type. This categorization of video scenes
by distortion type enables a distinguished (distortion-
specific) evaluation of the stabilization algorithm.
It is of course the case that multiple distortion
types occur in some video scenes (or in parts of them)
although only associated with a particular distortion
type in its test case (e.g. a video with foreground ob-
jects that also contains smoke and body fluids). (It
is of course also not excluded that the same video
source is used for several test cases, be it with differ-
ent scenes.) This can generally not be prevented but
compensated for by increasing the sample size (i.e.
the number of test cases and scene lengths) per dis-
tortion type. At the same time, the high computation
OptimizationofEndoscopicVideoStabilizationbyLocalMotionExclusion
67

−15
−10
−5
0
5
10
15
20
25
Pixelmotion in y
0
50 100 150 200 250
Frames
Figure 5: Difference of motion between Original Global Camera Motion and Smoothened Global Camera Motion (solid line),
Smoothened difference curve (dashed) and replaced peak values used for the Image Composition (dotted).
time of the stabilization algorithm (which at this level
is not optimized for runtime performance) sets some
limits on the number of frames that can be stabilized
in a justifiable time. For this reason, the screening
of the over 1400 videos only selects 5 test cases per
distortion type. As an exception, only two scenes are
used for the Low Light distortion type. See the ap-
pendix for a full list of all distortion types, the num-
ber of videos used in each, and their respective cu-
mulative number of frames used for the stabilization
and quality calculation. This adds up to 52 test cases
comprising approximately 69,000 frames.
For dataset 1, both the LME and non-LME algorithms
are applied. The robustness of the Endostabf2f
LME
is further tested on distorion-specific videos of dataset
2 (i.e., only the non-LME version is used there). The
stabilization of all videos is carried out in Matlab.
Each test case first calculates the binary ROI mask de-
scribed earlier. Only content within this video mask
is considered during feature detection, and after the
final warping of each frame, the mask is applied to
the frame before writing it into the stabilized output
video. This makes the output video also visually sta-
ble, as it prevents a visually unstable ROI (except for
the resulting black areas within the mask).
6 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
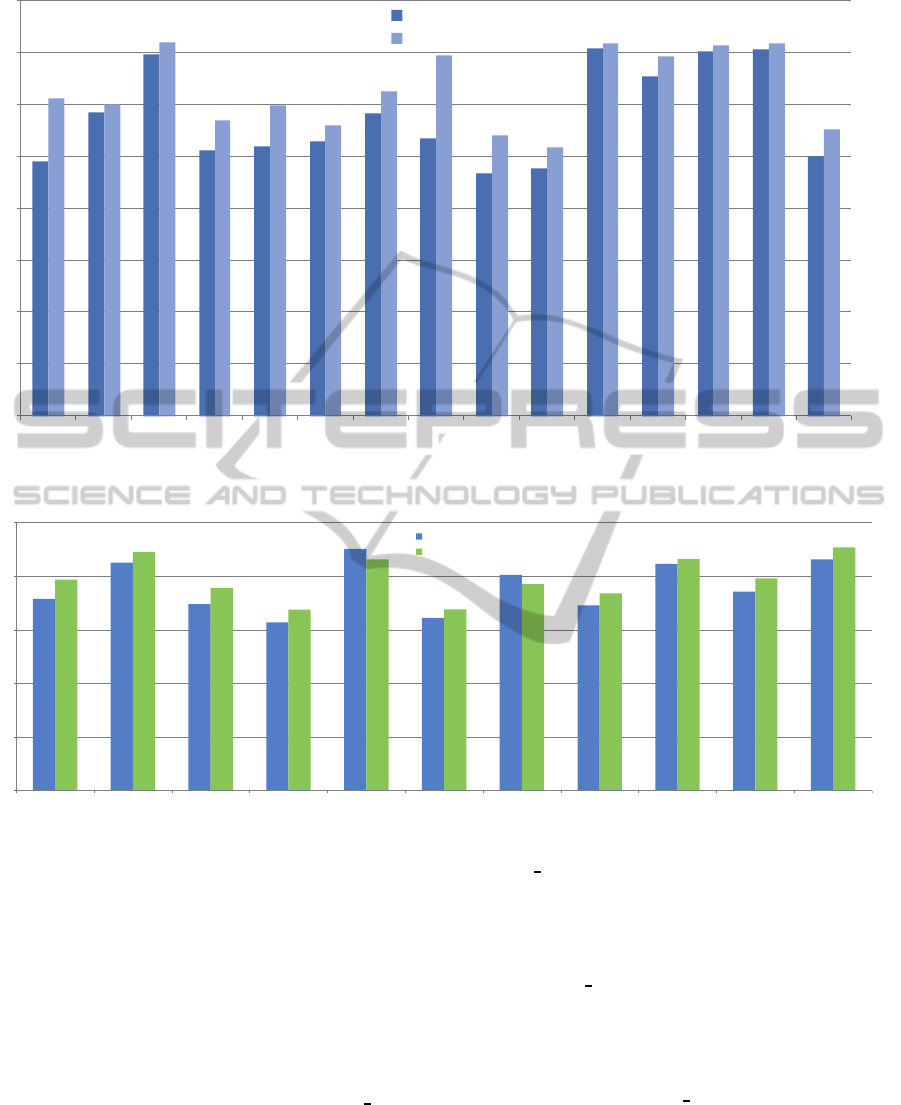
The benchmarking of the algorithm is done by using
the Inter-Frame Transformation Fidelity (ITF) (Mori-
motoa and Chellappa, 1998) where an average PSNR
is calculated between consecutive frames across the
whole video. For dataset 1, the results of EndoStabf2f
with LME is compared to the results of EndoStabf2f
without LME and evaluated per video. The videos
of data set 1 that are stablized using the Endostabf2f
with LME, shows better quality (i.e. higher PSNR
values) compared to the stabilized videos using the
Endostabf2f with the LME. As shown in Figure 6,
the endoscopic videos with heavy foreground move-
ments show a very high difference in quality for the
Endostabf2f
LME compared to the other with higher
PSNR values. This shows that excluding the local
motion from the estimation of the global camera mo-
tion does have a positive impact on the overall quality
of the stabilized videos.
For dataset 2, the PSNR metric both for the origi-
nal (unstabilized) video scene and for the stabilized
one are calculated to identify their improvements
across different distortion types as follows: The met-
ric is first calculated for every original and stabi-
lized video scene of a test case: PSNR for neigh-
bouring frames of the test scene (i.e. between neigh-
bouring frames in the intervals between start and end
frame according to the test database) is determined.
PSNR is calculated as shown in the ITF calculation in
(C.Offiah et al., 2012). An average PSNR value for
all frames of the original and stabilized video, respec-
tively, is then calculated. Next, the distortion-specific
PSNR value is obtained by using a weighted average
from all test cases pertaining to the specific distor-
tion, where the scene lengths of the associated videos
in numbers of frames are used as weights. The results
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
68
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o
f2f_PSNR
f2f_LME_PSNR
Figure 6: Estimated video quality using PSNR.
0
5
10
15
20
25
Foreground object Body Fluids Smoke Camera Shaking Shaking ROI Luminance Changes Body Movements Spotlights Low Contrasts Special Distortion Low Light
PSNR Original
PSNR Stabilized
Figure 7: Comparision of the calculated PSNR values in dB for the original and the stabilized videos.
as shown in Figure 7 show that some dB of improve-
ments of the original video are made by using the
non-LME algorithm. This holds for most distortion
types, with only a shaking ROI and body movements
as an exception. This further underscores the conclu-
sions drawn from dataset 1, that non-LME achieves
an overall improvement of the video quality.
The exclusion of local motion vectors makes the
algorithm robust against presence or absence of im-
mense foreground moving objects. As shown in
Figure 8, a comparison between Endostabf2f
LME
(LMV in the figure) and state-of-the-art stabilization
algorithms is made along frames from a scene where
some internal body movements and no foreground
moving objects are present as well as the endoscope
moves slightly for examination. In such a case, the
Adobe AE shows tremendous frame jump unlike En-
dostabf2f
LME and YouTube. Youtube also does
some scaling and cropping and thus loses some re-
gion as seen along the bottom right-hand corner of
the frames which might have some useful information
for the surgeon. But these problems are dealt well by
the Endostabf2f
LME. Further, in Figure 9, the scene
contains introduction and rigorous movement of a for-
cep. In such a case, again a frame jump is seen in
the stabilized frame number 675 for the Adobe AE
which could be because of the loss of trajectory on
scene change. Endostabfef
LME handles problems
specific to endoscopic vidoes well. However, there
is still scope for improvement in motion estimation
and handling foreground moving objects when these
objects consume major part of the frame making it
difficult for the stabilization algorithm to distinguish
foreground and background.
OptimizationofEndoscopicVideoStabilizationbyLocalMotionExclusion
69

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work as a part of the PENDOVISION-project is
funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education
and Research (BMBF) under the registration identi-
fication 17PNT019. The financial project organiza-
tion is directed by the Research Center J¨ulich. The
work was conducted under supervision of Markus
Borschbach.
REFERENCES
Amin, N., Gross, T., Offiah, M. C., Rosenthal, S., El-
Sourani, N., and Borschbach, M. (2014). Stabilization
of endoscopic videos using camera path from global
motion vectors. In To appear in the 9th International
Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and
Computer Graphics Theory and Applications.
Berna, E. and Faouzi, K. (2000). Partitioning of video ob-
jects into temporal segments using local motion infor-
mation. In ICIP, pages 945–948.
Bradski1, G. R. and Davis2, J. W. (2002). Motion segmen-
tation and pose recognition with motion history gradi-
ents. In Machine Vision and Applications.
Charit´e Berlin (2013). Universit¨atsmedizin Berlin.
http://www.charite.de.
C.Offiah, M., Amin, N., Gross, T., El-Sourani, N., and
Borschbach, M. (2012). Towards a benchmarking
framework for quality-optimized endoscopic video
stabilization. In ELMAR, Sep.,2012 Proceedings,
pages 23–26.
Flores-Mangas, F. and Jepson, A. D. (2013). Fast rigid
motion segmentation via incrementally-complex local
models. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition.
Frey, A. (2012). Research center borstel - leibniz center
for medicine and biosciences, germany. http://www.fz-
borstel.de/cms/index.php.
Georgia, A. M., Alexander, G., Andreas, K., Thomas, S.,
Marta, M., and M., K. A. (2009). Global motion es-
timation using variable block sizes and its application
to object segmentation. In WIAMIS, pages 173–176.
Grundmann, M., Kwatra, V., and Essa, I. (2011). Auto-
directed video stabilization with robust l1 optimal
camera paths. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vi-
sion and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
Han, M., Xu, W., and Gong, Y. (2006). Video foreground
segmentation based on sequential feature clustering.
In 18th International Conference on Pattern Recogni-
tion, ICPR 2006., volume 1, pages 492–496.
HTWK Leipzig (2013). Forschungszentrum.
http://www.htwk-leipzig.de.
Liyuan Li, W. H., Gu, I. Y., and Tian, Q. (2003). Fore-
ground object detection from videos containing com-
plex background. In In Proc. of the eleventh ACM
international conference.
Morimotoa, C. and Chellappa, R. (1998). Evaluation of
image stabilization algorithms. In Proc. IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal
Processing, 5:2789–2792.
Offiah, M. C., Amin, N., Gross, T., El-Sourani, N., and
Borschbach, M. (2012). On the ability of state-of-
the-art tools to stabilize medical endoscopic video se-
quences. In MedImage 2012, Mumbai.
Shafie, A. A., Hafiz, F., and Ali, M. H. (2009). Motion
detection techniques using optical flow. In World
Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology.
Shi, J. and Tomasi, C. (1994). Good features to track.
In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, pages 593–600.
Tomasi, C. and Kanade, T. (1991). Detection and track-
ing of point features. In Carnegie Mellon University
Technical Report CMU-CS-91-132.
Walker, J. T. (1999). Statistics in Criminal Justice: Analysis
and Interpretation. Aspen Puplishers Inc.
Zhao, F., Wang, H., Chai, X., and Ge, S. (2009). A fast and
effective outlier detection method for matching uncal-
ibrated images. In ICIP, pages 2097–2100.
Zhou, Z., Jin, H., and Ma, Y. (2013). Content-preserving
warps for 3d video stabilization. In IEEE Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
70
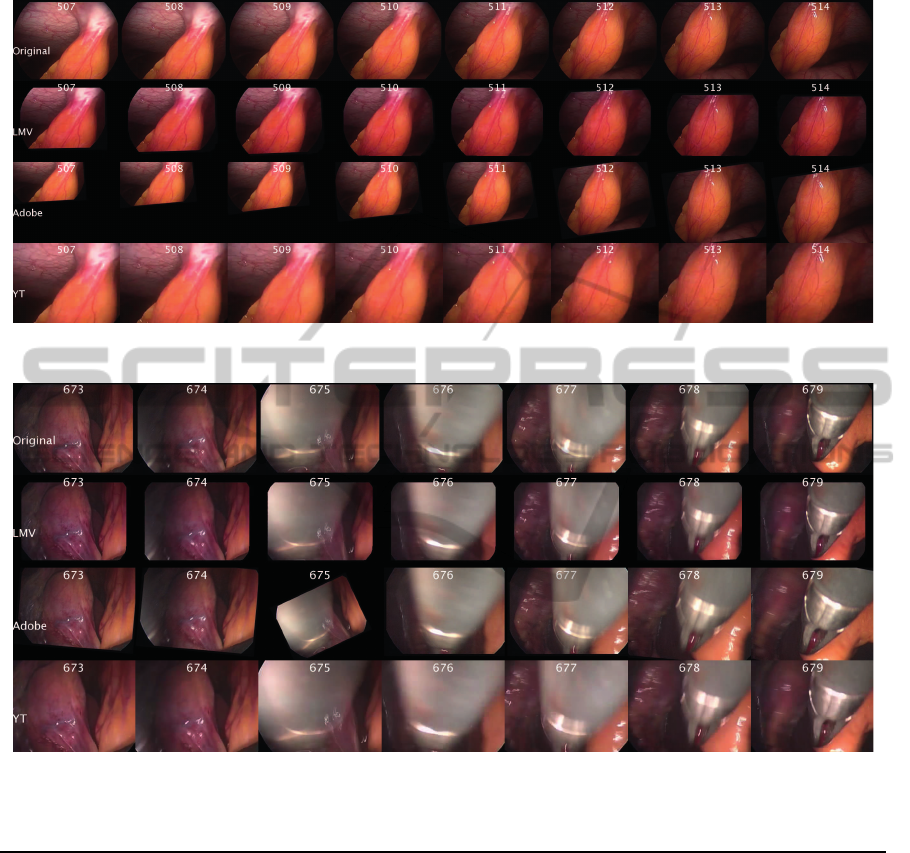
APPENDIX
Figure 8: Comparision of the state-of-the-art algorithms for a stabilized scene having no fore-ground moving object.
Figure 9: Comparision of the state-of-the-art algorithms for a stabilized scene having fore-ground moving object.
Table 1: List of the videos used for stabilization.
Video Description
a Bronchoscopic staboptic video of a rat with circular content
b Bronchoscopic staboptic video of a rat with rectangular content and moving camera
c Bronchoscopic staboptic video of a rat with rectangular content and steady camera
d Shaky video of a hippo
e Human Rhinoscopic 1 with rectangular content and steady camera
f Human Rhinoscopic 2 with rectangular content and steady camera
g Human Rhinoscopic 3 with rectangular content and steady camera
h Human surgery video with scalpel moving in the foreground
i Lab video 1 with forward and backward movement
j Lab video 2 with forward and backward movement
k Bronchoscopic grid removed fibreoptic video of a rat with steady camera
l Bronchoscopic grid removed fibreoptic video of a rat with moving camera and distortion (Bubbles)
m Bronchoscopic grid removed fibreoptic video of a rat with forward-backward movement of camera
n Bronchoscopic grid removed fibreoptic video of a rat with rectangular content and steady camera
o Shaky video of a tiger with jittery motion
OptimizationofEndoscopicVideoStabilizationbyLocalMotionExclusion
71

Table 2: Dataset 1- List of the videos used for Distortion-Specific stabilization.
Videos Distortions Frames
19 Foreground Objects 10981
12 Body Fluids 3283
23 Smoke 7754
23 Camera Shaking 6311
22 Shaking ROI 8333
23 Luminance Changes 7382
15 Body Movements 2815
15 Spotlights 5545
25 Low Contrast 6849
5 Dirty Lens 6150
2 Low Light 3601
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
72
