
Description of Accessible Learning Resources by Using Metadata
Salvador Otón, Concha Batanero, Eva Garcia, Antonio Garcia and Roberto Barchino
Department of Computer Science, University of Alcalá, Alcalá de Henares, Spain
Keywords: Accessibility, eLearning, IMS AfA, Learning Object, Metadata.
Abstract: This paper presents IMS Access for All v3.0 specification, which main objective is to simplify the definition
of the accessibility metadata for learning objects and the preferences and needs of the users of these objects,
thereby achieving an inclusive learning process. The AfAPad tool has been created for helping the
accessible content creators to complete the set of specification’s accessibility metadata and to create the
XML files that represent them. This tool also helps users to create their XML files with the preferences and
needs metadata. This tool has been developed by the authors at the University of Alcala (Spain) in the field
of project ESVIAL. This paper exposes the practical steps to be followed by a content creator to perform an
accessible training activity, explaining the specifications and standards that can be used and the necessary
tools.
1 INTRODUCTION
The first public reference to the accessibility concept
emerged in 1974 in the Expert Group Meeting on
Barrier-Free Design in New York (Arjona, 2012),
where disabilities that restrict the free movement of
people were highlighted. Since then evolution in this
field has been slow and uneven across countries,
having spent 40 years without reaching the expected
inclusion, in general, and in education, in particular.
Online learning has many advantages over
traditional learning, being the most important the
possibility of access by those people who, due to
their different type of access to information, are
deprived of it.
The information held in an online educative
course is divided or organized into smaller units, so
that it can be easily published for a better
understanding. Each of these parts is a learning
object (LO).
LOs have some metadata associated, so that they
can be reusable through Internet searches. The literal
meaning of metadata is “data over data” and its
function is to describe a LO’s characteristic. LOs,
besides regular metadata, must have associated
accessibility metadata that describe their
accessibility characteristics and that make them
accessible to all people. These metadata are the
fields used for searching LOs.
This paper presents the technical process
necessary to enable content authors the creation of
accessible LOs based on IMS Access For All v3.0
specification (IMS, 2012) throw the inclusion of
accessibility metadata into LOs. The authors have
developed the AfAPad tool which helps in these
tasks.
2 LEARNING OBJECTS
LOs are the minimum unit in which educational
content is organized. To enable LOs searches and
that they can be reused by different people and in
different training activities, they must be described
by including their metadata, which are a set of fields
that provide information about the LO such as, for
example, its identifier, the language in which it is
written or its scope.
There are some specifications and standards
commonly used, such as Dublin Core (DC, 2013) or
LOM (LOM, 2002), which indicate what metadata
or metainformation should be inserted in LOs for a
correct description of these.
One way to facilitate the search and therefore
their reuse is to store them in repositories, which are
places where learning objects’ storing and searching
operations are provided. Searches are performed
based on their metadata, hence the importance of
clearly and correctly describing the resources, which
provides more precise searches.
620
Otón S., Batanero C., Garcia E., Garcia A. and Barchino R..
Description of Accessible Learning Resources by Using Metadata.
DOI: 10.5220/0004895606200626
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2014), pages 620-626
ISBN: 978-989-758-028-4
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

When users need to perform a training activity
they use these repositories to find the learning
objects that better adapt to that training, thus
drawing up a new course from the learning objects
found in the repository or repositories to they can
access.
Metadata should be inserted in a XML
(eXtensible Markup Language) file (W3C, 2008),
composed of each of the fields (each field
corresponds to a metadata) described following one
of the standards published for this purpose such as,
for example, LOM (Learning Object Metadata)
(LOM, 2002). This work is provided by metadata
editors such as, for example, LomPad, known for
being one of the most used (Licef, 2004).
Figure 1: LomPad Editor.
As shown in Figure 1, the LomPad editor allows
completing the LOM specification fields. Once all
data have been inserted, a XML file containing all
information is generated.
The process for sharing content and distributing
it among different information systems is to pack
it in a compressed file composed of the content and
metadata that describe it. In this scope there are two
specifications widely used, such as SCORM
(Sharable Content Object Reference Model)
(SCORM, 2009) and IMS Common Cartridge (IMS,
2009). Just as there are editors to help content
authors to describe the metadata, there are also
editors that help to pack this content along with
metadata. One of the most known editors is Reload
Editor (Reload, 2013).
3 IMS ACCESS FOR ALL (AfA)
V3.0
IMS AfA v3.0 specification is created with the aim
of simplifying the ISO/IEC 24751 standard
(ISO/IEC 24751-1-2-3, 2008) due to the difficulties
encountered when putting it into practice. Both
standard and specification in version 3.0 cover the
entire process from reading the user needs to the
search mechanism needed to find the LO that meets
those needs or preferences.
It has two data models to describe:
Personal Needs and Preferences (PNP):
Description model of the users’ needs and
preferences to access and interact with the digital
resources.
Digital Resource Description (DRD): Description
model of the accessibility metadata for the digital
training resources.
AfA PNP aims to provide a way forward for the
personal needs of the students (or those due to
disability environments) are satisfied. It presents a
method for expressing the user’s PNPs and lets their
reading in an automated manner, all with respect to
the digital learning. AfA PNP can be used
independently, for example, to import or export the
user’s PNP to other educational systems, or in
combination with AfA DRD to deliver digital
resources that meet the needs and/or preferences of a
user.
3.1 Digital Resource Description
(DRD)
AfA DRD defines the accessibility metadata of a
resource that will be used for searching and using
the most adequate learning resource to each user
according to his/her PNPs.
For LOs searches can be carried out, two types of
LOs must exist: original and adapted. An original
resource corresponds to an initial resource, while an
adapted resource presents the same educational
information than the initial or original resource. For
example, a PDF format file as the original resource
and an audio-description of its content as an adapted
Figure 2: Digital Resource Description (DRD) properties.
DescriptionofAccessibleLearningResourcesbyUsingMetadata
621

resource. The first one presents textual access while
the adaptation presents auditory access to the same
educational content.
Original resources may have any number of
adaptations, which may be total or partial, i.e., or
they are adaptations of the whole educational
content or they are just a part of this.
Figure 2 shows the accessibility properties or
metadata of a resource and how they relate to each
other, as IMS AfA v3.0 specification presents them.
As seen in the figure, in order to simplify as much as
possible the data model, the metadata have been
organized in two clearly distinguished levels:
1 Those belonging to a basic core (core profile),
containing the most important metadata,
necessary for a proper description of the
resource.
2 Those belonging to the full specification, which
extent and complement the basic core
information.
3.2 Personal Needs and Preferences
(PNP)
The specification shows a common information
model to define and describe the student’s or user’s
PNPs with a different sensory perception mode or
who is in a disability context.
The recommended method to generate the
student’s PNPs is the presentation of a form with
various options (like aforementioned or preferred
sensory mode). The PNPs will be generated from
students’ responses to these questions.
The declaration of PNPs is associated to one
person. In turn one person can generate several sets
of PNPs for being used in the environment he/she is
at each moment (for example, in the dark or in a
noisy area). Like any software application, user’s
Figure 3: Personal Needs and Preferences (PNP)
properties.
PNPs should be easily modified by editing the user
profile and allowing its extension, replacement or
removal.
Figure 3 shows the user’s accessibility properties
and how they relate to each other. In the same
manner as AfA DRD specification, there are
properties belonging to the basic profile (Core
Profile) and those belonging to the full specification.
4 AfAPad TOOL
This section presents AfAPad tool, which has been
developed from the need to create accessible LOs
that allow an equal education without social
discrimination and in order to cover the existing
technological gap in the field of accessibility. This
tool has been developed by the authors at the
University of Alcala (Spain) in the field of project
ESVIAL (ESVIAL, 2013), funded by the ALFA III
program of the European Union. The objective of
the project is to improve the accessibility of virtual
higher education, through the creation and
implementation of methodologies to establish a
working model for compliance with accessibility
requirements and standards in the context of virtual
training, especially through web.
AfAPad allows the content authors and the
learning platform users to insert accessibility
metadata of LOs (DRDs) and students PNPs,
respectively, generating both XML format files. This
tool allows to complete the properties of DRDs and
PNPs graphically and to generate the corresponding
XML file following the IMS AfA v3.0 specification.
The tool shows all properties of DRDs and
PNPs. The properties belonging to the Core Profile
are highlighted in blue, and the other properties that
cover the full specification are highlighted in black.
The properties of IMS AfA may have two types of
cardinality, [0..N] or [0..1], and being defined for a
set of default values or having a free value. If a
property has a cardinality [0..N] and a set of default
values, the user has the possibility of choosing the
values from a dropdown list. Once the values are
selected, they will appear in a text field, separated by
commas and in the same order they were selected. If
the property has a cardinality [0..N] and a free value,
the user can write different values in a text field
separating each value with commas. Finally, if the
cardinality is [0..1] a dropdown list is shown, which
displays the metadata space values, where only one
value can be chosen.
AfAPad tool has been developed as a desktop
application in Java Swing and therefore it is portable
ICEIS2014-16thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
622
across platforms. The following section details its
utilization.
4.1 Application Scenario
In this section a scenario of use of IMS AfA v3.0
specification is described, in addition to other e-
learning specifications and standards previously
explained, describing all stages for getting an
accessible learning object.
Firstly, a content author plans to carry out a
learning resource that contains a video tutorial
(original resource) of an educational course. Two
alternative content (adapted resources) are created to
provide access to this course to the students with
disabilities: on the one hand, an audio description
(audio file that describes the images containing
meaningful information) and on the other hand, an
expanded text (text file containing an explanation
about all the information presented by the video).
The content author uses LomPad or Reload to
describe the LOM metadata of the video tutorial,
thus describing the educational material so that it
can be located and reused in different training
activities.
Then it is necessary to include the accessibility
metadata of the original resource, thus the type of
sensorial perception is described, which is needed to
understand the training content. As this is a video,
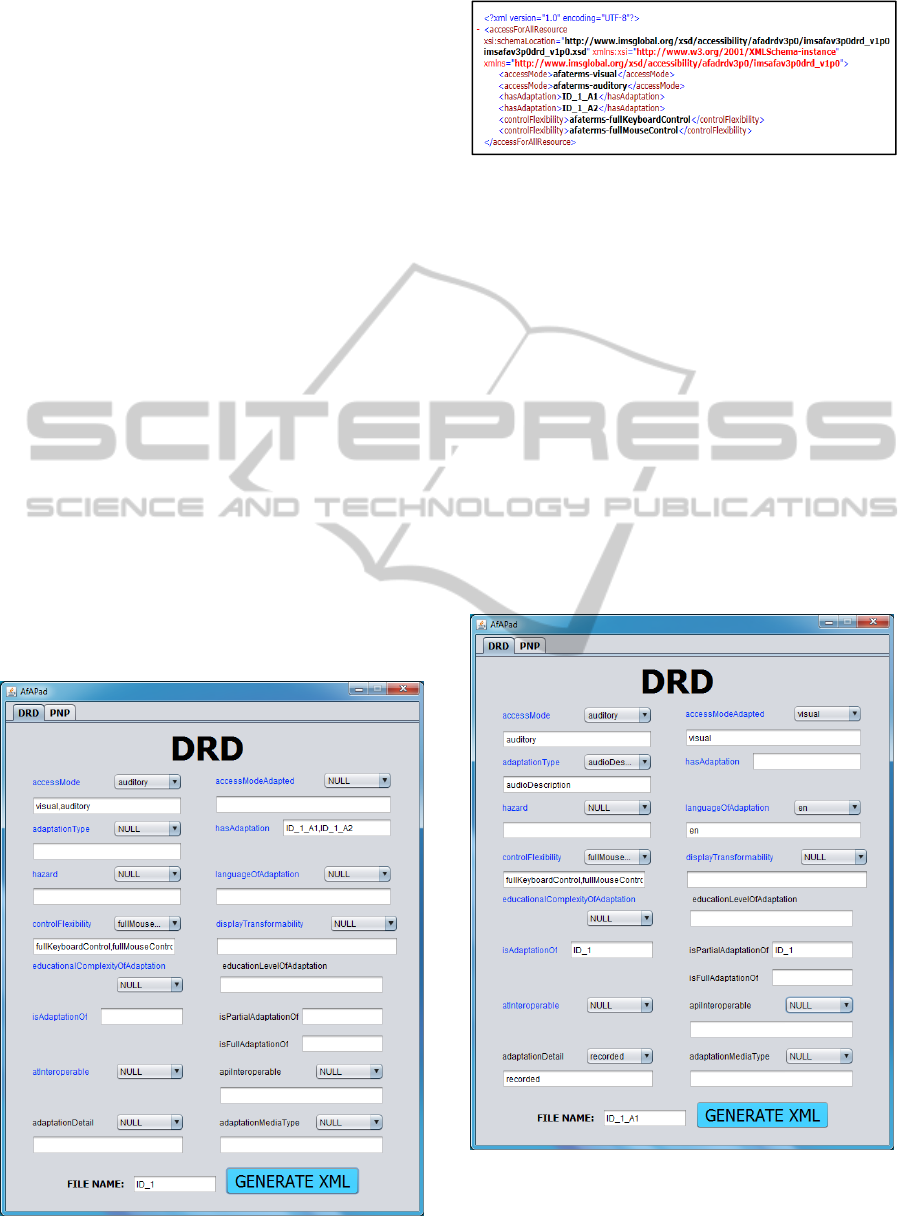
Figure 4: Original resource’s DRD properties.
Figure 5: Original resource’s DRD XML
(afadrdv3p0_ID_1.xml).
both the visual and the auditory senses are needed.
For inserting the accessibility metadata by following
IMS AfA specification the author uses AfAPad tool
as shown in Figure 4 and whose ultimate goal is to
generate the XML file shown in Figure 5.
In the XML file generated, which is shown in
Figure 5, it is described that the original resource has
two access modes: visual and auditory, it has two
adaptations: ID_1_A1 and ID_1_A2, and it can be
controlled using the keyboard and mouse.
The following step will be creating the
description for one of the adapted learning object,
which contains the audio description. Using AfAPad
the accessibility metadata are filled as shown in
Figure 6 and generated the XML file shown in
Figure 7.
Figure 6: Adapted resource’s A1 DRD properties.
In the XML file generated, which is shown in Figure
7, it is described that the adapted resource has an
DescriptionofAccessibleLearningResourcesbyUsingMetadata
623
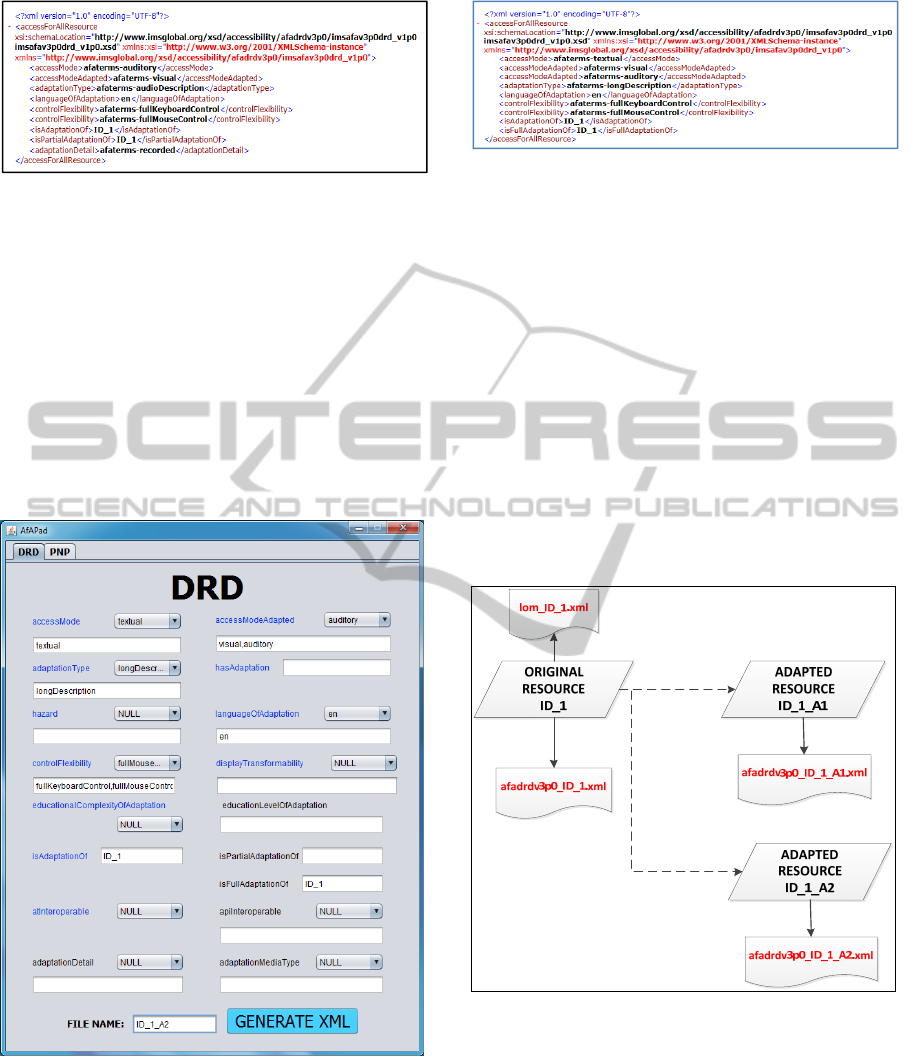
Figure 7: Adapted resource’s A1 DRD XML
(afadrdv3p0_ID_1_A1.xml).
auditory access mode and it adapts a visual one.
More details about the type of adaptation are given
through property “adaptationType” and it is
specified that it is an audio description. It has full
control by keyboard and mouse. It is an adaptation
of the original resource ID_1 and it is a partial
adaptation. Finally, it states that the audio is
recorded using a human voice.
The same actions will be performed for the
description of the expanded text’s metadata and they
are shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9.
Figure 8: Adapted resource’s A2 DRD properties.
In the XML file generated, which is shown in Figure
9, it is described that the adapted resource has a
textual access mode and it adapts both, the visual
and the auditory modes of the original resource. By
means of property “adaptationType” more details
about the type of adaptation are given and it
Figure 9: Adapted resource’s A2 DRD XML
(afadrdv3p0_ID_1_A2.xml).
specifies that it is a long description. It has full
control by keyboard and mouse. It is an adaptation
of the original resource ID_1 and it is a full
adaptation.
Once the resources are created and the metadata
are defined in their corresponding XML files, a
package containing all information and following
SCORM specification will be created. As shown in
Figure 10, the SCORM package will be composed of
three resources (the original and the two adaptations)
and their metadata files. The original resource will
have associated two metadata files, one with its
LOM metadata and another one with the IMS AfA
metadata. Adapted resources only need the IMS AfA
metadata.
Figure 10: SCORM content.
Furthermore, AfAPad tool allows generating XML
files containing the users’ PNPs. For example, if a
blind person wants to describe his/her preferences,
he/she has to fill the metadata as shown in Figure 11
and generate the XML file shown in Figure 12.
In the XML file generated and shown in Figure
12 it is described that, for visual content, the user
prefers adapted resources that have a textual or
auditory access mode. By means of property
ICEIS2014-16thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
624
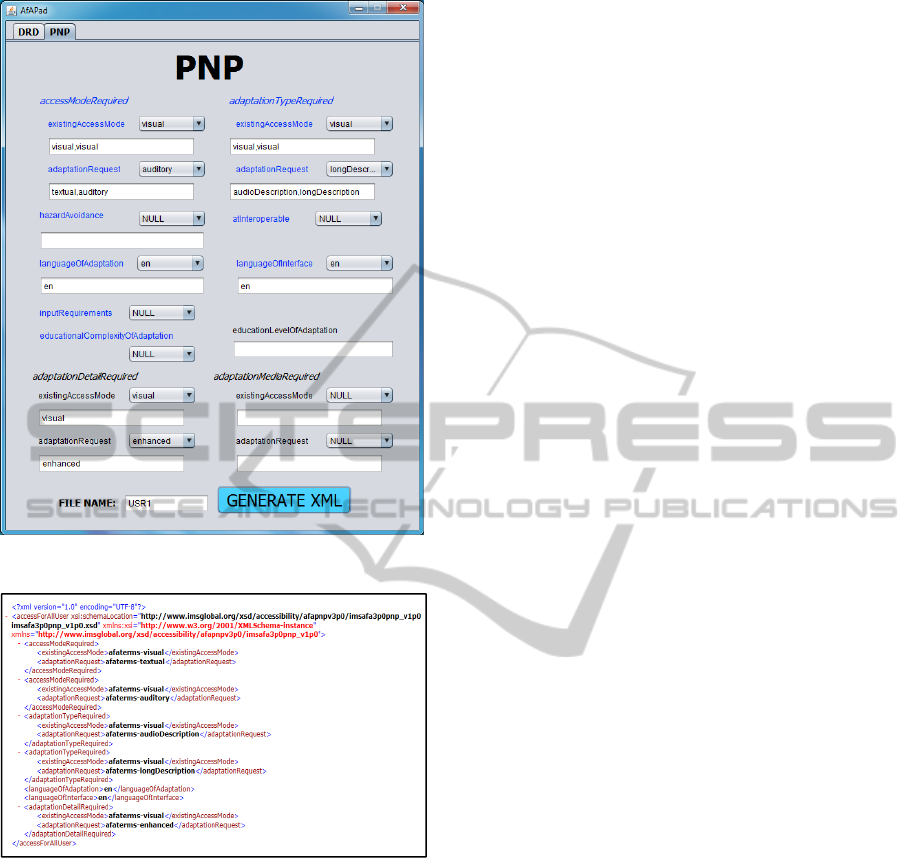
Figure 11: User PNP properties.
Figure 12: User PNP XML (afapnpv3p0_USR1.xml).
“adaptationTypeRequired”, more details about the
type of desired adaptation for visual content are
given, and it is specified that they should contain
audio and long descriptions. Finally, it is stated that
for visual content enhanced content is preferred, for
example, a video with a detailed audio description.
A learning system (educational platform,
learning object repository, etc.) that is able to
understand the PNP defined above and whose user is
interested in learning the educational resource of the
video tutorial which represents the original resource,
should show the adaptations that are associated with
it.
5 CONCLUSIONS
IMS AfA v3.0 specification presents to the content
authors and developers the technical way to follow
for achieving an accessible online teaching.
According to ISO/IEC 24751-2-3 standard and
IMS AfA v3.0 specification, the basic steps in
developing an accessible online course are: creating
accessible LOs, both original and adapted, by means
of inserting the accessibility metadata; reading the
users’ PNPs; and searching and presentation of LOs
meeting those PNPs.
For a LO can be used in an educational platform
it is necessary to pack all files shaping the LO with
the files containing its metadata, including the
accessibility ones, and following the standards
established.
There is a great lack of technical applications and
human resources to provide assistance in developing
accessible resources.
The AfAPad tool developed by the authors
avoids the standstill of the process of creating
accessible LOs in the absence of similar tools to
perform this task.
The usefulness of AfAPad tool will make more
sense in future work, already scheduled, consistent
in adapting learning platforms that are able to
interpret and read the file generated by the tool and
conclude the whole process of searching accessible
LOs.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is funded by the University of Alcalá
(grant ESVIAL project). Authors also want to
acknowledge support from the Master in Software
Engineering for the Web and the TIFyC research
group.
REFERENCES
Arjona, G., 2010. Historia de la accesibilidad III. La
accesibilidad es de tod@s. http://laaccesibilida
desdetodos.blogspot.com.
ATAG, 2013. Authoring Tool Accessibility Guidelines
(ATAG) 2.0. http://www.w3.org/TR/ATAG20/
DC, 2013. Dublin Core Metadata Initiative.
http://dublincore.org/
ESVIAL, 2013. Educación Superior Virtual Inclusiva –
América Latina. http://www.esvial.org/?lang=en_us.
IMS, 2009. IMS Common Cartridge. IMS Global
Learning Consortium, Inc. http://www.imsglobal.org/
DescriptionofAccessibleLearningResourcesbyUsingMetadata
625

commoncartridge.html.
IMS, 2012. IMS Access For All Version 3.0. IMS Global
Learning Consortium, Inc. http://imsglobal.org/
accessibility.
ISO 9241-171:2008, Ergonomics of human-systen
Interaction -- Part 171 Guidance on software
accesibility. International Standard Organization,
Geneve, Switzerland.
ISO/IEC 24751-1,2,3:2008, Information technology --
Individualized adaptability and accessibility in e-
learning, education and training -- International
Standard Organization, Geneve, Switzerland.
Licef, 2004. LOMPad, learning object metadata editor.
http://helios.licef.ca:8080/LomPad/en/index.htm.
LOM, 2002. 7. Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers, 2002. IEEE Learning Object Metadata
(LOM). http://www.ieeeltsc.org/
Merlot, 2013. MERLOT (Multimedia Educational
Resource for Learning and Online Teaching).
http://www.merlot.org/
Reload, 2013. Reload editor. Reusable eLearning Object
Authoring & Delivery. http://www.reload.ac.uk/
SCORM, 2009. Advanced Distributed Learning (ADL).
Sharable Content Object Reference Model (SCORM).
http://www.adlnet.org/scorm/
W3C, 2008. World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), 2008.
Extensible Markup Language (XML).
http://www.w3.org/XML/
ICEIS2014-16thInternationalConferenceonEnterpriseInformationSystems
626
