
A Methodology to Measure the Semantic Similarity between Words
based on the Formal Concept Analysis
Yewon Jeong, Yiyeon Yoon, Dongkyu Jeon, Youngsang Cho
and Wooju Kim
Department of Information & Industiral Engineering, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
Keywords: Query Expansion, Formal Concept Analysis, Semantic Similarity, Keyword-based Web Documents.
Abstract: Recently, web users feel difficult to find the desired information on the internet despite a lot of useful
information since it takes more time and effort to find it. In order to solve this problem, the query expansion
is considered as a new alternative. It is the process of reformulating a query to improve retrieval
performance in information retrieval operations. Although there are a few techniques of query expansion,
synonym identification is one of them. Therefore, this paper proposes the method to measure the semantic
similarity between two words by using the keyword-based web documents. The formal concept analysis and
our proposed expansion algorithm are used to estimate the similarity between two words. To evaluate the
performance of our method, we conducted two experiments. As the results, the average of similarity
between synonym pairs is much higher than random pairs. Also, our method shows the remarkable
performance in comparison with other method. Therefore, the suggested method in this paper has the
contribution to find the synonym among a lot of candidate words.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recently, the useful information on the internet has
been increasing due to the rapid development of
web. However, users feel difficult to find the desired
information on the internet because it takes more
time and efforts. In order to solve this problem, the
query expansion is considered as a new alternative.
It helps user to find the desired results and improve
the effectiveness of retrieval. As the process of
reformulating a query, the query expansion improves
retrieval performance in information retrieval
operations (Vechtomova and Wang, 2006). Thus, in
the search engines, it involves evaluating a user's
input and expanding the search query to match
additional documents. Even if there are a few
techniques of the query expansion, the synonym
identification is one of them.
Finding synonym on the basis of subjective
intuitions is considered as a daunting task. This is
the reason of that it is hard to define the synonym
due to a property that has no clear-cut boundaries
(Baroni and Bisi, 2004). Therefore, this paper
proposes the method to automatically measure how
much two words have the semantically similar
relation by using keyword-based web documents.
There are a lot of web documents which have tagged
words like papers. Therefore, this paper applied the
paper keywords to calculate the similarity between
two words through the formal concept analysis
(FCA).
The next section introduces the related work of
the formal concept analysis and other similarity
measurements. The section 3 provides a detailed
explanation of methodology to measure similarity
between two words. The section 4 presents the result
of experiments to evaluate performance of our
method. Finally, we draw the conclusion and suggest
future work in the section 5.
2 RELATED WORKS
2.1 Formal Concept Analysis
The formal concept analysis is a mathematical
approach which is used for conceptual data analysis
(Ganter et al., 2005). It has been studied in diverse
fields such as data mining, conceptual modelling,
software engineering, social networking and the
semantic web (Alqadah and Bhatnagar, 2011). It is
good to analyse and manage structured data
313
Jeong Y., Yoon Y., Jeon D., Cho Y. and Kim W..
A Methodology to Measure the Semantic Similarity between Words based on the Formal Concept Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0004855603130321
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST-2014), pages 313-321
ISBN: 978-989-758-024-6
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

(Wormuth and Becker, 2004). Thus, it helps user to
structure an interest domain (Ganter et al., 1997,
Wille, 2009). It models the world of data through the
use of objects and attributes (Cole and Eklund,
1999). Ganter et al.(1999) applied the concept lattice
from the formal concept analysis. This approach has
an advantage that users can refine their query by
searching well-structured graphs. These graphs,
known as formal concept lattice, are composed of a
set of documents and a set of terms. Effectively, it
reduces the task of setting bound restrictions for
managing the number of documents to be retrieved
required (Tam, 2004).
2.2 Related Works of Similarity
Measure between Two Words
Traditionally, a number of approaches to find
synonym have been published. The methodology to
automatically discover synonym from large corpora
have been popular topic in a variety of language
processing (Sánchez and Moreno, 2005, Senellart
and Blondel, 2008, Blondel and Senellart, 2011, Van
der Plas and Tiedemann, 2006). There are two kinds
of approaches to identify synonyms.
The first kind of approaches uses a general
dictionary (Wu and Zhou, 2003). In the area of
synonym extraction, it is common to use lexical
information in dictionary (Veronis and Ide, 1990). In
dictionary-based case, a similarity is decided on
definition of each word in a dictionary. This kind of
approaches is conducted through learning algorithm
based on information in the dictionary (Lu et al.,
2010, Vickrey et al., 2010). Wu and Zhou (2003)
proposed a method of synonym identification by
using bilingual dictionary and corpus. The bilingual
approach works on as follows: Firstly, the bilingual
dictionary is used to translate the target word.
Secondly, the authors used two bilingual corpora
that mean precisely the same. And then, they
calculated the probability of the coincidence degree.
The result of the bilingual method is remarkable in
comparison with the monolingual cases. Another
research builds a graph of lexical information from a
dictionary. The method to compute similarity for
each word is limited to nearby words of graph. This
similarity measurement was evaluated on a set of
related terms (Ho and Fairon, 2004).
The second kind of approaches to identity
synonym considers context of the target word and
computes a similarity of lexical distributions from
corpus (Lin, 1998). In the case of distributional
approaches, a similarity is decided on context. Thus,
it is important to compute how much similar words
are in a corpus. The approach of distributional
similarity for synonym identification is used in order
to find related words (Curran and Moens, 2002).
There has been many works to measure similarity of
words, such as distributional similarity (Lin et al.,
2003). Landauer and Dumais (1997) proposed a
similarity measurement to solve TOEFL tests of
synonym by using latent semantic analysis
(Landauer and Dumais, 1997). Lin (1998) proposed
several methodologies to identify the most probable
candidate among similar words by using a few
distance measures. Turney (2001) presented PMI
and IR method which is calculated by data from the
web. He evaluated this measure on the TOEFL test
in which the system has to select the most probable
candidate of the synonym among 4 words. Lin et al.
(2003) proposed two ways of finding synonym
among distributional related words. The first way is
looking over the overlap in translated texts of
semantically similar words in multiple bilingual
dictionaries. The second is to look through designed
patterns so as to filter out antonyms.
There are a lot of researches for measuring
similarity to identify the synonym. However, the use
of dictionary has been applied to a specific task or
domain(Turney, 2001). Hence, these existing
researches are hard to be applied in the changeable
web. And, the context-based similarity method deals
with unstructured web documents and it takes much
time to analysis since it needs to pre-treatment such
as morphological analysis. Therefore, this paper
proposes a methodology to automatically measure
the semantically similar relation between two words
by using keyword-based structured data from web.
3 METHOD TO MEASURE
SIMILARITY
In this section, we demonstrate the method to
measure semantic similarity between two distinct
words. This paper defined the ‘query’ as the target
word that we would like to compute the semantic
similarity. A pair of queries is defined as
,
which is the set of two different words
and
.
The overall procedure to estimate semantic
similarity between two queries of Q is composed of
three phases as shown in the Figure 1; preprocessing,
analysis and calculation phase. In the preprocessing
phase, base data for the analysis are collected and
refined on each query. Let us assume that the query
pair is Q=(contamination, pollution). The set of web
WEBIST2014-InternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
314

Figure 1: The overall procedure to calculate the semantic similarity between two queries.
documents for each queries contamination and
pollution are collected respectively. The formal
context for each query is constructed based on the
set of collected web documents, tags and binary
relations. Finally, the generated formal contexts are
refined according to two rules which are introduced
in the section 3.1.2. In the analysis phase, we apply
FCA and expansion algorithm to each refined formal
context. Implicit concepts from formal concept are
derived through the expansion algorithm which
helps us to compare queries in-depth. In the final
phase, we calculate the semantic similarity of the
pair of queries. On the basis of expanded formal
concepts, we can examine how many concepts are
duplicated by considering the matching concepts.
3.1 Preprocessing Phase
In order to measure the similarity between two
queries, web documents which have the keywords
should be collected on each query. And the
keywords of collected documents should include the
query. From these documents, we can get
information about relation between documents and
tagged words and also can make the formal context.
3.1.1 Generation of the Formal Context
A formal context is represented through a
two-dimensional matrix X. In general, the column
and row of X indicate objects and attributes
respectively. An object is a collected web document
and an attribute is one of the tagged words. Table 1
shows the example of the formal context given the Q
= (contamination, pollution). The checkmarks in the
table mean whether the object contains attributes or
not. In the case of
, as shown
in Table 1, the document
has four attributes such
as contamination, insulators, solutions and
flashover. The each set of attributes and objects are
defined as follows:
{contamination, insulators, humidity,
solutions, flashover, power lines}
i
q
A
(1)
12345
{, , , , }
i
q
O ddddd
(2)
{pollution, insulators, etching,
solutions, falshover, iron}
j
q
A
(3)
12345
{, , , , }
j
q
O ddddd
(4)
is the set of attributes and
is the set of
objects when
is given.
is composed of tags
from the collected documents and
consists of the
documents which is represented
.
AMethodologytoMeasuretheSemanticSimilaritybetweenWordsbasedontheFormalConceptAnalysis
315

Table 1: Examples of formal contexts.
= contamination
contami
nation
Insulat
ors
humidit
y
solution
s
flashov
er
power
lines
d
√ √ √ √
d
√ √ √
d
√ √ √
d
√ √ √ √
d
√ √ √ √
= pollution
pollution
Insulat
ors
etching
solution
s
flashov
er
iron
d
√ √ √
d
√ √ √
d
√ √ √
d
√ √ √
d
√ √ √ √
3.1.2 Refinement of the Formal Context
After two formal contexts are generated, the
refinement procedure is required for two reasons.
Our research supposes that the more semantically
similar relation two queries have, the more matching
tagged words they have. This study ultimately wants
to know how many words are matched between
tagged words from two queries. Therefore, the
attribute which is the same with query is
unnecessary in this comparison procedure. The first
refinement rule is to remove ‘query’ from attribute
set A, and then, the second rule is to remove
attributes which are contained in less than two
documents. The reason is that these attributes have
relatively weak effects to this method, and also it is
helpful to save the process time and system cost by
reducing the size of formal context. The summary of
refinement procedure is as follows:
1. Removing the query from (the set of attributes).
2. Removing the attributes contained in less than
two web documents.
Table 2 is an example of refined context when
the query is contamination and pollution. Because
the contamination is given by
, the attribute
contamination is removed by rule 1. For the same
reason, the attribute pollution is also removed. Since
the number of web documents contained in etching
is less than 2, the attribute etching is removed by
rule 2.
Table 2: Examples of refined formal contexts.
= contamination
insulators humidity solutions flashover
power
lines
d
√ √ √
d
√ √
d
√ √
d
√ √ √
d
√ √ √
= pollution
insulators solutions flashover iron
d
√
d
√ √
d
√ √
d
√ √
d
√ √ √
3.2 Analysis Phase
In this section, we introduce the analysis phase of
this method. First, the formal concept analysis is
conducted based on each formal context on
and
. However, a concept from the formal concept
analysis has only a few implicit concepts. Thus, we
expand the formal concepts through our proposed
expansion algorithm.
3.2.1 Formal Concept Analysis
To measure the similarity between the two queries,
formal concept analysis should be performed on
each formal context of
and
. According to these
analysis procedures, two sets of formal concepts are
generated by using formal concept analysis (Ganter
et al., 1997). When the query
is given, a set of
formal concepts is generated by formal concept
analysis as follows:
12
,,,
1, ,
iiii
qqqq
kn
SFC FC FC FC
where k n
(5)
In this equation, S
is the set of formal
concepts and
is the k th formal concept. And, n
is the number of formal concepts from the formal
context. A formal concept is composed of an intent
and extent as demonstrated in (6):
,1,,
iii
qqq
kkk
F
CIEwherek n
(6)
In this formula,
is an intent of the
and
is
an extent. The intent is subset of the attribute set
which is the keyword set. And, extent is subset of
WEBIST2014-InternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
316

object set
which is the set of documents. Every
object in
has every attribute in
by the
property of formal concept analysis. Thus,
is a
concept that implicates that the objects in
have
the common attributes in
.
From a set of formal concepts, we can get each
set of intent on certain query. A set of
is denoted
as
:
12
,,,
iii i
ii
qqq q
n
qq
k
III I
where I P A
(7)
An element of
is subset of
and intent of each
formal concepts. This set of intents is used when we
calculate similarity between two set of formal
concepts.
3.2.2 Expansion Algorithm
There are a few implicit concepts in a formal
concept. Let us assume that a concept has the
subsets of intent of other concepts. If it has the same
extent each other, it is not generated by formal
concept analysis. Therefore, we need to expand
formal concept in order to compare them in depth.
The detail procedure is as follows:
1. Find a formal concept (FC) which has the most
size of intent from the set of formal concepts (FCS).
2. Get an extent (EXT) and intent (INT) from the FC.
3. Generate the subset of FC of which size is n-1
when the size of intent is n, and define it as INTS.
4. Confirm whether INTS[i](an element of INTS) is
in the FCS.
5. If it isn’t, add the expanded concept which has
INTS [i] and EXT.
6. Repeat this procedure until all of the formal
concepts are expanded.
Firstly, the algorithm finds a formal concept
which has the largest intent size. It is represented by
the dotted outline in result of FCA in Figure 2. The
intent size of this concept is 3, so generate subset of
which size is 2. Then 3 subsets of an intent like
{solutions, flashover}, {solutions, insulators} and
{flashover, insulators} are made. Among these
subsets, a subset {solutions, insulators} doesn’t exist
in original set of formal concepts. Therefore, a new
concept which consists of {solutions, insulators},
{
} could be generated.
If the formal concepts go through expansion
procedure, some concepts are generated. The Figure
3 shows examples of the expanded concepts lattice.
The coloured boxes are the newly generated
concepts. In this figure, (a) is a concept lattice of a
context when the query
is contamination. There
are 6 concepts made by expansion. And, (b) is a
concept lattice of a context when the query
is
pollution. Two concepts are generated. The
expansion of formal concepts is helpful to compare
them because implicit concepts can be found.
3.3 Calculation Phase
Suppose that there are the two queries denoted by
and
. The semantic similarity between
and
is
calculated based on comparison of two sets of
formal concepts. To compare them, we need to find
the duplicated formal concepts.
3.3.1 Matching Formal Concepts
If there are two sets of formal concepts, the concepts
which have the same intent are called to ‘matching
Figure 2: An example of expansion process.
AMethodologytoMeasuretheSemanticSimilaritybetweenWordsbasedontheFormalConceptAnalysis
317
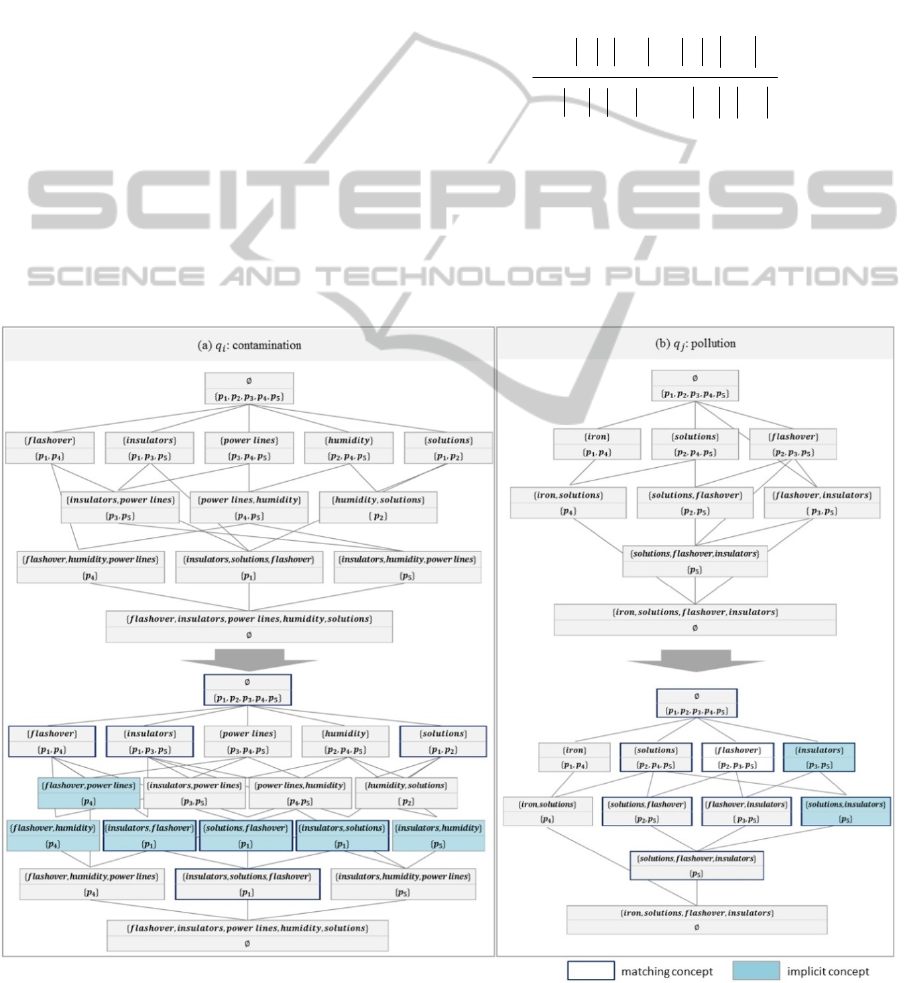
concepts’. In other word, it means that concepts
have the same intent from
and
respectively. In Figure 3, the concepts marked as
bold outline are the matching concepts. When two
queries,
and
, are given, the set of matching
concepts is as follows:
12
() ,,,
ij ij ij ij
qqqq
zc
SMC MC MC MC
(8)
is a set of matching concepts and
is the z th matching concept. And, c is the
number of matching concepts. A matching concept
is composed of an intent and two extents as follows:
*
*
*
,,
ij j
i
qq
q
zzzz
MC I E E
(9)
∗
is the intersection of
and
.
∗
is the
extent when the intent is
∗
and the
is given.
Also,
∗
is the extent when the intent is also
∗
and the
is given. The function MapFunc is a
function to find an extent corresponding with a
certain intent given query. The formulas are as
follows:
*
j
i
q
q
III
(10)
*
*
(,)
i
q
z
zi
E MapFunc I q
(11)
3.3.2 Calculation of Semantic Similarity
If we gain the set of matching concepts, we can
estimate the similarity between two queries,
and
. A measure of similarity is defined as:
*
*
**
1
11
(, )
100
j
i
jj
ii
ij
c
q
q
zz zz
z
nm
qq
qq
xx y y
xy
Similarity q q
IE IE
IE I E
(12)
It is the measure to calculate how many concepts are
duplicated. In this formula, we multiply the number
of intent elements by the number of extent
elements
because the concepts that have the bigger size of an
intent or extent have a great effect on measure. This
similarity has range from zero to 100. If the all
concepts are the same the similarity is 100. And if
Figure 3: An example of expansion and matching concepts.
WEBIST2014-InternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
318

there are not duplicated concepts, the result would
be zero.
4 EMPIRICAL EVALUATION
In order to evaluate the effectiveness of our method,
we had the two performance evaluations. Firstly, we
compared the similarity between two types of query
pairs; one is the set of synonym pairs and the other is
based on the randomly selected pairs. Secondly, we
used the type of TOEFL synonym questions to
verify the performance of this method.
4.1 Synonym Pairs Vs. Random Pairs
We prepared the 20 word pairs composed of 10
synonym pairs and 10 random pairs. In order to
make formal contexts about queries, we collected
papers tagged by each query from the IEEE Xplore
website.
This paper shows the result of 10 experiments
based on synonym pairs. The result of evaluation is
shown in Table 3. The best resulted synonym pair
scored as 5.22 is (optimization, optimisation). This
pair has six matched formal concepts. We could
know that it has the same meaning and significantly
similar relation. The worst resulted synonym pair
scored as 0.59 is (validation, verification) and has
three matching formal concepts. This pair has weak
similarity relation.
Table 3: The results of experiment (synonym pairs).
No.
Synonym pairs
Similarity
(
,
)
1 partition partitioning
0.60
2 optimization optimisation
5.22
3 classification categorization
4.13
4 cryptography steganography
1.71
5 reliability dependability
1.17
6 cluster clustering
4.95
7 contamination pollution
0.87
8 validation verification
0.59
9 encoding encryption
1.45
10 experiment experimentation
3.93
Average 2.46
In addition, we have experiment with 10 random
pairs. The result is shown in Table 4. The average of
all of the random pairs is approximately 0.37. The
best resulted random pair scored as 0.99 is
(normalization, segmentation). It has six matching
formal concepts. Although this query pair is not
synonym, we can understand that they have a little
relevant relation. There are the three worst results
scored as zero and this pairs are composed of
completely unrelated tags. (integration, forecasting),
(lifetime, authorization) and (correlation, evolution)
are unrelated pairs of experiment results. They don’t
have any common concepts each other and we could
know that they don’t have any semantic relations
between them.
Table 4: The results of experiment (random pairs).
No.
Random pairs
Similarity
(
,
)
1 aggregation android
0.62
2 calibration internet
0.25
3 transportation biometrics
0.35
4 context innovation
0.99
5 integration forecasting
0.00
6 lifetime authorization
0.00
7 visualization entropy
0.61
8 correlation evolution
0.00
9 normalization segmentation
0.67
10 sorting authentication
0.16
Average 0.37
While the average of similarity between synonym
pairs is about 2.46, the average of random pairs is
about 0.37. And it shows the remarkable difference
between two types of pairs. Therefore, the method to
measure similarity relation has the contribution to
find the synonym among a lot of candidates.
4.2 TOEFL Synonym Test
We prepared the 9 TOEFL synonym questions to
find the synonym of the target word. One question is
composed of a target word and four candidate words.
And, we measured the similarity between the target
word and each candidate word. In order to compare
the performance with the related works, we used the
AVMI(Baroni and Bisi, 2004) and cosine similarity
to compute similarity. In order to make contexts, we
also collect papers from the IEEE Xplore website.
And the result of experiments is shown as the Table
5. Our method has the 100 percentage of correct
answers, but the AVMI and cosine similarity had the
78%, 89% performance respectively. It is a
remarkable result in comparison with existing
researches.
AMethodologytoMeasuretheSemanticSimilaritybetweenWordsbasedontheFormalConceptAnalysis
319

Table 5: Result of TOEFL Synonym Test.
Target word
Candidate words
Our
method
AVMI
Cosine
similarit
y
partition
partitioning 0.597 -3.94 0.114
dependability 0.454 −∞ 0.037
android 0.000 -5.10 0.028
transportation 0.213 -7.17 0.033
optimization
optimisation 5.217 -4.16
0.065
calibration 0.542 -4.47
0.079
internet 0.000 -4.16 0.010
innovation 0.000 -6.24 0.007
classification
categorization 4.134
-4.49
0.405
transportation 0.135
-3.96
0.033
biometrics 0.675 -6.23 0.046
calibration 1.241 -5.11 0.058
cryptography
steganography
1.712 -2.54 0.202
context 0.408 -4.37 0.035
innovation 0.000 -7.23 0.010
android 0.662 -7.20 0.096
reliability
dependability 1.173
−∞
0.157
integration 0.483
-3.11
0.023
forecasting 0.192 -5.71 0.051
context 0.317 -5.44 0.048
cluster
clustering 4.952 -4.09 0.080
dependability 1.724 −∞ 0.070
authorization 0.000 -5.14 0.056
correlation 0.000 -4.94 0.049
contamination
pollution 0.871 -3.50 0.056
visualization 0.068 -6.02 0.021
entropy 0.000 −∞ 0.020
sorting 0.000 −∞ 0.007
encoding
encryption 1.452 -4.34 0.058
normalization 0.367 -4.79 0.050
segmentation 0.288 -4.65 0.025
lifetime 0.412 −∞ 0.026
experiment
experimentation 3.928 -4.92 0.186
sorting 0.000 -5.19 0.012
authentication 0.000 −∞ 0.009
aggregation 0.000 -5.02 0.037
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has presented a new method to measure
the similarity between two queries. The experiment
for evaluation shows that the effectiveness of this
method is quite persuasive by comparing the
semantic similarity of synonym and random pairs
and finding the synonym among four candidate
words. This method could be used to automatically
find synonym from a lot of candidate words. It could
cope with the changeable web since it uses the web
data.
In the future research, the more experiments
based on the larger sized dataset should be
conducted. Moreover, we will devise the
methodology to automatically generate candidate
words to find the correct synonym.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by Basic Science
Research Program through the National Research
Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry
of Education, Science and Technology(2010-
0024532)
REFERENCES
Alqadah, F. & Bhatnagar, R. 2011. Similarity Measures In
Formal Concept Analysis. Annals Of Mathematics And
Artificial Intelligence, 61, 245-256.
Baroni, M. & Bisi, S. Using Cooccurrence Statistics And
The Web To Discover Synonyms In A Technical
Language. Lrec, 2004.
Blondel, V. D. & Senellart, P. P. 2011. Automatic
Extraction Of Synonyms In A Dictionary. Vertex, 1,
X1.
Cole, R. & Eklund, P. W. 1999. Scalability In Formal
Concept Analysis. Computational Intelligence, 15, 11-
27.
Curran, J. R. & Moens, M. Improvements In Automatic
Thesaurus Extraction. Proceedings Of The Acl-02
Workshop On Unsupervised Lexical Acquisition-
Volume 9, 2002. Association For Computational
Linguistics, 59-66.
Ganter, B., Stumme, G. & Wille, R. 2005. Formal
Concept Analysis: Foundations And Applications,
Springer.
Ganter, B., Wille, R. & Franzke, C. 1997. Formal Concept
Analysis: Mathematical Foundations, Springer-Verlag
New York, Inc.
Ho, N.-D. & Fairon, C. Lexical Similarity Based On
Quantity Of Information Exchanged-Synonym
Extraction. Rivf, 2004. Citeseer, 193-198.
Landauer, T. K. & Dumais, S. T. 1997. A Solution To
Plato's Problem: The Latent Semantic Analysis Theory
Of Acquisition, Induction, And Representation Of
Knowledge. Psychological Review, 104, 211.
Lin, D. Automatic Retrieval And Clustering Of Similar
Words. Proceedings Of The 17th International
Conference On Computational Linguistics-Volume 2,
1998. Association For Computational Linguistics,
768-774.
Lin, D., Zhao, S., Qin, L. & Zhou, M. Identifying
Synonyms Among Distributionally Similar Words.
Ijcai, 2003. 1492-1493.
Lu, Z., Liu, Y., Zhao, S. & Chen, X. Study On Feature
Selection And Weighting Based On Synonym Merge
In Text Categorization. Future Networks, 2010.
Icfn'10. Second International Conference On, 2010.
Ieee, 105-109.
S Nchez, D. & Moreno, A. Automatic Discovery Of
Synonyms And Lexicalizations From The Web. Ccia,
2005. 205-212.
Senellart, P. & Blondel, V. D. 2008. Automatic Discovery
WEBIST2014-InternationalConferenceonWebInformationSystemsandTechnologies
320

Of Similarwords. Survey Of Text Mining Ii. Springer.
Tam, G. K. Focas–Formal Concept Analysis And Text
Similarity. Proceedings Of The 2nd International
Conference On Formal Concept Analysis, 2004.
Turney, P. 2001. Mining The Web For Synonyms: Pmi-Ir
Versus Lsa On Toefl.
Van Der Plas, L. & Tiedemann, J. Finding Synonyms
Using Automatic Word Alignment And Measures Of
Distributional Similarity. Proceedings Of The
Coling/Acl On Main Conference Poster Sessions,
2006. Association For Computational Linguistics,
866-873.
Vechtomova, O. & Wang, Y. 2006. A Study Of The Effect
Of Term Proximity On Query Expansion. Journal Of
Information Science, 32, 324-333.
Veronis, J. & Ide, N. M. Word Sense Disambiguation
With Very Large Neural Networks Extracted From
Machine Readable Dictionaries. Proceedings Of The
13th Conference On Computational Linguistics-
Volume 2, 1990. Association For Computational
Linguistics, 389-394.
Vickrey, D., Kipersztok, O. & Koller, D. An Active
Learning Approach To Finding Related Terms.
Proceedings Of The Acl 2010 Conference Short
Papers, 2010. Association For Computational
Linguistics, 371-376.
Wille, R. 2009. Restructuring Lattice Theory: An
Approach Based On Hierarchies Of Concepts,
Springer.
Wormuth, B. & Becker, P. Introduction To Formal
Concept Analysis. 2nd International Conference Of
Formal Concept Analysis February, 2004.
Wu, H. & Zhou, M. Optimizing Synonym Extraction
Using Monolingual And Bilingual Resources.
Proceedings Of The Second International Workshop
On Paraphrasing-Volume 16, 2003. Association For
Computational Linguistics, 72-79.
AMethodologytoMeasuretheSemanticSimilaritybetweenWordsbasedontheFormalConceptAnalysis
321
