
Understanding the Genesis of Cardiac Signals in Electrical
Impedance Tomography
M. Proença
1
, F. Braun
1
, M. Lemay
1
, B. Grychtol
2
, M. Bührer
3
, M. Rapin
1
, P. Krammer
4
, S. Böhm
4
,
J. Solà
1
and J.-Ph. Thiran
5, 6
1
Systems Division, Swiss Center for Electronics and Microtechnology (CSEM), Neuchâtel, Switzerland
2
Division of Medical Physics in Radiology, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany
3
Institute for Biomedical Engineering, University and ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
4
Swisstom AG, Landquart, Switzerland
5
Signal Processing Laboratory (LTS5), Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland
6
Department of Radiology, University Hospital Center (CHUV) and University of Lausanne (UNIL), Lausanne, Switzerland
Keywords: Electrical Impedance Tomography, EIT, Cardiac, Pulsatility, Perfusion, Origin, Genesis, Source.
Abstract: Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a safe and low-cost imaging technology allowing the monitoring
of ventilation. While most EIT studies have investigated respiration-related events, EIT-based
cardiovascular applications have received increasing attention over the last years only. Variations in intra-
thoracic blood volume induce impedance changes that can be monitored with EIT and used for the
estimation of hemodynamic parameters. There is, however, increasing evidence that variations in blood
volume are not the only factors contributing to cardiac impedance changes within the heart. The mechanical
action of the myocardium and movement of the heart-lung interface are suspected to generate impedance
changes of non-negligible amplitude. To test this hypothesis we designed a dynamic 2D bio-impedance
model from segmented human magnetic resonance data. EIT simulations were performed and showed that
EIT signals in the heart area might be dominated up to 70% by motion-induced impedance changes.
1 INTRODUCTION
Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a non-
invasive, non-ionizing and low-cost functional
imaging technique allowing real-time visualization
of impedance changes within the thorax. Its typical
monitoring system consists in a belt of electrodes
attached around the subject’s chest. Small
alternating electrical currents are injected in a
sequential pattern. Simultaneous voltage
measurements are performed on the non-injecting
electrodes and are then fed in an image
reconstruction algorithm.
With anatomical structures such as the lungs,
filled with air (low conductivity), and the heart and
blood vessels, filled with blood (high conductivity),
EIT can assess intra-thoracic ventilation and
perfusion distributions (Holder, 2005). While some
commercial EIT devices (such as the Dräger
PulmoVista® 500 monitor or, more recently,
Swisstom’s EIT Pioneer Set) exist and allow the
monitoring of ventilation, the diagnosis of
respiration-related disorders and the estimation of
hemodynamic parameters via EIT still remain
limited to the field of research.
1.1 Cardiac EIT
While research in EIT is mostly dedicated to
ventilation – see (Bayford, 2006) for a review –,
numerous studies have been carried out to evaluate
the potential of EIT for the measurement of
cardiogenic impedance variations, be it for the
assessment of cardiac hemodynamics (Brown, 1992;
Vonk-Noordegraaf, 2000; Grant, 2011) or lung
perfusion (Smit, 2004; Frerichs, 2009; Borges,
2011).
EIT produces image sequences of low spatial but
high temporal resolution. Frame rates as high as 50
images per second are common. It is thus possible to
visualize – for each pixel in the image sequence –
the temporal impedance variations occurring at its
27
Proença M., Braun F., Lemay M., Grychtol B., Bührer M., Rapin M., Krammer P., Böhm S., Solà J. and Thiran J..
Understanding the Genesis of Cardiac Signals in Electrical Impedance Tomography.
DOI: 10.5220/0004793400270034
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing (BIOSIGNALS-2014), pages 27-34
ISBN: 978-989-758-011-6
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

corresponding location. The impedance signal
observed is typically composed of the superposition
of a component at the respiratory frequency and
another component at the cardiac frequency, of
much smaller amplitude (typically less than 5% of
the respiratory component) (Barber, 1990).
Various methods have been proposed in the
literature to separate these two components. The
most common one consists in exploiting the
synchrony of cardiac EIT pulsatile signals with the
electrocardiogram (ECG). Using ECG as a
cardiogenic trigger, hundreds of cardiac cycles can
be aligned and averaged to produce one
representative impedance waveform where the
influence of the respiratory component is strongly
reduced (McArdle, 1988). Alternative methods
consist in filtering the respiratory component out of
the impedance signal, usually well separated from
the cardiac component in the frequency domain
(Leathard, 1994), or more recently by exploiting
principal component analysis (Deibele, 2008).
Although not appropriate for continuous monitoring
in contexts such as intensive care units, asking the
subject to hold his/her breath for a few seconds
remains the simplest and most effective approach
(Frerichs, 2002).
Thorough analysis of the spatial distribution of
the respiratory and cardiac components in EIT image
sequences allows the identification of thoracic
functional structures, such as the heart and lungs,
contained within the EIT electrode plane (Ferrario,
2012). With the respiratory component removed,
pixel-wise impedance signals depict cardiac-related
changes and can thus be processed for hemodynamic
parameters estimation and EIT-based cardiac
applications.
1.2 Controversial Origin
of Cardiac-related Signals
At each heartbeat, a certain amount of blood known
as stroke volume is ejected into both the systemic
and pulmonary circulations. These blood volume
displacements, along with the distensibility of the
vessels and the motion of the heart, generate
impedance variations at the cardiac frequency.
Dissociating these various sources of pulsatility, or
even quantifying their respective influence, is not
trivial. Yet the exploitation of cardiac-related signals
in EIT for studying hemodynamics depends on
solving this issue.
The very nature of EIT itself becomes a
challenging aspect when it comes to the
interpretation of cardiac-related signals. For
instance, from the EIT transverse plane view,
structures such as the atria can hardly be
discriminated from the ventricles (Vonk-
Noordegraaf, 2000). Moreover, the diffusive nature
of electrical currents several centimetres above and
below the electrode plane makes the interpretation of
EIT pixel-wise signals complex (Borges, 2011). For
example, a pixel located in the posterior region of
the heart could possibly undergo changes in
impedance originating from the atria, the ventricles,
the aorta and/or the pulmonary arteries, as well as
pulmonary perfusion and heart motion. In addition
to this puzzle, the well-known anatomical distortions
of impedance tomograms make the localization –
and thus the understanding – of cardiac-related
impedance changes even more challenging (Barber,
1990).
1.2.1 Lung Pulsatility
All these difficulties do not just concern the
monitoring of functional cardiac activity. In their
review, Nguyen et al. quote numerous studies that
have tackled the challenge that represents lung
perfusion via EIT (Nguyen, 2012). However,
uncertainties remain. In particular, the influence of
the heart’s motion on the lungs at the heart-lung
interface remains one of the main sources of
confusion (Frerichs, 2009). The unclear nature of
cardiac-related impedance changes taking place
within the lungs requires the use of a term more
neutral than perfusion, such as lung pulsatility
(Hellige, 2011).
Removing or isolating heart motion-induced
impedance changes is challenging. Many studies,
such as (Kunst, 1998; Vonk-Noordegraaf, 1998;
Smit, 2004), have tried to minimize the effects of the
motion of the heart on pulmonary pulsatility by
measuring EIT at the level of the third intercostal
space in human subjects with their arms stretched
above their head. However, this configuration is not
only unphysiologic and impractical for intensive
care or long-term monitoring, it has also been shown
to fail to suppress the influence of the heart’s motion
occasionally. These mechanical perturbations could
also be the source of inconsistencies between several
studies regarding the genesis of pulsatile signals in
EIT. For instance, Smit et al. reported that the
magnitude of the pulsatile signals in the lungs was
only dependent on the size of the pulmonary
microvascular bed – or, alternatively, on the
distensibility of pulmonary vessels – but not on
stroke volume (Smit, 2004). However, Fagerberg et
al. reported significant correlations with stroke
BIOSIGNALS2014-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
28
volume, concluding that vessel distensibility only
plays a minor role in the genesis of pulmonary
pulsatility (Fagerberg, 2009). Additional
contradictions regarding the origin of cardiac-related
signals in EIT have recently been highlighted
(Braun, 2013). Cardiac and pulmonary regions
showing high pulsatility energy did not spatially
match the passage of an impedance contrast agent
(hypersaline solution), suggesting that the heart’s
motion could be affecting significantly cardiac EIT
signals.
1.2.2 The Need for a Dynamic Model
In order to provide new insights to these unanswered
questions, we designed a novel experiment based on
the hypothesis that cardiac impedance changes in
EIT are not only blood volume-related but also
motion-induced. Testing this hypothesis as well as
localizing and quantifying these mechanical
perturbations requires the use of a dynamic bio-
impedance model. To that end, we developed an
anatomically-consistent dynamic model from
segmented human magnetic resonance (MR) data
and used it for EIT simulations. In particular, three
scenarios, each one depicting a specific cardiac
behaviour, were simulated. In one scenario,
impedance changes were induced by blood volume
variations only. In a second scenario, impedance
changes were induced by the heart's motion only.
Finally, in a third scenario, impedance changes were
induced by both, blood volume variations and heart
motion. The objective was to isolate and quantify the
effect of each factor on the global cardiac impedance
change. This whole process is described in more
details in Section 2. The simulation results are
provided in Section 3 and analysed in Section 4.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The MR data acquisition is detailed in Section 2.1.
Section 2.2 describes the creation process of our 2D
dynamic bio-impedance model. Finally, the EIT
simulations and image reconstruction details are
provided in Section 2.3.
2.1 MRI Acquisition
The subject enrolled in this experiment was an 83-
kg, 183-cm tall 50-year-old male with an underbust
girth of 100 cm. MR images were acquired with a
3T Philips Achieva instrument. ECG-gated breath-
held scans were performed in an oblique plane along
the heart’s long axis. A full cardiac cycle was
imaged with a temporal resolution of 43 ms,
resulting in a total of 20 2D image slices. The spatial
resolution in the medial-lateral and anterior-posterior
directions was 0.94 mm/pixel, and slice thickness 8
mm.
2.2 EIT Model Creation
2.2.1 Mr Data Segmentation
The cardiac cavities (atria and ventricles) and the
myocardium were segmented manually at each of
the 20 frames of the cardiac cycle in the MR images.
The lungs, the pericardium, the descending aorta, the
skeletal muscle, the spine and the thorax contour
were segmented manually in the first frame only.
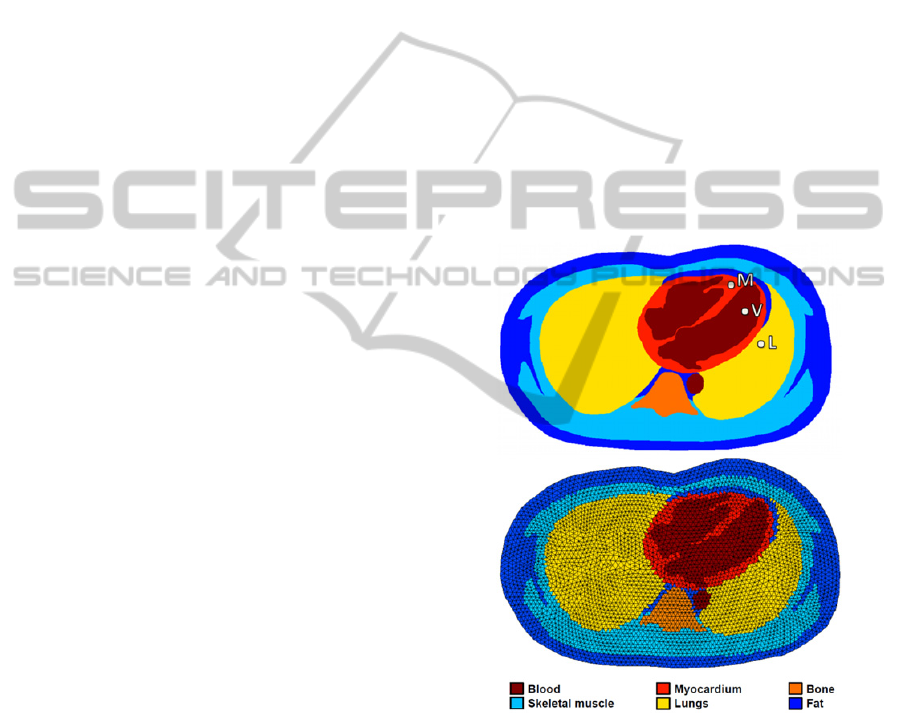
The resulting segmentation can be seen in the top
panel of Figure 1 (for one frame of the cardiac
cycle).
Figure 1: Top panel – Example of a segmented frame. The
highlighted myocardial (M), ventricular (V) and anterior
lung (L) locations will be used in Section 3. Bottom panel
– The corresponding bio-impedance mesh for EIT
simulations.
2.2.2 Model Assumptions
The following assumptions were made in the
creation of our model following today’s standard for
2D EIT:
Electrical currents travel within the volume
scanned by the MR instrument;
UnderstandingtheGenesisofCardiacSignalsinElectricalImpedanceTomography
29

Organs and tissues are isotropic (Guha, 1973);
The reactive part of the impedance of organs and
tissues is negligible in the EIT frequency range
(Malmivuo, 1995). Similarly, magnetic effects can
be neglected at those frequencies (Holder, 2005);
The thorax contains no internal current sources
(Holder, 2005);
All points on the body surface in contact with an
electrode have the same potential as the electrode
and at all other surface points the electrical
potential gradient normal to the surface is zero
(Guha, 1973). Under these two boundary
conditions, the generalized Laplace’s equation
governing the domain of interest has a unique
solution (Kim, 1988).
2.2.3 Bio-impedance Mesh Generation
An extruded mesh of tetrahedral elements was
generated using NETGEN and the open source
EIDORS toolbox (Grychtol, 2012), and fits the
subject’s thorax contour in the scanned oblique
plane. At each frame of the cardiac cycle, each finite
element was assigned an electrical conductivity
value of the organ or tissue it belonged to in the time
laps of the current frame. The biological values of
electrical conductivity used in this model are listed
in Table 1.
Table 1: Tissue conductivities for an excitation frequency
of 200 kHz (Gabriel, 1996).
Tissue Conductivity (S·m
-1
)
Blood 7 × 10
-1
Skeletal muscle 4 × 10
-1
Myocardium 2.5 × 10
-1
Lungs (inflated) 8.5 × 10
-2
Bone 8.5 × 10
-2
Fat 2.5 × 10
-2
2.3 EIT Simulations
2.3.1 Simulated Scenarios
Three different 2D dynamic meshes were created,
each depicting a specific cardiac behaviour:
Scenario A. Only the dynamics of the filling and
emptying cardiac cavities are used in this model
while the myocardium remains static throughout
the whole cardiac cycle (the same segmentation is
used for all frames, thereby suppressing other
changes). Similarly, all other organs and tissues
remain static for all frames. Therefore, this
scenario simulates blood volume-related
impedance changes only.
Scenario B. Only the dynamics of the myocardium
is maintained in this model. The cardiac cavities
remain static throughout the whole cardiac cycle
(the same segmentation is used for all frames, thus
suppressing other changes). Similarly, all other
organs and tissues remain static for all frames.
Therefore, this scenario simulates cardiac motion-
induced impedance changes only.
Scenario C. The dynamics of both, the cardiac
cavities and the myocardium are simulated in this
model. All other organs and tissues remain static
throughout the whole cardiac cycle. Therefore, this
scenario simulates both blood volume-related and
motion-induced impedance changes.
Modelling variations in blood volume and heart
motion separately allows isolating and thus
quantifying the effect of each one of these factors
affecting the global cardiac impedance change.
2.3.2 Image Sequences Reconstruction
EIT reconstruction is a severely ill-conditioned
inverse problem. The diffusive nature of electrical
current propagation only adds up to the complexity.
Obtaining absolute impedance values in EIT is not
only of great difficulty, but not necessary for most
EIT-based biomedical applications, which are more
interested in functional information (namely, the
variation of impedance around a reference baseline
value) (Denai, 2010). For this reason, difference EIT
is typically used. Instead of directly considering the
voltage measurements and the conductivity
distribution , it makes use of difference data
, where
is a reference set of voltages
typically obtained by averaging the measurements of
the first frames of an EIT recording. It corresponds
to the so-called background conductivity distribution
, used to define the difference conductivity
distribution
. As a result, linear EIT
reconstruction can be represented by an inverse
matrix R, which translates difference measurements
into a difference conductivity image
:
(1)
The computation of the inverse matrix depends on
the reconstruction method. In that context, the
GREIT algorithm (Adler, 2009) distinguishes itself
by encoding performance requirements directly
within the inverse matrix. In particular, is
pretrained by optimizing several figures of merit
such as amplitude response and position error.
Evaluating how much blood volume variations
and heart motion affect – particularly in terms of
amplitude – the the global cardiac impedance signal,
BIOSIGNALS2014-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
30

Figure 2: Impedance change occurring at the myocardial
(M), ventricular (V) and anterior lung (L) pixels for all
scenarios including the control scenario. A schematic ECG
is also displayed as an illustrative timing reference. The
meaning of the cardiac phases P1 to P5 (light and dark
grey areas) and their associated reference timings t
0
to t
4
is
detailed in Section 4.
requires such performance criteria to be optimal.
Consequently, the GREIT algorithm was used to
perform EIT simulations for each of the three
specific scenarios described in Section 2.3.1.
Difference data were obtained by using the first
frame (representing the end of diastole) as reference
data set. Each simulated scenario (A, B and C)
resulted in a 20-frame sequence of 60 × 40 pixel
images.
2.3.3 Control Scenario
An injected electrical current flowing through the
heart will sequentially go through tissues belonging
to the cardiac cavities and the myocardium, similarly
to a current flowing through impedances connected
in series. As a consequence, the impedances of
scenario C should theoretically be similar to the sum
of the impedances of scenarios A and B, since it
encompasses both of their respective behaviours
(blood volume-related impedance changes and
motion-induced impedance changes). For this
reason, a control scenario (scenario A+B) was
virtually created by summing the image sequences
reconstructed in scenarios A and B. It is expected to
behave similarly to scenario C.
3 RESULTS
Figure 2 illustrates, for all scenarios (A, B and C) as
well as the control scenario A+B, the impedance
changes occurring at the myocardial (M), ventricular
(V) and anterior lung (L) pixels shown in Figure 1.
Figure 3a illustrates the peak systolic impedance
value (value at frame 7) for all scenarios, including
the control scenario, at the myocardial (M),
ventricular (V) and anterior lung (L) pixels, while
Figure 3b illustrates the percentage of contribution
of blood volume-related (scenario A) and motion-
induced (scenario B) impedance changes to the
global impedance change (scenario C).
4 DISCUSSION
Three different scenarios were investigated to
evaluate the influence of blood volume changes and
heart motion on the EIT cardiac signals. A 2D
dynamic bio-impedance model was created from the
segmentation MR images. Three cardiac behaviours
– namely, blood volume-related (scenario A),
motion-induced (scenario B) or both blood volume-
related and motion-induced (scenario C) impedance
changes – were simulated, and EIT image sequences
reconstructed. A control scenario A+B was created
virtually by summing the image sequences of the
first two scenarios.
UnderstandingtheGenesisofCardiacSignalsinElectricalImpedanceTomography
31

In the following discussion, we first verify the
validity of the impedance waveforms observed at
three specific pixel locations (Section 4.1). We then
investigate the influence of each impedance-
affecting factor to the global cardiac EIT signal
(Section 4.2). Finally, we highlight some limitations
of our model and suggest some possible future
investigations (Section 4.3).
4.1 Impedance Waveforms
Morphology Validation
A standard cardiac cycle can be subdivided into two
isovolumetric phases (P1 and P3 in Figure 2), during
which blood volume remains constant in the
ventricles, and three anisovolumetric phases (P2, P4
and P5), during which changes in blood volume
occur.
In scenario A (dashed grey curves in Figure 2),
the only impedance-affecting factor is the change in
blood volume induced by volume variations of the
cardiac cavities. Shortly after the R peak of the ECG
(at time t
0
, corresponding to frame 0 in Figure 2), the
first isovolumetric phase (P1) begins. No variation
in blood volume occurs and thus the impedance
waveform remains flat. When the semilunar valves
open at t
1
≈ t
0
+ 80 ms (Levick, 2010)
(corresponding to frame 2), the first anisovolumetric
phase (ventricular ejection) starts, and blood volume
decreases in the cardiac cavities (phase P2 in Figure
2). The heart thus becomes less conductive and its
impedance increases steeply. A short isovolumetric
relaxation phase follows (P3). At t
3
≈ t
0
+ 440 ms
(Levick, 2010) (frame 9), when the atrioventricular
valves open, the ventricular volume starts returning
(rapidly at first, then slowly) to its baseline value as
ventricular filling begins (phase P4 in Figure 2). At
the start of atrial systole at t
4
≈ t
0
+ T – 160 ms
(Levick, 2010) (frame 16), where T is the cardiac
period, ventricular blood volume increases slightly
while atrial volume decreases by the same amount,
thus not influencing significantly the global
impedance change (phase P5 in Figure 2).
In scenario B (solid black curves in Figure 2),
only the dynamics of the myocardium are simulated.
The remaining organs and tissues remain static. This
scenario thus simulates motion-induced impedance
changes. During ventricular systole (phase P2 in
Figure 2), longitudinal shortening of the
myocardium begins as the apex is pulled towards the
atrioventricular plane. The space occupied by the
myocardium during diastole becomes occupied by
the pericardium, the conductivity of which is ten
times smaller than that of the cardiac muscle (Table
1). As a result, impedance increases abruptly. As the
semilunar valves close, the myocardium undergoes
elastic recoil and starts reoccupying the space it left
during ventricular systole, thus producing an
impedance decrease (phase P4 in Figure 2). The
synchrony between the waveforms of scenarios A
and B relates on the one hand to the simultaneous
beginning of the ejection phase and the myocardial
contraction, and on the other hand to the fact that the
opening of the atrioventricular valves (and thus
ventricular refilling) is caused by a sharp decrease in
pressure due to myocardial relaxation (Levick,
2010).
In scenario C (solid grey curves in Figure 2),
which aims at reflecting the real behaviour of the
heart, the dynamics of both, the cardiac cavities and
the myocardium are maintained to simulate both,
blood volume-related and motion-induced
impedance changes. The remaining organs and
tissues are static. As the strong similarity between
the solid grey and dashed back curves (scenario C
and control scenario A+B) of Figure 2 illustrates, the
contributions of blood volume variations and heart
motion add up to produce the impedance changes
observed in scenario C.
Figure 3: Left panel – Peak systolic impedance value for
all scenarios, including the control scenario, at the
myocardial (M), ventricular (V) and anterior lung (L)
pixels. Right panel – Contribution of blood volume-related
(scenario A) and motion-induced (scenario B) impedance
changes to the global impedance change (scenario C).
These percentages were computed as the ratio of the peak
systolic values of scenarios A and B (Figure 3a) with those
of scenario C.
4.2 Influence of each Factor Affecting
Impedance
The impedance changes occurring at three different
BIOSIGNALS2014-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
32

anatomical locations (M, V and L, depicted in
Figure 1) were investigated. The resulting
impedance waveforms are shown in Figure 2. It is
worth noting that the diffusive nature of electrical
current propagation makes the mapping of function
onto anatomy challenging (i.e. a pixel identified as
belonging to a given organ or tissue using MR
information does not necessarily only reflect the
functional impedance information of the said organ
or tissue). For instance, our anterior lung pixel (L) is
expected to be slightly affected by both, cardiac
blood volume-related and motion-induced
impedance changes, because of its proximity to both
sources of perturbations. Similarly, motion-induced
impedance changes are expected to be larger in the
myocardial (M) pixel than in the ventricular (V)
pixel. The opposite is expected for blood volume-
related changes.
These assumptions are confirmed in Figure 3a,
which illustrates how the amplitude of motion-
induced impedance changes (scenario B) decreases
as one moves away from the heart’s long axis (away
from pixel M). Conversely, the amplitude of blood
volume-related impedance changes (scenario A) is
maximal when measured in the ventricular pixel (V).
The amplitude of the impedance change in the
anterior lung pixel (L) is significantly smaller for
both factors. It would be interesting in a future study
to compare this amplitude to that of impedance
changes of pulmonary origin to assess the level of
perturbation caused by cardiogenic impedance
variations on the neighbouring lung region.
Figure 3b quantifies the influence of each factor
to the cardiac EIT signal. Based on these
simulations, it appears that in the myocardial (M)
and in the ventricular (V) pixels the signal is
dominated by impedance changes originating from
the heart’s motion. In the anterior lung pixel (L) the
influence of both factors is approximately the same.
According to our model, it thus appears that the
impedance change originating from the heart’s
motion is the main factor affecting the global cardiac
impedance change.
4.3 Limitations
Our observations have provided novel insights into
the understanding of the genesis of cardiac
impedance changes in EIT. However, these results
necessitate further investigations, as they are based
on a simplified simulation model showing three
main limitations:
The model is two-dimensional, while electrical
currents are known to propagate in three
dimensions. Impedance changes occurring above
and below the electrode plane are thus not
considered adequately.
The blood volume variations and the motion of the
remaining organs and tissues are not modelled. In
particular, the influence of respiratory movements,
pulmonary perfusion and blood volume changes in
the major elastic arteries, is not taken into account.
While this allows isolating the influence of each
individual factor in simulations, it neglects their
interdependencies acting in reality.
Only one subject was used in our experiment.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We developed a 2D dynamic bio-impedance model
for EIT simulations. Our study shows that EIT
signals in the heart area might be dominated by
motion-induced impedance changes.
Based on these important observations, it would
be interesting to investigate possible solutions, such
as exploiting larger frequency content or a multi-
frequency approach to perform source separation, or
enhancing the EIT signals using motion-
compensating models. It is worth mentioning that
these approaches could be exploited either before or
after image reconstruction.
Additionally, experimental and clinical studies
should be performed to confirm what we observed in
our model.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was made possible by grants from the
SNSF/Nano-Tera.CH’s project OBESENSE
(20NA21-1430801).
REFERENCES
Adler, A., Arnold, J. H., Bayford, R. et al., 2009. GREIT:
a unified approach to 2D linear EIT reconstruction of
lung images, Physiological Measurement, vol. 30, no.
16, pp. S35–S55.
Barber, D. C., 1990. Quantification in impedance imaging,
Clinical Physics and Physiological Measurement, vol.
11 (suppl A), pp. 45-56.
Bayford, R. H., 2006. Bioimpedance tomography
(electrical impedance tomography), Annual Review of
Biomedical Engineering, vol. 8, pp. 63-91.
Borges, J. B., Suarez-Sipmann, F., Böhm S. H. et al.,
2011. Regional lung perfusion estimated by electrical
UnderstandingtheGenesisofCardiacSignalsinElectricalImpedanceTomography
33

impedance tomography in a piglet model of lung
collapse, Journal of Applied Physiology, vol. 112, no.
11, pp. 225-236.
Braun, F., 2013. Systolic Time Intervals Measured by
Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT), Swiss
Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich, Switzerland.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-009947722.
Brown, B.H., Leathard, A., Sinton, A. et al., 1992. Blood
flow imaging using electrical impedance tomography,
Clinical Physics and Physiological Measurement, vol.
13 (suppl A), pp. 175-179.
Deibele, J. M., Luepschen H. and S. Leonhardt, 2008.
Dynamic separation of pulmonary and cardiac
changes in electrical impedance tomography,
Physiological Measurement, vol. 29, no. 16, pp. S1-
S14.
Denai, M. A., Mahfouf, M., Mohamad-Samuri, S. et al.,
2010. Absolute Electrical Impedance Tomography
(aEIT) Guided Ventilation Therapy in Critical Care
Patients: Simulations and Future Trends, IEEE
Transactions on Information Technology in
Biomedicine, vol. 14, no. 13, pp. 641-649.
Fagerberg, A., Stenqvist, O. and Åneman, A., 2009.
Monitoring pulmonary perfusion by electrical
impedance tomography: an evaluation in a pig model,
Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, vol. 53, no. 12,
pp. 152-158.
Ferrario, D., Grychtol, B., Solà, J. et al., 2012. Towards
morphological thoracic EIT: Major signal sources
correspond to respective organ locations in CT, IEEE
Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 59, no.
111, pp. 3000-3008.
Frerichs, I., Hinz, J., Herrmann, P. et al., 2002. Regional
lung perfusion as determined by electrical impedance
tomography in comparison with electron beam CT
imaging, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol.
21, no. 16, pp. 646-652.
Frerichs, I., Pulletz, S., Elke, G. et al., 2009. Assessment of
changes in distribution of lung perfusion by electrical
impedance tomography, Respiration, vol. 77, no. 13,
pp. 282-291.
Gabriel, S., Lau, R. W. and Gabriel, C., 1996. The
dielectric properties of biological tissues: III.
Parametric models for the dielectric spectrum of
tissues, Physics in Medicine and Biology, vol. 41, no.
111, pp. 2271–2293.
Grant, C. A., Pham, T., Hough, J. et al., 2011.
Measurement of ventilation and cardiac related
impedance changes with electrical impedance
tomography, Critical Care, vol. 15, no. 11, p. R37.
Grychtol, B., Lionheart, W. R. B., Bodenstein, M. et al.,
2012. Impact of Model Shape Mismatch on
Reconstruction Quality in Electrical Impedance
Tomography, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging,
vol. 31, no. 19, pp. 1754-1760.
Guha, S. K., Khan, M. R. and Tandon, S. N., 1973.
Electrical field distribution in the human body,
Physics in Medicine and Biology, vol. 18, no. 5, pp.
712-720.
Hellige, G., Hahn, G., 2011.
Cardiac-related impedance
changes obtained by electrical impedance
tomography: an acceptable parameter for assessment
of pulmonary perfusion?, Critical Care, vol. 15, p.
430.
Holder, D. S., 2005. Electrical impedance tomography:
methods, history and applications, Institute of Physics
Publishing. London.
Kim, D. W., Baker, L. E., Pearce, J. A. and Kim, W. K.,
1988. Origins of the impedance change in impedance
cardiography by a three-dimensional finite element
model, IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,
vol. 35, no. 112, pp. 993-1000.
Kunst, P. W. A., Vonk-Noordegraaf, A., Hoekstra, O. S. et
al., 1998. Ventilation and perfusion imaging by
electrical impedance tomography: a comparison with
radionuclide scanning, Physiological Measurement,
vol. 19, no. 14, pp. 481–490.
Leathard, A. D., Brown, B. H., Campbell, J. et al., 1994. A
comparison of ventilatory and cardiac related changes
in EIT images of normal human lungs and of lungs
with pulmonary emboli, Physiological Measurement,
vol. 15 (suppl 2A), pp. A137-A146.
Levick, J. R., 2010. An introduction to cardiovascular
physiology, Arnold. London, 5
th
edition.
Malmivuo, J. and Plonsey, R., 1995. 7: Volume source
and volume conductor, in Bioelectromagnetism:
Principles and Applications of Bioelectric and
Biomagnetic Fields, University Press. New York.
McArdle, F. J., Suggett, A. J., Brown, B. H. and Barber,
D. C., 1988. An assessment of dynamic images by
applied potential tomography for monitoring
pulmonary perfusion, Clinical Physics and
Physiological Measurement, vol. 9 (suppl A), pp. 87-
91.
Nguyen, D. T., Jin, C., Thiagalingam, A. and McEwan, A.
L., 2012. A review on electrical impedance
tomography for pulmonary perfusion imaging,
Physiological Measurement, vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 695–
706.
Smit, H. J., Vonk-Noordegraaf, A., Marcus, J. T. et al.,
2004. Determinants of pulmonary perfusion measured
by electrical impedance tomography, European
Journal of Applied Physiology, vol. 92, no. 1, pp. 45-
49.
Vonk-Noordegraaf, A., Kunst, P. W. A., Janse, A. et al.,
1998. Pulmonary perfusion measured by means of
electrical impedance tomography, Physiological
Measurement, vol. 19, no. 12, pp. 263–273.
Vonk-Noordegraaf, A., Janse, A., Marcus, J. T. et al.,
2000. Determination of stroke volume by means of
electrical impedance tomography, Physiological
Measurement, vol. 21, no. 12, pp. 285–293.
BIOSIGNALS2014-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
34
