
A Dynamic Hybrid Local-spatial Interest Point Matching Algorithm for
Articulated Human Body Tracking
Alireza Dehghani and Alistair Sutherland
School of Computing, Dublin City University, Dublin, Ireland
Keywords:
Interest Point Matching, Cyclic String Matching, Human Body Tracking.
Abstract:
Current interest point (IP) matching algorithms are either local-based or spatial-based. We propose a hybrid
local-spatial IP matching algorithm for articulated human body tracking. The first stage is local-based and
finds matched pairs of IPs from two lists of reference and target IPs through a local-feature-descriptors-based
matching method. The second stage of the algorithm is spatial-based. It starts with the confidently matched
pairs of the previous stage, and recovers more matched pairs from the remaining unmatched IPs through graph
matching and cyclic string matching. To compensate for the problem of Reference List Leakage (RLL), which
decreases the number of reference IPs throughout the frame sequence and causes failure of tracking, an IP
List Scoring and Refinement (LSR) strategy is proposed to maintain the number of reference IPs around a
specific level. Experimental results show that not only the proposed algorithm increases the precision rate
from 61.53% to 97.81%, but also it improves the recall rate from % 52.33 to 96.40%.
1 INTRODUCTION
The interest point (IP) representation is widely used
in image registration, pattern recognition, human mo-
tion tracking, etc. IP matching, which aims to find a
reliable correspondence between reference and target
IPs (extracted from reference and target images) us-
ing some similarity criteria, is a crucial and challeng-
ing process and has been studied widely. IPs are sup-
posed to be persistent across successive frames and
robust to changes in illumination, pose and viewpoint
(Maji, 2006). Current IP matching algorithms mainly
use either local or spatial similarity to establish a cor-
respondence between IPs. The local-based methods
mainly use feature descriptors to measure local simi-
larity of points, while the spatial-based methods use
geometric distance and spatial structure among IPs
(Liu et al., 2012).
Local feature descriptors use image properties
such as pixel intensities, colour, texture, and edges
to measure the distance between IPs in the matching
process. Many remarkable local feature descriptors
such as the Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT)
(Lowe, 2004), Speeded Up Robust Features (SURF)
(Bay et al., 2008), and Gradient Location and Orien-
tation Histogram (GLOH) (Mikolajczyk and Schmid,
2005) have been proposed in the literature. The ORB
(Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF) (Rublee et al.,
2011), which is rotation-invariant and resistant to
noise, performs same as SIFT and better than SURF,
while being twice as fast. The different feature de-
scriptors have been compared in literatures (Mikola-
jczyk and Schmid, 2005).
The above mentioned local descriptors are used
to match IPs in different applications. However, they
may collapse in some ambiguous situations such as
monotonous backgrounds, similar features, low res-
olution images, etc. In these cases, spatial-based
IP matching methods, which use information like
geometric distance or neighbourhood relations be-
tween points, can be used to compensate for these
drawbacks. The iterative Random Sample Consen-
sus method (RANSAC) (Fischler and Bolles, 1981),
which fits a mathematical model to a set of points in-
cluding outliers, can be reasonably used only when
there are reasonable level of outliers.
These methods work well only when there are
not many outliers. To compensate for this, the spa-
tial relation between points has been dealt with by
many authors. Consideration of local relations be-
tween IPs (Zheng and Doermann, 2006), graph es-
tablishment by Delaunay triangulation in a two-step
algorithm (Li et al., 2005), a Graph Transforma-
tion Matching (GTM) strategy for finding a consen-
sus nearest neighbour graph from candidate matches
(Aguilar et al., 2009), and using relative positions and
536
Dehghani A. and Sutherland A..
A Dynamic Hybrid Local-spatial Interest Point Matching Algorithm for Articulated Human Body Tracking.
DOI: 10.5220/0004786705360543
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM-2014), pages 536-543
ISBN: 978-989-758-018-5
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

angles of points for reduction of false matching have
been introduced in this regard.
Although the spatial-based methods are more ac-
curate and robust than the local-based ones, they are
not as quick particularly when there is a high num-
ber of IPs. Owing to both the pros and cons of these
local and spatial IP matching strategies, combined ap-
proaches (Wen et al., 2008) can be proposed to com-
plement each other. The local feature similarity used
in local-based IP matching approaches can be used to
cut down the search space for the spatial-based meth-
ods. On the other hand, the spatial-based methods can
compensate for the defects of local-based methods in
ambiguous situations such as duplicated local features
patterns between two reference and target images.
In articulated object tracking, the Reference-list
IPs are dynamically matched to the Target-list IPs
over the frame sequence (Li et al., 2003; Zhou et al.,
2009; Ma et al., 2013). During this process, the IPs in
the Reference-list are replaced by the matched points
in the Target-list at each frame. Since the matched
Target-list will always be shorter than the Reference-
list, (because of noise; changes in illumination; ar-
ticulation of the tracking object, and even the weak-
ness of the background subtraction algorithms) the to-
tal number of IPs will be reduced at each frame and
eventually this will lead to loss of tracking. We call
this problem the Reference List Leakage (RLL) prob-
lem in this paper. To tackle this problem, which we
call the Reference List Leakage (RLL) problem in this
paper, our IP matching algorithm is equipped with a
novel IP List Scoring and Refinement (LSR) strategy.
Summary: In this paper we propose a dynamic
hybrid local-spatial IP matching algorithm for hu-
man body tracking. In the first stage, the confi-
dently matched points are found using a local-based
IP matching strategy. Then, to compensate for mis-
matched and unmatched IPs, a new spatial-based
matching method based on graph matching and string
matching algorithms is applied. As a remedy for the
problem of RLL, a novel LSR strategy is applied.
The proposed approach benefits from: local-based IP
matching to avoid the expense of the distance and
neighbourhood comparison of the spatial-based meth-
ods; spatial-based IP matching to compensate for the
drawback of the first stage; and an IP List Scoring and
Refinement strategy to refine the IP lists and solve
the problem of RLL. The rest of this paper is out-
lined as follow: Section 2 presents the proposed al-
gorithm. Experimental results and conclusions will
be discussed in Sections 3 and 4, respectively.
2 INTEREST POINT MATCHING
ALGORITHM
The two stages of our proposed IP matching algorithm
as well as the IP List Scoring and Refinement (LSR)
strategy will be described in Sections 2.1, 2.2, and
2.3, respectively.
2.1 Stage 1: Local-based IP Matching
In this stage, first the local feature descriptors of
the IPs of Reference-list and Target-list are extracted.
Then, the IPs of these lists are matched to each other
in two directions, i.e. the Reference-list to the Target-
list and vice versa. This is carried out because the
results of matching in two different directions are not
same, no matter what type of matcher and distance
measure is used.
Then, two filtering steps are applied to these
matched lists: firstly, cross-checking is applied to re-
move any IPs which do not match both ways; sec-
ondly, displacement-checking is performed to remove
any IPs where the distance between reference and tar-
get is greater than a threshold based on smoothness
or small inter-frame motion assumptions, which are
valid to assume in human body tacking applications
(Herda et al., 2000). These two checks amend the
result and deliver ”confidently” matched IPs CR =
{cr
1
, . . . , cr
N
} & CT = {ct
1
, . . . , ct
N
} to the spatial
matching stage. This stage of algorithm is outlined
in Algorithm 1.
2.2 Stage 2: Spatial-based IP Matching
After finding the confidently matched sets CR and CT ,
the unmatched IPs of the Reference-list, i.e. UR =
{ur
1
, . . . , ur
M
}, are dealt with one by one to find their
possible corresponding matched IPs in the unmatched
target set UT = {ut
1
, . . . , ut
L
}. Before that, the IPs of
CR are clustered into K groups {CR
1
, . . . ,CR
K
} us-
ing the k-means clustering algorithm. The centroid of
each cluster C(x
c
, y
c
) is calculated by:
x
c
=
1
N
N
∑
i=1
x
i
, y
c
=
1
N
N
∑
i=1
y
i
(1)
Meanwhile, the corresponding K clusters of CT ,
i.e. {CT
1
, . . . ,CT
K
}, are obtained from correspon-
dence between the confidently matched IPs of CR
and CT . Then for each unmatched point ur
i
of UR,
the closest cluster CR
k
is found by comparing its Eu-
clidean distance to the centre of each cluster. Now, ur
i
and the confidently matched IPs of the closest cluster
CR
k
compose a star-shape graph g
R
(Figure 1).
ADynamicHybridLocal-spatialInterestPointMatchingAlgorithmforArticulatedHumanBodyTracking
537

Algorithm 1 Local-based IP Matching Algorithm.
1: Input: Two IP set Reference-list: {r
i
}
n
i=1
&
Target-list: {t
j
}
l
j=1
2: Output: Confidently matched set CR & CT
Unmatched set U R & UT
3: Extract feature descriptor for both IP lists.
4: Match Reference-list to Target-list: Matches RT.
5: Match Target-list to Reference-list: Matches TR.
6: Cross-Check:
7: for each matched pair (i
1
, j
1
) in Matches RT do
8: Find matched pair ( j
1
, i
2
) in Matches TR.
9: if i
1
= i
2
then
10: Keep pair (i
1
, j
1
) in Matches RT.
11: else
12: Pushback P
i
1
&P
j
1
to UR & UT respectively.
13: end if
14: end for
15: Displacement-Check:
16: for each matched pair (i, j) in Matches RT do
17: if distance(P
i
, P
j
) < threshold then
18: Pushback P
i
&P
j
to CR & CT respectively.
19: else
20: Pushback P
i
&P
j
to UR & UT respectively.
21: end if
22: end for
Figure 1: The Graph g
r
, confidently matched points
cr
1
, cr
2
, . . . , cr
n
, and unmatched point ur
i
.
To find a possible matching IP to this point, a rect-
angular search area is defined around the position of
ur
i
in the target image. All the unmatched points ut
j
in this search area are examined one by one to see if
there is any point which can be matched to the un-
matched point ur
i
. To do this, a similar graph g
T
is
constituted for any unmatched point ut
j
(inside the
search area) and it confidently matched IPs of the
corresponding cluster CT
k
. The point ur
i
is matched
to one of points ut
j
if graph g
R
is matched to one
of the graphs g
T
. Otherwise, this IP remains un-
matched. Figure 2 shows the graph formation step of
the spatial-based IP matching stage. Based on the size
of the search area (Figure 2(c)), a few possible graphs
g
T
(Figure 2(e)-2(i)) are composed for the unmatched
points ut
j
to be matched to graph g
R
of reference un-
matched point ur
i
(Figure 2(d)).
For the task of graph matching, the cyclic string
(a) Clustering. (b) Target IPs. (c) Search area.
(d) g
R
. (e) 1
st
g
T
. (f) 2
nd
g
T
.
(g) 3
rd
g
T
. (h) 4
th
g
T
. (i) 5
th
g
T
.
Figure 2: Graph formation: (a) the clustered confidently
matched IPs, (b) the unmatched target IPs, (c) search ar-
eas, (d) a reference graph, and (e-i) five target graphs for
unmatched target IPs in the search area.
matching algorithm (Maes, 1990) is used. In this or-
der, a primitive feature vector is first extracted for any
of the graphs g
R
and g
T
. This feature should be as
light-weight and small-size as possible, while robust
to translation, rotation, and scale. The reciprocal of
compactness (ROC) (Wu, 2011) is a good choice and
satisfies these requisites. To extract this feature vec-
tor for any graph g
R
, with central point ur
i
and con-
fidently matched IPs {cr
1
, cr
2
, . . . , cr
n
}, the triangle
ur
i
cr
i
cr
i+1
is composed for each point cr
i
, then the
feature value r
i
is calculated as:
r
i
=
a
i
p
2
i
(2)
where p
i
= |cr
i
cr
i+1
| + |cr
i
ur
i
| + |cr
i+1
ur
i
| is the
perimeter and a
i
is the area of the triangle.
Therefore, a vector [r
1
, r
2
, . . . , r
n
] of real numbers
is created for any graphs g
R
and g
T
. These vectors
compose strings ”s” and ”t” which are applied to the
string matching stage. To do this, an edit-weighted
graph (Wu, 2001) is constructed for these strings. The
string matching algorithm finds a minimum cost edit
sequence from ”s” to ”t” which is same as finding
the shortest path in the edit-weighted graph (Wagner
and Fischer, 1974). Since these strings are extracted
from cyclic graphs (no matter which point cr
i
is con-
sidered as the first point), the cyclic string-to-string
correction problem is applied to our graph matching
scenario. Algorithm 2 summarizes this stage. To find
the shortest path in the edit-weighted graph during the
cyclic string matching, the Dijkstra algorithm (Leiser-
son et al., 2001) which is a graph search algorithm for
finding the shortest path in a graph, is used. Here, the
edit cost function is considered as:
ε(s
i
→ t
′
j
) = |s
i
−t
′
j
| (3)
ICPRAM2014-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
538

Algorithm 2 Spatial-based IP Matching Algorithm.
1: Input: IP sets CR & CT and U R & UT .
2: Output: Matched IP sets MR & MT .
3: Push back CR & CT into MR & MT .
4: Cluster CR into K clusters {CR
1
, . . . ,CR
K
}.
5: Compose K clusters {CT
1
, . . . ,CT
K
}.
6: for each IP ur
i
of UR do
7: Find its closest cluster, compose graph g
R
, and
extract its ROC feature vector (string s).
8: Define search area around ur
i
in target image.
9: min cost ⇐ ∞
10: for each IP ut
j
inside search area do
11: Compose graph g
T
, extract its ROC feature
vector (string t).
12: Find minimum cost from string s to t us-
ing cyclic string matching and Dijkstra al-
gorithms.
13: if minimum cost< min cost then
14: min cost = minimum cost.
15: end if
16: end for
17: if min cost < threshold then
18: Push back ur
i
and ut
j
to MR&MT , respec-
tively.
19: end if
20: end for
2.3 LSR Strategy
Using IP matching to track an articulated object
through a long sequence of frames is much more
complicated than simply matching IPs of two static
frames. As the object changes its pose and shape
throughout the sequence, the two main problems
which occur are: IPs in the initial frame rapidly be-
come obsolete; New IPs, which were not in the pre-
vious frames, emerge. To keep track of the object
throughout the frame sequence, we must find some
way of removing obsolete IPs and replacing them
with new IPs.
Two lists of IPs are involved in any round of
matching: the Reference-list; and Target-list. The
Reference-list contains those IPs in the previous
frame, which we are reasonably confident and repre-
sent the previous state of the object. We match these
to the Target-List, which contains IPs from the cur-
rent frame. Any IP of the Reference-list, which finds
a matching IP in the Target-list, is replaced by the IP
of the Target-list.
A naive approach would be to delete any un-
matched Reference-list IPs on the grounds that they
are now obsolete. But this would be too severe. An
IP may fail to find a match in a particular round be-
cause of noise or occlusion and yet may find a match
in subsequent rounds. Therefore, we should retain un-
matched IPs in the Reference-list for a certain number
of rounds and delete them only if they fail to find a
match for several rounds in successions.
If we wish to replace deleted IPs, a naive ap-
proach would simply be to use unmatched IPs from
the Target-list on the grounds that these represent new
IPs generated by changes in the object. However, new
IPs may also be generated by noise or occlusions.
Therefore, we have to subject new IPs to a test be-
fore we admit them to the Reference-list. To do this,
we include unmatched IPs of the Target-list in a third
list, which we call the ”Reserved-list”. If an IP in this
list finds a match over a certain number of consecutive
frames then we promote it to the Reference-list.
The LSR strategy works based on two parameters:
Score (S); and Matching-Index (MI). These parame-
ters are assigned to each IP of the Reference-list and
Reserved-list at each round. The S parameter reflects
the success or failure of any IP through the previous
rounds of matching. The MI parameter also shows
the number of times IP has been either matched or
unmatched in previous rounds.
The LSR strategy comprises two stages:
• IP Scoring: the S and MI parameters of each IP
in the Reference-list and the Reserved-list are up-
dated based on the result of matching. Whenever
an IP is matched, its MI is increased by 1; oth-
erwise it is decreased by 1. The S parameter is
increased by a reward score of 3, each time the IP
is matched; otherwise it is decreased by a penalty
score given by MI, the number of previous un-
matched rounds. Algorithm 3 summarizes the IP
scoring system after each round of matching.
• List Refinement: the S value of the IPs are
compared with two empirical thresholds, namely
the Eligibility (E) and Merit (M) thresholds,
to find the obsolete IPs of the Reference-list
and Reserved-list and the competent IPs of the
Reserved-list. At each round, for each IP of the
Reference-list, if S < E, then that IP is deleted.
For each IP of the Reserved-list, if S > M, then
that IP is promoted to the Reference-List. The IPs
of the Reserved-list with S < E also are deleted
to prevent explosion in this list. The detail of this
stage is described in Algorithm 4.
As an example, if an IP of the Reference-list is
matched for the first time in round k it receives an
S value of 3. If it is matched in round k + 1, the S
value will go up to 6. If it is matched in round k + 2,
it will go up to 9. But, if it fails to match in round
k + 3, S will go down to 8 (because MI = −1). If
ADynamicHybridLocal-spatialInterestPointMatchingAlgorithmforArticulatedHumanBodyTracking
539

Algorithm 3 IP Scoring.
1: k: round of matching (k ⇐ 1)
2: for each IP i in Reference-list do
3: if IP i matched any IP j in Target-list then
4: Substitute IP i with IP j, S
k
i
= 3, MI
k
i
= 1
5: else
6: S
k
i
= −1 & MI
k
i
= −1
7: end if
8: end for
9: for each IP j in Target-list do
10: if IP j not-matched then
11: Move IP j to the Reserved-list
12: S
k
j
= −0.5 & MI
k
j
= 0
13: end if
14: end for
15: for rounds k > 1 do
16: for each IP i in Combined-list = [Reference-list
Reserved-list] do
17: if IP i matched any IP j in Target-list then
18: Substitute IP i with IP j
19: if IP i matched in round k − 1 then
20: MI
k
i
= MI
k−1
i
+ 1
21: else if IP i not-matched in round k − 1
then
22: MI
k
i
= 1
23: end if
24: S
k
i
= S
k−1
i
+ 3
25: else
26: if IP i matched in round k − 1 then
27: MI
k
i
= −1
28: else if IP i not-matched in round k − 1
then
29: MI
k
i
= MI
k−1
i
− 1
30: end if
31: S
k
i
= S
k−1
i
+ MI
k
i
32: end if
33: end for
34: for each IP j in Target-list do
35: if IP j not-matched then
36: Move IP j to the Reserved-list
37: S
k
j
= −0.5 & MI
k
j
= 0
38: end if
39: end for
40: end for
it fails to match in round k + 4, S will go down to 6
(because MI = −2). However, if it matches again in
round k + 5, S will go up to 9.
Figure 3 shows the different steps of LSR for
the first two rounds of matching. Step 1 is where
the Combined-list (Reserved-list concatenated to the
end of the Reference-list) and Target-list are prepared
to be fed into the matching algorithm. As can be
Algorithm 4 List Refinement.
1: k: round of matching
2: for rounds k > 1 do
3: for each IP i in Reference-list do
4: if IP S
k
i
< E (Eligibility threshold) then
5: Remove IP i from Reference-list
6: end if
7: end for
8: for each IP l in Reserved-list do
9: if IP S
k
i
> M (Merit threshold) then
10: Move IP l to the Reference-list
11: else if IP S
k
i
< E (Eligibility threshold) then
12: Remove IP l from Reserved-list
13: end if
14: end for
15: end for
Figure 3: The LSR for the first two rounds of matching.
seen, the Reserved-list is empty in the first round
and the S and MI values of the IPs are zero. Step
2 displays the status of the IPs after matching. The
red arrows show the matched pairs while the purple
ones show the unmatched IPs in Target-list, which
are moved to the Reserved-list. This leads into Step
3, where the matched Reference-list IPs are replaced
with their corresponding IPs in the Target-list and the
unmatched Target-list IPs are moved to the Reserved-
list with a penalty score of −0.5, which is a bias
penalty for unmatched IPs of Target-list. This step
is a basis for Step 1 in the next round of matching
where: the IPs of the Reference-list and Reserved-
ICPRAM2014-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
540

list are relabelled with Ref and Rsvd labels; the list
refinement procedure is applied to the Reference-list
and Reserved-list; and the Target-list is loaded with
the new IPs of target image.
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Based on the application in hand, human upper body
tracking, extracted FAST IPs from RGB acquired im-
ages with resolution of 240∗320 pixels, are passed to
an IP-based background subtraction algorithm (Fig-
ure 4(a)) proposed by the authors (This approach is
under examination as a patent). The resultant fore-
ground IPs (Figure 4(a)-right) of any two consecu-
tive frames, are fed to the local-based stage of algo-
rithm, where the SURF descriptor extractor and the of
BruteForce matcher of OpenCV are used to estimate
the initial correspondence. Then two further cross-
checking and displacement-checking procedures are
applied to reject the outliers as well as to keep as many
inliers as possible.
Table 1: Performance comparison on the image pairs in Fig-
ure 4. The values in the columns are the TP (True Positive),
FP (False Positive), FN (False Negative) (Benezeth et al.,
2010), Precision (%), and Recall (%) (Olson and Delen,
2008), respectively.
TP FP FN P R
BruteForce 56 35 51 61.53 52.33
Cross-checked 56 25 61 69.13 47.86
Confidentley 56 5 81 91.80 40.87
Combined 134 3 5 97.81 96.4
The results of our algorithm on two frames of
video are presented in Table 1. In this experiment,
there are 142 points in the Reference-list which are
matched to the Target-list IPs. As can be seen from
the first row of table, the traditional local matchers
like BrouteForce do not deliver good precision and
recall rates. Nevertheless, the cross-checking and
displacement-checking procedures improve the accu-
racy of the local-based IP matching stage (increas-
ing the precision rate from 61.53% for BruteForce
to 91.80% for Confidently matched IPs); meanwhile,
they decrease the number of confidently matched IPs
(the recall rate) from 52.33% to 40.87%. Although
they pull down the recall rate(up to 40.87%), the im-
provement in precision (up to 91.80%) is used as a ba-
sis for the spatial-based matching stage to cut down its
cost of search in comparison with when the only spa-
tial IP matching algorithm. Finally, the last row of Ta-
ble 1 shows the improvement which the spatial-based
stage creates in precision and recall rate. Figure 4
shows results graphically, where the left and right im-
ages ( 4(b)-4(e)) are the reference and target images,
respectively. It is also noteworthy to compare Figures
4(d) and 4(e) to realize the delivered improvement of
hybrid local-spatial algorithm in comparison with the
only local IP matching algorithm.
(a) Left to right: image, FAST IPs, foreground IPs.
(b) IP matching using BruteForce matcher.
(c) Matched IPs after cross-checking.
(d) Matched IPs after displacement-checking.
(e) Final Matched IPs after second stage.
Figure 4: Results of local-based stage of the proposed IP
matching algorithm: (a) left to right: the real image, FAST
IPs, and the foreground IPs, (b) BruteForce matching, (c)
cross-checking, (d) the confidently matched IPs.
Figure 5 represents the visual comparison of our
algorithm without and with the LSR approach over
eight successive rounds of matching. As can be seen
in Figure 5(a), the RLL problem causes loss of track
after a few rounds while the proposed LSR approach
prevents it and holds the number of reference IPs at
the same level as the first round. Moreover, if the
matching algorithm fails to find the matched pair for
many IPs, the LSR approach compensates for that in
the subsequent rounds. For instance, as the fifth round
of matching shows (3
rd
row and 1
st
column of 5(a)
and 5(b)), about the half IPs (those over the torso area)
have not been matched. This is the starting point for
the fail of track in Figure 5(a), whereas the LSR has
compensated for that in the next round (Figure 5(b)).
Besides, LSR refines the Reference-list by remov-
ing its obsolete IPs and replacing them with new com-
petent IPs from the Reserved-list. This advantage of
the LSR approach helps the matching algorithm to
follow the dynamic of the tracked object. These pros
of LSR deliver a significant improvement to the IP
ADynamicHybridLocal-spatialInterestPointMatchingAlgorithmforArticulatedHumanBodyTracking
541
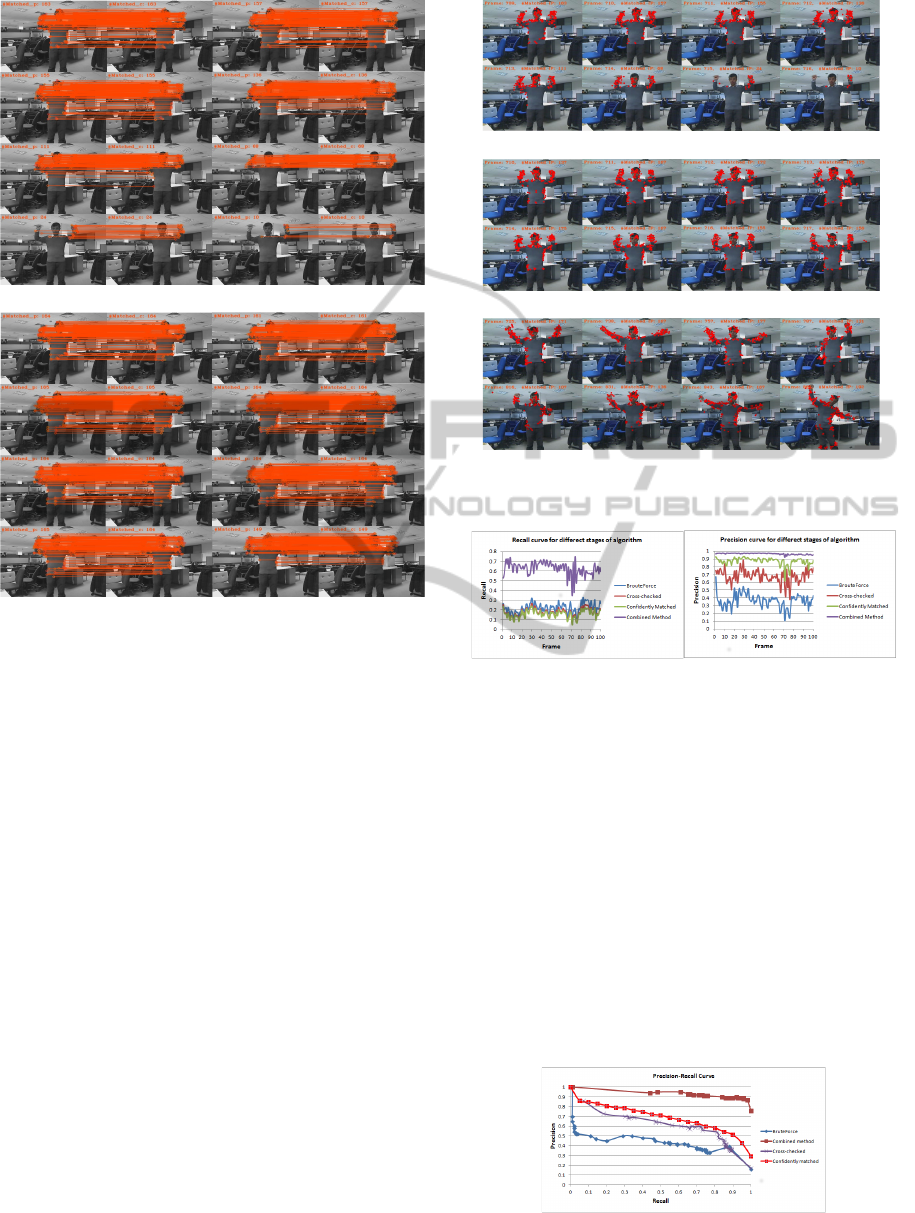
(a) Result of IP matching without LSR.
(b) Result of IP matching with LSR.
Figure 5: Final result of proposed IP matching algorithm
for some consecutive frames without (a) and with (b) the
scoring and refinement (LSR) strategy.
matching algorithm particularly in articulated object
tracking applications.
Figure 6 also shows the matched IPs of some con-
secutive and non-consecutive frames for both with
and without the LSR approach. Figures 6(a) and 6(b)
compares the effect of LSR over eight consecutive
frames while 6(c) shows the result for some random
frames over a 100 frames of video with different level
of articulation and deformations.
Figures 7 and 8 statistically compare different
stages of the proposed algorithm over a 100 frames
with different levels of articulation and deformation.
It is obvious from these figures that the proposed hy-
brid algorithm delivers the best precision and recall
values compared with the others. Although the pre-
cision curve of the Confidently-matched stage is so
close to the hybrid method (Figure 7-right), its recall
value is quite far from it (Figure 7-left). It confirms
that the local-based matching stage only delivers high
accuracy to the algorithm by filtering out the mis-
matched pairs while it leaves lots of IPs unmatched.
Although same level of precision and recall as
1
st
of the algorithm is acceptable in roughly tracking
(a) Matching without LSR over 8 consecutive frames.
(b) Matching with LSR over 8 consecutive frames.
(c) Matching with LSR for 8 non-consecutive frames.
Figure 6: Matched IPs of some frames.
Figure 7: Precision and Recall curves of the algorithm.
of objects, it is not acceptable in articulated object
tracking application with lots of details, such as hu-
man body tracking. In these situations, the reference
IPs should be accurately matched to the target IPs as
much as possible. In fact, Figure 7 shows the capa-
bility of the proposed hybrid IP matching algorithm
in improvement of the recall value while preserving
the precision rate. The efficiency of our approach in
terms of Precision-Recall is shown in Figure 8. The
output of the local-based stage of the algorithm per-
forms roughly the same as the hybrid method for re-
call values less than 0.1. However, they are not so
steady and good for the higher recall values, which it
is essential for articulated object tracking.
Figure 8: Precision-Recall curve of the algorithm.
ICPRAM2014-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
542

4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have proposed a new IP matching al-
gorithm for articulated object (human body) tracking
applications. The key characteristic of our approach
is the increase of precision and recall rates in two se-
quential stages: Firstly, a Local-based IP matching al-
gorithm is performed to find the confidently matched
pairs between the reference and target sets of IPs
(increasing the precision rate); Secondly, a spatial-
based matching algorithm is applied to the confidently
matched pairs to recovers more matched pairs from
the remaining unmatched IPs through graph match-
ing and cyclic string matching (enhancing the recall
rate while the precision rate is kept at high level). We
applied our approach to a sequence of frames with
different levels of articulation and deformations. Ex-
perimental results show promisingly that not only the
proposed algorithm increases the precision rate from
61.53% for BruteForce to 97.81%, but also it im-
proves the recall rate from % 52.33 for BruteForce
to 96.40%.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The proposed work was supported by the Irish Re-
search Council (IRC) under their Enterprise Partner-
ship Program.
REFERENCES
Aguilar, W., Frauel, Y., Escolano, F., Martinez-Perez, M. E.,
Espinosa-Romero, A., and Lozano, M. A. (2009). A
robust Graph Transformation Matching for non-rigid
registration. Image and Vision Computing, 27(7):897–
910.
Bay, H., Ess, A., Tuytelaars, T., and Van Gool, L. (2008).
Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Computer vision
and image understanding, 110(3):346–359.
Benezeth, Y., Jodoin, P.-M., Emile, B., Laurent, H., and
Rosenberger, C. (2010). Comparative study of back-
ground subtraction algorithms. Journal of Electronic
Imaging, 19(3):33003.
Fischler, M. A. and Bolles, R. C. (1981). Random sample
consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with appli-
cations to image analysis and automated cartography.
Communications of the ACM, 24(6):381–395.
Herda, L., Fua, P., Plankers, R., Boulic, R., and Thalmann,
D. (2000). Skeleton-based motion capture for robust
reconstruction of human motion. In Computer Anima-
tion 2000. Proceedings, pages 77–83. IEEE.
Leiserson, C. E., Rivest, R. L., Stein, C., and Cormen, T. H.
(2001). Introduction to algorithms. The MIT press.
Li, B., Meng, Q., and Holstein, H. (2003). Point pattern
matching and applications-a review. In Systems, Man
and Cybernetics, 2003. IEEE International Confer-
ence on, volume 1, pages 729–736. IEEE.
Li, Y., Tsin, Y., Genc, Y., and Kanade, T. (2005). Ob-
ject detection using 2d spatial ordering constraints.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2005.
CVPR 2005. IEEE Computer Society Conference on,
volume 2, pages 711–718. IEEE.
Liu, Z., An, J., and Jing, Y. (2012). A Simple and robust
feature point matching algorithm based on restricted
spatial order constraints for aerial image registration.
Geoscience and Remote Sensing, IEEE Transactions
on, 50(2):514–527.
Lowe, D. G. (2004). Distinctive image features from scale-
invariant keypoints. International journal of computer
vision, 60(2):91–110.
Ma, J., Zhao, J., Tian, J., Tu, Z., and Yuille, A. L. (2013).
Robust estimation of nonrigid transformation for point
set registration. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE.
Maes, M. (1990). On a cyclic string-to-string correction
problem. Information Processing Letters, 35(2):73–
78.
Maji, S. (2006). A Comparison of Feature Descriptors. Uni-
versity of California, Berkeley.
Mikolajczyk, K. and Schmid, C. (2005). A perfor-
mance evaluation of local descriptors. Pattern Analy-
sis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on,
27(10):1615–1630.
Olson, D. L. and Delen, D. (2008). Advanced data mining
techniques [electronic resource]. Springer.
Rublee, E., Rabaud, V., Konolige, K., and Bradski, G.
(2011). ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or
SURF. In Computer Vision (ICCV), 2011 IEEE In-
ternational Conference on, pages 2564–2571. IEEE.
Wagner, R. A. and Fischer, M. J. (1974). The string-
to-string correction problem. Journal of the ACM
(JACM), 21(1):168–173.
Wen, G.-J., Lv, J.-j., and Yu, W.-x. (2008). A high-
performance feature-matching method for image reg-
istration by combining spatial and similarity informa-
tion. Geoscience and Remote Sensing, IEEE Transac-
tions on, 46(4):1266–1277.
Wu, W. Y. (2001). Two-dimensional object recognition
through string matching. Imaging science journal,
49(4):213–221.
Wu, W.-Y. (2011). A string matching method for hand
recognition. In Natural Computation (ICNC), 2011
Seventh International Conference on, volume 3, pages
1598–1601. IEEE.
Zheng, Y. and Doermann, D. (2006). Robust point matching
for nonrigid shapes by preserving local neighborhood
structures. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,
IEEE Transactions on, 28(4):643–649.
Zhou, H., Yuan, Y., and Shi, C. (2009). Object tracking
using sift features and mean shift. Computer Vision
and Image Understanding, 113(3):345–352.
ADynamicHybridLocal-spatialInterestPointMatchingAlgorithmforArticulatedHumanBodyTracking
543
