
A Problem-based Learning Case Study for Teaching Voice over
Internet Protocol - VoIP
Using Asterisk as a Tool for Teaching VoIP for Information Technology Classes
M. C. Dias
1,2
, C. F. Gabi
1
, E. P. Rodrigues
1
, V. R. Souza
1
and A. Perkusich
2
1
Coordination of Electrical Engineering, Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Paraíba – IFPB,
João Pessoa, Brazil
2
Post-Graduate Program in Electrical Engineering – PpgEE – COPELE, Electrical Engineering Department,
Federal University of Campina Grande – UFCG, Campina Grande, Brazil
Keywords: Problem-based Learning - PBL, Asterisk, Voice over IP - VoIP.
Abstract: This paper shows the use of PBL (Problem-Based Learning) technique as a key to learning VoIP in courses
like Electrical Engineering and Computer Networks in conjunction with open source and the public domain
software called Asterisk which was used to create the scenario of the experiment and the problems
presented to the students. In order to make the validation, the experiment was applied to students of
Bachelor in Electrical Engineering and in Communication Technology System, undergraduate courses at the
Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Paraíba – IFPB, in the Telephony subject, with
promising results. The Asterisk software was presented as a useful and flexible tool for constructing
scenarios and problems for the teaching of VoIP technologies and the used approach resulted as effective
for improving the attainment of the defined learning objectives.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the context of the technological evolution of
communications networks, the reality that the
telephone networks and data switching networks are
converging to an infrastructure, that will allow both
voice and data to be transmitted over the same
network, is becoming more feasible for the
technology and communication professionals on a
daily basis. This fact affects professionals from the
most diverse backgrounds, who work in the
convergent network area, from courses in
information technology up to the electrical and
telecommunication engineering fields.
The convergence of data networks with
telephone networks makes information technology
professionals face the challenge of working with
scenarios involving IP networks as well as with the
existent infrastructure of the traditional telephone
networks. Increasingly, the solution to this challenge
is related to the use of "Voice over IP" (VoIP)
technology in which the phone calls travel through a
broadband connection instead of traveling by
conventional telephone networks (Keller 2009).
In contrast to such development, the formation of
most of these professionals is still based on
traditional methodologies in which the teacher is the
holder of knowledge and the mass production of
labor force is prioritized.
However, methods have been changed and the
universities´ great challenge is to provide training
courses with the purpose to frame the content
according to the student so that he/she can become a
technically qualified professional in addition to
being able to adapt to frequent changes and demands
of the labor market (Silva & Viana, 2013).
With the change of teaching methods, an
approach is proposed in which learning is based on
practical problems solution (PBL). Such problems
are applied in scenarios that simulate a company´s
environment and allow students to develop and
clarify, in practice, the theoretical concepts that were
learned in the classroom, but that were formed in an
obscure and abstract way (Fernandes, 2013).
According to Ali and Samaka (2013), problem-
based learning is a student-centered, self-directed,
inherently collaborative pedagogy where students
learn by working in groups through solving
197
C. Dias M., F. Gabi C., P. Rodrigues E., R. Souza V. and Perkusich A..
A Problem-based Learning Case Study for Teaching Voice over Internet Protocol - VoIP - Using Asterisk as a Tool for Teaching VoIP for Information
Technology Classes.
DOI: 10.5220/0004848701970204
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU-2014), pages 197-204
ISBN: 978-989-758-021-5
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

problems and reflecting their experiences. These
students are supervised by a tutor or supervisor.
The literature suggests that strategies, in which
learning is based on problem solving, are effective in
teaching in summarily practical areas, such as
information technology. According to Cavalcante
and Embiruçu (2013), it is possible to realize how
this practice has been established around the world
and how it can be applied in engineering courses.
The use of VoIP technology has also been
established. Furthermore, its importance in the
communication systems, that are about to come, is
highlighted in Goode (2002). Recently, Dias (et al.
2013) showed that the use of practical experiments
can aid in teaching practical concepts of traditional
telephony and IP telephony.
This paper will present a case study on the
implementation of the Asterisk software as an aid
tool related to the practical teaching by using the
PBL approach to teach concepts of VoIP technology
and its interaction with the traditional telephone
system. This methodology was employed in courses
in Electrical Engineering and Telecommunication
System Technology, but it could easily be applied to
any course which had subjects with VoIP
technologies in their course programs.
The PBL technique was chosen so as the concept
and the motivation could be introduced to the
students at the beginning of the subject. This
method consists of groups´ choice and of the
fulfillment of practical problems which will be
solved through the use of software, laboratory
practices, theoretical content and the professor´s
support. Such method aids the undergraduate
students to solve practical questions by themselves
(Lamar et. al. 2012).
According to Ribaud and Saliou (2013), PBL can
help students to learn with the complexity and
perceive that there are no simple responses for
problem scenarios, nevertheless learning and life do
occur in contexts which can alter the available and
possible type of solution.
The problem-based learning method was initially
carried out in the Telephony subject with emphasis
on the telecommunication area. The students were
evaluated in accordance with their theoretical and
practical performance, being their critical sense
analyzed in relation to the proposed problem.
This paper is organized as follows: section 2 will
focus on a bibliographical review on the concepts of
VoIP and a presentation of the Asterisk tool; section
3 will describe the materials and methods used in the
design of the proposed experiment; in section 4, the
results obtained from the experiment will be
presented and in section 5, we present the
conclusions.
2 VOICE OVER IP AND
ASTERISK CONCEPTS
2.1 Voice over IP (VoIP)
Voice over IP is a set of networking protocols that
have the function to normalize and regulate the
sending of the voice from a source to a destination
by using TCP/IP data networks (Keller, 2009). That
is, an analog voice signal is converted into a set of
digital signals, which is then sent through an internet
connection in the form of packets with IP
addressing.
The main difference between VoIP and
traditional telephony is related to the way the voice
is transported. This difference suggests that the only
requirement to use VoIP technology is concerned
with the use of a TCP / IP connection between two
points with end to end delay less than 150 ms. This
requirement creates some unique advantages to
VoIP, such as (Keller 2009; Goode 2002):
Cost reduction: expenditure decrease with
traditional telecom operators and the use of
softphones instead of conventional phones;
Unique infrastructure: the convergence of voice
and data networks will also make the physical
network unique;
Mobility: the branch line must be in a position
where you can connect to the Internet;
The telephone system control: reduces the users´
dependence from the telephone exchange
maintenance company; and
New features: some of them which are not
available in the traditional telephony become
possible, such as voice encryption during calls.
In VoIP technology, signaling protocols are
responsible for determining a standard that specifies
the data format and the rules to be followed by data
traffic. Moreover, these signaling protocols are used
to establish connections, determine the destination
and also for issues related to signs such as: ring,
caller ID, disconnection, among others. Currently
the major signaling protocols for VoIP are (Silva,
2010):
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP);
Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP);
Jingle;
H.248/Megaco; and
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
198

Inter-Asterisk eXchange (IAX).
Taking into account what has been mentioned, it
is observed that information technology
professionals, who work with communication
networks, need practical tools that help them to learn
the concepts of IP telephony during their training.
The Asterisk, the software already mentioned,
however, is presented as an alternative to building
practical experiments of similar complexity and low
cost for the reality of the job market.
2.2 The Asterisk Platform
The Asterisk software is able to perform the function
of a private telephone exchange, which has as one of
its primary functions the management of audio
transmitted in digital communication channels
(Madsen, Meggelen & Bryant, 2011). Asterisk can
be used as an extremely powerful and flexible tool
designed for the learning of VoIP technologies and
protocols once it allows reproducing in laboratories
situations and problems only seen in real public or
private telephone networks.
Moreover, one of the advantages of working with
Asterisk in the classroom is the fact that Asterisk is
free software distributed by Digium® that is based
on the GPL (General Public License) (Martín, 2009).
The free version of Asterisk eliminates the need for
a conventional private telephone exchange because
its version has no limits of application. Additionally,
Asterisk receives users´ contributions from all over
the world, making this software always updated
(Madsen, Meggelen & Bryant, 2011).
Asterisk's architecture was designed with great
care so that there was as much flexibility as possible
with regard to the operation of different types of
hardware and software (Martín, 2009). Figure 1
shows the Asterisk internal architecture which is
formed by a core and specific APIs (Application
Programming Interfaces) which support the
switching of internal information to PBX.
Information processing in the Asterisk core
occurs in such a way that the specific protocols,
codecs and hardware interfaces are abstracted from
the information. This allows Asterisk to be able to
connect to any hardware technology available (either
current or future) to perform its essential functions
(Silva, 2010).
The functioning and operation of Asterisk are
based on the use of modules that the programmer
can choose to use or not, depending on the
application that he/she is working with. Table 1
describes the main modules for the correct
functioning of an Asterisk server (Asterisk, 2010).
Figure 1: Arquitetura Interna do Asterisk (Asterisk, 2011).
Table 1: Asterisk modules.
Module Description
Channel
Drivers
The channel drivers make the
communication with devices
outside Asterisk possible by
translating the signaling, or
protocol, to the core.
Dialplan
Applications
This module provides call
functionality to the system.
Dialplan
Functions
This module is used to set and
retrieve parameters of
configurations on a call.
Resources
Used to provide resources to
Asterisk, like music on hold
and call parking.
CODECs
This module is used to encode
and decode audio or video so it
takes less bandwidth.
File Format
Drivers
Used to save media to disk in
specific file formats and
convert files back to media
streams on the network.
Call Detail
Record
(CDR)
Drivers
Used to write call logs to a disk
or to a database.
Call Event
Log (CEL)
Drivers
Similar to CDR, but with
details of what happened inside
Asterisk during a particular call.
Bridge
Drivers
Used by bridging architecture
in Asterisk to provide various
methods of bridging call media
between participants in a call.
When installing Asterisk, the student will be
automatically deploying the use of VoIP (Keller,
AProblem-basedLearningCaseStudyforTeachingVoiceoverInternetProtocol-VoIP-UsingAsteriskasaToolfor
TeachingVoIPforInformationTechnologyClasses
199

2009). The software use provides the broadening of
learning so that the student can study from the
creation of the used VoIP extension lines up to the
monitoring of packets sent and the signaling
exchange between the terminals. With the purpose
of carrying out this investigation, an additional
program called Wireshark will be used (Wireshark,
2011).
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The experiment was carried out in five phases:
1. Definition of the learning objectives;
2. Construction of a scenario to be set up in a
laboratory;
3. Definition of the problems to be presented for the
students to solve them;
4. Validation in an undergraduate subject with 60
credit hours, in the minimum, and that had VoIP
in its course description; and
5. Evaluation of the obtained results.
The following learning objectives were defined
in the first phase:
Define what VoIP is;
Differentiate VoIP technologies from the other
ones used for establishing telephone calls both in
public and private telephony;
Understand the functioning of SIP, RTP and
SRTP protocols; and
Set up the Asterisk software for establishing
telephone calls using VoIP technologies.
In the second phase, the scenario was defined
and constructed to be used in the phase related
specifically to PBL. The chosen scenario
encompasses studies on VoIP with analog terminals
and IPs telephones, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Scenario of the proposed solution.
The objective of this scenario is to provide an
environment where students can understand the
basic operation of a server set up with Asterisk and
that they can, through the Asterisk configuration,
make calls between IP terminals that are connected
to the server. Subsequently, to understand how the
signaling and voice traffic occur on the TCP/IP
network, a network monitoring is carried out, in
which calls and SIP protocols are captured and
RTP/SRTP are analyzed.
When assembling the scenario, the following
pieces of equipment available in the IFPB
Telephony and Convergent Networks Laboratory
were used: Computer with 4GB RAM, processor
Intel QUAD CORE, plate FXS / FXO, E1 board,
Impacta 68 Intelbras hybrid telephone exchange and
Grandstream GXP-1200 VoIP phones.
After defining the scenario, the Linux operating
system is installed on a computer which serves as a
platform for the use of Asterisk. Figure 3 shows the
Asterisk console after it is installed on Linux. It is
through the console that the main information
regarding Asterisk operation is accessed as well as it
is possible to give operation commands to the
software.
Figure 3: Initiation of Asterisk Server.
Then, it is necessary to create the SIP
communication channels so that the Asterisk server
can identify each extension. Creating SIP channels
with Asterisk occurs by editing the sip.conf
configuration file. The code segment below shows
how to create four SIP extensions.
[general]
Bindport = 5060
Bindaddr = 0.0.0.0
disallow = all
allow = alaw
language = en_US
[commom_to_branches](!)
type = friend
context = branches
host = dynamic
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
200

[2000](commom_to_branches)
secret = 1234
mailbox = 2000
[2001](commom_to_branches)
secret = 1234
mailbox = 2001
[3000](commom_to_branches)
secret = 1234
mailbox = 3000
[3001](commom_to_branches)
secret = 1234
mailbox = 3001
In order to have communication among the
created extensions, it is necessary to set the Asterisk
server dial plan. The dial plan is created by editing
the Asterisk extensions.conf. The following code
segment shows how the dial plan setup is made for
the scenario in Figure 2.
[branches]
; Impacta 68 branches
exten => 2000,1,Dial(SIP/2000,30)
exten => 2001,1,Dial(SIP/2001,30)
; IP phones branches
exten => 3000,1,Dial(SIP/3000,30)
exten => 3001,1,Dial(SIP/3001,30)
The use of analog terminals is allowed by setting
the central Impacta 68 using specific software, as
shown in Figure 4. It is interesting to note that the
Impacta 68 central exchange recognizes the Asterisk
server as a registration server on the network.
Without this setting, it would not be possible to
make Impacta 68 extensions to connect with the
GXP-1200 IP terminals.
Figure 4: Configuração do Servidor de Registro da
Impacta 68.
An IP terminal configuration can be performed on
the phone itself or via the web server with the
terminal IP address. Figure 5 shows the web server
configuration for GXP-1200.
Figure 5: Programming Interface for GXP-1200.
After configuring the extension lines, the
terminals send a registration request to the Asterisk
server and connect to the server. Figure 6 shows the
register of the terminals on the Asterisk server.
Figure 6: Registration of SIP Channels in Asterisk Server.
In addition to the default implementation, it is
possible to activate SRTP protocol on the devices
that will provide greater security in the sent packets.
Encrypted data, even with packets being captured by
network monitoring software, will not give access to
the content within them. Therefore, the devices
become secure on the network.
In the showed scenario (Figure 2), it is possible
to observe how the Asterisk server is able to
establish communication with the IP telephony
devices and the Impacta 68 Central Telephone
through the Internet. Such scenario has great
importance to students´ training in the Telephony
and Convergent Networks areas, given that its
market performance will involve working from
assembly to the understanding of the concepts that
were applied in practice, in the classroom.
In the next phase, the problems were made up so
as to be presented to the students. After researching
in workplaces of several telecommunication
AProblem-basedLearningCaseStudyforTeachingVoiceoverInternetProtocol-VoIP-UsingAsteriskasaToolfor
TeachingVoIPforInformationTechnologyClasses
201
companies and interviews with their professionals,
the problems were defined to be presented to the
students. The main objective was to focus on
problems that reflected situations commonly found
in professional environments involving VoIP.
For the validation phase, the Telephony subject
of the Electrical Engineering and
Telecommunication System Technology courses
was chosen. Such subject presents all the necessary
requirements: class load higher than 60 hours and
has VoIP in the course description. In the PBL, the
students were evaluated by the professor, by using
continuous evaluation in several sessions that the
presented problem demanded it, taking into account
the learning objectives. At the end, grades were
expressed on a scale of 0-100 and they were
attributed to each one of the students.
In the evaluation phase, the students answered to
a questionnaire of satisfaction and the professor of
the mentioned subject carried out a subjective
evaluation on the experience. This feedback allowed
outlining new actions for improving the used
approach. Furthermore, a comparison regarding the
repetition and final general mean of the group´s
grades in relation the previous semester was
accomplished.
4 RESULTS
The mentioned scenario was established several
times by students of Telephony discipline, of the
Bachelor in Electrical Engineering and the Higher
Course in Telecommunication System Technology
from the Federal Institute of Education, Science and
Technology of Paraíba (IFPB), which covers
detailed study of VoIP. This enabled students to
carry out the implementation of all practice and
successfully absorb the theoretical content
previously seen in the classroom.
Using Wireshark to monitor the network, it was
possible to capture packets related to the exchange
of SIP protocol signaling sent from the terminals to
the Asterisk server and vice versa. It was also
possible to capture the data stream transmitted
among the terminals which uses the RTP protocol.
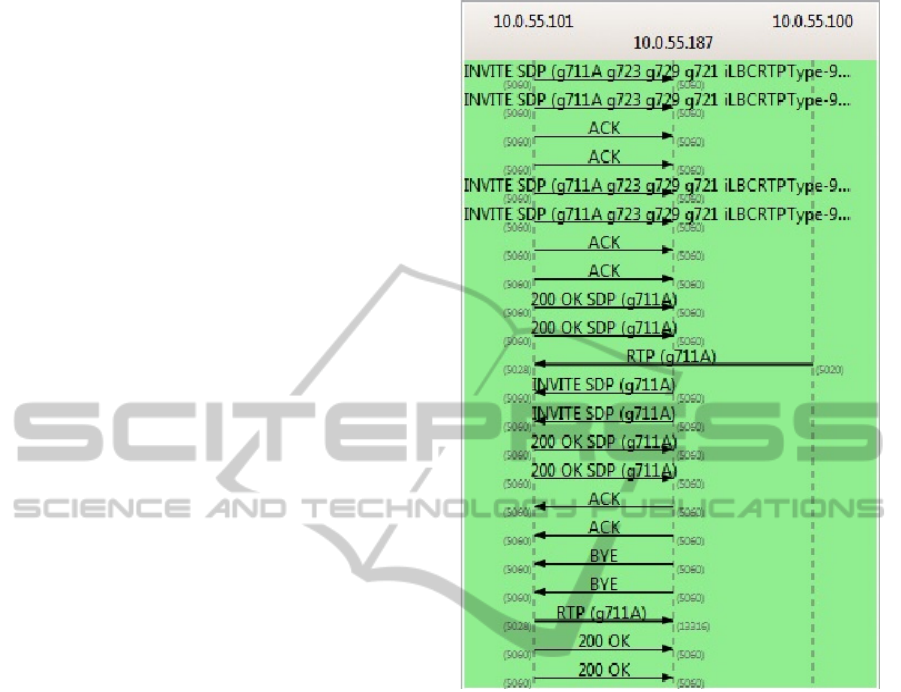
Figure 7 shows an example of the exchange of SIP
signaling captured during the experiment.
At the end of the experiment, the students were
able to further increase the tab because two IP
telephone protocols, RTP and SRTP, were used for
security check in sending packets on the network. It
was realized that when the SRTP mode is chosen in
the terminals, the packets travel on the network in
Figure 7: SIP Protocol Signaling Exchanged Between Two
Terminals.
the safest way and it will not be possible to hear the
content of the calls made, even with the capture of
the packets. However for the RTP protocol, it was
possible to examine the content of the calls when
fulfilling the capture of the packets on the network.
The experiment accomplishment in the
classroom allows the understanding of the
theoretical content on VoIP technology because the
use of Asterisk develops concepts related to both the
traditional telephony and IP telephony as well as
convergent networks. Furthermore, the use of
Asterisk adds to the training of information
technology professional a powerful and low cost
solution to problems related to voice traffic in
computer networks.
After validation, results were encouraging. While
comparing with the numbers of the same subject, in
the previous semester, the repetition rate was
reduced to zero and the final general mean of the
group´s grades also increased meaningfully from
61,7 to 81 – an increase of 31,35%. Students were
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
202

questioned in relation to the PBL satisfaction level
to detriment of the classical approach (in which the
professor only transmits knowledge and the student
has a secondary role in the learning process) as well
as in regard to the general satisfaction with the
subject. These results are presented in Figures 8 and
9. In both questionings, the students should mark
only one of the following alternatives: very satisfied,
satisfied, fairly satisfied, little satisfied or not
satisfied.
Figure 8: Satisfaction with PBL compared with the
classical approach.
Figure 9: General Satisfaction with the Telephony Subject.
The subjective evaluation of the professor
pointed out four important aspects:
1. The proposition of non-trivial problems and with
no unique solution increased the challenge level
for the students and it acted as stimulus to the
participation in the activities of the subject.
2. Students faced difficulty in coping with the
diversity of pieces of equipment that make up the
scenario of the experiment, though they have had
the professor´s explanation about the functioning
and operation of such devices at the beginning of
the class.
3. There was a noteworthy evolution in regard to
the attainment of the general learning objectives
in the group from the previous semester.
4. In relation to the PBL, the professor managed to
improve the students´ performance, but he/she
highlighted the need for teacher´s assistant in
case of groups larger than 24 students.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The experience with the PBL using Asterisk as a
tool for making up scenarios and problems for VoIP
technology teaching was extremely positive both for
the professor and the students. In the experimental
phase of the mentioned subject, the students´
satisfaction level with the PBL reached 87,5% (
satisfied and very satisfied as shown in Figure 8).
Furthermore, the evaluation by means of grade and
the professor´s subjective perception indicated
progress regarding the attainment of the learning
objectives on the students´ behalf.
With Asterisk, it was possible to create a
reasonable complexity scenario which is present in
several telecommunication companies that offer
VoIP services; all of this with low cost when
compared with the proprietary solutions available in
the market. Therefore, providing the students
problems that are close to the professional reality,
which they will face in the job market, constituted a
feasible activity.
As consequence of the analysis of the results,
before presenting the problems to be solved for the
students´ appreciation, three simple laboratory
practices, with the aim to make the students familiar
with the equipment and software to be used in the
proposed scenario, were introduced. Hence, it is
expected to mitigate the problem pointed out by the
professor regarding the students´ difficulty in
dealing with such devices and the associated
software during the resolution phase of the presented
problems, in addition to allowing an enhanced focus
on the work itself.
Currently, this approach is being used in the
same subject and the results will be evaluated in a
continuous improvement process. The objective is to
consolidate and improve the model so as it can be
used for the VoIP technology teaching in the
Engineering, Computing and Technology courses.
12,5
75
0
12,5
0
SatisfactionwiththePBL(%)
VerySatisfied
Satisfied
FairlySatisfied
LittleSatisfied
NotSatisfied
25
62,5
0
12,5
0
GeneralSatisfactionwith
TelephonySubject(%)
VerySatisfied
Satisfied
FairlySatisfied
LittleSatisfied
notsatisfied
AProblem-basedLearningCaseStudyforTeachingVoiceoverInternetProtocol-VoIP-UsingAsteriskasaToolfor
TeachingVoIPforInformationTechnologyClasses
203

REFERENCES
Keller, A., 2009. Asterisk na Prática. São Paulo: Novatec
Editora Ltda.
Zeyad, A. and Samaka, M., 2013. ePBL: Design and
Implementation of a Problem Based Learning
Environment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Global
Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON),
Berlim, March 2013. Germany.
Silva, M. and Viana, D., 2013. Variáveis operacionais a
serem consideradas no planejamento de disciplinas de
projeto para aplicação do PBL nos cursos de
engenharia. In: Proceedings of the 41st COBENGE,
Gramado, September 2013. Gramado: ABENGE.
Fernandes, B. L., 2013. Projetos interdisciplinares:
aprendizagem baseada em problemas (PBL). In:
Proceedings of the 41st COBENGE, Gramado,
September 2013. Gramado: ABENGE.
Cavalcante, F. and Embiruçu, M., 2013. Aprendizado com
base em problemas: como entusiasmar os alunos a
reduzir a evasão nos cursos de graduação em
engenharia. In: Proceedings of the 41st COBENGE,
Gramado, September 2013. Gramado: ABENGE.
Goode, B., 2002. Voice over internet protocol (VoIP). In:
Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 90, nº. 9, September
2002, pp. 1495-1517 (doi: 10.1109/
JPROC.2002.802005).
Dias, M. et al. 2013. Uso do Asterisk como ferramenta de
auxílio no ensino prático de telefonia. In: Proceedings
of the 41st COBENGE, Gramado, September 2013.
Gramado: ABENGE.
Lamar, Diego G. et al. 2012. Experiences in the
Application of Project-Based Learning in a Switching-
Mode Power Supplies Course. IEEE Transactions on
Education, Vol. 55, no. 1, February 2012.
Ribaud, V. and SALIOU, P., 2013. The cost of Problem-
Based Learning: an example in information in systems
engineering. In: Proceedings of the 26
th
International
Conference on Software Engineering Education and
Training, San Francisco, May 2013. San Franciso:
IEEE.
Madsen, L., Meggelen, J. V. and Bryant, R., 2011.
Asterisk
TM
: The Definitive Guide. 3
rd
ed. Sebastopol:
O’Reilly Media, Inc.
Martín, S. G. (2009) Contribution to Asterisk Open Source
Project. Thesis (MSc). Universitat Oberta de
Catalunya.
Finnerty, I. (2009) Per-extension voip call rating for the
Asterisk PBX system. Thesis (MSc). National
University of Ireland.
Silva, V. (2010) Soluções wireless/voip para redes
comunitárias. Thesis (MSc).Universidade de Aveiro.
Asterisk Project, 2011. Asterisk Architecture, The Big
Picture. [Online]. Available from: https://
wiki.asterisk.org/wiki/display/AST/Asterisk+Architect
ure%2C+The+Big+Picture [Accessed 10/10/2013].
Asterisk Project, 2010. Types of Asterisk Modules.
[Online]. Available from: https://wiki.asterisk.org/
wiki/display/AST/Types+of+Asterisk+Modules
[Accessed 10/10/2013].
Wireshark, 2011.VoIP calls [Online]. Available from:
http://wiki.wireshark.org/VoIP_calls [Accessed
10/10/2013].
CSEDU2014-6thInternationalConferenceonComputerSupportedEducation
204
