
General Lower Bounds for the Total Completion Time in a Flowshop
Scheduling Problem
MaxPlus Approach
Nhat-Vinh Vo
1
, Pauline Fouillet
2
and Christophe Lent
´
e
1
1
Universit
´
e Franc¸ois-Rabelais de Tours, CNRS, LI EA 6300, OC ERL CNRS 6305, Tours, France
2
Universit
´
e Franc¸ois-Rabelais de Tours, Polytech, Tours, France
Keywords:
Scheduling, Flowshop, Total Completion Time, Lower Bound.
Abstract:
The flowshop scheduling problem has been largely studied for 60 years. As a criterion, the total completion
time also receives a great amount of attention. Many studies have been carried out in the past but they are
limited in the number of machines or constraints. MaxPlus algebra is also applied to the scheduling theory but
the literature focuses on some concrete constraints. Therefore, this study presents a new method to tackle a
general permutation flowshop problem, with additional constraints, to elaborate on lower bounds for the total
completion time. These lower bounds can take into account several constraints, like delays, blocking or setup
times, but they imply to solve a Traveling Salesman Problem. The theory is developed, based on a MaxPlus
modeling of flowshop problems and experimental results are presented.
1 INTRODUCTION
The m-machine flowshop scheduling problem has
been largely studied for 60 years. The makespan is
the most studied criterion, especially for permutation
flowshop problems. However, the total completion
time criterion also receives a great amount of atten-
tion. It reflects ”the total manufacturing waiting time
experienced by all customers” (Emmons and Vairak-
tarakis, 2013). Even with only two machines, prob-
lem F
2
||
∑
C
i
is NP − hard in the strong sense and so
are problems with more machines. Therefore, results
that help to solve these problems are interesting.
Total completion time criterion has been stud-
ied largely. A branch-and-bound algorithm, incor-
porating a lower bound, dominance relation and an
upper bound is presented by Allahverdi and Al-
Anzi in (Allahverdi and Al-Anzi, 2006). That study
solves total completion time minimization problem
F
3
|perm,S
nsd
|
∑
C
i
where separate setup times are
taken into account. The number of visited nodes and
the percentage between this number and that of pos-
sible nodes are considered. This percentage shows us
that their lower bound is effective as the number of
visited nodes is quite small. Separate setup times are
also investigated by Su and Lee (Su and Lee, 2008) in
a two-machine flowshop no-wait scheduling problem
with a single server in order to minimize total com-
pletion time. In another research, eleven heuristics
based on the Shortest Processing Time (SPT) rule are
implemented by Aydilek and Allahverdi (Aydilek and
Allahverdi, 2010). Their study is to minimize total
completion time of a two-machine flowshop schedul-
ing problem, in which processing times are bounded.
A lower bound based on the first machine of problem
F
2
||
∑
C
i
is presented as the sum of a previously ex-
isting lower bound and the optimum of an asymmet-
ric traveling salesman problem (ATSP) (Della Croce
et al., 1996). These aforementioned studies only deal
with limited number of machines and few constraints.
It is not easy to generalize them to any number of ma-
chines or any constraint.
In this study, the proposed approach is based on
MaxPlus algebra (see 2.1). It has been widely used
in control systems, especially in relation with Petri
Nets but rarely in the scheduling theory. Nevertheless,
some articles can be cited on project scheduling prob-
lems (Giffler, 1963), on cyclic parallel machine prob-
lems (Hanen and Munier, 1995), on cyclic flowshop
scheduling problems (Cohen et al., 1985; Gaubert,
1992) and on cyclic jobshop scheduling problems
(Gaubert and Maisresse, 1999). The MaxPlus al-
gebra is applied to modeling and scheduling flow-
shop problems with minimal delays, setup and re-
moval times (Lent
´
e, 2001; Bouquard et al., 2006). It
is also applied to flowshop problems with minimal-
382
Vo N., Fouillet P. and Lenté C..
General Lower Bounds for the Total Completion Time in a Flowshop Scheduling Problem - MaxPlus Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0004833403820389
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES-2014), pages 382-389
ISBN: 978-989-758-017-8
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

maximal delays for two-machines (Bouquard and
Lent
´
e, 2006) or for any number of machines (Augusto
et al., 2006). In these studies, jobs are associated
to MaxPlus square matrices and lower bounds, up-
per bounds and/or dominance conditions are derived
by applying transformations to those matrices. More-
over, this approach is used effectively to model flow-
shop problems with minimal-maximal delays, setup
and removal times and to highlight a central problem
(Vo and Lent
´
e, 2013).
The objective of this study is to address a general
permutation flowshop problem in terms of constraints
taken into account. We elaborate on lower bounds for
the total completion time that are based on the reso-
lution of two sub-problems: one problem similar to
the one machine total completion time minimization
problem and the other similar to a traveling salesman
problem. These lower bounds are incorporated in a
branch-and-bound procedure to be tested.
The next section presents the background of the
study: MaxPlus algebra and flowshop scheduling
problem. We recall in section 3 how MaxPlus alge-
bra can be used to model a general flowshop prob-
lem. The lower bound construction is then explained
in section 4. Finally, a branch-and-bound algo-
rithm is explained and some tests concerning prob-
lem F3|perm; S
nsd
|
∑
C
i
and problem F
m
|perm|
∑
C
i
are presented as experimental results.
2 CONTEXT AND DEFINITIONS
2.1 MaxPlus Algebra
MaxPlus algebra is briefly described as follows; a
more detailed presentation can be found in (Gunawar-
dena, 1998).
In MaxPlus algebra, the maximum is denoted by
⊕ and the addition by ⊗. The former, ⊕, is idempo-
tent, commutative, associative and has a neutral ele-
ment (−∞) denoted by 0. The latter, ⊗, is associa-
tive, distributive on ⊕ and has a neutral element (0)
denoted by 1. The null element, 0, is an absorbing
element for ⊗. These properties can be summarized
by stating that R
max
= (R ∪{−∞},⊕,⊗) is a dioid. It
is important to note that in MaxPlus algebra in partic-
ular, and in dioids in general, the first operator ⊕ can
not be simplified, that is a ⊕ b = a ⊕ c 6⇒ b = c. Fur-
thermore, in R
max
, the second operator ⊗ is commu-
tative, and except 0, every element is invertible: the
inverse of x is denoted by x
−1
or 1/x. For simplicity,
we denote the ordinary subtractions by x/y instead of
x ⊗ y
−1
and by xy the product x ⊗ y.
It is possible to extend these two operators to m ×
m matrices of elements of R
max
. Let A and B be two
matrices of size m × m, operators ⊕ and ⊗ are defined
by
∀(i, j) ∈ {1, ...,m}
2
,[A ⊕B]
i j
= [A]
i j
⊕ [B]
i j
∀(i, j) ∈ {1, ...,m}
2
,[A ⊗B]
i j
=
m
M
k=1
[A]
ik
⊗ [B]
k j
where [.]
i j
is the element at the i
th
row and j
th
col-
umn of the corresponding matrix. It is not difficult to
show that the set of m × m matrices in R
max
is a dioid.
However, ⊗ is not commutative and not every matrix
is invertible.
The two following lemmas can be derived from
the previous definitions. They will be useful for the
development of the lower bound.
Lemma 1. ∀ j ∈ {1,. . . , m} :
[A ⊗B]
1 j
=
m
M
k=1
[A]
1k
⊗ [B]
k j
≥ [A]
11
⊗ [B]
1 j
(1)
Lemma 2. ∀`, j ∈ {1,. . . , m} :
[A ⊗B]
1 j
≥ [A]
1`
⊗ [B]
` j
(2)
[A ⊗B]
` j
≥ [A]
``
⊗ [B]
` j
(3)
2.2 Flowshop Scheduling Problem
Since the paper of Johnson (Johnson, 1954), flow-
shop problems have been studied largely (Em-
mons and Vairaktarakis, 2013). Basically, a flow-
shop scheduling problem consists of a set of n-
jobs J = {J
1
,..., J
n
} and another set of m-machines
{M
1
,..., M
m
}. Each job must go through all ma-
chines in the same predefined order, let us say from
M
1
to M
m
and each machine can load only one job at
a time (Brucker, 2006). If all jobs must be executed
in the same order over all machines, the problem is
called a permutation flowshop problem. In this case,
there exists an ordered list of jobs (or a sequence) σ
that is identically scheduled on all machines. We limit
our current study to permutation flowshop problems.
Each job J
i
is composed of m operations O
ik
(1 ≤ k ≤
m): one per machine. An operation is at least de-
scribed by a processing time p
ik
: the processing time
of job J
i
on machine M
k
(or equivalently, the process-
ing time of the k
th
operation of job J
i
). The comple-
tion time of job J
i
on machine M
k
(C
ik
) and the com-
pletion time of job J
i
(C
i
) are related by C
i
= C
im
.
Over the years, several additional constraints have
been taken into consideration (Emmons and Vairak-
tarakis, 2013). Some of them can be modeled us-
ing MaxPlus algebra (Vo and Lent
´
e, 2013). One of
GeneralLowerBoundsfortheTotalCompletionTimeinaFlowshopSchedulingProblem-MaxPlusApproach
383
the most common constraints is the permutation con-
straint (perm) which has just been mentioned above.
A constraint of no − wait appears in problems where
there is no delay allowed between two successive op-
erations of a job. On the contrary, constraints of
min − delay, max − delay, min − max delay indicate
a flowshop problem with delays between two suc-
cessive operations of a job. Depending on the case,
these delays may have to meet a lower bound, an up-
per bound or both. It may also exist separate non-
sequence dependent setup times (S
nsd
) and/or removal
times (R
nsd
) before and after each operation. Finally,
some authors have considered blocking constraints,
due to the non-existence of intermediate storage be-
tween consecutive machines or to specific interactions
between machines. These constraints are referred to
as RSb, RCb and RCb
∗
in (Trabelsi et al., 2012).
The most studied criterion is the makespan, or the
maximal completion time (C
max
). It is defined by the
completion time of the last operation scheduled on the
last machine (M
m
). In this article we focus on the total
completion time (
∑
C
i
) which is the sum of the com-
pletion times of the different jobs in a given schedule.
3 MaxPlus MODELING OF
FLOWSHOP SCHEDULING
PROBLEMS
Our problem can be noted F
m
|perm β|γ using
notations proposed by Graham et al. (Graham
et al., 1979). It is a m machine permuta-
tion flowshop problem with a set of constraints
β that is a subset of {min − max delay, no −
wait, S
nsd
, R
nsd
, RSb,RCb,RCb
∗
}. Criterion γ can
be whatever we desire since it does not interfere in
the modeling process. The total completion time cri-
terion is investigated in the following of this article.
Basically, the modeling process follows this
scheme:
• Given the k
th
operation O
ik
of a job J
i
, four dates
are considered: date δ
k
of availability of machine
M
k
(before execution of operation O
ik
), starting
time St
ik
of operation O
ik
, its completion time
C
ik
and date of liberation D
ik
of machine M
k
(af-
ter execution of operation O
ik
), that is the date
when job J
i
leaves machine M
k
to be placed in
a stock or on the following machine. In most
flowshop problems, dates C
ik
and D
ik
are equal;
however, they can be different in case of block-
ing constraints or removal times. Date of liber-
ation of the last machine (D
im
) is equal to the
completion time C
i
of the job, except if there ex-
ist removal times. In this case D
im
is equal to
C
i
plus the removal time of operation O
im
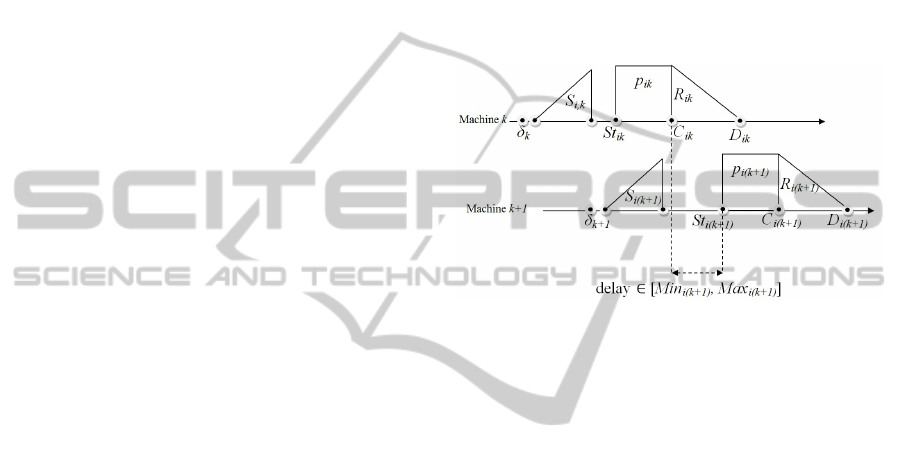
. Fig-
ure 1 shows an example of flowshop problem
F
m
|perm,min − max delay, S
nsd
,R
nsd
|
∑
C
i
where
triangles illustrate setup and removal times and
rectangles illustrate processing times.
• Formulate the system (S) of inequalities that link
these different variables.
• Calculate the smallest (D
ik
) (1 ≤ k ≤ m),(1 ≤ i ≤
n) solutions of the system (S).
Figure 1: Example of flowshop problem: F
m
|perm,min −
max delay,S
nsd
,R
nsd
|
∑
C
i
.
Whatever the set of constraints β is, these calcula-
tions lead to a MaxPlus linear relation between dates
of liberation D
ik
and dates of availability δ
k
(Lent
´
e,
2011), (Vo and Lent
´
e, 2013). More precisely, we can
state the following proposition:
Proposition 1 (Matrix associated to a job). Let
~
δ
(resp.
~
D
i
) be the line vector of the m dates δ
k
(resp.
D
ik
): it exists a m × m MaxPlus matrix T
i
computed
from data of job J
i
such that
~
D
i
=
~
δ ⊗ T
i
(4)
Matrix T
i
is called the associated matrix of job J
i
: it
entirely characterizes job J
i
.
Various elements of matrix T
i
will be denoted t
i
`c
,
in other words, t
i
`c
= [T
i
]
`c
. This matrix sums up the
job data (processing times, setup times, delays and so
on) and the flowshop constraints.
T
i
=
t
i
11
t
i
12
... t
i
1m
t
i
21
t
i
22
... t
i
2m
... ... ... . . .
t
i
m1
t
i
m2
... t
i
mm
(5)
These results can be generalized to a sequence of
jobs (Lent
´
e, 2011), (Bouquard et al., 2006).
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
384

Definition 1 (Matrix associated to a sequence). Let
σ be a sequence of ν jobs: its associated matrix is
matrix T
σ
defined by
T
σ
=
ν
O
i=1
T
σ(i)
(6)
Proposition 2. If
~
δ is the vector of dates of availabil-
ity of machines and
~
D
σ
the vector of dates of libera-
tion of machines, after the execution of sequence σ,
we have the relation
~
D
σ
=
~
δ ⊗ T
σ
(7)
4 PROPOSED LOWER BOUNDS
This section presents lower bounds for problem
Fm|perm, β|
∑
C
i
, with β ⊂ {min − max delay, no −
wait, S
nsd
, R
nsd
, RSb,RCb, RCb
∗
}. To develop the
calculations, we assume that C
i
= D
im
(1 ≤ i ≤ n). It
is true unless there exists removal times: this particu-
lar case will be discussed at the end of this section.
4.1 The first lower bound
We first present a lower bound of the completion time
of the k
th
job in a sequence before elaborating on a
lower bound for the total completion time.
4.1.1 Lower bound of completion time of a job
Proposition 3. Let σ a sequence of jobs and
~
δ the
line vector of dates of availability of the machines (
~
δ
= (δ
1
,δ
2
,..., δ
m
)). The completion time of the job in
k
th
position in the sequence verifies relation:
i f k = 1 : C
σ(1)
≥ δ
1
T
σ(1)
1m
i f k = 2 : C
σ(2)
≥ δ
1
T
σ(1)
T
σ(2)
1m
i f k > 2 : C
σ(k)
≥ δ
1
k−2
O
j=1
(t
σ( j)
11
)
T
σ(k−1)
T
σ(k)
1m
Proof. Let τ be the sub-sequence composed of the
first k jobs of sequence σ. Proposition 2 and defini-
tion 1 result in:
~
D
τ
=
~
δ ⊗ T
τ
=
~
δ ⊗
k
O
i=1
T
τ(i)
=
~
δ ⊗
k
O
i=1
T
σ(i)
(8)
Moreover
~
D
σ(k)
=
~
D
τ
and by assumption C
σ(k)
=
D
σ(k)m
, which is the last element of vector
~
D
σ(k)
, we
have,
C
σ(k)
=
h
~
D
τ
i
1m
=
"
~
δ ⊗
k
O
i=1
T
σ(i)
#
1m
(9)
If k = 1, the application of lemma 1 results in:
C
σ(1)
≥
h
~
δ
i
11
T
σ(1)
1m
= δ
1
T
σ(1)
1m
(10)
If k ≥ 2, by iteratively applying this lemma into equa-
tion (9), we obtain:
C
σ(k)
≥
h
~
δ
i
11
⊗
k−2
O
j=1
T
σ( j)
11
T
σ(k−1)
T
σ(k)
1m
(11)
Inequality (11) can be rewritten as
C
σ(k)
≥ δ
1
k−2
O
j=1
(t
σ( j)
11
)
T
σ(k−1)
T
σ(k)
1m
(12)
4.1.2 Lower bound of the Total Completion
Time
Definition 2 (Lower Bound LB
1
V FL
.).
Given a sequence σ of n-jobs, we define:
A
1
(σ) =
n−1
O
j=1
(t
σ( j)
11
)
n− j
B
1
(σ) =
T
σ(1)
1m
n
O
j=2
T
σ( j−1)
T
σ( j)
1m
t
σ( j−1)
11
!
Proposition 4.
∀σ sequence :
n
O
i=1
C
σ(i)
≥ δ
n
1
⊗ A
1
(σ) ⊗B
1
(σ)
Proof. Considering proposition 3, we have:
n
O
i=1
C
σ(i)
≥ δ
1
T
σ(1)
1m
⊗
n
O
i=2
δ
1
i−2
O
j=1
(t
σ( j)
11
)
T
σ(i−1)
T
σ(i)
1m
!
(13)
Rearranging the factors on the right side of inequality
(13):
n
O
i=1
C
σ(i)
≥ (δ
1
)
n
⊗
n−2
O
i=1
t
σ(i)
11
n−i−1
⊗
T
σ(1)
1m
n
O
i=2
T
σ(i−1)
T
σ(i)
1m
(14)
GeneralLowerBoundsfortheTotalCompletionTimeinaFlowshopSchedulingProblem-MaxPlusApproach
385

and then multiplying the inequality (14) by
n−1
O
i=1
t
i
11
n−1
O
i=1
t
i
11
,
we complete the proof.
At this point, we can obtain a lower bound of the
Total Completion Time by computing the optimal val-
ues of factors A
1
and B
1
. The two following proposi-
tions explain how to do.
Proposition 5 (Minimisation of A
1
).
Let σ
1
SPT
the sequence obtained by sorting jobs in
non-decreasing order of the coefficient t
11
. This se-
quence minimizes criterion A
1
.
Proof.
A
1
(σ) =
n−1
O
j=1
(t
σ( j)
11
)
n− j
=
n
O
j=1
(t
σ( j)
11
)
n− j+1
.
1
n
O
j=1
(t
σ( j)
11
)
(15)
The second factor is a constant, so we have to mini-
mize
n
O
j=1
(t
σ( j)
11
)
n− j+1
. It is similar to the total comple-
tion time criterion in a one-machine problem (1||
∑
C
i
)
where processing times are the t
i
11
s. This criterion is
minimized by using Smith’s rule (Smith, 1956).
Proposition 6 (Minimisation of B
1
).
Let us consider an Asymmetric Traveling Salesman
Problem (ATSP) defined by the following distances
between n + 1 towns, numbered from 0 to n:
∀i ∈ {1,. . . , n}: d(0, i) = [T
i
]
1m
∀i ∈ {1,. . . , n}: d(i, 0) = 1 (= 0)
∀(i, j) ∈ {1, ...,n}
2
: d(i, j) =
[T
i
T
j
]
1m
t
i
11
(16)
Let sequence σ
1
AT SP
be an optimal cycle of this ATSP:
B
1
(σ
1
AT SP
) is the optimal value of criterion B
1
Proof. With these notations, B
1
(σ) can be rewritten
as the length of a cycle:
B
1
(σ) = d(0,σ(1))
n−1
O
i=1
d(σ(i),σ(i + 1))
!
d(σ(n),0)
(17)
All these results lead to the next proposition.
Proposition 7 (Lower Bound LB
1
V FL
).
Let LB
1
V FL
= (δ
1
)
n
⊗ A
1
(σ
1
SPT
) ⊗ B
1
(σ
1
AT SP
): LB
1
V FL
is a lower bound of the Total Completion Time.
In usual notations, this lower bound is defined by:
LB
1
V FL
= nδ
1
+ A
1
(σ
1
SPT
) +B
1
(σ
1
AT SP
) (18)
It is needed to solve a traveling salesman prob-
lem to compute this lower bound; however, the proce-
dures for solving that problem are rather effective on
medium size instances.
This lower bound is similar to the one presented
by Della Croce et al. (Della Croce et al., 1996) for
two machines, but it works with m machines and more
constraints.
4.1.3 Existence of Removal Times
If there are removal times, the date of liberation of
machine M
m
by job J
i
(D
im
) is equal to the sum of
completion time C
i
of job J
i
and removal time of the
last operation of O
im
of J
i
. Thus, the total sum of
D
im
(1 ≤ i ≤ n) is equal to the total completion time
plus a constant term which is equal to the sum of re-
moval times of all last operations. Therefore, to ob-
tain a lower bound of the total completion time we
only have to subtract this constant from LB
1
V FL
.
4.2 Additional Similar Lower Bounds
A similar approach to the construction of the first
lower bound can be developed to achieve the `
th
lower
bound (∀` ∈ {1,...,m}). Using iteratively lemma 2,
we obtain:
C
σ(1)
≥ δ
`
T
σ(1)
`m
C
σ(2)
≥ δ
`
T
σ(1)
T
σ(2)
`m
∀i > 2 : C
σ(i)
≥ δ
`
i−2
O
j=1
t
σ( j)
``
!
T
σ(i−1)
T
σ(i)
`m
(19)
Defining A
`
(σ) and B
`
(σ):
A
`
(σ) =
n−1
O
j=1
(t
σ( j)
``
)
n− j
(20)
B
`
(σ) =
T
σ(1)
`m
n
O
j=2
T
σ( j−1)
T
σ( j)
`m
t
σ( j−1)
``
!
(21)
we have
n
O
i=1
C
σ(i)
≥ δ
n
`
A
`
(σ)B
`
(σ) (22)
Similarly to propositions 5 and 6, we can find
σ
`
SPT
to minimize A
`
(σ) and σ
`
AT SP
to minimize
B
`
(σ). The `
th
lower bound of the total completion
time of the initial flowshop problem is then:
LB
`
V FL
= (δ
`
)
n
A
`
(σ
`
SPT
)B
`
(σ
`
AT SP
) (23)
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
386

Table 1: The performance of branch-and-bound procedure for different k values.
Jobs PV N
AA
(k = 0.3) PVN
V FL
(k = 0.3) PVN
AA
(k = 0.5) PVN
V FL
(k = 0.5) PVN
AA
(k = 0.8) PVN
V FL
(k = 0.8)
7 5.12 × 10
−1
6.86 × 10
−1
4.39 × 10
−1
7.01 × 10
−1
5.12 × 10
−1
10.36 × 10
−1
8 2.20 × 10
−1
2.60 × 10
−1
2.74 × 10
−1
2.66 × 10
−1
2.92 × 10
−1
3.08 × 10
−1
9 5.11 × 10
−2
7.77 × 10
−2
6.46 × 10
−2
6.82 × 10
−2
6.05 × 10
−2
10.03 × 10
−2
10 3.56 × 10
−2
1.63 × 10
−2
2.79 × 10
−2
1.94 × 10
−2
2.40 × 10
−2
2.64 × 10
−2
11 1.63 × 10
−2
0.49 × 10
−2
1.28 × 10
−2
0.58 × 10
−2
1.43 × 10
−2
0.74 × 10
−2
12 3.08 × 10
−3
0.71 × 10
−3
2.74 × 10
−3
1.12 × 10
−3
3.12 × 10
−3
1.44 × 10
−3
13 6.31 × 10
−4
1.87 × 10
−4
6.30 × 10
−4
3.48 × 10
−4
4.71 × 10
−4
3.87 × 10
−4
14 5.02 × 10
−5
4.79 × 10
−5
1.22 × 10
−4
0.52 × 10
−4
1.37 × 10
−4
1.30 × 10
−4
15 2.38 × 10
−5
1.74 × 10
−5
2.19 × 10
−5
1.48 × 10
−5
2.46 × 10
−5
2.13 × 10
−5
16 1.20 × 10
−5
0.18 × 10
−5
1.21 × 10
−5
0.17 × 10
−5
1.24 × 10
−5
0.50 × 10
−5
17 5.70 × 10
−6
0.34 × 10
−6
5.30 × 10
−6
1.03 × 10
−6
5.60 × 10
−6
1.33 × 10
−6
18 5.40 × 10
−7
5.52 × 10
−7
5.00 × 10
−7
4.75 × 10
−7
5.20 × 10
−7
1.62 × 10
−7
20 - 7.04 × 10
−9
- 0.67 × 10
−9
- 3.78 × 10
−9
5 BRANCH-AND-BOUND
ALGORITHM
In order to validate the lower bounds we proposed, we
have incorporated them in a branch-and-bound proce-
dure. A branch-and-bound procedure is an enumer-
ation method that builds dynamically a search tree.
Lower bounds or other criteria like dominance re-
lations are used to cut some useless branches. We
have used the separation scheme introduced by Ignall
and Schrage (Ignall and Schrage, 1965): a partial se-
quence is progressively built as we go deeper in the
search tree. A node corresponds to a partial sequence
and a set of free jobs. The separation of a node con-
sists in adding a free job at the end of the sequence.
A node has as many children as its free jobs. The
branching strategy is Depth-First-Search (DFS). An
upper bound is computed at the root node and updated
at each node. For this purpose, we have used heuris-
tic PR4(15) presented by Pan and Ruiz (Pan and Ruiz,
2013).
The branch-and-bound procedure is detailed in
Algorithm 1 and numerical results are presented in
section 6. In this algorithm, L is the list of nodes that
have not yet been separated and LC the list of child
nodes built after separation of a node.
6 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
There are few studies on exact resolution of flow-
shop scheduling problems with criterion of total com-
pletion times. We decided to compare our branch-
and-bound procedure to the one developed by Al-
lahverdi and Al-Anzi (Allahverdi and Al-Anzi, 2006)
for problem F3|perm; S
nsd
|
∑
C
i
. According to the
approach proposed by Allahverdi and Al-Anzi, the
processing and setup times values were randomly
generated respectively from the uniform distribu-
tion on the interval [1,100] and on the interval
[0,100k]. We considered problems of n-jobs (n =
Algorithm 1: Branch-and-Bound.
1: procedure BRANCH-AND-BOUND
2: BestUB ← ∞
3: Generate Root tree NRoot // an empty node
4: Compute LB(NRoot) and UB(NRoot)
5: Add NRoot to list L
6: while L is not empty do
7: N ← top(L) // move the first node of list L
8: BestUB ← min{BestUB,U B(N)}
9: if LB(N) < BestUB then
10: Generate children list LC of N
11: for each NChild in LC do
12: Compute LB(NChild)
13: Compute UB(NChild)
14: end for
15: Sort LC
16: // in non-increasing order of LB(NChild)
17: for each NChild in LC do
18: if LB(NChild) < BestUB then
19: top(L) ← NChild
20: else
21: Delete NChild
22: end if
23: end for
24: else
25: Delete N
26: end if
27: end while
28: end procedure
7,8,9,10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 20). A class of
thirty instances was generated for each number of jobs
and each k value. The k value for each data set was
assigned to 0.3, 0.5 and 0.8. It was assumed that
all machines were available from the time zero (δ
k
=
0, 1 ≤ k ≤ m). To compute lower bounds LB
V FL
s,
we used the ATSP solving procedure developed by
G. Carpaneto, M. Dell’amico and P. Toth (Carpaneto
et al., 1995). The used machine is based on an Intel
Duocore 2.6GHz 4GB RAM.
In their study, Allahverdi and Al-Anzi did not in-
GeneralLowerBoundsfortheTotalCompletionTimeinaFlowshopSchedulingProblem-MaxPlusApproach
387

dicate computation times, they prefer computing the
percentage of visited nodes to solve an instance rela-
tively to the total number of nodes of the whole search
tree. Therefore, we did the same in order to perform
a comparison. We have reported in table 1 the mean
percentage of visited nodes over the thirty instances
of each class (n,k) of problems for our branch-and-
bound (columns PV N
V FL
(k = 0.3), PV N
V FL
(k = 0.5)
and PV N
V FL
(k = 0.8)) and for Allahverdi and Al-
Anzi’s branch-and-bound (columns PV N
AA
(k = 0.3),
PV N
AA
(k = 0.5), PV N
AA
(k = 0.8)).
Furthermore, we have indicated in table 2 the
mean computation times (in second) of our branch-
and-bound procedure for each class of instances. For
instances with strictly less than 18 jobs, we used the
three lower bounds LB
1
V FL
,LB
2
V FL
and LB
3
V FL
in the
branch-and-bound, while for instances of 18 jobs we
use only LB
1
V FL
and LB
3
V FL
and for instances of 20
jobs, we use LB
2
V FL
and LB
3
V FL
.
In the other hand, we developed another version
of this branch-and-bound procedure using only a very
simple lower bound SLB. Lower bound SLB of a node
is equal to the total completion time of its correspond-
ing partial sequence. We limited computation times
to 1500 (3000 and 9000, respectively) seconds in case
of n ∈ {7,8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14,15} (n ∈ {16,17} and
n ∈ {18,20}, respectively). The mean computation
times of that branch-and-bound have been also re-
ported in table 2. When it appears something like ”¿
1500”, it means that the branch-and-bound has never
found the optimal solution within time limit of 1500
seconds over the thirty instances of the class. This
version allowed us to evaluate the effectiveness of our
proposed lower bounds.
Table 2: The mean computation time for each class.
Jobs k=0.3 k=0.5 k=0.8 LB
7
0.048 0.049 0.058 LB
1
V FL
,LB
2
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
0.030 0.039 0.041 SLB
8
0.100 0.098 0.176 LB
1
V FL
,LB
2
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
0.099 0.102 0.121 SLB
9
0.212 0.165 0.193 LB
1
V FL
,LB
2
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
0.683 0.602 0.709 SLB
10
0.291 0.285 0.353 LB
1
V FL
,LB
2
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
6.654 5.629 6.748 SLB
11
0.730 0.838 0.932 LB
1
V FL
,LB
2
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
73.674 66.924 74.569 SLB
12
1.313 1.779 2.33 LB
1
V FL
,LB
2
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
906.030 1173.178 905.417 SLB
13
4.589 7.593 7.995 LB
1
V FL
,LB
2
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
¿ 1500 ¿ 1500 ¿ 1500 SLB
14
16.317 15.306 34.569 LB
1
V FL
,LB
2
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
¿ 1500 ¿ 1500 ¿ 1500 SLB
15
68.559 50.609 68.467 LB
1
V FL
,LB
2
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
¿ 1500 ¿ 1500 ¿ 1500 SLB
16
152.996 155.756 404.959 LB
1
V FL
,LB
2
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
¿ 3000 ¿ 3000 ¿ 3000 SLB
17
419.347 1478.93 1894.091 LB
1
V FL
,LB
2
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
¿ 3000 ¿ 3000 ¿ 3000 SLB
18
7984.230 7638.810 2694.640 LB
1
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
¿ 9000 ¿ 9000 ¿ 9000 SLB
20
2850.320 346.510 1640.350 LB
2
V FL
,LB
3
V FL
¿ 9000 ¿ 9000 ¿ 9000 SLB
Table 1 shows that lower bounds LB
1
V FL
, LB
2
V FL
and LB
3
V FL
are useful in reducing the number of vis-
ited nodes. They are really effective when compared
to the performance in the study of Allahverdi and Al-
Anzi (Allahverdi and Al-Anzi, 2006) for instances
with more than nine jobs.
Table 2 shows that with a small number of jobs, it
takes a very short time to achieve the optimum. As the
number of jobs is increasing, the version using SLB
proves that an effective lower bound like LB
V FL
is
very important to achieve the optimum within a time
limit. In other words, LB
V FL
s are effective to elimi-
nate unworthy branches. However, as the number of
jobs is large, we need to have also a strategy in or-
der to shorten the computation time. This strategy is
under investigation.
7 CONCLUSIONS
We proposed a MaxPlus approach to tackle a m-
machine flowshop problem with several additional
constraints. The MaxPlus approach enables the trans-
formation of a general flowshop problem into a matrix
problem. Then some computations over these matri-
ces allow us to highlight new lower bounds for the
total completion time criterion, based on the resolu-
tion of a one-machine problem and an asymmetric
traveling salesman problem. Despite the necessity of
solving an NP-hard problem, experimental results and
comparison to a previously published research have
shown the effectiveness of these lower bounds.
Our further research will aim at improving these
lower bounds LB
V FL
as well as improving a branch-
and-bound algorithm. In some cases as the number of
jobs is large, a strategy in order to improve the qual-
ity of lower bounds and to shorten the computation
time of the whole branch-and-bound algorithm will be
also studied. Moreover, more specific constraints for
a flowshop problem can be studied such as no − wait,
min − max delay, S
nsd
,R
nsd
, limited stocks between
machines or blocking constraints by modifying only
matrix T
i
associated to job J
i
. The study can be also
extended to the weighted total completion time crite-
rion
n
∑
i=1
w
i
C
i
.
REFERENCES
Allahverdi, A. and Al-Anzi, F. S. (2006). A branch-and-
bound algorithm for three-machine flowshop schedul-
ing problem to minimize total completion time with
ICORES2014-InternationalConferenceonOperationsResearchandEnterpriseSystems
388

separate setup times. European Journal of Opera-
tional Research, 169(3):767–780.
Augusto, V., Lent
´
e, C., and Bouquard, J.-L. (2006).
R
´
esolution d’un flowshop avec delais minimaux et
maximaux. In MOSIM.
Aydilek, H. and Allahverdi, A. (2010). Two-machine flow-
shop scheduling problem with bounded processing
times to minimize total completion time. Computers
& Mathematics with Applications, 59(2):684–693.
Blazewicz, J., Ecker, K.-H., Pesch, E., Schmidt, G., and
Weglarz, J. (1996). Scheduling in computer and man-
ufacturing processes. Springer Verlag, Berlin.
Bouquard, J.-L. and Lent
´
e, C. (2006). Two-machine flow
shop scheduling problems with minimal and maximal
delays. 4or, 4(1):15–28.
Bouquard, J.-L., Lent
´
e, C., and Billaut, J.-C. (2006). Appli-
cation of an optimization problem in Max-Plus alge-
bra to scheduling problems. Discrete Applied Mathe-
matics, 154(15):2064–2079.
Brucker, P. (2006). Scheduling Algorithms. Springer, 5 edi-
tion.
Carpaneto, G., Dell’amico, M., and Toth, P. (1995). Exact
solution of large asymmetric traveling salesman prob-
lems. ACM Transactions on Methematical Software,
21(4):394–409.
Cohen, G., Dubois, D., Quadrat, J.-P., and Viot, M. (1985).
A linear system-theoretic view of discret-event pro-
cesses and its use for performance evaluation in man-
ufacturing. IEEE Trans. Automatic Control, 30:210–
220.
Della Croce, F., Narayan, V., and Tadei, R. (1996). The two-
machine total completion time flow shop problem.
European Journal Of Operational Research, 90:227–
237.
Emmons, H. and Vairaktarakis, G. (2013). Flow Shop
Scheduling. Springer US, New York, 182 edition.
Gaubert, S. (1992). Th
´
eorie des syst
`
emes lin
´
eaires dans les
dio
¨
ıdes. PhD thesis.
Gaubert, S. and Maisresse, J. (1999). Modeling and analysis
of timed Petri nets using heaps of pieces. IEEE Trans.
Automatic Control, 44(4):683–698.
Giffler, B. (1963). Schedule algebras and their use in for-
mulating general systems simulations. In Industrial
schduling. Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
Graham, R. L., Lawler, E. L., Lenstra, J. K., and Rinnooy
Kan, A. H. (1979). Optimization and approximation
in deterministic sequencing and scheduling: A survey.
Annals of Discrete Mathematics, 5(2):287–326.
Gunawardena, J. (1998). Idempotency. Publications of the
Newton Institute.
Hanen, C. and Munier, A. (1995). Cyclic scheduling on
parallel processors: an overview. John Wiley.
Ignall, E. and Schrage, L. (1965). Application of branch-
and-bound technique to some flow shop problems.
Operations Research, 13(3):400–412.
Johnson, S. M. (1954). Optimal two- and three-stage pro-
duction schedules with setup times included. Naval
Research Logistics, 1:61–68.
Lent
´
e, C. (2001). Analyse Max-Plus de probl
`
emes
d’ordonnancement de type Flowshop. PhD thesis,
Universit
´
e Franc¸ois Rabelais de Tours.
Lent
´
e, C. (2011). Math
´
ematiques, Ordonnancement et
Sant
´
e. Habilitation
`
a diriger des recherches, Univer-
sit
´
e Franc¸ois Rabelais de Tours.
Pan, Q.-K. and Ruiz, R. (2013). A comprehensive review
and evaluation of permutation flowshop heuristics to
minimize flowtime. Computers & Operations Re-
search, 40(1):117–128.
Smith, W. E. (1956). Various optimizers for single-stage
production. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 3(1-
2):59–66.
Su, L.-H. and Lee, Y.-Y. (2008). The two-machine flow-
shop no-wait scheduling problem with a single server
to minimize the total completion time. Computers &
Operations Research, 35(9):2952–2963.
Trabelsi, W., Sauvey, C., and Sauer, N. (2012). Heuris-
tics and metaheuristics for mixed blocking constraints
flowshop scheduling problems. Computers & Opera-
tions Research, 39(11):2520–2527.
Vo, N. V. and Lent
´
e, C. (2013). Equivalence between Two
Flowshop Problems - MaxPlus Approach. In Proceed-
ings of the 2nd International Conference on Opera-
tions Research and Enterprise Systems, pages 174–
177, Barcelona. SciTePress - Science and and Tech-
nology Publications.
GeneralLowerBoundsfortheTotalCompletionTimeinaFlowshopSchedulingProblem-MaxPlusApproach
389
