
A Fast Computation Method for IQA Metrics Based on their Typical Set
Vittoria Bruni
1,2
and Domenico Vitulano
2
1
Dept. of SBAI, Faculty of Engineering, Univ. of Rome ”Sapienza”, Via A. Scarpa 16, 00161 Rome, Italy
2
Istituto per le Applicazioni del Calcolo ”M. Picone” - C.N.R., Via dei Taurini 19, 00185 Rome, Italy
Keywords:
Information Theory, SSIM, Asymptotic Equipartition Property, Image Quality Assessment.
Abstract:
This paper deals with the typical set of an image quality assessment (IQA) measure. In particular, it focuses on
the well known and widely used Structural SIMilarity index (SSIM). In agreement with Information Theory,
the visual distortion typical set is composed of the least amount of information necessary to estimate the
quality of the distorted image. General criteria for an effective and fruitful computation of the set will be
given. As it will be shown, the typical set allows to increase IQA efficiency by considerably speeding up its
computation, thanks to the reduced number of image blocks used for the evaluation of the considered IQA
metric.
1 INTRODUCTION
Several neurological studies proved that a few points
attract human attention in the early vision (Monte
et al., 2005; Frazor and Geisler, 2006). Those points
are able to code the significant content of the scene
and are known as fixation points (Monte et al., 2005;
Frazor and Geisler, 2006; Winkler, 2005). They al-
low to synthesize (and understand (Grunwald, 2004))
image information in a very small lapse of time —
200-300 msecs per fixation point. A wide literature
focused on methods and algorithms able to find these
characteristic points and most of them rely on the con-
cept of saliency maps (Wang et al., 2010; Rivera et al.,
2007; Benabdelkader and Boulemden, 2005; Bruni
et al., 2011) i.e., those maps that label image con-
tent in a hierarchical way, according to its visual ap-
pearance. As a matter of fact, bearing in mind some
well-known concepts of Information Theory (IT), the
aforementioned set of points can be seen as the typical
set of the ”source image” (Cover and Thomas, 1991)
i.e., the one that contains all the information concern-
ing the visual content of the image; that is why we
will refer to it as the visual typical set. On the other
hand, recently the growing need of measures that cor-
relate with the Human Visual System (HVS) better
than the classical Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) (Win-
kler, 2005; Gonzalez and Woods, 2002) led to the def-
inition of new Full Reference (FR) quality measures,
that compare the original image I with a distorted ver-
sion J (Sheikh et al., 2005; Sheikh and Bovik, 2006;
Zhang and Jernigan, 2006; Wang and E.P.Simoncelli,
2005; Wang and Li, 2011; Bruni et al., 2013a; Bruni
et al., 2013b). Despite their high correlation with
HVS, most of the proposed FR measures are compu-
tationally more demanding than SNR or PSNR (Peak
Signal to Noise Ratio) and then less attractive for real
time applications, especially video processing based
applications. The objective of this paper is to ask
whether there exists a Visual Distortion Typical Set
A
ε
M
for a given FR quality measure M. In other words
we are wondering if a given FR measure can be suc-
cessfully evaluated from a reduced number of image
pixels. In fact, as it happens in the observation pro-
cess of a single image, an observer usually ’looks at’
just some salient regions in the observed image, rather
than checking all its pixels, before assigning a qual-
ity score to it. It turns out that it is reasonable to
assume that there exists an ’absolute’ Visual Distor-
tion Typical Set: the one employed by HVS in the ob-
servation process. For image quality assessment, A
ε
M
will be then composed of a subset of corresponding
pixels in the original image I and in the distorted J
and it will also depend on the FR quality measure M
and on ε. The latter represents the distance between
M estimated on A
ε
M
(i.e.
ˆ
M) and M estimated on the
whole images I and J (i.e. M). Since the search of A
ε
M
seems to be not straightforward at all, this paper will
focus on the A
ε
M
for a specific Full Reference mea-
sure, namely the Structural SIMilarity index (SSIM)
(Wang et al., 2004a; Wang et al., 2004b), and it will be
studied from both a practical and theoretical point of
199
Bruni V. and Vitulano D..
A Fast Computation Method for IQA Metrics Based on their Typical Set.
DOI: 10.5220/0004820301990206
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM-2014), pages 199-206
ISBN: 978-989-758-018-5
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Figure 1: Venn diagram for the typical sets of SSIM, SNR
and HVS (unknown).
view. We expect that any FR measure has a different
A
ε
M
, with a partial (hopefully wide) intersection with
the absolute one, as depicted in Fig. 1, according to
what extent the FR measure correlates with HVS. The
estimation of the visual distortion typical set A
ε
M
is
twofold advantageous. From a practical point of view,
it would allow to estimate
¯
M just from a subset of the
available information (I and J) within a small error
ε, with a considerable computational saving. From a
more theoretical point of view, it would permit to bet-
ter understand the HVS and i) to design new and more
precise FR measures, able to simulate the complexity
of the human vision ii) to embed FR quality measures
in the minimization of ’HVS based functionals’, iii)
to make a basis for a formal explanation of Visual In-
formation Theory (Bruni et al., 2013b), with effects
on new visive image coding schemes etc..
In this paper we will focus on the reduction of the
computational complexity of FR measures, with par-
ticular reference to SSIM. The aim is to show that A
ε
M
allows to speed up SSIM evaluation with a very small
estimation error i.e., SSIM can be estimated from a
selected subset of blocks with high precision. Experi-
mental results on LIVE database show the robustness
of the proposed method to different kinds of degrada-
tion.
The outline of the paper is the following. Next
section addresses the problem of how to define A
ε
M
and how to look for a sequence belonging to it. Some
theoretical findings that guide a correct SSIM compu-
tation and its complexity reduction will be presented.
Section 3 presents some experimentalresults that con-
firm the theoretical findings of Section 2. Concluding
remarks and guidelines for future research are given
in the last Section.
2 VISUAL DISTORTION
TYPICAL SET
The estimation of the visual distortion typical set A
ε
M
yields as side effect some interesting theoretical re-
sults that will be a good ground basis for practical
purposes. In order to better understand them, we will
consider one of the most effective and widely used
HVS-based FR IQA measures: SSIM (Wang et al.,
2004a; Wang et al., 2004b). Starting from an W
1
×W
2
(original) image I and a distorted version J, SSIM can
be computed via the following simple algorithm:
1. Split I into a set of N
0
overlapping blocks {b
i
} of
size l × l and centered at each pixel of I (note that
W
1
×W
2
l×l
≤ N
0
≤ W
1
×W
2
). Make the same for the
distorted version J, achieving blocks {d
i
}.
2. For each couple of blocks (b
i
, d
i
), estimate SSIM:
M
i
=
2µ
b
i
µ
d
i
+C
1
µ
2
b
i
+µ
2
d
i
+C
1
2σ
b
i
d
i
+C
3
σ
2
b
i
+σ
2
d
i
+C
2
, where C
1
,C
2
and C
3
are numerical stabilizing constants (see (Wang
et al., 2004a) for details). The array M (or the
matrix, as to each pixel of I or J can be assigned
the corresponding SSIM value) is then produced.
3. Compute the mean
1
of M:
M =
1
N
0
∑
N
0
i=1
M
i
.
SSIM is computed in correspondence to each pixel of
the image, it involves block-based operations and it
adopts a pooling strategy by assigning equal weights
to each pixel. However, one may wonder if these are
the best implementation choices. For instance, one
may ask for:
1. Reduction of the Information. Is the whole I
and J’s information really important?
2. Selection of the Best Reduction Domain. Is it
more convenient to reduce I and J’s information
or to reduce the M’s information?
3. Locality of the Selected Information. Is it more
convenient to select I (J) samples from local re-
gions (for instance, blocks) or to select them ran-
domly (not locally) from I (J)?
4. Overlapping Blocks. In the case of blocks based
measures, have blocks to be overlapped?
5. ProcedureforFinding A
ε
M
. Is there a formal (and
possibly fast) procedure to find this reduced infor-
mation?
A formal answer to these questions is given below.
2.1 Reduction of Information
From a qualitative point of view, the visual distor-
tion typical set A
ε
M
can be defined as a subset of all
sequences composed of samples of I (and the corre-
sponding ones of J) such that they give an approxi-
mated value (
ˆ
M) of the expected value
M of M within
an error ε, i.e.: |
ˆ
M − M| < ε. More formally, A
ε
M
can
be thought in terms of Information Theory quantities
(Cover and Thomas, 1991). Shannon typical set is
1
If the mean is computed in the whole image for N
0
=
W
1
× W
2
, it corresponds to the expected value of M, i.e.
E[M]. However, in order to make the notation less heavy,
the symbol
· will be used in the paper.
ICPRAM2014-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
200

Figure 2: The original image I is composed of two homo-
geneous regions X
1
, X
2
. Y
1
and Y
2
are the corresponding
regions in the distorted copy J.
defined as the set of sequences of fixed size whose
entropy is close to the entropy of the source. Simi-
larly, we can think about the original image I as the
first source associated to the variable X, its distorted
version J associated to the variable Y while the vari-
able Z = M(X,Y) characterizes the source M which,
in turn, depends on X and Y. A
ε
M
also depends, even
though not explicitly, on the kind of degradation D
J
that produces J starting from the original image I:
J = D
J
(I). However, D
J
can be considered ’embed-
ded’ in J and it will not explicitly mentioned in the
sequel. A
ε
M
will be then composed of the subset of se-
quences {X
1
, .., X
N
r
,Y
1
, ..,Y
N
r
} of size 2N
r
< 2N
0
such
that for a fixed ε > 0 it holds
|
M(X,Y) − M(X
1
, .., X
N
r
,Y
1
, ..,Y
N
r
)| < ε. (1)
The existence of A
ε
M
is guaranteed by existing infor-
mation theoretic results (Cover and Thomas, 1991),
that is why we will focus on how to select and char-
acterize the sequence (X
1
, .., X
N
r
,Y
1
, ..,Y
N
r
) such that
eq. (1) is satisfied. This problem can be seen as
an application of the weak law of large numbers,
which states that for i.i.d. r.v.s X
i
it holds
1
n
∑
n
i=1
X
i
P
→
E[X] n → ∞, where P indicates the convergence
in probability and E[X] is the expected value of X.
However, it is more convenient to use the equiva-
lent concept, known as the Asymptotic Equiparti-
tion Property (AEP) (Cover and Thomas, 1991), i.e.:
1
n
log
1
p(X
1
,X
2
,..,X
n
)
P
→ H(X) n → ∞, where H(X) is
the entropy of X and X
i
are i.i.d. r.vs. That is why
in the sequel just the entropy will be considered. En-
tropy is more mathematically tractable as it gradually
increases as the number of samples grows (Cover and
Thomas, 1991), while it is not so for the mean value,
as proved by the following Proposition whose proof
is in the Appendix.
Prop. 1 Let X ∼ Q with finite alphabet χ and
{X
1
} ∼ p
1
, {X
1
, X
2
} ∼ p
2
, ...{X
1
, X
2
, . . . X
n
} ∼ p
n
, ...
while µ
n
be the mean value of the pdf p
n
, µ be the
mean value of the pdf Q and M
n
= max
x∈χ
|x|. Then
1. in general, the sequence {µ
n
} is not monotonic for
increasing n;
2. |µ
n
− µ|
2
≤ 2M
2
n
D
KL
(p
n
||Q), ∀ n
Figure 3: Original images of LIVE database used in this
paper: Ocean, Stream, Lighthouse, Flowersonih35, House,
Sailing4.
2.2 Best reduction Domain
In order to get a typical subsequence
{X
1
, .., X
N
r
,Y
1
, ..,Y
N
r
}, one may ask whether it is
more convenient to reduce information of the sources
X and Y and then to estimate
¯
M from them (and then
Z) or to leave X and Y unchanged, whereas to reduce
Z’s information. This is the topic of the following
Proposition:
Prop. 2 H(Z) ≡ H(M(X,Y)) ≤ H(X,Y).
The proof is omitted since it straightforwardly de-
rives from the well-known result: H( f(X)) ≤ H(X),
for any function f and random variable X (Cover and
Thomas, 1991). In practice, since part of the informa-
tion of X and Y is lost in the computation of M(X,Y),
it is more convenient to leave X and Y unchanged and
to reduce Z.
2.3 Locality of Information
Though the results above would lead to select infor-
mation directly from M, it is necessary to find a strat-
egy to only take part of the information directly from
X andY. In fact, with regard to SSIM, it is unuseful to
firstly build the whole vector M to take just a subset of
its samples. It corresponds to the use of two weights
(1 or 0) for M
i
in the pooling step (step 3 of SSIM
algorithm). More formally, we can think of the subse-
quence {X
1
, .., X
N
r
,Y
1
, ..,Y
N
r
} to be built in a progres-
sive manner, i.e. {X
1
,Y
1
}, . . . , {X
1
, .., X
N
r
,Y
1
, ..,Y
N
r
},
till the constraint in eq. (1) is verified with ε fixed ’a
priori’ — i.e., the precision required to the estimation
is fixed. Since the original image I can be supposed
to be composed of a finite number of ’homogeneous’
regions (for instance ’grass’, ’sky’, ’sea’, ’buildings’,
etc.), without lack of generality, we can consider only
two regions, as in Fig. 2, and prove the following
Proposition:
Prop. 3 Be X =
X
1
with prob. α
X
2
with prob. 1 − α
and
Y =
Y
1
with prob. α
Y
2
with prob. 1− α,
with α ∈ R, 0 ≤ α ≤ 1,
X
1
and X
2
disjoint variables (the same for Y
1
and Y
2
),
and let Z = M(X,Y). By denoting with p
∗
is the pdf
of the variable ∗, then
H(p
Z
) ≤ H(α) + H(p
M(X
1
,Y
1
)
) + H(p
M(X
2
,Y
2
)
).
AFastComputationMethodforIQAMetricsBasedontheirTypicalSet
201

Proof is in Appendix. For a suitable cardinality (> 2)
of the alphabet of M, H(α) (whose maximum is equal
to 1) can be neglected and then the mixture leads to
a lower entropy. Hence, in order to build the subse-
quence {X
1
, .., X
N
r
,Y
1
, ..,Y
N
r
} belonging to the typical
set of M, it is more convenient to select them in lo-
cal regions of the images I and J, rather than point-
wise randomly in the whole image domain. In this
way, we maximize {X
1
, .., X
N
r
, Y
1
, ..,Y
N
r
} entropy by
minimizing, at the same time, its length 2N
r
. This
theoretical result shows that the practical choice of a
blockwise implementation of SSIM is really the most
convenient: local isolated blocks better capture image
information. It is not fortuitous that also HVS follows
the same procedure (see for instance (Monte et al.,
2005; Frazor and Geisler, 2006)): fixation points are
foveated, since they depend on the local content of the
fovea region, and they are the ones that maximize the
entropy of the visual contrast in the fovea region.
2.4 Overlapping Blocks
According to previous results, next proposition,
whose proof is in the Appendix, proves that non over-
lapping blocks maximize the entropy of the measure
M (i.e. the variable Z).
Prop. 4 If Z
1
, Z
2
, .., Z
T
are defined considering
repetitions of X and Y’s samples while
¯
Z
1
,
¯
Z
2
, ..,
¯
Z
R
are the ones achieved by considering X and Y’s sam-
ples just one time, (i.e. they are indipendent and such
that R < T), then
H(Z
1
, Z
2
, .., Z
T
)
T
≤
H(
¯
Z
1
,
¯
Z
2
, ..,
¯
Z
R
)
R
T > R.
2.5 How to Find an A
ε
M
Sequence
The objective of this paper is to go beyond the teoreti-
cal existence of A
ε
M
. We want to identify at least ONE
subsequence ∈ A
ε
M
with the least size (i.e. the least
N
r
) — and we want to do that with a low computa-
tional effort, if possible. Mathematically, if L = 2N
r
,
we ask for the existence of a subset of indices
{i
1
, .., i
L
} : argmin
L
|∆M| < ε, (2)
with ∆M =
M(X,Y) − M(x
i
1
, .., x
i
L
, y
i
1
, .., y
i
L
).
Though the search of {i
1
, .., i
L
} may be performed
with a more sophisticated and efficient strategy, in
this paper it will done by randomly selecting non
overlapping blocks within the original image I and its
distorted version J, in agreement with the theoretical
observations of previous subsections. As it will be
shown in the experimental results, this suboptimal
criterion still allows to get satisfactory results.
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The theoretical findings above have been validated on
several images contained in different databases. In
this section, only a representative subset of images
will be considered. They are shown in Fig. 3 and
belong to LIVE database (Sheikh et al., ). The latter
is composed of 779 images having different amount
of (five kinds of) distortion: Fast Fading, Gaussian
Blur, JPEG2K, JPEG and Additive Gaussian Noise.
In the sequel, we will first test the theoretical findings
in Section 2. Then, based on these criteria, for each
degraded image a subset of information is extracted
for approximating the corresponding SSIM value.
Reduction of Information. To verify that not all
I and J samples are really necessary to get a quite pre-
cise estimate of SSIM, Fig. 4 refers to Ocean image
and its copy distorted by fastfading. Even though this
work focuses on SSIM, Fig. 4 also contains results
for SNR. This allows us to show that theoretical find-
ings can be properly extended to other FR measures.
16×16 non overlapping blocks have been considered
in all tests. They have been randomly selected in the
original image and the corresponding ones have been
extracted from the degraded image. In addition, the
curves depicted in Fig. 4 have been normalized (di-
vided by the corresponding maximum value) in or-
der to design them on the same plot. Finally, a uni-
form quantization step with bins of width (∆) equal
to 10
−4
has been used for storing IQA measure —
this reduces the quantization distortion that is propor-
tional to log(∆) (Cover and Thomas, 1991). In their
first part, SSIM and SNR curves oscillate till they ap-
proach values close to the true ones. On the contrary,
the corresponding entropy curves have an increasing
trend with a critical curvature after which they tend to
the entropy of the whole available sample (i.e. the true
one). Both the fast ascending trend of entropies and
the oscillating trend of SSIM and SNR stop in corre-
spondence to quite the same point. It is worth out-
lining that the behavior plotted in Fig. 4 is common
to all the analysed images, for each kind and level of
distortion. These preliminary results give a clear ev-
idence of the fact that it is possible to drastically re-
duce the information sent by the two sources I and J
in order to assess quite precisely the visual quality of
J, independently of the involved quality measure. In
other words, the visual distortion typical set is com-
posed of few samples of image pixels, in agreement
with the Shannon’s typical set. Fig. 4 also suggests
that this reduced information can be easily found by
measuring the entropy of the samples of the metric
under study rather than the metric itself, because of
the more regular entropy behaviour.
ICPRAM2014-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
202
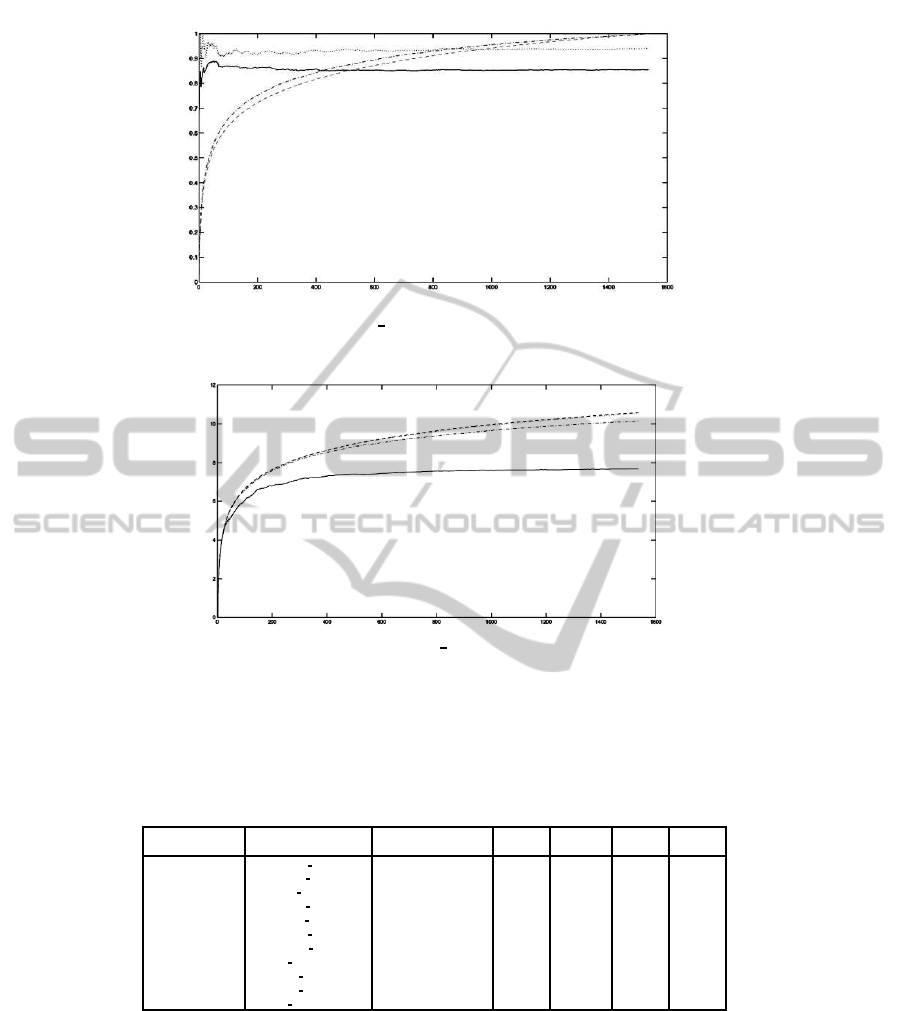
Figure 4: Ocean image and its fastfaded copy (img7 ocean in Table 1): SSIM (solid line), SNR (dotted), SSIM entropy
(increasing dot-line) and SNR entropy (increasing dashed) curves versus the number of blocks.
Figure 5: Ocean image and its Gaussian blurred copy (img57 ocean in Table 1). Entropy versus number of blocks (or an
equivalent number of random pixels). (Bottom-up): SSIM entropy via random pixels (solid) and non overlapping blocks
(dashdot), SNR entropy via random pixels (dotted) and non overlapping blocks (dashed).
Table 1: Images in Fig. 3: Entropy of: the original image (H(X)), the distorted image given the original one (H(Y|X)), SSIM
with overlapping blocks (H(Z)) and SSIM for non overlapping blocks (H(
¯
Z)). For each kind of distortion the parameters used
in LIVE database have been given: the standard deviation of the gaussian kernel for the gaussian blurring, the SNR of the
distortion strength for fastfading, the quality score for jpeg and the standard deviation of the noise distribution for the white
noise. More details in (Sheikh et al., ).
Original Image Distorted Image Distortion kind H(X) H(Y|X) H(Z) H(
¯
Z)
ocean img57 ocean Gaussian blur (1.48) 7.1785 4.8630 5.0798 5.3230
stream img58 stream Gaussian blur (3.08) 7.4230 6.6357 5.9525 5.9997
lighthouse img97 lighthouse Gaussian blur (1.48) 7.3799 5.3012 5.1560 5.4239
sailing4 img127 sailing4 Gaussian blur (1.51) 6.8476 5.2000 5.0161 5.1369
ocean img7 ocean fastfading (18.9) 7.1785 4.7998 4.6848 4.8755
house img73 house fastfading (20.3) 7.1803 4.6494 4.0312 4.3385
stream img100 stream jpeg (0.29) 7.4230 6.4137 5.2691 5.5687
flowersonih35 img27 flowersonih35 jpeg (0.93) 7.7161 5.6465 3.4555 3.6996
ocean img118 ocean.bmp white noise (0.035) 7.1785 4.6308 4.2645 4.6762
house img109 house.bmp white noise (0.125) 7.1803 6.4434 6.1604 6.1460
flowersonih35 img72 flowersonih35 white noise (0.070) 7.7161 5.5789 3.6160 3.8698
Selection of the Best Reduction Domain. To test
the results in Section 2.2, the entropy H(X) has been
computed for each image in Fig. 3. Bins width, nec-
essary to build the empirical p.d.f., has been set equal
to 1. With regard to the distorted image J, for each ex-
ample the conditional entropy H(Y|X) has been con-
sidered. The latter has been estimated from H(X−Y),
i.e. by looking at the distortion as an additive term —
even though the process may be much more compli-
cated. However, X −Y really gives the difference of
information between the original image I and the dis-
torted one J. The size of the bin width of H(Y|X)
has been set equal to 1, while 32× 32 blocks have
been used. The entropy H(Z) of the SSIM vector M
has been computed by quantizing M with a bin width
equal to .01. Using these settings, Table 1 shows
that H(Z) < H(X) + H(Y|X). This behavior does not
change for a different setting of parameters. Hence,
SSIM naturally reduces entropy of the original im-
ages.
AFastComputationMethodforIQAMetricsBasedontheirTypicalSet
203

Locality of the Selected Information. Section
2.3 proves that it is more convenient to build FR qual-
ity measure samples using blocks rather than ran-
dom pixels in I and J. Fig. 5 shows that SSIM en-
tropy curve, that has been built using non overlapping
and randomly selected blocks, always assumes val-
ues larger than those of SSIM entropy curve that has
been built using randomly selected pixels. The same
happens for SNR but the effect is strongly less visi-
ble: curves are very close to each other. In all teste,
quantization bins have been set to 10
−4
, even though
different settings confirm the same trend.
Overlapping Blocks. Theoretical results in Sec-
tion 2.4 state that it is more convenient to select non
overlapping blocks from I and J rather than taking
overlapping ones. A simple practical proof has been
made by taking all possible (non overlapping) blocks
from images in Fig. 3 and computing SSIM using
them. Considering a bin width of .01 for this new
vector of measures, the corresponding entropy H(
¯
Z)
has been computed. Tests have been performed using
32× 32 blocks. The last column of Table 1 shows that
non overlapping blocks lead to a higher entropy and
then they convey a greater amount of information.
How to find a A
ε
M
Sequence. In order to manually
estimate a sequence belonging to A
ε
M
, the sequence
size has been fixed and the corresponding error has
been measured. Table 2 contains the results achieved
on Ocean image and its copies distorted by Gaussian
blur, fastfading and white noise. Fig. 6 shows 100
randomly selected 16× 16 blocks that have been used
for the evaluation of SSIM. Both SSIM and SNR have
been considered and the number of samples has been
set equal to 100. On the contrary, the size of the
blocks on I and J has been changed: 8× 8, 16 × 16
and 32× 32. The blocks on I (and the corresponding
in J) have been randomly selected. That’s why the
results in Table 2 have been achieved as average on
30 trials, i.e. 30 different choices of 100 non over-
lapping blocks, in order to get a more fair evaluation
of the estimation error for the considered IQA metric.
Specifically, the mean and the standard deviation of
the the relative error
|
M −
ˆ
M|
M
(3)
has been computed. For each image and each dis-
tortion kind, the estimation errors always are smaller
than 5% of the true IQA measure. Table 3 contains the
results obtained using different sizes for the selected
sequence of FR values, respectively 50, 100 and 200
blocks on both the original I and the distorted image
J. Again, apart from just one case (in bold) errors are
always under 5%, confirming that few blocks (a little
part of the available information) are required to give
Figure 6: 100 Randomly selected 16× 16 blocks used for
the estimation of SSIM of Ocean image.
a good estimate of the involved FR measure.
The speed up obtained in the computation of the
considered image quality assessment metric on the
typical set depends on the number of blocks that are
used for the evaluation of SSIM. The computational
gain is G =
N
0
N
r
, where N
0
is the number of blocks
that are used for the computation of SSIM in the
whole image (using the standard algorithm), while N
r
is the number of blocks belonging to the visual dis-
tortion typical set i.e, the reduced set of blocks from
which it is possible to get an quite precise estimation
of SSIM. For example, if an image can be partioned
into 1536 non overlapping blocks, the gain using just
50, 100 or 200 non overlapping blocks respectively is
30.72, 15.36 and 7.68. This gain increases if the im-
age is partitioned into non overlapping blocks, while
it decreases for images having small dimension. For
example, for images composed of 1280 non overlap-
ping blocks the gain becomes 27, 13.5 and 6.75 re-
spectively for 50, 100 or 200 non overlapping blocks
in the visual distortion typical set.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The paper has presented a study concerning the def-
inition of a visual distortion typical set in agreement
with the general concept of asymptotic equipartition
property and the neurological studies on those points
that attract human attention in the early vision. Gen-
eral criteria for the characterization and the practical
definition of this typical set have been given. The typ-
ical set has been used for reducing the amount of in-
formation necessary to assess the quality of an image
using a standard full reference image quality assess-
ment measure. This typical set makes the FR IQA
metric less computational demanding. Achieved re-
sults are very encouraging since they are robust to
changes of image subject, parameters settings and dis-
tortion kinds. Future research will focus on designing
an optimized procedure to find the minimum budget
of information for a fixed error.
ICPRAM2014-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
204
Table 2: Ocean image and its copy distorted by respectively Gaussian blurring (top), fastfading (middle) and white noise
(bottom). Mean and standard deviation (in the brackets) of the relative error (%) for the estimation of the true value of SSIM
and SNR using just 100 blocks with size equal to: 8× 8, 16× 16 and 32× 32.
Block size = 8 /No. Blocks = 100 Block size = 16 /No. Blocks = 100 Block size = 32 /No. Blocks = 100
Total blocks: 6144 Total blocks: 1536 Total blocks: 384
SSIM error SNR error SSIM error SNR error SSIM error SNR error
1.84% (1.41%) 2.46%(2.14%) 1.25%(1.01%) 2.43%(1.63)% 1.40%(1.20%) 2.2% (1.72%)
1.33%(1.42%) 2.75%(2.00%) 1.39%(0.80%) 2.50%(1.90%) 0.79%(0.55%) 2.25%(1.71%)
1.14%(0.87%) 1.31%(1.03%) 1.09%(0.20%) 1.07%(0.70%) 0.71%(0.54%) 0.81%(0.57%)
Table 3: Images in Fig. 3 with different kinds of distortions. Mean value and standard deviation (in brackets) of the relative
error (%) as in eq. (3) for the estimation of the true value of SSIM and SNR considering just 50, 100 and 200 non overlapping
blocks with size equal to 16× 16.
Blk size:16 / Sel. Blks:50 Blk size:16 / Sel. Blks:100 Blk size:16 / Sel. Blks:200
Image Dist Blks SSIM error SNR error SSIM error SNR error SSIM error SNR error
Ocean Gb 1536 2.53% (2.49) 4.15% (2.70) 1.25% (1.01) 2.43% (1.63) 1.16%(1.03) 1.82% (1.18)
Stream Gb 1536 3.50%(3.00) 2.65%(2.25) 3.45%(3.01) 2.29% (1.80) 2.43%(2.01) 1.66%(1.02)
Lighth. Gb 1350 2.45%(2.20) 3.72%(2.01) 2.30%(1.80) 2.39%(2.22) 1.56%(1.21) 1.75%(1.15)
Sail4 Gb 1536 2.13%(2.00) 3.53%(2.99) 1.47%(0.80) 3.26%(2.22) 1.02%(0.45) 1.47%(0.89)
Ocean Ff 1536 1.53% (1.20) 3.18%(2.05) 1.39%(0.80) 2.50%(1.90) 0.83%(0.52) 1.86%(1.01)
House Ff 1536 1.08%(0.99) 2.68%(1.90) 0.75%(0.57) 1.73%(1.60) 0.55%(0.21) 1.36%(0.94)
Stream Jp 1536 2.93%(2.90) 2.78%(2.09) 1.95%(1.50) 1.84%(1.30) 1.56%(0.98) 1.11%(0.80)
Flower Jp 1280 0.58%(0.50) 4.01%(3.03) 0.30%(0.15) 2.62%(2.15) 0.23%(0.09) 1.89%(1.01)
Ocean Wn 1536 1.19%(0.70) 1.29%(0.90) 1.09%(0.80) 1.07%(0.70) 0.61%(0.30) 0.72%(0.31)
House Wn 1536 5.46%(2.09) 2.04%(1.77) 4.40%(2.87%) 1.93%(1.35) 2.72%(2.51) 0.93%(0.80)
Flower Wn 1280 2.82%(2.77) 1.45% (1.35) 1.86%(1.52%) 0.90%(0.50) 1.09%(1.08) 0.56% (0.53)
REFERENCES
Benabdelkader, S. and Boulemden, M. (2005). Recursive
algorithm based on fuzzy 2-partition entropy for 2-
level image thresholding. In Pattern Recognition, 38.
Elsevier.
Bruni, V., Rossi, E., and Vitulano, D. (2013a). Jensen-
shannon divergence for visual quality assessment. In
Signal Image and Video Prcessing 7(3). Springer.
Bruni, V., Vitulano, D., and Ramponi, G. (2011). Image
quality assessment through a subset of the image data.
In Proc. of ISPA 2011. IEEE.
Bruni, V., Vitulano, D., and Wang, Z. (2013b). Special issue
on human vision and information theory. In Signal
Image and Video Prcessing 7(3). Springer.
Cover, T. M. and Thomas, J. A. (1991). Elements of Infor-
mation Theory. John Wiley & sons.
Frazor, R. and Geisler, W. (2006). Local luminance and
contrast in natural in natural images, 46. In Vision
Research.
Gonzalez, R. C. and Woods, R. E. (2002). Digital Image
Processing. Prentice Hall, 2nd edition.
Grunwald, P. D. (2004). A tutorial introduction to the min-
imum description length principle. In Advances in
Minimum Description Length: Theory and Applica-
tions. Myung Grunwald, Pitt,.
Monte, V., Frazor, R., Bonin, V., Geisler, W., and Corandin,
M. (2005). Independence of luminance and contrast
in natural scenes and in the early visual system 8(12).
In Nature Neuroscience.
Rivera, M., Ocegueda, O., and Marroquin, J. L. (2007).
Entropy-controlled quadratic markov measure field
models for efficient image segmentation. In IEEE
Trans. on Image Proc. 16(12).
Sheikh, H. R. and Bovik, A. C. (2006). Image information
and visual quality. In IEEE Trans. on Image Proc.,
15(2).
Sheikh, H. R., Bovik, A. C., and Veciana, G. D. (2005). An
information fidelity criterion for image quality assess-
ment using natural scene statistics. In IEEE Trans. on
Image Proc., 14(12).
Sheikh, H. R., Wang, Z., Cormack, L., and
Bovik, A. C. Live image quality assess-
ment database release 2. [Online]. Avail-
able:http://live.ece.utexas.edu/research/quality.
Wang, W., Wang, Y., Huang, Q., and Gao, W. (2010). Mea-
suring visual saliency by site entropy rate. In Proc. of
CVPR10. IEEE.
Wang, Z., Bovik, A. C., Sheikh, H. R., and Simoncelli, E. P.
(2004a). Image quality assessment: From error visi-
bility to structural similarity. In IEEE Trans. on Image
Proc., 13.
Wang, Z. and E.P.Simoncelli (2005). Reduced-reference
image quality assessment using a wavelet-domain nat-
ural image statistic model. In Proc. of Human Vision
and Electronic Imaging X, vol. 5666. SPIE.
Wang, Z. and Li, Q. (2011). Information content weight-
ing for perceptual image quality assessment. In IEEE
Trans. on Image Proc. 20(5).
Wang, Z., Lu, L., and Bovik, A. (2004b). Video quality as-
AFastComputationMethodforIQAMetricsBasedontheirTypicalSet
205

sessment based on structural distortion measurement.
In Signal Processing: Image Communications, 19(2).
Winkler, S. (2005). Digital Video Quality, Vision Models
and Metrics. Wiley.
Zhang, D. and Jernigan, E. (2006). An information theo-
retic criterion for image quality assessment based on
natural scene statistics. In Proc. of ICIP 2006. IEEE.
APPENDIX
Proof 1 1. µ
n+1
− µ
n
=
∑
x∈χ
x(p
n+1
(x) − p
n
(x)) =
∑
x∈χ
−
x
n+1
p
n
(x) +
x
n+1
n+1
=
1
n+1
(x
n+1
− µ
n
). The sign
of the difference between two successive mean
values depends on x
n+1
and the convergence is
not monotonic. 2. |µ
n
− µ|
2
= |
∑
x∈χ
x(p
n
(x) −
Q(x))|
2
≤ M
2
n
V
2
(p
n
, Q) where V(p
n
, Q) is the vari-
ational distance between p
n
and Q i.e., V(p
n
, Q) =
∑
x∈χ
|p
n
(x) − Q(x)|. Since the Kullbach-Leibler di-
vergence D
KL
(p
n
||Q) =
∑
x
p
n
(x)log
p
n
(x)
Q(x)
is such
that D
KL
(p
n
||Q) ≥
1
2
V
2
(p
n
, Q), then |µ
n
− µ|
2
≤
2M
2
n
D
KL
(p
n
||Q). Hence, for n: D
KL
(p
n
||Q) ≤
ε
2M
2
n
, ε > 0, then |µ
n
− µ|
2
≤ ε•
Proof 3 H(X) = H(α) + αH(X
1
) + (1 −
α)H(X
2
) (Cover and Thomas, 1991) and the same
holds for H(Y). Since Z = M(X,Y), then Z =
M(X
1
,Y
1
) with prob. α
M(X
2
,Y
2
) with prob. 1− α
where M(X
1
,Y
1
)
and M(X
2
,Y
2
) are not disjoint. Z ∼ p
z
where
p
Z
= αp
M(X
1
,Y
1
)
+ (1− α)p
M(X
2
,Y
2
)
. Hence, H(p
Z
) ≤
H(α) + αH(p
M(X
1
,Y
1
)
) + (1− α)H(p
M(X
2
,Y
2
)
). In fact,
let’s suppose that
H(p
Z
) > H(α) + αH(p
M(X
1
,Y
1
)
) +
+(1− α)H(p
M(X
2
,Y
2
)
) (4)
and let us consider the Jensen-Shannon
divergence D
α
JS
(p
M(X
1
,Y
1
)
||p
M(M(X
2
,Y
2
)
) =
H(p
Z
) − αH(p
M(X
1
,Y
1
)
) + (1 − α)H(p
M(X
2
,Y
2
)
),
then D
α
JS
(p
M(X
1
,Y
1
)
||p
M(X
2
,Y
2
)
) > H(α), that is
absurd since 0 ≤ D
α
JS
(p
M(X
1
,Y
1
)
||p
M(X
2
,Y
2
)
) ≤
H(α). Since H(p
M(X
1
,Y
1
)
) ≤ H(p
(X
1
,Y
1
)
)
and H(p
M(X
2
,Y
2
)
) ≤ H(p
(X
2
,Y
2
)
) we have
H(p
Z
) ≤ H(α) + αH(p
(X
1
,Y
1
)
) + (1− α)H(p
(X
2
,Y
2
)
)•
Proof 4 Let
ˆ
Z
j
= {Z
1
, Z
2
, .., Z
N
j
} be a col-
lection of N
j
variables Z
i
selected in {Z
1
, Z
2
, .., Z
T
}
and let be K the number of possible N
j
−ples
such that:
S
K
j=1
ˆ
Z
j
= {Z
1
, Z
2
, .., Z
T
}. Since for
generic variables S
1
, .., S
n
, it holds H(S
1
, S
2
, .., S
n
) ≤
∑
n
i=1
H(S
i
), then H(Z
1
, Z
2
, .., Z
T
) ≤
∑
K
j=1
H(
ˆ
Z
j
) ≤
∑
K
j=1
H(
¯
Z
1
,
¯
Z
2
, ..,
¯
Z
R
) = KH(
¯
Z
1
,
¯
Z
2
, ..,
¯
Z
R
) =
KR
H(
¯
Z
1
,
¯
Z
2
,..,
¯
Z
R
)
R
•
ICPRAM2014-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
206
