
Visual Exploration of Relationships between Document Clusters
Ilir Jusufi
1,2
, Andreas Kerren
1
, Jiayi Liu
1
and Bj
¨
orn Zimmer
1
1
Linnaeus University, Department of Computer Science, ISOVIS Group, V
¨
axj
¨
o, Sweden
2
Institute for Data Analysis and Visualization, Department of Computer Science, University of California, Davis, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Network Visualization, Multivariate Data, Clustering, Document Visualization, Text Visualization, Interac-
tion, Visual Analytics.
Abstract:
The visualization of networks with additional attributes attached to the network elements is one of the ongoing
challenges in the information visualization domain. Such so-called multivariate networks regularly appear
in various application fields, for instance, in data sets which describe friendship networks or co-authorship
networks. Here, we focus on networks that are based on text documents, i.e., the network nodes represent
documents and the edges show relationships between them. Those relationships can be derived from common
topics or common co-authors. Attached attributes may be specific keywords (topics), keyword frequencies,
etc. The analysis of such multivariate networks is challenging, because a deeper understanding of the data
provided depends on effective visualization and interaction techniques that are able to bring all types of in-
formation together. In addition, automatic analysis methods should be used to support the analysis process
of potentially large amounts of data. In this paper, we present a visualization approach that tackles those
analysis problems. Our implementation provides a combination of new techniques that shows intra-cluster
and inter-cluster relations while giving insight into the content of the cluster attributes. Hence, it facilitates
the interactive exploration of the networks under consideration by showing the relationships between node
clusters in context of network topology and multivariate attributes.
1 INTRODUCTION
Researchers across different domains of science deal
with an increasing number of network data. A com-
plicating fact is that real life networks usually have at-
tributes associated with their elements. The data types
of those attributes can be either homogeneous or het-
erogeneous. Attributes of a co-authorship network,
for example, with nodes representing documents and
edges indicating if documents share a common topic
(keywords) could be considered homogeneous since
the keywords are always quantified as connections be-
tween documents. In other words, all attributes (key-
words) have the same data type depending on what
the edges actually represent: either Boolean (con-
tained in a document or not) or Integer (frequency
in a document). A more complex social network, in-
volving age, gender, salary, favorite sports team, and
other preferences, however, would be considered het-
erogeneous. Homogeneous attributes have the advan-
tage that they can all be visualized using the same
metaphor (visual representation). The visualization of
such multivariate networks is one of the ongoing chal-
lenges in the information visualization domain [Ker-
ren et al., 2013].
Often, researchers who analyze such networks do
not have any inherent understanding about the struc-
ture or the values of the data at hand. This problem
has been increased by the growing amount of data
produced with the help of new technologies. Some-
times it is even hard to ask interesting research ques-
tions or forming a simple hypothesis on specific as-
pects of the data. Therefore, we often need a start-
ing point for our visual exploration. One solution
to find such an initial state may be Shneiderman’s
mantra “overview first, zoom and filter, then details-
on-demand” [Shneiderman, 1996]. Another possibil-
ity is given by automatic analyses, such as methods
for unsupervised clustering (k-means, etc.) to make
sense of large input data sets [Mirkin, 2005].
Let us assume that we applied a clustering algo-
rithm on our multivariate network to group the nodes
on the basis of their attributes. It is often insuffi-
cient to show only relationships between clusters as
there may exist significant connections between clus-
ters and individual data elements. In consequence, the
visualization of the underlying network together with
the attributes and the derived cluster data may help
researchers revealing interesting data patterns. Here,
the visual analysis of the links between the network
195
Jusufi I., Kerren A., Liu J. and Zimmer B..
Visual Exploration of Relationships between Document Clusters.
DOI: 10.5220/0004754301950203
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information Visualization Theory and Applications (IVAPP-2014), pages 195-203
ISBN: 978-989-758-005-5
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

nodes within a specific cluster may be an important
help to discover possible correlations between the at-
tributes and the network topology. Additionally, the
presence of strong relationships between nodes from
different clusters may indicate the existence of unique
connection types that are unrelated to the concrete at-
tribute values (as such relationships do not exist in
one single cluster only). A straightforward approach
to visualize attribute-based clusters in networks is to
aggregate clustered nodes into super-nodes. However,
this approach both neglects to include intra-cluster
(i.e., cluster-local) relationships and to identify indi-
vidual cluster members that are highly connected to
other clusters.
In this paper, we present a visualization prototype
that is used to visually analyze scientific conference
articles which form a co-authorship network. Ad-
ditional metadata has been used to cluster the docu-
ments, and the results are represented through our vi-
sualization and interaction techniques. Our visualiza-
tion and interaction techniques supported by the pro-
totype tackle the problem of representing intra-cluster
relationships in networks while providing additional
insight into the attributes of the elements within the
clusters. Thus, users are able to visualize intra-cluster
relationships, inter-cluster relationships, and relation-
ships between clusters and individual elements with
the help of different interaction techniques. Although
similar approaches that deal with such tasks exist (for
instance the work of [Henry et al., 2007]), our pro-
totype introduces a combination of techniques that
shows intra-cluster and inter-cluster relations while
giving insight into the content of the cluster attributes.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows: a
brief discussion of related work is presented in Sec-
tion 2. The description of our main visualization and
interaction ideas are discussed in Section 3. Technical
details of our prototype are highlighted in Section 4
followed by two use cases in Section 5. Finally, we
conclude the paper with a brief summary and a de-
scription of our planned efforts for the future.
2 RELATED WORK
Various systems visualize multivariate network data
and the topology of the network itself. [Borisjuk et al.,
2005] employ small diagrams as nodes instead of sim-
ple circles or rectangles in metabolic networks. Each
diagram represents experimental data that is related
to the node. To handle the clutter that could be in-
troduced if the embedded diagrams cause too many
overlaps, magic lenses can be used to show different
multivariate attributes on demand [Jusufi et al., 2010].
GraphTrail [Dunne et al., 2012] is another system to
analyze multivariate data and supports the exploration
of heterogeneous networks. It also introduces an in-
teraction history to allow users to refer back to previ-
ous exploration steps. These approaches do not pro-
vide any clustering mechanisms for data analysis.
Another approach to avoid clutter is to use so-
called Semantic Substrates [Shneiderman and Aris,
2006]. Nodes are placed in non-overlapping regions
based on their attributes. A related technique de-
veloped by [Wattenberg, 2006] uses a grid-layout to
show the relationships between node attributes and
links. [Pretorius and van Wijk, 2008] arrange edge la-
bels in a list and place rectangular regions contain-
ing source and target nodes at each side. The re-
gions are partitioned according to the attributes of the
nodes and are connected to corresponding edge labels
via straight lines. Based on this idea, parallel node-
link bands [Ghani et al., 2013] separate nodes into
multiple regions and visualize them similar to a par-
allel coordinates plot. Previous work of [Pretorius
and van Wijk, 2007] introduces hierarchical cluster-
ing based on node attributes to place nodes in spe-
cific regions. Related techniques are presented by
[Archambault et al., 2009, Archambault et al., 2008].
However, the underlying graph topology is not com-
pletely visible or hard to perceive with the aforemen-
tioned techniques. Most of these tools place the nodes
in distinct regions which could be considered as a
clustering or grouping. However, none of them pro-
vides insight into the attributes of the clusters/groups
or into their context. A slightly different technique
is introduced by [Jusufi et al., 2013]. They use an
attribute-driven layout to steer node positioning based
on multivariate attributes, while still showing the gen-
eral network structure. Similar works have been pub-
lished before [Bezerianos et al., 2010, Wu and Takat-
suka, 2006]. One drawback of those tools is that the
visualization of clusters is either not possible or lim-
ited.
There are different techniques to visualize text-
based attributes. Tag clouds [Kaser and Lemire,
2007] are one approach to visualize the frequency of
words in a document or the keywords of a document
collection, and there are several very popular tools
which extend the original work, such as Wordle [Vie-
gas et al., 2009], ManiWorlde [Koh et al., 2010], or
ProjCloud [Paulovich et al., 2012]. Our prototype
uses a simple version of tag clouds to show common
keywords of documents that were clustered together.
WordBridge [Elmqvist and Ebert, 2011] combines tag
clouds with node-link diagrams in order to show the
details of relationships between the entities in text col-
lections. They use tag clouds to represent nodes and
IVAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonInformationVisualizationTheoryandApplications
196
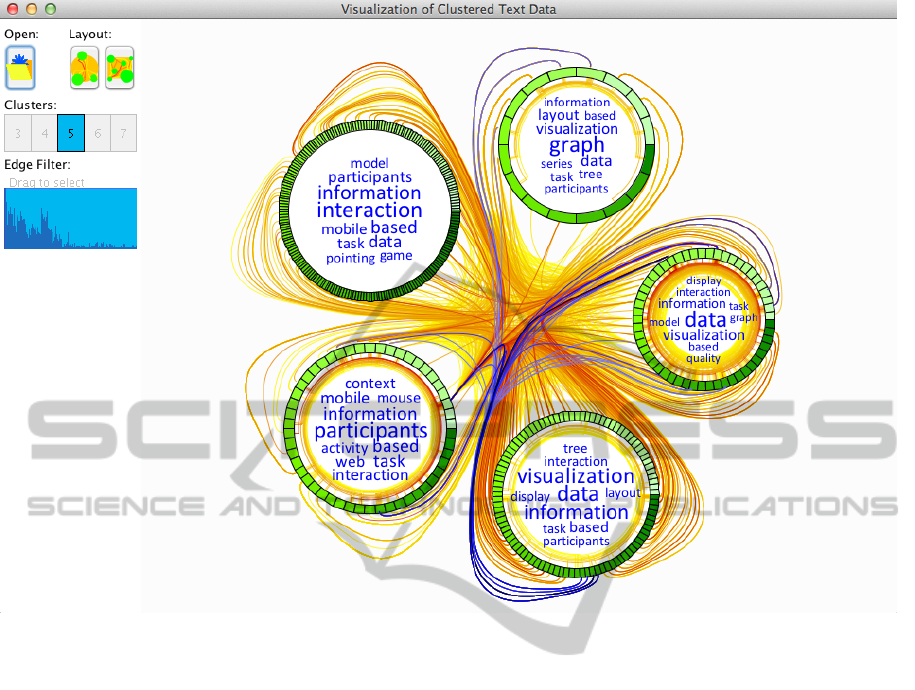
Figure 1: A screenshot of our implementation. The toolbox is placed on the left hand side: the first button is used for opening
data files, the next two buttons provide switching between two alternative cluster layouts, and the radio buttons (numbered
from 3 to 7) specify the number of desired clusters. The histogram shows the edge weight distribution, i.e., the x-axis
represents the weight and the y-axis the corresponding number of edges. It can be used to select ranges of edge weights. In
the main drawing area on the right hand side, the visualization of five distinct clusters is shown together with external edges
routed through the center (circular cluster layout). The edges are highlighted in blue color, if they are hovered (note that the
edge bundling algorithm may superimpose edges).
edges, but do not employ clustering techniques on the
data. A brief overview of state-of-the-art text visu-
alization techniques can be found in [Kerren et al.,
2012]. Another recent tool for text document analy-
sis is iVisClustering [Lee et al., 2012]. The system
focuses on the interactive analysis of clustered docu-
ments and uses multiple coordinated views to assist
the user refining the clustering results. While iVis-
Clustering is used for text document collections only,
our system could also be applied to general multivari-
ate networks.
Even with all the presented techniques at hand, the
visualization of multivariate networks is still a chal-
lenge. Our prototype supports the interactive explo-
ration of clustered multivariate data and the relation-
ships inside of and between clusters. Instead of show-
ing a complete node-link drawing of the multivari-
ate network at the beginning of the analysis, we de-
cided to show the resulting cluster graph directly. In
order to do this more efficiently, we have developed
a novel cluster visualization approach that combines
tag clouds with cluster graphs (Figure 1). As such,
our new layout integrates the original nodes and edges
into the visualization. The design and features of this
new approach are explained in the following section.
3 VISUALIZATION AND
INTERACTION TECHNIQUES
In this section, we present our main interaction and
visualization techniques. We start with a description
of the data set used to test our approach.
3.1 Example Data Set
Our tool was tested with a Jigsaw data set contain-
ing metadata for every IEEE InfoVis conference paper
from 1995 to 2011 as well as VAST papers from 2006
to 2011 [Jigsaw, 2011]. The papers themselves are
represented by (network) nodes, and co-authorship is
VisualExplorationofRelationshipsbetweenDocumentClusters
197
represented by links, i.e, if two papers share an author,
then their node representations are connected with an
edge. Both together form a co-authorship network.
The weight of an edge corresponds to the number
of shared authors. So-called concept terms [Jigsaw,
2011] describe the paper’s contents and are used as
node attributes. They are metadata that were identi-
fied by parsing the paper titles and abstracts. There-
fore, each (node) attribute in this data set has only
boolean values: one and zero, i.e., either a term exists
in a specific paper or not. In addition, the Jigsaw data
set provides more attributes, such as the publication
year for each paper.
3.2 Document and Cluster Visualization
After loading the data, the user is prompted to select
the desired attributes to be clustered and visualized
through a dialog box. In this way, one can filter out
uninteresting attributes in advance. Additionally, the
user can specify one specific node attribute (e.g., the
publication year) from the list of already chosen at-
tributes whose values should be mapped to the node
representations directly.
As stated in [Kerren and Schreiber, 2012], there
are several ways to integrate automatic analysis re-
sults into visualizations. For simplicity and the other
reasons described in Section 1, we decided to start
with the automatic analysis and to use its results for
the subsequent visualization (other architectural de-
signs of the tool are possible and useful depending on
the analysis tasks). After k-means clustering (the user
is able to choose an appropriate k), the network nodes
are arranged on the screen according to their cluster
membership. By referring to our example data set,
each paper is represented by a network node drawn
in form of a donut slice shape and placed on a cir-
cular layout. In consequence, all nodes that belong
to the same cluster build a node ring as depicted in
Figure 2. The nodes in this figure have been ordered
based on the preselected attribute value as described
above. Therefore, the saturation of the node color
(green) in the screenshot changes gradient-wise. Plac-
ing clusters in a circular layout is a common practice
in graph drawing, with one of the earliest works pre-
sented by [Kar et al., 1988]. This approach supports
the easy identification of clusters while showing the
overall network structure.
The weighted edges which represent co-
authorship between documents are drawn by using
curved lines with a yellow-to-red color gradient. The
gradient visualizes the number of authors shared
between two documents (edge weights) with yellow
being the lowest number of common co-authors (at
least one) and red the highest number (normalized
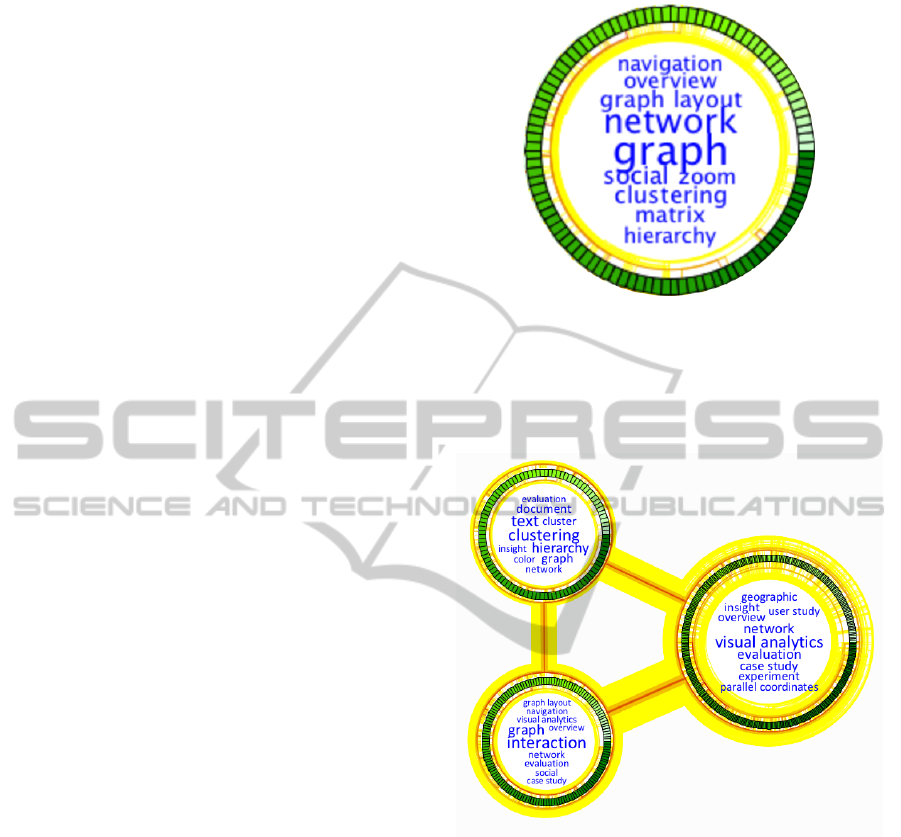
Figure 2: A cluster representation showing the nodes ar-
ranged radially. They are colored in green, and the color
saturation represents the value of any preselected attribute
(in this concrete case the publication year). The concept
terms of all nodes (papers) are arranged in the center. The
edges between these nodes are routed around the terms in
order to avoid overlaps.
Figure 3: Clusters visualized by using our free cluster lay-
out method (k = 3). External edges are partitioned into sev-
eral bundles in order to connect neighbored clusters (node
rings).
over a maximum number of common co-authors).
The edges have been routed inside of the node ring to
facilitate the drawing of the tag cloud that represents
the concept terms. This tag cloud gives insight into
the main concepts described in this particular group
of documents. Since we are dealing with text data in
this case, tag clouds are an intuitive choice of visual
metaphor. However, the cluster attributes can be
visualized using any appropriate metaphor without
modifying the general framework.
Figure 1 shows the graphical user interface (GUI)
of our implemented prototype. On the left hand side, a
toolbox featuring different controls is located. On the
right hand side, the main visualization view is visible.
IVAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonInformationVisualizationTheoryandApplications
198

Figure 4: A list of all documents is shown on the left. The selected document is highlighted in orange, while the documents
connected to it are highlighted in yellow. Those tags that are not associated with the selected document are faded out in the
corresponding node ring (the one at the top in our screenshot; k = 3).
It is possible to specify the number of desired clus-
ters through a user control. The clustered nodes are
drawn as previously described and placed in a circu-
lar layout with the edges bundled through the center
of the view. Because the edges originate and end at
data elements on the perimeter of the cluster nodes,
we retain information about both cluster connections
and element connections. Such inter-cluster edges are
called external edges while the edges within a single
cluster are called internal edges in the remainder of
this paper. External edges are color-coded based on
the edge weight in the same way as internal edges.
The edge routing within the circular arrangement
of the cluster rings might introduce visual clutter in
case the number of nodes and edges is very high.
Therefore, an interactive free cluster layout method
was added to avoid such issues. Here, the cluster rings
can be arranged manually, see Figure 3. We imple-
mented a different edge routing method for this layout
to reduce the visual complexity. All outgoing (exter-
nal) edges from a particular cluster are radially routed
outside the node ring to a specific control point that
leads them to other clusters and vice versa. In this
way, the two control points of neighbored node rings
(clusters) establish a kind of a beachhead. All pass-
ing external edges are bundled together in due con-
sideration of a specific order: the edges with the high-
est weight (i.e., links with most shared authors) are
placed in the middle of the bundle. Users can switch
between our two layouts by clicking the correspond-
ing icons located in the upper-right corner of the tool-
box (Figure 1). More details about the edge routing
for both layouts are given in Section 4.
3.3 Interaction Techniques
Several standard interaction techniques are supported
to facilitate the visual exploration in our prototype.
If the user selects a node, then the internal edges of
the corresponding cluster and all the external edges
that are not connected to the selected node are filtered
out. This is helpful for the identification of related
documents, i.e., all papers that share at least one au-
thor in our case. A tooltip with the document name
appears once the user hovers the mouse over a corre-
sponding node. Our software can also display a list
with all documents as shown in Figure 4. The se-
lected document is highlighted in orange. Tags not
found in the selected document will be faded out; the
present tags give a quick overview of the content of
the selected document. In the current version of our
implementation, the user has to follow the edges to
identify related papers and to select these to get the
corresponding concept terms. Our approach can be
easily extended to support the selection of several re-
lated nodes which would give the user the possibility
to see, for instance, common concept terms visualized
by the tag clouds.
Edge selection can be cumbersome when dealing
with a lot of edges routed through narrow areas as
VisualExplorationofRelationshipsbetweenDocumentClusters
199

seen in Figure 1. Therefore, we implemented a spe-
cific selection possibility when several edges are close
to the mouse cursor when a click action is performed.
Initially, all edges close to the mouse cursor are high-
lighted in blue as shown in Figure 1; optionally a
tooltip shows the number of highlighted edges. After
clicking, only these highlighted edges remain visible
and all other edges are filtered out. This operation can
be repeated consecutively until only one edge can be
selected. This usually does not require many clicks
until the view becomes uncluttered. The tooltip of the
remaining edge finally displays the shared authors be-
tween the two linked documents. A left mouse click
is used to cancel the selection (all edges are shown
again). Additionally, the user can filter out edges with
the help of the interactive histogram in the toolbox,
which shows the edge weight distribution (Figure 5)
and also mimics range sliders [Williamson and Shnei-
derman, 1992]. All edges with weights outside the
specified range are filtered out, reducing clutter. Our
interactive histogram provides insight about possible
interesting range selections that could be made simi-
lar to data visualization sliders [Eick, 1994]. As ex-
pected, most of the documents share exactly one au-
thor in our data set (cf. Figure 5).
Figure 5: A histogram shows the edge weight distribution.
It can also be used as selection tool of weight ranges. In this
particular example, the majority of edges have the weight 1,
i.e., the documents share one author.
Our visualization approach was tested using a net-
work comprised of 578 nodes. It is obvious that scal-
ability issues are introduced with the increasing num-
ber of nodes and/or clusters. We have not performed
experiments yet to find out what the maximum num-
ber of nodes and/or clusters is that users can analyze
with our approach. This will be part of our future
work.
4 TECHNICAL ASPECTS
In this section, a description of used tools and details
about our edge routing approaches are provided. Our
prototype is implemented in Java to guarantee a cer-
tain level of platform independence. For clustering
the attribute data, we used the k-means algorithm al-
though other clustering algorithms could be used as
well. We have integrated the clustering functionality
with the help of the trickl-cluster library which offers
several clustering algorithms that could be used alter-
natively [Trickl, 2011].
Quadratic B
´
ezier curves [Farin, 2002] were used
for the implementation of the edge routing for the cir-
cular cluster layout. A circular area through which
all external edges should pass is defined in the center
of the layout as exemplified in Figure 6 (the dashed
circle). The first couples of anchor points (P
0
, P
1
)
and (P
4
, P
5
) close to the node rings make sure that
the edges are connected to the nodes at a perpendic-
ular angle. Each node ring has a different diameter.
Therefore, the edges are drawn in such a way that they
do not stretch over a specific radius from the current
ring while going through the middle in order to avoid
edge crossings with neighboring rings. This is imple-
mented by using the anchor points P
2
and P
3
. Each
of them is specified as point of intersection between
a node ring tangent originating from the center of the
dashed circle and the circle itself.
Figure 6: The diagram exemplifies the edge routing ap-
proach in our circular cluster layout.
Figure 7: The diagram describes the edge routing in the free
cluster layout.
As indicated in the previous section, straight seg-
ments are used to connect the clusters in the free clus-
ter layout. However, the edges are routed around the
node rings in order to reach the straight line. The ap-
proach is schematically displayed in Figure 7. First,
a straight line is drawn from the node, i.e., from point
IVAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonInformationVisualizationTheoryandApplications
200

P
0
to point P
1
. From there, a circle segment is drawn
around the entire node ring up to the point P
2
. This
point and P
3
serve as beachheads between the two
rings and are connected with a new straight line. From
this point, the algorithm uses the same steps as ex-
plained for the first node ring. More implementation
details can be found in the thesis [Liu, 2013].
5 USE CASE
Our tool facilitates the local exploration of the con-
nectivity between documents grouped into clusters
and helps to get insight into the node attributes—in
our case concept terms of the documents belonging
to a particular cluster. For instance, a high number
of internal edges with high weight values might indi-
cate specific patterns, e.g., that groups of people have
been published together a high number of papers on
a specific topic as exemplified in the following. Dur-
ing the interactive exploration of our data set, we no-
ticed that only one group of three authors published
two papers in the same year. This can be seen af-
ter filtering out all papers in the same cluster with
less than three authors, compare Figure 8. One of
the internal edges is very short which gives us a hint
that these two papers were published in the same year
(because the two corresponding nodes have the same
green color). After the selection of one of the papers,
the unrelated concept terms are faded out. This gives
us insight into the content of the specified document
in context of the corresponding cluster. Here, the most
prominent concept term is “graph” as it is the largest
word in the tag cloud. The selected document has
this concept term and is not faded out. This shows
both: it has a strong connection to most of the cluster
members, and the authors of the aforementioned pa-
pers published work on graphs twice in the same year.
The selected paper is “MoleView: An Attribute and
Structure-Based Semantic Lens for Large Element-
Based Plots” by Telea, Hurter, and Ersoy published
at the InfoVis conference in 2011. The same au-
thors joined by Paulovich and Cantereiro published
the other paper in 2011 titled “Skeleton-Based Edge
Bundling for Graph Visualization” at the same con-
ference.
Another use case demonstrates the application of
our approach to show external relationships of nodes
in different clusters. By using our tool, we can easily
see that one of the nodes has a lot of external edges;
some of them have a high weight which connects this
node to two separate clusters. Again, edges with a
low number of co-authors were filtered out (Figure 9).
After selecting the corresponding paper (cf. the high-
Figure 8: A cluster with a selected node in orange color. It
shows that a relatively high number of co-authors published
two papers within the same area in the same year—the black
arrow points to the corresponding edge. The publication
year is represented by a green color gradient. Concept terms
that are not contained in the selected paper were faded out.
Figure 9: The screenshot shows the relation of a specific
selected document with other documents belonging to other
clusters (k = 3).
lighted paper in Cluster A), we are able to see that four
co-authors published papers together that were placed
in different clusters. The tag cloud indicates concept
terms of the selected paper. By clicking on the related
papers in the other node rings (Clusters A and B), it
turns out that the papers in the other rings have almost
no similarities in terms of tag clouds except for the tag
“interaction” (a pretty general concept term) which is
present in all the clusters involved in our case. The
selected paper in Figure 9 (Cluster A) is “Comparing
Different Levels of Interaction Constraints for Deriv-
ing Visual Problem Isomorphs” where the “visual an-
alytics” concept term is prominently displayed. This
is an indicator for the VAST conference where the pa-
per was presented in 2010. The authors of this pa-
per are Ribarsky, Chang, Dou, Ziemkiewicz, Jeong,
VisualExplorationofRelationshipsbetweenDocumentClusters
201

Harrison, Ryan, and Wang. From these, Wang, Dou,
Ribarsky, and Chang co-authored the paper “Parallel-
Topics: A Probabilistic Approach to Exploring Doc-
ument Collections” shown in Cluster B and related
to text and document visualization. The other paper
“Evaluating the Relationship Between User Interac-
tion and Financial Visual Analysis”—shown on the
lower right hand side (Cluster C) of Figure 9—was
written by Jeong, Dou, Chang, Ribarsky, Lipford, and
Stukes and published in 2008 at the VAST confer-
ence as well. This shows that a group of authors has
worked together in various topics of visual analytics
since their papers are found in different clusters, but
they are related to each other.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
A set of new techniques for the visual analysis of mul-
tivariate network clusters has been presented in this
paper. They facilitate the exploration of clustered data
by (1) showing the cluster content through the use of
tag clouds and (2) giving insight into the underlying
network through the use of two different cluster lay-
out techniques and edge routing algorithms. The anal-
ysis process is enriched with various interaction tech-
niques, such as interactive edge filtering.
There are several improvements that could further
strengthen our prototype. At the moment, only one at-
tribute can be mapped to the nodes. By simply adding
more donut slices on top of the existing node ring and
using different colors, it is possible to visualize more
attributes. This approach might be limited, because
the size of the node rings will increase. Another im-
provement would be to introduce standard zooming
and panning. At the current state, our implementa-
tion does not allow this due to the Java 2D graphics
renderer performance. Therefore, we have to port the
application to OpenGL. The edge routing algorithm
in the circular cluster layout can be improved by rout-
ing the edges directly between cluster neighbors. This
will help to reduce clutter in the center, but it might
introduce a lot of additional edge crossings around
the clusters. Another possibility for clutter reduction
is to display the most interesting edges first (subject
to user defined parameters) and to add more on de-
mand. The current interaction possibilities have to be
extended, for instance, by multiple selection of nodes
in order to provide comparisons of the concept terms
between related documents inside and outside of the
same cluster. Last but not least, we have to evaluate
our approach with respect to usability, efficiency, and
scalability.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Alfredo Gimenez for carefully
proof-reading the final version of this paper.
REFERENCES
Archambault, D., Munzner, T., and Auber, D. (2008).
GrouseFlocks: Steerable exploration of graph hier-
archy space. Visualization and Computer Graphics,
IEEE Transactions on, 14(4):900 –913.
Archambault, D., Munzner, T., and Auber, D. (2009).
TugGraph: Path-preserving hierarchies for browsing
proximity and paths in graphs. In Visualization Sym-
posium, 2009. PacificVis ’09. IEEE Pacific, pages 113
–120.
Bezerianos, A., Chevalier, F., Dragicevic, P., Elmqvist, N.,
and Fekete, J.-D. (2010). GraphDice: A system for
exploring multivariate social networks. Computer
Graphics Forum (Proc. EuroVis 2010), 29(3):863–
872.
Borisjuk, L., Hajirezaei, M.-R., Klukas, C., Rolletschek, H.,
and Schreiber, F. (2005). Integrating data from biolog-
ical experiments into metabolic networks with the dbe
information system. In Silico Biol, 5(2):93–102.
Dunne, C., Riche, N. H., Lee, B., Metoyer, R., and Robert-
son, G. (2012). GraphTrail: Analyzing large multi-
variate, heterogeneous networks while supporting ex-
ploration history. In Proceedings of the ACM Confer-
ence on Human Factors in Computer Systems, pages
1663–1672.
Eick, S. G. (1994). Data visualization sliders. In Proceed-
ings of the 7th annual ACM symposium on User inter-
face software and technology, UIST ’94, pages 119–
120, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Elmqvist, N. and Ebert, D. S. (2011). WordBridge: Using
composite tag clouds in node-link diagrams for visual-
izing content and relations in text corpora. 2011 44th
Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences,
pages 1–8.
Farin, G. (2002). Curves and Surfaces for CAGD: A Prac-
tical Guide. Morgan-Kaufmann, 5th edition.
Ghani, S., Chul Kwon, B., Lee, S., Yi, J., and Elmqvist,
N. (2013). Visual analytics for multimodal social net-
work analysis: A design study with social scientists.
In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer
Graphics.
Henry, N., Fekete, J.-D., and McGuffin, M. J. (2007). Node-
Trix: a hybrid visualization of social networks. IEEE
Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graph-
ics, 13:1302–1309.
Jigsaw (2011). Visual Analytics for Exploring and Under-
standing Document Collections. http://www.cc.
gatech.edu/gvu/ii/jigsaw/datafiles.html,
last accessed: 2013-02-15.
Jusufi, I., Dingjie, Y., and Kerren, A. (2010). The network
lens: Interactive exploration of multivariate networks
using visual filtering. In Information Visualisation
IVAPP2014-InternationalConferenceonInformationVisualizationTheoryandApplications
202

(IV), 2010 14th International Conference, pages 35 –
42.
Jusufi, I., Kerren, A., and Zimmer, B. (2013). Multivariate
network exploration with JauntyNets. In Proceedings
of the 17th International Conference on Information
Visualisation (IV ’13), pages 19–27.
Kar, G., Madden, B., and Gilbert, R. (1988). Heuristic lay-
out algorithms for network management presentation
services. Network, IEEE, 2(6):29–36.
Kaser, O. and Lemire, D. (2007). Tag-cloud drawing: Al-
gorithms for cloud visualization. Proceedings of Tag-
ging and Metadata for Social Information Organiza-
tion (WWW ’07).
Kerren, A., Kyusakova, M., and Paradis, C. (2012). From
culture to text to interactive visualization of wine re-
views. In Marchese, F. T. and Banissi, E., editors,
Knowledge Visualization Currents: From Text to Art
to Culture, chapter 5, pages 85–110. Springer, Oxford.
Kerren, A., Purchase, H., and Ward, M. O. (2013). Informa-
tion Visualization - Towards Multivariate Network Vi-
sualization (Dagstuhl Seminar 13201). Dagstuhl Re-
ports, 3(5):19–42.
Kerren, A. and Schreiber, F. (2012). Toward the role of
interaction in visual analytics. In Proceedings of
the Winter Simulation Conference, WSC ’12, pages
420:1–420:13. Winter Simulation Conference.
Koh, K., Lee, B., Kim, B., and Seo, J. (2010). ManiWor-
dle: Providing flexible control over Wordle. IEEE
Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graph-
ics, 16:1190–1197.
Lee, H., Kihm, J., Choo, J., Stasko, J., and Park, H. (2012).
iVisClustering: An interactive visual document clus-
tering via topic modeling. Computer Graphics Forum,
31:1155–1164.
Liu, J. (2013). Visualization of relationships in clustered
text data. Master’s thesis, Linnaeus University, De-
partment of Computer Science, V
¨
axj
¨
o, Sweden.
Mirkin, B. (2005). Clustering for Data Mining: A Data Re-
covery Approach. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Ra-
ton, FL, USA.
Paulovich, F. V., Toledo, F. M. B., Telles, G. P., Minghim,
R., and Nonato, L. G. (2012). Semantic wordifica-
tion of document collections. Comp. Graph. Forum,
31(3):1145–1153.
Pretorius, A. J. and van Wijk, J. J. (2007). Bridging the
semantic gap: Visualizing transition graphs with user-
defined diagrams. Computer Graphics and Applica-
tions, IEEE, 27(5):58 –66.
Pretorius, A. J. and van Wijk, J. J. (2008). Visual inspec-
tion of multivariate graphs. Comput. Graph. Forum,
27(3):967–974.
Shneiderman, B. (1996). The eyes have it: a task by
data type taxonomy for information visualizations. In
Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Visual Lan-
guages, 1996, pages 336–343.
Shneiderman, B. and Aris, A. (2006). Network visualiza-
tion by semantic substrates. IEEE Transactions on Vi-
sualization and Computer Graphics, 12:733–740.
Trickl (2011). trickl-cluster. https://github.com/
trickl/trickl-cluster, last accessed: 2013-02-
15.
Viegas, F., Wattenberg, M., and Feinberg, J. (2009). Partic-
ipatory visualization with Wordle. IEEE Transactions
on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 15:1137–
1144.
Wattenberg, M. (2006). Visual exploration of multivari-
ate graphs. In CHI ’06: Proceedings of the SIGCHI
conference on Human Factors in computing systems,
pages 811–819, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Williamson, C. and Shneiderman, B. (1992). The dynamic
homefinder: evaluating dynamic queries in a real-
estate information exploration system. In Proceedings
of the 15th annual international ACM SIGIR confer-
ence on Research and development in information re-
trieval, SIGIR ’92, pages 338–346, New York, NY,
USA. ACM.
Wu, Y. and Takatsuka, M. (2006). Visualizing multivariate
network on the surface of a sphere. In Asia Pacific
Symposium on Information Visualisation, pages 77–
83.
VisualExplorationofRelationshipsbetweenDocumentClusters
203
