
Semi-Markov Modeling-Clustering of Human Sleep with Efficient
Initialization and Stopping
Chiying Wang
1
, Sergio A. Alvarez
2
, Carolina Ruiz
1
and Majaz Moonis
3
1
Department of Computer Science, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Worcester, MA 01609 U.S.A.
2
Department of Computer Science, Boston College, Chestnut Hill, MA 02467 U.S.A.
3
Department of Neurology, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA 01605 U.S.A.
Keywords:
Time Series, Dynamic Time Warping, Data Mining: Clustering, Modeling, Markov, Sleep.
Abstract:
Collective Dynamical Modeling-Clustering (CDMC) is an algorithmic framework for time series dynamical
modeling and clustering using probabilistic state-transition models. In this paper, an efficient initialization
technique based on Itakura slope-constrained Dynamic Time Warping is applied to CDMC. Semi-Markov
chains are used as the dynamical models. Experimental evaluation demonstrates the effectiveness of the pro-
posed approach in providing more realistic dynamical modeling of sleep stage dynamics than Markov models,
with improved clustering quality and convergence speed as compared with pseudorandom initialization.
1 INTRODUCTION
The dynamics of the sleep-wake cycle present
species-specific patterns with some underlying sim-
ilarities across mammalian species (Phillips et al.,
2010). In humans, a more detailed description
of sleep is available in terms of the sleep stages
determined via polysomnography, as described in
the Rechtschaffen-Kales (Rechtschaffen and Kales,
1968) and AASM (Iber et al., 2007) staging stan-
dards. An example of an all-night sleep stage se-
quence is shown in Fig. 1. Sleep stage transitions and
sleep stage durations provide essential indicators in
describing the relationship between sleep and health
(Kishi et al., 2008), (Hernandez et al., 2009), (Chervin
et al., 2009), and (Bianchi et al., 2010).
0 200 400 600 800 1000
Wake
REM
Stage 1
Stage 2
Stage 3
Time (epochs)
Sleep stage
Figure 1: Sample hypnogram
Scarcity of Dynamical Events in Sleep Data. We
are interested in the discovery of dynamical patterns
in sleep stage sequences by means of automated algo-
rithms. Sleep presents a particular challenge to such
algorithms, in that key dynamical events such as stage
transitions occur very sparsely within a hypnogram,
making it difficult to extract reliable dynamical infor-
mation from a single night of sleep for a given indi-
vidual (Bianchi et al., 2010).
The collective dynamical modeling-clustering
(CDMC) algorithm (Alvarez and Ruiz, 2013) ad-
dresses the problem of scarcity of dynamical events
by pooling sleep data across multiple individuals, si-
multaneously partitioning the collection of subjects
by sleep-dynamical similarity. CDMC reduces the
model variance by selectively aggregating instances
through clustering. This reduction in variance is ac-
complished in CDMC without the loss of detail that
would result by simply aggregating data without re-
gard for dynamical similarity. The result of CDMC
is a collection of groups of hypnograms such that
hypnograms within a given group are dynamically
similar, while hypnograms in different groups are not.
Scope of the Paper. CDMC is a general algorithmic
framework that leaves open several important choices.
Two main choices that must be made when applying
the CDMC framework are the clustering initializa-
tion technique and the dynamical model type. Stan-
61
Wang C., A. Alvarez S., Ruiz C. and Moonis M..
Semi-Markov Modeling-Clustering of Human Sleep with Efficient Initialization and Stopping.
DOI: 10.5220/0004824900610068
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing (BIOSIGNALS-2014), pages 61-68
ISBN: 978-989-758-011-6
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

dard choices are pseudorandom clustering initializa-
tion, and Markov dynamical models. These are the
choices used in (Alvarez and Ruiz, 2013). Markov
models have been widely used in previous applica-
tions to sleep (Zung et al., 1965) and (Kim et al.,
2009).
The present paper focuses on two main elements:
1. The use of Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) for
clustering initialization in CDMC. DTW has pre-
viously been applied to initialization of a differ-
ent clustering technique based on Hidden Markov
Models (Oates et al., 1999). We show that DTW
initialization significantly improves CDMC con-
vergence as compared with pseudorandom initial-
ization.
2. The use of semi-Markov dynamical models in
CDMC in order to better describe the dynamical
characteristics of human sleep as compared with
Markov models.
Experimental evaluation confirms the advantages
of the approach proposed in the paper.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Sec-
tion 2 briefly reviews the CDMC algorithm, presents
the application of dynamic time warping to cluster-
ing initialization in CDMC, and describes the semi-
Markov dynamical model version of CDMC. Sec-
tion 3 describes the synthetic and actual human sleep
datasets used for evaluation, together with the exper-
imental protocol. Section 4 presents experimental re-
sults and analysis of the proposed approach. Section 5
describes conclusions and ideas for future work.
2 PROPOSED APPROACH
This section describes the Collective Dynamical
Modeling-Clustering (CDMC) framework that con-
stitutes the foundation for this work (Algorithm 1),
the semi-Markov chains to be used as the dynamical
models in CDMC, the Dynamic Time Warping-driven
clustering initialization approach for CDMC (Algo-
rithm 2), and the clustering similarity metrics to be
used for the CDMC stopping criteria.
2.1 Collective Dynamical
Modeling-Clustering (CDMC)
CDMC is a general algorithmic strategy for simul-
taneous clustering and dynamical modeling of se-
quence data (Alvarez and Ruiz, 2013) that is shown
in pseudocode in Algorithm 1. CDMC simultane-
ously groups data instances by dynamical similarity
and induces a dynamical model of each group. The
following is an outline of the CDMC procedure:
• An initial grouping of instances x
1
, . . . , x
n
into k
clusters is provided.
• The grouping is iteratively refined by repeating
the following steps until the similarity of two suc-
cessive clusterings (e.g., c and c
old
) reaches a pre-
determined similarity threshold minSim (step 3):
- A maximum likelihood dynamical model M
i
is
built from each cluster C
i
(step 5).
- Each instance x is assigned to the cluster C(x)
for which the generative likelihood P(x | M
C(x)
)
is maximized (step 6).
• A final clustering c of the dataset and a genera-
tive model M
i
for each of the clusters are returned
(step 7).
Note that the details of cluster initialization, dynam-
ical model type, and similarity metric are left un-
specified in the general version of CDMC. (Alvarez
and Ruiz, 2013) includes an illustration that uses
pseudorandom initialization, hidden Markov models,
and the Rand index in these roles. The present pa-
per shows that improved results can be obtained by
using agglomerative distance-based clustering with
dynamic time warping for initialization, and semi-
Markov chains as the dynamical models.
2.2 Semi-Markov Dynamical Models
for CDMC
Markov chains and the related models with partially
observable state spaces, hidden Markov models, have
been used to model sleep stage transitions in previ-
ous work (Zung et al., 1965), (Kim et al., 2009), (Al-
varez and Ruiz, 2013). State transitions in a Markov
model occur with a fixed probability in every cycle
of a standard clock that is shared by all of the states.
The probability of transitioning from state i to state
j in a given clock cycle is a fixed probability value
p
i, j
. In particular, the probability of leaving state i
in a given clock cycle of a Markov model is the fixed
value p
i,?
=
∑
j6=i
p
i, j
. It follows that the probability of
remaining in state i for precisely n clock cycles, leav-
ing in the (n + 1)st cycle, is (1 − p
i,?
)
n
p
i,?
. Thus, the
duration of visits to a given state in a Markov model
has a geometric (discrete exponential) probability dis-
tribution.
Experimental results (Kim et al., 2009) and (Chu-
Shore et al., 2010) demonstrate that geometric distri-
butions are a poor fit for actual stage bout duration
BIOSIGNALS2014-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
62

Algorithm 1: Collective Dynamical Modeling-Clustering (CDMC, (Alvarez and Ruiz, 2013)).
Input: An unlabeled time-series dataset D = {x = (a
i
(x))|i = 1, 2, . . . , n}; a positive integer, k, for the desired
number of clusters; an initial guess c
0
: D → {1, . . . k} of the cluster label c
0
(x) of each instance x ∈ D; param-
eter values, s, specifying the desired configuration of the models (e.g., number of states); and a real number
minSim between 0 and 1 for the minimum clustering similarity required for stopping.
Output: A set M
1
, . . . M
k
of generative dynamical models (with configuration parameters s), together with a
cluster labeling c : D → {1 . . . k} that associates to each data instance, x, the index c(x) of a model M = M
c(x)
for which the generative likelihood
∏
x∈D
P(x|M
c(x)
) is as high as possible.
CDMC(D, k, c
0
, s, minSim)
1. c(x) = c
0
(x) for all x in D
2. c
old
(x) = 0 for all x ∈ D
3. while CLUSTERINGSIMILARITY(c, c
old
) < minSim
4. c
old
= c
5. (M
1
, . . . M
k
) = LEARNMLPROTOTYPES(D, k, c, s)
6. c = LEARNMLCLUSTERLABELS(D, M
1
, . . . M
k
)
7. return M
1
, . . . M
k
, c
distributions of human sleep.
1
For example, the wake
stage has a distribution of bout durations with a slowly
decaying tail that is more similar to a power-law func-
tion than to a discrete exponential. Motivated by this
fact, the present paper employs a semi-Markov chain
model for the sequence of sleep stages, instead of a
Markov model. In a semi-Markov model, the mech-
anism that determines the durations of state visits is
independent of any model-wide clock. Each state i in
a semi-Markov model of the type considered here has
a specified visit duration distribution P
i
(τ); upon ar-
riving in the given state, a random sample τ is taken
from this visit duration distribution; the model then
remains in state i for the duration τ, at the end of
which time the next state is selected from among all
states other than i, according to some Markov-type
transition probability matrix with zeros along the di-
agonal. Other varieties of semi-Markov models also
exist. For a general discussion, see (Yu, 2010).
Prior research (Wang et al., 2013) has established
that individual sleep stage durations are well modeled
by Weibull distributions. The present paper therefore
uses semi-Markov dynamical models in which the
state visit duration distributions belong to the Weibull
family. A completely observable state space is used,
with one state for each sleep stage considered. The
resulting semi-Markov chains are used as the dynam-
ical models within the CDMC framework discussed
above in section 2.1. Standard Markov models within
CDMC provide a benchmark for performance com-
parisons.
1
A stage bout is a maximal uninterrupted period during
which the stage of sleep remains the same.
2.3 Clustering Initialization and
Stopping Criteria for CDMC
This section proposes using agglomerative cluster-
ing with a distance function based on Dynamic Time
Warping as the clustering initialization technique for
CDMC. This idea is based on prior work (Oates et al.,
1999) that uses Dynamic Time Warping in conjunc-
tion with Hidden Markov Models to cluster time se-
ries data. The use of the modified Rand index as a
similarity metric in the CDMC stopping criterion in
order to account for the role of chance is also dis-
cussed.
2.3.1 Dynamic Time Warping (DTW)
Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) is a classical dy-
namic programming algorithm that provides an opti-
mal alignment between two time series by nonlinearly
warping their time dimensions (Berndt and Clifford,
1994). DTW has been extensively used in speech
recognition, periodic movement capture, and so on
(Sakoe and Chiba, 1978) and (Itakura, 1975). In this
paper, DTW is used as a measure of similarity for un-
supervised clustering of time series in section 2.3.2.
The standard dynamic programming approach to
DTW for input sequences of length n implicitly con-
siders all pairings of time indices in the two input se-
quences, leading to O(n
2
) time complexity. Subop-
timal constrained versions of DTW aim to reduce the
time complexity by restricting the portion of the index
space considered in the warping search. Itakura slope-
constrained DTW (Itakura, 1975) imposes slope con-
straints on the warping path, thereby constraining the
search for a warping path to a parallelogram in the
Semi-MarkovModeling-ClusteringofHumanSleepwithEfficientInitializationandStopping
63

index space. The Sakoe-Chiba approach (Sakoe and
Chiba, 1978) constrains the warping search to a band
in the index space. An alternative hierarchical mul-
tiresolution approach has the potential to reduce the
time complexity of DTW to O(n) (Salvador and Chan,
2007).
2.3.2 DTW Clustering Initialization (DTWC)
The core of the clustering initialization approach for
CDMC that is proposed in the present paper is de-
scribed in pseudocode in Algorithm 2. This approach
performs agglomerative metric clustering using the
distance function computed by DTW. The main steps
of the proposed DTWC initialization for CDMC are:
• Place each instance x
1
, . . . , x
n
in its own cluster
C
1
, . . . ,C
n
(step 1-2)
• Repeat until there are only k clusters left (step 3)
- Merge the closest clusters, C
i
and C
j
; the dis-
tance measure between two instances (i.e., x
s
and x
t
) is defined by DTW; the distance mea-
sure between two clusters is the average dis-
tance of instances in these clusters (step 4-5)
• Return the final partition of the dataset D into k
clusters (step 7)
Constrained DTW-Driven Clustering (cDTWC).
A faster variant of DTWC, constrained DTWC
(cDTWC), is obtained by using Itakura slope-
constrained DTW instead of the full DTW when
computing the distance metric in Algorithm 2.
These two initialization techniques for CDMC will
be compared with pseudorandom initialization in
section 4.2.
2.3.3 Stopping Criteria
The Rand index (RI) (Rand, 1971) is a measure of
agreement between two partitions of the same set,
and therefore could be used in Algorithm 1 to mea-
sure the similarity of two clusterings on the same
data. A drawback of this index is that it will pro-
duce a nonzero value for the comparison of two ran-
domly constructed partitions. The adjusted Rand in-
dex (ARI) (Hubert and Arabie, 1985) is based on
the Rand index but corrects for clustering agree-
ments due to chance. Normalized mutual information
(NMI) (Vinh et al., 2010) is a distinct way of evalu-
ating clusters by the tradeoff between the number of
clusters and qualities. In the present paper, these three
metrics are compared as the basis for the stopping cri-
terion in CDMC (Algorithm 1), using the resulting
CDMC convergence time (number of modeling-
Algorithm 2: DTW-driven Clustering (DTWC).
Input: An unlabeled time series dataset D =
{x
1
, x
2
, . . . , x
n
}; a positive integer, k, for the de-
sired number of clusters; a predefined local dis-
tance measure d : X × X → R
≥0
where X denotes
the space in which the x
i
take their values.
Output: A partition C of D into k clusters.
DTWC(D, k, d)
1. C
i
= {x
i
} for each x
i
in D
2. m = n
3. while m > k
4. (i
∗
, j
∗
) = arg min
i, j∈{1,···m}
d(C
i
,C
j
)
= arg min
i, j∈{1,···m}
n
∑
l(x
s
)=C
i
,l(x
t
)=C
j
DTW(x
s
,x
t
,d)
|C
i
|·|C
j
|
|x
s
, x
t
∈ D
o
5. Merge C
i
∗
and C
j
∗
so that C = {1, . . . , m − 1}
6. m = m − 1
7. return {C
1
, ··· ,C
k
}
clustering iterations) and classification accuracy over
labeled synthetic data for evaluation (see section 4).
3 EVALUATION
This section describes the synthetic and human sleep
datasets, as well as the protocols used for experimen-
tal evaluation of the approach proposed in section 2.
3.1 Data Description
3.1.1 Human Sleep Data
A collection of 200 fully anonymized human
polysomnographic recordings was extracted from
polysomnographic overnight sleep studies performed
in the Sleep Clinic at Day Kimball Hospital in Put-
nam, Connecticut, USA, with approval of the re-
spective Institutional Review Board for human sub-
jects research. The subjects of the recordings had re-
quested consultation due to sleep-related symptoms
(e.g., sleepiness during daytime hours), and hence
there is selection bias in the data. Each polysomno-
graphic recording is split into 30-second epochs.
Staging of each 30-second epoch into one of the stan-
dard sleep stages (wake, stage 1, stage 2, stage 3,
and REM) is carried out by trained sleep technicians.
Stages 1, 2, and 3 were subsequently grouped to-
gether into a single non-REM stage (NREM), result-
ing in a representation of human sleep in terms of
three stages: Wake, NREM, and REM.
BIOSIGNALS2014-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
64

3.1.2 Semi-Markov Mixture Data
A synthetic dataset was also generated from two dis-
tinct semi-Markov chains, each with two states, but
with different transition probability matrices and state
duration statistics. The use of synthetic data pro-
vides precise control over the generative statistical
parameters, whereas the generative parameters of hu-
man sleep data can only be estimated. Weibull state-
duration distributions are used for each of the semi-
Markov chains (see section 2.2).
Semi-Markov Chain Parameter Values. The fol-
lowing transition matrices and Weibull (shape, scale)
parameter values (in that order) were used for the two
semi-Markov chains. There are two Weibull distribu-
tions per chain, one for each state.
chain 1 :
0.90 0.10
0.10 0.90
(3, 5), (2.5, 4.5)
chain 2 :
0.15 0.85
0.85 0.15
(3, 4), (2.5, 3.5)
Generation of Synthetic Mixture Data. In order
to generate a sequence of a given length, L, from the
mixture model, a random choice is first made between
the two semi-Markov chains. A state sequence of the
desired length is then generated by the randomly se-
lected semi-Markov chain. The random chain selec-
tion and state sequence generation process continues
until a desired total number of sequences, N, has been
generated. See Algorithm 3.
In the present paper, N = 100 sequences, each of
length L = 100, were used in all trials involving syn-
thetic semi-Markov data.
Algorithm 3: Generation of synthetic data.
Input: Positive integers N and L, semi-Markov
chains S
1
, ··· , S
k
.
Output: A collection of N sequences, each of
length L, generated by a mixture of the semi-
Markov chains S
1
, ···S
k
.
genData(N, L, (S
1
, ··· , S
k
))
1. C = {}
2. for i = 1, ··· , N
3. j = random choice among {1, ···k}
4. x
i
= sequence of length L generated by S
j
5. C = C ∪ {x
i
}
6. return C
3.2 Experiment Description
Each experiment involved 100 trials. The human
sleep dataset of section 3.1.1 was used in the compar-
ative evaluation of semi-Markov and standard Markov
dynamical models (section 4.1). The synthetic semi-
Markov mixture dataset of section 3.1.2 was used in
the evaluation of initialization techniques and stop-
ping metrics. This allows the use of classification
accuracy to evaluate performance (section 3.3). For
the initialization experiments in section 4.2, the lo-
cal cost measure was defined as that if a pair of ele-
ments in two sequences are same, the cost is 0, other-
wise, 1. In section 4.3, the stopping metrics described
in section 2.3.3: the standard Rand index (RI), the
adjusted (chance-corrected) Rand index (ARI), and
Normalized Mutual Information (NMI), were used re-
spectively in CDMC, and the results were compared
in terms of the resulting classification accuracy and
number of iterations to convergence. The similar-
ity threshold for stopping in CDMC (Algorithm 1)
was set to 0.8. Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney statistical
hypothesis testing was used for comparison of medi-
ans (section 3.4). All experiments were performed in
MATLAB
R
(The MathWorks, 2012).
3.3 Cluster Validity
Clustering quality in section 2.3 is evaluated by com-
paring the clustering results to known class labels for
the synthetic data described in section 3.1.2. The class
label of an instance is the Markov chain that gener-
ates that instance. The classification accuracy (frac-
tion of instances that are classified correctly, relative
to the set of all instances) is used as the evaluation
metric. Higher classification accuracy of a clustering
indicates a more meaningful data partition.
3.4 Statistical Significance
Non-normality of the observed accuracy and conver-
gence time distributions was detected in some of the
experiments, making the standard t-test for the differ-
ence of population means inappropriate. Comparison
of population medians was therefore carried out by
using a non-parametric Wilcoxon rank sum (Mann-
Whitney) test at the p < 0.05 significance level.
4 RESULTS
This section discusses the results obtained using
CDMC with the proposed choices of semi-Markov
Semi-MarkovModeling-ClusteringofHumanSleepwithEfficientInitializationandStopping
65
dynamical models, DTW-distance clustering initial-
ization, and adjusted Rand index stopping criterion,
as discussed in section 2. The evaluation protocol is
discussed in section 3.
4.1 Semi-Markov Model
The human sleep data described in section 3.1.1 were
clustered using CDMC (Algorithm 1) with k = 2 clus-
ters, for each of two dynamical model types: semi-
Markov chains with Weibull state durations (sec-
tion 2.2), and Markov chains. Three-state chains
were used in both cases. The generative negative
log-likelihood P(obs|cluster) was used to measure
the quality of model fit, with lower negative log-
likelihood values (higher generative probabilities) in-
dicating a better model fit. Fig. 2 shows the re-
sults. The median negative log-likelihood of the semi-
Markov version is significantly better than that of the
Markov version (p < 0.05, Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney
test). Comparison of the semi-Markov version of
CDMC against a Hidden Markov Model (HMM) ver-
sion (results not shown) also resulted in superior per-
formance of the semi-Markov version (p < 0.05).
SMM MM
0
100
200
300
400
− log P(obs | model)
Figure 2: Negative generative log-likelihoods of CDMC
clusters for semi-Markov (left) and standard Markov (right)
dynamical models. Non-overlapping notches indicate sig-
nificant difference in medians (p < 0.05). Semi-Markov
models provide significantly better log-likelihood.
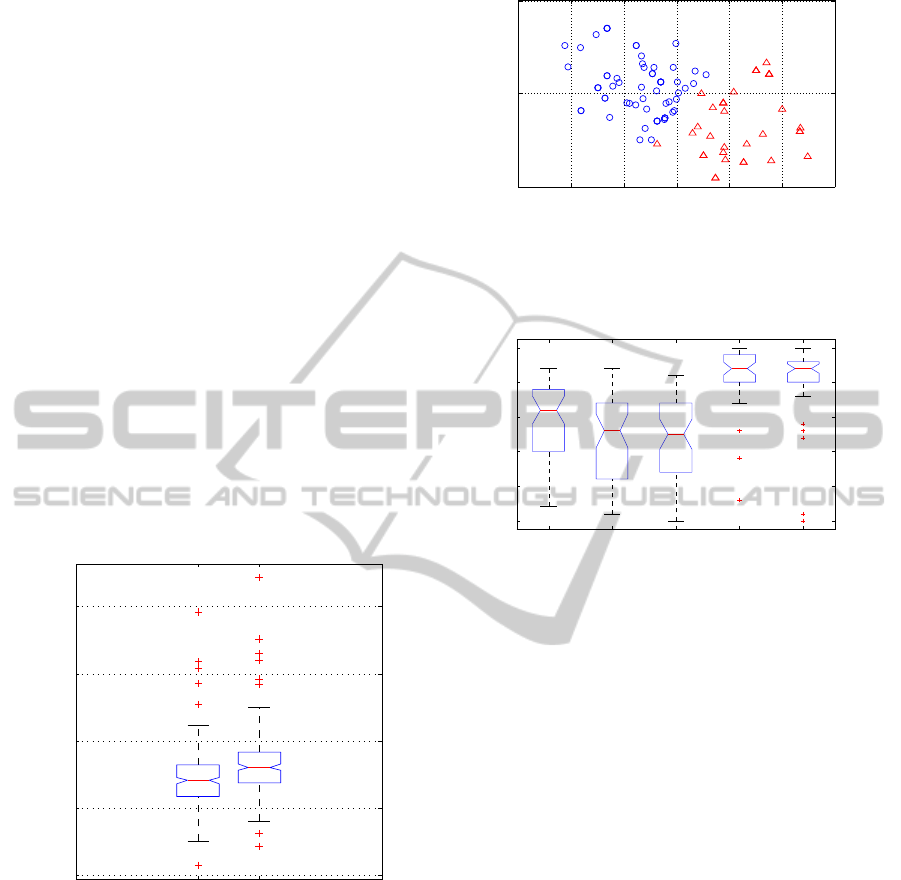
Fig. 3 illustrates the CDMC clustering results for
the semi-Markov dynamical models. The coordinates
of each instance are the estimated parameter values of
the Weibull distribution for that instance’s wake du-
ration distribution. Cluster centroids are significantly
separated along both parameter axes (p < 0.05).
0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5
−0.8
−0.2
0.4
log(scale)
log(shape)
Figure 3: Visualization of CDMC clustering of human sleep
data with Weibull semi-Markov dynamical model. Coordi-
nates of each instance are parameter values of wake stage
Weibull model fit individually to the instance.
CDMC−rand DTWC cDTWC CDMC−DTW CDMC−cDTW
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
Accuracy
Figure 4: Accuracies for randomly initialized CDMC,
DTW-only clustering (DTWC), constrained DTW-only
clustering (cDTWC), DTW-initialized CDMC, and con-
strained DTW-initialized CDMC. Non-overlapping notches
indicate significant difference in medians (p < 0.05). DTW-
initialized and CDTW-initialized CDMC yield significantly
better accuracies than the other clustering techniques.
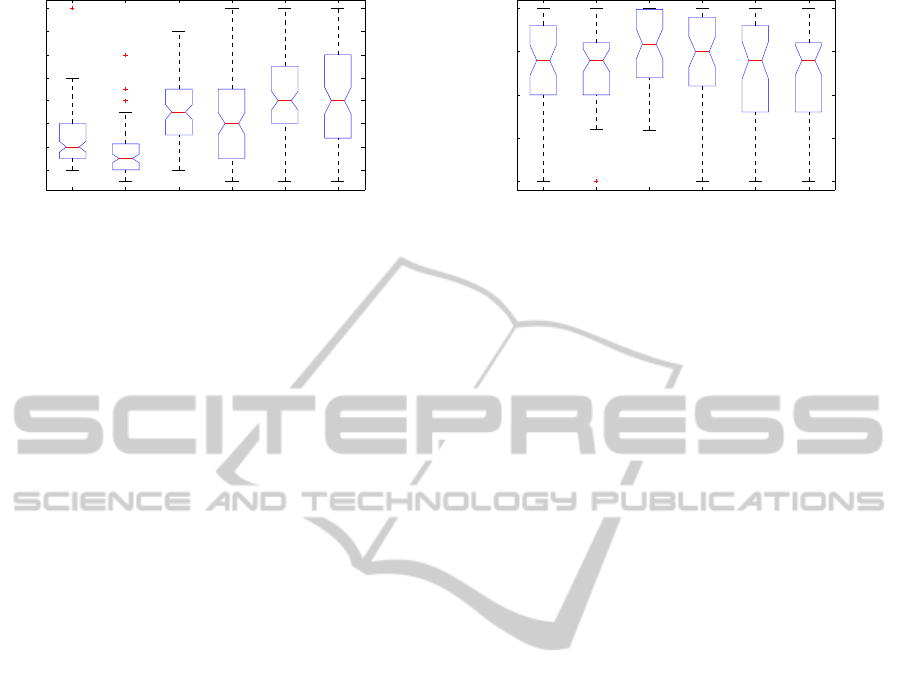
4.2 Initialization Technique
Pseudo-random initialization for CDMC was com-
pared with DTW-distance clustering and Itakura con-
strained DTW (cDTW) clustering initializations for
CDMC (section 2.3.2), as well as with the DTW and
cDTW clustering results directly. Fig. 4 shows the
resulting accuracy values. Pseudorandomly initial-
ized CDMC (median accuracy 0.82) is not signifi-
cantly more accurate than the two DTW-only clus-
tering techniques without CDMC (medians 0.76 and
0.75, for full and constrained DTW, respectively).
However, the DTW-initialized CDMC (median accu-
racy 0.94) significantly outperforms all other tech-
niques. Furthermore, DTW initialization provides
significantly faster convergence than pseudorandom
initialization in the case of the Rand index as the sim-
ilarity metric (left two boxes in Fig. 5.) Statistical
significance is assessed at the p < 0.05 level, using a
Wilcoxon rank sum test (Mann-Whitney test).
BIOSIGNALS2014-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
66
RI−rand RI−DTW ARI−rand ARI−DTW NMI−rand NMI−DTW
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
Figure 5: Iterations to convergence for different stop-
ping criteria. Random and DTW-initialized CDMC. Semi-
Markov mixture data. Stopping metrics: RI (two left), ARI
(two center), NMI (two right). Non-overlapping notches
indicate significant difference in medians (p < 0.05).
RI stopping is significantly faster than others. DTW initial-
ization significantly speeds up convergence for RI stopping.
4.3 Stopping Criterion
The criterion for stopping the iterative process in
CDMC depends on the clustering similarity metric.
Three similarity metrics were compared (see sec-
tion 2.3.3): the standard Rand index (RI), the adjusted
Rand index (ARI) intended to correct for chance clus-
tering agreements, and Normalized Mutual Informa-
tion (NMI). The resulting numbers of iterations re-
quired for convergence are shown in Fig. 5. RI is seen
to lead to a significantly lower median number of it-
erations to convergence (4 and 3, for pseudorandom
initialization and DTW initialization, respectively) as
compared with ARI (7 and 6 iterations) and NMI (8
iterations for both random and DTW initialization).
The faster convergence observed for RI as com-
pared with ARI is in itself not surprising, as the nu-
merical threshold minSim used for stopping in Al-
gorithm 1 is the same for the three similarity met-
rics, while ARI has lower values than RI due to the
intended correction of clustering agreement due to
chance. One would therefore also expect that the
more stringent ARI criterion would lead to better dif-
ferentiated clusters. However, as Fig. 6 shows, the
resulting median accuracy values from testing over la-
beled synthetic semi-Markov mixture data are not sig-
nificantly different at the level p < 0.05 (Wilcoxon-
Mann-Whitney test). The combination of faster con-
vergence and comparable accuracy points to RI as the
superior choice of stopping criterion for CDMC.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
The collective dynamical modeling-clustering
(CDMC) algorithmic framework (Alvarez and Ruiz,
RI cRI ARI cARI NMI cNMI
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
Figure 6: Accuracies for different stopping criteria of DTW-
initialized and constrained DTW-initialized CDMC over
semi-Markov mixture data. Stopping metrics: RI (two
left), ARI (two center), NMI (two right). Non-overlapping
notches indicate significant difference in medians (p <
0.05). Median accuracy values do not differ significantly.
2013) is designed to more reliably identify rare
dynamical events in sequence data by selectively
aggregating instances based on dynamical similarity
to increase sample size for modeling, simultaneously
yielding a dynamics-based clustering.
The present paper uses semi-Markov chains as
the CDMC dynamical models, as they better capture
the dynamics of human sleep in comparison with the
more widely used Markov models. Our experimental
results over data from human sleep studies confirm
the validity of this statement.
The use of distance-based dynamic time warping
clustering for CDMC initialization is found in this pa-
per to lead to significantly more accurate CDMC clus-
tering results in experiments with labeled synthetic
data than pseudorandom initialization does, as well
as significantly faster CDMC convergence.
The adjusted Rand index was tested as the cluster-
ing similarity metric that defines the CDMC stopping
criterion, in order to correct for clustering agreements
due to chance. However, this was shown not to lead to
significantly more accurate clusterings, while signifi-
cantly increasing the number of iterations required for
convergence as compared with the standard Rand in-
dex. Similar statements hold for the Normalized Mu-
tual Information metric as compared with the standard
Rand index. Therefore, the standard Rand index is
the best choice of similarity metric for CDMC among
these candidates.
One direction for future work is the use of par-
tially observable semi-Markov models as the dynam-
ical models.
REFERENCES
Alvarez, S. A. and Ruiz, C. (2013). Collective probabilis-
tic dynamical modeling of sleep stage transitions. In
Proc. Sixth International Conference on Bio-inspired
Semi-MarkovModeling-ClusteringofHumanSleepwithEfficientInitializationandStopping
67

Systems and Signal Processing (BIOSIGNALS 2013),
pages 209–214, Barcelona, Spain. SciTePress.
Berndt, D. J. and Clifford, J. (1994). Using dynamic time
warping to find patterns in time series. In KDD Work-
shop, volume 10 (16), pages 359–370. Seattle, WA.
Bianchi, M. T., Cash, S. S., Mietus, J., Peng, C.-K.,
and Thomas, R. (2010). Obstructive sleep apnea al-
ters sleep stage transition dynamics. PLOS ONE,
5(6):e11356.
Chervin, R. D., Fetterolf, J. L., Ruzicka, D. L., Thelen, B. J.,
and Burns, J. W. (2009). Sleep stage dynamics differ
between children with and without obstructive sleep
apnea. Sleep, 32(10):13251332.
Chu-Shore, J., Westover, M. B., and Bianchi, M. T. (2010).
Power law versus exponential state transition dynam-
ics: application to sleep-wake architecture. PLOS
ONE, 5(12):e14204.
Hernandez, T. L., Ballard, R. D., Weil, K. M., Shep-
ard, T. Y., Scherzinger, A. L., Stamm, E. R., Sharp,
T. A., and Eckel, R. H. (2009). Effects of maintained
weight loss on sleep dynamics and neck morphology
in severely obese adults. Obesity, 17(1):84–91.
Hubert, L. and Arabie, P. (1985). Comparing par-
titions. Journal of Classification, 2:193–218.
10.1007/BF01908075.
Iber, C., Ancoli-Israel, S., Chesson, A., and Quan, S.
(2007). The AASM Manual for the Scoring of
Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology
and Technical Specifications. Westchester: American
Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Itakura (1975). Minimum prediction residual principle ap-
plied to speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on
Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 23(1):52–
72.
Kim, J., Lee, J. S., Robinson, P., and Jeong, D. U. (2009).
Markov analysis of sleep dynamics. Physical Review
Letters, 102(17):178104.
Kishi, A., Struzik, Z. R., Natelson, B. H., Togo, F., and
Yamamoto, Y. (2008). Dynamics of sleep stage tran-
sitions in healthy humans and patients with chronic
fatigue syndrome. American Journal of Physiology-
Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology,
294(6):R1980–R1987.
Oates, T., Firoiu, L., and Cohen, P. R. (1999). Clustering
time series with hidden Markov models and dynamic
time warping. In Proceedings of the IJCAI-99 Work-
shop on Neural, Symbolic and Reinforcement Learn-
ing Methods for Sequence Learning, pages 17–21.
Phillips, A. J., Robinson, P. A., Kedziora, D. J., and Abey-
suriya, R. G. (2010). Mammalian sleep dynamics:
how diverse features arise from a common physiolog-
ical framework. PLOS Computational Biology, 6(6).
Rand, W. M. (1971). Objective criteria for the evaluation of
clustering methods. Journal of the American Statisti-
cal Association, 66(336):846–850.
Rechtschaffen, A. and Kales, A. (1968). A manual of stan-
dardized terminology, techniques and scoring system
for sleep stages of human subjects. US Department of
Health, Education, and Welfare Public Health Service
- NIH/NIND.
Sakoe, H. and Chiba, S. (1978). Dynamic programming
algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition.
IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal
Processing, 26(1):43–49.
Salvador, S. and Chan, P. (2007). Toward accurate dynamic
time warping in linear time and space. Intelligent Data
Analysis, 11(5):561–580.
Vinh, N. X., Epps, J., and Bailey, J. (2010). Informa-
tion theoretic measures for clusterings comparison:
Variants, properties, normalization and correction for
chance. The Journal of Machine Learning Research,
9999:2837–2854.
Wang, C., Alvarez, S. A., Ruiz, C., and Moonis, M.
(2013). Computational modeling of sleep stage dy-
namics using Weibull semi-Markov chains. In Proc.
Sixth International Conference on Health Informat-
ics (HEALTHINF 2013), pages 122–130, Barcelona,
Spain. SciTePress.
Yu, S.-Z. (2010). Hidden semi-Markov models. Artificial
Intelligence, 174(2):215 – 243. Special Review Issue.
Zung, W. W., Naylor, T. H., Gianturco, D. T., and Wilson,
W. P. (1965). Computer simulation of sleep EEG pat-
terns with a Markov chain model. Recent advances in
biological psychiatry, 8:335–355.
BIOSIGNALS2014-InternationalConferenceonBio-inspiredSystemsandSignalProcessing
68
