
Instructor Support in Collaborative Multiplayer Serious Games for
Learning
Game Mastering in the Serious Game ’Woodment’
Viktor Wendel, Michael Gutjahr, Stefan G
¨
obel and Ralf Steinmetz
Multimedia Communication Labs - KOM, TU Darmstadt, Rundeturmstr. 10, 64283 Darmstadt, Germany
Keywords:
Serious Games, Collaborative Learning, CSCL, Game Mastering, Adaptation.
Abstract:
In collaborative digital learning scenarios with small groups (3-6 users), the role of the instructor is vital as
he/she is responsible for preparation of the setting, observation, coaching, moderation and adaptation. Cur-
rently, in multiplayer Serious Games, the role of the instructor is only insufficiently considered. Only very few
approaches for integrating or supporting instructors in collaborative multiplayer Serious Games exist today,
to the best of our knowledge. In this paper, we propose a concept for integration and support of instruc-
tors in team-based collaborative 3D multiplayer Serious Games. Our approach is based on Game Mastering
principles known from roleplay games. It combines those principles with concepts for collaborative learning
scenarios. We applied our concept to the existing 3D multiplayer Serious Game Woodment and tested it in a
vocational school with 26 players in four groups (age: m= 19.12; sd= 2.03). Results indicate that an instruc-
tor using our Game Master framework to moderate and adapt the game at runtime can have a positive effect
on both the players’ learning success and perceived user experience. Moreover, a positive effect on players’
gaming behavior can be observed.
1 MOTIVATION
Although many promising examples of Serious
Games for learning are existing today, most of those
are single player games.This is true even for social Se-
rious Games (Konert et al., 2012) which are usually
played alone despite asynchronous interaction with
other players/friends. We believe that multiplayer Se-
rious games can be a promising opportunity to com-
bine the advantages of Serious Games with the con-
cepts of collaborative learning, especially Computer-
supported Collaborative Learning (CSCL). However,
in (computer-supported) collaborative learning sce-
narios, the role of the instructor is vital. (H
¨
am
¨
al
¨
ainen
et al., 2006) argue that ”Computer-supported Collab-
orative Learning (CSCL) must provide instructional
support”. The instructor is responsible for various
tasks in and around the learning process. According
to (Haake et al., 2004), page 30, those are, among
others, analysis, monitoring, moderation, guidance,
coaching, and intervention. However, to the best of
our knowledge there are only very few approaches to
support an instructor in digital game-based collabora-
tive learning scenarios.
Our approach uses concepts from Game Mas-
tering (in pen&paper roleplay games), collaborative
learning, and collaborative gaming. In (Wendel et al.,
2012a), as a first step, we proposed a model-based ap-
proach for a Game Master concept in 3D Multiplayer
Serious Games. The paper focused on the interface
between the game and the Game Master frontend as
well as on a group model consisting of a player model,
a learner model, and an interaction model. The main
contribution of this paper is an extension of our model
by proposing methods and concepts for providing a
Game Master with the ability to analyze, monitor,
coach, intervene, and adapt at runtime from inside the
game. Therefore, we will describe methods for get-
ting required information from the game to perform
those tasks as well as for providing adequate methods
of adaptation of the game. We implemented our ex-
tended concept as an extension to the existing collab-
orative multiplayer Serious Game Woodment (Wen-
del et al., 2010) and performed a user-centered eval-
uation at a vocational school in Germany. Our hy-
pothesis is that an instructor using our approach can
positively influence both game experience and learn-
ing outcome of players in an immersive way. The
study was conducted at a vocational school in Ger-
many with 26 students (age: m= 19.12; sd= 2.03).
49
Wendel V., Gutjahr M., Göbel S. and Steinmetz R..
Instructor Support in Collaborative Multiplayer Serious Games for Learning - Game Mastering in the Serious Game ’Woodment’.
DOI: 10.5220/0004836900490056
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2014), pages 49-56
ISBN: 978-989-758-022-2
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

Results show that an instructor using our Game Mas-
ter frontend to moderate and adapt the gaming process
at runtime can have a positive effect on both the learn-
ing success and the perceived user experience of the
players. Moreover, different effects on the gaming be-
havior of players can be observed like a more focused
play style and a more coordinated teamwork.
2 RELATED WORK
The concept of Computer-supported Collaborative
learning (CSCL) is being used in various learning
scenarios ranging from learning at school, university
learning, to training scenarios in corporate environ-
ment (Shell et al., 2005), (Stahl et al., 2006), (On-
rubia and Engel, 2009), and (Larusson and Alterman,
2009). As stated by (Kearsley, 2000) or (Chiriac and
Granstr
¨
om, 2012), the instructor’s role is vital in col-
laborative learning scenarios. Instructors have vari-
ous important tasks during collaborative learning ses-
sions. (Mutwarasibo, 2013) states that “the instruc-
tor’s role in student group work is that of a guide or
facilitator”. A more detailed description of instructor
tasks in collaborative learning scenarios, especially in
CSCL scenarios is given in (Haake et al., 2004), page
30. There, the tasks of an instructor are described as:
analysis, monitoring, moderation, guidance, coach-
ing, and intervention.
Grand challenges of multiplayer Serious Games
research are: multiplayer Serious Game design, in-
teraction and communication on game-based collab-
orative learning scenarios, and the role of the in-
structor as well as instructor support. (H
¨
am
¨
al
¨
ainen
et al., 2006) describe a concept for designing collab-
oration in a 3D virtual game environment. The role
of the instructor concerning real-time orchestration in
a 3D game is discussed in (H
¨
am
¨
al
¨
ainen and Oksa-
nen, 2012). Design guidelines for incorporation of
features of collaborative learning in video games are
presented by (Zea et al., 2009). (Wendel et al., 2010)
describe the design of a collaborative multiplayer Se-
rious Game for collaborative learning. The work pre-
sented here is based on this game.
The concept of Game Mastering as it will be used
in this paper, is derived from pen&paper roleplay
games. In such games, the Game Master (GM) is
responsible for telling a suspenseful and interesting
story to a group of players which are active parts in
that story. Thus, they are able to actively influence
that story, oftentimes against the GM’s plan. The
GM’s task is to keep the story meaningful while at
the same time allowing a maximum of freedom for
the players without giving them the feeling that their
actions are futile. Thus, it is the GM’s task to unite
those goals (well considered story vs. player free-
dom). This problem is often referred to as the Nar-
rative Paradox (Louchart and Aylett, 2003). There-
fore, the GM needs to be able to observe the game in
the context of the whole story and be able to adapt
his/her plan ad-hoc according to the needs and prefer-
ences of the players. These requirements are similar
to those of an instructor in a (game-based) collabora-
tive learning scenario. First concepts to formalize the
work of a Game Master in order to transfer the Game
Master concept to digital games have been proposed
by (Tychsen et al., 2005) and (Tychsen, 2008).
Various concepts for modeling player behavior
and preferences have been proposed up to today. The
most prominent player model is Bartle’s model for
roleplay types (Bartle, 1996). A more generic model
has been proposed by (Houlette, 2004). A compre-
hensive overview over player models is provided in
(Smith et al., 2011). They provide a taxonomy of
player modeling. In terms of learner modeling, the
concept of (Kolb and Kolb, 2005) is one of the most
prominent concepts. However, for the scope of this
work, we focus on modeling the learning progress
of learners. Therefore, we need to model what a
player/learner has already learned. It is also desirable
to be able to make suggestions for the next learning
unit based on already learned content. Therefore, a hi-
erarchical approach to modeling learner skills seems
suitable like proposed by (Korossy, 1999).
3 OUR APPROACH
The approach presented in this paper is based on our
concept for Game Mastering as described in (Wen-
del et al., 2012a). There we propose a component-
based model for describing a 3D multiplayer Serious
Game. Our concept defines a ’group model’ to model
players/learners. The group model is composed of
a player model, a learner model, and an interaction
model. In this paper, we want to extend that model
about a client sided interface declaring how informa-
tion from a game can be extracted to be presented to
an instructor in a useful manner. Furthermore, the ex-
tended model defines an interface for accessing rel-
evant game entities in order to be able to adapt the
game at runtime.
3.1 Architecture
The architecture of our framework (see Figure 1) con-
tains two main elements: One is the 3D game itself,
the other one is the Game Master frontend. Via the
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
50

Figure 1: GM Framework Architecture
defined interface (between game and frontend), the
Game Master frontend can access relevant data from
the game and on the other hand adapt game rules or
entities. The Game Master can use the GM frontend
to receive necessary information and to influence the
game according to his/her professional knowledge in
order to optimize learning success, gaming experi-
ence, and collaboration. The interface is split into four
sub-components: Entities Compound, Group Model,
Information Model, and Adaptation Model. The com-
ponents will be explained in more detail below.
3.2 Entities Compound
The Entities Compound defines all relevant game en-
tities. According to (Wendel et al., 2012a), 3rd person
3D games consist of three main parts: Game World,
Players, and Interaction. The Entities Compound de-
scribes the former two of those. It defines all relevant
game entities. Relevant entities are all those game en-
tities which’s state influences the state of the game.
Those are of course the player entities. Additionally,
all 3D assets which have a purpose beyond setting the
scene, i.e. background images, static 3D objects, and
terrain. Generally, those are all game entities a player
can interact with in any way. It is task of the game de-
signer to define which game entities are relevant and
which ones have only a decoration purpose. A game
entity exists of a description, describing the function
of the entity in the game, and a list of parameters. For
each parameter the game designer needs to define if
it is only informational or if it can be changed. Addi-
tionally, a parameter description needs to be provided,
explaining the parameter’s function for the entity.
3.3 Group Model
The Group Model contains the state of the group of
learners. It is described in detail in (Wendel et al.,
2012a). It provides information about player behav-
ior and preferences in play style (player model). Fur-
thermore, it describes the learning progress for each
player. Finally, it contains information about interac-
tion and communication between players.
The Player Model describes preferences in gam-
ing behavior for a player, e.g. if a player prefers ac-
tion, socializing with other players, or wants to ex-
perience every aspect of a game, i.e. find every hid-
den piece of it. The most common and best fit player
model for those RPG-similar 3D multiplayer games is
the player model of Bartle (Bartle, 1996). It classifies
players along two axes (players - world, acting - inter-
acting) resulting in the four stereotypical player types:
killer (player, acting), achiever (world, acting), social-
izer (player, interacting), and explorer (world, inter-
acting). Again, the game designer(s) need to specify
which action and decision a player can take during
the game relates to which player type. In our model,
this is done by assigning player model modification
values to relevant player actions.
The purpose of the Learner Model is to give the in-
structor a structured insight into the learning progress
of players. Following the hierarchical model of Ko-
rossy (Korossy, 1999), the game designers/subject
matter experts define a set of skill which will should
be learned throughout the game. Those are ordered
in a hierarchical structure indicating dependencies be-
tween skills. A skill depends on another skill if that
other skill should be learned before this skill is looked
at.
The Interaction Model is meant to provide the in-
structor with information about interaction between
InstructorSupportinCollaborativeMultiplayerSeriousGamesforLearning-GameMasteringintheSeriousGame
'Woodment'
51

players. This contains any means of communication.
Usually, this includes a chat protocol. A more de-
tailed look into communication between players con-
tains statistics about the frequency of communica-
tions between players. Apart from communication,
interactions are taken into account. Therefore, the
game designer needs to define which actions in a
game taken by a player are an interaction with an-
other player. This is similar to the actions defined for
the player model.
3.4 Information Module
Apart from collected data like the group model, it is
useful for the instructor to be able to directly observe
the gaming progress (Haake et al., 2004) in order to
be able to extract information about the collaborative
learning process. Moreover, it might be useful for
recognition of problems players might have at certain
points in the game. Therefore, it seems useful for the
GM to be able to move freely in the game world, i.e.
have a free camera perspective. Moreover, in order
to be able to spectate what all players are doing at a
certain point of time when players are split up, it is
useful to provide a split-screen camera. Apart from
this, the GM should be provided with the information
of the group model. Finally, general game parameters
as well as information about the state of game entities
should be displayed.
3.5 Adaptation Module
The Adaptation Module is the part where the instruc-
tor can influence the game by adapting game param-
eters, adapting parameters of an entity, and adapting
a game rule.
Therefore, it needs access to the basic game pa-
rameters as well as to the game entities. Thus, it is
connected to the Entities Compound. In addition to
that, it needs to access the rule base of the game. As
game rules significantly influence a game on a very
basic layer, the game designer needs to define which
rules may be changed in which way. For example, it
could be allowed to perform a certain action or not. In
order to simplify this access, an abstraction interface
will be put between the game rule base and the Adap-
tation Module. Changing game rules can be imple-
mented through adapting a set of (boolean) parame-
ters, provided game rules are designed carefully. Note
that learning parameters, like difficulty of questions,
etc., are capsuled in game parameters or parameters
of (learning) entities. However, they should be dis-
played to the GM in a suitable way separating them
from gaming parameters. Thus, via the adaptation
module, the GM is able to manipulate relevant 3D
objects, game rules (i.e. interaction rules, rules for
collaboration, game actions), and difficulty in terms
of gaming, or learning.
4 PROOF-OF-CONCEPT
4.1 Woodment
As a proof-of-concept, we implemented our approach
as an extension to the existing Serious Game pro-
totype Woodment. The game has been chosen be-
cause it has a rather high level of interaction and a
trainer/teacher can freely define the learning content.
It is possible to create, save, and reuse question sets
of various content domains and even to mix them if
so wished. Woodment is a 3D 3rd person multiplayer
digital educational game for 6 players. The game
has been developed by the authors and been enhanced
during practical courses or theses. One enhancement
of Woodment was performed as a part of a diploma
thesis which focused on Game Mastering concepts
and team leadership (Rodenberger, 2012). Some of
the visualization concepts presented in this paper have
been reimplemented from this work.
Woodment as well as the enhancements imple-
mented as a proof-of-concept for the work presented
here, was implemented using the Unity3d game en-
gine. The game can be played both in browser (Unity
browser plugin required) and as a standalone applica-
tion (for PC and Mac), providing us with the neces-
sary platform independence for evaluations on vary-
ing hardware in different vocational schools.
4.2 Game Entities
Question orbs contain questions which can be trig-
gered when a player enters the orb. They provide a
game relevant resource (food, workers, or ship tokens
to sell wood) if the answer is correct. The Game Mas-
ter can adjust their size and movement speed as well
as the frequency each question orb type spawns with.
Skill canisters can be picked up in order to be able to
run faster, freeze an enemy player for a period of time,
or to ignite the enemy base forcing the enemy team to
spend time to extinguish the fire. The GM can adjust
their spawning frequency. Workers gather resources
provided that they have sufficient food. They cannot
be accessed directly by the GM. The player base is
the center of operations for a team. The GM can view
it and see if it is currently burning, but not directly
adjust that fact.
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
52

4.3 Group Model
We defined several player actions like ’Pickup Skill
Canister’, ’Trigger Question’, ’Answer Question Cor-
rectly’, ’Ask For Help’, or ’Help Player With Ques-
tion’, which affect one or more of the player model
items (killer, achiever, socializer, explorer).
Woodment contains an integrated editor enabling
the instructor to create a custom set of questions.
The set of questions as well as dependencies between
questions are created by the instructor according to
the learning content. Thus, it is possible to model the
learning space according to the Competence-based
Knowledge Space theory (Korossy, 1999). The ac-
tual learner modeling is done by modeling the learn-
ers’ initial knowledge and monitoring the acquisition
of knowledge during the gaming phase and updating
the learners’ knowledge state accordingly.
All player chat is directly visible to the GM. In ad-
dition, player chats are aggregated such that for each
player it is known how often he/she communicated
with each other player. This is presented to the GM
graphically. In terms of interaction, the game records
whenever a player asks for help or gives help for a
question. Also, whenever a player freezes an op-
ponent or de-freezes a fellow player, the interaction
counter for the affected players increases. This is also
presented graphically.
4.4 GM Observation Frontend
To satisfy the needs for observation of the gaming oc-
currence, we implemented a ’fly mode’ for the GM,
i.e. the GM can move freely within the game world.
This includes a smooth zoom. Moreover, the GM
can automatically follow each player by clicking the
player’s name. A split screen mode was not imple-
mented as dividing the screen into 6 parts seemed
to be too confusing. The group model is displayed
in a special window providing overview over each
player’s player model, learner model, and interaction
model. The GM can view game entities directly in the
game world and see their parameters in the settings
window.
4.5 GM Adaptation Frontend
The GM can adapt game entity parameters (if al-
lowed) in the settings window. Moreover, the GM
can directly adjust the most significant game parame-
ters directly on the main screen. Those are the num-
ber of wood gathered, workers, ship tokens, food, or
gold for each team. Further, the GM can adapt some
visual options like sunlight, brightness or fog which
indirectly influence the game (difficulty). Poor sight
makes finding question orbs harder which increases
the need for communication among team members.
5 EVALUATION
5.1 Hypothesis and Setup
Our Hypothesis is that an instructor is able to sup-
port and positively influence the collaborative learn-
ing process as well as the game experience of a gam-
ing session, especially the game flow. A Game Master
(GM) frontend is implemented, following the concept
presented in this paper. Therefore it is hypothesized:
1. Comparing with a scenario without a GM, a GM
increases the flow experience and user experience.
2. Comparing with a scenario without a GM, a GM
increases the learning success.
Participants were playing one of two versions of
Woodment. The treatment group was playing Wood-
ment with support of a GM, while the control group
was playing the standard version without the support
of a GM. Both groups were playing Woodment for
40 minutes and answered a questionnaire after play-
ing the game. The questionnaire was a modified ver-
sion of the user experience questionnaire described
in (Wendel et al., 2012b) and includes an overall user
experience (UX) score, as well as seven UX sub-
scales. The in-game answers to the content of the
curriculum were logged, too, as well as all player and
GM actions. For both groups (treatment and control
group), two gaming sessions with 6(7)
1
players each
were conducted. Players were from different classes
of a vocational school in Germany. The study in-
cludes 26 participants, 18 male, 5 female and 3 not
stated. Age m= 19.12 (sd= 2.03). To analyze the data
an ANOVA between subjects was used. The present
of the GM was used as independent variable and the
overall scale, as well as the seven sub-scales were
used as independent measurements.
5.2 Results
The GM version (m=6.14; sd=1.44) triggered more
overall user experience (F(1,23)=6.93; p=.015) than
the control group without a GM (m=4.90; sd=0.89).
To detect which aspects of user experience are es-
pecially distinct in the GM version, the seven sub-
scales were tested, too. The sub-scales Immer-
sion (F(1,23)=7.54; p=.012), Flow (F(1,23)= 11.50;
1
due to class sizes, in two groups we had 7 players, two
students each played together on one computer
InstructorSupportinCollaborativeMultiplayerSeriousGamesforLearning-GameMasteringintheSeriousGame
'Woodment'
53
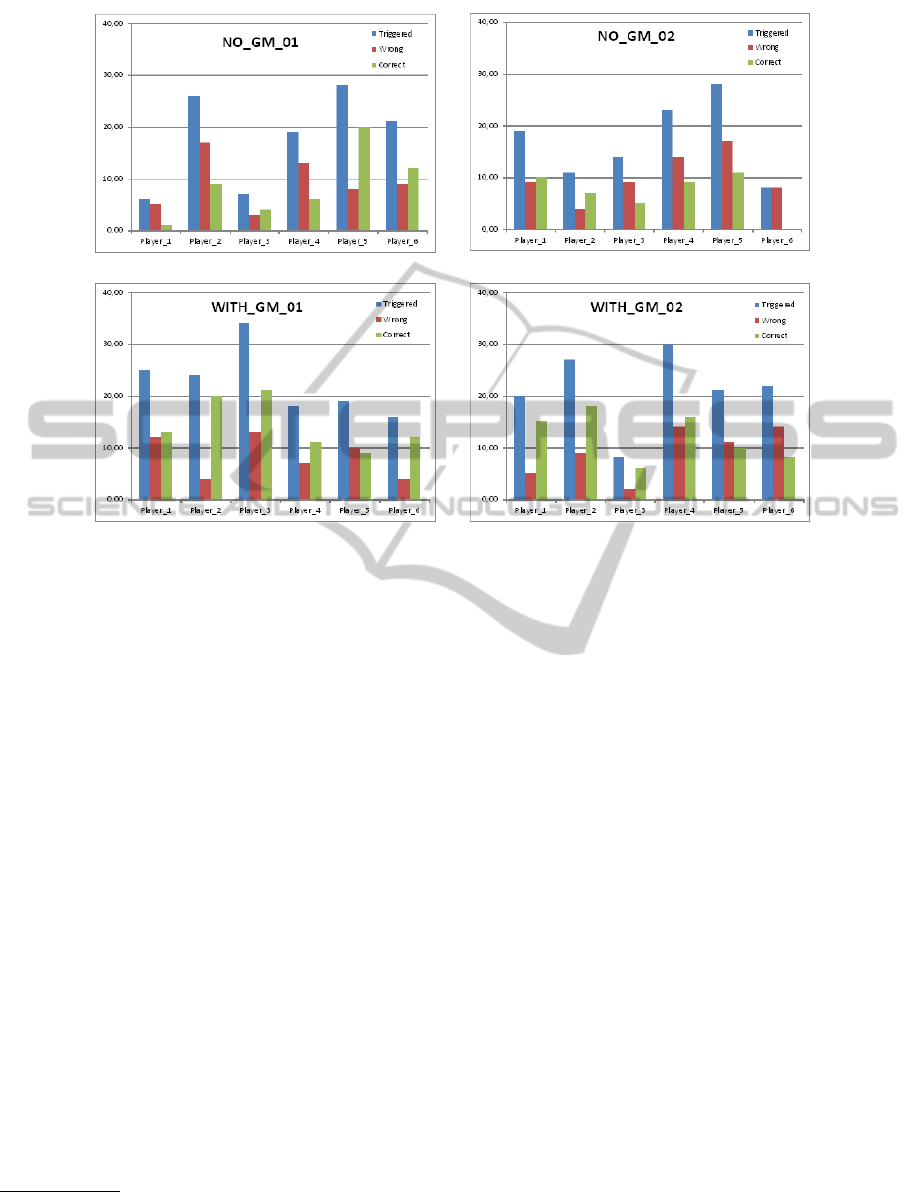
Figure 2: Questions answered by player
p=.003), and Arousal (F(1,23)= 4.25; p=.051) showed
an effect in favor of the GM version.
During the gaming sessions, the game logged all
relevant data. Logged data contains all GM and player
actions, triggered questions and answers, chat data
and all game variables logged in a one second in-
terval. From the post-processed data we could see
the progress of resources (wheat, fish, workers, idle
workers, lumber, gold) for each team over time
2
.
Moreover, we aggregated the data for the questions
answered (see Figure 2) by the players and the player
models (see Figure 3).
Figure 2 shows the number of questions triggered,
and answered correctly or wrong for each player.
More questions (F(1,22)=6.77; p=.016) have been
solved correctly in versions with a GM (m=13.25;
sd=4.81) than in versions without a GM (m=7.83;
sd=5.37). Also, the percentage of correctly solved
questions is higher (F(1,22)=7.53; p=.012) in ver-
sions with a GM (m=61.21; sd=14.24) than in ver-
sions without a GM (m=41.58; sd=20.29). As an in-
dicator for the overall success of a team, we looked
at the gold they were able to achieve. Without a GM,
the teams got 2/2 (red/blue) and 2/3 (red/blue) gold
(9 gold total among all four teams). The teams with
2
For reasons of clarity and available space, we cannot
include all of those plots in this paper. However, they are
available from the authors upon request.
a GM got 3/3 (red/blue) and 2/4 (red/blue) gold (12
gold total).
5.3 Discussion
Results show that both UX questions and the percent-
age of correctly answered questions are significantly
larger in the game sessions where the GM was present
and used the GM frontend. Thus, we can accept both
hypotheses.
Comparing the player models, it comes to the
fore in the sessions where a GM was present, play-
ers were generally more active. The values for ex-
plorer (232/254 with GM, 158/152 without GM) show
that players tend to move more when a GM is present.
This indicates that players were more actively search-
ing for question orbs or supporting fellow players
(e.g. de-freezing). However, as we cannot track the
purpose of a movement, it needs to be clarified that
higher explorer values can also mean that the respec-
tive player might just be moving around for other rea-
sons. Achiever values (350/333 with GM, 264/238
without GM) indicate that players play more com-
petitive when a GM is present. Collaboration values
do not differ greatly (84/77 with GM, 50/84 without
GM). Killers are also more active (100/134 with GM,
73/93 without GM) when the GM was present. Over-
all the activity (total number of actions performed)
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
54

Figure 3: Player Model
was higher in those games where the GM was present
(766/798 with GM, 545/567 without GM).
From the observations described above, we con-
clude that the GMs were able to make students focus
on their tasks by reducing disturbing behavior and by
recognizing problems in teams. Moreover, it seems
that GMs were able to recognize problems/errors at
answering questions and that they were able to pro-
vide useful help, thus increasing both the average
number of questions triggered, and the amount of cor-
rectly answered questions. This indicates that the GM
was able to fulfill his/her traditional tasks like obser-
vation or coaching, and help players learn better while
improving UX.
5.4 Limitations
The findings of this paper are limited by the follow-
ing constraints. The game sessions have been con-
ducted with only a small number (26) of participants
of which 18 ware male. Although the students en-
thusiasm towards playing the game and their motiva-
tion during the gaming time was seen as very positive
by their teachers, it needs to be considered that this
might at least partially result from the fact that play-
ing a game was just a more fun alternative to regular
class sessions. Our concept was only evaluated using
one implementation for one game (Woodment), thus
a general validity for all types of collaborative multi-
player Serious Games can not be derived.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper we proposed a model for assisting an
instructor in orchestrating a collaborative multiplayer
Serious Game. Our concept is an extension to our
prior work on a framework for Game Mastering in
collaborative multiplayer Serious Games. It defines
an interface for game developers and subject matter
experts, which can use it to define relevant game enti-
ties, game parameters, or learning content. We further
provide a concept for a group model based on player
modeling, learner modeling and interaction model-
ing. Our concept addresses a suitable way of present-
ing relevant information to the instructor (GM) and
meaningful ways of adapting the game state and game
rules via the interface. We implemented our concept
as an extension of the collaborative multiplayer Seri-
ous Game Woodment and conducted a user-centered
evaluation with 26 users. Our hypothesis was that an
instructor is able to use a frontend implemented ac-
cording to our model in order to perform vital instruc-
tor tasks in collaborative learning scenarios and sub-
InstructorSupportinCollaborativeMultiplayerSeriousGamesforLearning-GameMasteringintheSeriousGame
'Woodment'
55

sequently be able to improve player performance in
terms of game experience and learning success. Our
results indicate that our hypothesis can be accepted
with some limitations. Both UX and learning perfor-
mance are significantly higher in the gaming sessions
where a Game Master was using the GM frontend
implemented according to our concept compared to
those sessions where no GM was intervening.
REFERENCES
Bartle, R. (1996). Hearts, clubs, diamonds, spades: Play-
ers who suit MUDs. Journal of Virtual Environments,
1(1):19.
Chiriac, E. H. and Granstr
¨
om, K. (2012). Teachers Leader-
ship and Students Experience of Group Work. Teach-
ers and Teaching, 18(3):345–363.
Haake, J., Schwabe, G., and Wessner, M. (2004). CSCL-
Kompendium: Lehr-und Handbuch zum computerun-
terst
¨
utzten kooperativen Lernen. Oldenbourg Wis-
senschaftsverlag.
H
¨
am
¨
al
¨
ainen, R., Manninen, T., J
¨
arvel
¨
a, S., and H
¨
akkinen, P.
(2006). Learning to Collaborate: Designing Collabo-
ration in a 3-D Game Environment. The Internet and
Higher Education, 9(1):47 – 61.
H
¨
am
¨
al
¨
ainen, R. and Oksanen, K. (2012). Challenge of sup-
porting vocational learning: Empowering collabora-
tion in a scripted 3d game - how does teachers’ re-
altime orchestration make a difference? Comp. and
Educ., 59:281–293.
Houlette, R. (2004). Player modelling for adaptive games.
AI Game Programming Wisdom II, pages 557–566.
Kearsley, G. (2000). Online Education: Learning and
Teaching in Cyberspace, volume 91. Wadsworth Bel-
mont, CA.
Kolb, A. Y. and Kolb, D. A. (2005). The Kolb Learning
Style Inventory - Version 3.1 Technical Specifications.
Technical report, HayGroup, Boston, USA.
Konert, J., G
¨
obel, S., and Steinmetz, R. (2012). Towards a
Social Game Interaction Taxonomy. In G
¨
obel, S. and
Wiemeyer, J., editors, Proceedings of the Intl. Conf.
on Serious Games (GameDays) in conjunction with
Intl. Conf. on E-Learning and Games (Edutainment),
pages 99–110, Darmstadt, Germany. Springer.
Korossy, K. (1999). Modeling knowledge as competence
and performance. Knowledge spaces: Theories, em-
pirical research, and applications, pages 103–132.
Larusson, J. and Alterman, R. (2009). Wikis to Support the
Collaborative Part of Collaborative Learning. Interna-
tional Journal of Computer-Supported Collaborative
Learning, 4(4):371–402.
Louchart, S. and Aylett, R. (2003). Solving the Narrative
Paradox in VEs–Lessons from RPGs. In Rist, T.,
Aylett, R., Ballin, D., and Rickel, J., editors, Intelli-
gent Virtual Agents, volume 2792 of Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, pages 244–248. Springer Berlin /
Heidelberg.
Mutwarasibo, F. (2013). Promoting University Stu-
dents Collaborative Learning through Instructor-
guided Writing Groups. International Journal of
Higher Education, 2(3):p1.
Onrubia, J. and Engel, A. (2009). Strategies for Collab-
orative Writing and Phases of Knowledge Construc-
tion in CSCL Environments. Computers & Education,
53(4):1256 – 1265.
Rodenberger, C. (2012). Conception and Implementation of
Game Mastering and Team Leadership Components
for a Collaborative 3D Multiplayer Serious Game.
Diploma thesis, Technische Universit
¨
at Darmstadt.
Shell, D. F., Husman, J., Turner, J. E., Cliffel, D. M., Nath,
I., and Sweany, N. (2005). The Impact of Computer
Supported Collaborative Learning Communities on
High School Students’ Knowledge Building, Strategic
Learning, and Perceptions of the Classroom. Journal
of Educational Computing Research, 33(3):327–349.
Smith, A. M., Lewis, C., Hullet, K., and Sullivan, A. (2011).
An inclusive view of player modeling. In Proceedings
of the 6th International Conference on Foundations of
Digital Games, pages 301–303. ACM.
Stahl, G., Koschmann, T., and Suthers, D. (2006). Cam-
bridge Handbook of the Learning Sciences, chapter
Computer-supported Collaborative Learning: An His-
torical Perspective, pages 409–426. Cambridge Uni-
versity Press.
Tychsen, A. (2008). Tales for the Many: Process and Au-
thorial Control in Multi-player Role-Playing Games.
In ICIDS ’08: Proceedings of the 1st Joint Interna-
tional Conference on Interactive Digital Storytelling,
pages 309–320, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
Tychsen, A., Hitchens, M., Brolund, T., and Kavakli, M.
(2005). The Game Master. In Proceedings of the sec-
ond Australasian conference on Interactive entertain-
ment, pages 215–222. Creativity & Cognition Studios
Press.
Wendel, V., Babarinow, M., H
¨
orl, T., Kolmogorov, S.,
G
¨
obel, S., and Steinmetz, R. (2010). Woodment:
Web-Based Collaborative Multiplayer Serious Game,
volume 6250 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
pages 68–78. Springer, 1st edition.
Wendel, V., G
¨
obel, S., and Steinmetz, R. (2012a).
Game Mastering in Collaborative Multiplayer Seri-
ous Games. In E-Learning and Games for Training,
Education, Health and Sports - LNCS, volume 7516,
pages 23–34, Darmstadt, Germany. Springer.
Wendel, V., Gutjahr, M., G
¨
obel, S., and Steinmetz, R.
(2012b). Designing Collaborative Multiplayer Serious
Games for Collaborative Learning. In Proceedings of
the CSEDU 2012.
Zea, N. P., S
´
anchez, J. L. G., Guti
´
errez, F. L., Cabrera,
M. J., and Paderewski, P. (2009). Design of Educa-
tional Multiplayer Videogames: A Vision From Col-
laborative Learning. Advances in Engineering Soft-
ware, 40(12):1251–1260.
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
56
