
A Framework for 3D Object Identification and Tracking
Georgios Chliveros
2
, Rui P. Figueiredo
1
, Plinio Moreno
1
,
Maria Pateraki
2
, Alexandre Bernardino
1
, Jose Santos-Victor
1
and Panos Trahanias
2
1
Instituto de Sistemas e Robotica, Instituto Superior Tecnico, Lisboa, Portugal
2
Institute of Computer Science, Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas, Heraklion, Greece
Keywords:
Object Tracking, Object Detection, Relative Pose Estimation, Robot Vision.
Abstract:
In this paper we present a framework for the estimation of the pose of an object in 3D space: from the
detection and subsequent recognition from a 3D point-cloud, to tracking in the 2D camera plane. The detection
process proposes a way to remove redundant features, which leads to significant computational savings without
affecting identification performance. The tracking process introduces a method that is less sensitive to outliers
and is able to perform in soft real-time. We present preliminary results that illustrate the effectiveness of the
approach both in terms of accuracy and computational speed.
1 INTRODUCTION
The identification and subsequent relative pose track-
ing of objects in 3D space (6 degrees of freedom) is
an important problem in service robotics. Recently,
several software solutions have become available; e.g.
the case of ViSP
1
and BLORT
2
.
In ViSP, recognition is not taken into account.
This is the case with earlier works (Harris, 1992;
Koller et al., 1993), the refinement of the estimated
object pose does not consider evaluation and/or pre-
diction of hypothesised object poses. In BLORT,
recognition and multiple pose hypotheses is consid-
ered via probabilistic frameworks; for example, in
(Azad et al., 2011; Choi and Christensen, 2012).
However, it assumes good pose priors which may lead
to losing track of the object.
In recent past, Drost et al. (Drost et al., 2010)
proposed an efficient approach for detecting and sub-
sequent tracking. Given an object model, a descrip-
tion is extracted using point pair features, thus en-
coding the geometric relation between oriented point
pairs. The method is robust to sensor noise and out-
performs other feature-based state-of-the-art methods
like Spin Images (Johnson and Hebert, 1999) and
Tensors (Mian et al., 2006), in terms of robustness to
occlusion and clutter.
Tracking on a 2D camera plane can be performed
faster than those required in 3D space. Recently avail-
able low-cost range sensors (e.g. Kinect) can be used
1
http://www.irisa.fr/lagadic/visp/visp.html
2
http://users.acin.tuwien.ac.at/mzillich/?site=4
in such a way. However, for not affecting accuracy,
the pose hypotheses space is an important issue to
explore. This comes alongside the use of generated
model feature points which can reduce perspective-
n-point ambiguities in data association (Puppili and
Calway, 2006). Thus, issues that need addressing for
efficient tracking are:
• reliably detect the object in question and identify
their model equivalent;
• by tracking the object, estimate and refine its pose;
• suitable for online applications.
In this paper we introduce an approach under
which an object is recognized and its (initial) pose is
estimated through an acquired 3D point cloud (Sec-
tion 3). Identification and initial pose estimation is
achieved via a fast extension (Figueiredo et al., 2013)
of Drost et al. (Drost et al., 2010) algorithm (Section
3). These serve as inputs to the tracking of the 6DoF
pose on the 2D camera plane using multiple hypothe-
ses (Chliveros et al., 2013) (Section 4). Preliminary
results for the described methods, are presented in
Section 5. Finally, some concluding remarks and fu-
ture work is provided in Section 6.
2 HYPOTHESES SPACE
As previously mentioned, the hypotheses space from
known 3D models is an important aspect for accuracy
and error compensation. We generate a representative
search space over rotations (α
x
+ δα
x
,α
y
+ δα
y
,α
z
+
672
Chliveros G., P. Figueiredo R., Moreno P., Pateraki M., Bernardino A., Santos-Victor J. and Trahanias P..
A Framework for 3D Object Identification and Tracking.
DOI: 10.5220/0004751506720677
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP-2014), pages 672-677
ISBN: 978-989-758-009-3
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

δα
z
). The term δα can be assigned as dictated by a
number of increment steps (N) over the full rotation
range (0,π) of the corresponding axis.
In the detection process case (see Section 3), all
retrieved pose hypotheses whose position and orien-
tation do not differ more than a predefined threshold
are clustered together (Section 3.3).
Note that in order to deal with symmetry, before
clustering, we collapse all redundant hypotheses to a
single pose. This additional step removes the rota-
tional component around the object axis of symme-
try, ensuring that all redundant poses are gathered in
the same cluster. Thus, the process allocates less re-
sources, reduces the number of computations and be-
comes more stable.
In the tracking process case (see Section 4), new
hypotheses are generated only when the error of the
error minimisation step (see Section 4.2) exceeds a
predefined threshold. However, the generation of
hypotheses is dictated within a short-term window.
That is to say, all pose hypotheses between all frames
within said time window are used as constraints in the
generation of new pose candidates. New pose candi-
dates are randomly sampled around the median of the
time-window retrieved poses (i.e. converged solution
of the minimisation step).
The uncertainty of tracking pose candidates is also
handled in Section 4.1. This is performed via a time-
window and is depicted by the covariance matrix S
p
i
.
In Section 4.2, the covariance matrix is updated, by
means of compensating re-projection errors (see Sec-
tion 4.2) (Haralick, 1994; Lourakis, 2010).
3 OBJECT DETECTION
An object description suitable for object identification
and pose estimation is created through the analysis
of all possible permutations of surflet pairs. The ba-
sic units to describe surface shape are surflets (Wahl
et al., 2003) s = (p,n), where p represents sample
points in the surface and n are the associated surface
normals.
We consider rotationally symmetric objects,
where shape is invariant to rotations around a given
axis. We assume that the Z axis of the object’s refer-
ence frame is the axis of symmetry and the X-Y-Z Eu-
ler representation. We search for surflet pairs whose
aligning transformation is very close in translation,
roll and pitch. Similar surflet pairs are collapsed into
the same feature.
p
r
p
i
n
r
n
i
f
4
f
2
f
3
d
f
1
= kdk
Figure 1: Point Pair Feature.
3.1 Detection process
The identification process consists of matching sur-
flet pairs (s
s
r
,s
s
i
) from a scene, to surflet pairs (s
m
r
,s
m
i
)
extracted from a database of model objects.
For s
r
and s
i
being two surflets, the Point Pair
Feature (PPF) F ∈ F ⊂ R
4
is defined as a 4-tuple
composed by the distance between the reference p
r
,
and secondary points p
i
, as well as the angle between
the normal of the reference point n
r
and the vector
d = |p
i
−p
r
|, the angle between the normal of the sec-
ondary point n
i
and d and, finally, the angle between
n
r
and n
i
as illustrated in Fig. 1.
This could be formally described by
F = PPF(s
r
,s
i
) = ( f
1
, f
2
, f
3
, f
4
)
= (kdk,∠(n
r
,d),∠(n
i
,d),∠(n
r
,n
i
)) (1)
3.2 Initial Pose Estimation
A set of reference surflets on the scene R
s
⊂ S is uni-
formly sampled from S and each of them is paired
with all the other surflets on the scene. The num-
ber of reference points is given by
|
R
s
|
= ξ
|
S
|
where
ξ ∈ [0; 1] is the reference points sampling ratio control
parameter.
For each scene surflet pair (s
s
r
,s
s
i
) ∈ S
2
, PPF(s
s
r
,s
s
i
)
is computed and set of similar model surflet pairs is
retrieved from the hash table. From every match be-
tween a scene surflet pair (s
s
r
,s
s
i
) ∈ S
2
and a model sur-
flet pair (s
m
r
,s
m
i
) ∈ M
2
, one is able to compute the rigid
transformation that aligns the matched model with the
scene. This is done first by computing the transfor-
mations T
m→g
and T
s→g
that align s
m
r
and s
s
r
, respec-
tively, to the object reference coordinate frame x axis,
and secondly by computing the rotation α around the
x axis that aligns p
m
i
with p
s
i
. The transformation that
aligns the model with the scene is then computed con-
sidering the ensuing expression:
T
m→s
= T
−1
s→g
R(α)T
m→g
(2)
The transformations T
m→g
and T
s→g
translate p
m
r
and p
s
r
, respectively, to the reference coordinate frame
origin and rotates their normals n
m
r
and n
s
r
onto the x
axis. After applying these two transformations, p
m
i
and p
s
i
are still misaligned. The transformation R(α)
AFrameworkfor3DObjectIdentificationandTracking
673

n
m
r
p
m
i
p
m
r
n
s
r
p
s
i
p
s
r
x
z
y
T
s→g
T
m→g
α
α
s
α
m
n
m
r
,n
s
r
p
xy
Figure 2: Pose acquisition by surflet pair aligment.
applies the final rotation needed to align these two
points. The previous reasoning is depicted in Fig. 2.
The transformation expressed in eq. (2) can be
parametrized by a surflet on the model and a rotation
angle α. In (Drost et al., 2010), this pair (s
m
r
,α) is
mentioned as the local coordinates of the model with
respect to reference point s
s
r
.
3.3 Voting Scheme
This method uses a voting scheme similar to the GHT
for pose estimation. For each scene reference sur-
flet, a two-dimensional accumulator array that repre-
sents the discrete space of local coordinates is cre-
ated. The number of rows, N
m
, is the same as the
number of model sample surflets
|
M
|
, and the number
of columns N
angle
is equal to the number of sample
steps of the rotation angle α.
A vote is placed in an accumulator array. The
position index corresponding to the local coordinates
(s
m
r
,α) is incremented by 1. After pairing s
s
r
with all
s
s
i
, the highest peak (the position with more votes) in
the accumulator corresponds to the optimal local co-
ordinate.
4 TRACKING PROCESS
Given the detected model recognised by the detection
process (Section3.1) and the initial estimated pose
(Section 3.2), the tracking process in the 2D camera
frame can be instantiated.
For any pose s from a known model m
i
we extract
the 3D-to-2D projected feature model points
ˆ
m
i
. The
set of model points are matched with image observed
feature points
ˆ
p
j
. This is performed by employing
a nearest neighbour search by overlaying in the 2D
camera frame a uniform grid.
We query for each model feature points
ˆ
m
i
and
find the Euclidean distance for given image observed
feature points
ˆ
p
j
. The image observed feature points
are produced from the contour and edges of the
model, as per method described in (Baltzakis and Ar-
gyros, 2009) and further extended in (Pateraki et al.,
2013).
The overall treatment of feature points (from ex-
traction to association) is much faster than other meth-
ods for associating contour points and has the addi-
tional benefit of finding intersections in relatively dif-
ficult to observe edges. The alternative of finding ap-
proximate nearest neighbours (Muja and Lowe, 2009)
would be computationally more expensive (Franklin,
2006). Uniform structures, which are optimized for
metrics in the Euclidean space E
(2)
, force query times
to be limited to O(N). Furthermore, this design
choice is not sensitive to noise and is capable of point
locations inclusion in planar graphs.
4.1 Pose Estimation
Our object pose estimation can be performed via point
correspondences C found between P = {
ˆ
p
j
} and M =
{
ˆ
m
i
} from an Iterative Closest Point (ICP) algorithm.
However, in the presence of noise and artifacts result-
ing, for example, from a cluttered background, the
ICP process can rapidly deteriorate.
This is not the case when using the Least Trimmed
Squares (LTS) estimator (Rousseeuw, 1984) in ICP
(TrICP; (Chetverikov et al., 2005)), since it allows
for the two point sets to contain unequal number of
points (i 6= j) and a percentage of points is offered in
a ‘trimming’ operation. The best possible alignment
between data / model sets is found by ‘sifting’ (e.g.
sorting) through nearest-neighbour combinations and
‘trimming’ (e.g. discarding) the less significant pairs
(but not exceeding 50%). This is in an attempt to find
the subset with lowest sum of individual Mahalanobis
distances, defined as
d
2
i j
= (
ˆ
m
i
−
ˆ
p
j
)
T
(S
m
i
+ S
p
j
)
−1
(
ˆ
m
i
−
ˆ
p
j
) (3)
where S
m
i
is the covariance, thus the uncertainty, on
the position of point feature
ˆ
m
i
; and respectively for
S
p
j
of
ˆ
p
j
, which depends on ‘outliers’ and thus the
feature space.
It should be noted that in practice the (robust) LTS
estimator and trimming does not guarantee the ab-
sence of outliers. Thus, we apply a non-linear re-
finement after the TrICP step to ensure that the influ-
ence of outliers is further reduced; similarly to (Koller
et al., 1993; Fitzgibbon, 2003; Chliveros et al., 2013).
4.2 Error Minimisation
This minimisation step is performed in an effort to re-
duce the pose estimation errors that may arise from
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
674

outliers and abrupt camera motion, but more im-
portantly in order to initiate the generation of new
pose candidates; i.e. take into account issues of re-
initialisation.
The objective function can be formulated as a sum
of squares of a large number of nonlinear real-valued
factors:
ˆ
s
t
= argmin
s
n
∑
i=1
||p
i
− f (s,m
i
)||
2
(4)
where f (·) is the function that projects the 3D
model points to the image plane, according to the
parametrised pose s, at translational terms (r
x
,r
y
,r
z
),
and rotational terms (α
x
,α
y
,α
z
).
Equation 4 describes a non-linear minimisation
problem which can be solved via the Levenberg-
Marquardt (LM) algorithm. The Jacobians required
by LM were formulated analytically by performing
symbolic differentiation of the objective function.
5 RESULTS
To evaluate the accuracy and speed of the proposed
methods we have employed a set of tests first for the
detection accuracy and then for the tracking perfor-
mance. As previously mentioned, the detection pro-
cess outputs the object model ID and its initial pose,
and the tracking process begins by accepting these as
inputs.
Evaluation of Detection
To evaluate the performance gains of the proposed
strategies to handle rotationally symmetries effi-
ciently, in the presence of noisy visual sensors, we
created an experimental scenario similar to the one
referred in (Drost et al., 2010). In this experimental
scenario the models library comprises only one model
at a time and we generated 200 synthetic scenes con-
taining a single instance of a given model from the
ROS household objects library (see (Ciocarlie, )), on
a random pose. Before the down-sampling step, each
scene was corrupted by different levels of additive
Gaussian noise, with standard deviation σ propor-
tional to the model diameter diam(M). By using syn-
thetically generated scenes, we were able to compare
the algorithm pose results with a known ground truth.
During identification we select 5% of the scene
points as reference points by setting ξ to 0.05. A
higher percentage would increase the robustness to
noise but also the recognition runtime. A recov-
ered pose was considered to be correct if the error
relative to the ground truth pose was smaller than
diameter(M)/10 for the position and 12 for the orien-
tation. We considered three different pose thresholds
(φ
th
and t
th
) to jointly represent features considered
redundant. Figure 3 shows recognition performance
results and speed gains for all the considered mod-
els and thresholds. When t
th
and φ
th
are both set to
0 (blue markers), no features are jointly represented.
Therefore the computational savings are only due to
collapsing of pose hypotheses around the axis of rota-
tional symmetry, during the pose clustering step. As
we increase the pose thresholds t
th
and φ
th
, we are
able to jointly represent more features and hence have
computational savings not only on the clustering but
also on the matching step.
For the tests with the cup model and pose thresh-
olds set to t
th
= 0.025 and φ
th
= 6
◦
(red markers),
we were able to discard 93.17% surflet pairs during
the creation of the model description, and reduce the
number of computations during pose detection. As
shown in Figure 3, the recognition rate drops slightly
for high levels of noise due to sampling effects, but
the recognition time performance increases signifi-
cantly. For
|
S
|
≈ 5000, our method achieves iden-
tification in time 300 times faster than (Drost et al.,
2010). However, the number of jointly represented
surflet pairs depends heavily on the object geomet-
ric configuration. For objects whose shape has a
smaller radius relative to the axis of symmetry, and
also lower surflet density on the surface, less perfor-
mance gains can be achieved. For the tests compris-
ing the champagne glass model we were only able
to discard 55.33% surflet pairs (with t
th
= 0.025 and
φ
th
= 6
◦
) during the creation of the model description,
and achieve no more than 3.5 times speed improve-
ments during recognition relatively to (Drost et al.,
2010).
Overall, we were able to obtain major improve-
ments on recognition speed. The latter does not have
significant cost on recognition performance.
Evaluation of Tracking
In Table 1, quantitative analysis of our tracking
approach in a ‘cup’ (as a recognised) model se-
quence is provided. As a reference method, we
have used the default particle filter implementation of
BLORT’s software implementation. The experiments
performed provide representative cases for the max
number of hypotheses (depicted as ‘max hyp: n’) and
for corresponding number of minimisation iterations
allowed (depicted as ‘LM iter’).
The results of Table 1, illustrate that ‘growth time’
dependence for tracking the 6DoF pose of an object
is somewhat predictable and comparable in perfor-
mance to that of BLORT. It seems that the higher
AFrameworkfor3DObjectIdentificationandTracking
675
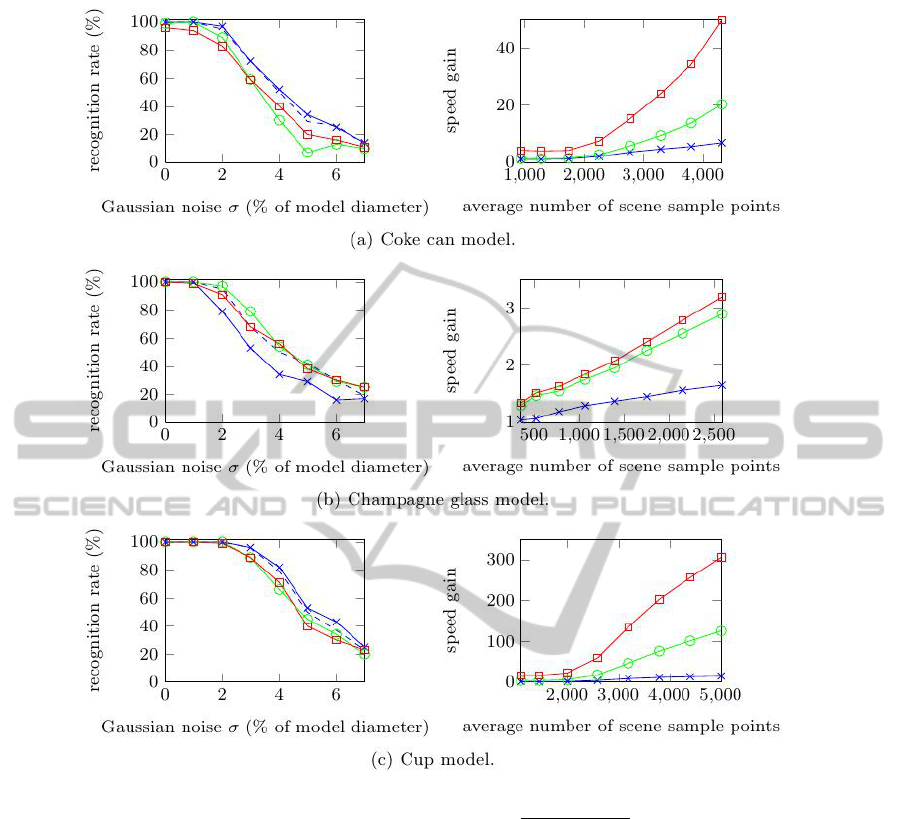
Figure 3: Comparison results of our approach (continuous lines) against the original method of Drost et al. (dashed lines),
with ξ = 0.05; Left: Recognition rate (%). Right: Time performance gain
Drost et al. runtime
Our runtime
.
Parameters: t
th
= 0, φ
th
= 0
◦
(blue markers), t
th
= 0.005, φ
th
= 1.2
◦
(green markers), t
th
= 0.025, φ
th
= 6
◦
(red markers).
the number of max hypotheses the higher the step in-
crease in terms of computational runtime. We note
that our implementation does not utilse hardware ac-
celaration. Optimisations are performed with re-
spect to custom matrix and array operations (based on
uBLAS and Lapack libraries). For completeness we
also report the computational time required by each
method.
Overall, our method is close to BLORT and for
this test case, it is applicable for on-line applications.
6 CONCLUDING REMARKS
In this paper we have suggested the use of a recogni-
tion method that uses its output as an input to a pose
tracking process. The savings in computational speed
do not affect recognition rates and tracking perfor-
mance. For the tests performed and results presented,
the combination of these two methods supports suit-
ability for online applications.
In future works we intent to perform further tests
on the framework’s accuracy (e.g. environmental con-
ditions). We also aim to exploring the effect certain
robot grasping strategies may have (e.g. object com-
ing out of the field of view).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially supported by the European
Commission under contract number FP7-248258
(First-MM project).
VISAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonComputerVisionTheoryandApplications
676

Table 1: Results on MH3DOT tuning versus performance and accuracy. A ‘cup’ sequence and model is used with (partial)
ground truth data. As a reference for these test results we use the BLORT software implementation.
Total Error (952 frames) Time
Roll Pitch Yaw Scale (msec)
BLORT (max = 100) 11.1 11.7 3.5 2.3 141
MH3DOT (LM iter = 10) max hyp: n = 20 14.4 12.9 7.1 2.4 97
max hyp: n = 30 11.2 11.9 5.2 2.2 122
max hyp: n = 50 2.8 5.8 2.4 1.9 158
max hyp: n = 100
2.8 5.8 2.3 1.9 225
MH3DOT (LM iter = 20) max hyp: n = 20 13.9 11.5 6.5 2.1 103
max hyp: n = 30 9.8 7.7 4.4 1.9 179
max hyp: n = 50 2.7 5.8 2.3 1.8 254
max hyp: n = 100 2.7 5.6 2.3 1.8 335
REFERENCES
Azad, P., M
¨
unch, D., Asfour, T., and Dillmann, R. (2011).
6-DoF model-based tracking of arbitrarily shaped 3D
objects. In IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automa-
tion, pages 5204–5209.
Baltzakis, H. and Argyros, A. (2009). Propagation of pixel
hypotheses for multiple objects tracking. In Advances
in Visual Computing, volume 5876 of Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 140–149.
Chetverikov, D., Stepanov, D., , and Krsek, P. (2005).
Robust euclidean alignment of 3D point sets: the
trimmed iterative closest point algorithm. Image and
Vision Computing, 23:299–309.
Chliveros, G., Pateraki, M., and Trahanias, P. (2013). Ro-
bust multi-hypothesis 3d object pose tracking. In
Computer Vision Systems, volume 7963 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 234–243.
Choi, C. and Christensen, H. I. (2012). Robust 3D vi-
sual tracking using particle filtering on the special Eu-
clidean group: A combined approach of keypoint and
edge features. The International Journal of Robotics
Research, 31(4):498–519.
Ciocarlie, M. Household objects database. accessed 19-
July-2012.
Drost, B., Ulrich, M., Navab, N., and Ilic, S. (2010). Model
globally, match locally: Efficient and robust 3d object
recognition. IEEE Transactions on Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pages 998 – 1005.
Figueiredo, R., Moreno, P., and Bernardino, A. (2013). Fast
3d object recognition of rotationally symmetric ob-
jects. In Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis,
volume 7887 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
pages 125–132.
Fitzgibbon, A. (2003). Robust registration of 2D and
3D point sets. Image and Vision Computing,
21(13):1145–1153.
Franklin, W. (2006). Nearest point query on 184,088,599
points with a uniform grid. Technical report, Rensse-
laer Polytechnic Institute, USA.
Haralick, R. (1994). Propagating covariance in computer
vision. In Proceedings of the 12th IAPR International
Conference on Pattern Recognition, volume 1, pages
493–498.
Harris, C. (1992). Tracking with rigid objects. MIT press.
Johnson, A. E. and Hebert, M. (1999). Using spin images
for efficient object recognition in cluttered 3D scenes.
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, pages 433–449.
Koller, D., Daniilidis, K., and Nagel, H. (1993). Model-
based object tracking in monocular image sequences
of road traffic scenes. International Journal of Com-
puter Vision, 10:257–281.
Lourakis, M. (2010). Sparse non-linear least squares opti-
mization for geometric vision. In European Confer-
ence on Computer Vision, pages 43–56.
Mian, A. S., Bennamoun, M., and Owens, R. (2006). Three-
dimensional model-based object recognition and seg-
mentation in cluttered scenes. IEEE Transactions on
Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell, 28:1584–1601.
Muja, M. and Lowe, D. G. (2009). Fast approximate near-
est neighbors with automatic algorithm configuration.
In Int. Conf. on Computer Vision Theory and Applica-
tions (VISAPP), pages 331–340.
Pateraki, M., Sigalas, M., Chliveros, G., and Trahanias, P.
(2013). Visual human-robot communication in social
settings. In IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automa-
tion.
Puppili, M. and Calway, A. (2006). Real time camera track-
ing using known 3D models and a particle filter. In
IEEE Int. Conf. on Pattern Recognition.
Rousseeuw, P. J. (1984). Least median of squares regres-
sion. Journal of the American Statistical Association,
79(388):871–880.
Wahl, E., Hillenbrand, U., and Hirzinger, G. (2003). Surflet-
pair-relation histograms: A statistical 3D-shape repre-
sentation for rapid classification. 3D Digital Imaging
and Modeling, International Conference on, page 474.
AFrameworkfor3DObjectIdentificationandTracking
677
