
Human Action Description Based on Temporal Pyramid Histograms
Yingying Liu and Arcot Sowmya
School of Computer Science and Engineering, The University of New South Wales, Kensington, Australia
Keywords:
Action Recognition, Action Description, Temporal Pyramid Histograms.
Abstract:
In this paper, we present an approach to action description based on temporal pyramid histograms. Bag of
features is a widely used action recognition framework based on local features, for example spatio-temporal
feature points. Although it outperforms other approaches on several public datasets, sequencing information
is ignored. Instead of only calculating the occurrence of code words, we also encode their temporal layout in
this work. The proposed temporal pyramid histograms descriptor is a set of histogram atoms generated from
the original video clip and its subsequences. To classify actions based on the temporal pyramid histograms
descriptor, we design a function to calculate the weights of the histogram atoms according to the corresponding
sequence lengths. We test the descriptor using nearest neighbour for classification. Experimental results show
that, in comparison to the state-of-the-art, our description approach improves action recognition accuracy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human action recognition in videos is a challeng-
ing and popular topic in computer vision with several
promising applications, such as video surveillance,
video indexing and human-computer interaction.
Action description is one of the key issues in hu-
man action recognition. A variety of feature extrac-
tion and description approaches have been proposed
and applied to human action recognition. These ap-
proaches can be divided into two types, namely global
and local representations. Global representations en-
code the human actions in a video as a whole, while
local representations describe the human actions as
a collection of local descriptors or patches (Poppe,
2010).
Global representations are obtained by stacking
the features over all of the video frames. For exam-
ple, (Bobick and Davis, 2001) proposed an approach
based on stacking the human silhouette. They cal-
culate 7 Hu moments of the Motion Energy Image
(MEI) and Motion History Image (MHI), which are
obtained from all of the video frames. There are sev-
eral variations on the silhouette. For example (Wang
et al., 2007) applied the R transform on the human sil-
houette and (Blank et al., 2005) applied Poisson equa-
tion on the stacked silhouette volume. Besides the
silhouette, optical flow is also used for action repre-
sentation. (Efros et al., 2003) introduced optical flow
based human action recognition to sports footage.
Based on their experiments, the approach can work
when the human size is small and video resolution
is relatively low. Although these global representa-
tion approaches have been tested effectively on sev-
eral public and private datasets, there are some draw-
backs. The global approaches are sensitive to noise,
partial occlusion and variation in viewpoints. They
require background subtraction or human tracking,
which is hard to do when the video content is com-
plex, for example, when the background is cluttered
or the camera is moving, or other moving objects oc-
cur in the video.
Local representations do not require pre-
processing, which makes them robust and more
suitable for complex action recognition. The most
popular local representations are space-time feature
points, which are an extension of related 2D repre-
sentations. (Laptev and Lindeberg, 2003) extended
2D Harris functions to the time dimension to obtain
3D data volume. Local maxima are selected as the
3D feature points. The approach has been found to
be effective on several public datasets, including the
Hollywood2 human action and scenes dataset, which
consist of video clips extracted from movies (Marsza-
lek et al., 2009). The drawback of this approach is
that the number of feature points is quite low, and
may not be sufficient to recognize complex action
types. To solve the problem, (Doll
´
ar et al., 2005) pro-
posed an approach based on separable filters. They
applied separable Gabor filters on the video volume,
629
Liu Y. and Sowmya A..
Human Action Description Based on Temporal Pyramid Histograms.
DOI: 10.5220/0004825206290636
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM-2014), pages 629-636
ISBN: 978-989-758-018-5
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

and then picked the local maxima as the feature
points. Besides these methods, (Oikonomopoulos
et al., 2005) extended the 2D salient point detector
into XYT space, and (Willems et al., 2008) extended
2D SURF into XYT space. (Scovanner et al., 2007)
introduced a 3D SIFT descriptor. (Wang et al., 2009)
provide a review on different spatio-temporal features
for action recognition. Bag-of-features is widely
employed when using local features. Bag-of-features
utilizes the statistical characteristics of feature points.
After clustering the feature points into a codebook,
recognition is achieved on the histograms of code
words, which measures the occurrence of features.
Compared to global representations, local repre-
sentations have achieved better performance on sev-
eral public datasets. However, sequencing (temporal)
information in videos is ignored in the bag-of-features
framework, as the letter only encode the occurrence of
code words. (Niebles et al., 2006) introduced an unsu-
pervised action recognition approach based on spatio-
temporal feature points and video sequential struc-
ture learned by pLSA. (Gilbert et al., 2009) learned
a multi stage classifier from simple features. These
two approaches mainly focus on the learning ap-
proaches. (Sun et al., 2009) proposed a hierarchical
spatio-temporal context modeling approach for action
recognition with point-level context (SIFT average
descriptor), intra-trajectory context (trajectory tran-
sition descriptor) and inter-trajectory context (trajec-
tory proximity descriptor). (Choi et al., 2008) intro-
duced a spatio-temporal pyramid matching for sports
videos from both dynamic features (optical flow) and
static features (SIFT).
In this work, we introduce a new temporal pyra-
mid histogram description approach by exploring the
temporal structure of spatio-temporal feature points.
In our approach, an action video is described by
temporal pyramid histograms, which is a set of his-
tograms of code words obtained from the original
video clip and its subsequences. Therefore, the tem-
poral pyramid histogram not only encodes the occur-
rence of the code words, but also their temporal lay-
out.
1.1 Related Work
The closest related work is that due to (Bosch et al.,
2007) and (Lazebnik et al., 2006).
Bosch et al. use a pyramid histogram of gradi-
ents as an object descriptor encoding object shape
and spatial layout. They divide an image using in-
creasingly finer spatial grids by repeatedly doubling
the number of divisions in each axis direction, and
then describe each grid by a histogram of orientation
gradients (HOG). Our approach proposes a tempo-
ral pyramid histogram to describe actions and their
temporal layout. An action video is segmented into
subsequences of the same length repeatedly and then
each of the video sequences, including the orginal se-
quence and the subsequences, is described by a his-
togram of code words.
Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natu-
ral scene categories was introduced by Lazebnik et
al. In their approach, they employ a spatial pyramid
and compute histograms of local features, and weight
the regions at each level as a power of 2. We em-
ploy a similar weighting scheme, except that relative
weights of regions are differently set.
1.2 Contribution
The contribution of this work is the novel temporal
pyramid descriptor of actions. We describe an ac-
tion video by a set of histogram atoms correspond-
ing to the original video clip and its subsequences.
In our approach, spatio-temporal feature points are
extracted, followed by codebook generation using
kmeans clustering. Then we divide the video clip into
its subsequences repeatedly, and obtain the histogram
of codewords corresponding to the original video clip
and its subsequences. Based on the length of a se-
quence, a weight is assigned to its corresponding his-
togram. In the end, we classify actions by a 1-NN
classifier with weighted histograms. Experimental re-
sults show that our approach improves action recog-
nition accuracy, compared to the state-of-the-art.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
In section 2, we describe the temporal pyramid his-
tograms descriptor in detail. In section 3, we describe
the process of extracting the temporal pyramid his-
tograms for action recognition in videos. In section
4, experimental results are shown. The summary and
conclusion of our work is in section 5.
2 ACTION DESCRIPTION WITH
TEMPORAL PYRAMID
HISTOGRAMS
Our objective is to represent the actions in a video
by both the occurrence and their temporal layout of
their code words. This is based on the observation
that an action consists of a series of action atoms,
each of which can be described individually. For ex-
ample, “hand waving” consists of “lift arms up” and
“put arms down”. In this paper, rather than seperating
the action atoms in each action, we divides the orig-
ICPRAM2014-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
630

inal video clip into subsequences of the same length
repeatedly, and describe them with a set of histograms
corresponding to the subsequences, so that the repre-
sentation not only encodes the code word occurrences
but also their temporal variation.
2.1 Temporal Pyramid Histograms
The temporal pyramid histograms description con-
sists of a set of histograms generated from the original
video clip and its subsequences. Ideally, the subse-
quences should correspond to different action atoms.
However, we simplify the segmentation problem by
subdividing each video clip into two subsequences
of the same length repeatedly, and obtain the cor-
responding histograms of code words. All the his-
tograms computed on the same video are concate-
nated into a histogram matrix to obtain the video de-
scriptor, written in the following form:
pH = [H
1
,H
2
,H
3
,...,H
l
,...H
L
]
H
l
= [h
1
,h
2
,h
3
,...,h
i
,...h
n
]
(1)
pH is the temporal pyramid histograms action de-
scriptor; H
l
are the histograms on the l
th
layer; L is the
number of temporal layers. On the l
th
layer, the his-
togram set H
l
consists of n = 2
l−1
histograms, which
are the histograms of code words obtained from corre-
sponding video fragments. Note that every histogram
in pH is normalized.
For example, in Fig. 1, with the single action
“hand waving”, we set the layer number to 2. There-
fore we get the temporal pyramid histograms:
pH = [H
1
,H
2
]
H
1
= [h
1
]
H
2
= [h
li ft arms up
, h
put arms down
]
(2)
On layer 1, H
1
contains the histogram h
1
of the
whole video, which is obtained from all the frames
in the video. On layer 2, we divide the video into
two equal subsequences, which correspond to “lift
arms up” and “put arms down” respectively. There-
fore H
2
contains two histogram atoms H
li f t arms up
and H
put arms down
.
2.2 Weight Definition
After the temporal pyramid histogram is obtained, we
introduce a weight function to assign weights to the
histogram atoms. In Lazebnik et al’s (2006) work, a
power function of 2 is employed as the weight func-
tion of the regions on each level. We too employ a
power function of 2 as the weight function.
W = [w
1
,w
2
,w
3
,...,w
l
,...w
L
] (3)
where w
l
= 1/2
l−1
is the weight on the l
th
layer. The
weights of the action atoms are related to the lengths
of their corresponding sequences. In our approach,
longer sequences have larger weights, as they are
likely to be more informative about actions.
3 HUMAN ACTION
RECOGNITION WITH
TEMPORAL PYRAMID
HISTOGRAMS
In this section, we discuss the application of the tem-
poral pyramid histograms to human action recogni-
tion. A flowchart describing the action recognition
process based on the proposed temporal pyramid his-
tograms descriptor is shown in Fig 2. At first, we
extract spatio-temporal feature points using existing
algorithms. Then we calculate the temporal pyramid
histograms by dividing the video sequence into sub-
sequences repeatedly. Finally, we test the descriptor
using a 1-NN classifier with weighted histograms.
3.1 Temporal Pyramid Histograms
Description
In our work, we utilize the cuboid feature points pro-
posed by (Doll
´
ar et al., 2005). Although there are
several different spatio-temporal feature point extrac-
tion approaches, most of them generate sparse feature
points due to rarity. That makes it difficult to employ
in our algorithm. Because we also need to describe
small subsequences, they might contain no feature
points at all if we apply these feature points extrac-
tion algorithms. Doll
´
ar et al.’s cuboid feature points
approach errs on the side of generating more feature
points rather than too few. Therefore, we choose to
extract the cuboid feature points, which are detected
by calculating the response function based on linear
separable Gabor filters:
R = (I ∗ g ∗ h
ev
)
2
+ (I ∗ g ∗ h
od
)
2
(4)
where g(x,y;δ) is the 2D Gaussian smoothing ker-
nel, applied along the spatial dimension; h
ev
(t;τ,ω)=-
cos(2πtω)e
−t
2
/τ
2
and h
od
(t;τ,ω)=-sin(2πtω)e
−t
2
/τ
2
are
a quadrature pair of 1D Gabor filters applied tempo-
rally. The parameters δ and τ correspond to the spatial
and temporal scales of the detector. The detector has
strong responses on the regions with spatially distin-
guishing characteristics undergoing motion. For de-
scription, Doll
´
ar et al. translated the cuboid into fea-
ture descriptors, for example gradient, windowed op-
HumanActionDescriptionBasedonTemporalPyramidHistograms
631
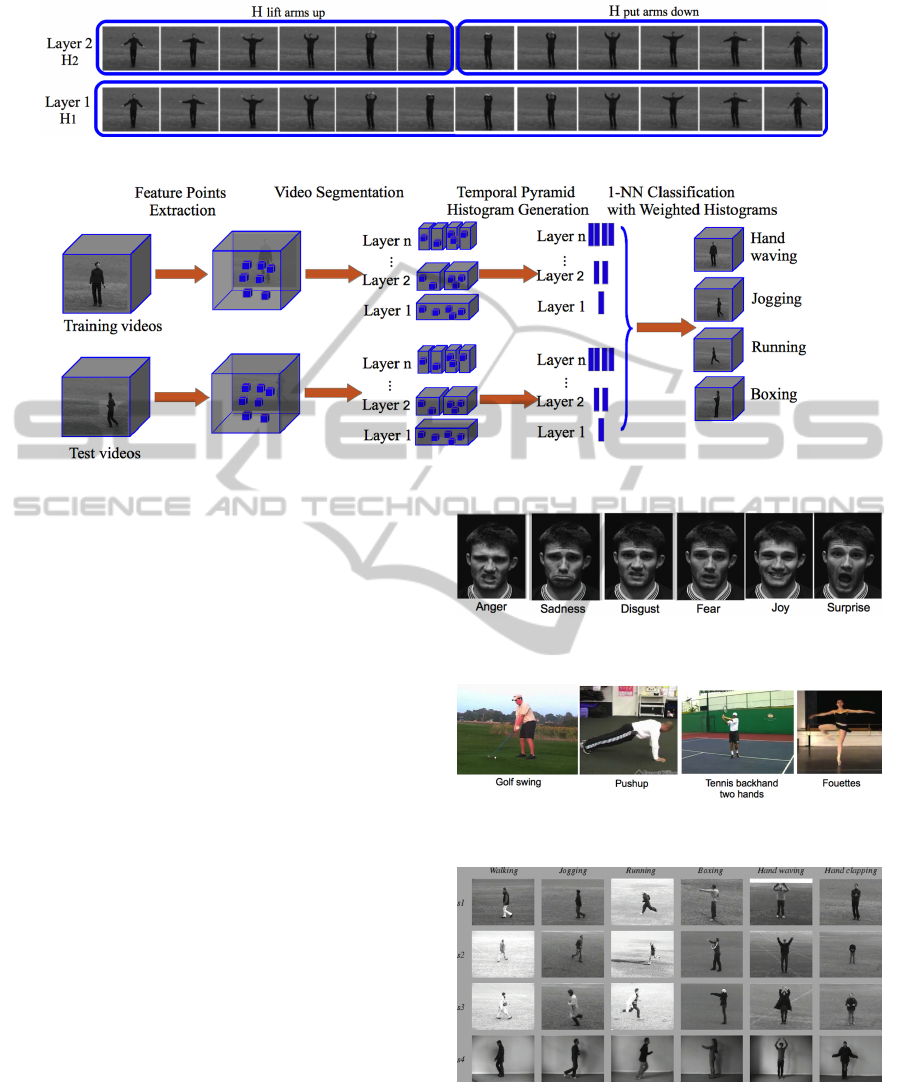
Figure 1: Illustration of temporal pyramid histogram.
Figure 2: Flowchart of action recognition based on temporal pyramid histogram.
tical flow and normalized brightness. We use the gra-
dient descriptor because it has the best performance
according to (Doll
´
ar et al., 2005).
After obtaining the spatio-temporal feature points,
videos are segmented into subsequences and the cor-
responding histograms computed. This is done on
both training and test videos. In our approach,
we segment a video sequence into subsequences re-
peatedly. Histograms corresponding to these subse-
quences are calculated, and a feature codebook gen-
erated by kmeans clustering. The action descriptor
is a histogram set including all the subsequence his-
tograms. By this method, the structure of the actions
is captured in the temporal pyramid histogram.
3.2 Classification with Weighted
Histograms
Similar to (Doll
´
ar et al., 2005)’s work, the 1-nearest
neighbour classifier is used as the classifier in our ex-
periments.
As described in section 2, different weights are
assigned to the histograms. Therefore, based on the
structure of the proposed temporal pyramid histogram
descriptor, we introduce a the weight function:
For H
i
= {h
i
1
,h
i
2
,...,h
i
N
}
and H
j
= {h
j
1
,h
j
2
,...,h
j
N
},
K(H
i
,H
j
) =
∑
k∈N
(w
k
∗ d(h
i
k
,h
j
k
))
(5)
where H
i
and H
j
are the video descriptors of
video clip i and video clip j respectively. K(H
i
,H
j
)
Figure 3: Sample frames corresponding to different types
of facial expression (Doll
´
ar et al., 2005).
Figure 4: Sample frames corresponding to different types
of action in UCF-CIL dataset (Shen and Foroosh, 2008).
Figure 5: KTH sample frames corresponding to different
types of actions and scenarios (Schuldt et al., 2004).
measures the distance between the two clips; w
k
is the
weight of the k
th
histogram, which is defined in (3) ac-
cording to its layer number; d
l
(h
i
k
,d
j
k
) is the distance
metric between the two histograms h
i
k
and h
j
k
. In our
ICPRAM2014-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
632

work, we use euclidean distance as it has the best per-
formance in our experiments. The weight function
measures the similarity between two videos. Finally,
1-NN classification is performed on the weighted his-
tograms.
4 EXPERIMENTS
Based on the structure of the proposed pyramid tem-
poral histograms representation method, the ideal
data for the approach is well-aligned videos contain-
ing only one nonrepeating action. However, most
available public datasets contain repeating actions,
e.g., walking. Also videos in these datasets were not
always well-aligned, because different videos of the
same action were not recorded from the same pose
and view. Therefore, to explore the capability of the
proposed action descriptor, we tested it on a facial ex-
pression dataset (well-aligned, nonrepeating action),
a subset of the UCF-CIL action dataset (not well-
aligned, nonrepeating action), and KTH action dataset
(not well-aligned, repeating action).
The facial expression dataset was created
by (Doll
´
ar et al., 2005). There are 6 types of facial
expressions (anger, disgust, fear, joy, sadness and
surprise) in the dataset, performed by two individuals
under two different lighting setups. Each video starts
with a neutral expression, followed by an emotion,
and then returns to neutral. All the videos are about
2 seconds long. There are 192 videos in total and the
clips are well-aligned. Sample frames corresponding
to different types of facial expressions are shown in
Fig. 3.
The UCF-CIL action dataset was introduced
by (Shen and Foroosh, 2008). It consists of 56 se-
quences of 8 actions: 4 of ballet fouettes, 12 of bal-
let spin, 6 of push-up exercise, 8 of golf-swing, 4 of
one-handed tennis backhand stroke, 8 of two-handed
tennis backhand stroke, 4 of tennis forehand stroke
and 10 of tennis serve. The videos are taken from the
internet. Clips in each group may have different start-
ing and ending times. Sample frames corresponding
to different types of actions in UCF-CIL dataset are
shown in Fig. 4.
The KTH dataset (Schuldt et al., 2004) contains
six types of human actions (walking, jogging, run-
ning, boxing, hand waving and hand clapping) per-
formed several times by 25 subjects in four scenarios.
Each video contains an action performed by one per-
son. The database contains 2391 sequences. Each
action is repeated several times in each video. Sam-
ple frames corresponding to different types of actions
and scenarios are shown in Fig. 5.
Figure 6: Average recognition accuracy on facial expression
dataset. The four experiments are set up as: train on subject
A and test on subject B under the same illumination; train
on subject B and test on subject A under the same illumina-
tion; train on subject A and test on subject B under different
illumination; train on subject B and test on subject A under
different illumination.
Because of different parameter and experiment
settings, we do not attempt to compare our approach
with other published results. However, the layer num-
ber one of the temporal pyramid histogram corre-
sponds to Doll
´
ar et al.’s work, and may be compared.
In the following experiments, we show that action
recognition accuracy improves as the layer number
increases to an optimal value.
4.1 Facial Expression Dataset
Identical to the experiment setup in (Doll
´
ar et al.,
2005)’s work, We test the data under two conditions:
(1) training on a single subject under one of the two
lighting setups and testing on the other subject under
the same illumination. (2) training on a single subject
under one of the two lighting setups and testing on the
other subject under a different lighting setups. The di-
mension of the spatio-temporal feature point descrip-
tor is 100, and the codebook size is 250.
We vary the layer number L in equation (1) from
1 to 8. Fig. 6 shows the average recognition accu-
racies on different layers under different experimen-
tal setups. Generally, the average recognition accu-
racy improves when the layer number increases, and
drops or remains stable after reaching a peak. The
results reveal the fact that sub-clips of the original
video do contain useful information for recognition.
It can also been concluded that if the temporal lay-
ers are too many, recognition accuracy will be not be
further improved. This is because too small sub-clips
of the original video may not be meaningful for ac-
tion recognition, and may also introduce noise in the
representation.
A comparison between our method and Doll
´
ar et
al.’s when training and test datasets are under the same
HumanActionDescriptionBasedonTemporalPyramidHistograms
633

Table 1: Comparison of our result and (Doll
´
ar et al., 2005)’s result on two subjects A and B under the same illumination in
facial expression dataset.
Method/Accuracy A/B (same illum.) B/A (same illum.)
(Doll
´
ar et al., 2005) 0.853 0.835
Our approach, layer 1, untuned 0.750 0.708
Our approach, average over 8 layers 0.828 0.758
Our approach, best 0.896 0.813
Table 2: Confusion matrix of our best result, train on subject A/Test on subject B (under the same illumination).
A/B anger disgust fear joy sadness superise
anger 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
disgust 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
fear 0.25 0.375 0.375 0.125 0.0 0.0
joy 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0
sadness 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0
suprise 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
Table 3: Confusion matrix of our best result, train on subject B/Test on subject A (under the same illumination).
B/A anger disgust fear joy sadness superise
anger 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
disgust 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
fear 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
joy 0.125 0.0 0.0 0.875 0.0 0.0
sadness 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0
suprise 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0
illumination settings are shown in Table 1. In Tables 2
and 3 the confusion matrices of our best results are
shown, obtained when the training and test datasets
are under the same illumination settings. In Tabel 2,
fear is misrecognized as anger, disgust and joy. In
Table 3, joy is misrecognized as anger. This is be-
cause the degree of mouth opening is smilar among
these emotions, see Figure 3. From the experiments,
we can conclude that the accuracy of our method im-
proves the recognition as the layer number increases.
The best accuracy achieved (last row, Table 1) is com-
pareble to Doll
´
ar et al.’s result (first row, Table 1).
4.2 UCF-CIL Action Dataset
In our experiment, we include 5 action types of ac-
tions, namely golf-swing, one handed tennis back-
hand stroke, two-handed tennis backhand stroke, ten-
nis forehand stroke and tennis serve from the origi-
nal dataset. This is because the intuition behind our
description approach is to describe not only the code-
words but also their temporal sequence, while in re-
peated actions like fouettes, push up and spin, the
temporal sequence of code words is not obvious.
During the experiment, we select one clip from
each action to generate the codebook. During testing
on the remaining data, we compare every clip to the
Figure 7: Average recognition accuracy on a subset of UCF-
CIL Action dataset.
other clips. The dimension of spatio-temporal feature
points is 100. The codebook size is 500.
From Fig. 7, we can conclude that the proposed
temporal pyramid histogram description improves the
recognition accuracy from 0.48 to 0.55 and the max-
imum accuracy is achieved for 3 layers. The over-
all recognition accuracy is not high. This is because
two clips of the same action may start from difference
poses and end at different ones. This affects the ca-
pability of the temporal pyramid histogram descrip-
tor, as it is designed for well-aligned clips ideally.
However, we can conclude that temporal pyramid his-
togram does work on clips that are not well-aligned
and also improve accuracy with more layers.
ICPRAM2014-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
634
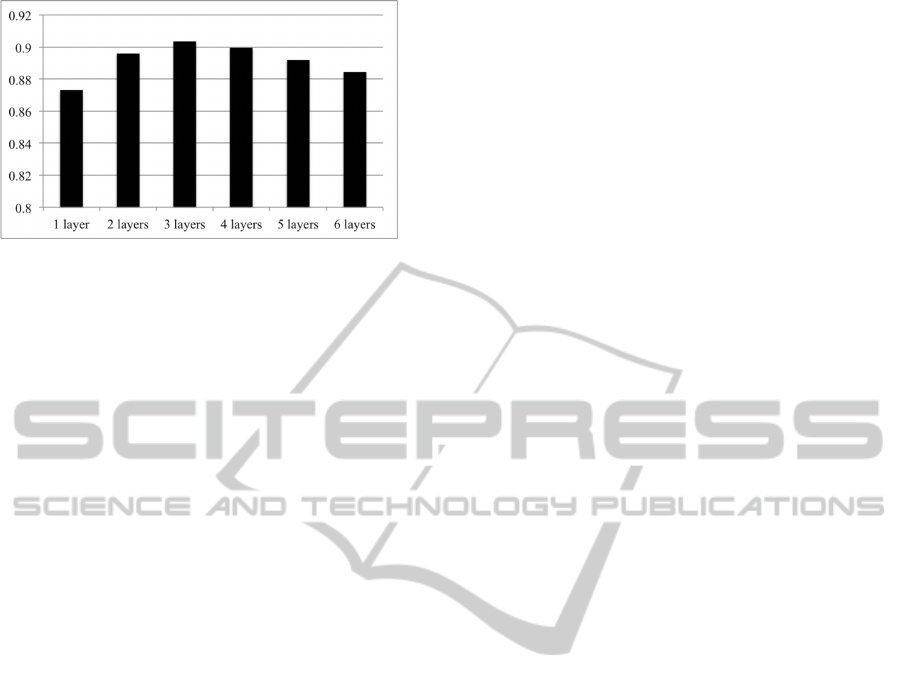
Figure 8: Average recognition accuracy on KTH dataset.
4.3 KTH Human Action Dataset
For the KTH dataset, considering size of the dataset,
we obtain the codebook from the videos of three sub-
jects according to the standard codebook generation
approach. Then on the remaining 22 subjects, we
compute pyramid histograms for 21 subjects, and rec-
ognize the last subject by comparing its pyramid his-
tograms to the 21 training pyramid histograms.
The layer number L in equation (1) is varied from
1 to 6. The average recognition accuracy with dif-
ferent layers is in Fig 8. The dimension of spatio-
temporal feature points is 100, and the codebook size
is 500.
From Fig. 8, we can see that there is a small im-
provment in recognition accuracy from 0.87 to 0.90
when the layer number changes from 1 to 3. The
reason that improvement is not dramatic is that com-
pared to facial expression data, the actions in KTH are
repeating actions, for example, walking or running.
The proposed pyramid temporal histograms descrip-
tor can not describe the temporal structure of such
repeating actions, because each action is performed
several times in each video. However, the proposed
temporal pyramid histogram description method does
enhance the stability of the code words occurrence by
calculating the histograms of code words on different
layers, as the representative code words of each action
occur frequently in all of the subsequences.
(Doll
´
ar et al., 2005) obtained over 0.80 on KTH
action dataset. According to the evaluation of (Wang
et al., 2009) on current spatio-temporal feature point
algorithms, the highest recognition accuracy on KTH
action dataset based on (Doll
´
ar et al., 2005) work is
0.90. Because the parameter settings are not available
and the experiment settings are different, the results
are not directly comparable. However, the result from
the first layer in our approach corresponds to Doll
´
ar
et al.’s work, and our approach is able to improve the
recognition accuracy and match the best.
4.4 Summary
As the baseline parameter settings employed by oth-
ers for feature extraction and codebook generation are
not available, direct comparisons of our method with
published results are problematic. However, the re-
sults due to (Doll
´
ar et al., 2005) correspond to our first
layer, therefore our best results, achieved at optimal
layers, are equal to or better than the state-of-the-art.
From the results, we can conclude that the tempo-
ral pyramid histograms work better when the clips are
well-aligned and contain non-repeating actions. How-
ever, it can still work when these two conditions are
not met.
In the facial expression dataset, because the ex-
pression is performed just once in each video and
the videos are well-aligned, the proposed descrip-
tion method gets the code words layout correctly. In
UCF-CIL action dataset and KTH dataset, the pro-
posed approach also improves the recognition re-
sults. This demonstrates the capability of the pyramid
histogram descriptor approach in dealing with clips
that are not well-aligned or contain repeated actions,
though the recognition accuracy cannot be greatly im-
proved. This is because the subsequence segmen-
tation method we employed cannot always pick up
meaningful subsequences. In future, we shall explore
a more flexible subsequence selection approach to ob-
tain more meaningful action atoms.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we introduce a temporal pyramid
histograms-based action descriptor approach. In-
spired by the spatial pyramid descriptor proposed
by (Bosch et al., 2007), we divide the video into sub-
sequences repeatedly, and then concatenate the his-
tograms obtained, from the video parts. To enhance
the descriptors ability, we assign different weights
to the histogram atoms. The intuition is to encode
not only the occurrence of the code words, but also
their temporal structure. Although we utilize his-
togram of code words approach based on the spatio-
temporal feature points introduced by (Doll
´
ar et al.,
2005), it is not hard to conclude that other descrip-
tion approaches, for example, silhouettes, can also be
employed in this description framework.
In all our experiments, we obtain improved accu-
racies as the number of layers is increased to an op-
timal value, which is the main contribution of the pa-
per. The proposed description approach was tested
and found to be most effective in classifying well-
aligned clips containing non-repeating actions.
HumanActionDescriptionBasedonTemporalPyramidHistograms
635

However, this approach does require the videos to
be already well segmented and aligned, which means
that in each video, there should be only one full per-
formance of an action, i.e. actions of the same type
start from the same pose and end at the same pose. In
future work, we shall explore automatic subsequence
segmentation methods, in order to obtain meaningful
subsequences corresponding to action atoms. There-
fore, the performance could be improved further on
different kinds of datasets. Also, in this work, the
weight of each histogram is set by experience, which
can be learned automatically in future.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Dr. Piotr Doll
´
ar for gener-
ously sharing the feature extraction source code and
toolbox.
REFERENCES
Blank, M., Gorelick, L., Shechtman, E., Irani, M., and
Basri, R. (2005). Actions as space-time shapes. In
ICCV 2005, volume 2, pages 1395–1402 Vol. 2.
Bobick, A. and Davis, J. (2001). The recognition of human
movement using temporal templates. Pattern Analy-
sis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on,
23(3):257–267.
Bosch, A., Zisserman, A., and Munoz, X. (2007). Repre-
senting shape with a spatial pyramid kernel. In Pro-
ceedings of the 6th ACM international conference on
Image and video retrieval, pages 401–408. ACM.
Choi, J., Jeon, W. J., and Lee, S.-C. (2008). Spatio-temporal
pyramid matching for sports videos. In Proceedings
of the 1st ACM International Conference on Multime-
dia Information Retrieval, MIR ’08, pages 291–297.
ACM.
Doll
´
ar, P., Rabaud, V., Cottrell, G., and Belongie, S. (2005).
Behavior recognition via sparse spatio-temporal fea-
tures. In Visual Surveillance and Performance Eval-
uation of Tracking and Surveillance, 2005. 2nd Joint
IEEE International Workshop on, pages 65–72.
Efros, A., Berg, A., Mori, G., and Malik, J. (2003). Rec-
ognizing action at a distance. In Computer Vision,
2003. Proceedings. Ninth IEEE International Confer-
ence on, pages 726–733 vol.2.
Gilbert, A., Illingworth, J., and Bowden, R. (2009). Fast
realistic multi-action recognition using mined dense
spatio-temporal features. In Computer Vision, 2009
IEEE 12th International Conference on, pages 925–
931.
Laptev, I. and Lindeberg, T. (2003). Space-time inter-
est points. In Computer Vision, 2003. Proceedings.
Ninth IEEE International Conference on, pages 432–
439 vol.1.
Lazebnik, S., Schmid, C., and Ponce, J. (2006). Beyond
bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recog-
nizing natural scene categories. In CVPR2006, vol-
ume 2, pages 2169–2178.
Marszalek, M., Laptev, I., and Schmid, C. (2009). Actions
in context. In CVPR 2009, pages 2929–2936.
Niebles, J. C., Wang, H., and Fei-fei, L. (2006). Unsu-
pervised learning of human action categories using
spatial-temporal words. In In Proc. BMVC.
Oikonomopoulos, A., Patras, I., and Pantic, M. (2005). Spa-
tiotemporal salient points for visual recognition of hu-
man actions. Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B:
Cybernetics, IEEE Transactions on, 36(3):710–719.
Poppe, R. (2010). A survey on vision-based human action
recognition. Image Vision Comput., 28(6):976–990.
Schuldt, C., Laptev, I., and Caputo, B. (2004). Recognizing
human actions: a local svm approach. In ICPR 2004,
volume 3, pages 32–36 Vol.3.
Scovanner, P., Ali, S., and Shah, M. (2007). A 3-
dimensional sift descriptor and its application to ac-
tion recognition. In Proceedings of the 15th Inter-
national Conference on Multimedia, pages 357–360.
ACM.
Shen, Y. and Foroosh, H. (2008). View-invariant recogni-
tion of body pose from space-time templates. In CVPR
2008, pages 1–6.
Sun, J., Wu, X., Yan, S., Cheong, L.-F., Chua, T.-S., and Li,
J. (2009). Hierarchical spatio-temporal context mod-
eling for action recognition. In CVPR 2009, pages
2004–2011.
Wang, H., Ullah, M. M., Klser, A., Laptev, I., and Schmid,
C. (2009). Evaluation of local spatio-temporal fea-
tures for action recognition. In University of Central
Florida, U.S.A.
Wang, Y., Huang, K., and Tan, T. (2007). Human activ-
ity recognition based on r transform. In CVPR2007,
pages 1–8.
Willems, G., Tuytelaars, T., and Gool, L. (2008). An effi-
cient dense and scale-invariant spatio-temporal inter-
est point detector. In Proceedings of the 10th Euro-
pean Conference on Computer Vision: Part II, pages
650–663. Springer-Verlag.
ICPRAM2014-InternationalConferenceonPatternRecognitionApplicationsandMethods
636
