
Teachers Can Be Involved in the Design of Location-based Learning
Games
The Use of the Puzzle Board Metaphor
Javier Melero, Davinia Hernández-Leo and Josep Blat
Department of Information and Communication Technologies, Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Barcelona, Spain
Keywords: M-learning, Game-based Learning, Puzzle-based Games, Location-based Games, Instructional Design
Strategy, Game Design Task.
Abstract: Recent research in the Game-Based Learning domain shows that location-based games can lead to positive
effects in students’ motivation and engagement. However, the potential effectiveness of these approaches
depends on to what extent their design is aligned with the requirements of specific educational situations.
For this reason, involving teachers in the design of their own location-based learning games becomes crucial
to fulfil their teaching requirements. This paper presents a metaphor based on puzzle boards as a technique
to involve teachers in the design of their own location-based games. A design-based research methodology
has been followed to evaluate the proposed metaphor. Previous research experiments have shown the
feasibility of the puzzle-based games approach to allow secondary education teachers the design of these
types of learning experiences. However, some issues in terms of understanding specific elements of the
proposed metaphor were detected. A second iteration of the research methodology is described in the paper
to evaluate the changes made to the definitions of the metaphor’s elements and the dynamics of the game
design task. The evaluation is carried out with 20 primary and secondary education teachers who completed
a paper-based design task. The main findings show that teachers did not have problems using the proposed
metaphor and they successfully designed their own location-based learning games.
1 INTRODUCTION
Over the past few years, handle devices have
enabled learning situations that were hindered in the
past by time and spatial limitations (Jones and Jo,
2004). These mobile technologies have brought the
possibility to enhance learning and promote the
creation of situated learning activities. In fact,
mobile learning (m-learning) is an emerging field of
educational research that is starting to attract the
interest of practitioners in all phases of education to
facilitate learning in informal settings within formal
educational contexts (Bachmair et al., 2010). Most
of these m-learning activities are characterised by
integrating elements based on games (Bohannon,
2010). This leads to the creation of location-based
games (Davis, 2002), based on mobile technology to
implement pervasive and ubiquitous experiences.
Location-based games bring opportunities to: create
learning experiences that involve exploration and
cooperation (Hwang et al., 2008); access to
contextualized information, communication, analysis
and interrelation of real place (Roschelle, 2003);
entertain and increase students’ motivation towards
learning (Davis, 2002; Yatani, 2004).
In order to create meaningful location-based
learning games, it is important that they are aligned
with the requirements of specific educational
situations. In this line, it becomes crucial to involve
teachers in the design of game-based learning
activities (Tornero et al., 2010). However, teachers
are faced with the difficulty to set these approaches
so they fit into the educational process and the
accomplishment of the pursued learning objectives
(Tornero et al., 2010; van Rosmalen et al., 2011).
Besides, the support by teachers is not
straightforward, and the limited experience of
teachers severely reduces the amount and quality of
feedback a learner might receive. In this line,
providing scaffolding strategies could be significant
to foster the involvement of teachers in the design
and implementation of their own location-based
learning games. In general, scaffolding techniques
involve different type of processes (e.g.: coaching
179
Melero J., Hernández-Leo D. and Blat J..
Teachers Can Be Involved in the Design of Location-based Learning Games - The Use of the Puzzle Board Metaphor.
DOI: 10.5220/0004777301790186
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2014), pages 179-186
ISBN: 978-989-758-022-2
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

through prompts, templates, guides or strategies)
that teachers implement to support students in
problem solving activities whose goals would be
beyond their unassisted efforts (Wood et al., 1976).
Particularly, this paper focuses on providing a
strategy that could scaffold teachers in the design
process of their own location-based learning games.
With the aim of facilitating teachers in the design
of location-based learning games, a metaphor based
on puzzle boards has been proposed (Melero et al.,
2013). The metaphor simplifies a model for
designing computing-supported puzzle-based games
(Melero & Hernández-Leo, accepted). In this
context, metaphors have been widely used as well-
known concepts that facilitate reasoning about
design in unfamiliar contexts (Lakoff, 1993).
Besides, the use of puzzle game boards seem to offer
a strategy to feasibly involve participants as game
designers (Huang et al., 2007). Also, the structural
design of location-based games is often inspired by
board games (Nicklas, 2001; Schlieder et al., 2006).
However, there are not research evidences on
involving teachers in the design of location-based
learning games considering puzzle game boards as a
design strategy.
The originality of this paper relies on considering
elements of traditional puzzle boards as a design
technique to create location-based games. The
remainder of the paper is structured as follows.
Section 2 presents an overview of the proposed
approach to design location-based games. Section 3
describes the research methodology to evaluate the
puzzle board metaphor. Section 4 describes the
workshop in which the teachers used the proposed
metaphor to design their own location-based games.
The main findings obtained from the analysis of the
teachers’ opinions and designs are reported in
Section 5. Then, Section 6 is devoted to a discussion
of the findings presented in this paper. Finally,
Section 7 concludes with the main highlights
obtained from the results and future research lines.
2 THE PUZZLE BOARD
METAPHOR
A puzzle board metaphor has been proposed (Melero
et al., 2013) as a design technique to facilitate
teachers the creation of location-based games. This
metaphor considers a conceptual model for creating
computer-supported puzzle-based games (Melero
and Hernández-Leo, accepted). An exploratory user
study involving teachers from secondary and higher
education were also described in (Melero and
Hernández-Leo, accepted). Some of the findings
revealed the need of providing a strategy to support
teachers the creation of devoted environments.
Then, the aim of the proposed metaphor is to
facilitate teachers the design of location-based
learning games that are mainly characterised by
containing routes of geolocated questions. As
described in (Bontchev and Vassileva, 2010), these
games consist in presenting quizzes in map where
knowledge from course material is taught in a safe
navigation.
In order to design location-based games of
geolocated questions, the puzzle board metaphor
considers the following elements (see Figure 1):
Figure 1: Representation of the puzzle board metaphor.
The “board” is the physical space where the
questions are located.
The “slots” are the different questions, while the
“pieces” are the options associated to a question.
Just one “piece” can fit in a concrete “slot”,
meaning that there is only a correct option for
each question.
A “board” with a set of “slots” and the associated
“pieces” forms the “puzzle”.
Several “puzzles” can be defined in a location-
based learning game. Each puzzle has to be
associated to a “level”. A designer can define as
different “levels” as he/she wants.
Several “scoring” mechanisms can be defined to
reflect the students’ performance: a) correct
answers add points to the overall player’s score,
b) incorrect answers subtract points the overall
player’s score, and c) consulting hints subtract
points the overall player’s score.
Scoring can have associated a “feedback” to
specific range of points in order to describe to
the students their performance.
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
180

An extra “bonus” of points can be also designed
whether all the questions for a given level have
been correctly answered. The extra bonus is a
reward to engage and encourage students to
correctly complete the different puzzles of the
whole learning activity.
Finally, “hints” can be provided in order to avoid
frustrations and advance forward the location-
based learning game.
3 METHODOLOGY
A design-based research (Barab and Squire, 2004)
methodology has been followed to evaluate the
puzzle board metaphor. Overall, this research
methodology involves a continuous cycle of design,
enactment, analysis, and redesign. The cycle of this
research methodology involves revisions to test and
refine a proposed innovative learning approach. This
iterative process permits not only to validate the
findings of the analysis phase, but also to reflect on
how these findings alter the outcomes of the other
phases (Barab and Squire, 2004).
A first iteration involved four experiments with
11 secondary education teachers that became
designers of their own location-based games. The
first iteration has reported the feasibility of applying
the proposed approach in real learning contexts
(Melero et al., 2013; Melero and Hernández-Leo,
accepted). Besides, the resulted designs of the
location-based learning games were implemented in
“QuesTInSitu: The Game”, a mobile aplication
compliant with the conceptual model presented in
(Melero and Hernández-Leo, accepted). In concrete,
the four experiments consisted of: a) an
extracurricular activity with the purpose of
discovering and learning about the city where the
school is placed; b) an activity associated to
formatively assess their students in the art history of
a city; c) an activity also with the aim of enquiring
about the heritage and the city where the school is
located; and d) an activity to practise the concepts
associated to different pictures of a museum of
contemporary art. Results showed that the different
teachers were able to design their own activities, but
some issues were detected: 1) a need of devoting
more time in the explanation and provision of more
examples in relation to the puzzle board metaphor;
and 2) a reformulation in the definition of the “level”
element, indicating that it may typically refer to
specific physical zones or geographical areas (not
only difficulty).
Thus, this paper presents a second iteration of the
research methodology to gain more insights about
the use of the puzzle board metaphor. To this end, a
workshop session was conducted involving 20
primary and secondary education teachers in a game
design task. The aim was to evaluate some changes
taking into account the aforementioned
considerations. The evaluation was focused on
analysing the acceptance of the proposed puzzle
board metaphor by the teachers, and the feasibility
of using this approach to create location-based
games for different educational purposes and
education levels (not only secondary education, as in
the first iteration).
4 GAME DESIGN PROCESS
A 4-hour workshop was carried out to evaluate the
puzzle board metaphor with different teachers. Upon
an open call for participation via the network for
educational telematics of Catalonia (http://
www.xtec.cat), 20 primary and secondary education
teachers from different schools and not familiar with
designing location-based games participated in the
workshop. The session was divided as follows:
Introduction (30 min). First, we introduced the
context of the workshop focused on designing
location-based games. Then, we present the
proposed metaphor and a description of the
different elements involved in the metaphor.
Several examples of using the metaphor in real
learning contexts (e.g. Melero et al., 2013) were
also described in order to facilitate the teachers’
comprehension of the proposed approach.
1st Questionnaire (15 min). The teachers were
asked to fill a questionnaire concerning the
different aspects presented before. In concrete,
we asked them to: a) give an opinion about the
perceived benefits of using the puzzle board
metaphor; b) rate the importance of the elements
involved in the metaphor, and the difficulties
understanding these elements; and c) highlight
the aspects that (positively or negatively) caught
their attention.
Game design task (60 min). The teachers were
engaged in designing a location-based game
meaningful to their particular teaching practices.
In this sense, we encouraged teachers to think
about an activity relevant to their teaching
practices and provided the teachers with a set of
templates (see Figure 2), conforming the
proposed puzzle board metaphor. These
templates aim to facilitate the design of the
structure and content of their location-based
TeachersCanBeInvolvedintheDesignofLocation-basedLearningGames-TheUseofthePuzzleBoardMetaphor
181
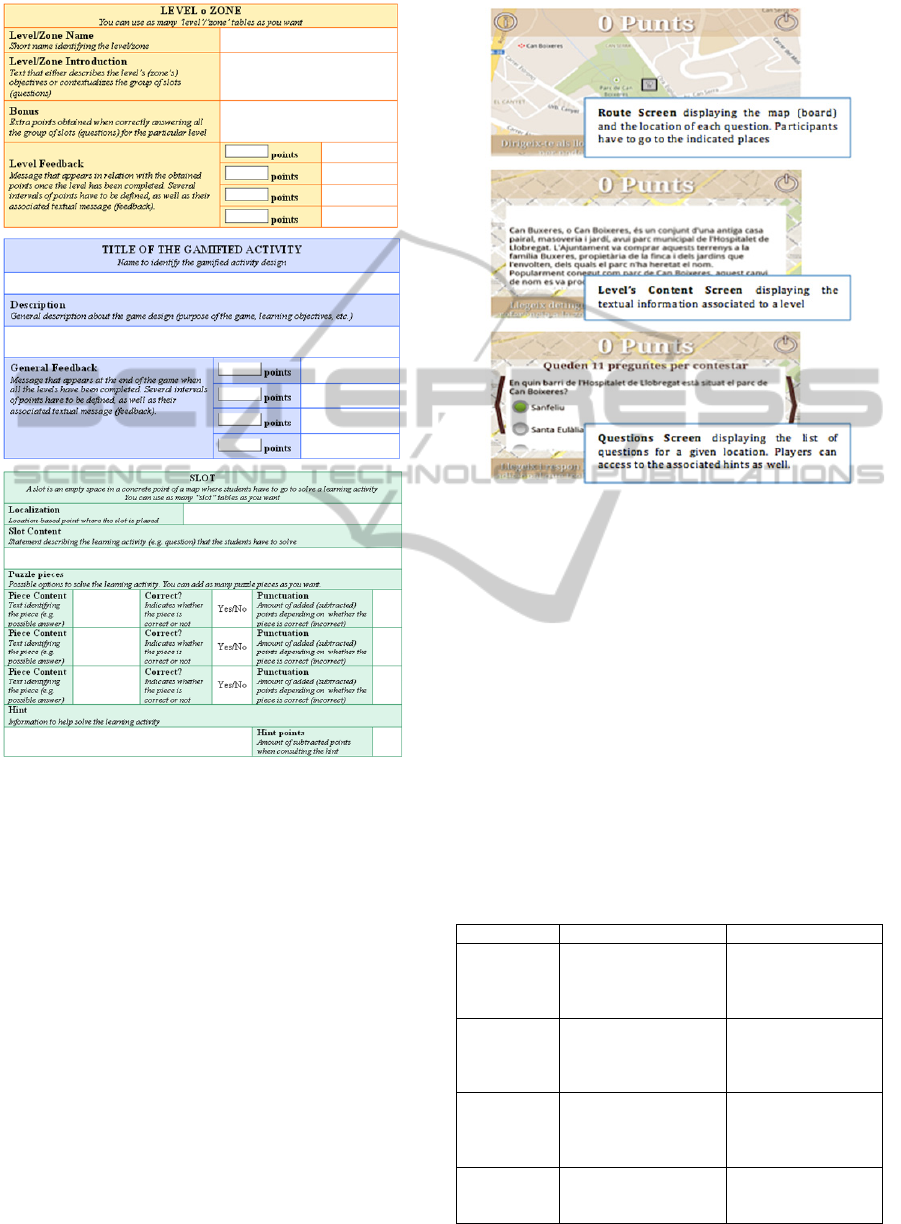
learning games.
Figure 2: Templates for game designing.
2nd Questionnaire (15 min). After finishing the
game design task, each teacher filled out a
second questionnaire about the following items:
a) whether the use of the templates constrain the
design of the game or not; b) the understanding
of the different elements of the templates; and c)
the steps followed to design the location-based
learning game.
Test a demo game (45 min). The teachers, using
their own smartphones, were able to test a
mobile application demo using “QuesTInSitu:
The Game” (see Figure 3). The demo contained
2 levels, and 3 multiple-choice questions per
level about different locations near the place of
the workshop.
Discussion group (45 min). Finally, a discussion
group with the teachers was carried out to share
the main impressions about the proposed
metaphor and the templates.
Figure 3: Some screenshots of the mobile application.
5 EVALUATION
A mixed method has been followed (Cairns and
Cox, 2008) including several data sources (see Table
1) to evaluate different aspects of the proposed
metaphor and the teachers’ game designs. The
obtained qualitative and quantitative gathered data
have been contrasted and triangulated (Guba, 1981).
Quantitative data, obtained from the ratings given by
the teachers in the questionnaires, provide insights
into teachers’ acceptance about the metaphor. This
obtained information will be supported or rejected
by the qualitative data (Guba, 1981).
Table 1: Data gathering techniques.
Data source Type of data Label
First
Questionnaire
Quantitative ratings and
qualitative opinions by
the different participants
[1st-Quest-X]
Where X is the number
of the participant, from
1 to 20.
Second
Questionnaire
Quantitative ratings and
qualitative opinions by
the different participants
[2nd-Quest-Y]
Where Y is the number
of the participant, from
1 to 13.
Game Designs
Paper-based templates
that capture the game
designs
[Design-Y]
Where Y is the number
assigned to a design,
from 1 to 11.
Observations
Record of direct
observations taken during
the discussion group
[Observation]
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
182

5.1 Resulted Designs
The teachers were provided with a set of templates
(Figure 2) intended to allow them to design a
location-based learning game formed by 2 levels and
6 questions. 7 teachers did not get involved in the
game design tasks. Some of them left the room
because of personal matters, and others because they
expected to use an authoring tool to perform the
task: “I think it would be more interesting to use the
application” [1st-Quest -15], “Disappointed to not
could use the authoring tool” [1st-Quest -19].
11 designs resulted from this task. 9 participants
individually designed their own location-based
game, while 4 worked in pairs. 3 of these games
were designed for primary education [Design-2-6-7],
6 for secondary education [Design-1-3-5-8-10-11],
and 2 designs did not specify the educational level
[Design-4-9]. Besides, these m-learning activities
were designed for different subject matters: natural
science [Design-1-7], multidisciplinary activity
(physical education, technology, etc.) [Design-2-3-4-
9], arts [Design-5-11], literature [Design-6],
technology [Design-8], and social science [Design-
10].
The purpose of each design was: an activity
about Olot’s volcanos [Design-1]; a walking tour in
Barcelona to discover different monuments [Design-
2]; an activity for discovering the city of El Prat
[Design-3]; a gymkhana in Ripoll’s river [Design-4];
an activity in the school yard about several well-
known design objects [Design-5]; a learning route
about the streets of Sabadell named with popular
poets names [Design-6]; a situated activity in the
Zoo of Barcelona about wild animals [Design-7]; a
learning activity about structures, types, and
functionalities, history of different buildings and/or
materials [Design-8]; an activity about the
recognition of certain landscape features near the
high school [Design-9]; a route for different
economic institutions [Design-10]; an activity about
modernist buildings in Barcelona [Design-11].
Teachers followed different approaches to design
the content of the different levels. In concrete, the
information of the levels was designed as a
description of the geographical zone in which the
questions are located [Design-1-2-7], as a textual
information about the content of the questions
[Design-5-8], or as instructions about the dynamics
of the game for the particular level [Design-4-9-11].
The rest of participants [Design-3-6-10] did not fill
out the information associated to levels’ content.
Paying attention to the hints, 9 out of the 11
designs included hints as additional information
about the statement of the questions [Design-1-3-4-
5-6-7-8-9-11]. Only 1 participant used the hints’
content to indicate physical places to find useful
information [Design-2].
About the design of scoring mechanisms two
approaches were followed: one more oriented to
traditional tests (e.g. 1 point correct answers, -0.3
points incorrect answers) [Design-3-11], and other
more oriented to games (e.g. 100 or 50 points correct
answers, 50 or 10 points incorrect answers) [Design-
1-2-4-5-6-7-8-9-10]. Besides, different bonus
strategies were followed: adding the same amount of
points as correct answers [Design-3-4-5-7-11],
adding higher amount of points than correct answers
[Design-8-10], and adding lower amount of points
than correct answers [Design-1-5-9]. Furthermore,
considering the design of points when accessing the
hints, some participants chose to subtract: the same
points as incorrect answers [Design-1-5], higher
points than incorrect answers [Design-3-7], and
lower points than incorrect answers [Design-2-4-8-
9-10-11].
5.2 Results on the Proposed Metaphor
In general, the teachers had no problems
understanding the different elements involved in the
proposed metaphor. Specifically, all the teachers
quite or totally agreed that they did not have
problems understanding the role of “slots”, “bonus
points”, “hints”, and “feedback” associated to the
completeness of a level and the whole game. Also,
19 out of the 20 teachers quite or totally agreed that
they understood the meaning of a “level” and a
“puzzle piece”. However, one of the teachers said, “I
think it is difficult to implement this approach in
Primary Education. I should have played the game
before trying to do my own design to know how to
apply this approach in my teaching practices” [1st-
Quest-14]. But, as other of the teachers indicated “I
think this approach could be perfectly implemented
in primary education. Besides, it is a good approach
to interpret maps and put in practice orientation
skills” [Observation].
Paying attention to the definitions of each
element involved in the metaphor the results were as
follows. 14 out of the 20 quite or totally agreed on
the definition of allowing students to solve each
question as many times as needed. But, after the
game design task, some teachers pointed out that the
number of trials to solve a question should have a
maximun attempt limit: “The questions should not
be answered indefinitely. Otherwise, the students
could do trial and error” [1st-Quest-3-4], “I would
TeachersCanBeInvolvedintheDesignofLocation-basedLearningGames-TheUseofthePuzzleBoardMetaphor
183

set up a maximum number of attempts” [1st-Quest-
13], “if students have a limit amount of attempts to
solve the questions, I think they would pay more
attention” [Observation]. However, each element
involved in the metaphor should not be seen as a
standalone item as agreed in the discussion group:
“in order to make a right use of attempts when
answering the different questions (to avoid trial and
error), the scoring should be designed accordingly”
[Observation]. Besides, all the teachers totally
agreed that the hints allow guiding the students to
find the correct answers. However, two thirds of the
teachers (15/ 20) indicated that hints should be
designed in those cases that were relevant.
Otherwise, designing hints could become a tough
task: “we did not design hints to motivate more the
exploration” [Observation], “I have problems to
define hints that were not obvious” [Observation].
17 out of the 20 teachers quite or totally agreed that
bonus points are a good mechanism to motivate
students. Also, almost all the teachers (19/20) quite
or totally agreed on the importance of providing
feedback and adapted scores depending on the
number of attempts when solving questions.
Furthermore, 18 out of the 20 teachers quite or
totally agreed that the points and feedbacks are good
approaches to reflect the correct and incorrect
students’ actions. Some comments were: “Feedback
is indispensable when learning” [1st-Quest-17].
However, some difficulties arosed: “I found difficult
to design the intervals for the scoring mechanisms”
[2nd-Quest-13], “I think higher points, similar to
games (such as tetris), would engage more the
students in the learning activity task” [Observation],
“I had to be very careful with the different amount of
points to design a meaningful activity”
[Observation], and “I was not sure about the amount
of points to define as bonus” [Observation]. These
results indicate that despite the elements involved in
the metaphor are understandable, in some cases (e.g.
desining scores), it is necessary to provide teachers
with recommendations to their concrete
requirements.
5.3 Results on the Use of Templates
Once the teachers finished the game design task,
they filled out a questionnaire intended to gather
major impressions about the metaphor and use of the
templates in the design task. Concerning the
question “Will you find useful the metaphor to
create your own location-based game?”, all the 13
teachers agreed that they would use the proposed
approach. Some comments were: “This approach
could be implemented in different subject topics of
mine” [2nd-Quest-9], and “I would definitely use this
approach to design punctual activities such as field
trips” [2nd-Quest-3]. The teachers also highlighted
several educational benefits: puzzle board metaphor
was considered a motivating approach [2nd-Quest-2-
3-13] that could encourage students to
outperforming themselves [2nd-Quest-4], promote
learning in groups [2nd-Quest-5-7-8-12], and engage
students to become more active [2nd-Quest-5-10].
When asking the teachers about the use of paper-
based templates, all the teachers considered the
templates a useful approach to structure the design
of their location-based games. Some comments
were: “the templates help to structure the
information” [2nd-Quest-7], “[…] to structure the
whole game” [2nd-Quest-3], and “I understood all
the elements” [2nd-Quest-11]. Also, most of the
teachers quite or totally agreed on the user-
friendliness of the templates for designing the levels
(9/13), slots (9/13), puzzle pieces (10/13), scoring
(10/13), hints (9/13), and feedbacks (9/13).
Finally, we asked the teachers to order a list of
actions according to their process when designing
the location-based game: a) fill the information
according to the both game’s title and description; b)
indicate the level’s (zone’s) name and description; c)
define the level’s scoring and feedback; d) specify
the slot’s description; e) define the hint associated to
a slot; f) define the overall scoring and feedback of
the game; g) define the bonus associated to a level;
h) indicate the localization of the slots; i) define the
points associated to the slot’s answers; and j) define
the points associated to the hints. In this line, all the
participants started defining the game’s name and its
description, followed by the level’s name and its
description as well. But after this, participants
followed different paths for designing their games.
For instance, some of them continued their design
process by defining the slot’s description [2nd-
Quest-2-5-7-8-13] and others by indicating the
localization of the slots [2nd-Quest-3-10-11-12].
6 DISCUSSION
Over the past years, some research efforts have been
done towards supporting teachers in the creation of
game-based learning environments. However, the
implementation of this type of environments has not
been as broadly adopted as one could has expected.
Most of tools have reported problems, such as, hard
to adapt to specific teaching practices, requiring too
many resources and too much time for development.
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
184

Thus, focusing on location-based games, it seems
relevant to provide teachers with approaches that
facilitate the design of this type of m-learning
activities to their specific educational situations.
We believe that proposing a metaphor could be
relevant to facilitate and guide teachers in the design
of their own location-based games. The reason of
using a metaphor can be significant to present a
familiar context to the teachers in order to facilitate
the comprehension of the game design task. Using
puzzles boards becomes relevant in this context
because these are well-known games used in
educational context. Besides, board games in general
has been already considered to be mapped as
location-based games. Then, the proposed metaphor
could be a potential approach to scaffold teachers in
the design of their own location-based games.
The puzzle board metaphor has been proved a
suitable approach to design location-based games.
Previous experiments, despite of some
misunderstandings, have reported the feasibility of
designing and enacting location-based learning
games for secondary education. Teachers perceived
the proposed approach relevant to their teaching
practices. Besides, the enactment with secondary
education students revealed that the proposed
approach promoted students being more active when
solving the designed questions. Specifically,
students tried to avoid losing points by paying more
attention to elements of the physical place, asking
people and searching the Internet. Further research
was needed to analyse a second iteration of the
metaphor in different educational levels. This second
iteration, presented in this paper, has reported that
elements involved in the puzzle board metaphor
were properly understood. Different location-based
game designs for primary and secondary education
resulted from the task. Besides, participants were
able to design their location-based games according
to their specific requirements.
Furthermore, paper-based templates have been
proved to be a good approach to put into real
practice the proposed metaphor. The templates has
been useful to structure the content of the designed
location-based games. Also, this paper-based
approach gives insights towards the design and the
development of an authoring tool compliant with the
puzzle board metaphor. In this context, the authoring
tool has to be flexible enough to allow teachers to
follow different paths when desining their own
location-based games.
When designing location-based learning games it
is important to consider the effects of design
decisions in concrete elements will have on the rest;
the different elements involved when designing this
type of activities should not be treated in isolation.
For instance, the design of the scoring mechanisms
could influence on answering questions or accessing
to the hints. Besides, results have shown that it
would be advisable to provide recomandations to the
teachers about scoring mechanisms. Different
strategies can be followed to design diverse types of
scoring mechanisms: adding/subtracting higher
amount of points (e.g. 100 points correct answers, -
50 points incorrect answers) versus following a more
traditional assessment approach (e.g. 1 point correct
answers, -0.3 points incorrect answers). Thus, it
seems relevant to integrate some kind of guidance
for teachers that recommends which scoring strategy
follow considering his/her educational needs.
7 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has described a strategy based on a
puzzle board metaphor to facilitate teachers the
design of their own location-based learning games.
Particularly, in the frame of a design-based research
methodology, the paper presents a second iteration
in the formulation of the metaphor and the
associated design process. The evaluation of the
iterated approach focused on analysing the changes
performed in the definition of the “level” element
and the dynamic of the game design task. Results
have shown that teachers have properly understood
the proposed approach and highlighted many
educational benefits. The great majority of teachers
agreed with the definitions of the different elements
involved in the proposed metaphor. Besides,
participants become aware of the importance of not
considering the elements of the metaphor as isolated
items. Designing appropriate scores could influence
in avoiding trial and error.
The puzzle board metaphor has been proved also
to be a feasible approach to define location-based
games for different contexts and educational
purposes. Besides, the use of paper-based templates
have been positively valued for structuring the
content of the activities, as well as for flexibly
designing these m-learning activities.
As a whole, teachers positively adopted the
proposed approach and sought for an authoring tool.
In this line, results obtained in the evaluation have
provided insights to further work in the
implementation of an authoring tool that allows the
creation of location-based games. Results obtained
in the design process indicate that teachers follow
different paths when designing their own location-
TeachersCanBeInvolvedintheDesignofLocation-basedLearningGames-TheUseofthePuzzleBoardMetaphor
185

based learning game. This suggests that the
authoring tool should not enforce a guided process.
Instead, the tool should provide enough freedom to
allow the teachers to follow their own desired path
to create their location-based games. Besides, one of
the findings is about the dificulties when designing
adapted scores because teachers are not sure which
would be the better approach to follow.
Implementing recommendations in an authoring tool
to facilitate this task is one aspect that requires
further research.
Finally, a follow-up experiment with teachers
who attended the workshop would be relevant to
evaluate more deeply the usefulness of the proposed
approach. Previous real experiments have proved the
feasibility of implementing location-based learning
games for secondary education using the paper-
based templates. However, this study has presented
designs in other educational levels and subject topics
that could be worthwhile to implement in order to
evaluate the impact of using the proposed approach.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research has been partially funded by the
Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness
in the EEE Project (TIN2011-28308-C03-03).
REFERENCES
Bachmair, B., Cook, J., and Kress, G. R. (2010). Mobile
learning: structures, agency, practices. Boston, MA.
Barab, S., and Squire, K. (2004). Design-based research:
putting a stake in the ground. The Journal of the
Learning Sciences, 13(1):1-14.
Bohannon, R. (2010). Location, Location, Location: An
Exploration of Location-Aware Learning Games for
Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of Society for
Information Technology & Teacher Education
International Conference, pages 1839-1842,
Chesapeake, VA: AACE.
Bontchev, B., & Vassileva, D. (2010). Modeling
educational quizzes as board games. In Proccedings of
IADIS International Conference e-Society, pages 1-8,
Porto, Portugal.
Cairns, P., and Cox, A. L. (2008). Research methods for
human-computer interaction, NY, USA: Cambridge
University Press New York.
Davis, S. M. (2002). Research to Industry: Four Years of
Observations in Classrooms Using a Network of
Handheld Devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Workshop on Wireless and Mobile
Technologies in Education, pp. 31-38, Växjö, Sweden.
Guba, E. G. (1981). Criteria for assessing the
trustworthiness of naturalistic inquiries. Educational
Communication and Technology, 29(2):75-91.
Huang, O. W. S., Cheng, H. N. H., and Chan, T. W.
(2007). Number Jigsaw Puzzle: A Mathematical
Puzzle Game for Facilitating Players’ Problem
Solving Strategies. In Proceedings of the First IEEE
International Workshop on Digital Game and
Intelligent Toy Enhanced Learning, pages 130-134,
Jhongu, Taiwan.
Hwang, G., Tsai, C., and Yang, S. J. H. (2008). Criteria,
strategies and research issues of context-aware
ubiquitous learning. Educational Technology &
Society, 11(2): 81-91.
Jones, V., and Jo, H. J. (2004). Ubiquitous learning
environment: an adaptive teaching system using
ubiquitous Technology. In Proceedings of the 21st
ASCILITE Conference, pages 468-474, Perth, Western
Australia.
Lakoff, G. (1993). The contemporary theory of metaphor.
In A. Ortony (Ed.), Metaphor and thought, pages 202-
251, New York: Cambridge University Press.
Melero, J., and Hernández-Leo, D. (accepted). A Model
for the Design of Puzzle-based Games including
Virtual and Physical Objects, Educational Technology
& Society.
Melero, J., Santos, P., Hernández-Leo, D., and Blat, J.
(2013). Puzzle-based Games as a Metaphor for
Designing Situated Learning Activities. In
Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on
Games Based Learning, , pp. 674-682, Porto, Portugal.
Nicklas, D. Pfisterer, Ch., and Mitschang, B. (2001).
Towards Location-based Games. In Proceedings of the
International Conference on Applications and
Development of Computer Games in the 21st Century,
pages 61-67, Hongkong Special Administrative
Region, China.
Roschelle, J. (2003). Unlocking the learning value of
wireless mobile devices. Journal Computer Assisted
Learning, 19(3): 260-272.
Schlieder, C., Kiefer, P., and Matyas, S. (2006).
Geogames: Designing Location-based games from
classic board games. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 21(5):
40-46.
Tornero, R., Torrente, J., Moreno-Ger, P., and Manjón, B.
(2010). e-Training DS: An Authoring Tool for
Integrating Portable Computer Games in e-Learning.
In Advances in Web-Based Learning – ICWL, Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, Springer Berlin.
van Rosmalen, P., Klemke, R., and Westera, W. (2011).
Alleviating the entrance to serious games by exploring
the use of commonly available tools. In Proceedings
of the 5th European Conceference on Games Based
Learning, pages 613-619, Athens, Greece.
Wood, D. J., Bruner, J. S., and Ross, G. (1976). The role
of tutoring in problem solving, Journal of Child
Psychiatry and Psychology, 17(2): 89-100.
Yatani, K., Onuma, M., Sugimoto, M., and Kusunoki, F.
(2004). Musex: A system for supporting children’s
collaborative learning in a museum with PDAs.
Systems and Computers in Japan, 35(14): 773-782.
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
186
