
Shortest Path Challenging Problem
Context of Mobile Devices in Urban Area Considering Weakened GPS Signal and
Data Network Traffic
Philippe Lacomme
1
, Libo Ren
2
, Nicolay Tchernev
2
and Benjamin Vincent
1
1
Université Blaise Pascal (LIMOS UMR 6158) Campus des Cézeaux, 63173, Aubière, France
2
Université d’Auvergne (LIMOS UMR 6158), Campus des Cézeaux, 63173, Aubière, France
Keywords: Shortest Path, Mobile Device, Web Services.
Abstract: The shortest path problem is a well know routing problem which received a considerable amount of
attention for several decades. This problem is the cornerstone of any real-world routing problem including
the VRP or the Hub Location. The majority of efficient methods dedicated to these problems consist in
computing first the matric of shortest path between nodes. Furthermore, in recent years there has been a
revival of interest in the shortest path problem used in the context of various transportation engineering
applications. This paper relates to the conception of efficient routing algorithms tuned for mobility. More
precisely, it is targeted to the field of pedestrian mobility in an urban environment. In a mobile environment,
specific constraints as wireless network traffic disturbances must be taken into account. The architecture
that we tune for the project is based on an active monitoring system, which required new shortest path
calculation using the exposed web service API. The web service is performed when a specific constraint
appears or a new part of the path is required. Using of such architecture offers a new approach in
operational research algorithms and our contribution stands at the crossroads of optimization research
community and the web service community expectations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Distributed Computing Technologies and Web
services are growing rapidly in importance in
today’s computing environment and are already
widely accepted as industrial standards. By
combining modern computing technologies and
Operations Research, Optimization Services will
reach a larger audience informed of, and benefit
from, an increasing amount of OR software
implemented gaining gradual quality.
Moreover advances in digital electronics and
wireless communications have enabled the
development of low-cost Global Positioning
Systems (GPS) which can be used by pedestrian
mobility in urban environment. In wireless network
traffic, loss of connection due to network overload
and bad localization lead to a significant increase in
travel times and a decrease in the probability of
being on-time at the final destination.
Generally, pedestrians using GPS have a very
little knowledge on the path they walk. When the
GPS signal is broken, pedestrian can easily be lost
by taking a wrong direction or can be forced to wait
for GPS signal. Never mind the case, regarding
pedestrian needs, an inadequate paths planning can
lead to an "unfriendly walking environment" with
people feeling insecurity.
From a road safety viewpoint, pedestrians should
be provided with safe conditions where they avoid
being distracted by watching their GPS until the
signal returns. However, that cannot always be
achieved. A series of measures should be considered
to improve pedestrian safety and mobility.
Therefore, it is essential to use routing that
effectively respond to the wirelee network
disruptions and give high quality solutions within
acceptable calculation times. One important question
to be answered is how to use the level of online
information needed to obtain higher solution quality
with lower calculation times.
In this paper, we focus on the dynamic shortest
path problems with stochastic disruptions in the
wireless network. We are particulary interested in
networks where a single pedestrian has a certain
393
Lacomme P., Ren L., Tchernev N. and Vincent B..
Shortest Path Challenging Problem - Context of Mobile Devices in Urban Area Considering Weakened GPS Signal and Data Network Traffic.
DOI: 10.5220/0004753403930400
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES-2014), pages 393-400
ISBN: 978-989-758-017-8
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

origin–destination pair. The pedestrian gets the real-
time information from the GPS at each node which
is an intersection of roads and/or streets. At every
intersection, the GPS determines the next road to
follow depending on the current state of the
pedestrian.
We concentrate more particularly on the design
of efficient routing algorithms tuned for pedestrian
mobility in an urban environment. The main
contributions of this paper are as follows: 1) we
develop a dynamic shortest path algorithm dedicated
to a mobility implementation; 2) we package this
operational research algorithm as a software service
based on Web services paradigm that facilitate
distributed computing; 3) next to this we design a
basic pedestrian system for Android using the
exposed web service API; 4) we test the efficiency
of our dynamic shortest path algorithm and copare
this to the optimal solutions find with Dijkstra
algorithm. The numerical results show that the
average gap is promizing.
The paper is organised as follows: the section 2
presents the context of this research. Section 3
descibes the system architecture for pedestrian
guidance system in an urban environment. An
example on the creation of a client is explained in
section 4. In Section 5, the numerical results and the
important insights are discussed before the
conclusion.
2 CONTEXT
2.1 Shortest Path
In recent years, there has been a revival of interest in
the shortest path problem for use in various
transportation-engineering applications. Without any
doubt it could be directly attributed to the recent
developments in Intelligent Transportation Systems
(ITS), particularly in the field of Route Guidance
System (RGS) and real time Automated Vehicle
Dispatching System (AVDS). In both cases, there is
a definite need to find the shortest paths from an
origin to a destination in a quick and accurate
manner.
In the above applications, the traditional optimal
shortest path algorithms often cannot be used
because in a large dense network the computation of
the shortest path can take a long time and is too
computationally intensive to be feasible for real-time
systems.
A number of heuristic search strategies have
been developed for increasing the computational
efficiency of shortest path search.
Most of these heuristic search strategies
originated in the artificial intelligence (AI) field
including but not limited to (Hart et al., 1968),
(Nilsson, 1971), (Pearl, 1984) where the shortest
path problem is used as a mechanism to validate the
effectiveness of these heuristics.
The current RGS field in both North America,
and Europe have generated renewed interest in using
heuristic algorithms to find shortest paths in a traffic
network for real-time vehicle routing operations.
(Guzolek and Koch, 1989) discussed how heuristic
search methods could be used in vehicle navigation
system. (Kuznetsov, 1993) debated applications of
an A* algorithm (first proposed by Hart et al. 1968),
a bi-directional search method, and a hierarchical
search method.
Since then, a huge number of researchers have
followed the trend and tried to introduce a
worldwide strategy for improving the efficiency of
the shortest path search process. These efforts have
resulted in a large literature including a wide
spectrum of search strategies and mechanisms.
For a recent survey it is possible to refer to (Fu et
al., 2006) who proposes a state of the art and
examines the implementation and performance of
numerous heuristic algorithms. A recent survey of
(Garroppo et al., 2010) focuses on the multi-
constrained approximated shortest path algorithms
representing by recent publications of (Gubichev et
al., 2010) or (Willhalm, 2005).
2.2 Web Services
2.2.1 Historical Perspective
In recent decades, web services based solver servers
offered access to commercial or non-commercial
implementation of algorithms for solving non-linear
and linear problems. The well known formats as
MPS (Mathematical Programming System (IBM
1976)) and some others (MPL (Maximal Software,
2002), LINGO (Lindo Systems Inc, 2008), and
CAMPS (Lucas and Mitra, 1988)) specific to a given
solver are commonly used as a file format for
presenting and archiving linear programming (LP)
and mixed integer programming (MIP) problems.
Each client submits a text file which contains the
model and the data to a server. The results were sent
back to the client either via email or via a file which
could be downloaded from the server using the ftp or
http protocol. A comprehensive review of modelling
systems, formats and their features can be found in
(Dominguez-Ballesteros et al., 2002).
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
394
The design, development, implementation and
deployment of decision support systems have been
transformed by web based technologies. (Cohen et
al., 2001) give examples of web-based decision
support systems in Supply Chain Management,
Inventory Control or supplier management.
(Bhargava et al., 2007) reviews and summarises
recent technology developments, current usage of
Web-based DSS, and trends in the deployment of
such systems.
2.2.2 Definition and Standard
Web service is defined as a communication
techonologie between two devices over Internet. It
relies on the using of HTTP with an XML
serialization. Web services are characterized by their
great interoperability and extensibility due to the use
of XML, and they can then be combined in a loosely
coupled way in order to achieve complex operations
(Wang et al., 2004). During the last decade several
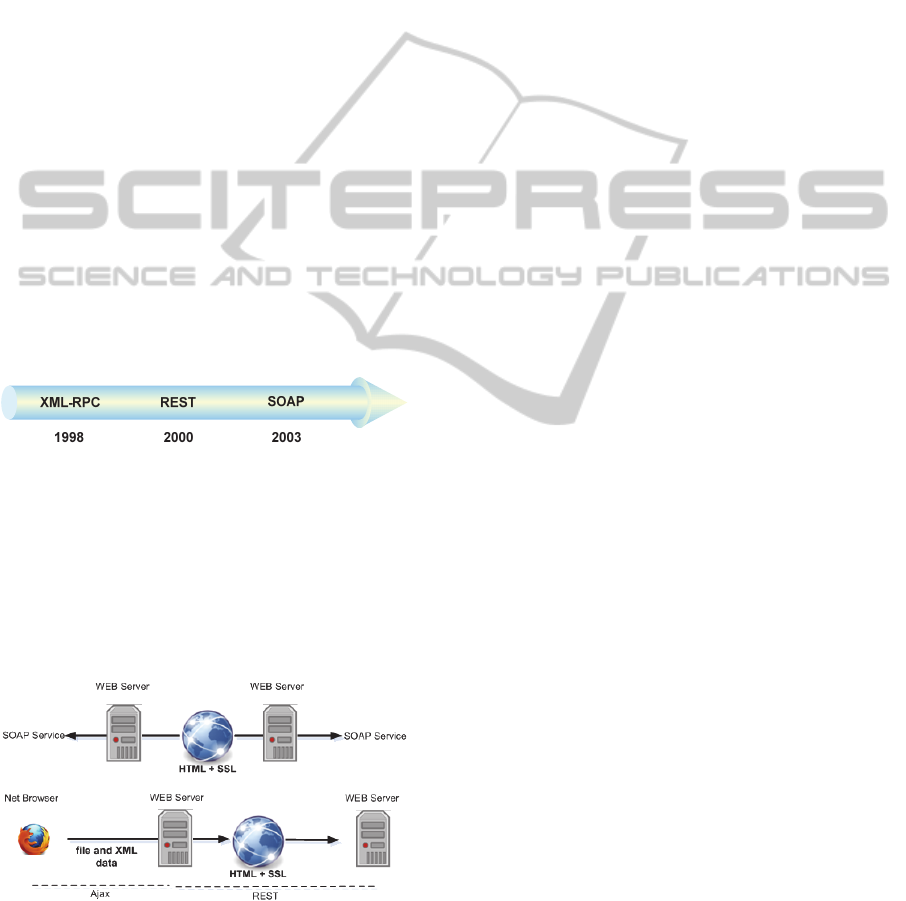
technologies have been used including: XML-RPC
(Remote Procedure Call), REST (REpresentational
State Transfer (Fielding 2002)) and lately SOAP
(Simple Object Access Protocol (Gudgin et al.,
2003) (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Client-Server architecture evolution.
According to W3C, the difference between
REST architecture and SOAP architecture concerns
the data exchange and the availability of some
language description which is a guaranty of an easy
to use and easy to spread web service (Figure 2). In
this paper, we are interested more particularly in
SOAP architecture.
Figure 2: Difference between REST and SOAP.
2.2.3 Soap Web Services
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) is
fundamentally a stateless, one-way message
exchange paradigm that enables applications to
create more complex interaction patterns (e.g.,
request/response, request/multiple responses, etc.)
by combining one-way exchanges with features
provided by an underlying protocol and/or
application-specific information. SOAP provides
automatic discovery of the service and take
advantages of several languages and protocol wide
spread on the web:
XML (eXtensible Mark-up Language) to
underlay representation format of the data
exchanged. The language is used to specify the
header and body elements of the SOAP message;
WSDL (Web Service Definition Language) used
to described the public interface of the service
(Chinnici et al., 2007), i.e. computer-readable
description of Web services;
UDDI (Universal Description, Discovery and
Integration) to register and spread a web service
(UDDI, 2002).
Messages must be carried by the SOAP and
formatted by the rules of it, and the description
(exposed interface) of the service must be defined in
WSDL, i.e. the XML based language used to
describe and locate a SOAP web service).
3 SHORTEST PATH WEB
SERVICE
3.1 Proposed Web Service
The definition of the system architecture is based on
the SOAP Web Service definition that exposed 4
methods:
Demarrer_Guidage is an asynchronous method
which starts the shortest path computation on the
server;
TesterEtatDemande allow checking the state of
the execution of Demarrer_Guidage method
which returns 1 if the job is in progress, 0
otherwise;
RecupererEtatGuidage permits to obtain the
shortest path computed;
LireCodeRetour permits to decode a state code.
3.2 Network Data Source
The first step to compute a shortest path is to obtain
a real-world road network data. To do so, there
exist numerous sources including but not limited to
ShortestPathChallengingProblem-ContextofMobileDevicesinUrbanAreaConsideringWeakenedGPSSignaland
DataNetworkTraffic
395

Google Maps, ArcGis, Bing Maps, Mapquest, Via
Michelin and OpenStreetMap (OSM). Among them,
OSM has the great advantage to be an open-source
collaborative project that has reached 1 million users
in 2013. Around 30% of users have contributed to
OSM database. OSM consists of open data that are
freely available and it offers a data source for
researchers in the area of OR.
3.3 Proposed Shortest Path Algorithm
This paper aims to elaborate a dynamic shortest path
algorithm. As shown in Algorithm 1, the main loop
(lines 10-17) takes advantages of three
considerations:
since it has been commonly recognized that the
computational effort required solving a generic
search grows faster than the size of the problem,
the original problem can be decomposed into
small sub-problems (lines 11-13), substantial
computational time saving can be achieved;
the branch pruning techniques is considered. It
consists in discarding nodes from the scan
eligible nodes list after proving to be located out
of the assumed good solutions area (line 14). The
branch pruning algorithm maintains a strongly
limited set of eligible nodes as compared to A*
and provided a better complexity;
a sub-goal based method (lines 15-16) can be
defined into a sub-problems especially for
shortest path problem in a road traffic network
where goals could be nodes or links located
between the origin and destination localization.
3.4 Integration of a Shortest Path
Algorithm into the Web Method
The web method Demarrer_Guidage is
asynchronous: it closes the communication
immediately and launches a long time process into a
thread. The main advantage is that one client can
continue its execution (Figure 3) in very short
delays.
The thread is linked to the client and more
precisely to the API Key which is used as session
identification. Into the thread the following
operations are achieved:
The step 1 consists in verification of the API key
with the objective to check its validity and the
reach of maximal number of requests per day.
The step 2 consists in downloading the road
network map from OpenStressMap using the
corresponding web service
(http://api.openstreetmap.org/).
The step 3 consists in creation of the graph
representing the road network.
The step 4 is the computation of the shortest path
using the method Shortest_Path on the obtained
graph.
Algorithm 2 gives some details on the thread.
The procedure first checks the key and stops
immediately if the key is not valid (line 11). The line
12 consists in using the SOAP OSM API to obtain a
road network.
Line 13 involves extra web communication and
could be time consuming depending on the network
size. Line 14 consists in transforming the road
Algorithm 1: Shortest Path algorithm.
1. procedure Shortest_Path
2. Global parameters
3. L : sub-graph size
4. input parameters
5. G : the graph which models the urban network
6. Nx : initial nodes in the graph (pedestrian localization)
7. Ny : final nodes in the graph
8. output parameters
9. trip : set of nodes
10. begin
11. Compute the Euclidean distance from Nx to Ny
12. Compute the line equation from Nx to Ny
13. Define G'a subgraph around node Nx which models a sub-network around L meters
14. Reduce the number of nodes and arcs in G’
15. Determine N
out
the output node closest to the right intersection between the
line Nx_Ny and the border of rectangle including G’
16. Call Dijkstra algorithm to find shortest path in G’ between Nx and N
out
17. end
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
396
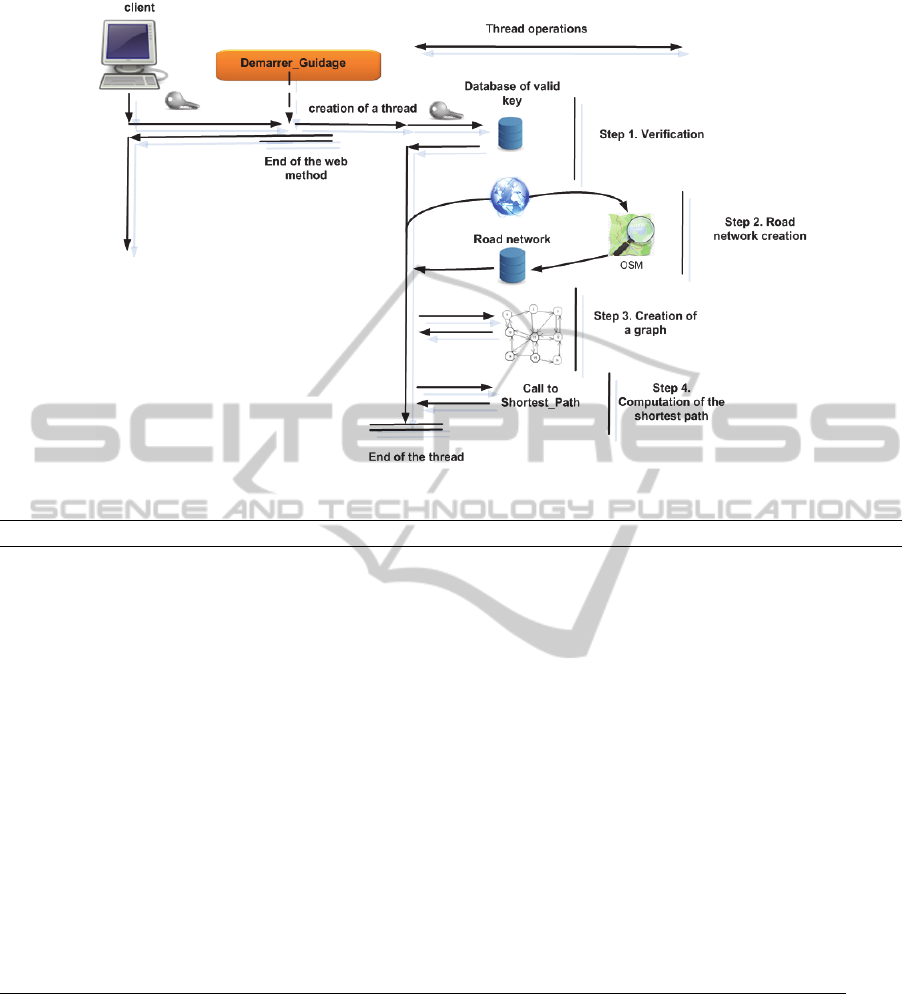
Figure 3: Web method Demarrer_guidage.
Algorithm 2: Thread_computation.
1. procedure Thread_computation
2. input parameters
3. G : the graph which modelize the urban network
4. (latx, longx) : the current position
5. (laty, longy) : the final position
6. Nx : initial nodes in the graph
7. Ny : final nodes in the graph
8. output parameters
9. trip : set of nodes
10. begin
11. call procedure Key_verification ()
12. if (key invalid) stop;
13. Connect to the mapquest web service and download the road network
14. Transform the road network into a graph (G)
15. Convert the position (latx, longx) into a node Nx in the graph
16. Convert the position (laty, longy) into a node Ny in the graph
17. Trip = call Shortest_Path (G, Nx, Ny)
18. T'= Convert trip into positions into the road network
19. return T'
20. end
network into a graph G. Line 15 consists in
conversion of position (latitude/longitude) into one
node in the graph. Note that this conversion could
require (according to the road network coding of
MapQuest) creation of new nodes. Similar remarks
hold for line 16. Line 17 consists in using the short
path procedure which provides a shortest path as a
sequence of nodes in G. The shortest path is then
transformed into a sequence of (latitude/longitude)
points on the road network.
3.5 Wireless Traffic Disturbances
In urban area mainly, the connection to the mobile
network depends on numerous parameters including
the internet provider quality equipment; the number
of users connected at the same time and modulation
of electromagnetic waves propagation. The last point
means that radio waves interact with the
environment though exotic physical mechanisms
including reflection, refraction, fast fading, slow
ShortestPathChallengingProblem-ContextofMobileDevicesinUrbanAreaConsideringWeakenedGPSSignaland
DataNetworkTraffic
397

fading and of course attenuation. Experts in wireless
networks stated it is impossible to predict the real-
life performances of such system one fully deployed
and that performances can be strongly modulated
especially in a mobile scenario.
The consequence is that mobile device
connection to a web service could be delayed or
impossible and could require conception of a mobile
solution where a graph is saved into the mobile
device allowing computation of a shortest path using
the mobile CPU only.
4 CONCEPTION OF CLIENT
USING WEB SERVICE
A client application using the proposed web service
contains three components: User interface, business
layer and SOAP layer. Among those three
components, SOAP layer could be created
automatically by a modern integrated development
environment.
The business layer can be divided into 3 steps to
make a demonstration of the different methods
execution:
Step 1. The client has to create a instance of the
class RecuperationDonnee and to define a
port assigned with
getRecuperationDonneePort .
Step 2. The client can access to the asynchrone
DemarrerGuidage method providing a valid
API key, and two (latitude/longitude)
positions.
Step 3. The client can periodically investigate if the
result is available or not using the
RecupererResultatGuidage method
providing only the key which is the session
identification.
With the objective to validate the principle and the
performance of the tune shortest path algorithm in
the real life conditions, an android application has
been created and it could be downloaded at: http://
www.isima.fr/~lacomme/ORWebServices/GPS4ped
estrian/source/Gps_android.apk
5 COMPUTATIONAL RESULTS
AND ANALYSIS
In this paragraph we present the performance of the
proposed dynamic shortest path algorithm in real
problem. The network corresponds to the urban
traffic system of Clermont-Ferrand city. Based on
these data, 27 instances were randomly generated.
The Origin and destination points are chosen such
that their distance corresponds to an hour walk (in
average 2,5km).
Two types of experiments have been performed.
The first one concerns the hypothesis that the
pedestrian does not deviate from the path proposed
by the algorithm (he never loses his way). The
second one concerns the hypothesis that the
pedestrian loses his path with a given probability.
The following notations are used in table 1 and 2:
N: instance number;
h*: optimal distance found by Dijkstra
algorithm (in meters) ;
h(p%): distance found by the proposed
algorithm with p probability that the
user loses its way (in meters);
Gap%: percentage deviation of optimal
solution;
I: number of algorithm iterations needed
to reach final destination;
, %: average distance from x executions of
27 instances (in meters).
Test results show that average gap from the optimal
solution is 5.62% and for 10 of instances the
algorithm found the optimal value.
Table 2 shows the results for the second
hypothesis: the pedestrian loses at each intersection
his way with a given probability p (p=1, 2, 5 and
10%). All results in table 2 are average values from
100 executions on the all 27 instances. Results prove
that the proposed algorithm has a promising
performance. The added distance is due to the
likelihood of pedestrian to lose his way. This
distance is near 7% the path in the case of
probability p=10%.
6 CONCLUDING REMARKS
The shortest path routing problem which is well-
known as a seminal problem in routing has been
chosen to study how constraints linked to mobility
push us into modifying routing algorithms to provide
efficient services. The Web services technologies
offer also to a community the possibility to reuse the
methods for a very small programming effort. The
Web Service paradigm is a new approach in
spreading operational research algorithms and our
contribution stands at the crossroads of optimization
research community and the web service community
expectations.
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
398

Figure 4
:
Example design of a client application using the Web service
.
Table 1: Test results for first hypothesis.
N° Origin point Destination point
*
0%
Gap % I
1 45.7581 3.1101 45.7780 3.0831 3629.80 3812.60
5.04
14
2 45.7792 3.1168 45.7580 3.0784 4509.11 5613.92
24.50
22
3 45.7848 3.1028 45.7746 3.0947 1639.40 1639.40
0.00
4
4 45.7890 3.0951 45.7704 3.1188 4047.20 4496.63
11.10
11
5 45.7780 3.1104 45.7884 3.0983 1866.19 1882.40
0.87
6
6 45.7751 3.0829 45.7710 3.0926 1245.82 1289.56
3.51
5
7 45.7701 3.0808 45.7801 3.1184 3278.60 3388.53
3.35
20
8 45.7821 3.0985 45.7636 3.1078 2737.98 2737.98
0.00
7
9 45.7705 3.0656 45.7651 3.0769 1525.79 1699.48
11.38
6
10 45.7819 3.1027 45.7647 3.0974 2417.21 3079.71
27.41
8
11 45.7590 3.1159 45.7856 3.0735 5440.46 5659.44
4.03
20
12 45.7789 3.0836 45.7823 3.1019 1789.43 1943.73
8.62
8
13 45.7890 3.1001 45.7707 3.0757 3383.98 3741.73
10.57
14
14 45.7683 3.1066 45.7816 3.1239 2750.92 2770.76
0.72
8
15 45.7645 3.1053 45.7812 3.0903 2529.81 2529.81
0.00
7
16 45.7728 3.0727 45.7662 3.0680 1260.14 1260.14
0.00
3
17 45.7805 3.1001 45.7763 3.0770 2074.18 2137.08
3.03
12
18 45.7592 3.0841 45.7777 3.0703 2588.66 2588.66
0.00
8
19 45.7620 3.1248 45.7612 3.0934 3033.87 3094.42
2.00
12
20 45.7691 3.1079 45.7879 3.0997 3103.75 3703.95
19.34
7
21 45.7773 3.0907 45.7877 3.0861 1677.82 1682.47
0.28
4
22 45.7764 3.0713 45.7664 3.0796 1454.39 1454.39
0.00
5
23 45.7725 3.0936 45.7668 3.1143 2047.18 2373.95
15.96
9
24 45.7613 3.0906 45.7867 3.0788 3356.14 3356.14
0.00
10
25 45.7682 3.0893 45.7654 3.0984 1127.62 1127.62
0.00
5
26 45.7654 3.0892 45.7654 3.0882 884.33 884.33
0.00
1
27 45.7659 3.1079 45.7804 3.0874 2594.19 2594.19
0.00
13
Avg. 2518.30 2686.78 5.62 9.22
Table 2: Test results for second hypothesis.
Value (m) GAP % Distance added (m) Standard deviation (m) I
*
2518,30 - - - 1
0%
2686,78 5,62 - - 9,22
100,1%
2704,57 6,32 17,79 58,87 9,39
100,2%
2725,76 7,18 38,98 88,18 9,55
100,5%
2783,59 9,49 96,81 139,47 10,12
100,10%
2896,78 13,96 210,00 206,35 11,20
ShortestPathChallengingProblem-ContextofMobileDevicesinUrbanAreaConsideringWeakenedGPSSignaland
DataNetworkTraffic
399

The first experimentation reported in this paper
pushes us into considering that complexity and proof
of optimality are not the only key of efficient
algorithms in the context of mobility but persuade us
that a valuable quality of service strongly depends of
a correct integration of components into a global
system.
Also, the following developments are suggested
for the future research; Besides Dijkstra’s algorithm,
other algorithms can also be applied in the dynamic
approach to improve the computational aspects of
the proposed algorithm.
REFERENCES
Bhargava, H. K., Power, D. J. and D. Sun, 2007, Progress
in Web-based decision support technologies, Decision
Support Systems, 43, pp. 1083-1095. 2007.
Chinnici R., J. Moreau, A. Ryman and S. Weerawarana
(Eds.), 2007, Web Services Description Language
(WSDL) Version 2.0 Part 1: Core Language, W3C
Proposed recommendation, May 23.
Cohen M. D., C. B. Kelly and A. L. Medaglia. 2001,
Decision support with web-enables software.
Interfaces. 31(2), pp. 109-129.
Dominguez-Ballesteros B., G. Mitra, C. Lucas and N.-S.
Koutsoukis, Modelling and solving environments for
Mathematical Programming (MP): a status review and
new directions, Journal of The Operational Research
Society. 53(10). pp. 1072-1092. 2002.
Fielding R.T. and R.N. Taylor. Principled design of the
modern web architecture, ACM Trans. Internet
Technol. (TOIT), 2(2), pp. 115–150. 2002.
Fu, L., Sun, D. and L. R. Rilett, Heuristic shortest path
algorithms for transportation applications: State of the
art, Computers & Operations Research 33, pp. 3324–
3343, 2006.
Garroppo, R., Giordano, S., Tavanti, L., 2010. A survey
on multi-constrained optimal path computation: Exact
and approximate algorithms, Computer Networks, 54,
pp. 3081–3107.
Guzolek J, Koch E. Real-time route planning in road
network. Proceedings of VINS, September 11–13,
1989. Toronto, Ontario, Canada, p. 165–9.
Gubichev,A. Bedathur, S., Seufert, S. and G. Weikum.
2010. Fast and Accurate Estimation of Shortest Paths
in Large Graphs. CIKM’10, October 26–30, Toronto,
Ontario, Canada.
Gudgin M., M. Hadley, N. Mendelsohn, J. J. Moreau and
H. Nielsen, SOAP version 1.2. Part 1. Messaging
framework, http://www.w3.org/TR/soap12-part1/,
2003.
Hart E. P., Nilsson N. J., Raphael B., 1968. A formal basis
for the heuristic determination of minimum cost paths.
IEEE Transaction, System Science and Cybernetics;
SSC-4(2):100–7.
IBM World Trade Corporation. IBM Mathematical
Programming System Extended /370 (MSPX/370):
Program Reference No. SH19-1095-1, New York
&Paris. Reference No. SH19-1095-1. 1976.
Kuznetsov T. High performance routing for IVHS. IVHS
America 3rd Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, April,
1993.
Lindo Systems Inc,. LINGO Modelling System Version
12.0. Manual. Chicago IL, USA: Lindo Systems Inc
Lindo Systems Inc. 2008.
Lucas C. and G. Mitra, Computer-assisted Mathematical-
Programming (Modelling) System—CAMPS, The
Computer Journal, 31(4), pp. 364-375. 1988.
Maximal Software, MPL Modelling System, Release 4.2,
2002.
Nilsson J. N. Problem-solving methods in artificial
intelligence. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1971.
Pearl J. Heuristics: intelligent search strategies for
computer problem solving. Addison-Wesley
Publishing Company; 1984.
UDDI Version 2.04 API Specification, UDDI Committee
Specification, 19 July 2002, available on
http://uddi.org/pubs/ProgrammersAPI_v2.htm.
Wang H., Huang, J. Z., Qub, Y. and J. Xia. Web services:
problems and future directions, Web Semantics:
Science, Services and Agents on the World Wide Web.
1 (3). pp. 309–320. 2004.
Kuznetsov T. High performance routing for IVHS. IVHS
America 3rd Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, April,
1993.
Willhalm. T., 2005. Engineering Shortest Paths and
Layout Algorithms for Large Graphs. Dissertation der
Universität Fridericiana zu Karlsruhe (TH).
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
400
