
Arduino based System for Indoor and Outdoor ECG Monitoring
Functions and Extended User Model Ontology
Carmelo Pino and Alfio Costanzo
Department of Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering,
University of Catania, Viale Andrea Doria 6, Catania, 95125, Italy
Keywords: Health Monitoring Systems, Arduino Shields, ECG Sensors, General User Model Ontology.
Abstract: In this paper a system for monitoring the environment and biometric parameters like ECG for cardiac
patients is presented. Monitoring Health Environment can be considered important like monitoring the
patient in direct way. In this paper we propose an architecture consisting of a sensors network to monitor the
patient environment in conjunction with other biometric parameters like ECG with the aim to control the
health status in outdoor and indoor conditions. The monitoring system makes use of different sensors such
as: oxygen level, air quality, humidity, temperature, ECG, integrated with an Arduino controller. The
observed data are sent via GPRS or Wi-Fi to a server to activate the regulation of the environment
conditions. Patient environment and health status can be monitored in remote way by mobile thanks to a
specific App.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays monitoring the patient during its daily
activities represents an essential tool in order to
understand her/his health status (Cho, 2010),
(Gargiulo, 2010). Some typology of patients spends
most of the day at home, and consequently
monitoring the environment conditions can be useful
to enrich the set of information about the patient
status.
Patient status depends on different factors
dealing with the specific pathology, but often
environmental conditions could affect the patient
health too.
Usually in the telemedicine applications (Xie,
2010), each patient is monitored by a specific sensor
to collect data and by a communication module to
send the biometric data to a remote center. Data
received are passed to a doctor to check if the
patient conditions are critical and to plan the
required intervention.
Often a first intervention can be done by simply
modifying the environmental conditions (e.g.,
improving the oxygen concentration, modulating the
room temperature, humidity or light conditions,
etc.). For this reason, in the telemedicine projects
we find an increase of systems for remote patient
monitoring, portal equipment and specific homecare
devices (Cho, 2010).
The idea behind this work is related to the
creation of a system that allows us to carry our an
indoor monitoring of the patient health status by
using the proper biometric and environment sensors
with the aim of regulating the environment
conditions when needed. Also, patients in outdoor
condition are monitored to plan first aid rescue or to
suggest suitable actions in case the patient status is
becoming critical. In the latter case, we will take into
account weather and traffic conditions so that the
patient decisions or the external interventions may
take into account of both the patient ambient and the
urban context in which s/he is located.
Although the methodology may be used to
monitor the patient affected by any pathology, in the
paper we take into account cardiac patients since
they represent a suitable field of application of the
proposed approach. The system architecture to
monitor the environment temperature, humidity, air
condition and oxygen concentration has been
developed by using an Arduino controller provided
with the appropriate set of shields and it is described
in a companion paper, whereas the sensors in order
to measure the patient ECG in both indoor and
outdoor conditions are illustrated in this paper.
The requirement of accessing the user data from
any remote computing system to plan the right
331
Pino C. and Costanzo A..
Arduino based System for Indoor and Outdoor ECG Monitoring - Functions and Extended User Model Ontology.
DOI: 10.5220/0004762203310335
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Physiological Computing Systems (PhyCS-2014), pages 331-335
ISBN: 978-989-758-006-2
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
interventions is fulfilled by using a suitable extended
user ontology, named GUMO+, proposed in
(Costanzo, 2013) consisting of all the personal and
context data useful for supporting the needed health
assistance systems in either indoor and outdoor
conditions. In the next section, details about the
system architecture and functionalities are given,
whereas in sect. 3 hardware materials and the
implementation methodology are pointed out. Sect.4
briefly describes how the mentioned extended user
model ontology may be used for implementing the
open and interoperable data organization needed for
an effective ubiquitous health assistance system. In
the concluding remarks, a comparison with similar
works is done and ideas for future developments are
given.
2 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
AND MAIN FUNCTIONS
The proposed system is based on a network of
sensors connected to an Arduino controller. The set
of sensors has been chosen to monitor the
environmental conditions and the cardiac patient
conditions. For this aims we have used:
Sensors for biometric data acquisition, in
particular for ECG acquisition (Celler, 2003). The
ECG is acquired through specific electrodes
connected to the patient in order to retrieve
pulsation and possible critical situations (e.g.
Tachycardia, arrhythmia, etc.). The electrodes are
connected to a module that can be brought by the
patient in a pocket. Data collected by the ECG
sensors are transmitted via GPRS or Wi-Fi to a
server.
Sensors for environmental data acquisition, in
particular for: oxygen concentration, air quality,
temperature, and humidity. This set of sensors is
positioned in different room of the patient house.
Actuators: the actuators are used to interact with
the devices present into the patient house, in
particular we recognize the actuator for aeration
conductors, heating boiler, and dehumidifier.
The architecture supports indoor and outdoor
scenarios:
Indoor: in this first scenario we assume that the
patient is at home and the information about the
ECG are combined with information coming from
the other environment sensors positioned in each
room.
Outdoor: in this second scenario we assume that
the patient is outside the home, and then only the
data about ECG are considered, whereas a GPS
module is used to identify the position and
relative speed of the patient. In the outdoor
scenario not only this information to understand
the correlation between the patient speed and
number of pulse is used but also the car traffic and
weather data stored on the city server to better
plan the patient rescue.
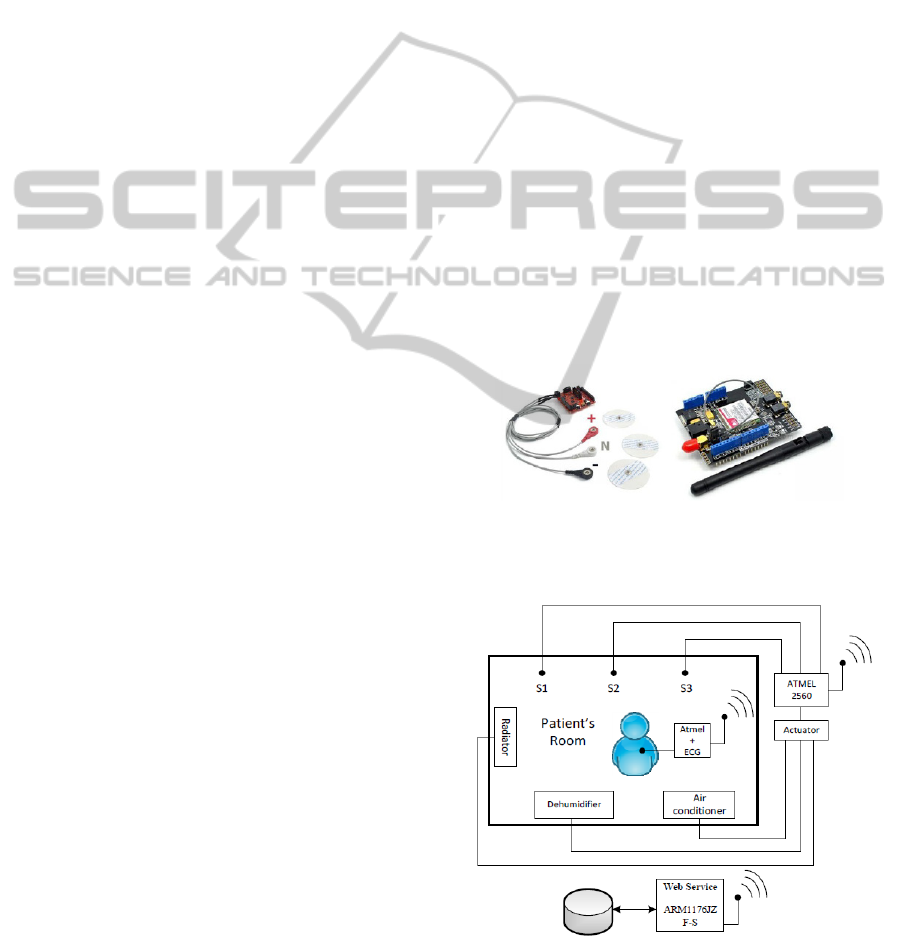
Data collected from the sensors with an Arduino
module (fig. 1), are stored in a micro SD according
to the mentioned GUMO+, i.e., the user ontology,
named GUMO (Heckmann, 2005), powered by a
mobility ontology, e.g., (Faro, 2003), and
successively sent to a microcontroller that works like
a Web Service (WS) (see fig. 2).
The Web Service receives the data and returns
the response to the actuators drawn in fig. 2 to
modify the environment conditions. In particular, the
data coming from the sensors S1, S2 and S3 dealing
with humidity, temperature and luminosity are
collected by the Arduino (ATMEL 2560) and sent to
the WS through the GPRS module. Each home
device influencing the environment conditions (e.g.,
radiator, dehumidifier, air conditioner) is actuated
when needed.
Figure 1: ECG with the acquisition shield (left) and the
GPRS shield for data communication (right) used in the
implementation.
Figure 2: Indoor Monitoring System Architecture.
Different combinations of data coming from the
PhyCS2014-InternationalConferenceonPhysiologicalComputingSystems
332

sensors can be considered as critical conditions.
With the term “critical conditions” we mean all the
situations in which a patient could be in hazardous
health conditions. Indoor and outdoor thresholds to
delimit the normal conditions are as follows
(Basilakis, 2007):
Indoor - a) Relaxation State: 100 bpm with a
speed less than 10 Km/h; b) Sustained Activity: 150
bpm with a speed greater than 10 Km/h.
Outdoor - a) Humidity: 100 bpm and humidity
greater than 30%; b) Oxygen concentration: 150
bpm and oxygen concentration less of 18%. c)
Temperature: if temperature is greater than 26 C°
and the pulse is less than 80 bmp.
When one of the thresholds is exceeded an SMS
or an alert message is sent to relatives, doctor or
hospital first aid service that may access the Web
Service to evaluate the situation.
3 HW MATERIALS AND SW
IMPLEMENTATION
The architecture consists of different hardware and
software modules. HW modules are as follows: a)
Arduino Mega 2560, a microcontroller based on
ATMEGA2560, b) E-Health Shield is an Arduino
compatible board that allows us for health
monitoring. It’s has different types of sensors such
as pulse, oxygen in the blood, respiration, body
temperature, ECG, glucometer, pressure, patient
position, c) GPRS and GPS Shields, and d)
Raspberry Pi
single-board computer with a 700 MHz
processor and a GPU.
The software modules implement the
functionalities illustrated in the previous sections,
i.e.: a) Software for ATMEL 2560 implemented on
the Arduino Mega for the acquisition of the data
coming from the sensors and for controlling the
environmental devices, and b) Software for ECG to
collect the data coming from the ECG sensors that
are worn by the patient. The acquired data are sent
by a GPRS module to the Web Service.
The Web Service has been developed to offer a
suitable processing data service due to the low
processing capabilities of the Arduino mega shield.
The data coming from the Arduino mega shield are
sent in JSON format to WS where they are stored in
XML/RDF format as shown in fig. 3 so that the
patient data base could interoperate with other
authorized applications. Also, the Web Service is
able to process the data in order to automatically
change the environment conditions and manage any
critical cardiac situation.
Figure 3: Example of JSON code for both Outdoor and
Indoor scenarios.
Smartphone APPs allow the patient to monitor
her/his health status and the doctor to monitor the
patient at distance using a mobile. Fig.4-left shows
the APP interface that allows the user to visualize
the data coming from each sensor and to fine control
the environment conditions.
Figure 4: APP functions (left) and ECG displayed on
mobile.
The circuit used by the Arduino system to measure
the environmental conditions is illustrated in a
companion paper (Costanzo, 2014), whereas the
ECG may be displayed on the mobile as shown in
fig.4-right using a specific APP visualization
procedure.
4 EXTENDED USER MODEL
ONTOLOGY FOR E-HEALTH
All the data coming from the Arduino based sensors
are coded in JSON. However, to allow the collected
data to be used by any remote software applications
it is necessary to adopt a standard codification
system and an agreed ontology, i.e., a shared
semantics about the terms used in the e-health
application and their properties. For this reason, the
data are converted into XML/RDF format and are
organized according to the general user model
ArduinobasedSystemforIndoorandOutdoorECGMonitoring-FunctionsandExtendedUserModelOntology
333
ontology (GUMO) shown in fig.5.
Figure 5: Extended user model ontology GUMO+.
In particular the biometric data follow the
terminology of the physiology section, whereas the
indoor and outdoor environment data are coded
according to the section environment. Other GUMO
sections of interest of our e-health application are
the current state and location. The former to know
how the status of the user (current task, activity and
possible disease) evolves over the time, the latter to
know in which road s/he is driving/waking or in
which room s/he is located.
However, the need of mobility information to
implement an effective user health assistance,
implies that the GUMO sections should be extended
to include information about the car traffic and the
available health services at urban scale such as
hospitals, and first aid centers. For this reason,
further sections were added to GUMO dealing with
Traffic and Services as illustrated by the extended
GUMO, named GUMO+, drawn in fig.5.
Fig.6 shows a sample of representation of data of
user interest in XML/RDF format according to the
mentioned GUMO+ sections. Therefore, after
collecting the user data according to proprietary
protocols and formats, the monitoring systems
should convert them in real time in standard formats
so that all the collected data may used by the
software processes resident on other computing
systems to suggest to the users the most suitable
actions depending on the current state and to plan
the right first aid services in case of sudden illness.
Figure 6: XML/RDF representation of data for e-Health.
Figure 7: Optimal path to be followed by an ambulance for
timely rescuing a people.
In this way, any mobile software may access the
data that will be provided to the users by using
GUMO+
People to rescue
Ambulance
Center
Hospital
PhyCS2014-InternationalConferenceonPhysiologicalComputingSystems
334

Google maps based applications to display the
nearest hospital to the patients which are able to
drive or to walk, otherwise, the health assistance
software should send the best path for the patient
rescue, as illustrated in (Faro, 2008-2011), to the
ambulance if the patient is in critical conditions as
shown in fig.7. We plan to integrate the proposed
system in the city information architecture named
Wi-City (Costanzo, 2013) to offer a complete
assistance to mobile people.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this work a simple and cheap system to monitor at
distance the cardiac status of a patient during her/his
daily life has been presented. The system is provided
with wearable sensors for cardiac data detection
(ECG) (Costanzo, 2014). Correlating data from
multiple sources allows the system to identify the
more appropriate actions for the patient health
status. Before activating the interventions of the
rescuers, the system regulates the indoor
environmental conditions by using sensors to
measure indoor conditions and domotic equipments.
In the paper we taken into account only cardiac
sensors, but other wearable sensors have been added
to the proposed architecture, thus increasing the
pathologies the system can manage, e.g., in the
mentioned companion paper, a similar system to
measure blood pressure and respiration rate with a
portable system is illustrated.
In the future the proposed e-health assistant will
be able to monitor other types of relevant
information e.g. emotional status that will be
identified with specific wearable sensors, such
galvanic skin response, and by recognizing facial
features by computer vision techniques (Faro, 2006),
(Radhakrishnan, 2013) even in noisy context
(Cannavò, 2006), (Crisafi, 2008).
REFERENCES
Basilakis J., N. H. Lovell, and B. G. Celler, "A decision
support architecture for telecare patient management
of chronic and complex Disease," in Proc. 29th
Annual Int. Conf. of IEEE Engineering in Medicine
and Biology Society, pp. 4335-4338, 2007.
Cannavò F., G. Nunnari, D. Giordano, C. Spampinato,
Variational Method for Image Denoising by
Distributed Genetic Algorithms on GRID
Environment. Workshops on Enabling Technologies:
Infrastructure for Collaborative Enterprises, WETICE
'06. 227-234, IEEE, 2006.
Celler B. G., N. H. Lovell, and J. Basilakis, "Using
information technology to improve the management of
chronic disease," The Medical journal of Australia,
vol. 179, pp. 242-246, 2003.
Cho, S., Jo, H., Jang, S., Park, J., Jung, H. J., Yun, C. B.,
Spencer, Jr., B.F . and Seo, J., “Structural health
monitoring of a cable-stayed bridge using smart
sensor technology: data analysis”, Smart Struct. Syst.,
6(5-6), 461-480, 2010.
Costanzo A., A. Faro, D. Giordano, Towards Open and
Interoperable Information Platforms for Mobile
Users: RDF Methodology and Case Study, AICT 13,
Baku, 2013.
Costanzo A., A. Faro, D. Giordano, Wi-City: living,
deciding and planning using mobiles in Intelligent
Cities , 3rd International Conference on Pervasive
and Embedded Computing and Communication
Systems, PECCS13, Barcelona, INSTICC, 2013.
Costanzo A., C. Pino, A Portable Arduino based Health
Monitoring System for Elderly People Living at Home.
Submitted to PhyCS 2014, Lisbon.
Crisafi A., Giordano D., Spampinato C., GRIPLAB 1.0:
Grid Image Processing Laboratory for Distributed
Machine Vision Applications. Proc. Int. Workshop on
Enabling Technologies: Infrastructure for
Collaborative Enterprises, WETICE '08. 188-191,
IEEE, 2008.
Faro A., D. Giordano, A. Musarra, Ontology Based
Mobility Information Systems. Proc. of IEEE Systems,
Men and Cybernetics SMC03, vol.3, 4288-4293, 2003.
Faro A., D. Giordano, C. Spampinato, Integrating
Location Tracking, Traffic Monitoring and Semantics
in a Layered ITS Architecture. Intelligent Transport
Systems, vol.5(3), 197-206, 2011.
Faro A., D. Giordano, C. Spampinato, Evaluation of the
traffic parameters in a metropolitan area by fusing
visual perceptions and CNN processing of webcam
images, IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks, Vol.19(6),
pp.1108-1129, 2008.
Faro A., D. Giordano, C. Spampinato, An automated tool
for face recognition using visual attention and active
shape models analysis, Proc. 28th Annual
International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in
Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS'06, 2006.
Gargiulo G., et. al., “Wearable dry sensors with bluetooth
connection for use in remote patient monitoring
systems”. Global Telehealt, 2010.
Heckmann D., et al., GUMO, the General User Model
Ontology, LNCS, N.3538, Springer, 2005.
Radhakrishnan K., et al., “Use of a homecare electronic
health record to find associations between patient
characteristics and re-hospitalizations in patients with
heart failure using telehealth”. J Telemed Telecare,
2013.
Xie Y., et. al, Lovell Effect of ECG Quality Measures on
Piecewise- Linear Trend Detection for Telehealth
Decision Support System, Annual Conference,
Proceedings of the Annual International Conference
of the IEEE EMBS, 2010.
ArduinobasedSystemforIndoorandOutdoorECGMonitoring-FunctionsandExtendedUserModelOntology
335
